
Rice Science ›› 2016, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (1): 51-55.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2016.01.006
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2015-03-02
接受日期:2015-10-28
出版日期:2016-01-20
发布日期:2015-11-05
. [J]. Rice Science, 2016, 23(1): 51-55.
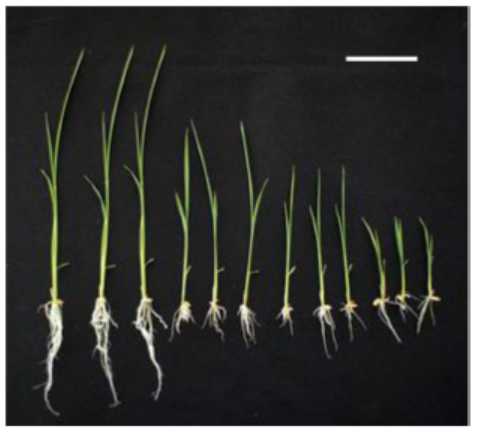

Fig. 2. Effect of Yucaizol on retardation plant height in rice seedlings. The plants were treated with Yucaizol at the specified concentrations. From left, control (the first three plants); 0.5 μmol/L (the second three plants) 1.0 μmol/L (the third three plants) and 10.0 μmol/L (three plants from right). Plants were grown under the conditions described in the experimental section for 10 d. Bar = 2 cm. All the experiments were done at least three times to establish the repeatability.
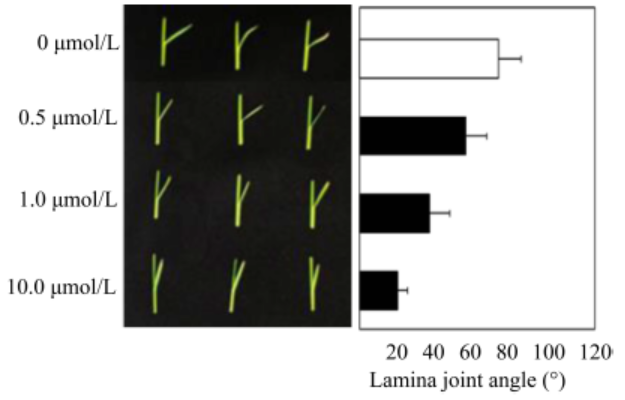
Fig. 3. Effect of Yucaizol on lamina joint bending angle in rice seedlings.The plants were treated with Yucaizol at the specified concentration (0-10 μmol/L) and grown under the conditions described in the experimental section for 10 d. The average bending angle of the lamina joint was measured (n = 8). Error bars represent SD. All the experiments were done at least three times to establish the repeatability.
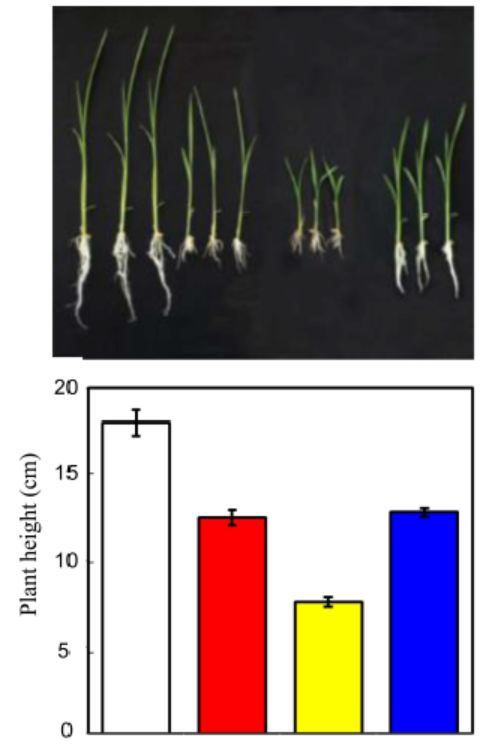
Fig. 4. Effects of Yucaizol and Trinexapac-ethyl (TPE) on growth of rice seedlings. The plants were treated with Yucaizol from left: 0, 0.5, 0.5 and 0 μmol/L mixed with TPE at a concentration of (from left): 0, 0, 0.5 and 0.5 μmol/L. Rice plants were grown under the conditions described in the experimental section for 10 d. The upper picture displays the chemical induced phenocopy of rice. The plant height was measured (n = 8). Error bars represent SD. All the experiments were done at least three times to establish the repeatability.
