
Rice Science ›› 2018, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (3): 161-168.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2018.02.005
收稿日期:2017-09-06
接受日期:2018-02-02
出版日期:2018-05-04
发布日期:2018-03-07
. [J]. Rice Science, 2018, 25(3): 161-168.

Fig. 1. Distribution of heading date based on F2 segregating populations of W31-SSSL (A) and W32-SSSL (B).W31-SSSL, W32-SSSL and HJX74 headed at (132.3 ± 1.4) d, (135.5 ± 1.4) d and (104.5 ± 1.7) d, respectively.Bar represents standard deviation.
| Population | Marker | Genotype 1 | Genotype 2 | Genotype 3 | χ20.05 (3:1) |
| W31-SSSL (197 lines) | RM587 | 38 | 107 | 52 | 3.47 |
| RM510 | 40 | 102 | 55 | 1.53 | |
| RM204 | 42 | 100 | 55 | 1.76 | |
| RM225 | 42 | 98 | 57 | 2.29 | |
| PSM677 | 40 | 102 | 55 | 1.53 | |
| PSM678 | 40 | 102 | 55 | 1.53 | |
| W32-SSSL (201 lines) | RM587 | 54 | 89 | 58 | 2.79 |
| PSM672 | 53 | 90 | 58 | 2.44 | |
| RM204 | 53 | 90 | 58 | 2.44 | |
| PSM676 | 52 | 90 | 59 | 2.68 | |
| PSM678 | 54 | 89 | 58 | 2.79 | |
| Genotype 1 is identical to the receipt; Genotype 2 is heterozygous; and Genotype 3 is identical to the donor. | |||||
Table 1 Co-segregating of genotypes for heading date in two populations.
| Population | Marker | Genotype 1 | Genotype 2 | Genotype 3 | χ20.05 (3:1) |
| W31-SSSL (197 lines) | RM587 | 38 | 107 | 52 | 3.47 |
| RM510 | 40 | 102 | 55 | 1.53 | |
| RM204 | 42 | 100 | 55 | 1.76 | |
| RM225 | 42 | 98 | 57 | 2.29 | |
| PSM677 | 40 | 102 | 55 | 1.53 | |
| PSM678 | 40 | 102 | 55 | 1.53 | |
| W32-SSSL (201 lines) | RM587 | 54 | 89 | 58 | 2.79 |
| PSM672 | 53 | 90 | 58 | 2.44 | |
| RM204 | 53 | 90 | 58 | 2.44 | |
| PSM676 | 52 | 90 | 59 | 2.68 | |
| PSM678 | 54 | 89 | 58 | 2.79 | |
| Genotype 1 is identical to the receipt; Genotype 2 is heterozygous; and Genotype 3 is identical to the donor. | |||||
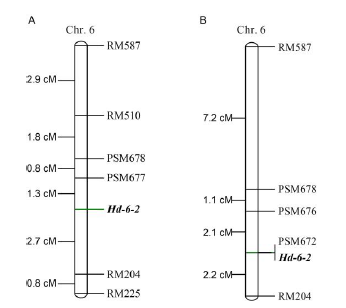
Fig. 2. Linkage map of Hd-6-2 locus for heading date using the segregating populations from W31-SSSL (A) and W32-SSSL (B).Numbers on the left are genetic distances between the upper and below markers.
