
Rice Science ›› 2024, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 328-342.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2024.02.005
收稿日期:2023-11-14
接受日期:2024-01-17
出版日期:2024-05-28
发布日期:2024-06-04
. [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(3): 328-342.
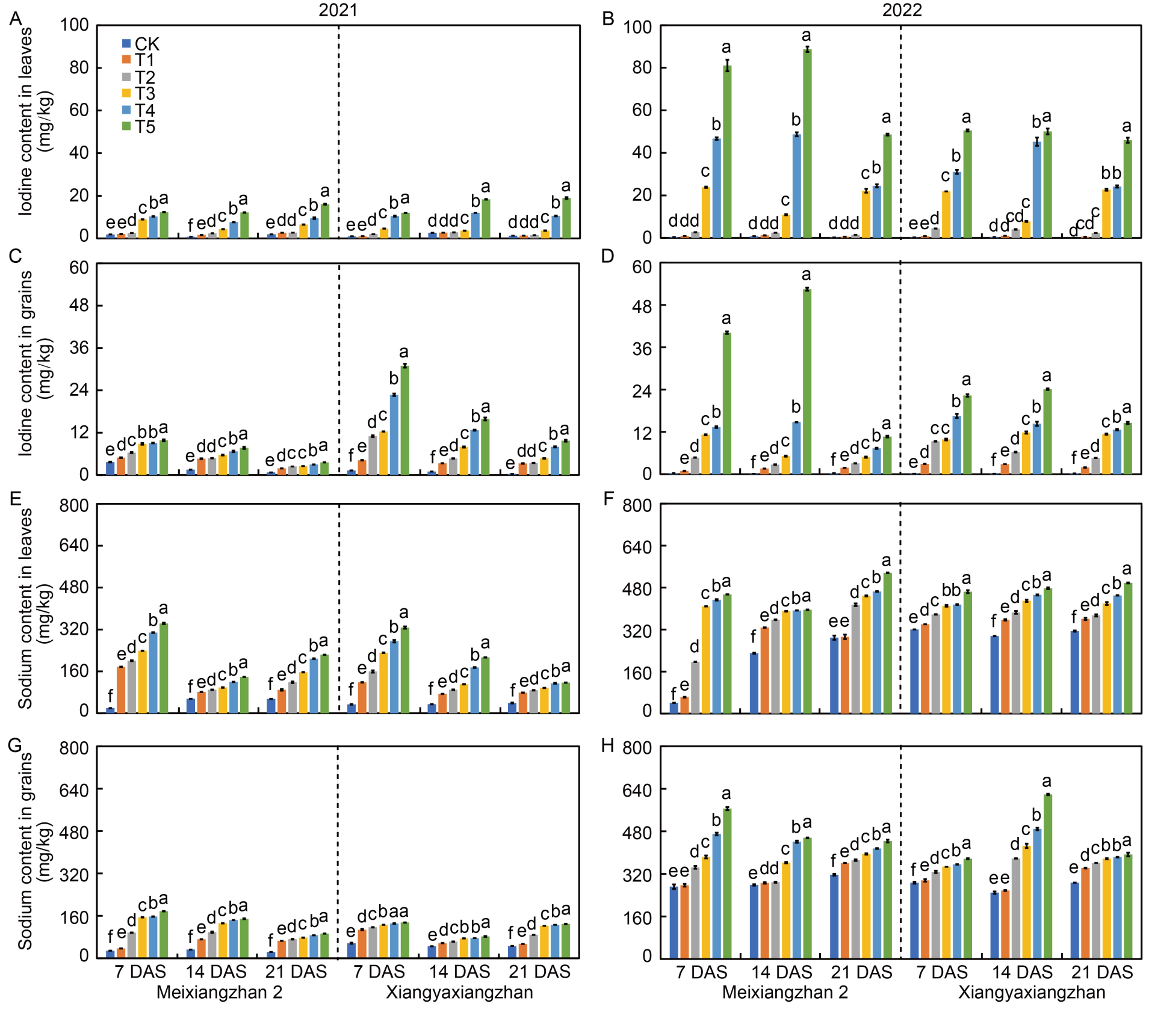
Fig. 1. Effects of foliar application of sodium iodide on iodine and sodium contents in leaves (A, B, E and F) and grains (C, D, G and H) of aromatic rice at different stages in 2021 and 2022. CK, Foliar spray with distilled water; T1‒T5, Foliar spray with 0.010%, 0.025%, 0.050%, 0.075%, and 0.100% sodium iodide, respectively; 7 DAS, 7 d after spraying; 14 DAS, 14 d after spraying; 21 DAS, 21 d after spraying. Bars that share the same lowercase letters for a given parameter do not differ significantly at P < 0.05 based on the least significant difference test. Error bars represent standard errors of means.
