
Rice Science ›› 2016, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (6): 287-296.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2016.09.002
• • 下一篇
收稿日期:2016-07-25
接受日期:2016-09-22
出版日期:2016-12-12
发布日期:2016-08-10
. [J]. Rice Science, 2016, 23(6): 287-296.
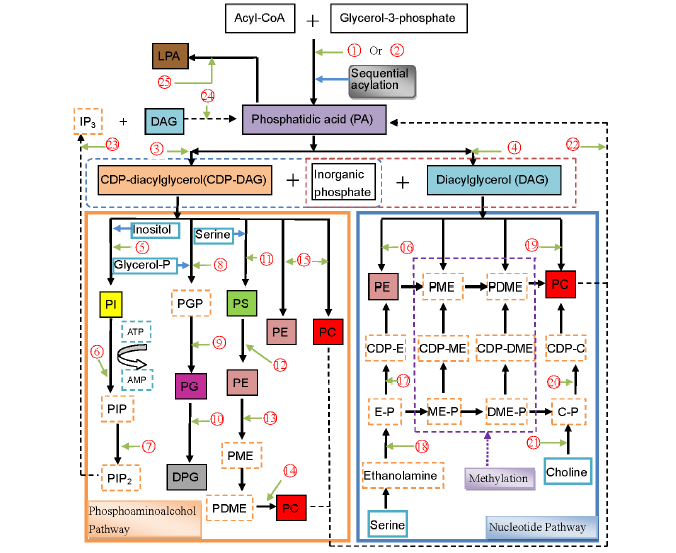
Fig. 1. Conceivable biosynthetic pathways of phospholipids in cereals. Drawn based on Kinney (1993), D’Arrigo and Servi (2010) and Liu et al (2013). E, Ethanolamine; ME, Methylethanolamine; DME, Dimethylethanolamine; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate; LPA, Lysophosphatidic acid; C, Choline; P, Phosphate; CDP, Cytidinediphosphate; PE, Phosphatidylethanolamine; PME, Phosphatidylmethylethanolamine; PDME, Phosphatidyldimethyle- thanolamine; PC, Phosphatidylcholine; PS, Phosphatidylserine; PI, Phosphatidylinositol; PIP, Phosphatidylinositol phosphate; PIP2, Phosphati- dylinositolbisphosphate; PGP, Phosphoglycerol phosphate; PG, Phosphatidylglycerol; DPG, Diphosphatidylglycerol; , Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase; , 1-monoacylglycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase; , CDP-diacylglycerol synthase (CTP: phosphatidatecytidylyltransferase); , Phosphatidatephosphohydrolase; , PI synthase (CDP-diacylglycerol: myo-inositol phosphatidyltransferase); , PI 4-kinase (ATP: phosphati- dylinositol-4-phosphotransferase); , PIP kinase (ATP: phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-phosphotransferase); , PGP synthase (CDP-diacylgly- cerolphosphatidyltransferase); , PGP phosphatase (phosphatidylglycerol-phosphate phosphohydrolase); , CDP diacylglycerolphosphatidly- transerase; , PS synthase (CDP-diacylglycerol: L-serine O-phosphatidyltransferase); , PS decarboxylase; , PE N-methyltransferase; , Phospholipid N-methyltransferase; , Aminoalcoholphosphotransferase; , Ethanolaminephosphotransferase (CDP-ethanolamine: 1,2-diacylglycerol cytidylyltransferase); , Ethanolamine phosphate cytidylyltransferase (CTP: ethanolamine phosphate cytidylyltransferase); , Ethanolamine kinase (ATP: ethanolamine phosphotransferase); , Cholinephosphotransferase (CDP-choline: 1,2-diacylglycerol cytidylyltransferase); , Choline phosphate cytidylyltransferase (CTP: choline phosphate cytidylyltransferase); , Choline kinase (ATP: choline phosphotransferase); , Phospholipase D (PLD) (Phosphatidylcholinephosphatidohydrolase); , Phospholipase C (PLC); , Diacylglycerol (DAG) kinase; , Phospholipase A2 (PLA2).
