
Rice Science ›› 2016, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (4): 184-195.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2015.10.001
收稿日期:2015-07-09
接受日期:2015-10-19
出版日期:2016-07-28
发布日期:2016-04-11
. [J]. Rice Science, 2016, 23(4): 184-195.
| Genotype | Type | Condition | Important characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Suwandel | L | Upland | White pericarp, exquisite aroma, special milky taste (ideal choice for festive occasions) |
| Murungakayan | L | Upland | Resistant to stem borer and blast, susceptible to lodging |
| Sudubalawee | L | Upland | Resistant to gall midge (biotype I), brown planthopper, blast and bacterial blight |
| Suduheenati | L | Upland | Antioxidant properties, resistant to blast |
| Hondarawala | L | Upland | Resistant to blast and brown planthopper |
| Marss | L | Upland | Red pericarp, good eating quality, moderately resistant to blast and bacterial blight |
| Kokuwellai | L | Upland | Wide adaptability |
| Kaluheenati | L | Upland | High nutritional and medicinal values |
| Pokkali | L | Upland | Resistant to brown planthopper and tolerant to salinity |
| Rathuheenati | L | Upland | High medicinal values and resistant to brown planthopper |
| Rathel | L | Upland | High nutritional and medicinal values |
| Sudurusamba | L | Upland | Resistant to brown planthopper and blast |
| H10 | OI | Lowland | Red pericarp |
| H4 | OI | Lowland | Red pericarp, wide adaptability and resistant to blast |
| H7 | OI | Lowland | Good grain quality |
| At 353 | NI | Lowland | Red pericarp, suitable for parboiling, moderately resistant to blast and bacterial blight, tolerant to salinity |
| At 306 | NI | Lowland | Red pericarp, similar with Basmati like grain quality with long seeds, moderately resistant to blast and bacterial blight, and tolerant to salinity |
| At 362 | NI | Lowland | Red pericarp, moderately resistant to brown planthopper, blast and bacterial blight |
| At 354 | NI | Lowland | White pericarp, tolerant to salinity and resistant to lodging |
| Bg 403 | NI | Lowland | White pericarp, resistant to blast and bacterial blight |
| Bg 250 | NI | Lowland | White pericarp, ultra-short in maturity and resistant or moderately resistant to brown planthopper and blast |
| Bg 358 | NI | Lowland | High yielding, small grains, resistant to brown planthopper, blast, bacterial blight and moderately tolerant to iron toxicity |
| Bg 357 | NI | Lowland | High yielding, resistant to brown planthopper, gall midge (biotypes I and II), moderately resistant to thrips, resistant to blast and moderately resistant to iron toxicity |
| Bg 300 | NI | Lowland | High yielding, early maturity, higher adaptability, resistant to gall midge (biotype I), brown planthopper, blast and bacterial blight |
| Bg 450 | NI | Lowland | Resistant to gall midge (biotype I) |
| Bg 94-1 | NI | Lowland | White pericarp, high yielding and suitable for parboiling |
| Bg 352 | NI | Lowland | White pericarp, intermediate sized bold type grains, high yielding, early maturity, wide adaptability and resistant to blast and brown planthopper |
| Bg 379-2 | NI | Lowland | Resistant to brown planthopper, bacterial blight and iron toxicity |
| Bw 364 | NI | Lowland | Red pericarp, resistance to gall midge (biotype I) and iron toxicity |
| Ld 356 | NI | Lowland | Short round grains, moderately tolerant to iron toxicity, resistant to seed spotting and gall midge (biotype I) |
Table 1 Rice genotypes screened for phosphorous deficiency tolerance.
| Genotype | Type | Condition | Important characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Suwandel | L | Upland | White pericarp, exquisite aroma, special milky taste (ideal choice for festive occasions) |
| Murungakayan | L | Upland | Resistant to stem borer and blast, susceptible to lodging |
| Sudubalawee | L | Upland | Resistant to gall midge (biotype I), brown planthopper, blast and bacterial blight |
| Suduheenati | L | Upland | Antioxidant properties, resistant to blast |
| Hondarawala | L | Upland | Resistant to blast and brown planthopper |
| Marss | L | Upland | Red pericarp, good eating quality, moderately resistant to blast and bacterial blight |
| Kokuwellai | L | Upland | Wide adaptability |
| Kaluheenati | L | Upland | High nutritional and medicinal values |
| Pokkali | L | Upland | Resistant to brown planthopper and tolerant to salinity |
| Rathuheenati | L | Upland | High medicinal values and resistant to brown planthopper |
| Rathel | L | Upland | High nutritional and medicinal values |
| Sudurusamba | L | Upland | Resistant to brown planthopper and blast |
| H10 | OI | Lowland | Red pericarp |
| H4 | OI | Lowland | Red pericarp, wide adaptability and resistant to blast |
| H7 | OI | Lowland | Good grain quality |
| At 353 | NI | Lowland | Red pericarp, suitable for parboiling, moderately resistant to blast and bacterial blight, tolerant to salinity |