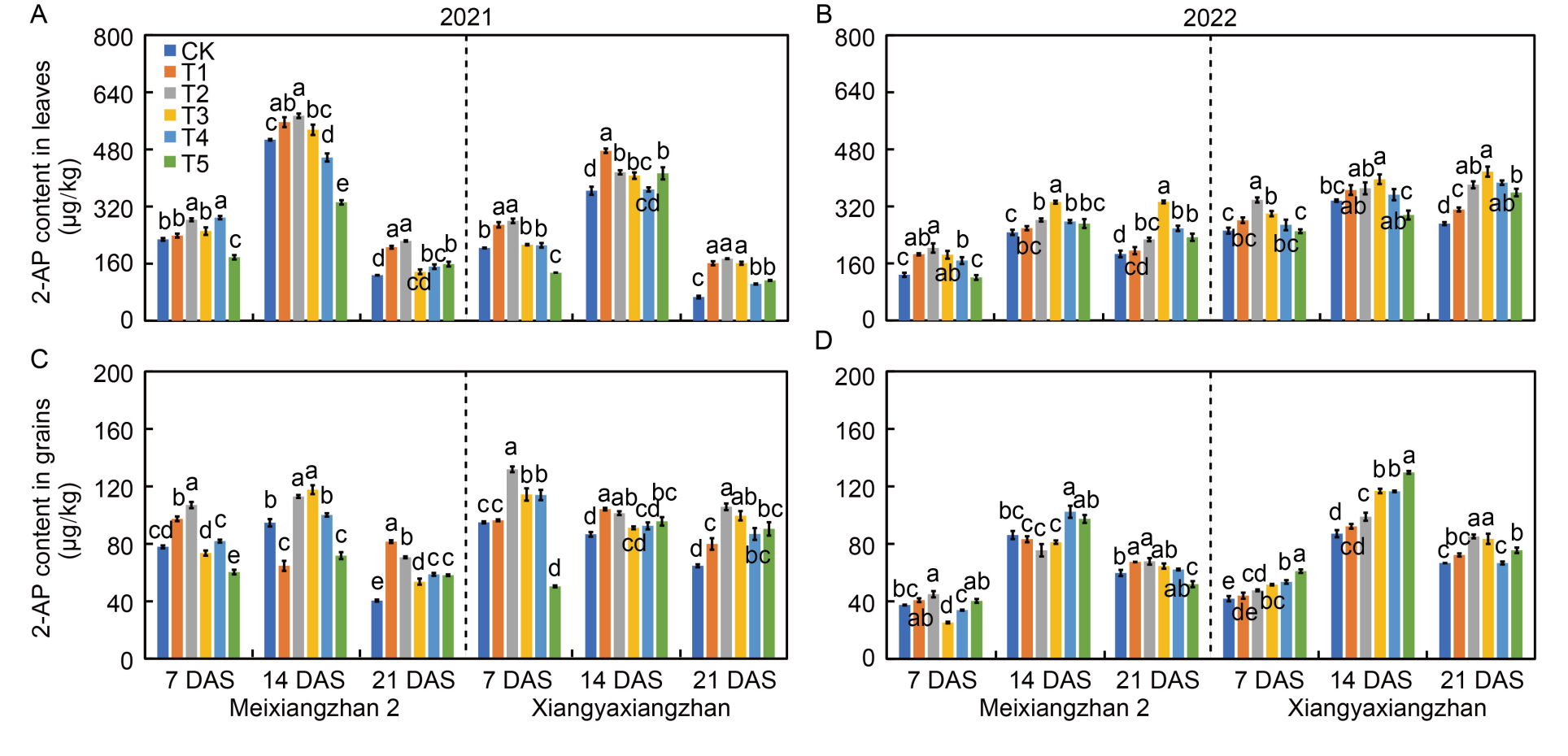
Fig. 2. Effects of foliar application of sodium iodide on 2-AP content in leaves (A and B) and grains (C and D) of aromatic rice at different stages in 2021 and 2022. 2-AP, 2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline; CK, Foliar spray with distilled water; T1‒T5, Foliar spray with 0.010%, 0.025%, 0.050%, 0.075%, and 0.100% sodium iodide, respectively; 7 DAS, 7 d after spraying; 14 DAS, 14 d after spraying; 21 DAS, 21 d after spraying. Bars that share the same lowercase letters for a given parameter do not differ significantly at P < 0.05 based on the least significant difference test. Error bars represent standard errors of means.
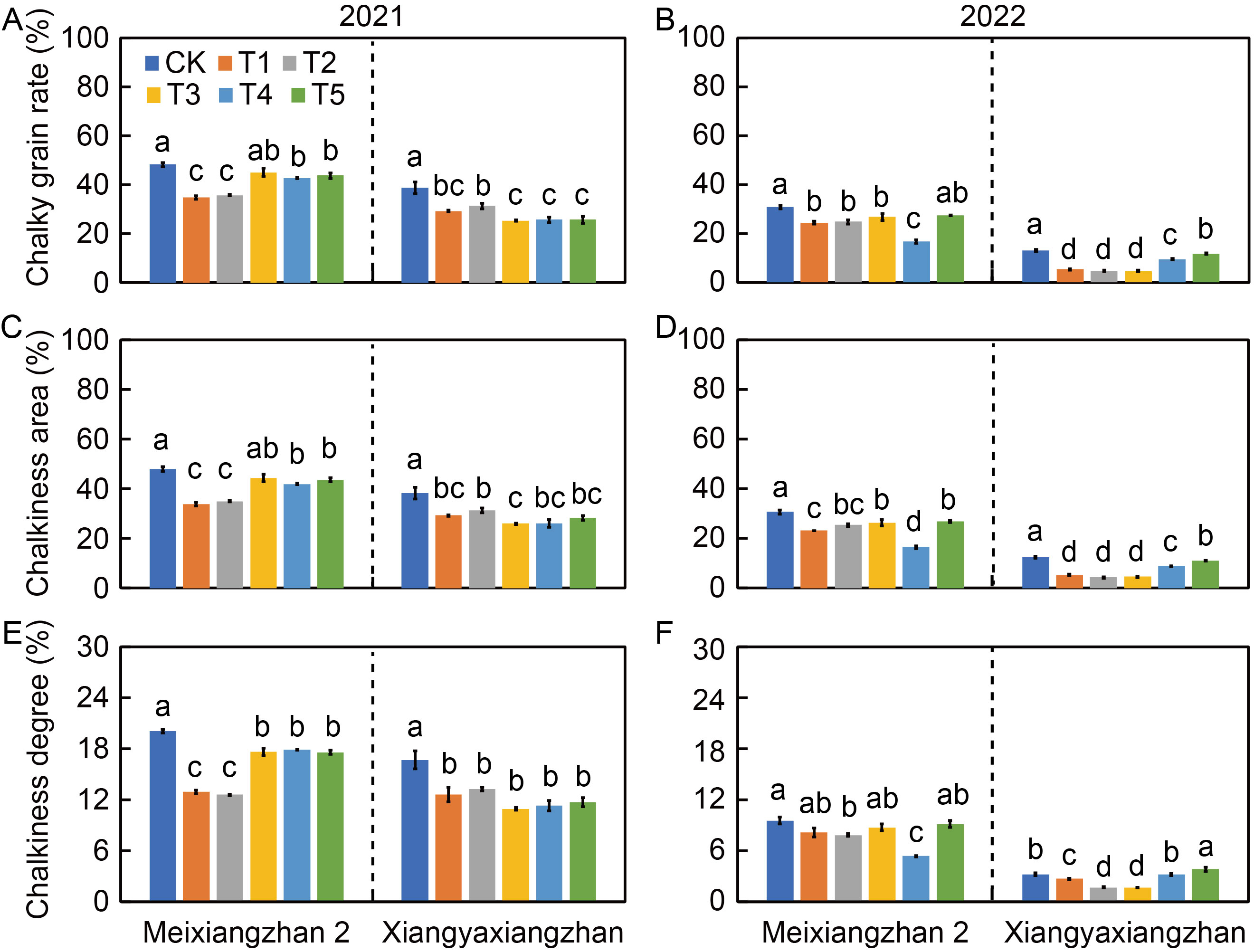
Fig. 3. Effects of foliar application of sodium iodide on chalky grain rate (A and B), chalkiness area (C and D), and chalkiness degree (E and F) of aromatic rice in 2021 and 2022. CK, Foliar spray with distilled water; T1‒T5, Foliar spray with 0.010%, 0.025%, 0.050%, 0.075%, and 0.100% sodium iodide, respectively. Bars that share the same lowercase letters for a given parameter do not differ significantly at P < 0.05 based on the least significant difference test. Error bars represent standard errors of means.
