
Rice Science ›› 2016, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (6): 317-325.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2016.05.003
收稿日期:2016-03-26
接受日期:2016-05-24
出版日期:2016-12-12
发布日期:2016-08-10
. [J]. Rice Science, 2016, 23(6): 317-325.
| Score | Observation | Tolerance |
| 1 | Normal growth, no leaf symptoms | Highly tolerant |
| 3 | Nearly normal growth, only the tips of few leaves whitish and rolled | Tolerant |
| 5 | Growth severely retarded, most leaves rolled, the two youngest leaves were still elongating | Moderately tolerant |
| 7 | Complete cessation of growth, all lower leaves dried out, the two youngest leaves started to wilt | Susceptible |
| 9 | The whole plant dried out and dead | Highly susceptible |
Table 1 Scoring criteria for salt tolerance (Gregorio et al, 1997)
| Score | Observation | Tolerance |
| 1 | Normal growth, no leaf symptoms | Highly tolerant |
| 3 | Nearly normal growth, only the tips of few leaves whitish and rolled | Tolerant |
| 5 | Growth severely retarded, most leaves rolled, the two youngest leaves were still elongating | Moderately tolerant |
| 7 | Complete cessation of growth, all lower leaves dried out, the two youngest leaves started to wilt | Susceptible |
| 9 | The whole plant dried out and dead | Highly susceptible |
| Genotype | Designation | Source | Score | Reaction to salinity | Genotype | Designation | Source | Score | Reaction to salinity |
| IRSSTN25 (CK) | FL478 (IR66946-3R-178-1-1) | IRRI | 3 | T | KMR3 | KMR3 | India | 9 | HS |
| IRSSTN24 (CK) | IR28 | IRRI | 7 | S | IET19543 | DRRH3 | India | 5 | MT |
| IET22631 | RP Bio 4919-13-5 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 5 | MT | IET23124 | RP Bio 4918-7-1 (Swarna × O. nivara) | India | 9 | HS |
| IET22625 | RP Bio 4918-250 (Swarna × O. nivara) | India | 7 | S | IET21542 | RP Bio 4918-248 (Swarna × O. nivara) | India | 9 | HS |
| IET21943 | RP Bio 4919-50-13 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 3 | T | IET21944 | RP Bio 4919-13-7 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 3 | T |
| IET22636 | RP Bio 4919-86-18 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 5 | MT | IET21940 | RP Bio 4919-463 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 3 | T |
| IET23183 | RP Bio 4918-230 (Swarna × O. nivara) | India | 9 | HS | IET22628 | RP Bio 4919-50-12 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 5 | MT |
| IET22627 | RP Bio 4919-50-10 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 7 | S | IET22633 | RP Bio 4919-495 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 7 | S |
| IET22624 | RP Bio 4918-24 (Swarna × O. nivara) | India | 7 | S | IET22626 | RP Bio 4919-50-7 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 5 | MT |
| IET3116 | Vikas | India | 5 | MT | IRSSTN19 | IRT11173 | IRRI | 5 | MT |
| IET19487 | DRR Dhan 39 | India | 5 | MT | IRSSTN5 | IRT11237 | IRRI | 7 | S |
| IET9341 | CST7-1 | India | 5 | MT | IRSSTN14 | IRT11160 | IRRI | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN15 | IRT11176 | IRRI | 5 | MT | IRSSTN3 | IRT11239 | IRRI | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN29 | IR45427-2B-2-2B-1-1 | IRRI | 3 | T | IRSSTN21 | Pokkali (ACC108921) | IRRI | 3 | T |