| At 306 | NI | Lowland | Red pericarp, similar with Basmati like grain quality with long seeds, moderately resistant to blast and bacterial blight, and tolerant to salinity |
| At 362 | NI | Lowland | Red pericarp, moderately resistant to brown planthopper, blast and bacterial blight |
| At 354 | NI | Lowland | White pericarp, tolerant to salinity and resistant to lodging |
| Bg 403 | NI | Lowland | White pericarp, resistant to blast and bacterial blight |
| Bg 250 | NI | Lowland | White pericarp, ultra-short in maturity and resistant or moderately resistant to brown planthopper and blast |
| Bg 358 | NI | Lowland | High yielding, small grains, resistant to brown planthopper, blast, bacterial blight and moderately tolerant to iron toxicity |
| Bg 357 | NI | Lowland | High yielding, resistant to brown planthopper, gall midge (biotypes I and II), moderately resistant to thrips, resistant to blast and moderately resistant to iron toxicity |
| Bg 300 | NI | Lowland | High yielding, early maturity, higher adaptability, resistant to gall midge (biotype I), brown planthopper, blast and bacterial blight |
| Bg 450 | NI | Lowland | Resistant to gall midge (biotype I) |
| Bg 94-1 | NI | Lowland | White pericarp, high yielding and suitable for parboiling |
| Bg 352 | NI | Lowland | White pericarp, intermediate sized bold type grains, high yielding, early maturity, wide adaptability and resistant to blast and brown planthopper |
| Bg 379-2 | NI | Lowland | Resistant to brown planthopper, bacterial blight and iron toxicity |
| Bw 364 | NI | Lowland | Red pericarp, resistance to gall midge (biotype I) and iron toxicity |
| Ld 356 | NI | Lowland | Short round grains, moderately tolerant to iron toxicity, resistant to seed spotting and gall midge (biotype I) |
| Season | Genotype | Early vegetative stage | Late vegetative stage | Flowering stage | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | ||||
| Yala | H4 | 34.69 a | 65.01 a | 41.00 a | 67.69 a | 70.43 b | 58.12 a | 81.16 a | 73.31 d | 80.13 a | ||
| Suduheenati | 34.38 a | 70.75 a | 38.43 b | 74.63 a | 79.37 a | 56.94 a | 97.50 a | 85.63 b | 75.50 a | |||
| H10 | 34.88 a | 65.13 a | 41.06 a | 68.17 a | 85.56 a | 59.62 a | 83.43 a | 87.19 b | 76.68 a | |||
| Murungakayan | 35.19 a | 60.50 a | 36.50 b | 72.48 a | 67.50 b | 51.06 a | 88.31 a | 69.25 a | 71.83 a | |||
| H7 | 35.50 a | 66.62 a | 40.12 a | 67.94 a | 89.00 a | 55.25 a | 89.84 a | 95.13 a | 84.94 a | |||
| Bg 403 | 17.63 b | 56.81 b | 27.34 d | 42.02 b | 69.31 b | 39.62 b | 55.53 c | 72.19 d | 58.50 a | |||
| Bg 358 | 23.44 b | 57.68 b | 28.88 d | 51.75 b | 70.75 b | 41.80 b | 67.39 b | 79.31 c | 55.23 a | |||
| Bg 379-2 | 22.06 b | 52.00 b | 26.88 d | 38.35 b | 57.06 c | 35.19 b | 46.14 c | 64.31 d | 47.79 a | |||
| Bg 352 | 25.81 b | 52.00 b | 25.69 d | 53.00 b | 67.25 b | 36.69 b | 63.53 b | 69.63 d | 51.19 a | |||
| Bg 357 | 24.88 b | 43.50 c | 31.75 c | 48.69 b | 44.55 d | 42.00 b | 58.10 b | 46.75 e | 53.53 a | |||
| At 354 | 22.25 b | 40.75 c | 27.50 d | 54.46 b | 42.75 d | 39.94 b | 61.66 b | 45.50 e | 52.80 a | |||
| Maha | H4 | 46.54 a | 43.13 a | 44.54 a | 65.08 a | 59.63 a | 56.13 a | 102.58 a | 70.69 c | 94.00 a | ||
| Marss | 30.38 c | 35.75 b | 29.42 b | 41.63 b | 44.69 b | 38.25 b | 76.00 c | 61.00 c | 75.90 c | |||
| Suduheenati | 42.88 a | 43.63 a | 43.71 a | 53.08 a | 62.94 a | 44.83 a | 91.25 b | 71.50 c | 89.25 a | |||
| H10 | 50.25 a | 43.38 a | 42.00 a | 69.21 a | 56.81 a | 48.67 a | 109.17 a | 94.00 a | 91.42 a | |||
| Rathel | 35.08 c | - | 30.92 b | 52.63 a | - | 41.13 b | 94.73 b | - | 82.91 b | |||
| Kaluheenati | 46.50 a | - | 45.63 a | 61.46 a | - | 54.88 a | 90.82 b | - | 91.80 a | |||
| Murungakayan | 43.96 a | 45.31 a | 46.42 a | 53.54 a | 62.75 a | 53.42 a | 85.00 b | 80.63 b | 92.00 a | |||
| Kokuwellai | 31.83 c | - | 27.79 b | 44.38 b | - | 35.67 b | 73.50 c | - | 66.17 c | |||
| H7 | 46.33 a | 43.13 a | 42.71 a | 59.58 a | 60.88 a | 50.29 a | 92.83 b | 94.81 a | 92.92 a | |||
| Sudubalawee | 46.71 a | 44.63 a | 45.71 a | 55.38 a | 63.63 a | 47.33 a | 94.58 b | 102.69 a | 93.58 a | |||
| Bg 94-1 | 31.33 c | 31.13 b | 29.08 b | 37.54 b | 44.50 b | 33.42 b | 53.92 e | 66.69 c | 59.50 d | |||
| Bg 403 | 29.63 c | 32.50 b | 27.75 b | 36.46 b | 43.31 b | 30.88 b | 64.92 d | 63.19 c | 59.58 d | |||
| At 362 | 33.75 c | 35.06 b | 32.21 b | 41.75 b | 50.13 b | 37.83 b | 77.58 c | 71.06 c | 74.58 c | |||
| Pokkali | 43.38 a | - | 42.58 a | 53.79 a | - | 48.17 a | 93.83 b | - | 95.83 a | |||
| Bg 358 | 27.42 c | 32.13 b | 22.88 c | 30.42 b | 46.94 b | 28.38 b | 61.42 d | 66.00 c | 66.92 c | |||
| Bg 450 | 23.88 c | 30.75 b | 22.50 c | 25.71 c | 44.69 b | 25.18 b | 65.45 d | 52.44 d | 63.18 c | |||
| Sudurusamba | 31.25 c | - | 31.79 b | 35.92 b | - | 35.92 b | 60.75 d | - | 83.83 b | |||
| Bg 379-2 | 28.33 c | 30.94 a | 24.92 b | 38.50 b | 41.19 b | 27.38 b | 42.58 f | 52.88 d | 52.25 e | |||
| Hondarawala | 46.46 a | 45.19 a | 45.58 a | 51.00 a | 69.44 a | 56.63 a | 74.33 c | 96.56 a | 95.08 a | |||
