
Rice Science ›› 2024, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 285-299.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2023.12.003
收稿日期:2023-10-15
接受日期:2023-12-07
出版日期:2024-05-28
发布日期:2024-06-04
. [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(3): 285-299.

Fig. 1. Causes of rice necrotic lesion formation. Alterations in the expression of related genes, ROS enzyme system, PCD, membrane proteins, chloroplast structure, chloroplast synthesis, and environmental factors (light and humidity) lead to cell death, ROS accumulation, thereby producing necrotic lesions. ROS, Reactive oxygen species; PCD, Programmed cell death; JA, Jasmonic acid; SA, Salicylic acid; ET, Ethylene; CAT, Catalase; SOD, Superoxide dismutase; APX, Ascorbate peroxidase; PRs, Pathogenesis-related genes. ‘→’ symbol indicates activation or next step, and ‘├’ symbol indicates inhibition.
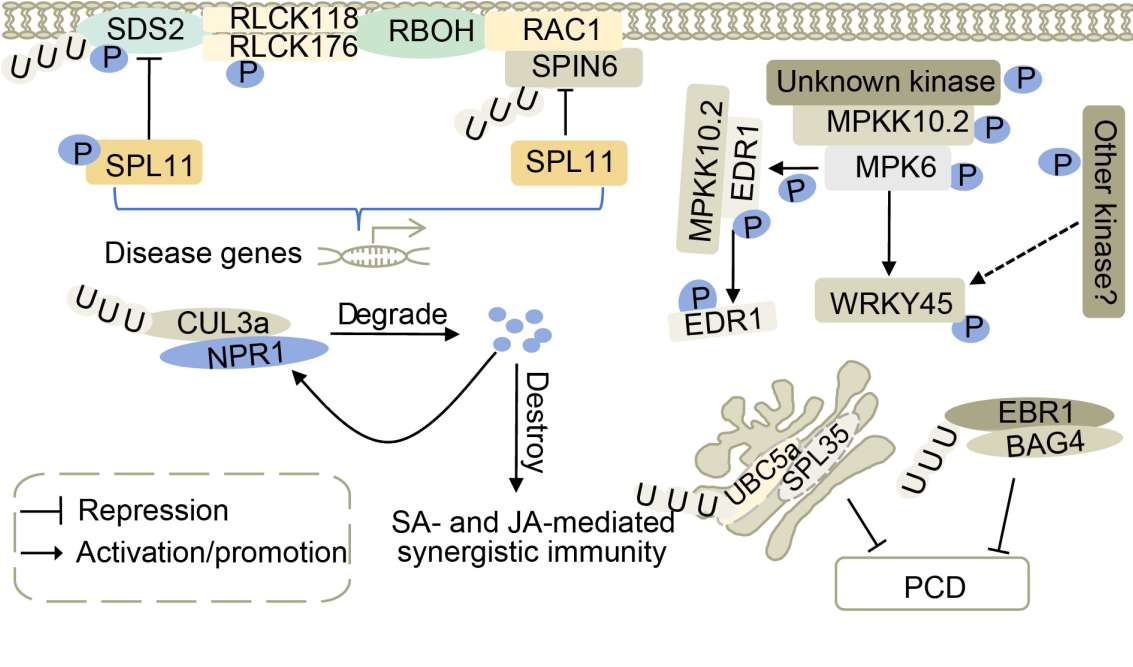
Fig. 2. Necrotic lesion genes are involved in mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling and ubiquitine pathways. Plants regulate in vivo defense responses by adjusting EDS1 phosphorylation and MPKK10.2 cascade status. SPL11-SDS2, SPL11-SPIN6, and RAC1 can jointly participate in pathogen resistance signaling pathways. SPL11 is a negative regulator of plant cell death and defense, and plays a critical role in SPIN6 and SDS2-mediated defense responses. BAG4 and SPL35 are positive regulators of programmed cell death (PCD), and excessive accumulation can lead to PCD. They are degraded by an E3 ubiquitin ligase. The NPR1 is degraded by enhancing the association between NPR1 and CUL3a, which disrupts the salicylic acid (SA)- and jasmonic acid (JA)-mediated synergistic immunity in rice.
| Gene name | Accession number | Protein function | Disease resistance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPL28, PSL50 | Os01g0703600 | A subunit of clathrin-associated adaptor protein | Magnaporthe oryzae and Xanthomonas oryzae (Xoo) | Qiao et al, |
| NPR1, NH1 | Os01g0194300 | Salicylic acid receptor | M. oryzae and Xoo | Li et al, |
| LMR, LRD6-6 | Os06g0130000 | ATP; AAA ATPase | M. oryzae and Xoo | Fekih et al, |
| SPIN6 | Os07g0658300 | Rho GTPase activating protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Liu et al, |
| SPL11 | Os12g0570000 | E3 ubiquitin ligase | M. oryzae and Xoo | Liu et al, |
| EBR1 | Os05g0279400 | E3 ubiquitin ligase | M. oryzae and Xoo | You et al, |
| BAG4 | Os01g0831200 | BAG protein; Molecular chaperone regulatory proteins | M. oryzae and Xoo | You et al, |
| CUL3a | Os02g0746000 | Cullin protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Liu et al, |
| SDS2 | Os01g0783800 | Receptor-like kinase | M. oryzae | Fan et al, |
| SCYL2 | Os01g0616100 | Clathrin-coated vesicle components | Xoo | Yao et al, |
Table 1. Necrotic lesion genes are involved in mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and ubiquitination pathways and clathrin-mediated vesicle transport pathway.