| Trait | Year | Model | QTL | Chr | Position a (bp) | P-value | Major allele | Minor allele | Minor allele frequency | Allelic effect (R2) | |
| LPC16:0 | 2011 | K | qC160-6-1 | 6 | 26 685 967 | 4.72 × 10-3 | C | T | 0.30 | 0.8011 | |
| 2012 | K | qC160-6-2 | 6 | 3 235 560 | 4.41 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.5573 | ||
| qC160-8 | 8 | 8 481 084 | 3.64 × 10-3 | A | G | 0.40 | 0.5872 | ||||
| LPC18:1 | 2012 | Q+K | qC181-2 | 2 | 14 522 544 | 3.15 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.20 | 0.8346 | |
| qC181-1 | 1 | 27 729 601 | 4.20 × 10-3 | C | T | 0.30 | 0.8107 | ||||
| LPC18:2 | 2011 | K | qC182-9 | 9 | 15 125 638 | 4.37 × 10-3 | C | T | 0.20 | 0.5585 | |
| 2012 | K | qC182-11 | 11 | 17 847 796 | 4.07 × 10-3 | A | T | 0.30 | 0.5698 | ||
| LPC18:3 | 2011 | K | qC183-1 | 1 | 23 517 183 | 3.27 × 10-3 | A | C | 0.25 | 0.6047 | |
| 2012 | K | qC183-1 | 1 | 23 517 183 | 4.89 × 10-3 | A | C | 0.25 | 0.5411 | ||
| TLPC | 2011 | ANOVA | qC-5 | 5 | 23 465 186 | 4.20 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.5647 | |
| qC-9 | 9 | 15 125 638 | 2.62 × 10-3 | C | T | 0.20 | 0.6409 | ||||
| qC-12 | 12 | 21 175 392 | 3.73 × 10-3 | T | A | 0.25 | 0.5835 | ||||
| 2012 | K | qC-10 | 10 | 5 339 258 | 4.36 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.5589 | ||
| LPE16:0 | 2011 | ANOVA | qE160-1 | 1 | 6 971 525 | 3.33 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.6016 | |
| LPE18:1 | 2011 | Q+K | qE181-2 | 2 | 14 522 544 | 3.26 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.20 | 0.7802 | |
| 2012 | Q+K | qE181-2 | 2 | 14 522 544 | 2.17 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.20 | 0.8364 | ||
| LPE18:2 | 2011 | K | qE182-1 | 1 | 23 585 360 | 3.23 × 10-3 | C | T | 0.25 | 0.6064 | |
| qE182-4 | 4 | 31 271 474 | 4.23 × 10-3 | T | C | 0.20 | 0.5637 | ||||
| qE182-11 | 11 | 17 943 118 | 3.82 × 10-3 | T | A | 0.35 | 0.5798 | ||||
| LPE18:3 | 2011 | K | qE183-1 | 1 | 23 517 183 | 4.27 × 10-3 | A | C | 0.25 | 0.5623 | |
| 2012 | K | qE183-1 | 1 | 23 517 183 | 4.33 × 10-3 | A | C | 0.25 | 0.5600 | ||
| TLPE | 2011 | ANOVA | qE-10 | 10 | 5 339 258 | 4.69 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.5477 | |
| TLPL | 2011 | ANOVA | qL-9 | 9 | 15 125 638 | 2.92 × 10-3 | C | T | 0.20 | 0.6229 | |
| qL-10 | 10 | 5 339 258 | 4.67 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.5482 | ||||
| qL-12 | 12 | 21 175 392 | 4.93 × 10-3 | T | A | 0.25 | 0.5399 | ||||
| 2012 | K | qL-10 | 10 | 5 339 258 | 4.19 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.5649 | ||
