
Rice Science ›› 2016, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (3): 144-151.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2015.11.004
收稿日期:2015-09-11
接受日期:2015-11-13
出版日期:2016-06-08
发布日期:2016-02-04
. [J]. Rice Science, 2016, 23(3): 144-151.
| Primer name | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| xa13FM1 | TTGGAGACCCTCCACTTTTG | CCAAATGGCAACAGACACAC |
| xa13FM2 | ACGTGTCATATTGCCCCTCA | GCTAGAGAGGAAGGCTTAAGTGC |
| xa13FM3 | GGAGACCCTCCACTTTTGGT | TCTCCAAATGGCAACAGACA |
| xa13-prom | GGCCATGGCTCAGTGTTTAT | GAGCTCCAGCTCTCCAAATG |
Table 1 Sequences of the primers designed for xa13.
| Primer name | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| xa13FM1 | TTGGAGACCCTCCACTTTTG | CCAAATGGCAACAGACACAC |
| xa13FM2 | ACGTGTCATATTGCCCCTCA | GCTAGAGAGGAAGGCTTAAGTGC |
| xa13FM3 | GGAGACCCTCCACTTTTGGT | TCTCCAAATGGCAACAGACA |
| xa13-prom | GGCCATGGCTCAGTGTTTAT | GAGCTCCAGCTCTCCAAATG |
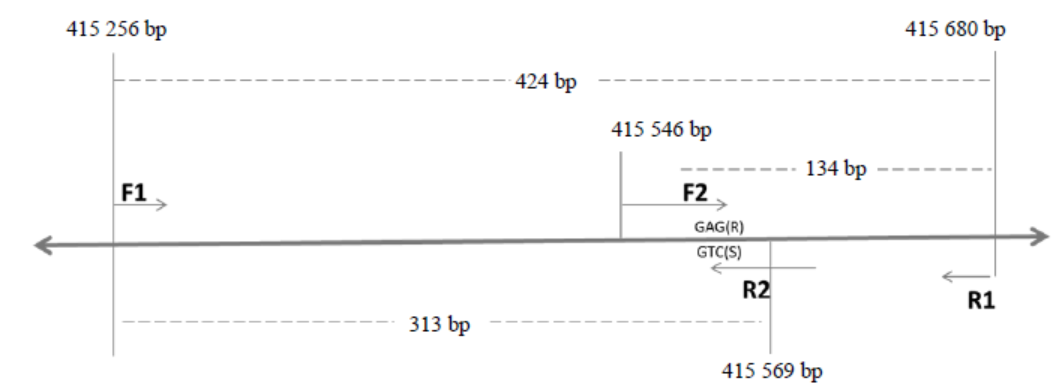
Fig. 1. Strategy for designing a functional PCR-based marker for xa5.Targeting a 2-bp functional nucleotide polymorphism in exon II of the candidate gene encoding transcription factor IIA, a set of four primers were designed. F1 and R1 target a 424-bp region which is common to both resistant and susceptible alleles. The 3′ end of the primer F2 target the resistant allele (i.e. GAG) and the amplicon devided from F2 and R1 (amplified only in genotypes possessing the resistant allele, whether homozygous or heterozygous) is 134-bp long, while the 3′ end of the primer R2 targets the susceptible allele (i.e. GTC) and the amplicon devided from F2 and R1 (amplified only in genotypes possessing the susceptible allele, whether homozygous or heterozygous) is 313-bp long. Homozygous resistant genotypes amplify 424-bp and 134-bp fragments, homozygous susceptible genotypes amplify 424-bp and 313-bp fragments, while heterozygous individuals amplify all the three fragments.
| Gene | Primer name | Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Xa21 | PTA248 F | AGACGCGGAAGGGTGGTTCCCGGA |
| PTA248 R | AGACGCGGTAATCGAAAGATGAAA | |
| xa13 | xa13-prom F | GGCCATGGCTCAGTGTTTAT |
| xa13-prom R | GAGCTCCAGCTCTCCAAATG | |
| xa5 | xa5FM-SF | GTCTGGAATTTGCTCGCGTTCG |
| xa5FM-SR | TGGTAAAGTAGATACCTTATCAAACTGGA | |
| xa5FM-RF | AGCTCGCCATTCAAGTTCTTGAG | |
| xa5FM-RR | TGACTTGGTTCTCCAAGGCTT |
Table 2 Functional primer sequences for Xa21, xa13 and xa5.