| Year | Cultivar | Treatment | Panicle number per m2 | Grain number per panicle | Filled-grain rate (%) | 1000-grain weight (g) | Grain yield (g/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | Meixiangzhan 2 | CK | 348.80 ± 18.98 a | 102.00 ± 0.47 ab | 57.51 ± 0.47 b | 19.94 ± 0.04 c | 886.67 ± 10.89 a |
| T1 | 353.60 ± 11.16 a | 97.33 ± 1.19 bc | 60.02 ± 1.03 ab | 20.60 ± 0.06 b | 850.00 ± 23.57 a | ||
| T2 | 334.40 ± 7.95 a | 103.33 ± 1.19 a | 68.70 ± 4.54 a | 21.13 ± 0.10 a | 933.33 ± 59.32 a | ||
| T3 | 361.60 ± 5.69 a | 101.00 ± 1.41 abc | 57.35 ± 1.92 b | 19.69 ± 0.10 cd | 883.33 ± 13.61 a | ||
| T4 | 366.40 ± 25.43 a | 101.00 ± 1.70 abc | 55.77 ± 3.78 b | 19.51 ± 0.10 de | 733.33 ± 13.61 b | ||
| T5 | 339.20 ± 3.46 a | 95.33 ± 2.13 c | 64.39 ± 0.77 ab | 19.27 ± 0.08 e | 850.00 ± 4.71 a | ||
| Xiangyaxiangzhan | CK | 348.80 ± 3.46 a | 108.00 ± 0.47 a | 62.93 ± 1.51 a | 19.54 ± 0.12 b | 926.67 ± 30.31 bc | |
| T1 | 355.20 ± 15.84 a | 101.67 ± 4.28 abc | 68.94 ± 1.41 a | 19.78 ± 0.05 b | 1066.67 ± 36.00 a | ||
| T2 | 339.20 ± 10.20 a | 100.00 ± 4.50 abc | 63.78 ± 2.55 a | 20.31 ± 0.16 a | 1016.67 ± 36.00 ab | ||
| T3 | 355.20 ± 11.31 a | 104.67 ± 1.52 ab | 64.00 ± 2.90 a | 19.31 ± 0.08 bc | 916.67 ± 36.00 bc | ||
| T4 | 331.20 ± 2.26 a | 95.00 ± 0.47 bc | 62.26 ± 2.35 a | 19.26 ± 0.16 bc | 833.33 ± 36.00 c | ||
| T5 | 358.40 ± 6.91 a | 92.00 ± 0.47 c | 69.99 ±1.30 a | 18.93 ± 0.17 c | 950.00 ± 20.55 b | ||
| 2022 | Meixiangzhan 2 | CK | 305.60 ± 13.83 a | 115.04 ± 7.86 ab | 60.98 ± 1.30 bc | 19.58 ± 0.18 bc | 563.33 ± 27.32 a |
| T1 | 310.40 ± 3.46 a | 120.50 ± 5.27 ab | 65.66 ± 0.55 a | 19.92 ± 0.27 ab | 555.00 ± 10.80 a | ||
| T2 | 299.20 ± 8.57 a | 113.53 ± 3.34 ab | 64.07 ± 0.34 ab | 20.33 ± 0.13 a | 578.33 ± 15.69 a | ||
| T3 | 307.20 ± 18.52 a | 142.92 ± 5.47 a | 65.09 ± 1.05 a | 19.60 ± 0.17 bc | 440.00 ± 15.46 b | ||
| T4 | 286.40 ± 7.95 a | 100.27 ± 16.64 b | 66.97 ± 1.11 a | 19.20 ± 0.02 c | 443.33 ± 24.19 b | ||
| T5 | 294.40 ± 13.83 a | 102.93 ± 11.84 b | 59.02 ± 1.21 c | 19.04 ± 0.06 c | 390.00 ± 18.41 b | ||
| Xiangyaxiangzhan | CK | 297.60 ± 13.76 a | 100.34 ± 0.67 a | 61.81 ± 0.85 ab | 19.78 ± 0.05 c | 588.33 ± 11.14 ab | |
| T1 | 307.20 ± 11.76 a | 108.30 ± 1.96 a | 64.65 ± 1.12 a | 20.95 ± 0.16 b | 636.67 ± 24.19 a | ||
| T2 | 321.60 ± 27.15 a | 103.27 ± 0.87 a | 65.26 ± 1.23 a | 21.74 ± 0.07 a | 644.33 ± 23.51 a | ||
| T3 | 315.20 ± 21.74 a | 106.09 ± 0.72 a | 63.66 ± 1.29 ab | 19.60 ± 0.11 c | 550.00 ± 20.55 b | ||
| T4 | 280.00 ± 6.91 a | 105.37 ± 13.91 a | 63.39 ± 0.88 ab | 19.80 ± 0.20 c | 546.67 ± 10.89 b | ||
| T5 | 289.60 ± 3.46 a | 106.51 ± 0.85 a | 59.12 ± 1.25 b | 20.53 ± 0.16 b | 556.67 ± 11.86 b |
Table 1. Effects of foliar application of sodium iodide on grain yield and yield components of aromatic rice in 2021 and 2022.