| Bg 352 | 31.35 c | 31.38 b | 28.88 b | 36.63 b | 43.13 b | 29.92 b | 63.42 d | 68.94 c | 64.67 c | |||
| Bg 250 | 29.92 c | - | 29.42 b | 41.63 b | - | 32.79 b | 68.25 d | - | 68.33 c | |||
| Bw 364 | 31.54 c | - | 28.00 b | 37.67 b | - | 33.46 b | 64.75 d | - | 62.58 c | |||
| At 353 | 31.54 c | 33.31 b | 26.00 b | 34.92 b | 48.81 b | 29.17 b | 66.25 d | 79.69 b | 69.00 c | |||
| Suwandel | 37.58 b | - | 36.00 b | 44.38 b | - | 39.42 b | 73.67 c | - | 87.55 a | |||
| Ld 356 | 31.58 c | - | 32.71 b | 40.92 b | - | 36.71 b | 62.17 d | - | 73.92 c | |||
| Rathuheenati | 46.92 a | - | 46.67 a | 56.30 a | - | 46.50 a | 77.09 c | - | 83.10 b | |||
| Bg 357 | 27.88 c | 30.44 b | 26.96 b | 33.25 b | 43.06 b | 29.83 b | 58.08 d | 61.19 c | 58.83 d | |||
| At 306 | 31.50 c | 36.63 b | 29.46 b | 36.96 b | 47.06 b | 35.50 b | 60.50 d | 62.44 c | 69.63 c | |||
| At 354 | 25.21 c | 33.81 b | 25.75 b | 28.42 c | 48.00 b | 32.50 b | 54.08 e | 70.94 c | 61.92 c | |||
| Bg 300 | 32.04 c | 35.69 b | 31.29 b | 34.58 b | 47.00 b | 36.29 b | 63.08 d | 73.50 c | 70.36 c | |||
Table 2 Plant height of the tested rice genotypes.
| Season | Genotype | Early vegetative stage | Late vegetative stage | Flowering stage | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | ||||
| Yala | H4 | 34.69 a | 65.01 a | 41.00 a | 67.69 a | 70.43 b | 58.12 a | 81.16 a | 73.31 d | 80.13 a | ||
| Suduheenati | 34.38 a | 70.75 a | 38.43 b | 74.63 a | 79.37 a | 56.94 a | 97.50 a | 85.63 b | 75.50 a | |||
| H10 | 34.88 a | 65.13 a | 41.06 a | 68.17 a | 85.56 a | 59.62 a | 83.43 a | 87.19 b | 76.68 a | |||
| Murungakayan | 35.19 a | 60.50 a | 36.50 b | 72.48 a | 67.50 b | 51.06 a | 88.31 a | 69.25 a | 71.83 a | |||
| H7 | 35.50 a | 66.62 a | 40.12 a | 67.94 a | 89.00 a | 55.25 a | 89.84 a | 95.13 a | 84.94 a | |||
| Bg 403 | 17.63 b | 56.81 b | 27.34 d | 42.02 b | 69.31 b | 39.62 b | 55.53 c | 72.19 d | 58.50 a | |||
| Bg 358 | 23.44 b | 57.68 b | 28.88 d | 51.75 b | 70.75 b | 41.80 b | 67.39 b | 79.31 c | 55.23 a | |||
| Bg 379-2 | 22.06 b | 52.00 b | 26.88 d | 38.35 b | 57.06 c | 35.19 b | 46.14 c | 64.31 d | 47.79 a | |||
| Bg 352 | 25.81 b | 52.00 b | 25.69 d | 53.00 b | 67.25 b | 36.69 b | 63.53 b | 69.63 d | 51.19 a | |||
| Bg 357 | 24.88 b | 43.50 c | 31.75 c | 48.69 b | 44.55 d | 42.00 b | 58.10 b | 46.75 e | 53.53 a | |||
| At 354 | 22.25 b | 40.75 c | 27.50 d | 54.46 b | 42.75 d | 39.94 b | 61.66 b | 45.50 e | 52.80 a | |||
| Maha | H4 | 46.54 a | 43.13 a | 44.54 a | 65.08 a | 59.63 a | 56.13 a | 102.58 a | 70.69 c | 94.00 a | ||
| Marss | 30.38 c | 35.75 b | 29.42 b | 41.63 b | 44.69 b | 38.25 b | 76.00 c | 61.00 c | 75.90 c | |||
| Suduheenati | 42.88 a | 43.63 a | 43.71 a | 53.08 a | 62.94 a | 44.83 a | 91.25 b | 71.50 c | 89.25 a | |||
| H10 | 50.25 a | 43.38 a | 42.00 a | 69.21 a | 56.81 a | 48.67 a | 109.17 a | 94.00 a | 91.42 a | |||
| Rathel | 35.08 c | - | 30.92 b | 52.63 a | - | 41.13 b | 94.73 b | - | 82.91 b | |||
| Kaluheenati | 46.50 a | - | 45.63 a | 61.46 a | - | 54.88 a | 90.82 b | - | 91.80 a | |||
| Murungakayan | 43.96 a | 45.31 a | 46.42 a | 53.54 a | 62.75 a | 53.42 a | 85.00 b | 80.63 b | 92.00 a | |||
| Kokuwellai | 31.83 c | - | 27.79 b | 44.38 b | - | 35.67 b | 73.50 c | - | 66.17 c | |||
| H7 | 46.33 a | 43.13 a | 42.71 a | 59.58 a | 60.88 a | 50.29 a | 92.83 b | 94.81 a | 92.92 a | |||
| Sudubalawee | 46.71 a | 44.63 a | 45.71 a | 55.38 a | 63.63 a | 47.33 a | 94.58 b | 102.69 a | 93.58 a | |||
| Bg 94-1 | 31.33 c | 31.13 b | 29.08 b | 37.54 b | 44.50 b | 33.42 b | 53.92 e | 66.69 c | 59.50 d | |||
| Bg 403 | 29.63 c | 32.50 b | 27.75 b | 36.46 b | 43.31 b | 30.88 b | 64.92 d | 63.19 c | 59.58 d | |||
| At 362 | 33.75 c | 35.06 b | 32.21 b | 41.75 b | 50.13 b | 37.83 b | 77.58 c | 71.06 c | 74.58 c | |||
| Pokkali | 43.38 a | - | 42.58 a | 53.79 a | - | 48.17 a | 93.83 b | - | 95.83 a | |||
| Bg 358 | 27.42 c | 32.13 b | 22.88 c | 30.42 b | 46.94 b | 28.38 b | 61.42 d | 66.00 c | 66.92 c | |||
| Bg 450 | 23.88 c | 30.75 b | 22.50 c | 25.71 c | 44.69 b | 25.18 b | 65.45 d | 52.44 d | 63.18 c | |||
| Sudurusamba | 31.25 c | - | 31.79 b | 35.92 b | - | 35.92 b | 60.75 d | - | 83.83 b | |||
| Bg 379-2 | 28.33 c | 30.94 a | 24.92 b | 38.50 b | 41.19 b | 27.38 b | 42.58 f | 52.88 d | 52.25 e | |||
| Hondarawala | 46.46 a | 45.19 a | 45.58 a | 51.00 a | 69.44 a | 56.63 a | 74.33 c | 96.56 a | 95.08 a | |||
| Bg 352 | 31.35 c | 31.38 b | 28.88 b | 36.63 b | 43.13 b | 29.92 b | 63.42 d | 68.94 c | 64.67 c | |||
| Bg 250 | 29.92 c | - | 29.42 b | 41.63 b | - | 32.79 b | 68.25 d | - | 68.33 c | |||
| Bw 364 | 31.54 c | - | 28.00 b | 37.67 b | - | 33.46 b | 64.75 d | - | 62.58 c | |||
| At 353 | 31.54 c | 33.31 b | 26.00 b | 34.92 b | 48.81 b | 29.17 b | 66.25 d | 79.69 b | 69.00 c | |||
| Suwandel | 37.58 b | - | 36.00 b | 44.38 b | - | 39.42 b | 73.67 c | - | 87.55 a | |||
| Ld 356 | 31.58 c | - | 32.71 b | 40.92 b | - | 36.71 b | 62.17 d | - | 73.92 c | |||