| Gene | Primer name | Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Xa21 | PTA248 F | AGACGCGGAAGGGTGGTTCCCGGA |
| PTA248 R | AGACGCGGTAATCGAAAGATGAAA | |
| xa13 | xa13-prom F | GGCCATGGCTCAGTGTTTAT |
| xa13-prom R | GAGCTCCAGCTCTCCAAATG | |
| xa5 | xa5FM-SF | GTCTGGAATTTGCTCGCGTTCG |
| xa5FM-SR | TGGTAAAGTAGATACCTTATCAAACTGGA | |
| xa5FM-RF | AGCTCGCCATTCAAGTTCTTGAG | |
| xa5FM-RR | TGACTTGGTTCTCCAAGGCTT |
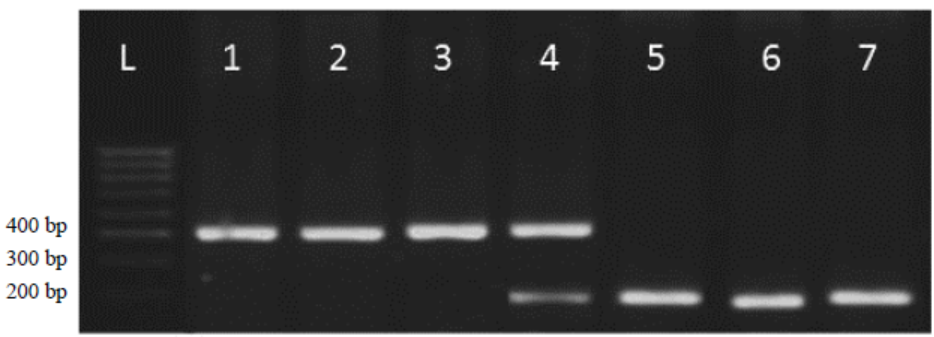
Fig. 2. Amplification pattern of polymorphic marker xa13-prom.L, 100-bp ladder marker; Lane 1, IRBB13; Lane 2, Improved Samba Mahsuri; Lanes 5 to 7, F1 plants in which the gene is in heterozygous condition (lane 4) and those which do not have the resistant allele of the gene. Individuals homozygous for the resistant allele amplify a 450-bp fragment, while those which are homozygous susceptible for the gene amplify a 220-bp fragment and heterozygous individuals amplify both the two fragments in a co-dominant fashion.
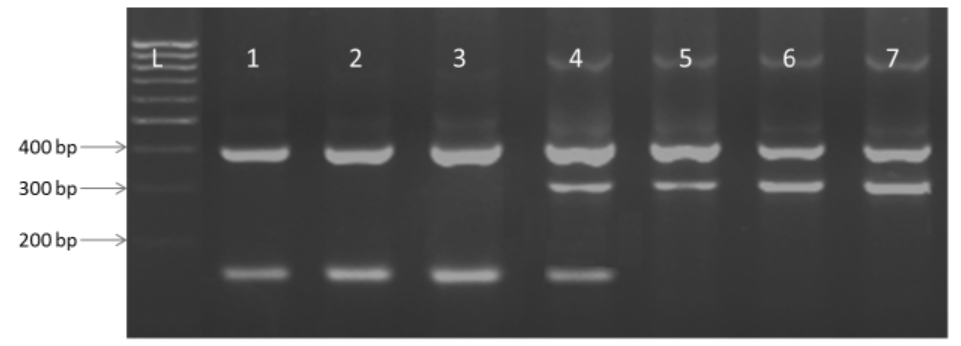
Fig. 3. Amplification pattern of polymorphic marker xa5FM.The functional marker was analyzed in a set of rice genotypes which possess xa5 (lanes 1 to 3). F1 plants in which the gene is in heterozygous condition (lane 4) and those which do not have the resistant allele of the gene (lanes 5 to 7). Individuals homozygous for the resistant allele amplify 424-bp and 134-bp fragments, while those which are homozygous susceptible for the gene amplify 424-bp and 313-bp fragments and heterozygous individuals amplify all the three fragments in a co-dominant fashion. L, 100-bp ladder marker; Lane 1, IRBB5; Lane 2, Improved Samba Mahsuri; Lane 3, SS1113; Lane 4, F1 of Improved Samba Mahsuri/IR64; Lane 5, IR64; Lane 6, TN1; Lane 7, Samba Mahsuri.