| Year | Cultivar | Treatment | Panicle number per m2 | Grain number per panicle | Filled-grain rate (%) | 1000-grain weight (g) | Grain yield (g/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | Meixiangzhan 2 | CK | 348.80 ± 18.98 a | 102.00 ± 0.47 ab | 57.51 ± 0.47 b | 19.94 ± 0.04 c | 886.67 ± 10.89 a |
| T1 | 353.60 ± 11.16 a | 97.33 ± 1.19 bc | 60.02 ± 1.03 ab | 20.60 ± 0.06 b | 850.00 ± 23.57 a | ||
| T2 | 334.40 ± 7.95 a | 103.33 ± 1.19 a | 68.70 ± 4.54 a | 21.13 ± 0.10 a | 933.33 ± 59.32 a | ||
| T3 | 361.60 ± 5.69 a | 101.00 ± 1.41 abc | 57.35 ± 1.92 b | 19.69 ± 0.10 cd | 883.33 ± 13.61 a | ||
| T4 | 366.40 ± 25.43 a | 101.00 ± 1.70 abc | 55.77 ± 3.78 b | 19.51 ± 0.10 de | 733.33 ± 13.61 b | ||
| T5 | 339.20 ± 3.46 a | 95.33 ± 2.13 c | 64.39 ± 0.77 ab | 19.27 ± 0.08 e | 850.00 ± 4.71 a | ||
| Xiangyaxiangzhan | CK | 348.80 ± 3.46 a | 108.00 ± 0.47 a | 62.93 ± 1.51 a | 19.54 ± 0.12 b | 926.67 ± 30.31 bc | |
| T1 | 355.20 ± 15.84 a | 101.67 ± 4.28 abc | 68.94 ± 1.41 a | 19.78 ± 0.05 b | 1066.67 ± 36.00 a | ||
| T2 | 339.20 ± 10.20 a | 100.00 ± 4.50 abc | 63.78 ± 2.55 a | 20.31 ± 0.16 a | 1016.67 ± 36.00 ab | ||
| T3 | 355.20 ± 11.31 a | 104.67 ± 1.52 ab | 64.00 ± 2.90 a | 19.31 ± 0.08 bc | 916.67 ± 36.00 bc | ||
| T4 | 331.20 ± 2.26 a | 95.00 ± 0.47 bc | 62.26 ± 2.35 a | 19.26 ± 0.16 bc | 833.33 ± 36.00 c | ||
| T5 | 358.40 ± 6.91 a | 92.00 ± 0.47 c | 69.99 ±1.30 a | 18.93 ± 0.17 c | 950.00 ± 20.55 b | ||
| 2022 | Meixiangzhan 2 | CK | 305.60 ± 13.83 a | 115.04 ± 7.86 ab | 60.98 ± 1.30 bc | 19.58 ± 0.18 bc | 563.33 ± 27.32 a |
| T1 | 310.40 ± 3.46 a | 120.50 ± 5.27 ab | 65.66 ± 0.55 a | 19.92 ± 0.27 ab | 555.00 ± 10.80 a | ||
| T2 | 299.20 ± 8.57 a | 113.53 ± 3.34 ab | 64.07 ± 0.34 ab | 20.33 ± 0.13 a | 578.33 ± 15.69 a | ||
| T3 | 307.20 ± 18.52 a | 142.92 ± 5.47 a | 65.09 ± 1.05 a | 19.60 ± 0.17 bc | 440.00 ± 15.46 b | ||
| T4 | 286.40 ± 7.95 a | 100.27 ± 16.64 b | 66.97 ± 1.11 a | 19.20 ± 0.02 c | 443.33 ± 24.19 b | ||
| T5 | 294.40 ± 13.83 a | 102.93 ± 11.84 b | 59.02 ± 1.21 c | 19.04 ± 0.06 c | 390.00 ± 18.41 b | ||
| Xiangyaxiangzhan | CK | 297.60 ± 13.76 a | 100.34 ± 0.67 a | 61.81 ± 0.85 ab | 19.78 ± 0.05 c | 588.33 ± 11.14 ab | |
| T1 | 307.20 ± 11.76 a | 108.30 ± 1.96 a | 64.65 ± 1.12 a | 20.95 ± 0.16 b | 636.67 ± 24.19 a | ||
| T2 | 321.60 ± 27.15 a | 103.27 ± 0.87 a | 65.26 ± 1.23 a | 21.74 ± 0.07 a | 644.33 ± 23.51 a | ||
| T3 | 315.20 ± 21.74 a | 106.09 ± 0.72 a | 63.66 ± 1.29 ab | 19.60 ± 0.11 c | 550.00 ± 20.55 b | ||
| T4 | 280.00 ± 6.91 a | 105.37 ± 13.91 a | 63.39 ± 0.88 ab | 19.80 ± 0.20 c | 546.67 ± 10.89 b | ||
| T5 | 289.60 ± 3.46 a | 106.51 ± 0.85 a | 59.12 ± 1.25 b | 20.53 ± 0.16 b | 556.67 ± 11.86 b |

Fig. 4. Effects of foliar application of sodium iodide on aromatic rice leaves in 2021 and 2022. CK, Foliar spray with distilled water; T1‒T5, Foliar spray with 0.010%, 0.025%, 0.050%, 0.075%, and 0.100% sodium iodide, respectively.