| Rathuheenati | 46.92 a | - | 46.67 a | 56.30 a | - | 46.50 a | 77.09 c | - | 83.10 b | |||
| Bg 357 | 27.88 c | 30.44 b | 26.96 b | 33.25 b | 43.06 b | 29.83 b | 58.08 d | 61.19 c | 58.83 d | |||
| At 306 | 31.50 c | 36.63 b | 29.46 b | 36.96 b | 47.06 b | 35.50 b | 60.50 d | 62.44 c | 69.63 c | |||
| At 354 | 25.21 c | 33.81 b | 25.75 b | 28.42 c | 48.00 b | 32.50 b | 54.08 e | 70.94 c | 61.92 c | |||
| Bg 300 | 32.04 c | 35.69 b | 31.29 b | 34.58 b | 47.00 b | 36.29 b | 63.08 d | 73.50 c | 70.36 c | |||
| Season | Genotype | Early vegetative stage | Late vegetative stage | Flowering stage | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | ||||
| Yala | H4 | 3.3 b | 2.1 a | 2.3 a | 3.6 b | 2.6 b | 2.9 b | 4.4 c | 2.7 b | 3.7 c | ||
| Suduheenati | 1.6 c | 1.7 c | 1.1 d | 3.1 b | 2.0 c | 1.3 c | 5.2 a | 2.2 b | 4.3 c | |||
| H10 | 2.1 c | 1.7 c | 2.0 b | 2.3 c | 1.9 c | 2.3 b | 2.7 f | 2.0 b | 4.2 c | |||
| Murungakayan | 2.0 c | 1.7 b | 1.6 c | 2.5 c | 2.0 c | 1.6 c | 5.1 b | 2.3 b | 4.7 c | |||
| H7 | 2.3 c | 2.2 a | 1.9 b | 3.2 b | 2.2 b | 2.2 b | 4.7 b | 2.6 b | 3.8 c | |||
| Bg 403 | 2.0 c | 2.3 a | 2.5 a | 2.7 c | 2.7 a | 3.9 a | 4.6 c | 3.2 a | 6.4 a | |||
| Bg 358 | 2.3 c | 1.7 c | 1.4 d | 3.1 b | 2.1 c | 2.2 b | 4.9 b | 2.1 b | 4.1 c | |||
| Bg 379-2 | 1.8 c | 1.8 b | 2.2 a | 2.1 c | 2.3 b | 2.5 b | 4.1 d | 2.5 b | 3.3 c | |||
| Bg 352 | 3.4 b | 1.7 b | 1.3 d | 3.5 b | 2.1 b | 1.4 c | 5.0 b | 2.2 b | 3.3 c | |||
| Bg 357 | 3.1 b | 1.9 b | 1.8 b | 3.4 b | 1.9 c | 2.7 b | 3.8 e | 2.1 b | 2.8 d | |||
| At 354 | 4.2 a | 1.9 b | 2.2 a | 4.6 a | 2.0 c | 2.8 b | 4.9 b | 2.2 b | 5.8 b | |||
| Maha | H4 | 1.1 b | 2.2 a | 1.2 d | 2.1 b | 2.7 a | 3.1 d | 2.1 b | 2.8 a | 3.1 d | ||
| Marss | 1.0 c | 2.3 a | 2.0 b | 1.7 c | 2.7 a | 4.5 b | 1.7 c | 2.9 a | 4.5 b | |||
| Suduheenati | 1.0 c | 1.6 d | 1.3 d | 1.3 d | 1.9 c | 3.6 c | 1.3 d | 2.0 c | 3.6 c | |||
| H10 | 1.2 b | 1.7 c | 1.5 c | 2.2 b | 2.0 c | 2.8 d | 2.2 b | 2.1 c | 2.8 d | |||
| Rathel | 1.0 c | - | 1.4 c | 1.5 d | - | 2.7 d | 1.5 d | - | 2.7 d | |||
| Kaluheenati | 1.0 c | - | 1.8 b | 1.8 c | - | 2.6 d | 1.8 c | - | 2.6 d | |||
| Murungakayan | 1.0 c | 1.7 c | 1.1 d | 1.0 e | 2.0 c | 2.8 d | 1.0 e | 2.1 c | 2.8 d | |||
| Kokuwellai | 1.2 b | - | 1.9 b | 3.3 a | - | 4.3 b | 3.3 a | - | 4.3 b | |||
| H7 | 1.0 c | 2.2 a | 1.6 b | 1.6 c | 2.2 b | 2.2 d | 1.6 c | 2.5 b | 2.2 d | |||
| Sudubalawee | 1.0 c | 1.6 d | 1.4 c | 1.0 e | 1.6 d | 2.6 d | 1.0 e | 1.7 d | 2.6 d | |||
| Bg 94-1 | 1.5 a | 2.5 a | 2.8 a | 3.1 a | 2.6 a | 5.3 a | 3.1 a | 2.7 b | 5.3 a | |||
| Bg 403 | 1.0 c | 2.3 a | 1.7 b | 1.9 c | 3.0 a | 4.1 b | 1.9 c | 3.0 a | 4.1 b | |||
| At 362 | 1.0 c | 1.4 e | 1.2 d | 1.7 c | 1.7 d | 2.9 d | 1.7 c | 1.8 d | 2.9 d | |||
| Pokkali | 1.0 c | - | 1.0 d | 1.0 e | - | 2.0 d | 1.0 e | - | 2.0 d | |||
| Bg 358 | 1.0 c | 1.7 c | 1.3 d | 1.1 e | 2.0 c | 3.5 c | 1.1 e | 2.1 c | 3.5 c | |||
| Bg 450 | 1.0 c | 1.8 b | 1.7 b | 1.3 d | 2.4 b | 3.4 c | 1.3 d | 2.5 b | 3.4 c | |||
| Sudurusamba | 1.0 c | - | 1.1 d | 1.3 d | - | 2.8 d | 1.3 d | - | 2.8 d | |||
| Bg 379-2 | 1.0 c | 1.9 b | 1.5 c | 1.8 c | 2.4 b | 3.3 c | 1.8 c | 2.5 b | 3.3 c | |||
| Hondarawala | 1.0 c | 1.6 d | 1.1 d | 1.3 d | 1.8 c | 2.7 d | 1.3 d | 1.9 c | 2.7 d | |||
| Bg 352 | 1.0 c | 1.8 b | 1.3 d | 1.8 c | 2.1 b | 2.6 d | 1.8 c | 2.2 c | 2.6 d | |||
| Bg 250 | 1.0 c | - | 1.2 d | 1.9 c | - | 3.2 c | 1.9 c | - | 3.2 c | |||
| Bw 364 | 1.0 c | - | 1.6 b | 1.6 c | - | 4.0 b | 1.6 c | - | 4.0 b | |||
| At 353 | 1.0 c | 1.9 b | 1.2 d | 1.1 e | 2.2 b | 2.1 d | 1.1 e | 2.4 b | 2.1 d | |||
| Suwandel | 1.0 c | - | 1.0 d | 1.1 e | - | 2.3 d | 1.1 e | - | 2.3 d | |||
| Ld 356 | 1.0 c | - | 1.1 d | 1.4 d | - | 2.8 d | 1.4 d | - | 2.8 d | |||
| Rathuheenati | 1.0 c | - | 1.2 d | 1.3 d | - | 2.3 d | 1.3 d | - | 2.3 d | |||
| Bg 357 | 1.0 c | 1.7 c | 1.4 c | 1.0 e | 1.9 c | 3.4 c | 1.0 e | 2.0 c | 3.4 c | |||
| At 306 | 1.0 c | 1.5 d | 1.7 b | 1.3 d | 1.8 c | 3.3 c | 1.3 d | 1.8 c | 3.3 c | |||
| At 354 | 1.2 b | 1.9 b | 1.6 c | 1.1 e | 2.1 c | 4.0 b | 1.1 e | 2.2 c | 4.0 b | |||
| Bg 300 | 1.0 c | 1.8 b | 1.2 d | 1.4 d | 1.8 c | 2.7 d | 1.4 d | 1.9 c | 2.7 d | |||
Table 3 Mean number of tillers per plant of the tested rice genotypes.
| Season | Genotype | Early vegetative stage | Late vegetative stage | Flowering stage | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | ||||
| Yala | H4 | 3.3 b | 2.1 a | 2.3 a | 3.6 b | 2.6 b | 2.9 b | 4.4 c | 2.7 b | 3.7 c | ||
| Suduheenati | 1.6 c | 1.7 c | 1.1 d | 3.1 b | 2.0 c | 1.3 c | 5.2 a | 2.2 b | 4.3 c | |||
| H10 | 2.1 c | 1.7 c | 2.0 b | 2.3 c | 1.9 c | 2.3 b | 2.7 f | 2.0 b | 4.2 c | |||
| Murungakayan | 2.0 c | 1.7 b | 1.6 c | 2.5 c | 2.0 c | 1.6 c | 5.1 b | 2.3 b | 4.7 c | |||
| H7 | 2.3 c | 2.2 a | 1.9 b | 3.2 b | 2.2 b | 2.2 b | 4.7 b | 2.6 b | 3.8 c | |||
| Bg 403 | 2.0 c | 2.3 a | 2.5 a | 2.7 c | 2.7 a | 3.9 a | 4.6 c | 3.2 a | 6.4 a | |||
