
Rice Science ›› 2016, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (3): 119-131.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2016.04.001
收稿日期:2015-05-11
接受日期:2015-08-26
出版日期:2016-06-08
发布日期:2016-02-04
. [J]. Rice Science, 2016, 23(3): 119-131.
| Source of variance | df | Nitrogen | Phosphorus | Potassium | Silicon | Total free sugar in rice | Soluble protein in rice | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | BPH | Rice | BPH | Rice | BPH | in rice | ||||
| N | 2 | 2166.51** | 12.87** | 2.45 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 2 486.75** | 0.73 | 3 300.13** |
| P | 2 | 2.58 | 2.04 | 544.36** | 2.77 | 0.45 | 0.15 | 2.33 | 0.12 | 0.72 |
| K | 2 | 392.74** | 2.8 | 2.08 | 0.5 | 440.21** | 1.77 | 33.03** | 573.66** | 822.94** |
| N × P | 4 | 2.05 | 0.25 | 2.44 | 0.19 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.87 | 0.29 | 0.17 |
| N × K | 4 | 53.12** | 0.85 | 0.94 | 0.56 | 0.03 | 0.92 | 3.73** | 0.61 | 15.65** |
| P × K | 4 | 2.21 | 1.04 | 2.28 | 0.74 | 0.14 | 0.67 | 0.75 | 0.07 | 0.21 |
| N × P × K | 8 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 1.26 | 0.58 | 0.17 | 1.69 | 0.86 | 0.1 | 0.29 |
| Error | 81 | |||||||||
| CV (%) | 2.65 | 3.22 | 4.18 | 4.45 | 2.92 | 1.75 | 5.33 | 1.98 | 2.48 | |
Table 1 Analysis of variance for biochemical compositions in rice plants and brown planthopper (BPH) affected by nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) subsidies (F values).
| Source of variance | df | Nitrogen | Phosphorus | Potassium | Silicon | Total free sugar in rice | Soluble protein in rice | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | BPH | Rice | BPH | Rice | BPH | in rice | ||||
| N | 2 | 2166.51** | 12.87** | 2.45 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 2 486.75** | 0.73 | 3 300.13** |
| P | 2 | 2.58 | 2.04 | 544.36** | 2.77 | 0.45 | 0.15 | 2.33 | 0.12 | 0.72 |
| K | 2 | 392.74** | 2.8 | 2.08 | 0.5 | 440.21** | 1.77 | 33.03** | 573.66** | 822.94** |
| N × P | 4 | 2.05 | 0.25 | 2.44 | 0.19 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.87 | 0.29 | 0.17 |
| N × K | 4 | 53.12** | 0.85 | 0.94 | 0.56 | 0.03 | 0.92 | 3.73** | 0.61 | 15.65** |
| P × K | 4 | 2.21 | 1.04 | 2.28 | 0.74 | 0.14 | 0.67 | 0.75 | 0.07 | 0.21 |
| N × P × K | 8 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 1.26 | 0.58 | 0.17 | 1.69 | 0.86 | 0.1 | 0.29 |
| Error | 81 | |||||||||
| CV (%) | 2.65 | 3.22 | 4.18 | 4.45 | 2.92 | 1.75 | 5.33 | 1.98 | 2.48 | |
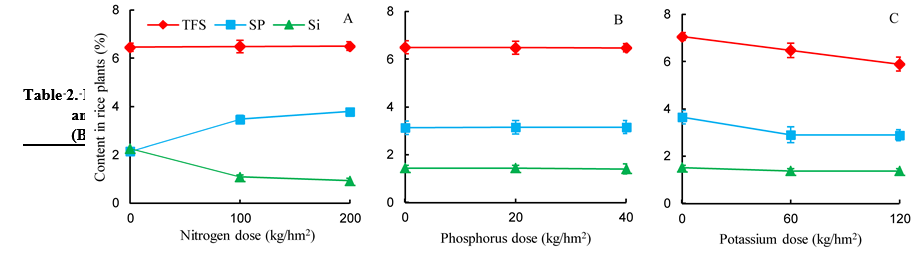
Fig. 2. Response of nutrient levels on silicon (Si), total free sugar (TFS) and soluble protein (SP) contents in rice plants.Bar indicates the standard error (SE).