| Gene name | Accession number | Protein function | Disease resistance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPL28, PSL50 | Os01g0703600 | A subunit of clathrin-associated adaptor protein | Magnaporthe oryzae and Xanthomonas oryzae (Xoo) | Qiao et al, |
| NPR1, NH1 | Os01g0194300 | Salicylic acid receptor | M. oryzae and Xoo | Li et al, |
| LMR, LRD6-6 | Os06g0130000 | ATP; AAA ATPase | M. oryzae and Xoo | Fekih et al, |
| SPIN6 | Os07g0658300 | Rho GTPase activating protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Liu et al, |
| SPL11 | Os12g0570000 | E3 ubiquitin ligase | M. oryzae and Xoo | Liu et al, |
| EBR1 | Os05g0279400 | E3 ubiquitin ligase | M. oryzae and Xoo | You et al, |
| BAG4 | Os01g0831200 | BAG protein; Molecular chaperone regulatory proteins | M. oryzae and Xoo | You et al, |
| CUL3a | Os02g0746000 | Cullin protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Liu et al, |
| SDS2 | Os01g0783800 | Receptor-like kinase | M. oryzae | Fan et al, |
| SCYL2 | Os01g0616100 | Clathrin-coated vesicle components | Xoo | Yao et al, |
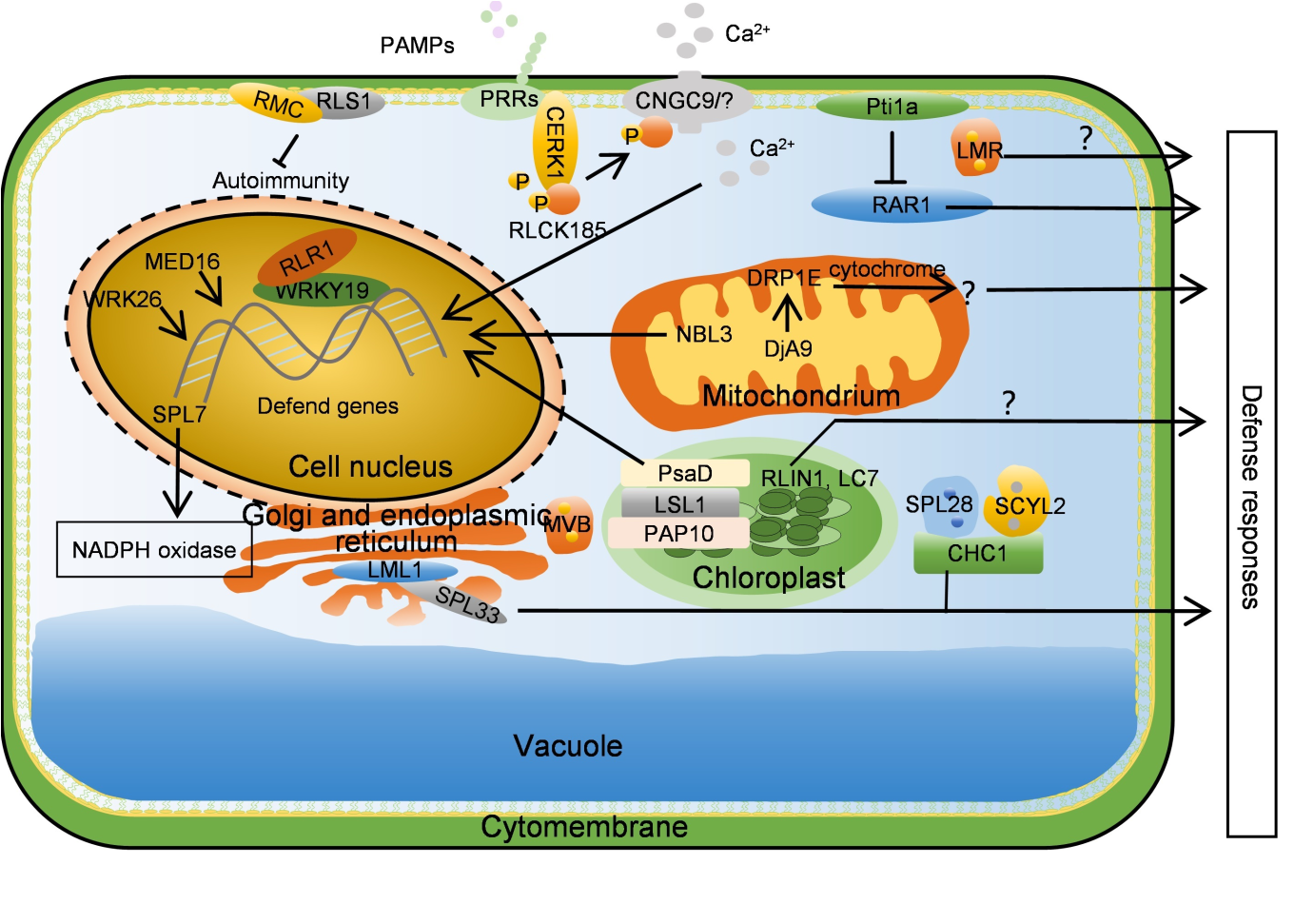
Fig. 3. Reactive oxygen species, clathrin-mediated vesicle transport, and other signaling pathways regulate necrotic lesion formation. WRK26, MED16, and NBL3 activate resistance genes, CNGC9 regulates resistance gene activation by regulating Ca2+ concentration, and RLR1 works with WRKY19 to activate resistance gene. SPL28- SCYL2 and LMR participate in the defense response by mediating vesicle transport. DjA9 and DRP1E affect mitochondrial size, thereby affecting reactive oxygen species, ultimately participating in immune regulation. LSL1 interacts with PsaD and PAP10 to affect chloroplast homeostasis, and RLIN1 and LC7 also participate in disease resistance by affecting chloroplast homeostasis. SPL7 regulates resistance by inhibiting NADPH enzyme activity, Pti1a inhibits RAR1 activity, while RMC and RLS1 both participate in disease resistance by inhibiting self-immunity. LML1 and SPL33 interact in the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby affecting protein folding. ‘→’ symbol indicates activation or next step, and ‘├’ symbol indicates inhibition.