| Bg 358 | 2.3 c | 1.7 c | 1.4 d | 3.1 b | 2.1 c | 2.2 b | 4.9 b | 2.1 b | 4.1 c | |||
| Bg 379-2 | 1.8 c | 1.8 b | 2.2 a | 2.1 c | 2.3 b | 2.5 b | 4.1 d | 2.5 b | 3.3 c | |||
| Bg 352 | 3.4 b | 1.7 b | 1.3 d | 3.5 b | 2.1 b | 1.4 c | 5.0 b | 2.2 b | 3.3 c | |||
| Bg 357 | 3.1 b | 1.9 b | 1.8 b | 3.4 b | 1.9 c | 2.7 b | 3.8 e | 2.1 b | 2.8 d | |||
| At 354 | 4.2 a | 1.9 b | 2.2 a | 4.6 a | 2.0 c | 2.8 b | 4.9 b | 2.2 b | 5.8 b | |||
| Maha | H4 | 1.1 b | 2.2 a | 1.2 d | 2.1 b | 2.7 a | 3.1 d | 2.1 b | 2.8 a | 3.1 d | ||
| Marss | 1.0 c | 2.3 a | 2.0 b | 1.7 c | 2.7 a | 4.5 b | 1.7 c | 2.9 a | 4.5 b | |||
| Suduheenati | 1.0 c | 1.6 d | 1.3 d | 1.3 d | 1.9 c | 3.6 c | 1.3 d | 2.0 c | 3.6 c | |||
| H10 | 1.2 b | 1.7 c | 1.5 c | 2.2 b | 2.0 c | 2.8 d | 2.2 b | 2.1 c | 2.8 d | |||
| Rathel | 1.0 c | - | 1.4 c | 1.5 d | - | 2.7 d | 1.5 d | - | 2.7 d | |||
| Kaluheenati | 1.0 c | - | 1.8 b | 1.8 c | - | 2.6 d | 1.8 c | - | 2.6 d | |||
| Murungakayan | 1.0 c | 1.7 c | 1.1 d | 1.0 e | 2.0 c | 2.8 d | 1.0 e | 2.1 c | 2.8 d | |||
| Kokuwellai | 1.2 b | - | 1.9 b | 3.3 a | - | 4.3 b | 3.3 a | - | 4.3 b | |||
| H7 | 1.0 c | 2.2 a | 1.6 b | 1.6 c | 2.2 b | 2.2 d | 1.6 c | 2.5 b | 2.2 d | |||
| Sudubalawee | 1.0 c | 1.6 d | 1.4 c | 1.0 e | 1.6 d | 2.6 d | 1.0 e | 1.7 d | 2.6 d | |||
| Bg 94-1 | 1.5 a | 2.5 a | 2.8 a | 3.1 a | 2.6 a | 5.3 a | 3.1 a | 2.7 b | 5.3 a | |||
| Bg 403 | 1.0 c | 2.3 a | 1.7 b | 1.9 c | 3.0 a | 4.1 b | 1.9 c | 3.0 a | 4.1 b | |||
| At 362 | 1.0 c | 1.4 e | 1.2 d | 1.7 c | 1.7 d | 2.9 d | 1.7 c | 1.8 d | 2.9 d | |||
| Pokkali | 1.0 c | - | 1.0 d | 1.0 e | - | 2.0 d | 1.0 e | - | 2.0 d | |||
| Bg 358 | 1.0 c | 1.7 c | 1.3 d | 1.1 e | 2.0 c | 3.5 c | 1.1 e | 2.1 c | 3.5 c | |||
| Bg 450 | 1.0 c | 1.8 b | 1.7 b | 1.3 d | 2.4 b | 3.4 c | 1.3 d | 2.5 b | 3.4 c | |||
| Sudurusamba | 1.0 c | - | 1.1 d | 1.3 d | - | 2.8 d | 1.3 d | - | 2.8 d | |||
| Bg 379-2 | 1.0 c | 1.9 b | 1.5 c | 1.8 c | 2.4 b | 3.3 c | 1.8 c | 2.5 b | 3.3 c | |||
| Hondarawala | 1.0 c | 1.6 d | 1.1 d | 1.3 d | 1.8 c | 2.7 d | 1.3 d | 1.9 c | 2.7 d | |||
| Bg 352 | 1.0 c | 1.8 b | 1.3 d | 1.8 c | 2.1 b | 2.6 d | 1.8 c | 2.2 c | 2.6 d | |||
| Bg 250 | 1.0 c | - | 1.2 d | 1.9 c | - | 3.2 c | 1.9 c | - | 3.2 c | |||
| Bw 364 | 1.0 c | - | 1.6 b | 1.6 c | - | 4.0 b | 1.6 c | - | 4.0 b | |||
| At 353 | 1.0 c | 1.9 b | 1.2 d | 1.1 e | 2.2 b | 2.1 d | 1.1 e | 2.4 b | 2.1 d | |||
| Suwandel | 1.0 c | - | 1.0 d | 1.1 e | - | 2.3 d | 1.1 e | - | 2.3 d | |||
| Ld 356 | 1.0 c | - | 1.1 d | 1.4 d | - | 2.8 d | 1.4 d | - | 2.8 d | |||
| Rathuheenati | 1.0 c | - | 1.2 d | 1.3 d | - | 2.3 d | 1.3 d | - | 2.3 d | |||
| Bg 357 | 1.0 c | 1.7 c | 1.4 c | 1.0 e | 1.9 c | 3.4 c | 1.0 e | 2.0 c | 3.4 c | |||
| At 306 | 1.0 c | 1.5 d | 1.7 b | 1.3 d | 1.8 c | 3.3 c | 1.3 d | 1.8 c | 3.3 c | |||
| At 354 | 1.2 b | 1.9 b | 1.6 c | 1.1 e | 2.1 c | 4.0 b | 1.1 e | 2.2 c | 4.0 b | |||
| Bg 300 | 1.0 c | 1.8 b | 1.2 d | 1.4 d | 1.8 c | 2.7 d | 1.4 d | 1.9 c | 2.7 d | |||
| Season | Genotype | SDW (g/pot) | SPC (mg/g) | SPU (mg/pot) | PUE (g/mg) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | |||||
| Yala | H4 | 29.80 a | 11.95 c | 33.93 a | 0.65 b | 0.68 a | 0.50 e | 15.70 a | 8.12 b | 21.80 a | 1.50 c | 1.50 c | 2.00 a | |||
| Suduheenati | 18.15 c | 21.18 a | 19.50 c | 0.75 a | 0.45 c | 1.04 a | 10.10 d | 9.53 b | 22.90 a | 1.30 d | 2.20 b | 1.00 b | ||||
| H10 | 14.20 d | 9.83 c | 17.55 c | 0.47 d | 0.60 b | 0.85 c | 8.10 e | 5.89 c | 19.80 b | 2.10 a | 1.70 c | 1.20 b | ||||
| Murungakayan | 20.40 c | 11.20 c | 24.90 b | 0.53 c | 0.38 d | 0.88 c | 12.00 c | 4.25 d | 15.00 d | 1.90 b | 2.60 b | 1.10 b | ||||
| H7 | 24.10 b | 11.88 c | 21.00 c | 0.64 b | 0.29 e | 0.59 d | 16.50 a | 3.44 d | 17.20 c | 1.60 b | 3.40 a | 1.70 a | ||||
| Bg 403 | 24.90 b | 21.28 a | 27.20 b | 0.59 b | 0.55 b | 0.55 d | 16.20 a | 11.70 a | 17.10 c | 1.70 b | 1.80 c | 1.80 a | ||||
| Bg 358 | 13.00 d | 16.08 b | 15.10 c | 0.69 b | 0.45 c | 0.79 c | 18.60 a | 7.23 b | 12.00 e | 1.40 c | 2.20 b | 1.30 b | ||||
| Bg 379-2 | 26.50 b | 18.75 b | 28.20 b | 0.68 b | 0.52 b | 0.61 d | 13.70 b | 9.75 b | 17.90 c | 1.50 c | 1.90 c | 1.60 a | ||||
| Bg 352 | 22.80 b | 15.40 b | 25.00 b | 0.55 c | 0.48 c | 0.91 b | 14.70 b | 7.39 b | 12.50 e | 1.80 b | 2.10 b | 1.10 b | ||||
| Bg 357 | 10.40 d | 23.60 a | 12.50 d | 0.47 d | 0.29 e | 0.82 c | 7.80 e | 6.84 c | 19.30 b | 2.10 a | 3.40 a | 1.20 b | ||||
| At 354 | 19.50 c | 23.00 a | 21.20 c | 0.52 c | 0.48 c | 0.85 c | 10.60 d | 11.04 a | 10.20 e | 1.90 b | 2.10 b | 1.20 b | ||||
| Maha | H4 | 32.00 a | 18.56 b | 25.93 a | 0.50 c | 0.65 c | 0.52 d | 16.00 b | 16.10 c | 13.48 c | 2.00 b | 1.50 c | 1.90 b | |||
| Marss | 24.93 b | 38.12 a | 26.87 a | 0.77 b | 0.61 c | 0.50 d | 19.20 a | 31.00 a | 13.44 c | 2.00 b | 1.60 c | 1.20 c | ||||
| Suduheenati | 23.61 b | 20.34 b | 28.27 a | 0.49 c | 0.81 a | 0.85 b | 11.57 c | 22.00 b | 24.03 a | 2.00 b | 1.20 d | 1.20 c | ||||