| IRSSTN6 | BR11-Saltol | IRRI | 9 | HS | IRSSTN1 | IRT11169 | IRRI | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN11 | IRT11236 | IRRI | 7 | S | IRSSTN9 | IRT11149 | IRRI | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN13 | IRT11260 | IRRI | 5 | MT | IRSSTN22 | Nonabokra | IRRI | 3 | T |
| IRSSTN10 | IRT11133 | IRRI | 7 | S | IET18076 | DRRH2 | India | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN17 | IRT11174 | IRRI | 5 | MT | IRSSTN16 | IRT11172 | IRRI | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN30 | A69-1 | India | 5 | MT | IET5656 | Swarna | India | 9 | HS |
| IET19046 | Sambha Mahsuri | India | 9 | HS | IET17340 | CSR36 | India | 3 | T |
| IRSSTN28 | AT401 | India | 3 | T | IRSSTN8 | IRT11252 | IRRI | 7 | S |
| IRSSTN12 | IRT11254 | IRRI | 5 | MT | IRSSTN7 | IRT11170 | IRRI | 7 | S |
| IRSSTN27 | IR55179-3B-11-3 | IRRI | 3 | T | IET15420 | Jarava | India | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN2 | IRT11158 | IRRI | 5 | MT | IRSSTN18 | IRT11141 | IRRI | 3 | T |
| IRSSTN4 | IRT11247 | IRRI | 5 | MT | IRSSTN20 | IRT11175 | IRRI | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN23 | IR29 | IRRI | 7 | S | IET13765 | CSR27 | India | 3 | T |
| T, Tolerant; MT, Moderately tolerant; S, Susceptible; HS, Highly susceptible; IRRI, International Rice Research Institute. | |||||||||
Table 2 Salinity stress reaction (EC = 10 dSm-1) of 54 rice genotypes at the seedling stage
| Genotype | Designation | Source | Score | Reaction to salinity | Genotype | Designation | Source | Score | Reaction to salinity |
| IRSSTN25 (CK) | FL478 (IR66946-3R-178-1-1) | IRRI | 3 | T | KMR3 | KMR3 | India | 9 | HS |
| IRSSTN24 (CK) | IR28 | IRRI | 7 | S | IET19543 | DRRH3 | India | 5 | MT |
| IET22631 | RP Bio 4919-13-5 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 5 | MT | IET23124 | RP Bio 4918-7-1 (Swarna × O. nivara) | India | 9 | HS |
| IET22625 | RP Bio 4918-250 (Swarna × O. nivara) | India | 7 | S | IET21542 | RP Bio 4918-248 (Swarna × O. nivara) | India | 9 | HS |
| IET21943 | RP Bio 4919-50-13 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 3 | T | IET21944 | RP Bio 4919-13-7 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 3 | T |
| IET22636 | RP Bio 4919-86-18 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 5 | MT | IET21940 | RP Bio 4919-463 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 3 | T |
| IET23183 | RP Bio 4918-230 (Swarna × O. nivara) | India | 9 | HS | IET22628 | RP Bio 4919-50-12 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 5 | MT |
| IET22627 | RP Bio 4919-50-10 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 7 | S | IET22633 | RP Bio 4919-495 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 7 | S |
| IET22624 | RP Bio 4918-24 (Swarna × O. nivara) | India | 7 | S | IET22626 | RP Bio 4919-50-7 (KMR3 × O. rufipogon) | India | 5 | MT |
| IET3116 | Vikas | India | 5 | MT | IRSSTN19 | IRT11173 | IRRI | 5 | MT |
| IET19487 | DRR Dhan 39 | India | 5 | MT | IRSSTN5 | IRT11237 | IRRI | 7 | S |