| Gene name | Accession number | Protein function | Disease resistance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSD1, LOL1 | Os08g0159500 | Zinc finger protein | Magnaporthe oryzae | Wang et al, |
| OsHsfA4d, SPL7 | Os05g0530400 | Heat shock transcription factors | M. oryzae and Xanthomonas oryzae (Xoo) | Hoang et al, |
| RLIN1, LLM1 | Os04g0610800 | Coproporphyrinogen III oxidase | Xoo | Sun et al, |
| lc7, SPL32, Fd-GOGAT1, ABC1 | Os07g0658400 | Glutamate synthase | Xoo | Chen et al, |
| SPL33 | Os01g0116600 | Eef1a-like protein; Eukaryotic translation extension factor alpha protein | M. oryzae and blight | Wang et al, |
| LMM5 | Os04g0596500 | Eef1a-like protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Zhao et al, |
| LML1 | Os04g0659900 | Eukaryotic release factor 1 albumen | M. oryzae and Xoo | Qin et al, |
| spl26 | Os07g0141200 | Protein kinase | M. oryzae and Xoo | Chen et al, |
| SPL35 | Os03g0205000 | CUE domain protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Ma et al, |
| LMM24 | Os03g0364400 | Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase | M. oryzae | Zhang et al, |
| NRAMP1 | Os07g0258400 | Metal ion transporter; Natural resistance- associated macrophage proteins. | M. oryzae and Xoo | Chang et al, |
| SPL36 | Os12g0182300 | Receptor-like protein kinase | Xoo | Rao et al, |
| LSL1/GRDP1 | Os11g0621300 | Glycine-enriched domain proteins | M. oryzae and Xoo | Zhao et al, |
Table 2. Necrotic lesion genes are involved in reactive oxygen species pathways.
| Gene name | Accession number | Protein function | Disease resistance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSD1, LOL1 | Os08g0159500 | Zinc finger protein | Magnaporthe oryzae | Wang et al, |
| OsHsfA4d, SPL7 | Os05g0530400 | Heat shock transcription factors | M. oryzae and Xanthomonas oryzae (Xoo) | Hoang et al, |
| RLIN1, LLM1 | Os04g0610800 | Coproporphyrinogen III oxidase | Xoo | Sun et al, |
| lc7, SPL32, Fd-GOGAT1, ABC1 | Os07g0658400 | Glutamate synthase | Xoo | Chen et al, |
| SPL33 | Os01g0116600 | Eef1a-like protein; Eukaryotic translation extension factor alpha protein | M. oryzae and blight | Wang et al, |
| LMM5 | Os04g0596500 | Eef1a-like protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Zhao et al, |
| LML1 | Os04g0659900 | Eukaryotic release factor 1 albumen | M. oryzae and Xoo | Qin et al, |
| spl26 | Os07g0141200 | Protein kinase | M. oryzae and Xoo | Chen et al, |
| SPL35 | Os03g0205000 | CUE domain protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Ma et al, |
| LMM24 | Os03g0364400 | Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase | M. oryzae | Zhang et al, |
| NRAMP1 | Os07g0258400 | Metal ion transporter; Natural resistance- associated macrophage proteins. | M. oryzae and Xoo | Chang et al, |
| SPL36 | Os12g0182300 | Receptor-like protein kinase | Xoo | Rao et al, |
| LSL1/GRDP1 | Os11g0621300 | Glycine-enriched domain proteins | M. oryzae and Xoo | Zhao et al, |
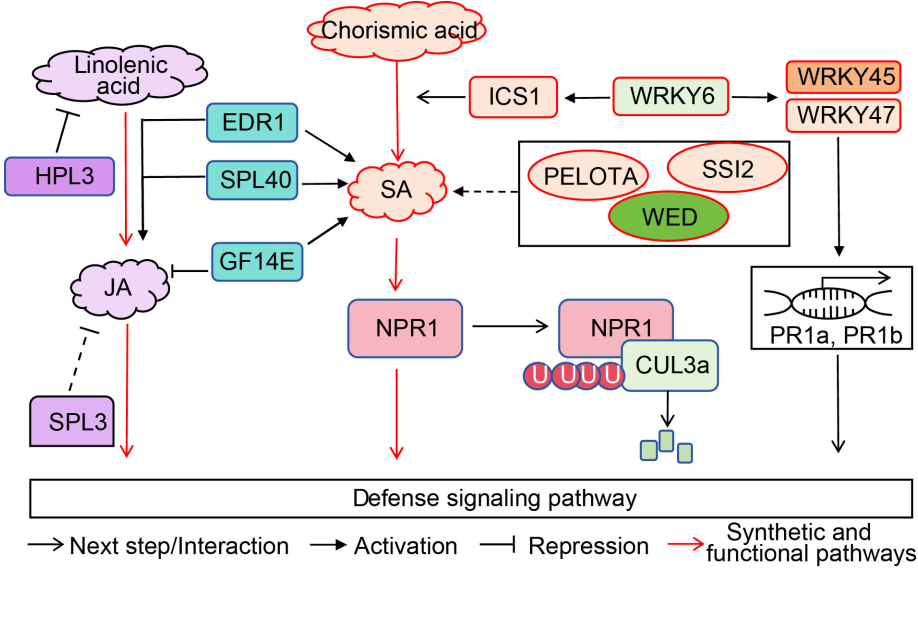
Fig. 4. Necrotic lesion genes are involved in hormone signaling pathways. NPR1 is involved in rice defense response by CUL3a ubiquitination degration and hormone level regulation. ICS1 is a key enzyme in the salicylic acid (SA) synthesis pathway and is regulated by WRKY6. WRKY6 also activates pathogenic resistance genes to participate in defense response by activating WRKY45 and WRKY47. SSI2, WED, PELOTA, and GF14E contribute to disease resistance by influencing salicylic acid content. HPL3 affects rice disease resistance by inhibiting linolenic acid. SPL3 and GF14E directly inhibit the jasmonic acid (JA) participation in rice defense response. EDR1 and SPL40 participate in the defense response by influencing SA and JA content.
