
Rice Science ›› 2016, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (1): 42-50.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2016.01.005
收稿日期:2015-06-18
接受日期:2015-08-18
出版日期:2016-01-20
发布日期:2015-11-05
. [J]. Rice Science, 2016, 23(1): 42-50.
| Code | Location | Agro-ecological zone |
| GA1, GA2, GA3, GA4, GA5 | Gazipur | Madhupur tract |
| GO1, GO2, GO3, GO4, GO5 | Godagari | High ganger river flood plain |
| TA1, TA2, TA3, TA4, TA5 | Tanor | High ganger river flood plain |
| CO1, CO2, CO3 | Comilla | Middle Meghna river flood plan |
Table 1 List of R. solani isolates with geographic locations.
| Code | Location | Agro-ecological zone |
| GA1, GA2, GA3, GA4, GA5 | Gazipur | Madhupur tract |
| GO1, GO2, GO3, GO4, GO5 | Godagari | High ganger river flood plain |
| TA1, TA2, TA3, TA4, TA5 | Tanor | High ganger river flood plain |
| CO1, CO2, CO3 | Comilla | Middle Meghna river flood plan |
| Character | Character state | ||
| Mycelial color on potato dextrose agar, color of sclerotia | 0, hyaline; 1, cream or faint brown; 2, light brown; 3, medium brown; 4, dark brown | ||
| Superficial sclerotia (SS) dispersed on whole colony, exudate droplets on sclerotium surface | 0, present; 1, absent | ||
| Colony reverse: pigment | 0, not present; 1, cream or faint brown; 2, light brown | ||
| Sclerotia on lid | 0, absent; 1, present | ||
| Topography of sclerotia | 0, immersed; 1, superficial | ||
| Shape of sclerotia | 0, flattened bottom and round top; 1, superficial; 2, irregularly globose with pitted surface; 3, irregular | ||
| Arial mycelial quality | 0, absent; 1, all hyphae close to surface of agar; 2, air space in dish half filled; 3, almost all airspace filled | ||
| Quantity of sclerotia, pseudo sclerotia, SS discrete, SS aggregated, SS scattered, SS near inoculum, SS near margin, dark brown runner hyphae in aerial mycelium and/or on colony surface, growth on lid | 0, absent; 1, few; 2, moderate; 3, abundant | ||
Table 2. Morphological characteristics description of R. solani isolates and their attributes.
| Character | Character state | ||
| Mycelial color on potato dextrose agar, color of sclerotia | 0, hyaline; 1, cream or faint brown; 2, light brown; 3, medium brown; 4, dark brown | ||
| Superficial sclerotia (SS) dispersed on whole colony, exudate droplets on sclerotium surface | 0, present; 1, absent | ||
| Colony reverse: pigment | 0, not present; 1, cream or faint brown; 2, light brown | ||
| Sclerotia on lid | 0, absent; 1, present | ||
| Topography of sclerotia | 0, immersed; 1, superficial | ||
| Shape of sclerotia | 0, flattened bottom and round top; 1, superficial; 2, irregularly globose with pitted surface; 3, irregular | ||
| Arial mycelial quality | 0, absent; 1, all hyphae close to surface of agar; 2, air space in dish half filled; 3, almost all airspace filled | ||
| Quantity of sclerotia, pseudo sclerotia, SS discrete, SS aggregated, SS scattered, SS near inoculum, SS near margin, dark brown runner hyphae in aerial mycelium and/or on colony surface, growth on lid | 0, absent; 1, few; 2, moderate; 3, abundant | ||
| Primer | Sequence | ||
| Variable number of tandem repeat (VNTR) | |||
| MR | GAGGGTGGCGGTTCT | ||
| RY | CAGCAGCAGCAGCAG | ||
| GF | TCCTCCTCCTCCTCC | ||
| Amplified fragment length polymorphisms (AFLP) | |||
| AFLP-C | GACTAGGATACATGCAGGC | ||
| AFLP-D | GACTACGTACATGKACKGKAC | ||
Table 3. List of primers and their sequences.