| [1] | Asami T, Mizutani M, Fujioka S, Goda H, Min Y K, Shimada Y, Nakano T, Takatsuto S, Matsuyama T, Nagata N, Sakata K, Yoshida S.2001. Selective interaction of triazole derivatives with DWF4, a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase of the brassinosteroid biosynthetic pathway, correlates with brassinosteroid deficiency in planta.J Biol Chem, 276(28): 25687-25691. |
| [2] | Asami T, Nakano T, Fujioka S.2005. Plant brassinosteroid hormones.Vitam Horm, 72(3): 479-504. |
| [3] | Blackwell H E, Zhao Y.2003. Chemical genetic approaches to plant biology.Plant Physiol, 133(2): 448-455. |
| [4] | Clouse S D, Sasse J M.1998. Brassinosteroids: Essential regulators of plant growth and development.Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol, 49: 427-451. |
| [5] | Clouse S D.2011. Brassinosteroid signal transduction: From receptor kinase activation to transcriptional networks regulating plant development.Plant Cell, 23(4): 1219-1230. |
| [6] | Dill A, Jung H S, Sun T P.2001. The DELLA motif is essential for gibberellin-induced degradation of RGA.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 98(24): 14162-14167. |
| [7] | Gomi K, Sasaki A, Itoh H, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M.2004. GID2, an F-box subunit of the SCF E3 complex, specifically interacts with phosphorylated SLR1 protein and regulates the gibberellin-dependent degradation of SLR1 in rice.Plant J, 37(4): 626-634. |
| [8] | He J X, Gendron J M, Yang Y L, Li J M, Wang Z Y.2002. The GSK3-like kinase BIN2 phosphorylates and destabilizes BZR1, a positive regulator of the brassinosteroid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 99(15): 10185-10190. |
| [9] | Hedden P.2003. The genes of the Green Revolution.Trends Genet, 19(1): 5-9. |
| [10] | Hoagland D R, Arnon D I.1950. The water-culture method of growing plants without soil.Calif Agric Exp Stat, 347(1): 1-32. |
| [11] | Inada S, Tominaga M, Shimmen T.2000. Regulation of root growth by gibberellin in Lemna minor.Plant Cell Physiol, 41(36): 657-665. |
| [12] | Kim T W, Guan S, Burlingame A L, Wang Z Y.2011. The CDG1 kinase mediates brassinosteroid signal transduction from BRI1 receptor kinase to BSU1 phosphatase and GSK3-like kinase BIN2.Mol Cell, 43(4): 561-571. |
| [13] | Li J, Wen J Q, Lease K A, Doke J T, Tax F E, Walker J C.2002. BAK1, an Arabidopsis LRR receptor-like protein kinase, interacts with BRI1 and modulates brassinosteroid signaling.Cell, 110(2): 213-222. |
| [14] | Matsumoto T, Yamada K, Iwasaki I, Yoshizawa Y, Oh K.2013. New compounds induce brassinosteroid deficient-like phenotypes in rice.Plants, 2(3): 521-529. |
| [15] | Min Y K, Asami T, Fujioka S, Murofushi N, Yamaguchi I, Yoshida S.1999. New lead compounds for brassinosteroid biosynthesis inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 9(3): 425-430. |
| [16] | Mussig C.2005. Brassinosteroid-promoted growth.Plant Biol, 7(2): 110-117. |
| [17] | Oh K, Matsumoto T, Yamagami A, Ogawa A, Yamada K, Suzuki R, Sawada T, Fujioka S, Yoshizawa Y, Nakano N T.2015. YCZ-18 is a new brassinosteroid biosynthesis inhibitor.PLoS One, 10(3): e0120812. |
| [18] | Oh K, Yamada K, Asami T, Yoshizawa Y.2012. Synthesis of novel brassinosteroid biosynthesis inhibitors based on the ketoconazole scaffold.Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 22(4): 1625-1628. |
| [19] | Oh K, Yamada K, Yoshizawa Y.2013. Asymmetric synthesis and effect of absolute stereochemistry of YCZ-2013, a brassinosteroid biosynthesis inhibitor.Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 23(24): 6915-6919. |