| LPC14:0, 1-myristoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; LPC16:0, 1-palmitoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; LPC18:1, 1-oleoyl- 2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; LPC18:2, 1-linoleoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; LPC18:3, 1-linolenoyl-2-hydroxy-sn- glycero-3-phosphocholine; LPE14:0, 1-myristoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; LPE16:0, 1-palmitoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3- phosphoethanolamine; LPE18:1, 1-oleoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; LPE18:2, 1-linoleoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; LPE18:3, 1-linolenoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; TLPC, Total lysophosphatidylcholine; TLPE, Total lysophosphatidylethanolamine; TLPL, Total lysophospholipid; Q, Population structure; K, Kinship; ANOVA, Analysis of variance; Chr, Chromosome. a, Position in base pairs for the leading SNP of rice sequence. | |||||||||||
Table 1 Genome-wide significantly associated QTLs for rice lysophospholipids (LPLs)
| Trait | Year | Model | QTL | Chr | Position a (bp) | P-value | Major allele | Minor allele | Minor allele frequency | Allelic effect (R2) | |
| LPC16:0 | 2011 | K | qC160-6-1 | 6 | 26 685 967 | 4.72 × 10-3 | C | T | 0.30 | 0.8011 | |
| 2012 | K | qC160-6-2 | 6 | 3 235 560 | 4.41 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.5573 | ||
| qC160-8 | 8 | 8 481 084 | 3.64 × 10-3 | A | G | 0.40 | 0.5872 | ||||
| LPC18:1 | 2012 | Q+K | qC181-2 | 2 | 14 522 544 | 3.15 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.20 | 0.8346 | |
| qC181-1 | 1 | 27 729 601 | 4.20 × 10-3 | C | T | 0.30 | 0.8107 | ||||
| LPC18:2 | 2011 | K | qC182-9 | 9 | 15 125 638 | 4.37 × 10-3 | C | T | 0.20 | 0.5585 | |
| 2012 | K | qC182-11 | 11 | 17 847 796 | 4.07 × 10-3 | A | T | 0.30 | 0.5698 | ||
| LPC18:3 | 2011 | K | qC183-1 | 1 | 23 517 183 | 3.27 × 10-3 | A | C | 0.25 | 0.6047 | |
| 2012 | K | qC183-1 | 1 | 23 517 183 | 4.89 × 10-3 | A | C | 0.25 | 0.5411 | ||
| TLPC | 2011 | ANOVA | qC-5 | 5 | 23 465 186 | 4.20 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.5647 | |
| qC-9 | 9 | 15 125 638 | 2.62 × 10-3 | C | T | 0.20 | 0.6409 | ||||
| qC-12 | 12 | 21 175 392 | 3.73 × 10-3 | T | A | 0.25 | 0.5835 | ||||
| 2012 | K | qC-10 | 10 | 5 339 258 | 4.36 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.5589 | ||
| LPE16:0 | 2011 | ANOVA | qE160-1 | 1 | 6 971 525 | 3.33 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.6016 | |
| LPE18:1 | 2011 | Q+K | qE181-2 | 2 | 14 522 544 | 3.26 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.20 | 0.7802 | |
| 2012 | Q+K | qE181-2 | 2 | 14 522 544 | 2.17 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.20 | 0.8364 | ||
| LPE18:2 | 2011 | K | qE182-1 | 1 | 23 585 360 | 3.23 × 10-3 | C | T | 0.25 | 0.6064 | |
| qE182-4 | 4 | 31 271 474 | 4.23 × 10-3 | T | C | 0.20 | 0.5637 | ||||
| qE182-11 | 11 | 17 943 118 | 3.82 × 10-3 | T | A | 0.35 | 0.5798 | ||||