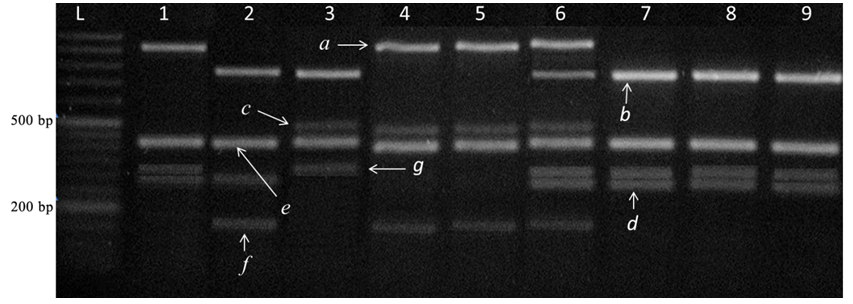
Fig. 4. Amplification pattern of PCR based multiplex marker system for simultaneous detection of Xa21, xa13 and xa5.L, 50-bp ladder marker separated on agarose gel to correlate the amplicon size; Lane 1, IRBB21 (possessing only Xa21); Lane 2, IRBB5 (possessing only xa5); Lane 3, IRBB13 (possessing only xa13); Lane 4, Improved Samba Mahsuri (possessing Xa21, xa13 and xa5); Lane 5, SS1113 (possessing Xa21, xa13 and xa5); Lane 6, F1 plant of Improved Samba Mahsuri/Vandana (heterozygous for all the three genes); Lane 7, IR64; Lane 8, TN1; Lane 9, Samba Mahsur.Lanes 7, 8 and 9 are the samples which are devoid of the resistant allele of all the three genes. Fragments a and b correspond to the resistant (950-bp) and susceptible alleles (660-bp) of Xa21, c and d correspond to resistant (450-bp) and susceptible alleles (220-bp) of xa13, while f and g correspond to the resistant (134-bp) and susceptible alleles (313-bp) of xa5 with 424-bp common fragment to both resistant and susceptible individuals. The multiplex marker system can clearly distinguish plants possessing Xa21, xa13 and xa5 from those do not possess the genes and also those which possess the genes in heterozygous condition.
| [1] | Anonymous.2002. Standard Evaluation System for Rice. Manila, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute: 56. |
| [2] | Antony G, Zhou J H, Huang S, Li T, Liu B, White F, Yang B.2010. Rice xa13 recessive resistance to bacterial blight is defeated by induction of the disease susceptibility gene Os-11N3.Plant Cell, 22(11): 3864-3876. |
| [3] | Balachiranjeevi C H, Bhaskar N S, Abhilash V, Akanksha S, Viraktamath B C, Madhav M S, Hariprasad A S, Laha G S, Prasad M S, Balachandran S M, Neeraja C N, Kumar M S, Senguttuvel P, Kemparaju K B, Bhadana V P, Ram T, Harika G, Swamy H K M, Hajira S K, Yugander A, Pranathi K, Anila M, Rekha G, Kousik M B V N, Dilip Kumar T, Swapnil R K, Giri A, Sundaram R M.2015. Marker-assisted introgression of bacterial blight and blast resistance into DRR17B, an elite fine-grain type maintainer line of rice.Mol Breeding, 35(7): 151. |
| [4] | Basavaraj S H, Singh V K, Singh A, Singh A, Singh A, Anand D, Yadav S, Ellur R K, Singh D, Krishnan S G, Nagarajan M, Mohapatra T, Prabhu K V, Singh A K.2010. Marker assisted improvement of bacterial blight resistance in parental lines of Pusa RH10, a superfine grain aromatic rice hybrid.Mol Breeding, 26(2): 293-305. |
| [5] | Blair M W, Garris A J, Iyer A S, Chapman B, Kresovich S, McCouch S R.2003. High resolution genetic mapping and candidate gene identification at the xa5 locus for bacterial blight resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Theor Appl Genet, 107(1): 62-73. |
| [6] | Cao L Y, Zhuang J Y, Yuan S J, Zhan X D, Zheng K L, Cheng S H.2003. Hybrid rice resistant to bacterial leaf blight developed by marker assisted selection.Rice Sci, 11(1): 68-70. |
| [7] | Chen S, Xu C J, Lin X H, Zhang Q Q.2001. Improving bacterial blight resistance of ‘6078’ an elite restorer line of hybrid rice, by molecular marker-assisted selection.Plant Breeding, 120(2): 133-137. |
| [8] | Chen X W, Shang J J, Chen D X, Lei C L, Zou Y, Zhai W X, Liu G Z, Xu J C, Ling Z Z, Cao G, Ma B T, Wang Y P, Zhao X F, Li S G, Zhu L H.2006. A β-lectin receptor kinase gene conferring rice blast resistance.Plant J, 46(5): 794-804. |
| [9] | Chu Z H, Fu B Y, Yang H, Xu C G, Li Z K, Sanchez A, Park Y J, Bennetzen J L, Zhang Q F, Wang S P.2006a. Targeting xa13, a recessive gene for bacterial blight resistance in rice.Theor Appl Genet, 112(3): 455-461. |