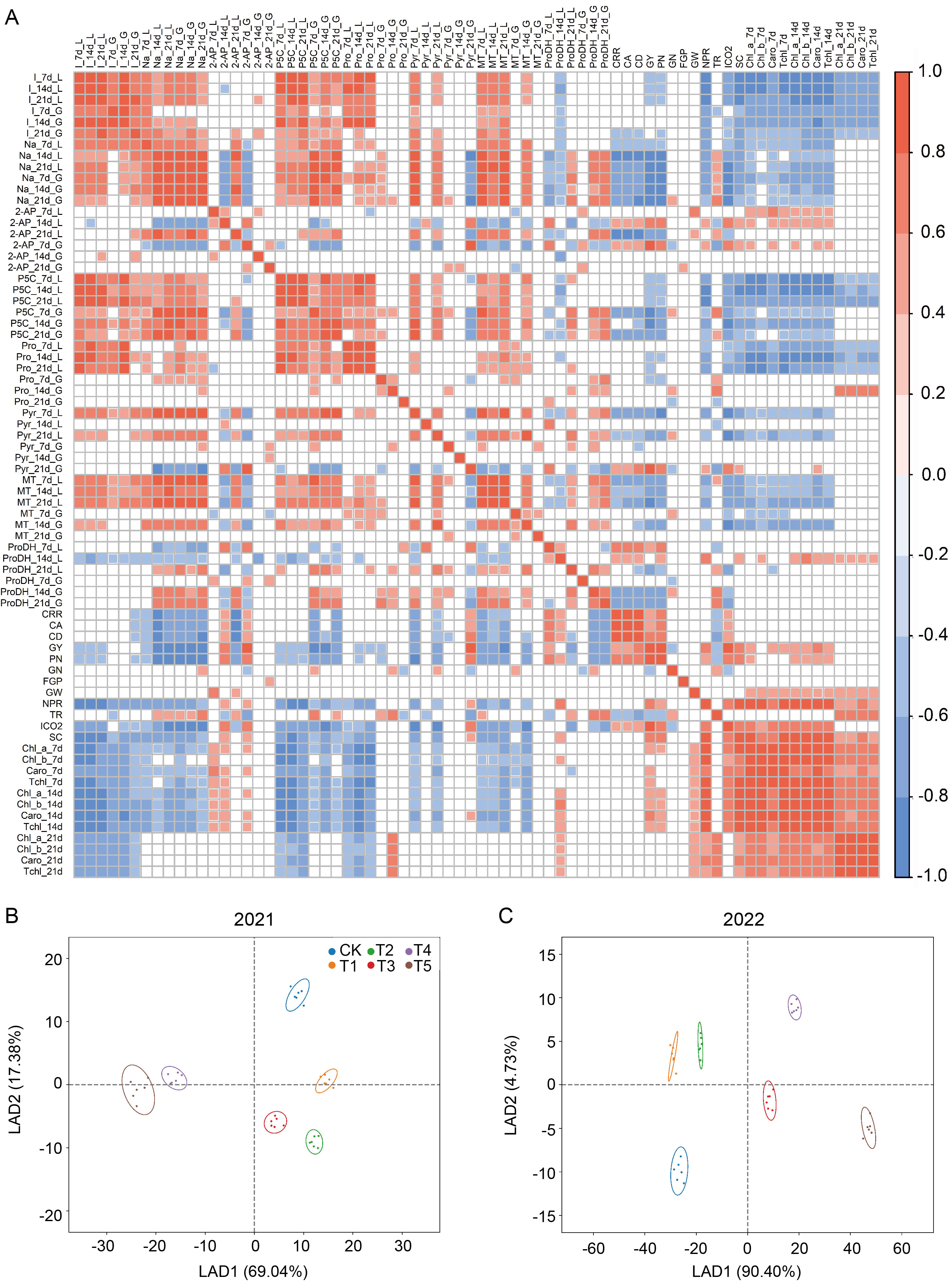
Fig. 5. Correlation analysis (A) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) of investigated parameters in 2021 (B) and 2022 (C). I, Iodine; Na, Sodium; 2-AP, 2-Acetyl- 1-pyrroline; P5C, 1-Pyrroline-5- carboxylic acid; Pro, Proline; Pyr, 1-Pyrroline; MT, Methylglyoxal; ProDH, Proline dehydrogenase; CRR, Chalky grain rate; CA, Chalkiness area; CD, Chalkiness degree; GY, Grain yield; PN, Panicle number per m2; GN, Grain number per panicle; FGP, Filled-grain rate; GW, 1000- grain weight; NPR, Net photosynthetic rate; TR, Transpiration rate; ICO2, Intercellular CO2 concentration; SC, Stomatal conductance; Chl, Chlorophyll content; Caro, Carotenoid content; Tchl, Total chlorophyll content; 7d, 7 d after spraying; 14d, 14 d after spraying; 21d, 21 d after spraying; L, Leaves; G, Grains. The presence of color indicates a significant level of correlation (P < 0.05).