| LPE18:3 | 2011 | K | qE183-1 | 1 | 23 517 183 | 4.27 × 10-3 | A | C | 0.25 | 0.5623 | |
| 2012 | K | qE183-1 | 1 | 23 517 183 | 4.33 × 10-3 | A | C | 0.25 | 0.5600 | ||
| TLPE | 2011 | ANOVA | qE-10 | 10 | 5 339 258 | 4.69 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.5477 | |
| TLPL | 2011 | ANOVA | qL-9 | 9 | 15 125 638 | 2.92 × 10-3 | C | T | 0.20 | 0.6229 | |
| qL-10 | 10 | 5 339 258 | 4.67 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.5482 | ||||
| qL-12 | 12 | 21 175 392 | 4.93 × 10-3 | T | A | 0.25 | 0.5399 | ||||
| 2012 | K | qL-10 | 10 | 5 339 258 | 4.19 × 10-3 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.5649 | ||
| LPC14:0, 1-myristoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; LPC16:0, 1-palmitoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; LPC18:1, 1-oleoyl- 2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; LPC18:2, 1-linoleoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; LPC18:3, 1-linolenoyl-2-hydroxy-sn- glycero-3-phosphocholine; LPE14:0, 1-myristoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; LPE16:0, 1-palmitoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3- phosphoethanolamine; LPE18:1, 1-oleoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; LPE18:2, 1-linoleoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; LPE18:3, 1-linolenoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; TLPC, Total lysophosphatidylcholine; TLPE, Total lysophosphatidylethanolamine; TLPL, Total lysophospholipid; Q, Population structure; K, Kinship; ANOVA, Analysis of variance; Chr, Chromosome. a, Position in base pairs for the leading SNP of rice sequence. | |||||||||||
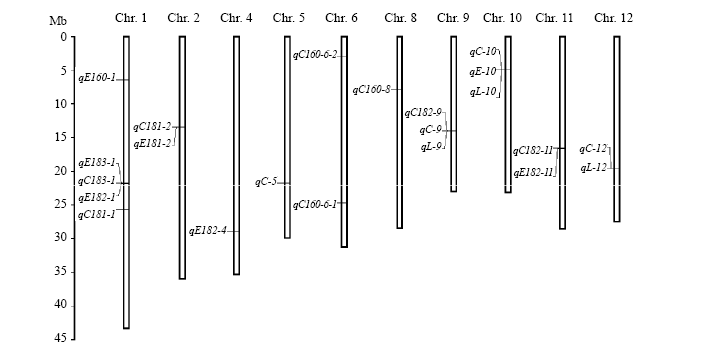
Fig. 2. Location of QTLs for rice starch lysophospholipids (LPLs) on chromosomes (Chr). C160, C181, C182, C183, E160, E181, E182, E183, C, E and L in the QTLs represent LPC16:0, LPC18:1, LPC18:2, LPC18:3, LPE16:0, LPE18:1, LPE18:2, LPE18:3, total lysophosphatidylcholine, total lysophosphatidylethanolamine and total lysophospholipid, respectively.
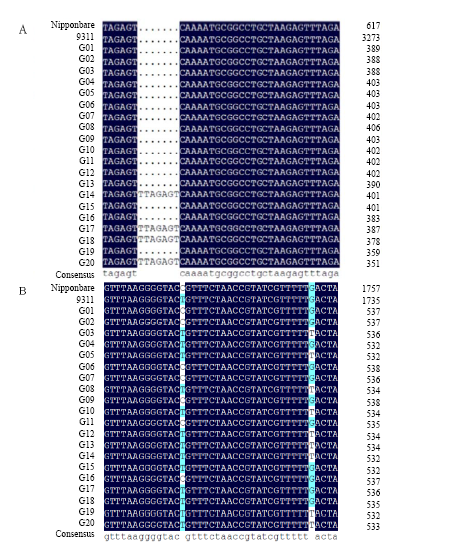
Fig. 4. Part sequence alignments of AAPT and PLA2 genes. A, InDel found in AAPT gene among G01-G20; B, Single nucleotide polymorphism found in PLA2 gene among G01-G20. AAPT, Aminoalcoholphosphotransferase; PLA2, Phospholipase A2.
| Primer | Type | Sequence (5′-3′) | PCR product (bp) | Restriction enzyme | Enzyme digestion product (bp) |
| AAPT1-F | InDel | CCAGCCTTGTTTCAATACCTG | 134/127 | - | - |
| AAPT1-R | AAATGTAGGAAGTTTTTACTTGC | ||||
| AAPT2-F | dCAPS | AAGAGCAAGTAAAAACTTCCTAAATT | 222 | ApoI | 22, 200 |
| AAPT2-R | GATACAAATGCCCAAATACCA | ||||
| AAPT3-F | dCAPS | CAAAGATCAATGCTGGGTAATTTC | 184 | SphI | 22, 162 |
| AAPT3-R | AGGTAAATCAGTTCACCTGTGCA | ||||