| Primer | Sequence | ||
| Variable number of tandem repeat (VNTR) | |||
| MR | GAGGGTGGCGGTTCT | ||
| RY | CAGCAGCAGCAGCAG | ||
| GF | TCCTCCTCCTCCTCC | ||
| Amplified fragment length polymorphisms (AFLP) | |||
| AFLP-C | GACTAGGATACATGCAGGC | ||
| AFLP-D | GACTACGTACATGKACKGKAC | ||
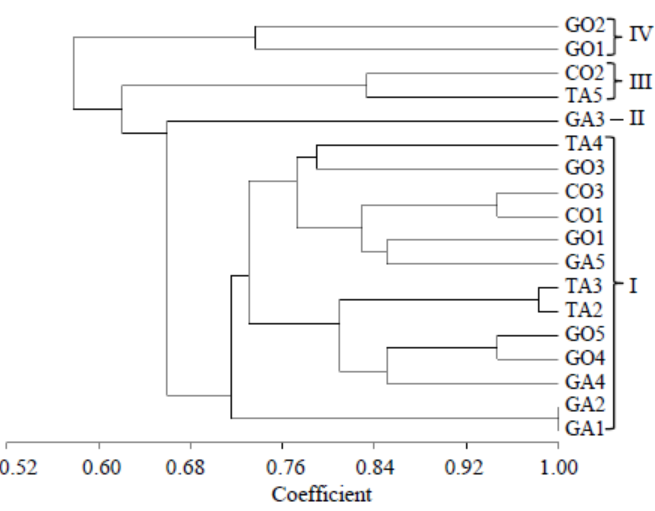
Fig. 2. Un-weighted pair group method with arithmetic mean dendrogram of R. solani isolates constructed with Multi Variaty Statistical Package ver. 3.1 using the Gower’s general similarity coefficient based on morphological characters.
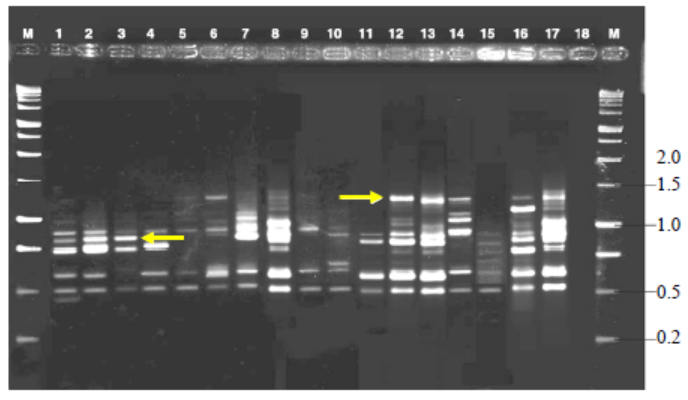
Fig. 3. Variable number of tandem repeat fingerprinting patterns of total genomic DNA of R. solani isolates with primer MR.M, Kilo base (kb) ladder; Lanes 1 to 18, Isolates GA1, GA2,GA3, GA4, GA5, GO1, GO2, GO3, GO4, GO5, TA1, TA2, TA3, TA4,TA5, CO1, CO2 and CO3, respectively.Arrow indicates polymorphic bands.