| Rice stage | df | N content | P content | K content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mid tillering | 26 | 150.32** | 111.80** | 80.90** |
| Panicle initiation | 26 | 106.79** | 134.16** | 21.95** |
| Heading | 26 | 163.32** | 136.40** | 162.92** |
| Maturity | 26 | 163.72** | 108.38** | 1.94 |
Table 2 Mean comparison results for nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) contents between brown planthopper (BPH) and its host rice plants (t value).
| Rice stage | df | N content | P content | K content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mid tillering | 26 | 150.32** | 111.80** | 80.90** |
| Panicle initiation | 26 | 106.79** | 134.16** | 21.95** |
| Heading | 26 | 163.32** | 136.40** | 162.92** |
| Maturity | 26 | 163.72** | 108.38** | 1.94 |
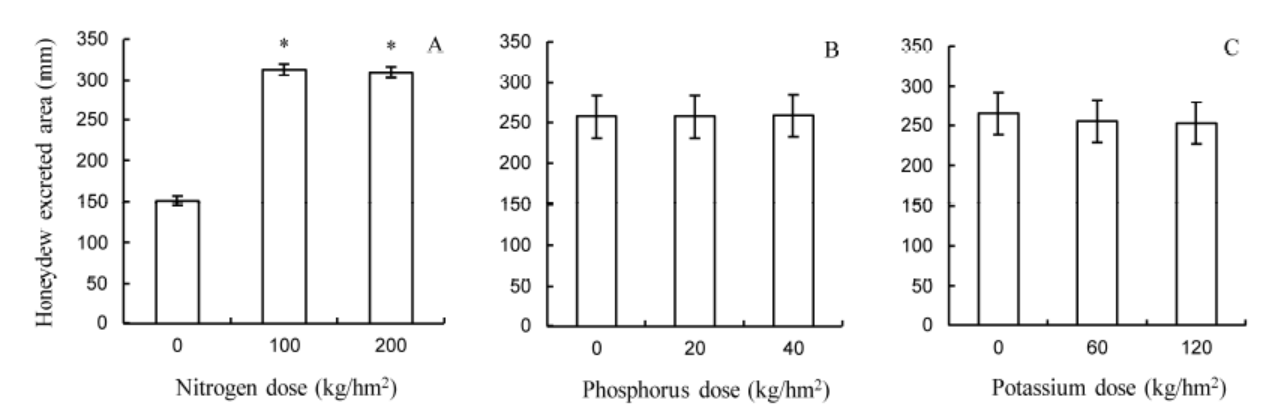
Fig. 4. Feeding of brown planthopper (BPH) measured indirectly by honeydew excretion in different nutrient treated rice plants.Bar indicates the standard error (SE).
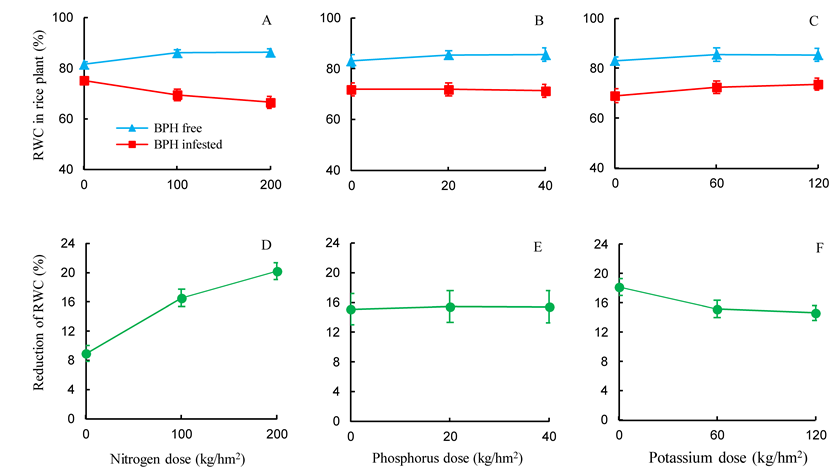
Fig. 5. Relative water content (RWC) and reduction of RWC due to brown planthopper (BPH) feeding after 5 d in different nutrient treated rice plants after release of BPH.Bar indicates the standard error (SE).
