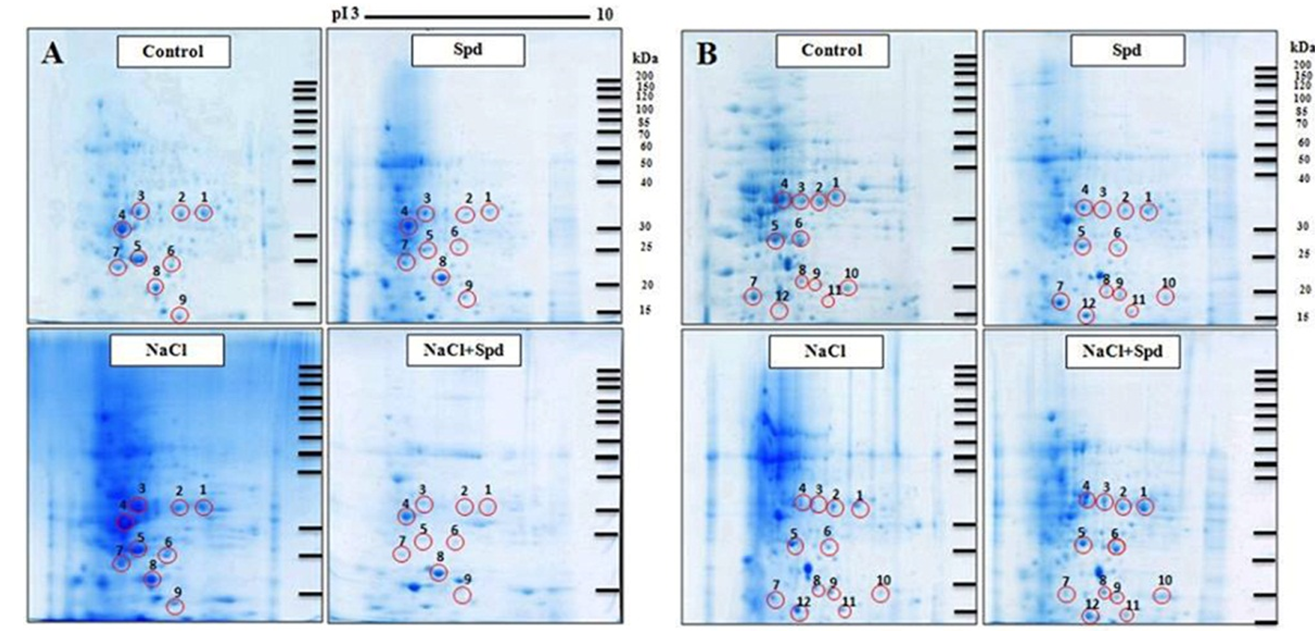
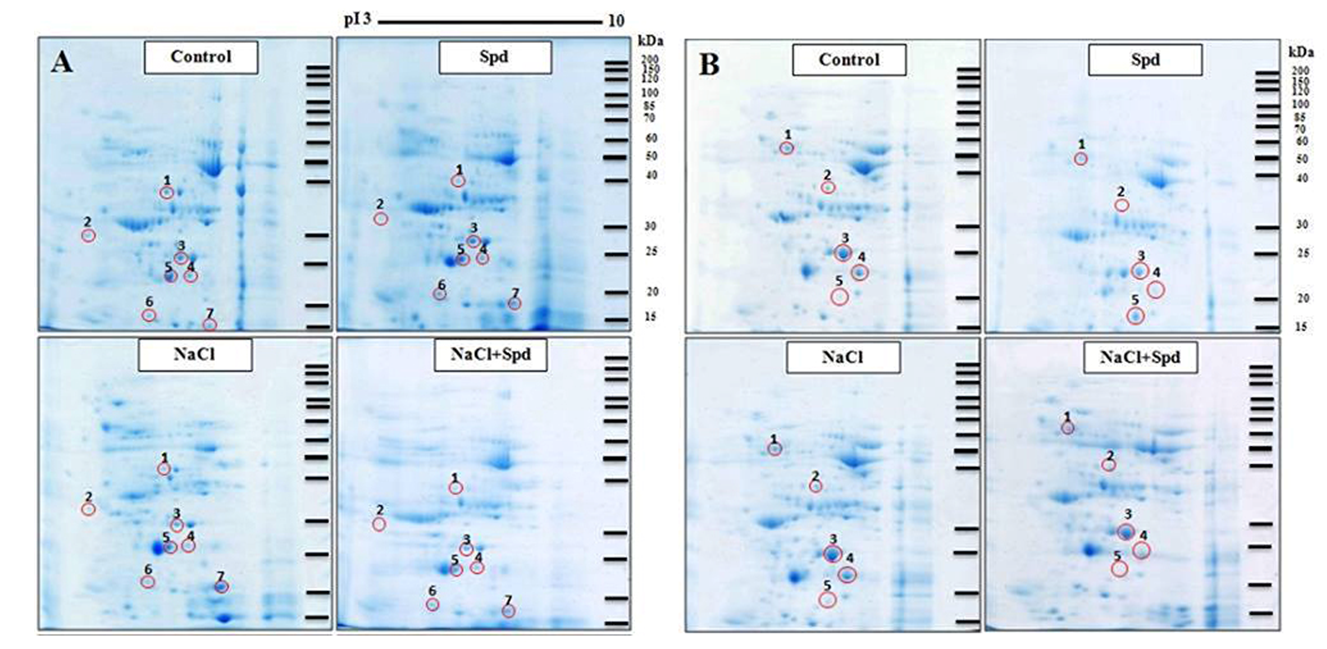
| [1] |
Abbasi F M, Komatsu S.2004. A proteomic approach to analyze salt-responsive proteins in rice leaf sheath.Proteomics, 4: 2072-2081.