| Gene name | Accession number | Protein function | Disease resistance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salicylic acid signaling pathway | ||||
| SSI2 | Os01g0919900 | Fatty acid dehydrogenase | Magnaporthe oryzae and Xanthomonas oryzae (Xoo) | Jiang et al, |
| NPR1, NH1 | Os01g0194300 | Salicylic acid receptor | M. oryzae and Xoo | Li et al, |
| WRKY6 | Os03g0798500 | WRKY transcriptional factor | M. oryzae | Choi et al, |
| CUL3a | Os02g0746000 | Cullin protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Liu et al, |
| PELOTA | Os04g0659900 | Eukaryotic translation release factor | Xoo | Zhang et al, |
| WED | Os11g0646300 | NLR protein | Xoo | Tang et al, |
| Jasmonic acid signaling pathway | ||||
| HPL3, cea62 | Os02g0110200 | Hydroperoxide lyase | Xoo | Liu et al, |
| LLB, SPL3, MTS1 | Os07g0247100 | Leucine carboxymethyltransferase | M. oryzae and Xoo | Tamiru et al, |
| Salicylic acid and jasmonic acid signaling pathways | ||||
| SPL3, EDR1, ACDR1, MAPKKK1 | Os03g0160100 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase | M. oryzae | Shen et al, |
| GF14e | Os02g0580300 | 14-3-3 protein | Xoo and corn sheath blight | Liu et al, |
| SPL40 | Os05g0312000 | Structural components of ribosomes | Xoo | Sathe et al, |
| Other hormone signaling pathway | ||||
| SL, ELL1, T5H, CYP71P1, CYP71A1 | Os12g0268000 | Tryptamine hydroxylase; Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase | M. oryzae and Xoo | Fujiwara et al, et al, 2020; Cui et al, |
| SPL29, UAP1 | Os08g0206900 | Uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase | Xoo | Wang et al, |
Table 3. Necrotic lesion genes are involved in hormonal pathways.
| Gene name | Accession number | Protein function | Disease resistance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salicylic acid signaling pathway | ||||
| SSI2 | Os01g0919900 | Fatty acid dehydrogenase | Magnaporthe oryzae and Xanthomonas oryzae (Xoo) | Jiang et al, |
| NPR1, NH1 | Os01g0194300 | Salicylic acid receptor | M. oryzae and Xoo | Li et al, |
| WRKY6 | Os03g0798500 | WRKY transcriptional factor | M. oryzae | Choi et al, |
| CUL3a | Os02g0746000 | Cullin protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Liu et al, |
| PELOTA | Os04g0659900 | Eukaryotic translation release factor | Xoo | Zhang et al, |
| WED | Os11g0646300 | NLR protein | Xoo | Tang et al, |
| Jasmonic acid signaling pathway | ||||
| HPL3, cea62 | Os02g0110200 | Hydroperoxide lyase | Xoo | Liu et al, |
| LLB, SPL3, MTS1 | Os07g0247100 | Leucine carboxymethyltransferase | M. oryzae and Xoo | Tamiru et al, |
| Salicylic acid and jasmonic acid signaling pathways | ||||
| SPL3, EDR1, ACDR1, MAPKKK1 | Os03g0160100 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase | M. oryzae | Shen et al, |
| GF14e | Os02g0580300 | 14-3-3 protein | Xoo and corn sheath blight | Liu et al, |
| SPL40 | Os05g0312000 | Structural components of ribosomes | Xoo | Sathe et al, |
| Other hormone signaling pathway | ||||
| SL, ELL1, T5H, CYP71P1, CYP71A1 | Os12g0268000 | Tryptamine hydroxylase; Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase | M. oryzae and Xoo | Fujiwara et al, et al, 2020; Cui et al, |
| SPL29, UAP1 | Os08g0206900 | Uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase | Xoo | Wang et al, |
| Gene name | Accession number | Protein function | Disease resistance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPL18 | Os10g0195600 | Acyltransferase | Magnaporthe oryzae and Xanthomonas oryzae (Xoo) | Mori et al, |
| PTI1A, TTM1 | Os05g0135800 | Protein kinase | M. oryzae and Xoo | Takahashi et al, |
| PLDβ1 | Os10g0524400 | Phospholipase D | M. oryzae and Xoo | Yamaguchi et al, |
| NLS1 | Os11g0249000 | CC-NB-LRR protein | Xoo | Tang et al, |
| SPL5, SF3b3, SL5 | Os07g0203700 | Splicing factor 3b subunit | M. oryzae and Xoo | Chen et al, |
| LMS | Os02g0639000 | Double-stranded RNA binding domain | M. oryzae | Undan et al, |
| CslF6 | Os08g0160500 | Cellulose-like synthase | Xoo | Vega-Sánchez et al, |
| DPF, bHLH025 | Os01g0196300 | bHLH transcription factor | M. oryzae | Yamamura et al, |
| WAK25 | Os03g0225700 | Cell wall associated receptor-like kinases | M. oryzae and Xoo | Harkenrider et al, |
| DRP1E | Os09g0572900 | Motor protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Li et al, |
| SPL30, ACL-A2, ACLA-3 | Os12g0566300 | ATP-citrate lyase | Xoo | Ruan et al, |
| CNGC9, CDS1 | Os09g0558300 | Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel | M. oryzae | Wang et al, |
| RLR1 | Os10g0163040 | CC-NB-LRR protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Du et al, |
| NBL3 | Os03g0159700 | Triangular pentapeptide repeat protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Qiu et al, |
| RBL1 | Os01g0758400 | CDP-DAG | M. oryzae and Xoo | Sha et al, |
| RLS1 | Os02g0203500 | NB-ARM protein | Xoo | Wang et al, |
| SPL38, MED16, SFR6 | Os10g0498700 | RNA polymerase II transcriptional mediator subunit | M. oryzae and Xoo | Zhang P et al, |
Table 4. Necrotic lesion genes are involved in other signaling pathways.