| Source of variation | df | Honeydew secretion | RWC of BPH | RWC at 5 d after | Reduction of RWC | 9th grade plant damage duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| free plants | infestation by BPH | |||||
| N | 2 | 601.80** | 274.53** | 1 338.95** | 1 385.84** | 242.70** |
| P | 2 | 0.04 | 9.36** | 0.55 | 0.56 | 0.66 |
| K | 2 | 2.74 | 37.75** | 17.56** | 16.46** | 19.70** |
| N × P | 4 | 0.08 | 0.82 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.69 |
| N × K | 4 | 0.14 | 4.55** | 11.48** | 10.41** | 2.62* |
| P × K | 4 | 0.06 | 0.72 | 1.45 | 1.44 | 1.43 |
| N × P × K | 8 | 0.08 | 1.24 | 1.46 | 1.39 | 1.01 |
| Error | 81 | |||||
| CV (%) | 4.78 | 0.78 | ########### | 2.43 | 8.54 | |
Table 3 Analysis of variance for honeydew secretion, changes in relative water content (RWC) and complete damage duration of rice plants feeding brown planthopper (BPH) as affected by nitrogen (N), phosphourus (P) and potassium (K) subsidies (F value).
| Source of variation | df | Honeydew secretion | RWC of BPH | RWC at 5 d after | Reduction of RWC | 9th grade plant damage duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| free plants | infestation by BPH | |||||
| N | 2 | 601.80** | 274.53** | 1 338.95** | 1 385.84** | 242.70** |
| P | 2 | 0.04 | 9.36** | 0.55 | 0.56 | 0.66 |
| K | 2 | 2.74 | 37.75** | 17.56** | 16.46** | 19.70** |
| N × P | 4 | 0.08 | 0.82 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.69 |
| N × K | 4 | 0.14 | 4.55** | 11.48** | 10.41** | 2.62* |
| P × K | 4 | 0.06 | 0.72 | 1.45 | 1.44 | 1.43 |
| N × P × K | 8 | 0.08 | 1.24 | 1.46 | 1.39 | 1.01 |
| Error | 81 | |||||
| CV (%) | 4.78 | 0.78 | ########### | 2.43 | 8.54 | |
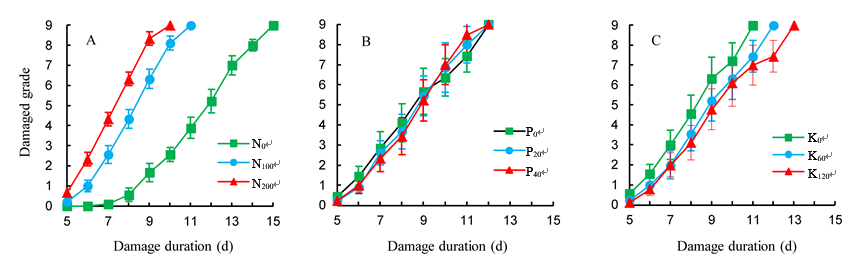
Fig. 6. Dynamics of damage grade of rice plants by brown planthopper (BPH) as affected by different levels of nutrient application.Bar indicates the standard error (SE).
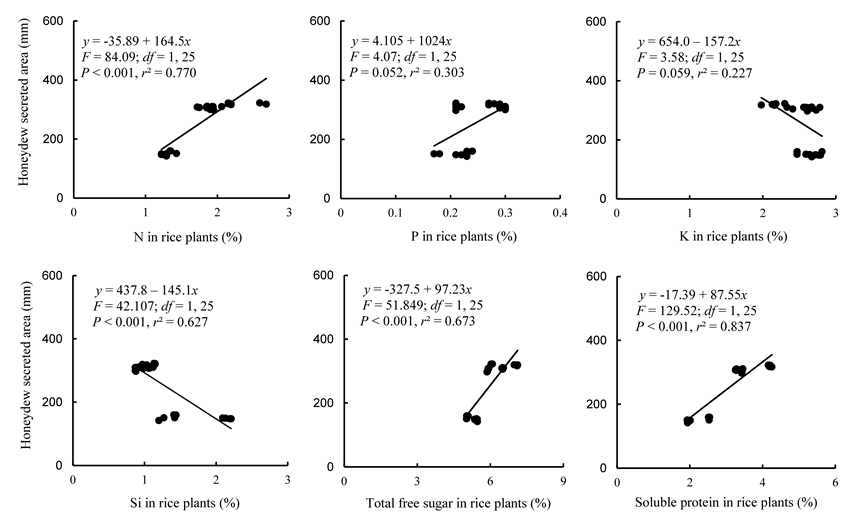
Fig. 7. Relationship between brown planthopper (BPH) feeding and different nutrients nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), silicon (Si), total free sugar and soluble proteins contents in rice plants.