|
| [2] |
Alcazar R, Marco F, Cuevas C J, Patron M, Ferrando A, Carrasco P, Tiburcio A F, Altabella T.2006. Involvement of polyamines in plant response to abiotic stress.Biotech Lett, 28: 1867-1876.
|
| [3] |
Baneyx F, Bertsch U, Kalbach C E, Vandervies S M, Soll J, Gatenby A A.1995. Spinach chloroplast Cpn21 co-chaperonin possesses two functional domains fused together in a toroidal structure and exhibits nucleotide-dependent binding to plastid chaperonin 60.J Biol Chem, 270: 10695-10702.
|
| [4] |
Barkla B J, Vera-Estrella R, Hermández-Coronado M, Pantoja O.2009. Quantitativeproteomics of the tonoplast reveals a role for glycolytic enzymes in salt tolerance.Plant Cell, 21(12): 4044-4058.
|
| [5] |
Battaglia M, Olvera-Carillo Y, Garciarrubio A, Campos F, Covarrubias A A.2008. The enigmatic LEA proteins and other hydrophilins.Plant Physiol, 148(1): 6-24.
|
| [6] |
Bhatt I, Tripathi B N.2011. Plant peroxiredoxins: Catalytic mechanisms, functional significance and future perspectives.Biotechnol Adv, 29(6): 850-859.
|
| [7] |
Bors W, Langebartels C, Michel C, Sanderman H.1989. Polyamines as radical scavengers and protectants against ozone damage.Phytochemistry, 28(6): 1589-1595.
|
| [8] |
Bradford M M.1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quanlities of protein utilizing the principal of protein-dry binding.Anal Biochem, 72: 248-254.
|
| [9] |
Cady C W, Crabtree R H, Brudvig G W.2008. Functional models for the oxygen-evolving complex of photosystem II.Coord Chem Rev, 252(3/4): 444-455.
|
| [10] |
Chang I F, Hsu J L, Hsu P H, Sheng W A, Lai S J, Lee C, Chen W C, Hsu J C, Wang S Y, Wang L Y, Chen C C.2012. Comparative phosphoproteomic analysis of microsomal fractions of Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa subjected to high salinity.Plant Sci, 185: 131-142.
|
| [11] |
Chattopadhyay M K, Tiwari B S, Chattopadhyay G, Bose A, Sengupta D N, Ghosh B.2002. Protective role of exogenous polyamines on salinity-stressed rice (Oryza sativa) plants.Physiol Plant, 116(2): 192-199.
|
| [12] |
Chourey K, Ramani S, Apte S K.2003. Accumulation of LEA proteins in salt (NaCl) stressed young seedlings of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivar Bura Rata and their degradation during recovery from salinity stress.J Plant Physiol, 160(10): 1165-1174.
|
| [13] |
Dietz K J.2003. Plant peroxiredoxins.Antioxid Redox Signal, 54(1): 93-107.
|
| [14] |
Du C X, Fan H F, Guo S R.2010. Applying spermidine for differential responses of antioxidant enzymes in cucumber subjected to short-term salinity.J Am Soc Hort Sci, 135: 18-24.
|
| [15] |
Duan J L, Cai W M.2012. OsLEA3-2, an abiotic stress induced gene of rice plays a key role in salt and drought tolerance.PLoS One, 7(9): e45117.
