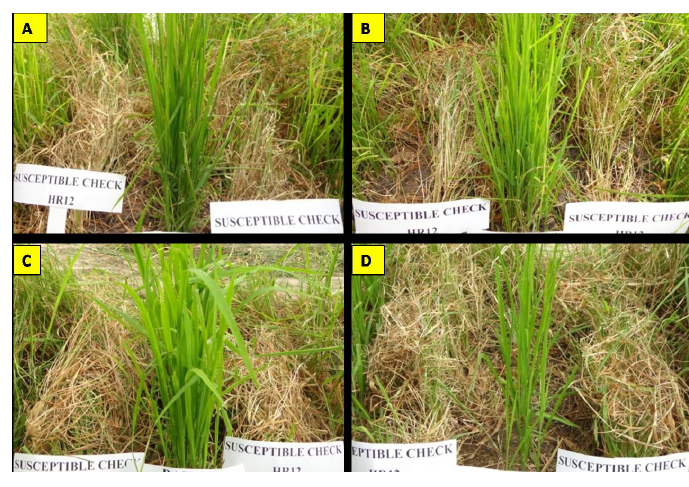
| [1] |
Amante B A, Sitch L A, Nelson R, Dalmacio R D, Oliva N P, Aswidinnoor H, Leung H.1992. Transfer of bacterial blight and blast resistance from the tetraploid wild rice Oryza minuta to cultivated rice, Oryza sativa.Theor Appl Genet, 84(3/4): 345-354.
|
| [2] |
Arunakanthi B, Prasad M S, Madhanmohan K, Balachandran S M, Madhav M S, Reddy C S, Viraktamath B C.2008. Introgression of major blast resistance genes Pi-1, Pi-2 and Pi-kh in indica rice cultivars Samba Mahsuri and Swarna.J Mycol Plant Pathol, 38(3): 625-630.
|
| [3] |
Ashikari M, Matsuoka M.2006. Identification, isolation and pyramiding of quantitative trait loci for rice breeding.Trends Plant Sci, 11(7): 344-350.
|
| [4] |
Ballini E, Morel J B, Droc G, Price A, Courtois B, Notteghem J L, Tharreau D.2008. A genome-wide meta-analysis of rice blast resistance genes and quantitative trait loci provides new insights into partial and complete resistance.Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 21(7): 859-868.
|
| [5] |
Berruyer R, Adreit H, Milazzo J, Gaillard S, Berger A, Dioh W, Lebrun M H, Tharreau D.2003. Identification and fine mapping of Pi33, the rice resistance gene corresponding to the Magnaporthe grisea avirulence gene ACE1.Theor Appl Genet, 107(6): 1139-1147.
|
| [6] |
Bonman J M, Dedios T I V, Khin M M.1986. Physiological specialization of Pyricularia oryzae in the Philippines.Plant Dis, 70(8): 767-769.
|
| [7] |
Brar D S, Khush G S.1997. Alien introgression in rice. In: Oryza: From Molecule to Plant. Netherlands: Springer: 10-47.
|
| [8] |
Cheema K K, Grewal N K, Vikal Y, Sharma R, Lore J S, Das A, Bhatia D, Mahajan R, Gupta V, Bharaj T S, Singh K.2008. A novel bacterial blight resistance gene from Oryza nivara mapped to 38 kb region on chromosome 4L and transferred to Oryza sativa L.Genet Res, 90(5): 397-407.
|
| [9] |
Chen Z W, Hu F Y, Xu P, Li J, Deng X N, Zhou J W, Li F, Chen S N, Tao D Y.2009. QTL analysis for hybrid sterility and plant height in interspecific populations derived from a wild rice relative, Oryza longistaminata.Breeding Sci, 59: 441-445.
|
| [10] |
Devanna N B, Vijayan J, Sharma T R.2014. The blast resistance gene Pi54of cloned from Oryza officinalis interacts with Avr-Pi54 through its novel non-LRR domains.PLoS One, 9(8): e104840.
|
| [11] |
Fjellstrom R, McClung A M, Conaway-Bormans C A, Anna M M, Marchetti M A, Shank A R, Park W D.2004. Development of DNA markers suitable for marker assisted selection of three Pi genes conferring resistance to multiple Pyricularia grisea pathotypes.Crop Sci, 44(5): 1790-1798.