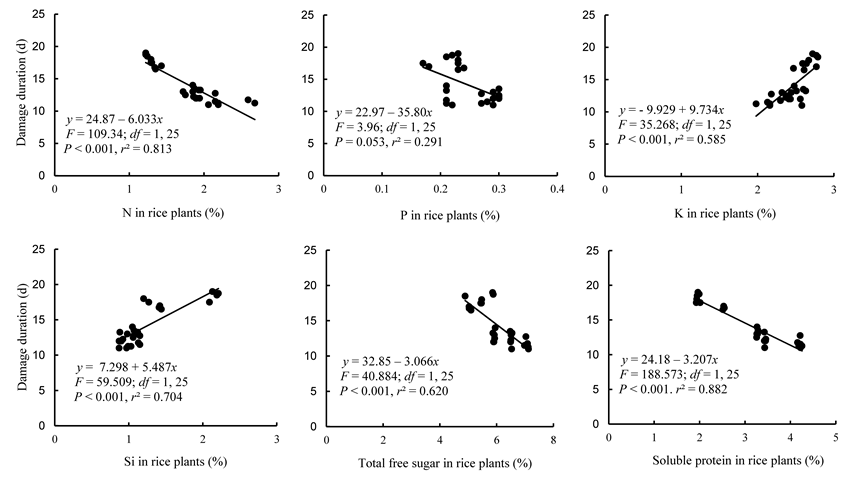
Fig. 8. Relationships between nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), silicon (Si), total free sugar and soluble protein contents in rice plants and its 9th grade damage by brown planthopper (BPH).
| [1] | Ali M P, Huang D C, Nachman G, Ahmed N, Begum M A, Rabbi M F.2014. Will climate change affect outbreak patterns of planthoppers in Bangladesh?PLoS One, 9: e91678. |
| [2] | Altieri M A, Nicholls C I.2003. Soil fertility management and insect pests: Harmonizing soil and plant health in agroecosystems.Soil Till Res, 72(2): 203-211. |
| [3] | Amtmann A, Troufflard S, Armengaud P.2008. The effect of potassium nutrition on pest and disease resistance in plants.Physiol Plant, 133(4): 682-691. |
| [4] | Awmack C S, Leather S R.2002. Host plant quality and fecundity in herbivorous insects.Annu Rev Entomol, 47: 817-844. |
| [5] | Bado S G, Rodriguez S M, Folcia A M.2002. Variation in abundance of aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) and predatory ladybirds (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in a barley cultivar at different practices of use of fertilizers.IDESIA, 20: 35-42. |
| [6] | Barbour J D, Farrar R R, Kennedy G G.1991. Interaction of fertilizer regime with host plant resistance in tomato.Entomol Exp Appl, 60(3): 289-300. |
| [7] | Baskaran P, Narayanasamy P, Pari A.1985. The role of potassium in incidence of insect pests among crop plants, with particular reference to rice. In: Role of Potassium in Crop Resistance to Insect Pests. Haryana: Potash Research Institute of India: 63-68. |
| [8] | Bernays E A.1990. Insect-Plant Interactions. Florida, USA: CRC Press. |
| [9] | Bottrell D G, Schoenly K G.2012. Resurrecting the ghost of green revolutions past: The brown planthopper as a recurring threat to high-yielding rice production in tropical Asia.J Asia-Pacific Entomol, 15(1): 122-140. |
| [10] | Chen Y, Ni X.2012. Nitrogen modulation on plant direct and indirect defenses. In: Liu T X, Kang L. Recent Advances in Entomological Research: From Molecular Biology to Pest Management. Beijing, China: Higher Education Press: 86-102. |
| [11] | Clark R B.1982. Plant response to mineral element toxicity and deficiency. In: Christiansen M N, Lewis C F. Breeding Plants for Less Favorable Environment. New York, USA: John Wily and Sons: 71-142. |
| [12] | Dale D.1988. Plant mediated effects of soil mineral stress on insects. In: Heinrich E A. Plant Stress Insect Interactions. New York, USA: John Wiley and Sons: 35-110. |
| [13] | Elser J J, Fagan W F, Denno R F, Dobberfuhl D R, Folarin A, Huberty A, Interlandi S, Kilham S S, McCauley E, Schulz K L, Siemann E H, Sterner R W.2000. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs.Nature, 408: 578-580. |
| [14] | Elser J J, Hayakawa K, Urabe J.2001. Nutrient limitation reduces food quality for zooplankton: Daphnia response to seston phosphorus enrichment.Ecology, 82(3): 898-903. |
| [15] | Fagan W F, Siemann E, Denno R F, Mitter C, Huberty A F, Woods H A, Elser J J.2002. Nitrogen in insects: Implications for trophic complexity and species diversification.Am Nat, 160: 784-802. |
| [16] | Fischer K, Fiedler K.2000. Response of the copper butterfly Lycaena tityus to increased leaf nitrogen in natural food plants: Evidence against the nitrogen limitation hypothesis.Oecologia, 124: 235-241. |