| H10 | 24.01 b | 14.59 c | 16.66 c | 0.56 c | 0.59 c | 0.70 c | 13.45 c | 11.50 d | 11.66 d | 1.80 c | 1.70 c | 1.40 c | ||||
| Rathel | 23.32 b | - | 25.32 a | 0.70 b | - | 0.46 d | 16.32 b | - | 11.65 d | 2.10 b | - | 1.00 d | ||||
| Kaluheenati | 22.05 b | - | 25.11 a | 0.59 c | - | 0.83 b | 13.01 c | - | 20.84 a | 1.40 d | - | 1.30 c | ||||
| Murungakayan | 21.03 b | 25.23 b | 28.07 a | 0.50 c | 0.51 d | 0.60 c | 10.52 c | 17.10 c | 16.84 b | 2.00 b | 2.00 b | 1.70 b | ||||
| Kokuwellai | 20.05 b | - | 21.59 b | 0.51 c | - | 0.75 c | 10.23 c | - | 16.19 b | 1.70 c | - | 1.10 d | ||||
| H7 | 18.44 b | 17.41 b | 18.25 b | 0.72 b | 0.85 a | 0.76 c | 13.28 c | 19.70 b | 13.87 c | 1.40 d | 1.20 d | 1.30 c | ||||
| Sudubalawee | 18.43 b | 14.43 c | 21.87 b | 0.59 c | 0.43 d | 0.90 b | 10.87 c | 8.30 f | 19.68 a | 0.80 d | 2.30 a | 0.80 e | ||||
| Bg 94-1 | 17.40 c | 15.51 c | 20.62 b | 0.79 b | 0.51 c | 0.65 c | 13.75 c | 10.40 e | 13.40 c | 2.00 b | 2.00 b | 1.30 c | ||||
| Bg 403 | 17.49 c | 19.13 b | 27.08 a | 0.52 c | 0.50 c | 0.83 b | 9.09 d | 12.80 d | 22.48 a | 1.90 c | 2.00 b | 1.20 c | ||||
| At 362 | 17.09 c | 20.31 b | 28.06 a | 0.70 b | 0.40 d | 0.54 d | 11.96 c | 10.80 e | 15.15 b | 1.00 d | 2.50 a | 1.00 d | ||||
| Pokkali | 15.80 d | - | 19.62 b | 0.70 b | - | 0.76 c | 11.06 c | - | 14.91 b | 2.40 a | - | 1.10 d | ||||
| Bg 358 | 15.20 d | 16.19 c | 22.53 b | 0.72 b | 0.48 d | 0.53 d | 10.94 c | 10.40 e | 11.94 d | 1.40 d | 2.10 b | 1.90 b | ||||
| Bg 450 | 13.87 d | 20.93 b | 24.37 a | 0.64 b | 0.81 a | 0.75 c | 8.88 d | 12.60 d | 18.28 b | 1.30 d | 1.20 d | 2.00 a | ||||
| Sudurusamba | 14.51 d | - | 20.28 b | 0.41 c | - | 0.88 b | 5.95 e | - | 17.85 b | 1.30 d | - | 1.00 d | ||||
| Bg 379-2 | 14.72 d | 23.79 b | 20.65 b | 0.70 b | 0.68 c | 0.82 b | 10.30 c | 21.60 b | 16.93 b | 1.40 d | 1.50 c | 1.20 c | ||||
| Hondarawala | 13.22 d | 15.57 c | 24.20 a | 0.52 c | 0.49 d | 0.56 d | 6.87 e | 10.20 e | 13.55 c | 1.70 c | 2.00 b | 1.20 c | ||||
| Bg 352 | 12.38 d | 16.28 c | 16.13 c | 0.48 c | 0.79 a | 0.94 b | 5.94 e | 17.10 c | 15.16 b | 2.10 b | 1.30 d | 1.10 d | ||||
| Bg 250 | 13.18 d | - | 14.62 c | 0.76 b | - | 1.03 b | 10.02 c | - | 15.06 b | 1.30 d | - | 1.50 c | ||||
| Bw 364 | 13.14 d | - | 21.38 b | 0.52 c | - | 0.93 b | 6.83 e | - | 19.88 a | 1.60 c | - | 1.30 c | ||||
| At 353 | 11.43 d | 15.19 c | 15.17 c | 0.49 c | 0.76 b | 0.63 c | 5.60 e | 15.40 c | 9.56 e | 1.40 d | 1.30 d | 1.90 b | ||||
| Suwandel | 10.63 d | - | 15.71 c | 0.48 c | - | 0.98 b | 5.10 e | - | 15.40 b | 1.80 c | - | 1.00 d | ||||
| Ld 356 | 11.34 d | - | 22.70 b | 0.56 c | - | 0.98 b | 6.35 e | - | 22.25 a | 1.40 d | - | 2.20 a | ||||
| Rathuheenati | 11.29 d | - | 17.45 c | 0.51 c | - | 0.86 b | 5.76 e | - | 15.01 b | 1.90 c | - | 1.10 d | ||||
| Bg 357 | 7.70 e | 14.51 c | 17.60 c | 1.09 a | 0.83 a | 0.95 b | 8.39 d | 15.40 c | 16.72 b | 0.90 d | 1.20 d | 1.10 d | ||||
| At 306 | 8.72 e | 11.61 d | 12.07 d | 1.25 a | 0.74 b | 1.26 a | 10.90 c | 16.00 c | 15.21 b | 2.00 b | 1.40 c | 1.60 c | ||||
| At 354 | 11.19 d | 14.76 c | 18.83 b | 0.81 b | 0.75 b | 0.98 b | 9.06 d | 11.50 d | 18.45 b | 1.20 d | 1.30 d | 1.00 d | ||||
| Bg 300 | 11.63 d | 13.50 c | 14.20 c | 1.01 a | 0.64 c | 0.98 b | 11.75 c | 14.80 c | 13.92 c | 1.90 c | 1.60 c | 1.80 b | ||||
Table 4 Shoot dry weight (SDW), shoot phosphorus concentration (SPC) and shoot phosphorus uptake (SPU), phosphorus utilization efficiency (PUE) of the tested rice genotypes under studied conditions.
| Season | Genotype | SDW (g/pot) | SPC (mg/g) | SPU (mg/pot) | PUE (g/mg) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | P0 GH | P0 F | P30 GH | |||||
| Yala | H4 | 29.80 a | 11.95 c | 33.93 a | 0.65 b | 0.68 a | 0.50 e | 15.70 a | 8.12 b | 21.80 a | 1.50 c | 1.50 c | 2.00 a | |||
| Suduheenati | 18.15 c | 21.18 a | 19.50 c | 0.75 a | 0.45 c | 1.04 a | 10.10 d | 9.53 b | 22.90 a | 1.30 d | 2.20 b | 1.00 b | ||||
| H10 | 14.20 d | 9.83 c | 17.55 c | 0.47 d | 0.60 b | 0.85 c | 8.10 e | 5.89 c | 19.80 b | 2.10 a | 1.70 c | 1.20 b | ||||
| Murungakayan | 20.40 c | 11.20 c | 24.90 b | 0.53 c | 0.38 d | 0.88 c | 12.00 c | 4.25 d | 15.00 d | 1.90 b | 2.60 b | 1.10 b | ||||
| H7 | 24.10 b | 11.88 c | 21.00 c | 0.64 b | 0.29 e | 0.59 d | 16.50 a | 3.44 d | 17.20 c | 1.60 b | 3.40 a | 1.70 a | ||||
| Bg 403 | 24.90 b | 21.28 a | 27.20 b | 0.59 b | 0.55 b | 0.55 d | 16.20 a | 11.70 a | 17.10 c | 1.70 b | 1.80 c | 1.80 a | ||||
| Bg 358 | 13.00 d | 16.08 b | 15.10 c | 0.69 b | 0.45 c | 0.79 c | 18.60 a | 7.23 b | 12.00 e | 1.40 c | 2.20 b | 1.30 b | ||||
| Bg 379-2 | 26.50 b | 18.75 b | 28.20 b | 0.68 b | 0.52 b | 0.61 d | 13.70 b | 9.75 b | 17.90 c | 1.50 c | 1.90 c | 1.60 a | ||||
| Bg 352 | 22.80 b | 15.40 b | 25.00 b | 0.55 c | 0.48 c | 0.91 b | 14.70 b | 7.39 b | 12.50 e | 1.80 b | 2.10 b | 1.10 b | ||||
| Bg 357 | 10.40 d | 23.60 a | 12.50 d | 0.47 d | 0.29 e | 0.82 c | 7.80 e | 6.84 c | 19.30 b | 2.10 a | 3.40 a | 1.20 b | ||||