| [1] | Bian X F, Liu X, Zhao Z G, Jiang L, Gao H, Zhang Y H, Zheng M, Chen L M, Liu S J, Zhai H Q, Wan J M.2011. Heading date gene,dth3 controlled late flowering in O. Glaberrima Steud by down-regulating Ehd1. Plant Cell Rep, 30(12): 2243-2254. |
| [2] | Chardon F, Damerval C.2005. Phylogenomic analysis of the PEBP gene family in cereals. J Mol Evol, 61: 579-590. |
| [3] | Corbesier L, Vincent C, Jang S, Fornara F, Fan Q Z, Searle I, Giakountis A, Farrona S, Gissot L, Turnbull C, Coupland G.2007. FT protein movement contributes to long-distance signaling in floral induction ofArabidopsis. Science, 316: 1030-1033. |
| [4] | Doi K, Izawa T, Fuse T, Yamanouchi U, Kubo T, Shimatani Z, Yano M, Yoshimura A.2004. Ehd1, a B-type response regulator in rice, confers short-day promotion of flowering and controls FT-like gene expression independently of Hd1. Genes Dev, 18: 926-936. |
| [5] | Fujino K, Yamanouchi U, Yano M.2013. Roles of the Hd5 gene controlling heading date for adaptation to the northern limits of rice cultivation. Theor Appl Genet, 126(3): 611-618. |
| [6] | Gao H, Zheng X M, Fei G, Chen J, Jin M, Ren Y, Wu W, Zhou K, Sheng P, Zhou F, Jiang L, Wang J, Zhang X, Guo X, Wang J L, Cheng Z, Wu C, Wang H, Wan J M.2013. Ehd4 encodes a novel and Oryza-genus-specific regulator of photoperiodic flowering in rice. PLoS Genet, 9(2): e1003281. |
| [7] | Gao H, Jin M N, Zheng X M, Chen J, Yuan D Y, Xin Y, Wang M Q, Huang D Y, Zhang Z, Zhou K N, Sheng P K, Ma J, Ma W W, Deng H F, Jiang L, Liu S J, Wang H Y, Wu C Y, Yuan L P, Wan J M.2014. Days to heading 7, a major quantitative locus determining photoperiod sensitivity and regional adaptation in rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 111: 16337-16342. |
| [8] | Hori K, Ogiso-Tanaka E, Matsubara K, Yamanouchi U, Ebana K, Yano M.2013. Hd16, a gene for casein kinase I, is involved in the control of rice lowering time by modulating the day-length response.Plant J, 76(1): 36-46. |
| [9] | Huang C F.2003. Development of position-specific microsatellite marker and mapping of insect resistant gene in rice. [Master thesis]. Guangzhou, China: South China Agricultural University. |
| [10] | Kim S K, Yun C H, Lee J H, Jang Y H, Park H Y, Kim J K.2008. OsCO3, a CONSTANS-LIKE gene, controls flowering by negatively regulating the expression of FT-like genes under SD conditions in rice.Planta, 228: 355-365. |
| [11] | Kojima S, Takahashi Y, Kobayashi Y, Monna L, Sasaki T, Araki T, Yano M.2002. Hd3a, a rice ortholog of the Arabidopsis FT gene, promotes transition to flowering downstream of Hd1 under short-day condition. Plant Cell Physiol, 43(10): 1096-1105. |
| [12] | Komiya R, Ikegami A, Tamaki S, Yokoi S, Shimamoto K.2008. Hd3a andRFT1 are essential for flowering in rice. Development, 135: 767-774. |
| [13] | Komiya R, Yokoi S, Shimamoto K.2009. A gene network for long-day flowering activates RFT1 encoding a mobile flowering signal in rice. Development, 136: 3443-3450. |
| [14] | Koo B H, Yoo S C, Park J W, Kwon C T, Lee B D, An G, Zhang Z, Li J, Li Z, Paek N C.2013. Natural variation in OsPRR37 regulates heading date and contributes to rice cultivation at a wide range of latitudes. Mol Plant, 6: 1877-1888. |
| [15] | Lander E S, Green P.1987. Construction of multilocus genetic linkage maps in human. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 84(8): 2363-2367. |
| [16] | Larkin M A, Blackshields G, Brown N P, Chenna R, McGettigan P A, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace I M, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson J D, Gibson T J, Higgins D G.2007. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0.Bioinformatics, 23(21): 2947-2948. |