| Gene name | Accession number | Protein function | Disease resistance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPL18 | Os10g0195600 | Acyltransferase | Magnaporthe oryzae and Xanthomonas oryzae (Xoo) | Mori et al, |
| PTI1A, TTM1 | Os05g0135800 | Protein kinase | M. oryzae and Xoo | Takahashi et al, |
| PLDβ1 | Os10g0524400 | Phospholipase D | M. oryzae and Xoo | Yamaguchi et al, |
| NLS1 | Os11g0249000 | CC-NB-LRR protein | Xoo | Tang et al, |
| SPL5, SF3b3, SL5 | Os07g0203700 | Splicing factor 3b subunit | M. oryzae and Xoo | Chen et al, |
| LMS | Os02g0639000 | Double-stranded RNA binding domain | M. oryzae | Undan et al, |
| CslF6 | Os08g0160500 | Cellulose-like synthase | Xoo | Vega-Sánchez et al, |
| DPF, bHLH025 | Os01g0196300 | bHLH transcription factor | M. oryzae | Yamamura et al, |
| WAK25 | Os03g0225700 | Cell wall associated receptor-like kinases | M. oryzae and Xoo | Harkenrider et al, |
| DRP1E | Os09g0572900 | Motor protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Li et al, |
| SPL30, ACL-A2, ACLA-3 | Os12g0566300 | ATP-citrate lyase | Xoo | Ruan et al, |
| CNGC9, CDS1 | Os09g0558300 | Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel | M. oryzae | Wang et al, |
| RLR1 | Os10g0163040 | CC-NB-LRR protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Du et al, |
| NBL3 | Os03g0159700 | Triangular pentapeptide repeat protein | M. oryzae and Xoo | Qiu et al, |
| RBL1 | Os01g0758400 | CDP-DAG | M. oryzae and Xoo | Sha et al, |
| RLS1 | Os02g0203500 | NB-ARM protein | Xoo | Wang et al, |
| SPL38, MED16, SFR6 | Os10g0498700 | RNA polymerase II transcriptional mediator subunit | M. oryzae and Xoo | Zhang P et al, |

Fig. 5. Mining and application potential of necrotic lesion genes. In the process of agricultural production, necrotic lesion mutants can reduce the use of pesticides and save on environmental costs because of their high resistance characteristics. However, it is difficult to implement them in agricultural production under normal conditions. We need to analyze the disease resistance mechanism of necrotic lesion genes using current molecular technology, establish germplasm resource banks through high-throughput genome sequencing, genome-wide association studies (GWAS), and QTL mapping. By integrating gene editing with traditional breeding methods, we can create a new balance of ‘high-yield and high-resistance’.
| [1] | Bruggeman Q, Raynaud C, Benhamed M, Delarue M. 2015. To die or not to die? Lessons from lesion mimic mutants. Front Plant Sci, 6: 24. |
| [2] | Chang J D, Huang S, Yamaji N, Zhang W W, Ma J F, Zhao F J. 2020. OsNRAMP1 transporter contributes to cadmium and manganese uptake in rice. Plant Cell Environ, 43(10): 2476-2491. |
| [3] | Chen H L, Li C R, Liu L P, Zhao J Y, Cheng X Z, Jiang G H, Zhai W X. 2016. The Fd-GOGAT1 mutant gene lc7 confers resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice. Sci Rep, 6: 26411. |
| [4] | Chen T, Chen Z, Sathe A P, Zhang Z H, Li L J, Shang H H, Tang S Q, Zhang X B, Wu J L. 2019. Characterization of a novel gain-of-function spotted-leaf mutant with enhanced disease resistance in rice. Rice Sci, 26(6): 372-383. |
| [5] | Chen X F, Hao L, Pan J W, Zheng X X, Jiang G H, Jin Y, Gu Z M, Qian Q, Zhai W X, Ma B J. 2012. SPL5, a cell death and defense- related gene, encodes a putative splicing factor 3b subunit 3 (SF3b3) in rice. Mol Breed, 30(2): 939-949. |
| [6] | Choi C, Hwang S H, Fang I R, Kwon S I, Park S R, Ahn I, Kim J B, Hwang D J. 2015. Molecular characterization of Oryza sativa WRKY6, which binds to W-box-like element 1 of the Oryza sativa pathogenesis-related (PR) 10a promoter and confers reduced susceptibility to pathogens. New Phytol, 208(3): 846-859. |
| [7] | Chu C L, Huang R Y, Liu L P, Tang G L, Xiao J H, Yoo H, Yuan M. 2022. The rice heavy-metal transporter OsNRAMP1 regulates disease resistance by modulating ROS homoeostasis. Plant Cell Environ, 45(4): 1109-1126. |
| [8] | Cui Y J, Peng Y L, Zhang Q, Xia S S, Ruan B P, Xu Q K, Yu X Q, Zhou T T, Liu H, Zeng D L, Zhang G H, Gao Z Y, Hu J, Zhu L, Shen L, Guo L B, Qian Q, Ren D Y. 2021. Disruption of early lesion leaf 1, encoding a cytochrome p450 monooxygenase, induces ROS accumulation and cell death in rice. Plant J, 105(4): 942-956. |
| [9] | Damalas C A, Eleftherohorinos I G. 2011. Pesticide exposure, safety issues, and risk assessment indicators. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 8(5): 1402-1419. |
| [10] | Danon A, Miersch O, Felix G, Camp R G L, Apel K. 2005. Concurrent activation of cell death-regulating signaling pathways by singlet oxygen in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J, 41(1): 68-80. |
| [11] | Du D, Zhang C W, Xing Y D, Lu X, Cai L J, Yun H, Zhang Q L, Zhang Y Y, Chen X L, Liu M M, Sang X C, Ling Y H, Yang Z L, Li Y F, Lefebvre B, He G H. 2021. The CC-NB-LRR OsRLR1 mediates rice disease resistance through interaction with OsWRKY19. Plant Biotechnol J, 19(5): 1052-1064. |