| At 354 | 19.50 c | 23.00 a | 21.20 c | 0.52 c | 0.48 c | 0.85 c | 10.60 d | 11.04 a | 10.20 e | 1.90 b | 2.10 b | 1.20 b | ||||
| Maha | H4 | 32.00 a | 18.56 b | 25.93 a | 0.50 c | 0.65 c | 0.52 d | 16.00 b | 16.10 c | 13.48 c | 2.00 b | 1.50 c | 1.90 b | |||
| Marss | 24.93 b | 38.12 a | 26.87 a | 0.77 b | 0.61 c | 0.50 d | 19.20 a | 31.00 a | 13.44 c | 2.00 b | 1.60 c | 1.20 c | ||||
| Suduheenati | 23.61 b | 20.34 b | 28.27 a | 0.49 c | 0.81 a | 0.85 b | 11.57 c | 22.00 b | 24.03 a | 2.00 b | 1.20 d | 1.20 c | ||||
| H10 | 24.01 b | 14.59 c | 16.66 c | 0.56 c | 0.59 c | 0.70 c | 13.45 c | 11.50 d | 11.66 d | 1.80 c | 1.70 c | 1.40 c | ||||
| Rathel | 23.32 b | - | 25.32 a | 0.70 b | - | 0.46 d | 16.32 b | - | 11.65 d | 2.10 b | - | 1.00 d | ||||
| Kaluheenati | 22.05 b | - | 25.11 a | 0.59 c | - | 0.83 b | 13.01 c | - | 20.84 a | 1.40 d | - | 1.30 c | ||||
| Murungakayan | 21.03 b | 25.23 b | 28.07 a | 0.50 c | 0.51 d | 0.60 c | 10.52 c | 17.10 c | 16.84 b | 2.00 b | 2.00 b | 1.70 b | ||||
| Kokuwellai | 20.05 b | - | 21.59 b | 0.51 c | - | 0.75 c | 10.23 c | - | 16.19 b | 1.70 c | - | 1.10 d | ||||
| H7 | 18.44 b | 17.41 b | 18.25 b | 0.72 b | 0.85 a | 0.76 c | 13.28 c | 19.70 b | 13.87 c | 1.40 d | 1.20 d | 1.30 c | ||||
| Sudubalawee | 18.43 b | 14.43 c | 21.87 b | 0.59 c | 0.43 d | 0.90 b | 10.87 c | 8.30 f | 19.68 a | 0.80 d | 2.30 a | 0.80 e | ||||
| Bg 94-1 | 17.40 c | 15.51 c | 20.62 b | 0.79 b | 0.51 c | 0.65 c | 13.75 c | 10.40 e | 13.40 c | 2.00 b | 2.00 b | 1.30 c | ||||
| Bg 403 | 17.49 c | 19.13 b | 27.08 a | 0.52 c | 0.50 c | 0.83 b | 9.09 d | 12.80 d | 22.48 a | 1.90 c | 2.00 b | 1.20 c | ||||
| At 362 | 17.09 c | 20.31 b | 28.06 a | 0.70 b | 0.40 d | 0.54 d | 11.96 c | 10.80 e | 15.15 b | 1.00 d | 2.50 a | 1.00 d | ||||
| Pokkali | 15.80 d | - | 19.62 b | 0.70 b | - | 0.76 c | 11.06 c | - | 14.91 b | 2.40 a | - | 1.10 d | ||||
| Bg 358 | 15.20 d | 16.19 c | 22.53 b | 0.72 b | 0.48 d | 0.53 d | 10.94 c | 10.40 e | 11.94 d | 1.40 d | 2.10 b | 1.90 b | ||||
| Bg 450 | 13.87 d | 20.93 b | 24.37 a | 0.64 b | 0.81 a | 0.75 c | 8.88 d | 12.60 d | 18.28 b | 1.30 d | 1.20 d | 2.00 a | ||||
| Sudurusamba | 14.51 d | - | 20.28 b | 0.41 c | - | 0.88 b | 5.95 e | - | 17.85 b | 1.30 d | - | 1.00 d | ||||
| Bg 379-2 | 14.72 d | 23.79 b | 20.65 b | 0.70 b | 0.68 c | 0.82 b | 10.30 c | 21.60 b | 16.93 b | 1.40 d | 1.50 c | 1.20 c | ||||
| Hondarawala | 13.22 d | 15.57 c | 24.20 a | 0.52 c | 0.49 d | 0.56 d | 6.87 e | 10.20 e | 13.55 c | 1.70 c | 2.00 b | 1.20 c | ||||
| Bg 352 | 12.38 d | 16.28 c | 16.13 c | 0.48 c | 0.79 a | 0.94 b | 5.94 e | 17.10 c | 15.16 b | 2.10 b | 1.30 d | 1.10 d | ||||
| Bg 250 | 13.18 d | - | 14.62 c | 0.76 b | - | 1.03 b | 10.02 c | - | 15.06 b | 1.30 d | - | 1.50 c | ||||
| Bw 364 | 13.14 d | - | 21.38 b | 0.52 c | - | 0.93 b | 6.83 e | - | 19.88 a | 1.60 c | - | 1.30 c | ||||
| At 353 | 11.43 d | 15.19 c | 15.17 c | 0.49 c | 0.76 b | 0.63 c | 5.60 e | 15.40 c | 9.56 e | 1.40 d | 1.30 d | 1.90 b | ||||
| Suwandel | 10.63 d | - | 15.71 c | 0.48 c | - | 0.98 b | 5.10 e | - | 15.40 b | 1.80 c | - | 1.00 d | ||||
| Ld 356 | 11.34 d | - | 22.70 b | 0.56 c | - | 0.98 b | 6.35 e | - | 22.25 a | 1.40 d | - | 2.20 a | ||||
| Rathuheenati | 11.29 d | - | 17.45 c | 0.51 c | - | 0.86 b | 5.76 e | - | 15.01 b | 1.90 c | - | 1.10 d | ||||
| Bg 357 | 7.70 e | 14.51 c | 17.60 c | 1.09 a | 0.83 a | 0.95 b | 8.39 d | 15.40 c | 16.72 b | 0.90 d | 1.20 d | 1.10 d | ||||
| At 306 | 8.72 e | 11.61 d | 12.07 d | 1.25 a | 0.74 b | 1.26 a | 10.90 c | 16.00 c | 15.21 b | 2.00 b | 1.40 c | 1.60 c | ||||
| At 354 | 11.19 d | 14.76 c | 18.83 b | 0.81 b | 0.75 b | 0.98 b | 9.06 d | 11.50 d | 18.45 b | 1.20 d | 1.30 d | 1.00 d | ||||
| Bg 300 | 11.63 d | 13.50 c | 14.20 c | 1.01 a | 0.64 c | 0.98 b | 11.75 c | 14.80 c | 13.92 c | 1.90 c | 1.60 c | 1.80 b | ||||
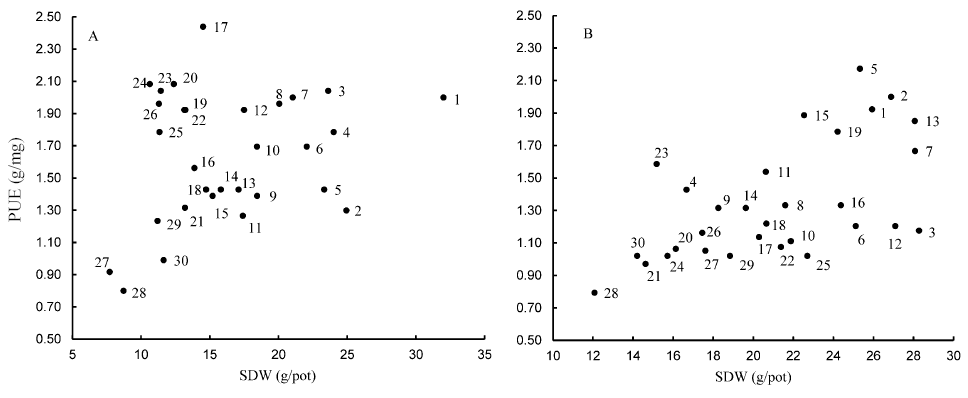
Fig. 1. Classification of 30 rice genotypes for shoot dry weight (SDW) and phosphorus utilization efficiency (PUE) under P0 (A) and P30 (B) soil conditions in Maha season, 2012.SDW, Shoot dry weight; PUE, Phosphorus utilization efficiency; 1, H4; 2, Marss; 3, Suduheenati; 4, H10; 5, Rathel; 6, Kaluheenati; 7, Murungakayan; 8, Kokuwellai; 9, H7; 10, Sudubalawee; 11, Bg 94-1; 12, Bg 403; 13, At 362; 14, Pokkali; 15, Bg 358; 16, Bg 450; 17, Sudurusamba; 18, Bg 379-2; 19, Hondarawala; 20, Bg 352; 21, Bg 250; 22, Bw 364; 23, At 353; 24, Suwandel; 25, Ld 356; 26, Rathuheenati; 27, Bg 357; 28, At 306; 29, At 354; 30, Bg 300.
| Type | Variety |
|---|---|
| Tolerant | H4 a, Marss, Suduheenati, H10, Rathel, Kaluheenati, Murungakayan, Kokuwellai, H7, Sudubalawee, Bg 94-1, Bg 403, At 362 |
| Moderately tolerant | Pokkali, Bg 358, Bg 450, Sudurusamba, Bg 379-2, Hondarawala, Bg 352, Bg 250, Bw 364, At 353, Suwandel, Ld 356, Rathuheenati |
| Sensitive | Bg 357 b, At 306, At 354, Bg 300 |
Table 5 Proposed scoring scheme for phosphorus deficiency tolerance (PDT) screening of rice genotypes.