| PLD1-F | dCAPS | CATCCTGCACTAAAAACAGTTGAAT | 214 | HinfI | 22, 192 |
| PLD1-R | TGCACAACACCAGAGCCCCACC | ||||
| PLD2-F | dCAPS | CCTCCCAAAGTTTAGGCGGAAAAGGCC | 187 | HpaII | 27, 160 |
| PLD2-R | TCAAAGCTCACAATAGCAGAATA | ||||
| PLA21-F | dCAPS | TTCCTATTGTTTCTTCCTCCCTCTT | 230 | HinfI | 20, 210 |
| PLA21-R | GAAAAAACAAAATTAAAAAAGAGT | ||||
| dCAPS, Development of derived cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences. Underlined letter means the mismatch base. | |||||
Table 2 Primers for enzyme digestion of several single nucleotide polymorphisms
| Primer | Type | Sequence (5′-3′) | PCR product (bp) | Restriction enzyme | Enzyme digestion product (bp) |
| AAPT1-F | InDel | CCAGCCTTGTTTCAATACCTG | 134/127 | - | - |
| AAPT1-R | AAATGTAGGAAGTTTTTACTTGC | ||||
| AAPT2-F | dCAPS | AAGAGCAAGTAAAAACTTCCTAAATT | 222 | ApoI | 22, 200 |
| AAPT2-R | GATACAAATGCCCAAATACCA | ||||
| AAPT3-F | dCAPS | CAAAGATCAATGCTGGGTAATTTC | 184 | SphI | 22, 162 |
| AAPT3-R | AGGTAAATCAGTTCACCTGTGCA | ||||
| PLD1-F | dCAPS | CATCCTGCACTAAAAACAGTTGAAT | 214 | HinfI | 22, 192 |
| PLD1-R | TGCACAACACCAGAGCCCCACC | ||||
| PLD2-F | dCAPS | CCTCCCAAAGTTTAGGCGGAAAAGGCC | 187 | HpaII | 27, 160 |
| PLD2-R | TCAAAGCTCACAATAGCAGAATA | ||||
| PLA21-F | dCAPS | TTCCTATTGTTTCTTCCTCCCTCTT | 230 | HinfI | 20, 210 |
| PLA21-R | GAAAAAACAAAATTAAAAAAGAGT | ||||
| dCAPS, Development of derived cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences. Underlined letter means the mismatch base. | |||||
| Accession | AAPT1 | AAPT2 | AAPT3 | PLD1 | PLD2 | PLA21 | Accession | AAPT1 | AAPT2 | AAPT3 | PLD1 | PLD2 | PLA21 |
| G01 | D | T | A | C | G | G | G18 | I | A | G | C | C | G |
| G02 | D | T | A | C | G | G | G19 | D | T | A | C | G | T |
| G03 | D | T | A | A | C | T | G20 | I | A | G | A | C | T |
| G04 | D | T | A | A | C | G | R01 | D | T | A | C | C | G |
| G05 | D | T | A | C | C | T | R02 | D | T | A | C | C | G |
| G06 | D | T | A | C | G | G | R03 | D | T | A | C | G | T |
| G07 | D | T | A | C | G | G | R04 | D | T | A | C | C | G |
| G08 | D | T | A | C | C | T | R05 | D | T | A | C | C | T |
| G09 | D | T | A | C | G | G | R06 | D | T | A | C | C | G |
| G10 | D | T | A | A | C | T | R07 | D | T | A | C | G | G |
| G11 | D | T | A | C | G | G | R08 | I | A | G | C | C | G |
| G12 | D | T | A | C | C | T | R09 | D | T | A | C | C | T |
| G13 | D | T | A | C | C | T | R10 | I | A | G | C | C | T |
| G14 | I | A | G | C | C | T | R11 | D | T | A | C | C | T |
| G15 | D | T | A | C | C | G | R12 | D | T | A | C | C | T |
| G16 | D | T | A | C | G | G | R13 | I | A | G | C | C | T |
| G17 | I | A | G | C | C | G | |||||||
| AAPT, Aminoalcoholphosphotransferase; PLD, Phospholipase D; PLA2, Phospholipase A2; I, Insertion; D, Deletion. | |||||||||||||
Table 3 Summary of alleles of three candidate genes.