| [12] | Fan J B, Bai P F, Ning Y S, Wang J Y, Shi X T, Xiong Y H, Zhang K, He F, Zhang C Y, Wang R Y, Meng X Z, Zhou J G, Wang M, Shirsekar G, Park C H, Bellizzi M, Liu W D, Jeon J S, Xia Y, Shan L B, Wang G L. 2018. The monocot-specific receptor-like kinase SDS2 controls cell death and immunity in rice. Cell Host Microbe, 23(4): 498-510.e5. |
| [13] | Fekih R, Tamiru M, Kanzaki H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kanzaki E, Saitoh H, Takagi H, Natsume S, Undan J R, Undan J, Terauchi R. 2015. The rice (Oryza sativa L.) LESION MIMIC RESEMBLING, which encodes an AAA-type ATPase, is implicated in defense response. Mol Genet Genomics, 290(2): 611-622. |
| [14] | Feng X J, Zhang L, Wei X L, Zhou Y, Dai Y, Zhu Z. 2020. OsJAZ13 negatively regulates jasmonate signaling and activates hypersensitive cell death response in rice. Int J Mol Sci, 21(12): 4379. |
| [15] | Fujiwara T, Maisonneuve S, Isshiki M, Mizutani M, Chen L T, Wong H L, Kawasaki T, Shimamoto K. 2010. Sekiguchi lesion gene encodes a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase that catalyzes conversion of tryptamine to serotonin in rice. J Biol Chem, 285(15): 11308-11313. |
| [16] | Gao C X. 2021. Genome engineering for crop improvement and future agriculture. Cell, 184(6): 1621-1635. |
| [17] | Gao X Q, Sun X Y, Peng Y Y, Huang Y Y, Liu M Q, Weng X Y. 2020. WRKY transcription factor functions as a transcriptional regulator of xylanase inhibitor RIXI, involved in rice disease resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae. J Plant Biol, 63(3): 177-188. |
| [18] | Harkenrider M, Sharma R, de Vleesschauwer D, Tsao L, Zhang X T, Chern M, Canlas P, Zuo S M, Ronald P C. 2016. Overexpression of rice wall-associated kinase 25 (OsWAK25) alters resistance to bacterial and fungal pathogens. PLoS One, 11(1): e0147310. |
| [19] | Hoang T V, Vo K T X, Rahman M M, Choi S H, Jeon J S. 2019. Heat stress transcription factor OsSPL7 plays a critical role in reactive oxygen species balance and stress responses in rice. Plant Sci, 289: 110273. |
| [20] | Im J H, Choi C, Park S R, Hwang D J. 2022. The OsWRKY6 transcriptional cascade functions in basal defense and Xa1- mediated defense of rice against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Planta, 255(2): 47. |
| [21] | Jiang C J, Shimono M, Maeda S, Inoue H, Mori M, Hasegawa M, Sugano S, Takatsuji H. 2009. Suppression of the rice fatty-acid desaturase gene OsSSI2 enhances resistance to blast and leaf blight diseases in rice. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact, 22(7): 820-829. |
| [22] | Jiao B B, Wang J J, Zhu X D, Zeng L J, Li Q, He Z H. 2012. A novel protein RLS1 with NB-ARM domains is involved in chloroplast degradation during leaf senescence in rice. Mol Plant, 5(1): 205-217. |
| [23] | Jiao R, Xu N, Hu J, Song Z L, Hu J Q, Rao Y C, Wang Y X. 2018. Advances in traits of lesion mimic mutants and its molecular mechanisms in rice. Chin J Rice Sci, 32(3): 285-295. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Jung Y H, Lee J H, Agrawal G K, Rakwal R, Kim J A, Shim J K, Lee S K, Jeon J S, Koh H J, Lee Y H, Iwahashi H, Jwa N S. 2005. The rice (Oryza sativa) blast lesion mimic mutant, blm, may confer resistance to blast pathogens by triggering multiple defense-associated signaling pathways. Plant Physiol Biochem, 43(4): 397-406. |
| [25] | Li R, Afsheen S, Xin Z J, Han X, Lou Y G. 2013. OsNPR1 negatively regulates herbivore-induced JA and ethylene signaling and plant resistance to a chewing herbivore in rice. Physiol Plant, 147(3): 340-351. |
| [26] | Li X Z, Yang D L, Sun L, Li Q, Mao B Z, He Z H. 2016. The systemic acquired resistance regulator OsNPR1 attenuates growth by repressing auxin signaling through promoting IAA-amido synthase expression. Plant Physiol, 172(1): 546-558. |
| [27] | Li Z Q, Ding B, Zhou X P, Wang G L. 2017. The rice dynamin- related protein OsDRP1E negatively regulates programmed cell death by controlling the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria. PLoS Pathog, 13(1): e1006157. |
| [28] | Li Z Y, Mo W P, Jia L Q, Xu Y C, Tang W J, Yang W Q, Guo Y L, Lin R C. 2019. Rice FLUORESCENT1 is involved in the regulation of chlorophyll. Plant Cell Physiol, 60(10): 2307-2318. |
| [29] | Liang C Z, Zheng G Y, Li W Z, Wang Y Q, Hu B, Wang H R, Wu H K, Qian Y W, Zhu X G, Tan D X, Chen S Y, Chu C C. 2015. Melatonin delays leaf senescence and enhances salt stress tolerance in rice. J Pineal Res, 59(1): 91-101. |
| [30] | Lin Z P, Zeng W, Guo H Y, Ye S H, Zhu G F, Zhai R R, Ye J, Wu M M, Zhang X M. 2022. Research progress on cloning and regulation mechanism of lesion mimic related genes in rice. Mol Plant Breed, 2022: 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Liu C T, Mao B G, Yuan D Y, Chu C C, Duan M J. 2022. Salt tolerance in rice: Physiological responses and molecular mechanisms. Crop J, 10(1): 13-25. |
| [32] | Liu J L, Park C H, He F, Nagano M, Wang M, Bellizzi M, Zhang K, Zeng X S, Liu W D, Ning Y S, Kawano Y, Wang G L. 2015. The RhoGAP SPIN6 associates with SPL11 and OsRac1 and negatively regulates programmed cell death and innate immunity in rice. PLoS Pathog, 11(2): e1004629. |