| Type | Variety |
|---|---|
| Tolerant | H4 a, Marss, Suduheenati, H10, Rathel, Kaluheenati, Murungakayan, Kokuwellai, H7, Sudubalawee, Bg 94-1, Bg 403, At 362 |
| Moderately tolerant | Pokkali, Bg 358, Bg 450, Sudurusamba, Bg 379-2, Hondarawala, Bg 352, Bg 250, Bw 364, At 353, Suwandel, Ld 356, Rathuheenati |
| Sensitive | Bg 357 b, At 306, At 354, Bg 300 |
| 1 | Bennett E M, Carpenter S R, Caraco N F.2001. Human impact on erodable phosphorus and eutrophication: A global perspective.Biol Sci, 51(3): 227-234. |
| 2 | Cancellier E L, Brandão D R, Silva J, Santos M M, Fidelis R R.2012. Phosphorus use efficiency of upland rice cultivars on Cerrado soil.Ambience, 8(2): 307-318. |
| 3 | Chaubey C N, Senadhira D, Gregorio G B.1994. Genetic analysis of tolerance for phosphorous deficiency in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Theor Appl Genet, 89(2): 313-317. |
| 4 | Chin J H, Lu X C, Haefele H M, Gamuyao R, Ismail A, Heuer S, Wissuwa M.2010. Development and application of gene-based markers for the major rice QTL Phosphorus uptake 1.Theor Appl Genet, 120: 1073-1086. |
| 5 | Chin J H, Gamuyao R, Dalid C, Bustamam M, Prasetiyono J, Moeljopawiro S, Wissuwa M, Heuer S.2011. Developing rice with high yield under phosphorus deficiency: Pup1 sequence to application.Plant Physiol, 156: 1202-1216. |
| 6 | Cordell D, Drangert J O, White S.2009. The story of phosphorus global food security and food for thought.Glob Environ Change, 19(2): 292-305. |
| 7 | Department of Agriculture, Sri Lanka. 2006a. Recommended varieties released list (. |
| 8 | Department of Agriculture, Sri Lanka. 2006b. Climate of rice growing regions in Sri Lanka (. |
| 9 | Dobermann A, Fairhurst T.2000. Rice: Nutrient Disorders and Nutrient Management. Manila, Philippines: Oxford Graphic Printers: 60-70. |
| 10 | Economic and Social Statistics of Sri Lanka.2013. Central Bank Report. 25: 30-37. |
| 11 | Fageria N K, Wright R J, Baligar V C.1988a. Rice cultivar evaluation for phosphorus use efficiency.Plant Soil Sci, 111: 105-109. |
| 12 | Fageria N K, Morais O P, Baligar V C, Wright R J.1988b. Response of rice cultivars to phosphorus supply on an oxisol.Fert Res, 16: 195-206. |
| 13 | Fageria N K, Baligar V C.1997. Upland rice genotypes evaluation for phosphorus use efficiency.J Plant Nutr, 20: 499-509. |
| 14 | Fageria N K, Santos A B.2002. Lowland rice genotypes evaluation for phosphorus use efficiency.J Plant Nutr, 25(12): 2793-2802. |
| 15 | Fageria N K, Salton N A, Baligar V C.2003. Nutrient management for improving lowland rice productivity and sustainability.Adv Agron, 80: 63-152. |
| 16 | Fageria N K, Santos A B, Barbosa Filho M P, Guimarães C M.2008. Iron toxicity in lowland rice.J Plant Nutr, 31: 1676-1697. |
| 17 | Fageria N K, Knupp A M.2013. Upland rice phenology and nutrient uptake in tropical climate.J Plant Nutr, 36: 1-14. |
| 18 | Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). 2014. Cereal Supply and Demand Brief World Cereal Production in 2014 to Surpass the Record in 2013, Rome. 20. |
| 19 | George T, Magbanua R, Roder W, Keer K V, Trebuil G, Reoma V.2001. Upland rice response to phosphorus fertilization in Asia.Agron J, 93: 1362-1370. |
| 20 | Grattan S R, Zeng L, Shannon M C, Roberts S R.2002. Rice is more sensitive to salinity than previously thought.Calif Agric, 56(6): 189-195. |
| 21 | Gunes A, Inal A, Alpaslan M, Cakmak I.2006. Genotypic variation in phosphorus efficiency between wheat cultivars grown under greenhouse and field conditions.Soil Sci Plant Nutr, 52: 470-478. |
| 22 | Hanson W C.1950. The photometric determination of phosphorus in fertilizers using the phosphovanado-molybdate complex.J Sci Food Agric, 1(6): 172-173. |
| 23 | Hedley M J, Kirk G J R, Santos M B.1994. Phosphorus deficiency and the forms of soil phosphorus utilized by upland rice cultivars.Plant Soil, 158: 53-62. |
| 24 | Herath H M G, Hardaker J B, Anderson J R.1982. Choice of varieties by Sri Lanka rice farmers: Comparing alternative decision models.Am J Agric Econ, 64: 87-93. |
| 25 | Huang N, Courtois B, Khush G S, Lin H X, Wang G L, Wu P, Zheng K L.1996. Association of quantitative trait loci for plant height with major dwarfing genes in rice.Heredity, 77: 130-137. |
| 26 | Kennedy G, Burlingame B, Nguyen V N.2002. Nutritional contribution of rice and impact of biotechnology and biodiversity in rice-consuming countries. Proceeding of the 20th session of the international rice commission. Bangkok, Thailand: Food and Agriculture Organization. |
| 27 | Kirk G J D, George T, Courtois B, Senadhira D.1998. Opportunities to improve phosphorus efficiency and soil fertility in rain fed lowland and upland rice ecosystems.Field Crops Res, 56: 73-92. |
| 28 | Kumaragamage D, Indraratne S P.2011. Systemic approach to diagnosing fertility problems in soils of Sri Lanka.Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal, 42(22): 2699-2715. |
| 29 | Lafitte H, Ismail A, Bennett J.2004. Abiotic stress tolerance in rice for Asia: Progress and the future. In: New Directions for a Diverse Planet Proceedings of the 4th International Crop Science Congress: 26 September to 1 October, 2004. Citeseer. |
| 30 | Leff B, Ramankutty N, Foley J A.2004. Geographic distribution of major crops across the world.Global Biogeochem Cycles, 18(1): 1-27. |
| 31 | MacDonald G K, Bennett E M, Potter P A, Ramankutty N.2011. Agronomic phosphorus imbalances across the world’s croplands.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 108(7): 3086-3091. |
| 32 | Maclean J L, Dawe D C, Hardy B, Hettel G P.2002. Rice Almanac: Source Book for the Most Important Economic Activity on Earth. Wallingford, UK: CABI Publishing. |
| 33 | Marschner H.2012. Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. New York, USA: Academic Press: 158-165. |
| 34 | Ni J J, Wu P, Lou A C, Tao Q N.1998. Rice seedling tolerance to phosphorus stress in solution culture and soil.Nutr Cycl Agroecosys, 51(2): 95-99. |
| 35 | Pandey S, Bhandari H S, Hardy B.2007. Economic Costs of Drought and Rice Farmers’ Coping Mechanisms: A Cross-Country Comparative Analysis. Los Baños, Philippines: International Rice Research Institute: 203. |
| 36 | Pathak M D, Khan R Z.1994. Insect Pests of Rice. Los Baños, Philippines: International Centre of Insect Physiology and Ecology, International Rice Research Institute: 89. |
| 37 | Raghothama K G.1999. Phosphate acquisition.Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol, 50: 665-693. |
| 38 | Rose T J, Rose M T, Pariasca-Tanaka J, Heuer S, Wissuwa M.2011. The frustration with utilization: Why have improvements in internal phosphorus utilization efficiency in crops remained so elusive?Front Plant Sci, 73(2): 1-5. |
| 39 | Rose T J, Wissuwa M.2012. Rethinking internal phosphorus utilization efficiency: A new approach is needed to improve PUE in grain crops.Adv Agron, 116: 186-211. |
| 40 | Septiningsih E M, Hidayatun N, Sanchez D L, Nugraha Y, Carandang J, Pamplona A M, Collard B C Y, Ismail A M, Mackill D J.2015. Accelerating the development of new submergence tolerant rice varieties: The case of Ciherang-Sub1 and PSB Rc18-Sub1.Euphytica, 202: 259-268. |
| 41 | Sirisena D N, Wanninayake W M N.2014. Identification of promising rice varieties for low fertile soils in the low country intermediate zone in Sri Lanka.Ann Sri Lanka Dep Agric, 14: 95-105. |
| 42 | Wissuwa M, Yano M, Ae N.1998. Mapping of QTLs for phosphorus deficiency tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Theor Appl Genet, 97: 777-783. |
| 43 | Wissuwa M, Ae N.2001. Genotypic variation for tolerance to phosphorus deficiency in rice and the potential for its exploitation in rice improvement.Plant Breeding, 120: 43-48. |
| 44 | Wissuwa M.2005. Combining a modelling with a genetic approach in establishing associations between genetic and physiological effects in relation to phosphorus uptake.Plant Soil, 269: 57-68. |
| 45 | Xing Y Z, Zhang Q F.2010. Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 61: 421-442. |
| 46 | Xu S, Muir W M.1992. Selection index updating.Theor Appl Genet, 83: 451-458. |
| 47 | Yan J Q, Zhu J, He C X, Benmoussa M, Wu P.1998. Molecular dissection of developmental behavior of plant height in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Genetics, 150: 1257-1265. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||