| [17] | Li D, Yang C H, Li X B, Gan Q, Zhao X F, Zhu L H.2009. Functional characterization of rice OsDof12. Planta, 229: 1159-1169. |
| [18] | Li W T, Zeng R Z, Zhang Z M, Zhang G Q.2002. Mapping of S-b locus for F1 pollen sterility in cultivated rice using PCR based markers. Acta Bot Sin, 44(4): 463-467. |
| [19] | Lin H X, Liang Z W, Sasaki T, Yano M.2003. Fine mapping and characterization of quantitative trait loci Hd4 and Hd5 controlling heading date in rice. Breeding Sci, 53: 51-59. |
| [20] | Liu G F, Zhu H T, Zhang G Q, Li L H, Ye G Y.2012. Dynamic analysis of QTLs on tiller number in rice (Oryza sativa L.) with single segment substitution lines. Theor Appl Genet, 125(1): 143-153. |
| [21] | Matsubara K, Ogiso-Tanaka E, Hori K, Ebana K, Ando T, Yano M.2012. Natural variation in Hd17, a homolog of Arabidopsis ELF3 that is involved in rice photoperiodic flowering. Plant Cell Physiol, 53(4): 709-716. |
| [22] | McCouch S R, Teytelman L, Xu Y B, Lobos K B, Clar K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z K, Xing Y Z, Zhang Q F, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L.2002. Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res, 9(6): 199-207. |
| [23] | Monna L, Lin H X, Kojima S, Sasaki T, Yano M.2002. Genetic dissection of a genomic region for a quantitative trait locus, Hd3, into two loci, Hd3a and Hd3b, controlling heading date in rice. Theor Appl Genet, 104(5): 772-778. |
| [24] | Nicholas K B, Nicholas H B.1996. GeneDoc: A tool for editing and annotating multiple sequence alignments.EMBnet News, 4: 14. |
| [25] | Ogiso-Tanaka E, Matsubara K, Yamamoto S, Nonoue Y, Wu J, Fujisawa H, Ishikubo H, Tanaka T, Ando T, Matsumoto T, Yano M.2013. Natural variation of the RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T1 contributes to lowering time divergence in rice. PLoS One, 8: e75959. |
| [26] | Panaud O, Chen X, McCouch S R.1996. Development of microsatellite markers and characterization of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Gen Genet, 252(5): 597-607. |
| [27] | Sun C H, Chen D, Fang J, Wang P R, Deng X J, Chu C C.2014. Understanding the genetic and epigenetic architecture in complex network of rice flowering pathways.Protein Cell, 5(12): 889-898. |
| [28] | Takahashi Y, Shomura A, Sasaki T, Yano M.2001. Hd6, a rice quantitative trait locus involved in photoperiod sensitivity, encodes the alpha subunit of protein kinase CK2.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 98: 7922-7927. |
| [29] | Takeuchi Y, Lin S Y, Sasaki T, Yano M.2003. Fine linkage mapping enables dissection of closely linked quantitative trait loci for seed dormancy and heading in rice.Theor Appl Genet, 107(7): 1174-1180. |
| [30] | Tamaki S, Matsuo S, Wong H L, Yokoi S, Shimamoto K.2007. Hd3a protein is a mobile flowering signal in rice.Science, 316: 1033-1036. |
| [31] | Wang J, Zhu J Y, Zhou Y, Yang J, Fan F J, Li W Q, Wang F Q, Zhong W G, Liang G H.2016. QTL analysis for heading date in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under different temperatures and light intensities. Chin J Rice Sci, 30(3): 247-255. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Wang J, Zhu J Y, Tao Y J, Zhou Y, Fan F J, Li W Q, Wang F Q, Zhong W G, Yang J, Liang G H.2017. Mapping of QTLs for heading date using whole-genome re-sequenced chromosome segment substitution lines in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 31(4): 364-370. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [33] | Wang S K, Wu K, Yuan Q B, Liu X Y, Liu Z B, Lin X Y, Zeng R Z, Zhu H T, Dong G J, Qian Q, Zhang G Q, Fu X D.2012. Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet, 44: 950-954. |