| Accession | AAPT1 | AAPT2 | AAPT3 | PLD1 | PLD2 | PLA21 | Accession | AAPT1 | AAPT2 | AAPT3 | PLD1 | PLD2 | PLA21 |
| G01 | D | T | A | C | G | G | G18 | I | A | G | C | C | G |
| G02 | D | T | A | C | G | G | G19 | D | T | A | C | G | T |
| G03 | D | T | A | A | C | T | G20 | I | A | G | A | C | T |
| G04 | D | T | A | A | C | G | R01 | D | T | A | C | C | G |
| G05 | D | T | A | C | C | T | R02 | D | T | A | C | C | G |
| G06 | D | T | A | C | G | G | R03 | D | T | A | C | G | T |
| G07 | D | T | A | C | G | G | R04 | D | T | A | C | C | G |
| G08 | D | T | A | C | C | T | R05 | D | T | A | C | C | T |
| G09 | D | T | A | C | G | G | R06 | D | T | A | C | C | G |
| G10 | D | T | A | A | C | T | R07 | D | T | A | C | G | G |
| G11 | D | T | A | C | G | G | R08 | I | A | G | C | C | G |
| G12 | D | T | A | C | C | T | R09 | D | T | A | C | C | T |
| G13 | D | T | A | C | C | T | R10 | I | A | G | C | C | T |
| G14 | I | A | G | C | C | T | R11 | D | T | A | C | C | T |
| G15 | D | T | A | C | C | G | R12 | D | T | A | C | C | T |
| G16 | D | T | A | C | G | G | R13 | I | A | G | C | C | T |
| G17 | I | A | G | C | C | G | |||||||
| AAPT, Aminoalcoholphosphotransferase; PLD, Phospholipase D; PLA2, Phospholipase A2; I, Insertion; D, Deletion. | |||||||||||||
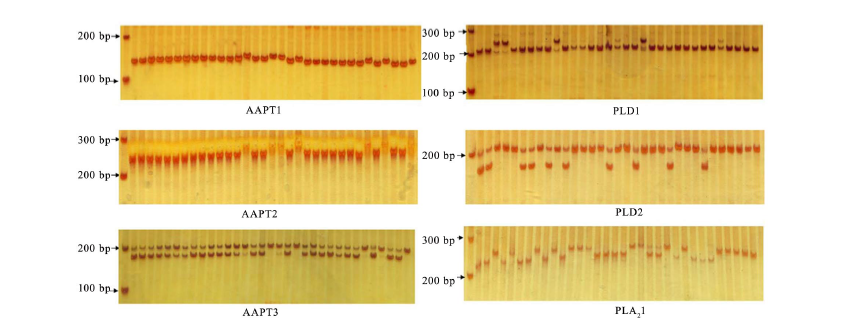
Fig. 5. Polymorphism of InDel and simple nucleotide polymorphisms in AAPT, PLD and PLA2 genes in rice accessions G01-G20 and R01-R13. AAPT, Aminoalcoholphosphotransferase; PLD, Phospholipase D; PLA2, Phospholipase A2. Lanes from left to right in each part are marker, G01-G20 and R01-R13, respectively.
| Gene | Marker | Trait | Non-waxy accession (31) | All rice accession (33) | QTL | |||
| p_Marker | R2_Marker | p_Marker | R2_Marker | |||||
| PLD | PLD1 | LPC16:0 | 0.0149 | 0.1876 | 0.0984 | 0.0856 | qC160-6-1 | |
| PLA2 | PLA21 | LPC18:2 | 0.0902 | 0.0958 | 0.0277 | 0.1468 | qC182-11, qE182-11 | |
| PLD, Phospholipase D; PLA2, Phospholipase A2. | ||||||||
Table 4 Marker loci associated with starch lysophospholipids (LPLs) traits detected with analysis of variance (ANOVA) model in 31 non-waxy and all the 33 rice accessions.