| IET9341 | CST7-1 | India | 5 | MT | IRSSTN14 | IRT11160 | IRRI | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN15 | IRT11176 | IRRI | 5 | MT | IRSSTN3 | IRT11239 | IRRI | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN29 | IR45427-2B-2-2B-1-1 | IRRI | 3 | T | IRSSTN21 | Pokkali (ACC108921) | IRRI | 3 | T |
| IRSSTN6 | BR11-Saltol | IRRI | 9 | HS | IRSSTN1 | IRT11169 | IRRI | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN11 | IRT11236 | IRRI | 7 | S | IRSSTN9 | IRT11149 | IRRI | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN13 | IRT11260 | IRRI | 5 | MT | IRSSTN22 | Nonabokra | IRRI | 3 | T |
| IRSSTN10 | IRT11133 | IRRI | 7 | S | IET18076 | DRRH2 | India | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN17 | IRT11174 | IRRI | 5 | MT | IRSSTN16 | IRT11172 | IRRI | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN30 | A69-1 | India | 5 | MT | IET5656 | Swarna | India | 9 | HS |
| IET19046 | Sambha Mahsuri | India | 9 | HS | IET17340 | CSR36 | India | 3 | T |
| IRSSTN28 | AT401 | India | 3 | T | IRSSTN8 | IRT11252 | IRRI | 7 | S |
| IRSSTN12 | IRT11254 | IRRI | 5 | MT | IRSSTN7 | IRT11170 | IRRI | 7 | S |
| IRSSTN27 | IR55179-3B-11-3 | IRRI | 3 | T | IET15420 | Jarava | India | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN2 | IRT11158 | IRRI | 5 | MT | IRSSTN18 | IRT11141 | IRRI | 3 | T |
| IRSSTN4 | IRT11247 | IRRI | 5 | MT | IRSSTN20 | IRT11175 | IRRI | 5 | MT |
| IRSSTN23 | IR29 | IRRI | 7 | S | IET13765 | CSR27 | India | 3 | T |
| T, Tolerant; MT, Moderately tolerant; S, Susceptible; HS, Highly susceptible; IRRI, International Rice Research Institute. | |||||||||
| Marker | Chromosome | Frequency of major allele | Number of alleles | PIC value |
| RM493 | 1 | 0.46 | 3 | 0.96 |
| RM3412 | 1 | 0.53 | 3 | 0.96 |
| RM7075 | 1 | 0.26 | 5 | 0.97 |
| RM8094 | 1 | 0.24 | 7 | 0.99 |
| RM10694 | 1 | 0.57 | 3 | 0.97 |
| RM10720 | 1 | 0.43 | 3 | 0.95 |
| RM10793 | 1 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.97 |
| RM10843 | 1 | 0.39 | 3 | 0.95 |
| RM10852 | 1 | 0.35 | 3 | 0.94 |
| RM289 | 5 | 0.70 | 2 | 0.55 |
| RM413 | 5 | 0.56 | 5 | 0.96 |
| RM264 | 8 | 0.70 | 3 | 0.90 |
| RM149 | 8 | 0.20 | 4 | 0.77 |
| RM222 | 10 | 0.35 | 5 | 0.96 |
Table 3 Frequency of major allele and polymorphic information content (PIC) value of SSR markers for 54 rice genotypes
| Marker | Chromosome | Frequency of major allele | Number of alleles | PIC value |
| RM493 | 1 | 0.46 | 3 | 0.96 |
| RM3412 | 1 | 0.53 | 3 | 0.96 |
| RM7075 | 1 | 0.26 | 5 | 0.97 |
| RM8094 | 1 | 0.24 | 7 | 0.99 |
| RM10694 | 1 | 0.57 | 3 | 0.97 |
| RM10720 | 1 | 0.43 | 3 | 0.95 |
| RM10793 | 1 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.97 |
| RM10843 | 1 | 0.39 | 3 | 0.95 |
| RM10852 | 1 | 0.35 | 3 | 0.94 |
| RM289 | 5 | 0.70 | 2 | 0.55 |
| RM413 | 5 | 0.56 | 5 | 0.96 |
| RM264 | 8 | 0.70 | 3 | 0.90 |
| RM149 | 8 | 0.20 | 4 | 0.77 |
| RM222 | 10 | 0.35 | 5 | 0.96 |
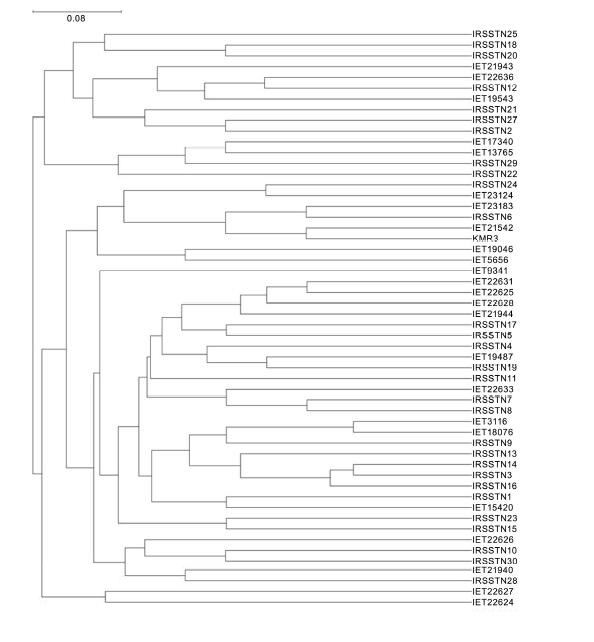
Fig. 2. Dendrogram showing grouping of 54 rice genotypes based on unweighted pair group method with arithmetic averages algorithm clustering and Jaccard coefficient analysis using 14 SSR markers.