| [34] | Wei X J, Xu J F, Guo H N, Jiang L, Chen S H, Yu C Y, Zhou Z L, Hu P S, Zhai H Q, Wan J M.2010. DTH8 suppresses lowering in rice, influencing plant height and yield potential simultaneously.Plant Physiol, 153(4): 1747-1758. |
| [35] | Wu W X, Zheng X M, Lu G W, Zhong Z Z, Gao H, Chen L P, Wu C Y, Wang H J, Wang Q, Zhou K N, Wang J L, Wu F Q, Zhang X, Guo X P, Cheng Z J, Lei C L, Lin Q B, Jiang L, Wang H Y, Ge S, Wan J M.2013. Association of functional nucleotide polymorphisms at DTH2 with the northward expansion of rice cultivation in Asia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 110(8): 2775-2780. |
| [36] | Xi Z Y, He F H, Zeng R Z, Zhang Z M, Ding X H, Li W T, Zhang G Q.2006. Development of a wide population of chromosome single-segment substitution lines in the genetic background of an elite cultivar of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genome, 49(5): 476-484. |
| [37] | Xue W Y, Xing Y Z, Weng X Y, Zhao Y, Tang W J, Wang L, Zhou H J, Yu S B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F.2008. Natural variation in Ghd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice. Nat Genet, 40: 761-767. |
| [38] | Yamamoto T, Kuboki Y, Lin S Y, Sasaki T, Yano M.1998. Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci Hd-1, Hd-2, and Hd-3, controlling heading date of rice, as single Mendelian factors. Theor Appl Genet, 97: 37-44. |
| [39] | Yan W H, Wang P, Chen H X, Zhou H J, Li Q P, Wang C R, Ding Z H, Zhang Y S, Yu S B, Xing Y Z, Zhang Q F.2011. A major QTL,Ghd8, plays pleiotropic roles in regulating grain productivity, plant height, and heading date in rice. Mol Plant, 4(2): 319-330. |
| [40] | Yano M, Sasaki T.1997. Genetic and molecular dissection of quantitative traits in rice. Plant Mol Biol, 35: 145-153. |
| [41] | Yano M, Katayose Y, Ashikari M, Yamanouchi U, Monna L, Fuse T, Baba T, Yamamoto K, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T, Umehara Y.2000. Hd1, a major photoperiod sensitivity quantitative trait locus in rice, is closely related to the Arabidopis flowering time gene CONSTANS. Plant Cell, 12: 2473-2483. |
| [42] | Yano M, Kojima S, Takahashi Y, Lin H X, Sasaki T.2001. Genetic control of lowering time in rice, a short-day plant.Plant Physiol, 127(4): 1425-1429. |
| [43] | Yano M, Kojima S, Takahashi Y, Lin H X, Sasaki T.2002. Genetic control of flowering time in rice, a short-day plant. Plant Physiol, 127: 1425-1429. |
| [44] | Ying Y Q, Zhu H T, Ye G Y, Zhang G Q, Li L H, Liu G F.2014. Detection of QTL on panicle number in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under different densities with single segment substitution lines. Euphytica, 195(3): 355-368. |
| [45] | Zhang G Q, Zeng R Z, Zhang Z M, Ding X H, Li W T, Liu G M, He F H, Tulukdar A, Huang C F, Xi Z Y, Qin L J, Shi J Q, Zhao F M, Feng M J, Shan Z L, Chen L, Guo X Q, Zhu H T, Lu Y G.2004. The construction of a library of single segment substitution lines in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice Genet Newsl, 21: 85-87. |
| [46] | Zhao J, Chen H Y, Ren D, Tang H W, Qiu R, Feng J L, Long Y M, Niu B X, Chen D P, Zhong T Y, Liu Y G, Guo J X.2015. Genetic interactions between diverged alleles of Early heading date 1 (Ehd1) and Heading date 3a (Hd3a)/ RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T1 (RFT1) control differential heading and contribute to regional adaptation in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol, 208(3): 936-948. |
| [47] | Zheng K L, Huang N, Bennett J, Khush G S.1995. PCR-based marker-assisted selection in rice breeding. International Rice Research Institute, Manila,the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute Discussion Paper: 12. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||