| Gene | Marker | Trait | Non-waxy accession (31) | All rice accession (33) | QTL | |||
| p_Marker | R2_Marker | p_Marker | R2_Marker | |||||
| PLD | PLD1 | LPC16:0 | 0.0149 | 0.1876 | 0.0984 | 0.0856 | qC160-6-1 | |
| PLA2 | PLA21 | LPC18:2 | 0.0902 | 0.0958 | 0.0277 | 0.1468 | qC182-11, qE182-11 | |
| PLD, Phospholipase D; PLA2, Phospholipase A2. | ||||||||
| 1 | Ambrosewicz-Walacik M, Tańska M, Rotkiewicz D.2015. Phospholipids of rapeseeds and rapeseed oils: Factors determining their content and technological significance: A review.Food Rev Int, 31(4): 385-400. |
| 2 | Bessoule J J, Moreau P.2004. Phospholipid synthesis and dynamics in plant cells. In: Daum G. Lipid Metabolism and Membrane Biogenesis. Berlin, Germany: Springer: 89-124. |
| 3 | Bohdanowicz M, Grinstein S.2013. Role of phospholipids in endocytosis, phagocytosis, and macropinocytosis.Physiol Rev, 93(1): 69-106. |
| 4 | Choi S K, Takahashi E, Inatsu O, Mano Y, Ohnishi M.2005. Component fatty acids of acidic glycerophospholipids in rice grains: Universal order of unsaturation index in each lipid among varieties.J Oleo Sci, 54(7): 369-373. |
| 5 | D’Arrigo P, Servi S.2010. Synthesis of lysophospholipids.Molecules, 15: 1354-1377. |
| 6 | Doyle J.1991. DNA protocols for plants: CTAB total DNA isolation. In: Hewitt G M, Johnston A. Molecular Techniques in Taxonomy. Berlin, Germany: Springer: 283-293. |
| 7 | Eastmond P J, Quettier A L, Kroon J T M, Craddock C, Adams N, Slabas A R.2010. PHOSPHATIDIC ACID PHOSPHOHYDRO- LASE1 and 2 regulate phospholipid synthesis at the endoplasmic reticulum inArabidopsis. Plant Cell, 22(8): 2796-2811. |
| 8 | Farquharson K L.2010. Regulation of phospholipid biosynthesis inArabidopsis. Plant Cell, 22(8): 2527. |
| 9 | Gaspar M L, Hofbauer H F, Kohlwein S D, Henry S A.2011. Coordination of storage lipid synthesis and membrane biogenesis evidence for cross-talk between triacylglycerol metabolism and phosphatidylinositol synthesis.J Biol Chem, 286(3): 1696-1708. |
| 10 | Hofbauer H F, Schopf F H, Schleifer H, Knittelfelder O L, Pieber B, Rechberger G N, Wolinski H, Gaspar M L, Kappe C O, Stadlmann J, Mechtler K, Zenz A, Lohner K, Tehlivets O, Henry S A, Kohlwein S D.2014. Regulation of gene expression through a transcriptional repressor that senses acyl-chain length in membrane phospholipids.Dev Cell, 29(6): 729-739. |
| 11 | Kinney A J.1993. Phospholipid head groups. In: Moore T S J. Lipid Metabolism in Plants. Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC Press: 259-284. |
| 12 | Kuhn S, Slavetinsky C J, Peschel A.2015. Synthesis and function of phospholipids inStaphylococcus aureus. Int J Med Microbiol, 305(2): 196-202. |
| 13 | Konieczny A, Ausubel F M.1993. A procedure for mappingArabidopsis mutations using co-dominant ecotype-specific PCR- based markers. Plant J, 4(2): 403-410. |
| 14 | Li H, Peng Z Y, Yang X H, Wang W D, Fu J J, Wang J H, Han Y J, Chai Y C, Guo T T, Yang N, Liu J, Warburton M L, Cheng Y B, Hao X M, Zhang P, Zhao J Y, Liu Y J, Wang G Y, Li J S, Yan J B.2013. Genome-wide association study dissects the genetic architecture of oil biosynthesis in maize kernels.Nat Genet, 45(1): 43-50. |
| 15 | Lipka A E, Tian F, Wang Q S, Peiffer J, Li M, Bradbury P J, Gore M A, Buckler E S, Zhang Z W.2012. GAPIT: Genome association and prediction integrated tool.Bioinformatics, 28(18): 2397-2399. |
| 16 | Liu L, Waters D L E, Rose T J, Bao J S, King G J.2013. Phospholipids in rice: Significance in grain quality and health benefits: A review.Food Chem, 139(1/2/3/4): 1133-1145. |
| 17 | Liu L, Tong C, Bao J S, Waters D L E, Rose T J, King G J.2014. Determination of starch lysophospholipids in rice using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS).J Agric Food Chem, 62(28): 6600-6607. |
| 18 | Liu W J, Zeng J, Jiang G H, He Y Q.2009. QTLs identification of crude fat content in brown rice and its genetic basis analysis using DH and two backcross populations.Euphytica, 169(2): 197-205. |
| 19 | Maniñgat C C, Juliano B O.1980. Starch lipids and their effect on rice starch properties.Starch Stärke, 32(3): 76-82. |