|
| [16] |
Duan J L, Li J, Guo S R, Kang Y Y.2008. Exogenous spermidine affects polyamine metabolism in salinity-stressed Cucumis sativus roots and enhances short-term salinity tolerance.J Plant Physiol, 165(15): 1620-1635.
|
| [17] |
Dure L, Greenway S C, Galau G A.1981. Developmental biochemistry of cottonseed embryogenesis and germination: Changing messenger ribonucleic acid populations as shown by in vitro and in vivo protein synthesis.Biochemistry, 20(14): 4162-4168.
|
| [18] |
Fadzilla N M, Finch R P, Burdon R H.1997. Salinity, oxidative stress and antioxidant responses in shoot cultures of rice.J Exp Bot, 48: 325-331.
|
| [19] |
Fatehi F, Hosseinzadeh A, Alizadeh H, Brimavandi T, Struik P C.2012. The proteome response of salt-resistant and salt-sensitive barley genotypes to long-term salinity stress.Mol Biol Rep, 39: 6387-6397.
|
| [20] |
Ferreira K N, Iverson T M, Maghlaoui K, Barber J, Iwata S.2004. Architecture of the photosynthetic oxygen-evolving center.Science, 303: 1831-1838.
|
| [21] |
Grattan S R, Zeng L, Shannon M C, Roberts S R.2002. Rice is more sensitive to salinity than previously thought.Calif Agric, 56(6): 189-198.
|
| [22] |
Gregorio G B, Senadhira D, Mendoza R D.1997. Screening rice for salinity tolerance. IRRI Discussion Paper Series Number 22. Manila, Philippines: International Rice Research Institute.
|
| [23] |
Gregorio G B, Senadhira D, Mendoza R D, Manigbas N L, Roxas J P, Querta C Q.2002. Progress in breeding for salinity tolerance and associated abiotic stresses in rice.Field Crops Res, 76: 91-101.
|
| [24] |
Ha H C, Sirisoma N S, Kuppusamy P, Zweier J L, Woster P M, Casero R A.1998. The natural polyamine spermine functions directly as a free radical scavenger.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 95: 11140-11145.
|
| [25] |
Henze K, Schnarrenberger C, Kellermann J, Martin W.1994. Chloroplast and cytosolic triosephosphate isomerases from spinach: Purification, microsequencing and cDNA cloning of the chloroplast enzyme.Plant Mol Biol, 26(6): 1961-1973.
|
| [26] |
Jankangram W, Thammasirirak S, Jones M G, Hartwell J, Theerakulpisut P.2011. Proteomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals evidence for the basis of salt sensitivity in Thai jasmine rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. KDML105).Afr J Biotechnol, 10: 16157-16166.
|
| [27] |
Jiang S Y, Ma Z, Ramachandran S.2010. Evolutionary history and stress regulation of the lectin super family in higher plants.BMC Evol Biol, 10: 79.
|
| [28] |
Jimenez-Bremont J F, Ruiz O A, Rodriguez-Kessler M.2007. Modulation of spermidine and spermine levels in maize seedlings subjected to long-term salt stress.Plant Physiol Biochem, 45: 812-821.
|
| [29] |
Kanawapee N, Sanitchon J, Lontom W, Theerakulpisut P.2012. Evaluation of salt tolerance at the seedling stage in rice genotypes by growth performance, ion accumulation, proline and chlorophyll content. Plant Soil, 358: 235-249.
|
| [30] |
Khan P S S V, Hoffmann L, Renauty J, Hausman J F.2007. Current initiatives in proteomics for the analysis of plant salt tolerance.Curr Sci, 93(6): 807-817.
|
| [31] |
Kim D W, Dr R R, Agrawal G K, Jung Y H, Shibato J, Jwa N S, Iwahashi Y, Iwahashi H, Kim D H, Shim L S, Usui K.2005. A hydroponic rice seedling culture model system for investigating proteome of salt stress in rice leaf.Electrophoresis, 26: 4521-4539.
|
| [32] |
Kubis J.2005. The effect of exogenous spermidine on superoxide dismutase activity, H2O2 and superoxide radical level in barley leaves under water deficit conditions.Acta Physiol Plant, 27(3): 289-295.
|
| [33] |
Lee D G, Park K W, An J Y, Sohn Y G, Ha J K, Kim H Y, Bae D W, Lee K H, Kang N J, Lee B H, Kang K Y, Lee J J.2011. Proteomics analysis of salt-induced leaf proteins in two rice germplasms with different salt sensitivity.Can J Plant Sci, 91(2): 337-349.