|
| [12] |
Fjellstrom R, McClung A M, Shank A R.2006. SSR markers closely linked to the Pi-z locus are useful for selection of blast resistance in a broad array of rice germplasm.Mol Breeding, 17(2): 149-157.
|
| [13] |
Fuentes J L, Correa-Victoria F J, Escobar F, Prado G, Aricapa G, Duque M C, Tohme J.2008. Identification of microsatellite markers linked to the blast resistance gene Pi1(t) in rice.Euphytica, 160: 295-304.
|
| [14] |
Fujita D, Santos R E, Ebron L A, Telebanco-Yanoria M J, Kato H, Kobayashi S, Uga Y, Araki E, Takai T, Tsunematsu H, Imbe T, Khush G S, Brar D S, Fukuta Y, Kobayashi N.2009. Development of introgression lines of an indica-type rice variety, IR64, for unique agronomic traits and detection of the responsible chromosomal regions.Field Crops Res, 114(2): 244-254.
|
| [15] |
Fukuoka S, Okuno K.2001. QTL analysis and mapping of pi21, a recessive gene for field resistance to rice blast in Japanese upland rice.Theor Appl Genet, 103(2/3): 185-190.
|
| [16] |
Fukuoka S, Yamamoto S I, Mizobuchi R, Yamanouchi U, Ono K, Kitazawa N, Yasuda N, Fujita Y, Nguyen T T T, Koizumi S, Sugimoto K, Matsumoto T, Yano M.2014. Multiple functional polymorphisms in a single disease resistance gene in rice enhance durable resistance to blast.Sci Rep, 4: 4550.
|
| [17] |
Gaikwad K B, Singh N, Bhatia D, Kaur R, Bains N S, Bharaj T S, Singh K.2014. Yield-enhancing heterotic QTL transferred from wild species to cultivated rice Oryza sativa L.PLoS One, 9(6): e96939.
|
| [18] |
Gowda M, Barman S R, Chattoo B B.2006. Molecular mapping of a novel blast resistance gene Pi38 in rice using SSLP and AFLP markers.Plant Breeding, 125(6): 596-599.
|
| [19] |
Gu J, Yin X, Stomph T J, Wang H, Struik P C.2012. Physiological basis of genetic variation in leaf photosynthesis among rice (Oryza sativa L.) introgression lines under drought and well-watered conditions.J Exp Bot, 63(14): 5137-5153.
|
| [20] |
Hayashi K, Yoshida H, Ashikawa I.2006. Development of PCR-based allele-specific and InDel marker sets for nine rice blast resistance genes.Theor Appl Genet, 113(2): 251-260.
|
| [21] |
Hayashi N, Inoue H, Kato T, Funao T, Shirota M, Shimizu T, Kanamori H, Yamane H, Hayanosaito Y, Matsumoto T, Yano M, Takatsuji H.2010. Durable panicle blast-resistance gene Pb1 encodes an atypical CC-NBS-LRR protein and was generated by acquiring a promoter through local genome duplication.Plant J, 64(3): 498-510.
|
| [22] |
He R F, Salvato F, Park J J, Kim M J, Nelson W, Balbuena T S, Willer M, Crow J A, May G D, Soderlund C A, Thelen J J, Gang D R.2014. A systems-wide comparison of red rice (Oryza longistaminata) tissues identifies rhizome specific genes and proteins that are targets for cultivated rice improvement.BMC Plant Biol, 14: 46.
|
| [23] |
Hittalmani S, Parco A, Mew T V, Zeigler R S, Huang N.2000. Fine mapping and DNA marker-assisted pyramiding of the three major genes for blast resistance in rice.Theor Appl Genet, 100(7): 1121-1128.
|
| [24] |
Imam J, Alam S, Mandal N P, Variar M, Shukla P.2014. Molecular screening for identification of blast resistance genes in North East and Eastern Indian rice germplasm (Oryza sativa L.) with PCR based makers.Euphytica, 196(2): 199-211.
|
| [25] |
Ingole Kishor D, Prashanthi S K, Krishnaraj P U.2014. Mining for major blast resistance genes in rice landraces of Karnataka.Ind J Genet Plant Breeding, 74(3): 378-383.