| [10] | Chu Z H, Yuan M, Yao J L, Ge X J, Yuan B, Xu C G, Li X H, Fu B Y, Li Z K, Bennetzen J L, Zhang Q F, Wang S P.2006b. Promoter mutations of an essential gene for pollen development result in disease resistance in rice.Genes Dev, 20: 1250-1255. |
| [11] | Devadath S.1989. Chemical control of bacterial blight of rice. In: International Rice Research Institute (IRRI). Bacterial Blight of Rice. Manila, the Philippines: IRRI: 89-98. |
| [12] | Dokku P, Das K M, Rao G J N.2013. Pyramiding of four resistance genes of bacterial blight in Tapaswini, an elite rice cultivar, through marker-assisted selection.Euphytica, 192(1): 87-96. |
| [13] | DRR Progress Report.2013. All India Coordinated Rice Improvement Programme (ICAR). Directorate of Rice Research, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad, India. |
| [14] | DRR Progress Report.2014. All India Coordinated Rice Improvement Programme (ICAR). Directorate of Rice Research, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad, India. |
| [15] | Hari Y, Srinivasarao K, Viraktamath B C, Hariprasad A S, Laha G S, Ahmed M, Natarajkumar P, Ramesha M S, Neeraja C N, Balachandran S M, Rani N S, Balaji Suresh P, Sujatha K, Pandey M, Ashok Reddy G, Madhav M S, Sundaram R M.2011. Marker-assisted improvement of a stable restorer line KMR-3R and its derived hybrid KRH2 for bacterial blight resistance and grain quality.Plant Breeding, 130(6): 608-616. |
| [16] | Hari Y, Srinivasarao K, Viraktamath B C, Hari Prasad A S, Laha G S, Ahmed M, Natarajkumar P, Sujatha K, Srinivas Prasad M, Pandey M, Ramesha M S, Neeraja C N, Balachandran S M, Rani N S, Kemparaju B, Mohan K M, Sama V S A K, Shaik H, Balachiranjeevi C, Pranathi K, Reddy G A, Madhav M S, Sundaram R M.2013. Marker-assisted introgression of bacterial blight and blast resistance into IR58025B, an elite maintainer line of rice. J Plant Breeding, 132(6): 586-594. |
| [17] | Huang N, Angeles E R, Domingo J, Magpantay G, Singh S, Zhang G, Kumaravadivel N, Bennett J, Khush G S.1997. Pyramiding of bacterial blight resistance genes in rice: Marker aided selection using RFLP and PCR.Theor Appl Genet, 95(3): 313-320. |
| [18] | Iyer A S, McCouch S R.2004. The rice bacterial blight resistance gene xa5 encodes a novel form of disease resistance.Mol Plant Microbe Inter, 17(12): 1348-1354. |
| [19] | Iyer-Pascuzzi A S, McCouch S R.2007. Functional markers for xa5-mediated resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Mol Breeding, 19(4): 291-296. |
| [20] | Joseph M, Gopalakrishnan S, Sharma R K, Singh V P, Singh A K, Singh N K, Mohapatra T.2004. Combining bacterial blight resistance and basmati quality characteristics by phenotypic and molecular marker assisted selection in rice.Mol Breeding, 13(4): 377-387. |
| [21] | Kauffman H E, Reddy A P K, Hsieh S P Y, Merca S D.1973. An improved technique for evaluating resistance of rice varieties toXanthomonas oryzae. Plant Dis Rep, 57(6): 537-541. |
| [22] | Khush G S, Mackill D J, Sidhu G S.1989. Breeding rice for resistance to bacterial leaf blight. In: International Rice Research Institute (IRRI). Bacterial Blight of Rice. Manila, the Philippines: IRRI: 207-217. |
| [23] | Khush G S, Angeles E R.1999. A new gene for resistance to race 6 of bacterial blight in rice, Oryza sativa L.Rice Genet Newsl, 16: 92-93. |
| [24] | Kim S M, Suh J P, Qin Y, Noh T H, Reinke R F, Jena K K.2015. Identification and fine-mapping of a new resistance gene, Xa40, conferring resistance to bacterial blight races in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Theor Appl Genet, 1238(10): 1933-1943. |