| 1 | Ahmadi J, Fotokian M H.2011. Identification and mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa) using SSR markers. Iran J Biotechnol, 9(1): 21-30. |
| 2 | All India Coordinated Rice Improvement Project (AICRIP). 2012. Annual Progress Report 2011-2012. Hyderabad, India: Directorate of Rice Research. |
| 3 | All India Coordinated Rice Improvement Project (AICRIP). 2013. Annual Progress Report 2012-2013. Hyderabad, India: Directorate of Rice Research. |
| 4 | Babu N N, Vinod K K, Krishnan S G, Bhowmick P K, Vanaja T, Krishnamurthy S L, Nagarajan M, Singh N K, Prabhu K V, Singh A K.2014. Marker based haplotype diversity ofSaltol QTL in relation to seedling stage salinity tolerance in selected genotypes of rice. Ind J Genet Plant Breeding, 74(1): 16-25. |
| 5 | Bimpong I K, Manneha B, Sock M, Diawa F, Amoah N K A, Ismail A M, Gregoriob G, Singh R K, Wopereis M.2016. Improving salt tolerance of lowland rice cultivar ‘Rassi’ through marker-aided backcross breeding in West Africa.Plant Sci, 242: 288-299. |
| 6 | Bonilla P S, Dvorak J, Mackill D, Deal K, Gregorio G.2002. RFLP and SSLP mapping of salinity tolerance genes in chromosome 1 of rice (Oryza sativa L.) using recombinant inbred lines. Philipp Agric Sci, 85: 64-74. |
| 7 | Das P, Nutan K K, Singla-Pareek S L, Pareek A.2015. Understanding salinity responses and adopting ‘omics-based’ approaches to generate salinity tolerant cultivars of rice.Front Plant Sci, 6: 712. |
| 8 | Dellaporta S L, Wood J, Hicks J B.1983. A plant DNA minipreparation: Version II.Plant Mol Biol Rep, 1(4): 19-21. |
| 9 | Eliades N G, Eliades D G.2009. Haplotype analysis: Software for analysis of haplotype data. Goettingen, Germany: Forest Genetics and Forest Tree Breeding, Georg-August University. |
| 10 | Emon R M, Islamb M M, Halderb J, Fan Y.2015. Genetic diversity and association mapping for salinity tolerance in Bangladeshi rice landraces.Crop J, 3(5): 440-444. |
| 11 | Ganeshan P, Jain A, Parmar B, Rao A R, Sreenu K, Mishra P, Mesapogu S, Subrahmanyam D, Ram T, Sarla N, Rai V.2016. Identification of salt tolerant rice lines among interspecific BILs developed by crossingOryza sativa × O. rufipogon and O. sativa × O. nivara. AJCS, 10(2): 220-228. |
| 12 | Ganie S A, Borgohain M J, Kritika K, Talukdar A, Pani D R, Mondal T K.2016. Assessment of genetic diversity ofSaltol QTL among the rice(Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. Physiol Mol Biol Plants, 22(1): 107-114. |
| 13 | Gregorio G B.1997. Tagging salinity tolerance genes in rice using amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP). Los Baños, the Philippines: University of the Philippines. |
| 14 | Gregorio G B, Senadhira D, Mendoza R D.1997. Screening Rice for Salinity Tolerance. Los Baños, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| 15 | Hossain H, Rahman M A, Alam M S, Singh R K.2015. Mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with reproductive-stage salt tolerance in rice.J Agron Crop Sci, 201(1): 17-31. |
| 16 | Huyen L T N, Cuc L M, Ismail A M, Ham L H.2012. Introgression the salinity tolerance QTLsSaltol into AS996, the elite rice variety of Vietnam. Am J Plant Sci, 3(7): 981-987. |
| 17 | Huyen L T N, Cuc L M, Ham L H, Khanh T D.2013. Introgression theSaltol QTL into Q5DB, the elite variety of Vietnam using marker-assisted-selection (MAS). Am J BioSci, 1: 80-84. |
| 18 | IRRI (International Rice Research Institute). 1997. Rice almanae. In: Maclean J L. Rice Geographical Distribution. 2nd edn. Los Baños, Laguna, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute (IRRI)-West Africa Rice Development Association (WARDA)-Centre for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT). |