|
| [26] |
Jena K K, Jeung J U, Lee J H, Choi H C, Brar D S.2006. High-resolution mapping of a new brown planthopper (BPH) resistance gene, Bph18(t), and marker-assisted selection for BPH resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Theor Appl Genet, 112(2): 288-297.
|
| [27] |
Jeung J U, Kim B R, Cho Y C, Han S S, Moon H P, Lee Y T, Jena K K.2007. A novel gene, Pi40(t), linked to the DNA markers derived from NBS-LRR motifs confers broad spectrum of blast resistance in rice.Theor Appl Genet, 115(2): 1163-1177.
|
| [28] |
Khan M A I, Sen P P, Bhuiyan R, Kabir E, Chowdhury A K, Fukuta Y, Ali A, Latif M A.2014. Phenotypic screening and molecular analysis of blast resistance in fragrant rice for marker assisted selection.Compt Rend Biol, 337(5): 318-324.
|
| [29] |
Khush G S.2013. Strategies for increasing the yield potential of cereals: Case of rice as an example.Plant Breeding, 132(5): 433-436.
|
| [30] |
Lang N T, Luy T T, Ha P T T, Buu B C.2009. Monogenic lines resistance to blast disease in rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Vietnam.Int J Genet Mol Biol, 1(7): 127-136.
|
| [31] |
Lei M P, Li G R, Zhou L, Li C H, Liu C, Yang Z J.2013. Identification of wheat-Secale africanum chromosome 2Rafr introgression lines with novel disease resistance and agronomic characteristics.Euphytica, 194(2): 197-205.
|
| [32] |
Linh L H, Hang N T, Jin F X, Kang K H, Lee Y T, Kwon S J, Ahn S N.2008. Introgression of a quantitative trait locus for spikelets per panicle from Oryza minuta to the O. sativa cultivar Hwaseongbyeo.Plant Breeding, 127(3): 262-267.
|
| [33] |
Lmam J, Alam S, Mandal N P, Variar M, Shukla P.2014. Molecular screening for identification of blast resistance genes in North East and Eastern Indian rice germplasm (Oryza sativa L.) with PCR based makers.Euphytica, 196(2): 199-211.
|
| [34] |
Mahender A, Swain D M, Subudhi H N, Rao G J N.2012. Molecular analysis of native Manipur rice accessions for resistance against blast.Afr J Biotechnol, 11(6): 1321-1329.
|
| [35] |
McCouch S R, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos K B, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, De Clerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L.2002. Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.).DNA Res, 9(6): 199-207.
|
| [36] |
Miah G, Rafii M Y, Ismail M R, Puteh A B, Rahim H A, Islam K N, Latif M A.2013. A review of microsatellite markers and their applications in rice breeding programs to improve blast disease resistance.Int J Mol Sci, 14: 22499-22528.
|
| [37] |
Nataraj Kumar P, Sujatha K, Laha G S, Srinivasa Rao K, Mishra B, Viraktamath B C, Hari Y, Reddy C S, Balachandran S M, Ram T, Sheshu Madhav M, Shobha Rani N, Neeraja C N, Ashok Reddy G, Shaik H, Sundaram R M.2011. Identification and fine- mapping of Xa33, a novel gene for resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv oryzae.Phytopathology, 102(2): 222-228.
|
| [38] |
Padmavathi G, Ram T, Satyanarayana K, Mishra B.2005. Identification of blast (Magnaporthe grisea) resistance genes in rice.Curr Sci, 88(4): 628-630.
|
| [39] |
Panguluri S K, Kumar A A.2013. Phenotyping for Plant Breeding. New York: Springer: 1-40.
|
| [40] |
Prasad M S, Kanthi B A, Balachandran S M, Seshumadhav M, Mohan K M, Viraktamath B C.2009. Molecular mapping of rice blast resistance gene Pi-1(t) in the elite indica variety Samba Mahsuri.World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 25(10): 1765-1769.
|
| [41] |
Prasad M S, Madhav M S, Laha G S, Ladhalakshmi D, Krishnaveni D, Satendrakumar M, Balachandran S M, Sundaram R M, Arunakanthi B, Madhanmohan K, Ratnamadhavi K, Kumar V, Viraktamath B C.2011. Rice Blast Disease and Its Management. Hyderabad, India: Directorate of Rice Research.