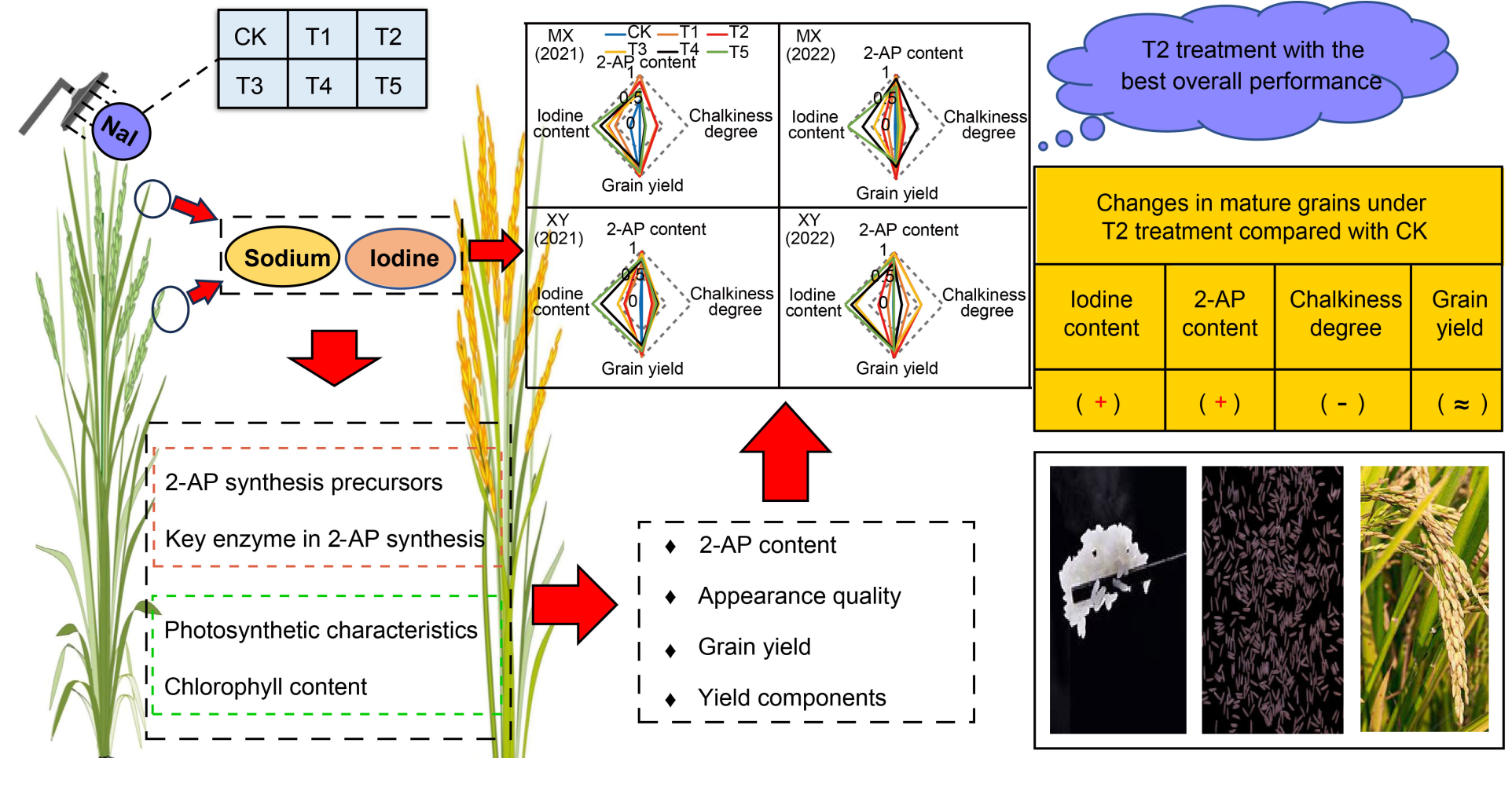
Fig. 7. Mechanism of foliar application of sodium iodide (NaI) affecting grain iodine, aroma, appearance quality, and yield. CK, Foliar spray with distilled water; T1‒T5, Foliar spray with 0.010%, 0.025%, 0.050%, 0.075%, and 0.100% odium iodide, respectively; 2-AP, 2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline; MX, Meixiangzhan 2; XY, Xiangyaxiangzhan.
| [1] | Amachi S. 2008. Microbial contribution to global iodine cycling: Volatilization, accumulation, reduction, oxidation, and sorption of iodine. Microbes Environ, 23(4): 269-276. |
| [2] | Amachi S, Kasahara M, Hanada S, Kamagata Y, Shinoyama H, Fujii T, Muramatsu Y. 2003. Microbial participation in iodine volatilization from soils. Environ Sci Technol, 37(17): 3885-3890. |
| [3] | Ambardekar A A, Siebenmorgen T J, Counce P A, Lanning S B, Mauromoustakos A. 2011. Impact of field-scale nighttime air temperatures during kernel development on rice milling quality. Field Crops Res, 122(3): 179-185. |
| [4] | Bao G G, Ashraf U, Wan X R, Zhou Q, Li S Y, Wang C L, He L X, Tang X R. 2021. Transcriptomic analysis provides insights into foliar zinc application induced upregulation in 2-acetyl-1- pyrroline and related transcriptional regulatory mechanism in fragrant rice. J Agric Food Chem, 69(38): 11350-11360. |
| [5] | Behera P K, Panda D. 2023. Germplasm resources, genes and perspective for aromatic rice. Rice Sci, 30(4): 294-305. |
| [6] | Blasco B, Leyva R, Romero L, Ruiz J M. 2013. Iodine effects on phenolic metabolism in lettuce plants under salt stress. J Agric Food Chem, 61(11): 2591-2596. |
| [7] | Budke C, Dierend W, Schön H G, Hora K, Mühling K H, Daum D. 2021. Iodine biofortification of apples and pears in an orchard using foliar sprays of different composition. Front Plant Sci, 12: 638671. |
| [8] | Caffagni A, Arru L, Meriggi P, Milc J, Perata P, Pecchioni N. 2011. Iodine fortification plant screening process and accumulation in tomato fruits and potato tubers. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal, 42(6): 706-718. |
| [9] | Cakmak I, Prom-u-thai C, Guilherme L R G, Rashid A, Hora K H, Yazici A, Savasli E, Kalayci M, Tutus Y, Phuphong P, Rizwan M, Martins F A D, Dinali G S, Ozturk L. 2017. Iodine biofortification of wheat, rice and maize through fertilizer strategy. Plant Soil, 418: 319-335. |
| [10] | Dangthaisong P, Sookgul P, Wanchana S, Arikit S, Malumpong C. 2023. Abiotic stress at the early grain filling stage affects aromatics, grain quality and grain yield in Thai fragrant rice (Oryza sativa) cultivars. Agric Res, 12(3): 285-297. |
| [11] | Dou Z, Tang S, Li G H, Liu Z H, Ding C Q, Chen L, Wang S H, Ding Y F. 2017. Application of nitrogen fertilizer at heading stage improves rice quality under elevated temperature during grain-filling stage. Crop Sci, 57(4): 2183-2192. |
| [12] | Du B, Wang W X, Jiang S C, Xie Y M, Cheng Y J, Xu J L, Xing D Y. 2021. Silicon and selenium fertilizer management improved productivity and aroma of fragrant rice. Crop Sci, 61(2): 936-946. |
| [13] | Gay F, Maraval I, Roques S, Gunata Z, Boulanger R, Audebert A, Mestres C. 2010. Effect of salinity on yield and 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline content in the grains of three fragrant rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.) in Camargue (France). Field Crops Res, 117(1): 154-160. |
| [14] | Ha P T T, Tuan T M, Tho N X, Tram N T N, Tram N T B. 2020. Salt stress affects the agronomic traits, phytic acid, and aroma of rice (Oryza sativa L.) M1 mutant lines. SABRAO J Breed Genet, 52(3): 216-230. |
| [15] | Hatch-McChesney A, Lieberman H R. 2022. Iodine and iodine deficiency: A comprehensive review of a re-emerging issue. Nutrients, 14(17): 3474. |
| [16] | Hurtevent P, Thiry Y, Levchuk S, Yoschenko V, Henner P, Madoz- Escande C, Leclerc E, Colle C, Kashparov V. 2013. Translocation of 125I, 75Se and 36Cl to wheat edible parts following wet foliar contamination under field conditions. J Environ Radioact, 121: 43-54. |
| [17] | Ishfaq M, Kiran A ur Rehman H, Farooq M, Ijaz N H, Nadeem F, Azeem I, Li X X, Wakeel A. 2022. Foliar nutrition: Potential and challenges under multifaceted agriculture. Environ Exp Bot, 200: 104909. |
| [18] | Itoh N, Toda H, Matsuda M, Negishi T, Taniguchi T, Ohsawa N. 2009. Involvement of S-adenosylmethionine-dependent halide/thiol methyltransferase (HTMT) in methyl halide emissions from agricultural plants: Isolation and characterization of an HTMT- coding gene from Raphanus sativus (daikon radish). BMC Plant Biol, 9: 116. |