| 19 | Islam M R, Gregorio G B, Salam M A, Collard B C Y, Tumimbang-Raiz E, Adorada D L, Mendoza R D, Singh R K, Hassan L.2011. Validation of a major QTL for salinity tolerance on chromosome 1 of rice in three different breeding populations.Agrochimica, 55: 355-366. |
| 20 | Islam M R, Gregorio G B, Salam M A, Collard B C Y, Singh R K, Hassan L.2012. Validation ofSaltol linked markers and haplotype diversity on chromosome 1 of rice. Mol Plant Breeding, 3(10): 103-114. |
| 21 | Ismail A M, Heuer S, Thomson M J, Wissuwa M.2007. Genetic and genomic approaches to develop rice germplasm for problem soils.Plant Mol Biol, 65(4): 547-570. |
| 22 | Ismail A M, Thomson M J, Vergara G V, Rahman M A, Singh R K, Gregorio G B, Mackill D J.2010. Designing resilient rice varieties for coastal deltas using modern breeding tools. In: Hoanh C T, Szuster B W, Pheng K S, Ismail A M, Nobel A D. Tropical Deltas and Coastal Zones: Food Production, Communities and Environment at the Land-Water Interface. Wallingford, UK: CAB International: 154-165. |
| 23 | Krishnamurthy S L, Sharma S K, Kumar V, Tiwari S, Batra V, Singh N K.2014. Assessment of genetic diversity in rice genotypes for salinity tolerance usingSaltol markers of chromosome 1. Ind J Genet Plant Breeding, 74(2): 243-247. |
| 24 | Krishnamurthy S L, Sharma S K, Kumar V, Tiwari S, Singh N K.2015. Analysis of genomic region spanningSaltol using SSR markers in rice genotypes showing differential seedlings stage salt tolerance. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol, 25(3): 331-336. |
| 25 | Kumar V, Singh A, Amitha Mithra S V, Krishnamurthy S L, Parida S K, Jain S, Tiwari K K, Kumar P, Rao A R, Sharma S K, Khurana J P, Singh N K, Mohapatra T.2015. Genome-wide association mapping of salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa). DNA Res, 22(2): 133-145. |
| 26 | Lakshmi V J, Swamy B P M, Kaladhar K, Sarla N.2010. BPH resistance in introgression lines of Swarna/Oryza nivara and KMR3/O. rufipogon. Direct Rice Res Newsl, 8: 4. |
| 27 | Lang N T, Yanagihara S, Buu B C.2000. Quantitative trait loci for salt tolerance in rice via molecular markers.Omonrice, 8: 37-48. |
| 28 | Lang N T, Li Z K, Buu B C.2001. Microsatellite markers linked to salt tolerance in rice.Omonrice, 9: 9-21. |
| 29 | Linh L H, Linh T H, Xuan T D, Ham L H, Ismail A M, Khanh T D.2012. Molecular breeding to improve salt tolerance of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in the red river delta of Vietnam. Int J Plant Genom, 2012: 1-9. |
| 30 | Liu K, Muse S V.2005. Power marker: An integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis.Bioinformatics, 21(9): 2128-2129. |
| 31 | Liu S, Anderson J A.2003. Targeted molecular mapping of major wheat QTL forFusarium head blight resistance using wheat ESTs and synteny with rice. Genome, 46(5): 817-823. |
| 32 | McCartney C A, Sommers D J, Fedak G, Cao W.2004. Haplotype diversity atFusarium head blight resistance QTLs in wheat. Theor Appl Genet, 109(2): 261-271. |
| 33 | Mishra S, Singh B, Panda K, Singh B P, Singh N, Misra P, Rai V, Singh N K.2016. Association of SNP haplotypes of HKT family genes with salt tolerance in Indian wild rice germplasm.Rice, 9: 15. |
| 34 | Mohammadi-Nejad G, Arzani A, Rezai A M, Singh R K, Gregorio G B.2008. Assessment of rice genotypes for salt tolerance using microsatellite markers associated with theSaltol QTL. Afr J Biotechnol, 7(6): 730-736. |
| 35 | Rahman M A, Thomson M J, Shah-E-Alam M, de Ocampo M, Egdane J, Ismail A M.2016. Exploring novel genetic sources of salinity tolerance in rice through molecular and physiological characterization.Ann Bot: 1-15. |
| 36 | Rai V, Sreenu K, Pushpalatha B, Babu A P, Brajendra, Sandhya G, Sarla N.2010. Swarna/Oryza nivara and KMR3/O. rufipogon introgression lines tolerant to drought and salinity. Direct Rice Res Newsl, 8: 4. |