| 20 | Martin P K, Li T, Sun D X, Biek D P, Schmid M B.1999. Role in cell permeability of an essential two-component system inStaphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol, 181(12): 3666-3673. |
| 21 | Nakamura A, Ocirc N T, Funahashi S.1958. Nature of lysolecithin in rice grains.Bull Agric Chem Soc Jpn, 22(5): 320-324. |
| 22 | Neff M M, Neff J D, Chory J, Pepper A E.1998. dCAPS, a simple technique for the genetic analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms: Experimental applications inArabidopsis thaliana genetics. Plant J, 14(3): 387-392. |
| 23 | Perry H J, Harwood J L.1993. Radiolabelling studies of acyl lipids in developing seeds ofBrassica napus: Use of [1-14C]acetate precursor. Phytochemistry, 33(2): 329-333. |
| 24 | Putseys J A, Lamberts L, Delcour J A.2010. Amylose-inclusion complexes: Formation, identity and physico-chemical properties.J Cereal Sci, 51(3): 238-247. |
| 25 | Qin Y, Kim S M, Zhao X H, Lee H S, Jia B Y, Kim K M, Eun M Y, Sohn J K.2010. QTL detection and MAS selection efficiency for lipid content in brown rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genes Genom, 32(6): 506-512. |
| 26 | Ren J, Zhao X Q, Ding Z S, Xiang C, Zhang J, Wang C, Zhang J W, Joseph C A, Zhang Q, Pang Y L, Gao Y M, Shi Y Y.2015. Dissection and QTL mapping of low-phosphorus tolerance using selected introgression lines in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 29(1): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 27 | Shen Y Y, Zhang W W, Liu X, Chen L M, Liu S J, Zheng L N, Li J J, Chen Y L, Wu T, Yu Y, Zhong Z Z, Jiang L, Wan J M.2012. Identification of two stably expressed QTLs for fat content in rice (Oryza sativa). Genome, 55(8): 585-590. |
| 28 | Shewry P R, Pinfield N J, Stobart A K.1973. Phospholipids and the phospholipid fatty acids of germinating hazel seeds (Corylus avellana L.). J Exp Bot, 24(6): 1100-1105. |
| 29 | Suzuki Y.2011a. Isolation and characterization of a rice (Oryza sativa L.) mutant deficient in seed phospholipase D, an enzyme involved in the degradation of oil-body membranes. Crop Sci, 51(2): 567-573. |
| 30 | Suzuki Y, Takeuchi Y, Shirasawa K.2011b. Identification of a seed phospholipase D null allele in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and development of SNP markers for phospholipase D deficiency. Crop Sci, 51(5): 2113-2118. |
| 31 | Tong C, Liu L, Waters D L E, Rose T J, Bao J S, King G J.2014. Genotypic variation in lysophospholipids of milled rice.J Agric Food Chem, 62(38): 9353-9361. |
| 32 | Tong C, Liu L, Waters D L E, Huang Y, Bao J S.2015. The contribution of lysophospholipids to pasting and thermal properties of nonwaxy rice starch.Carbohyd Polym, 133: 187-193. |
| 33 | Xu C C, Shanklin J.2016. Triacylglycerol metabolism, function, and accumulation in plant vegetative tissues.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 67: 179-206. |
| 34 | Xu F F, Tang F F, Shao Y F, Chen Y L, Tong C, Bao J S.2014. Genotype × environment interactions for agronomic traits of rice revealed by association mapping.Rice Sci, 21(3): 133-141. |
| 35 | Yang F, Chen Y L, Tong C, Huang Y, Xu F F, Li K H, Corke H, Sun M, Bao J S.2014. Association mapping of starch physicochemical properties with starch synthesis-related gene markers in nonwaxy rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breeding, 34(4): 1747-1763. |
| 36 | Ying J Z, Shan J X, Gao J P, Zhu M Z, Shi M, Lin H X.2012. Identification of quantitative trait loci for lipid metabolism in rice seeds.Mol Plant, 5(4): 865-875. |
| 37 | Yoshida H, Tanigawa T, Yoshida N, Kuriyama I, Tomiyama Y, Mizushina Y.2011. Lipid components, fatty acid distributions of triacylglycerols and phospholipids in rice brans.Food Chem, 129(2): 479-484. |
| 38 | Zhan X D, Yu P, Lin Z C, Chen D B, Shen X H, Zhang Y X, Fu J L, Cheng S H, Cao L Y.2014. QTL mapping of heading date and yield-related traits in rice using a recombination inbred lines (RILs) population derived from BG1/XLJ.Chin J Rice Sci, 28(6): 570-580. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 39 | (Managing Editor: Li Guan) |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||