|
| [42] |
Qu S, Liu G, Zhou B, Bellizzi M, Zeng L, Dai L, Han B, Wang G L.2006. The broad spectrum blast resistance gene Pi9 encodes a nucleotide-binding site leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of a multigene family in rice.Genetics, 172: 1901-1914.
|
| [43] |
Rahman L, Khanam S, Jaehwan R, Heejong K.2011. Mapping of QTLs Involved in resistance to rice blast (Magnaporthe grisea) using Oryza minuta introgression lines.Czech J Genet Plant Breeding, 47(3): 85-94.
|
| [44] |
Ram T, Bhadana V P, Laha G S, Padmakumari A P, Jyothibadri, Azam M M, Amtulwaris, Sarla N, Padmavathi G, Dinesh C, Divya B, Viraktamath B C.2013. Wild Species in Rice Improvement. Hyderabad, India: Directorate of Rice Research.
|
| [45] |
Rama Devi S J S, Singh K, Prasad M S, Umakanth B, Ram Kumar G, Viraktamath B C, Madhav M S.2013. Identification and mapping of new genetic resources for durable blast resistance in India. In: Sustainable Rice Production and Livelihood Security: Challenges and Opportunities. Cuttack: Central Rice Research Institute.
|
| [46] |
Ramkumar G, Srinivasarao K, Mohan K M, Sudarshan I, Sivaranjani A K P, Gopalakrishna K, Neeraja C N, Balachandran S M, Sundaram R M, Prasad M S, Shobha Rani N, Rama Prasad A M, Viraktamath B C, Madhav M S.2011. Development and validation of functional marker targeting an InDel in the major rice blast disease resistance gene Pi54 (Pikh).Mol Breeding, 27(1): 129-135.
|
| [47] |
Rangel P N, Brondani R P V, Rangel P H N, Brondani C.2008. Agronomic and molecular characterization of introgression lines from the interspecific cross Oryza sativa (BG90-2) × Oryza glumaepatula (RS-16).Genet Mol Res, 7(1): 184-195.
|
| [48] |
Ratna M K, Srinivas P M, Laha G S, Madhan M K, Sheshu M M, Viraktamath B C.2011. Combining blast and bacterial blight resistance in rice cultivar, improved Samba Mahsuri.Ind J Plant Prot, 39(2): 124-129.
|
| [49] |
Saghai M M A, Soliman K M, Jogensen R A, Allard R W.1984. Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location and population dynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 81(24): 8014-8018.
|
| [50] |
Sharma T R, Madhav M S, Singh B K, Shanker P, Jana T K, Dalal V, Pandit A, Singh A, Gaikwad K, Upreti H C, Singh N K.2005. High-resolution mapping, cloning and molecular characterization of the gene of rice, which confers resistance to rice blast.Mol Genet Genom, 274(6): 569-578.
|
| [51] |
Sié M, Sanni K, Futakuchi K, Manneh B, Mandé S, Vodouhé R, Dogbe S, Dramé K N, Ogunbayo A, Ndjiondjop M N, Traore K.2012. Towards a rational use of African rice (Oryza glaberrima Steud.) for breeding in Sub-Saharan Africa.Genes, Genom Genomics, 6(1): 1-7.
|
| [52] |
Tsunematsu H, Yanoria M J T, Ebron L A, Hayashi N, Ando I, Kato H, Imbe T, Khush G S.2000. Development of monogenic lines for rice blast resistance.Breeding Sci, 50: 229-234.
|
| [53] |
Zhang F T, Xie J K.2014. Genes and QTLs resistant to biotic and abiotic stresses from wild rice and their applications in cultivar improvements. In: Yan W G, Bao J S. Rice: Germplasm, Genetics and Improvement. Croatia, European Union: InTech.
|
| [54] |
Zhou Y L, Xie X W, Zhang F, Wang S, Liu X Z, Zhu L H, Xu J L, Gao Y M, Li Z K.2014. Detection of quantitative resistance loci associated with resistance to rice false smut (Ustilaginoidea virens) using introgression lines.Plant Pathol, 63(2): 365-372.
|