| [33] | Liu M M, Shi Z Y, Zhang X H, Wang M X, Zhang L, Zheng K Z, Liu J Y, Hu X M, Di C R, Qian Q, He Z H, Yang D L. 2019. Inducible overexpression of Ideal Plant Architecture1 improves both yield and disease resistance in rice. Nat Plants, 5(4): 389-400. |
| [34] | Liu Q, Yang J Y, Zhang S H, Zhao J L, Feng A Q, Yang T F, Wang X F, Mao X X, Dong J F, Zhu X Y, Leung H, Leach J E, Liu B. 2016. OsGF14e positively regulates panicle blast resistance in rice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 471(1): 247-252. |
| [35] | Liu Q E, Ning Y S, Zhang Y X, Yu N, Zhao C D, Zhan X D, Wu W X, Chen D B, Wei X J, Wang G L, Cheng S H, Cao L Y. 2017. OsCUL3a negatively regulates cell death and immunity by degrading OsNPR1 in rice. Plant Cell, 29(2): 345-359. |
| [36] | Liu X Q, Li F, Tang J Y, Wang W H, Zhang F X, Wang G D, Chu J F, Yan C Y, Wang T Q, Chu C C, Li C Y. 2012. Activation of the jasmonic acid pathway by depletion of the hydroperoxide lyase OsHPL3 reveals crosstalk between the HPL and AOS branches of the oxylipin pathway in rice. PLoS One, 7(11): e50089. |
| [37] | Ma H G, Li J, Ma L, Wang P L, Xue Y, Yin P, Xiao J H, Wang S P. 2021. Pathogen-inducible OsMPKK10.2-OsMPK 6 cascade phosphorylates the Raf-like kinase OsEDR1 and inhibits its scaffold function to promote rice disease resistance. Mol Plant, 14(4): 620-632. |
| [38] | Ma J, Wang Y F, Ma X D, Meng L Z, Jing R N, Wang F, Wang S, Cheng Z J, Zhang X, Jiang L, Wang J L, Wang J, Zhao Z C, Guo X P, Lin Q B, Wu F Q, Zhu S S, Wu C Y, Ren Y L, Lei C L, Zhai H Q, Wan J M. 2019. Disruption of gene SPL35, encoding a novel CUE domain-containing protein, leads to cell death and enhanced disease response in rice. Plant Biotechnol J, 17(8): 1679-1693. |
| [39] | Matsui H, Fujiwara M, Hamada S, Shimamoto K, Nomura Y, Nakagami H, Takahashi A, Hirochika H. 2014. Plasma membrane localization is essential for Oryza sativa Pto-interacting protein 1a-mediated negative regulation of immune signaling in rice. Plant Physiol, 166(1): 327-336. |
| [40] | McGrann G R D, Steed, Burt C, Nicholson P, Brown J K M. 2015. Differential effects of lesion mimic mutants in barley on disease development by facultative pathogens. J Exp Bot, 66(11): 3417-3428. |
| [41] | Meng X Z, Zhang S Q. 2013. MAPK cascades in plant disease resistance signaling. Annu Rev Phytopathol, 51: 245-266. |
| [42] | Mori M, Tomita C, Sugimoto K, Hasegawa M, Hayashi N, Dubouzet J G, Ochiai H, Sekimoto H, Hirochika H, Kikuchi S. 2007. Isolation and molecular characterization of a Spotted leaf 18 mutant by modified activation-tagging in rice. Plant Mol Biol, 63(6): 847-860. |
| [43] | Nalley L, Tsiboe F, Durand-Morat A, Shew A, Thoma G. 2016. Economic and environmental impact of rice blast pathogen (Magnaporthe oryzae) alleviation in the United States. PLoS One, 11(12): e0167295. |
| [44] | Qiao Y L, Jiang W Z, Lee J, Park B, Choi M S, Piao R H, Woo M O, Roh J H, Han L Z, Paek N C, Seo H S, Koh H J. 2010. SPL28 encodes a clathrin-associated adaptor protein complex 1, medium subunit μ1 (AP1M1) and is responsible for spotted leaf and early senescence in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol, 185(1): 258-274. |
| [45] | Qin P, Fan S J, Deng L C, Zhong G R, Zhang S W, Li M, Chen W L, Wang G L, Tu B, Wang Y P, Chen X W, Ma B T, Li S G. 2018. LML1, encoding a conserved eukaryotic release factor 1 protein, regulates cell death and pathogen resistance by forming a conserved complex with SPL33 in rice. Plant Cell Physiol, 59(5): 887-902. |
| [46] | Qiu T C, Zhao X S, Feng H J, Qi L L, Yang J, Peng Y L, Zhao W S. 2021. OsNBL3, a mitochondrion-localized pentatricopeptide repeat protein, is involved in splicing nad5 intron 4 and its disruption causes lesion mimic phenotype with enhanced resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Biotechnol J, 19(11): 2277-2290. |
| [47] | Rao Y C, Jiao R, Wang S, Wu X M, Ye H F, Pan C Y, Li S F, Xin D D, Zhou W Y, Dai G X, Hu J, Ren D Y, Wang Y X. 2021. SPL36 encodes a receptor-like protein kinase that regulates programmed cell death and defense responses in rice. Rice, 14(1): 34. |
| [48] | Ren D Y, Xie W, Xu Q K, Hu J, Zhu L, Zhang G H, Zeng D L, Qian Q. 2022. LSL1 controls cell death and grain production by stabilizing chloroplast in rice. Sci China: Life Sci, 65(11): 2148-2161. |
| [49] | Ren D Y, Ding C Q, Qian Q. 2023. Molecular bases of rice grain size and quality for optimized productivity. Sci Bull, 68(3): 314-350. |
| [50] | Reyes V P. 2023. Fantastic genes: Where and how to find them? Exploiting rice genetic resources for the improvement of yield, tolerance, and resistance to a wide array of stresses in rice. Funct Integr Genomic, 23(3): 238. |
| [51] | Ruan B P, Hua Z H, Zhao J, Zhang B, Ren D Y, Liu C L, Yang S L, Zhang A P, Jiang H Z, Yu H P, Hu J, Zhu L, Chen G, Shen L, Dong G J, Zhang G H, Zeng D L, Guo L B, Qian Q, Gao Z Y. 2019. OsACL-A2 negatively regulates cell death and disease resistance in rice. Plant Biotechnol J, 17(7): 1344-1356. |
| [52] | Saijo Y, Loo E P I. 2020. Plant immunity in signal integration between biotic and abiotic stress responses. New Phytol, 225(1): 87-104. |