|
| [34] |
Li W, Zhang C Y, Lu Q T, Wen X G, Lu C M.2011. The combined effect of salt stress and heat shock on proteome profiling in Suaeda salsa.J Plant Physiol, 168(15): 1743-1752.
|
| [35] |
Lutts S, Kine J M, Bouharmont J.1995. Changes in plant response to NaCl during development of rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties differing in salinity resistance.J Exp Bot, 46(12): 1843-1852.
|
| [36] |
Mahdavi F, Sariah M, Maziar M.2012. Expression of rice thaumatin-like protein genes in transgenic banana plants enhances resistance to fusariumwilt.Appl Biochem Biotechnol, 166: 1008-1019.
|
| [37] |
Minarik P, Tomaskov N, Kollarova M, Antalik M.2002. Malate dehydrogenases: Structure and function.Gene Physiol Biophys, 21(3): 257-265.
|
| [38] |
Moons A, Keyser A D, Montagu M V.1997. A group 3 LEA cDNA of rice, responsive to abscisic acid, but not to jasmonic acid, shows variety-specific differences in salt stress response.Gene, 191(2): 197-204.
|
| [39] |
Nam M H, Huh S M, Kim K M, Park W J, Seo J B, Cho K, Kim D Y, Kim B G, Yoon I S.2012. Comparative proteomic analysis of early salt stress-responsive proteins in roots of SnRK2 transgenic rice.Proteome Sci, 10: 2-19.
|
| [40] |
Ndimba B, Chivasa S, Simon W J, Slabas A R.2005. Identification of Arabidopsis salt and osmotic stress responsive proteins using two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry.Proteomics, 5(16): 4185-4196.
|
| [41] |
Ngara R, Ndimbab R, Borch-Jensenc J, Jensenc O N, Ndimbaa B.2012. Identification and profiling of salinity stress-responsive proteins in Sorghum bicolor seedlings.J Proteomics, 75(13): 4139-4150.
|
| [42] |
Nuanjan N, Nghia P T, Theerakulpisut P.2012. Exogenous proline and trehalose promote recovery of rice seedlings from salt-stress and differentially modulate antioxidant enzymes and expression of related genes.J Plant Physiol, 169(6): 596-604.
|
| [43] |
Olvera-Carrillo Y, Reyes J L, Covarrubias A A.2011. Late embryogenesis abundant proteins: Versatile players in the plant adaptation to water limiting environments.Plant Signal Behav, 6(4): 586-589.
|
| [44] |
Parker R, Flowers T J, Moore A L, Harpham N V J.2006. An accurate and reproducible method for proteome profiling of the effects of salt stress in the rice leaf lamina.J Exp Bot, 57(5): 1109-1118.
|
| [45] |
Patonnier M P, Peltier J P, Marigo G.1999. Drought-induced increase in xylem malate and mannitol concentrations and closure of Fraxinus excelsior L. stomata.J Exp Bot, 50: 1223-1229.
|
| [46] |
Patron N J, Rogers M B, Keeling P J.2004. Gene replacement of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase supports the hypothesis of a single photosynthetic ancestor of chromalveolates.Euk Cell, 3(5): 1169-1175.
|
| [47] |
Plaut Z, Edelstein M, Ben-Hur M.2013. Overcoming salinity barriers to crop production using traditional methods.Crit Rev Plant Sci, 32(4): 250-291.
|
| [48] |
Qaisar U, Irfan M, Meqbool A, Zahoor M, Barozai M Y K, Rashid B, Riazuddin S, Husnain T.2010. Identification, sequencing and characterization of a stress induced homologue of fructose bisphosphate aldolase from cotton.Can J Plant Sci, 90(1): 41-48.
|
| [49] |
Roy P, Niyogi K, Sengupta D N, Ghosh B.2005. Spermidine treatment to rice seedlings recovers salinity stress-induced damage to plasma membrane and H+-ATPase in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive rice cultivars.Plant Sci, 168(3): 583-591.
|
| [50] |
Roychoudhury A, Basu S, Sarkar S N, Sengupta D N.2008. Comparative physiological and molecular responses of a common aromatic indica rice cultivar to high salinity with non-aromatic indica rice cultivars.Plant Cell Rep, 27: 1395-1410.
|
| [51] |
Roychoudhury A, Basu S, Sengupta D N.2011. Amelioration of salinity stress by exogenously applied spermidine or spermine in three varieties of rice differing in their level of salt tolerance.J Plant Physiol, 168(4): 317-328.
|
| [52] |
Saleethong P, Kong-Ngern K, Sanitchon J, Theerakulpisut P.2011. Pretreatment with spermidine reverses inhibitory effects of salt stress in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars differing in salinity tolerance.Asian J Plant Sci, 10(4): 245-254.