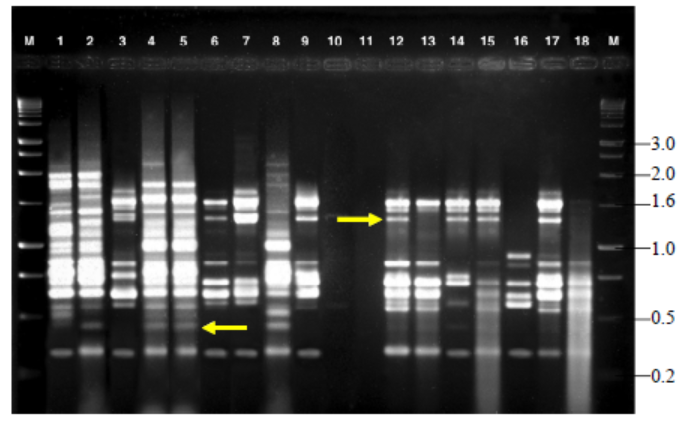
Fig. 4. Variable number of tandem repeat fingerprinting patterns of total genomic DNA of R. solani isolates with primer RY. M, Kilo base (kb) ladder; Lanes 1 to 18, Isolates GA1, GA2, GA3, GA4, GA5, GO1, GO2, GO3, GO4, GO5, TA1, TA2, TA3, TA4, TA5, CO1, CO2 and CO3, respectively.Arrow indicates polymorphic bands.
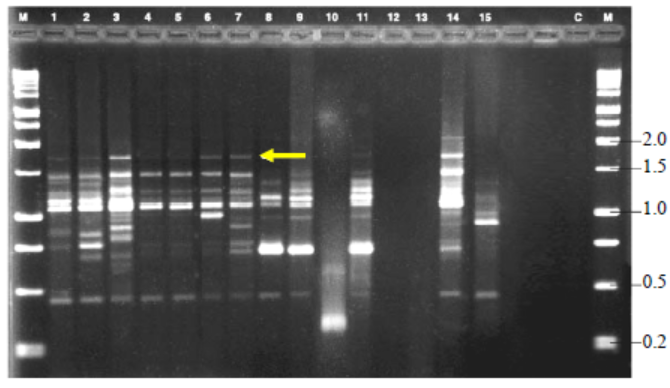
Fig. 5. Variable number of tandem repeat fingerprinting patterns of total genomic DNA of R. solani isolates with primer GF.M, Kilo base (kb) ladder; Lanes 1 to 18, Isolates GA1, GA2, GA3,GA4, GA5, GO1, GO2, GO3, GO4, GO5, TA1, TA2, TA3, TA4, TA5,CO1, CO2 and CO3, respectively.Arrow indicates polymorphic bands.
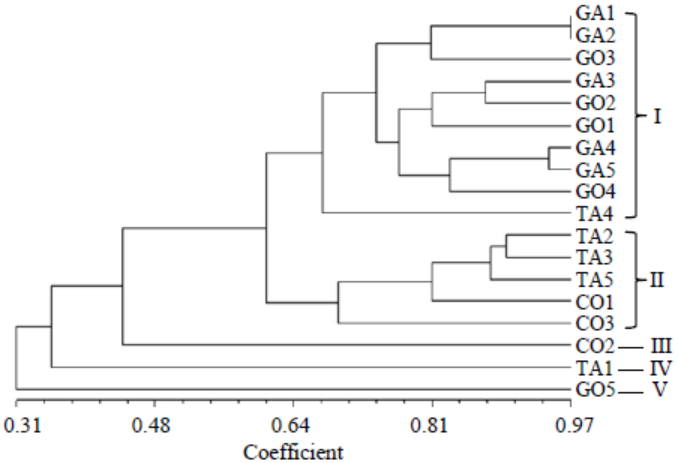
Fig. 6. Un-weighted pair group method with arithmetic mean dendrogram of R. solani isolates constructed with Multi Variety Statistical Package ver 3.1 using the Gower’s general similarity coefficient based on DNA fingerprinting (variable number of tandem repeat analysis of primers MR, RY, and GF).