| [17] | Huberty F A, Denno R F.2006. Consequences of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation for the performance of two planthoppers with divergent life-history strategies.Oecologia, 149(3): 444-455. |
| [18] | International Rice Research Institute (IRRI). 1980. Standard Evaluation System for Rice. Manila, the Phillipines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| [19] | International Rice Research Institute (IRRI). 2007. CROPSTAT for Windows, version 7.2. Manila, the Phillipines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| [20] | Jensen T C, Leinaas H P, Hessen D O.2006. Age-dependent shift in response to food elemental composition in Collembola: Contrasting effects of dietary nitrogen.Oecologia, 149(4): 583-592. |
| [21] | Kajimura T, Fujisaki K, Nakasuji F.1995. Effect of organic rice farming on leaffolder and planthoppers: II. Amino acid content in the rice phloem sap and survival rate of planthoppers.Appl Entomol Zool, 30(1): 17-22. |
| [22] | Lou Y, Baldwin I T.2004. Nitrogen supply influences herbivore-induced direct and indirect defenses and transcriptional responses in Nicotiana attenuata.Plant Physiol, 135(1): 496-506. |
| [23] | Lowry O H, Rosenbrough N J, Farr A L, Randall R J.1951. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent.J Biol Chem, 193(1): 265-275. |
| [24] | Lu Z X, Villareal S, Yu X P, Heong K L, Hu C.2004. Effect of nitrogen on water content, sap flow and tolerance of rice plants to brown planthopper.Rice Sci, 11(3): 129-134. |
| [25] | Lu Z X, Heong K L, Yu X P, Hu C.2005. Effects of nitrogen nutrient on the behavior of feeding and oviposition of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens on IR64. J Zhejiang Univ: Agric Life Sci, 31: 62-70. |
| [26] | Lu Z X, Heong K L.2009. Effects of nitrogen-enriched rice plants on ecological fitness of planthoppers. In: Heong K L, Hardy B. Planthoppers: New Threats to the Sustainability of Intensive Rice Production Systems in Asia. Manila, the Phillipines: International Rice Research Institute: 247-256. |
| [27] | Marazzi C, Patrian B, Stadler E.2004. Secondary metabolites of the leaf surface affected by sulphur fertilization and perceived by the diamondback moth.Chemoecology, 14(2): 81-86. |
| [28] | Marschner H.1995. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. London, UK: Academic Press. |
| [29] | Mongia A D, Singh N T, Mandal L N, Guha A.1998. Effect of liming, super phosphate and rock phosphate application to rice on the yield and uptake of nutrients on acid sulphate soils.J Ind Soc Soil Sci, 46(1): 61-66. |
| [30] | Moon D C, Stiling P.2000. Relative importance of abiotically induced direct and indirect effects on a salt-marsh herbivore.Ecology, 81(2): 470-481. |
| [31] | Myers S W, Gratton C.2006. Influence of potassium fertility on soybean aphid, Aphis glycines Matsumura (Hemiptera: Aphididae), population dynamics at a field and regional scale.Environ Entomol, 35(2): 219-227. |
| [32] | Panda N, Khush G S.1995. Host plant resistance to insects. Wallingford: CAB International. |
| [33] | Pathak P K, Heinrichs E A.1982. Bromocresol green indicator for measuring feeding activity of Nilaparvata lugens on rice varieties.Phil Entomol, 5(2): 209-212. |