| [19] | Izydorczyk G, Ligas B, Mikula K, Witek-Krowiak A, Moustakas K, Chojnacka K. 2021. Biofortification of edible plants with selenium and iodine: A systematic literature review. Sci Total Environ, 754: 141983. |
| [20] | Jian Y W, Fu J, Li B G, Zhou F. 2020. Increased extreme hourly precipitation over China’s rice paddies from 1961 to 2012. Sci Rep, 10(1): 10609. |
| [21] | Kandil E E, El-Banna A A A, Tabl D M M, Mackled M I, Ghareeb R Y, Al-Huqail A A, Ali H M, Jebril J, Abdelsalam N R. 2022. Zinc nutrition responses to agronomic and yield traits, kernel quality, and pollen viability in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front Plant Sci, 13: 791066. |
| [22] | Kittipornkul P, Treesubsuntorn C, Thiravetyan P. 2020. Effect of exogenous catechin and salicylic acid on rice productivity under ozone stress: The role of chlorophyll contents, lipid peroxidation, and antioxidant enzymes. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 27(20): 25774-25784. |
| [23] | Kumar S G, Reddy A M, Sudhakar C. 2003. NaCl effects on proline metabolism in two high yielding genotypes of mulberry (Morus alba L.) with contrasting salt tolerance. Plant Sci, 165(6): 1245-1251. |
| [24] | Lanning S B, Siebenmorgen T J, Counce P A, Ambardekar A A, Mauromoustakos A. 2011. Extreme nighttime air temperatures in 2010 impact rice chalkiness and milling quality. Field Crops Res, 124(1): 132-136. |
| [25] | Liu S L, Pu C, Ren Y X, Zhao X L, Zhao X, Chen F, Xiao X P, Zhang H L. 2016. Yield variation of double-rice in response to climate change in Southern China. Eur J Agron, 81: 161-168. |
| [26] | Liu X H, Chen G G, Vlantis A C, van Hasselt C A. 2009. Iodine mediated mechanisms and thyroid carcinoma. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci, 46(5/6): 302-318. |
| [27] | Luo H W, Du B, He L X, He J, Hu L, Pan S G, Tang X R. 2019. Exogenous application of zinc (Zn) at the heading stage regulates 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline (2-AP) biosynthesis in different fragrant rice genotypes. Sci Rep, 9: 19513. |
| [28] | Luo H W, He L X, Du B, Pan S G, Mo Z W, Duan M Y, Tian H, Tang X R. 2020. Biofortification with chelating selenium in fragrant rice: Effects on photosynthetic rates, aroma, grain quality and yield formation. Field Crops Res, 255: 107909. |
| [29] | Luo H W, He L X, Du B, Pan S G, Mo Z W, Yang S Y, Zou Y B, Tang X R. 2022. Epoxiconazole improved photosynthesis, yield formation, grain quality and 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline biosynthesis of fragrant rice. Rice Sci, 29(2): 189-196. |
| [30] | Maglione G, Vitale E, Costanzo G, Polimeno F, Arena C, Vitale L. 2022. Iodine enhances the nutritional value but not the tolerance of lettuce to NaCl. Horticulturae, 8(7): 662. |
| [31] | Medrano-Macías J, Leija-Martínez P, González-Morales S, Juárez- Maldonado A, Benavides-Mendoza A. 2016. Use of iodine to biofortify and promote growth and stress tolerance in crops. Front Plant Sci, 7: 1146. |
| [32] | Mo Z W, Lei S, Ashraf U, Khan I, Li Y, Pan S G, Duan M Y, Tian H, Tang X R. 2017. Silicon fertilization modulates 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline content, yield formation and grain quality of aromatic rice. J Cereal Sci, 75: 17-24. |
| [33] | Mo Z W, Li Y H, Nie J, He L X, Pan S G, Duan M Y, Tian H, Xiao L Z, Zhong K Y, Tang X R. 2019. Nitrogen application and different water regimes at booting stage improved yield and 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline (2AP) formation in fragrant rice. Rice, 12(1): 74. |
| [34] | Mohapatra P K, Panigrahi R, Turner N C. 2011. Physiology of spikelet development on the rice panicle: Is manipulation of apical dominance crucial for grain yield improvement? In: Sparks D L. Advances in Agronomy. Amsterdam, the Netherland: Elsevier: 333-359. |
| [35] | Nagatoshi Y, Nakamura T. 2007. Characterization of three halide methyltransferases in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Biotechnol, 24(5): 503-506. |
| [36] | National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. 2020. Determination of iodine in food: GB/T 5009.267-2020. Beijing, China: The National Standard of China. (in Chinese) |
| [37] | National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. 2016. Determination of multiple elements in food: GB 5009.268-2016. Beijing, China: The National Standard of China. (in Chinese) |