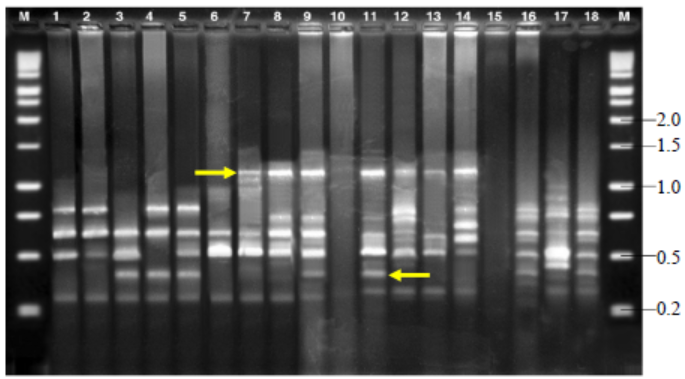
Fig. 7. Amplified fragment length polymorphisms fingerprinting patterns of total genomic DNA of R. solani isolates with primer AFLP-C.M, Kilo base (kb) ladder; Lanes 1 to 18, Isolates GA1, GA2, GA3, GA4, GA5, GO1, GO2, GO3, GO4, GO5, TA1, TA2, TA3, TA4, TA5, CO1, CO2 and CO3, respectively.Arrow indicates polymorphic bands.
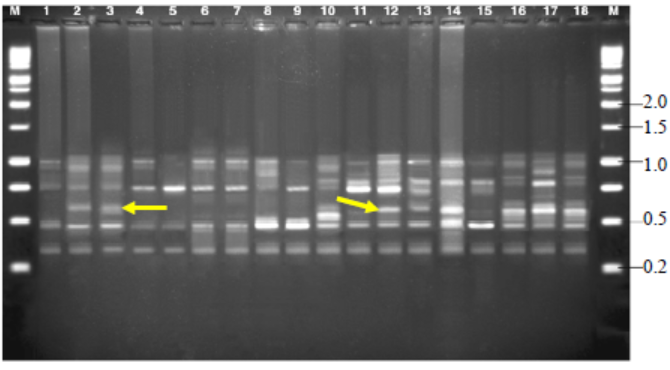
Fig. 8. Amplified fragment length polymorphisms fingerprinting patterns of total genomic DNA of R. solani isolates with primer AFLP-D.M, Kilo base (kb) ladder; Lanes 1 to 18, Isolates GA1, GA2, GA3,GA4, GA5, GO1, GO2, GO3, GO4, GO5, TA1, TA2, TA3, TA4, TA5,CO1, CO2 and CO3, respectively.
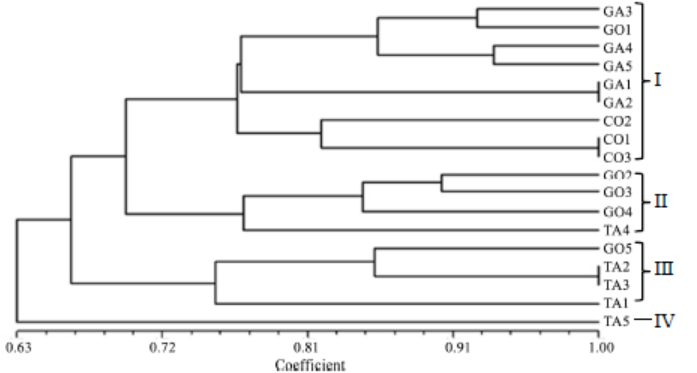
Fig. 9. Un-weighted pair group method with arithmetic mean dendrogram of relatedness of R. solani AG1 IA isolates constructed with Multi Variaty Statistical Package ver 3.1 using the Gower’s general similarity coefficient based on amplified fragment length polymorphism analysis of primers AFLP-C and AFLP-D.