|
| [53] |
Saleethong P, Sanitchon J, Kong-Ngern K, Theerakulpisut P.2013. Effects of exogenous spermidine (Spd) on yield, yield-related pretreatment and mineral composition of rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica) grains under salt stress.Aust J Crop Sci, 7(9): 1293-1301.
|
| [54] |
Sano N, Masaki S, Tanabata T, Yamada T, Hirasawa T, Kanekatsu M.2013. Proteomic analysis of stress-related proteins in rice seeds during the desiccation phase of grain filling.Plant Biotechnol, 30: 147-156.
|
| [55] |
Seki M, Kamei A, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K.2003. Molecular responses to drought, salinity and frost: Common and different paths for plant protection.Curr Opin Biotechnol, 14(2): 194-199.
|
| [56] |
Shannon M C, Rhoades J D, Draper J H, Scardaci S C, Spyres M D.1998. Assessment of salt tolerance in rice cultivars in response to salinity problems in California.Crop Sci, 38(2): 394-398.
|
| [57] |
Sharma S, Mustafiz A, Singla-Pareek S L, Srivastava P S, Sopory S K.2012. Characterization of stress and methylglyoxal inducible triose phosphate isomerase (OscTPI) from rice.Plant Signal Behav, 7(11): 1337-1345.
|
| [58] |
Singh N K, Kumar K R R, Kumar D, Shukla P, Kirti P B.2013. Characterization of a pathogen induced thaumatin-like protein gene AdTLP from Arachis deogoi, a wild peanut.PLoS One, 8(12): e83963.
|
| [59] |
Smirnoff N.1993. The role of active oxygen in the response of plants to water deficit and desiccation.New Phytol, 125(1): 27-58.
|
| [60] |
Stacy R A P, Nordeng T W, Cullanez-Macia F A, Aalen R B.1999. The dormancy-related peroxiredoxin anti-oxdant, PERI, is localized to the nucleus of barley embryo and aleurone cell.Plant J, 19(1): 1-8.
|
| [61] |
Sunkar R, Kapoor A, Zhu J K.2006. Posttranscriptional induction of two Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase genes in Arabidopsis is mediated by downregulation of miR398 and important for oxidative stress tolerance.Plant Cell, 18: 2051-2065.
|
| [62] |
Tripathi B N, Bhatt I, Dietz K J.2009. Peroxiredoxins: A less studied component of hydrogen peroxide detoxification in photosynthetic organisms.Protoplasma, 235: 3-15.
|
| [63] |
Wan X Y, Liu J Y.2008. Comparative proteomics analysis reveals an intimate protein network provoked by hydrogen peroxide stress in rice seedling leaves.Mol Cell Proteomics, 7(8): 1469-1488.
|
| [64] |
Wolkers W F, McCready S, Brandt W F, Lindsey G G, Hoekstra F A.2001. Isolation and characterization of a D-7 LEA protein from pollen that stabilizes glasses in vitro.Biochim Biophys Acta, 1544: 196-206.
|
| [65] |
Yan S T, Tang Z C, Su W A, Sun W N.2005. Proteomic analysis of salt stress responsive proteins in rice root.Proteomics, 5(1): 235-244.
|
| [66] |
Yoshida S, Forno D A, Cock J H, Gomez K A.1976. Laboratory Manual for Physiology Studies of Rice. 3rd ed. Los Banos, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute.
|
| [67] |
Zeng L H, Poss J A, Wison C, Draz A S E, Gregorio G B, Grieve C M.2003. Evaluation of salt tolerance in rice genotypes by physiological characters.Euphytica, 129: 281-292.
|
| [68] |
Zhang L, Tian L H, Zhao J F, Song Y, Zhang C J, Guo Y.2009. Identification of an apoplastic protein involved in the initial phase of salt stress response in rice root by two-dimensional electrophoresis.Plant Physiol, 149(2): 916-928.
|
| [69] |
Zhang W L, Peumans W J, Barre A, Astoul C H, Rovira P, Rougé P, Proost P, Truffa-Bachi P, Jalali A A H, van Damme E J M.2000. Isolation and characterization of a jacalin-related mannose-binding lectin from salt-stressed rice (Oryza sativa) plants.Planta, 210(6): 970-978.
|
| [70] |
Zhu H, Ding G H, Fang K, Zhao F G, Qin P.2006. New perspective on mechanism of alleviating salt stress by spermidine in barley seedlings.Plant Growth Regul, 49: 147-156.
|
| [71] |
Zhu J K.2002. Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 53: 247-273.
|