| [25] | Kumar P N, Sujatha K, Laha G S, Srinivasa Rao K, Mishra B, Viraktamath B C, Hari Y, Reddy C S, Balachandran S M, Ram T, Sheshu Madhav M, Shobha Rani N, Neeraja C N, Ashok Reddy G, Shaik H, Sundaram R M.2012. Identification and fine-mapping of Xa33, a novel gene for resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae.Phytopathology, 102(2): 222-228. |
| [26] | Laha G S, Reddy C S, Krishnaveni D, Sundaram R M, Srinivas P M, Ram T, Muralidharan K, Viraktamath B C.2009. Bacterial blight of rice and its management. In: DRR Technical Bulletin No. 41. Hyderabad, India: Directorate of Rice Research: 37. |
| [27] | Mew T W.1987. Current status and future prospects of research on bacterial blight of rice.Annu Rev Phytopath, 25: 359-382. |
| [28] | Mew T W, Alvarez A M, Leach J E, Swings J.1993. Focus on bacterial blight of rice.Plant Dis, 77(1): 5-12. |
| [29] | Ogawa T, Yamamoto T.1986. Inheritance of resistance to bacterial blight in rice. In: Rice Genetics. Manila, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute: 471-480. |
| [30] | Ou S H.1985. Rice Diseases. 2nd edn. Kew: Surrey Commonwealth Mycological Institute: 380. |
| [31] | Pandey M K, Rani N S, Sundaram R M, Laha G S, Madhav M S, Srinivasa Rao K, Sudharshan I, Hari Y, Varaprasad G S, Subba Rao L V, Suneetha K, Sivaranjani A K P, Viraktamath B C.2013. Improvement of two traditional Basmati rice varieties for bacterial blight resistance and plant stature through morphological and marker-assisted selection.Mol Breeding, 31(1): 239-246. |
| [32] | Perumalsamy S, Bharani M, Sudha M, Nagarajan P, Arul L, Saraswathi R, Balasubramanian P, Ramalingam J.2010. Functional marker-assisted selection for bacterial leaf blight resistance genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Plant Breeding, 129(4): 400-406. |
| [33] | Rajpurohit D, Kumar R, Kumar M, Paul P, Awasthi A, Basha P O, Puri A, Jhang T, Singh K, Dhaliwal H S.2011. Pyramiding of two bacterial blight resistance and a semidwarfing gene in Type 3 Basmati using marker-assisted selection.Euphytica, 178(1): 111-126. |
| [34] | Ramalingam J, Basharat H S, Zhang G.2001. Polymorphism of DNA markers linked to bacterial blight resistance genes in useful rice germplasm. Int Rice Res Notes, 26(2): 23-24. |
| [35] | Ramkumar G, Prahalada G D, Hechanova S L, Vinarao R, Jena K K.2015. Development and validation of SNP-based functional codominant markers for two major disease resistance genes in rice (O. sativa L.).Mol Breeding, 35: 129. |
| [36] | Rao P S, Kauffman H E.1971. New Indian host of Xanthomonas oryzae, incitant of bacterial leaf blight of rice.Curr Sci, 40: 271-272. |
| [37] | Ronald P C, Albano B, Tabien R, Abenes L, Wu K S, McCouch S, Tanksley S D.1992. Genetic and physical analysis of the rice bacterial blight resistance locus, Xa21.Mol General Genet, 236: 113-120. |
| [38] | Salgotra R K, Millwood R J, Agarwal S, Steward N C.2011. High throughput functional marker assay for detection of Xa/xa and fgr genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Electrophoresis, 32(16): 2216-2222. |
| [39] | Salgotra R K, Gupta B B, Millwood R J, Balasubramaniam M, Stewart J C N.2012. Introgression of bacterial leaf blight resistance and aroma genes using functional marker-assisted selection in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Euphytica, 187(3): 313-323. |
| [40] | Sanchez A C, Ilag L L, Yang D, Brar D S, Ausubel F, Khush G S, Yano M, Sasaki T, Li Z, Huang N.1999. Genetic and physical mapping of xa13, a recessive bacterial blight resistance gene in rice. Theor Appl Genet, 98(6): 1022-1028. |