| [1] | Ali M A.2002. Biological Variation and Chemical Control of Rhizoctnia solani Causing Rice Sheath Blight in Bangladesh. Department of Biological Sciences, Imperial College for Science, Technology and Medicine. Silwod Park, Ascot, Berkshire: 202. |
| [2] | Banerjee S, Datta S, Mondal A, Bhattacharya S.2012. Characterization of molecular variability in Rhizoctonia solani isolate from different agro-ecological zone by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers.Afr J Biotechnol, 11(40): 9543-9548. |
| [3] | Banniza S, Rutherford M A.2001. Diversity of isolates of Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA and their relationship to other anastomosis groups based on pectic zymograms and molecular analysis.Mycol Res, 105(1): 33-40. |
| [4] | Basu A, Gupta P K S.1992. Loss in yield and seed infection in promising genotypes of rice (Oryza sativa) due to sheath blight disease caused by Rhizoctonia solani.Ind J Agric Sci, 62(8): 570-571. |
| [5] | Bonman J M.1992. Durable resistance to rice blast disease: Environment influences.Euphytica, 63: 115-123. |
| [6] | Bruns T D, White T J, Taylor J W.1991. Fungal molecular systematics.Ann Rev Ecol Syst, 22: 525-564. |
| [7] | Flor H H.1971. Current status of the gene-for-gene concept.Ann Rev Phytopathol, 9: 275-296. |
| [8] | Jeffreys A J, Wilson V, Thien S L.1985a. Hyper-variable mini-satellite regions in human DNA.Nature, 314: 67-73. |
| [9] | Jeffreys A J, Wilson V, Thien S L.1985b. Individual specific fingerprints of human DNA.Nature, 316: 76-79. |
| [10] | Julian M C, Acero J, Salazar O, Keijer J, Rubio V.1999. Mating type correlated molecular markers and demonstration of heterokaryosis in the phytopathogenic fungus Thanatephorus cucumeris (Rhizoctonia solani) AG1 1C by AFLP DNA fingerprinting analysis.J Biotechnol, 67(1): 49-56. |
| [11] | Khodayari M, Safaie N, Shamsbakhsh M.2009. Genetic diversity of Iranian AG1-IA isolates of Rhizoctonia solani, the cause of rice sheath blight, using morphological and molecular markers.J Phytopathol, 157: 708-714. |
| [12] | Majer D, Mithen R, Lewis B G, Vos P, Oliver R P.1996. The use of AFLP fingerprinting for detection of genetic variation fungi.Mycol Res, 100(9): 1107-1111. |
| [13] | Matsumoto M, Furuya N, Matsuyama N.1996. PCR-RFLP analysis of amplified 28S ribosomal DNA for identification of Rhizoctonia spp., the causal agents of sheath diseases of rice plants.J Fac, 41: 39-44. |
| [14] | Mekwatanakarn P, Kositratana W, Phromraksa T, Zeigler R S.1999. Sexually fertile Magnaporthe grisea rice pathogens in Thailand.Plant Dis, 83(10): 939-943. |
| [15] | Mian M S, Stevens C, Mia M A T.2003. Diversity of the rice blast pathogen Pyricularia grisea from Bangladesh analysed by DNA fingerprinting.Bangl J Plant Pathol, 1: 81-85. |
| [16] | Nakamura Y, Leppert M, Connel P, Wolf R, Holm T, Culver M, Martin C, Fujimoti E, Holf M, Kumalin E, White R.1987. Variable number of tandem repeat (VNTR) marker for human gene mapping.Science, 235: 1616-1622. |
| [17] | Ogoshi A.1987. Ecology and pathogenicity of anastomosis and intra-specific groups of Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn.Ann Rev Phytopathol, 25: 125-143. |
| [18] | Parmeter J R, Sherwood R T, Platt W D.1969. Anastomosis grouping among isolates of Thanatephorus cucumaris. Phytopathology, 59: 1270-1278. |
| [19] | Parmeter J R, Whitney H S.1970. Taxonomy and nomenclature of the imperfect state. In: Parmeter J R. Rhizoctonia solani: Biology and Pathology. Berkely: University of California Press: 7-19. |