| [20] | Rademacher W.2000. Growth retardants: Effects on gibberellin biosynthesis and other metabolic pathways.Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol, 51: 501-531. |
| [21] | Richards D E, King K E, Ait-Ali T, Harberd N P.2001. How gibberellin regulates plant growth and development: A molecular genetic analysis of gibberellin signaling.Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol, 52: 67-88. |
| [22] | Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Ohnishi T, Sunohara H, Fujioka S, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Mizutani M, Sakata K, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Tanaka H, Kitano H, Matsuoka M.2006. Erect leaves caused by brassinosteroid deficiency increase biomass production and grain yield in rice.Nat Biotechnol, 24(1): 105-109. |
| [23] | Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D, Ishiyama K, Saito T, Kobayashi M, Khush G S, Kitano H, Matsuoka M.2002. Green revolution: A mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice.Nature, 416: 701-702. |
| [24] | Sasaki A, Itoh H, Gomi K, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Ishiyama K, Kobayashi M, Jeong D H, An G, Kitano H, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M.2003. Accumulation of phosphorylated repressor for gibberellin signaling in an F-box mutant.Science, 299: 1896-1898. |
| [25] | Sekimata K, Kimura T, Kaneko I, Nakano T, Yoneyama K, Takeuchi Y, Yoshida S, Asami T.2001. A specific brassinosteroid biosynthesis inhibitor, Brz2001: Evaluation of its effects on Arabidopsis, cress, tobacco, and rice.Planta, 213(5): 716-721. |
| [26] | Steber C M, McCourt P.2001. A role for brassinosteroids in germination in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol, 125(42): 763-769. |
| [27] | Tong H N, Xiao Y H, Liu D P, Gao S P, Liu L C, Yin Y H, Jing Y, Qian Q, Chu C C.2014. Brassinosteroid regulates cell elongation by modulating gibberellin metabolism in rice.Plant Cell, 26(11): 4376-4393. |
| [28] | Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Nakajima M, Katoh E, Ohmiya H, Asano K, Saji S, Xiang H Y, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Yamaguchi I, Matsuoka M.2007. Molecular interactions of a soluble gibberellin receptor, GID1, with a rice DELLA protein, SLR1, and gibberellin.Plant Cell, 19(7): 2140-2155. |
| [29] | Wada K, Marumo S, Ikekawa N, Morisaki M, Mori K.1981. Brassinolide and homobrassinolide promotion of lamina inclination of rice seedling.Plant Cell Physiol, 22(2): 323-325. |
| [30] | Wang Y H, Li J Y.2005. The plant architecture of rice (Oryza sativa).Plant Mol Biol, 59(1): 75-84. |
| [31] | Wang Z Y, Nakano T, Gendron J, He J X, Chen M, Vafeados D, Yang Y, Fujioka S, Yoshida S, Asami T, Chory J.2002. Nuclear-localized BZR1 mediates brassinosteroid-induced growth and feedback suppression of brassinosteroid biosynthesis.Dev Cell, 2(4): 505-513. |
| [32] | Yamada K, Yajima O, Yoshizawa Y, Oh K.2013. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel azole derivatives as selective potent inhibitors of brassinosteroid biosynthesis.Bioorg Med Chem, 21(3): 2451-2461. |
| [33] | Yamada K, Yoshizawa Y, Oh K.2012. Synthesis of 2RS, 4RS-1-[2-phenyl-4-[2-(2-trifluromethoxy-phenoxy)-ethyl]-1, 3-dioxolan- 2-yl-methyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole derivatives as potent inhibitors of brassinosteroid biosynthesis.Molecules, 17(4): 4460-4473. |
| [34] | Yang G X, Matsuoka M, Iwasaki Y, Komatsu S.2003. A novel brassinolide-enhanced gene identified by cDNA microarray is involved in the growth of rice.Plant Mol Biol, 52(4): 843-854. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||