| [41] | Sanchez A C, Brar D S, Huang N, Li Z, Khush G S.2000. Sequence tagged site markers assisted selection for three bacterial blight resistance genes in rice. Crop Sci, 40(3): 792-797. |
| [42] | Shaik H, Yugander A, Balachiranjeevi C H, Pranathi K, Anila M, Mahadevaswamy H K, Kousik B V N, Dilip Kumar T, Ashok Reddy G, Bhaskar S, Abhilash Kumar V, Harika G, Rekha G, Laha G S, Viraktamath B C, Balachandran S M, Neeraja C N, Sheshu Madhav M, Mangrauthia S K, Bhadana V P, Sundaram R M.2014. Development of durable bacterial blight resistant lines of Samba Mahsuri possessing Xa33, Xa21, Xa13 & Xa5.Progr Res, 9: 1224-1227. |
| [43] | Singh S, Sidhu J S, Huang N, Vikal Y, Li Z, Brar D S, Dhaliwal H S, Khush G S.2001. Pyramiding three bacterial blight resistance genes (xa-5, xa-13 and Xa-21) using marker-assisted selection into indica rice cultivar PR-106.Theor Appl Genet, 102(6): 1011-1015. |
| [44] | Song W Y, Wang G L, Chen L L, Kim H S, Pi L Y, Holsten T, Gardner J, Wang B, Zhai W X, Zhu L H, Fauquet C, Ronald P.1995. A receptor kinase like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene Xa-21.Science, 270: 1804-1806. |
| [45] | Suh J P, Jeung J U, Noh T H, Cho Y C, Park S H, Park H S, Shin M S, Kim C K, Jena K K.2013. Development of breeding lines with three pyramided resistance genes that confer broad- spectrum bacterial blight resistance and their molecular analysis in rice.Rice, 6: 5. |
| [46] | Sujatha K, Natarajkumar P, Laha G S, Mishra B, Rao K S, Viraktamath B C, Kirti P B, Hari Y, Balachandran S M, Rajendrakumar P, Ram T, Hajira S K, Madhav M S, Neeraja C N, Sundaram R M.2011. Inheritance of bacterial blight resistance in the rice cultivar Ajaya and high-resolution mapping of a major QTL associated with resistance.Genet Res Cambr, 93(6): 397-408. |
| [47] | Sundaram R M, Vishnupriya M R, Biradar S K, Laha G S, Reddy A G, Rani N S, Sarma N P, Sonti R V.2008. Marker assisted introgression of bacterial blight resistance in Samba Mahsuri, an elite indica rice variety.Euphytica, 160(3): 411-422. |
| [48] | Sundaram R M, Vishnupriya M R, Laha G S, Rani N S, Rao P S, Balachandran S M, Reddy G A, Sarma N P, Sonti R V.2009. Introduction of bacterial blight resistance into Triguna, a high yielding, mid-early duration rice variety by molecular marker assisted breeding.Biotechnol J, 4(3): 400-407. |
| [49] | Sundaram R M, Madhav M S, Balachandran S M, Neeraja C N, Mangrauthia S K, Padmavathi G, Bhadana V P, Laha G S, Prasad M S, Krishnaveni D, Bentur J S, Padmakumar A P, Katti G, Jhansi Lakshmi V, Shobha Rani N, Viraktamath B C.2014. Marker-Assisted Selection for Biotic Stress Resistance in Rice. Directorate of Rice Research, Rajendraganar, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India: 79. |
| [50] | Wang G L, Song W Y, Ruan D L, Sideris S, Ronald P C.1996. The cloned gene, Xa21, confers resistance to multiple Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae isolates in transgenic plants.Mol Plant Microbiol Inter, 9(9): 850-855. |
| [51] | Yoshimura S, Yoshimura A, Iwata N, McCouch S R, Abenes M L, Baraoidan M R, Mew T W, Nelson R J.1995. Tagging and combining bacterial blight resistance genes in rice using RAPD and RFLP markers.Mol Breeding, 1: 375-387. |
| [52] | Yuan Z, Gao S, Xue D W, Luo D, Li L T, Ding S Y, Yao X, Wilson Z A, Qian Q, Zhang D B.2009. Retarded Palea1 controls palea development and floral zygomorphy in rice.Plant Physiol, 149(1): 235-244. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||