| 37 | Ren Z H, Gao J P, Li L G, Cai X L, Huang W, Chao D Y, Zhu M Z, Wang Z Y, Luan S, Lin H X.2005. A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter.Nat Genet, 37: 1141-1146. |
| 38 | Samal R, Roy P S, Dash A K, Rao G J N. Bharathkumar S, Subudhi H N, Reddy J N.2016. Genetic diversity in the rice landraces (Oryza sativa L.) of coastal Sundarbans (India) and their adaptation to the local saline condition investigated both at molecular and physiological level. Acta Physiol Plant, 38: 56. |
| 39 | Singh A K, Gopala Krishnan S, Singh V P, Prabhu K V, Mohapatra T, Singh N K, Sharma T R, Nagarajan M, Vinod K K, Singh D, Singh U D, Chander S, Atwal S S, Seth R, Singh V K, Ellur R K, Singh A, Anand D, Khanna A, Yadav S, Goel N, Singh A, Shikari A B, Singh A, Marathi B.2011. Marker assisted selection a paradigm shift in Basmati breeding.Ind J Genet Plant Breeding, 71(2): 120-128. |
| 40 | Singh R K, Gregorio G B, Jain R K.2007. QTL mapping for salinity tolerance in rice.Physiol Mol Biol Plant, 13(2): 87-99. |
| 41 | Singh R K, Flowers T J.2010. The physiology and molecular biology of the effects of salinity on rice. In: Pessarakli M. Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress. 3rd edn. Boca Raton, Florida, USA: Taylor and Francis: 901-942. |
| 42 | Singh R, Singh Y, Xalaxo S, Verulkar S, Yadav N, Singh S, Singh N, Prasad K S N, Kondayya K, Ramana Rao P V, Rani M G, Anuradha T, Suraynarayana Y, Sharma P C, Krishnamurthy S L, Sharma S K, Dwivedi J L, Singh A K, Singh P K, Nilanjay, Singh N K, Kumar R, Chetia S K, Ahmad T, Rai M, Perraju P, Pande A, Singh D N, Mandal N P, Reddy J N, Singh O N, Kataral J L, Marandi B, Swain P, Sarkar R K, Singh D P, Mohapatra T, Padmawathi G, Ram T, Kathiresan R M, Paramsivam K, Nadarajan S, Thirumeni S, Nagarajan M, Singh A K, Vikram P, Kumar A, Septiningshih E, Singh U S, Ismail A M, Mackill D, Singh N K.2016. From QTL to variety-harnessing the benefits of QTLs for drought, flood and salt tolerance in mega rice varieties of India through a multi-institutional network.Plant Sci, 242: 278-287. |
| 43 | Tiwari S, Krishnamurthy S L, Kumar V, Singh B, Rao A R, Amitha Mithra S V, Rai V, Singh A K, Singh N K.2016. Mapping QTLs for salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by bulked segregant analysis of recombinant inbred lines using 50K SNP chip. PLoS One, 11(4): e0153610. |
| 44 | Thomson M J, de Ocampo M, Egdane J, Rahman M A, Sajise A G, Adorada D L, Tumimbang-Raiz E, Blumwald E, Seraj Z I, Singh R K, Gregorio G B, Ismail A M.2010. Characterizing theSaltol quantitative trait locus for salinity tolerance in rice. Rice, 3(2): 148-160. |
| 45 | van Berloo R.2008. GGT2.0: Versatile software for visualization and analysis of genetic data.J Hered, 99(2): 232-236. |
| 46 | Vinod K K, Gopala Krishnan S, Naresh Babu N, Nagarajan M, Singh A K.2013. Improving salt tolerance in rice: Looking beyond the conventional. In: Ahmad P, Azooz M M, Prasad M N V. Salt Stress in Plants: Signalling, Omics and Adaptations. New York, USA: Springer: 219-260. |
| 47 | Walia H, Wilson C, Condamine P, Liu X, Ismail A M, Zeng L, Wanamaker S I, Mandal J, Xu J, Cui X, Close T J.2005. Comparative transcriptional profiling of two contrasting rice genotypes under salinity stress during the vegetative growth stage.Plant Physiol, 139(2): 822-835. |
| 48 | Yoshida S, Forno D A, Cock J H, Gomez K A.1976. Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice. Los Baños, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| 49 | Zhou Y, Yang P, Cui F L, Zhang F T, Luo X D, Xie J K.2016. Transcriptome analysis of salt stress responsiveness in the seedlings of Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). PLoS One, 11: e0146242. |
| 50 | (Managing Editor: Li Guan) |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||