| [20] | Pascual C B, Toda T, Raymondo A D, Hyakumachi M.2000. Characterization by convential techiques and PCR of Rhizoctonia solani isolates causing banded leaf sheath blight in maize.Plant Pathol, 49: 108-118. |
| [21] | Raeder U, Broda P.1985. Rapid preparation of DNA from filamentous fungi.Lett Appl Microbiol, 1: 17-20. |
| [22] | Rashad Y M, Abdel-Fattah G M, Hafez E E, El-Haddad S A.2012. Diversity among some Egyptian isolates of Rhizoctonia solani based on anastomosis grouping, molecular identification and virulence on common bean.Afr J Microbiol Res, 6(37): 6661-6667. |
| [23] | Rohlf F J.2000. NTSYS-pc. Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate System version 2.11a. Exeter Software, Setauket, New York, USA. |
| [24] | Sambrook J, Russel D W.2001.Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 3rd edn. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laborary Press. |
| [25] | Sharma M, Gupta S K, Sharma T R.2005. Characterization of variability in Rhizoctonia solani by using morphological and molecular markers.Phytopathology, 153: 449-456. |
| [26] | Sharma N R, Akanda S I, Shahjahan A K M.1995. Development of sheath blight in short, tall, early and late maturing rice cultivars.Bangl J Bot, 24(2): 143-146. |
| [27] | Sherwood R T.1969. Morphology and pathology in four anastomosis groups ofThanatephorus cucumeris. J Phytopathol, 59: 1924-1929. |
| [28] | Silue D, Tharreau D, Notteghem J L.1992. Evidence of gene-for-gene relationship in the Oryza sativa-Magnaporthe grisea pathosystem.Phytopathology, 82: 577-580. |
| [29] | Singh A, Singh U S, Willocquet L, Savary S.1999. Relationship among cultural morphological characteristics, anastomosis behavior and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia solani Khun on rice.J Mycol Plant Pathol, 29: 306-316. |
| [30] | Singh V, Singh U S, Singh K P, Singh M, Kumar A.2002. Genetic diversity of Rhizoctonia solani isolated from rice: Differentiation by morphological characteristics, pathogenecity, anastomosis behaviour and RAPD fingerprinting.J Mycol Plant Pathol, 32(3): 332-344. |
| [31] | Sivalingan P N, Vishwakarma S N, Singh U S.2006. Role of seed-borne inoculum of Rhizoctonia solani in sheath blight of rice.Ind J Phytopath, 59(4): 445-452. |
| [32] | Sneh B, Burpee L, Ogoshi A.1991. Identification of Rhizoctonia species. St Paul, Minnesota: APS Press. |
| [33] | Tajick M A, Rahimianm H, Alizadeh A.2005. Studies on population of Rhizoctonia solani AG 1 1A isolated from rice by rDNA RFLP in Mazandaran Province.Iran J Plant Pathol, 41: 507-542. |
| [34] | Thakur R S, Sugha S K, Sharma B M.1992. Morphological grouping of different isolates of Rhizoctonia solani Khun.Plant Dis Res, 7: 58-59. |
| [35] | Toda T, Nasu H K, Kageyama K, Hyakumachi M.1998. Genetic identification of web-blight (Rhizoctonia solani AGI) obtained from European pear using RFLP of rDNA-ITS and RAPD analysis.Res Bull Fac Agric Gifu Univ, 63: 1-9. |
| [36] | Vijayam M, Chandrasekharan N M.1985. Anastomosis grouping of isolates of Rhizoctonia solani Kuha (Thanatephorus cucumeris (Frank) Donk) causing sheath blight of rice.Curr Sci, 54(6): 289-291. |
| [37] | Zhou E, Jia Y, Singh P, Correll J C, Lee F N.2007. Instability of the Magnaporthe oryzaea virulence gene AVR-Pitai alters virulence.Fungal Genet Biol, 44: 1024-1034. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||