| [34] | Prasad B R, Pasalu I C, Raju N B T, Lingaiah T.2005. Effect of nitrogen levels and rice varieties on brown planthopper adult weight and amount of honeydew excretion.Ann Plant Prot Sci, 13(1): 243-245. |
| [35] | Salim M.2002a. Effects of potassium nutrition on growth, biomass and chemical composition of rice plants and on host-insect interaction.Pak J Agric Res, 17(1): 14-21. |
| [36] | Salim M.2002b. Nitrogen induced changes in rice plants: Effect on host-insect interactions.Pak J Agric Res, 17(3): 210-220. |
| [37] | Sarwar M.2012. Effects of potassium fertilization on population build up of rice stem borers (lepidopteron pests) and rice (Oryza sativa L.) yield.J Cereals Oilseeds, 3(1): 6-9. |
| [38] | Sauge M H, Grechi1 I, Poëssel J L.2010. Nitrogen fertilization effects on Myzus persicae aphid dynamics on peach: Vegetative growth allocation or chemical defense?Entomol Exp Appl, 136(2): 123-133. |
| [39] | Slansky J F, Rodriguez J G.1987. Nutritional Ecology of Insects, Mites, Spiders and Related Invertebrates. New York: John Wiley & Sons. |
| [40] | Sogawa K, Liu G, Qiang Q.2009. Prevalence of whitebacked planthoppers in Chinese hybrid rice and whitebacked planthopper resistance in Chinese japonica rice. In: Heong K L, Hardy B. Planthoppers: New Threats to the Sustainability of Intensive Rice Production Systems in Asia. Manila, the Phillipines: International Rice Research Institute: 257-280. |
| [41] | SPSS.2007. SPSS for Windows, version 16. SPSS Inc, Chicago, USA. |
| [42] | Sterner R W, Elser J J.2002.Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere. New Jersey, USA: Princeton University Press. |
| [43] | Stiling P, Moon D C.2005. Quality or quantity: The direct and indirect effects of host plants on herbivore and their natural enemies.Oecologia, 142(3): 413-420. |
| [44] | Subbaiah P.1991. Effect of level and source of phosphorus on yield and nutrient uptake of rice (Oryza sativa L.).Ind J Agron, 36: 230-232. |
| [45] | Tisdale S L, Nelson W L, Beaton J D.1985. Soil Fertility and Fertilizers. New York, USA: Macmillan Publication. |
| [46] | Visanuvimol L, Bertram S M.2011. How dietary phosphorus availability during development influences condition and life history traits of the cricket,Acheta domesticus. J Insect Sci, 11: 1-17. |
| [47] | Walker D J, Leigh R A, Miller A J.1996. Potassium homeostasis in vacuolate plant cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 93(19): 10510-10514. |
| [48] | Wyn Jones R G, Pollard A.1983. Proteins, enzymes and inorganic ions. In: Lauchli A, Pirson A. Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology. Berlin, Germany: Springer: 528-562. |
| [49] | Wyn Jones R G.1999. Cytoplasmic potassium homeostasis: Review of the evidence and its implication. In: Oosterhuis D M, Berkowitz G A. Frontiers in Potassium Nutrition: New Perspectives on the Effects of Potassium on Physiology of Plants. Atlanta, Georgia, USA: CSSA, Special Publication, Potash and Phosphate Institute: 13-22. |
| [50] | Yoshida S, Forno D A, Cock J H, Gomez K A.1976. Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice. Manila, the Phillipines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||