| [38] | Ncube B, Finnie J F, Van Staden J. 2013. Dissecting the stress metabolic alterations in in vitro Cyrtanthus regenerants. Plant Physiol Biochem, 65: 102-110. |
| [39] | Niu J H, Liu C, Huang M L, Liu K Z, Yan D Y. 2021. Effects of foliar fertilization: A review of current status and future perspectives. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr, 21(1): 104-118. |
| [40] | Niu X L, Tang W, Huang W Z, Ren G J, Wang Q L, Luo D, Xiao Y Y, Yang S M, Wang F, Lu B R, Gao F Y, Lu T G, Liu Y S. 2008. RNAi-directed downregulation of OsBADH2 results in aroma (2-acetyl-1-pyrroline) production in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol, 8: 100. |
| [41] | Olum S, Gellynck X, Wesana J, Odongo W, Aparo N O, Aloka B, Ongeng D, De Steur H. 2021. Economic feasibility of iodine agronomic biofortification: A projective analysis with Ugandan vegetable farmers. Sustainability, 13(19): 10608. |
| [42] | Pang Y D, Liao Q H, Peng H G, Qian C, Wang F. 2023. CO2 mesophyll conductance regulated by light: A review. Planta, 258(1): 11. |
| [43] | Rakoczy R, Kopeć A, Piątkowska E, Smoleń S, Skoczylas Ł, Leszczyńska T, Sady W. 2016. The iodine content in urine, faeces and selected organs of rats fed lettuce biofortified with iodine through foliar application. Biol Trace Elem Res, 174(2): 347-355. |
| [44] | Rakoczy-Lelek R, Smoleń S, Grzanka M, Ambroziak K, Pitala J, Skoczylas Ł, Liszka-Skoczylas M, Kardasz H. 2021. Effectiveness of foliar biofortification of carrot with iodine and selenium in a field condition. Front Plant Sci, 12: 656283. |
| [45] | Redeker K R, Wang N Y, Low J C, McMillan A, Tyler S C, Cicerone R J. 2000. Emissions of methyl halides and methane from rice paddies. Science, 290: 966-969. |
| [46] | Ren Y, Zhu Y L, Liang F, Li Q Q, Zhao Q H, He Y, Lin X E, Qin X Y, Cheng S R. 2022. Effect of foliar copper application on grain yield, 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline and copper content in fragrant rice. Plant Physiol Biochem, 182: 154-166. |
| [47] | Shrestha S, Mahat J, Shrestha J, Madhav K C, Paudel K. 2022. Influence of high-temperature stress on rice growth and development: A review. Heliyon, 8(12): e12651. |
| [48] | Sun D J, Codling K, Chang S Y, Zhang S B, Shen H M, Su X H, Chen Z P, Scherpbier R W, Yan J. 2017. Eliminating iodine deficiency in China: Achievements, challenges and global implications. Nutrients, 9(4): 361. |
| [49] | Tateishi Y, Nakagawa T, Esaka M. 2005. Osmotolerance and growth stimulation of transgenic tobacco cells accumulating free proline by silencing proline dehydrogenase expression with double- stranded RNA interference technique. Physiol Plant, 125(2): 224-234. |
| [50] | Tu D B, Wu W G, Xi M, Zhou Y J, Xu Y Z, Chen J H, Shao C H, Zhang Y P, Zhao Q Z. 2022. Effect of temperature and radiation on indica rice yield and quality in middle rice cropping system. Plants, 11(20): 2697. |
| [51] | Wang X Y, Ren Y, Ashraf U, Gui R F, Deng H Z, Dai L, Tang X R, Wang Z M, Mo Z W. 2023. Optimization of liquid fertilizer management improves grain yield, biomass accumulation, and nutrient uptake of late-season indica fragrant rice. J Sci Food Agric, 103(14): 6800-6813. |
| [52] | Xie W J, Ashraf U, Zhong D T, Lin R B, Xian P Q, Zhao T, Feng H Y, Wang S L, Duan M Y, Tang X R, Mo Z W. 2019. Application of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and nitrogen regulates aroma biochemistry in fragrant rice. Food Sci Nutr, 7(11): 3784-3796. |
| [53] | Yoshihashi T, Huong N T T, Inatomi H. 2002. Precursors of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, a potent flavor compound of an aromatic rice variety. J Agric Food Chem, 50(7): 2001-2004. |
| [54] | Zhang Y J, Liu G S, Cheng Y D, Xu J N, Wang C, Yang J C. 2020. The effects of dry cultivation on grain-filling and chalky grains of upland rice and paddy rice. Food Energy Secur, 9(2): e198. |
| [55] | Zhao Q Y, Xi J Z, Xu X M, Yin Y, Xu D, Jin Y M, Tong Q Y, Dong L, Wu F F. 2022. Volatile fingerprints and biomarkers of Chinese fragrant and non-fragrant japonica rice before and after cooking obtained by untargeted GC/MS-based metabolomics. Food Biosci, 47: 101764. |
| [56] | Zheng J L, Chen T T, Wu Q, Yu J M, Chen W, Chen Y L, Siddique K H M, Meng W Z, Chi D C, Xia G M. 2018. Effect of zeolite application on phenology, grain yield and grain quality in rice under water stress. Agric Water Manage, 206: 241-251. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||