| [53] | Sakuraba Y, Rahman M L, Cho S H, Kim Y S, Koh H J, Yoo S C, Paek N C. 2013. The rice faded green leaf locus encodes protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase B and is essential for chlorophyll synthesis under high light conditions. Plant J, 74(1): 122-133. |
| [54] | Sathe A P, Su X N, Chen Z, Chen T, Wei X J, Tang S Q, Zhang X B, Wu J L. 2019. Identification and characterization of a spotted- leaf mutant spl40 with enhanced bacterial blight resistance in rice. Rice, 12(1): 68. |
| [55] | Sha G, Sun P, Kong X J, Han X Y, Sun Q P, Fouillen L, Zhao J, Li Y, Yang L, Wang Y, Gong Q W, Zhou Y R, Zhou W Q, Jain R, Gao J, Huang R L, Chen X Y, Zheng L, Zhang W Y, Qin Z T, Zhou Q, Zeng Q D, Xie K B, Xu J D, Chiu T Y, Guo L, Mortimer J C, Boutté Y, Li Q, Kang Z S, Ronald P C, Li G T. 2023. Genome editing of a rice CDP-DAG synthase confers multipathogen resistance. Nature, 618: 1017-1023. |
| [56] | Shang H H, Li P P, Zhang X B, Xu X, Gong J Y, Yang S H, He Y Q, Wu J L. 2022. The gain-of-function mutation, OsSpl26, positively regulates plant immunity in rice. Int J Mol Sci, 23(22): 14168. |
| [57] | Shen W X, Shi X P, Du H B, Feng Z M, Chen Z X, Hu K M, Fan J B, Zuo S M. 2022. Research advances in gene cloning and occurrence mechanism of rice lesion mimic mutants. Jiangsu J Agric Sci, 38(3): 837-848. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [58] | Shen X L, Liu H B, Yuan B, Li X H, Xu C G, Wang S P. 2011. OsEDR1 negatively regulates rice bacterial resistance via activation of ethylene biosynthesis. Plant Cell Environ, 34(2): 179-191. |
| [59] | Sun C H, Liu L C, Tang J Y, Lin A H, Zhang F T, Fang J, Zhang G F, Chu C C. 2011. RLIN1, encoding a putative coproporphyrinogen III oxidase, is involved in lesion initiation in rice. J Genet Genomics, 38(1): 29-37. |
| [60] | Sun X B, Dai X M, Wang Y J, Han L B. 2010. Advances in programmed cell death in plants. Biotechnol Bull, (11): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [61] | Takahashi A, Agrawal G K, Yamazaki M, Onosato K, Miyao A, Kawasaki T, Shimamoto K, Hirochika H. 2007. Rice Pti1a negatively regulates RAR1-dependent defense responses. Plant Cell, 19(9): 2940-2951. |
| [62] | Tamiru M, Takagi H, Abe A, Yokota T, Kanzaki H, Okamoto H, Saitoh H, Takahashi H, Fujisaki K, Oikawa K, Uemura A, Natsume S, Jikumaru Y, Matsuura H, Umemura K, Terry M J, Terauchi R. 2016. A chloroplast-localized protein lesion and lamina bending affects defence and growth responses in rice. New Phytol, 210(4): 1282-1297. |
| [63] | Tang J Y, Zhu X D, Wang Y Q, Liu L C, Xu B, Li F, Fang J, Chu C C. 2011. Semi-dominant mutations in the CC-NB-LRR-type R gene, NLS1, lead to constitutive activation of defense responses in rice. Plant J, 66(6): 996-1007. |
| [64] | Tang J Y, Wang Y Q, Yin W C, Dong G J, Sun K, Teng Z F, Wu X J, Wang S M, Qian Y W, Pan X B, Qian Q, Chu C C. 2019. Mutation of a nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat immune receptor-type protein disrupts immunity to bacterial blight. Plant Physiol, 181(3): 1295-1313. |
| [65] | Tian D G, Yang F, Niu Y Q, Lin Y, Chen Z J, Li G, Luo Q, Wang F, Wang M. 2020. Loss function of SL (sekiguchi lesion) in the rice cultivar Minghui 86 leads to enhanced resistance to (hemi) biotrophic pathogens. BMC Plant Biol, 20(1): 507. |
| [66] | Tong X H, Qi J F, Zhu X D, Mao B Z, Zeng L J, Wang B H, Li Q, Zhou G X, Xu X J, Lou Y G, He Z H. 2012. The rice hydroperoxide lyase OsHPL3 functions in defense responses by modulating the oxylipin pathway. Plant J, 71(5): 763-775. |
| [67] | Undan J R, Tamiru M, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kosugi S, Takagi H, Yoshida K, Kanzaki H, Saitoh H, Fekih R, Sharma S, Undan J, Yano M, Terauchi R. 2012. Mutation in OsLMS, a gene encoding a protein with two double-stranded RNA binding motifs, causes lesion mimic phenotype and early senescence in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genes Genet Syst, 87(3): 169-179. |
| [68] | Vega-Sánchez M E, Verhertbruggen Y, Christensen U, Chen X W, Sharma V, Varanasi P, Jobling S A, Talbot M, White R G, Joo M, Singh S, Auer M, Scheller H V, Ronald P C. 2012. Loss of Cellulose Synthase-like F6 function affects mixed-linkage glucan deposition, cell wall mechanical properties, and defense responses in vegetative tissues of rice. Plant Physiol, 159(1): 56-69. |
| [69] | Wang J, Ye B Q, Yin J J, Yuan C, Zhou X G, Li W T, He M, Wang J C, Chen W L, Qin P, Ma B T, Wang Y P, Li S G, Chen X W. 2015. Characterization and fine mapping of a light-dependent leaf lesion mimic mutant 1 in rice. Plant Physiol Biochem, 97: 44-51. |
| [70] | Wang J, Zhou L, Shi H, Chern M, Yu H, Yi H, He M, Yin J J, Zhu X B, Li Y, Li W T, Liu J L, Wang J C, Chen X Q, Qing H, Wang Y P, Liu G F, Wang W M, Li P, Wu X J, Zhu L H, Zhou J M, Ronald P C, Li S G, Li J Y, Chen X W. 2018. A single transcription factor promotes both yield and immunity in rice. Science, 361:1026-1028. |
| [71] | Wang J C, Liu X, Zhang A, Ren Y L, Wu F Q, Wang G, Xu Y, Lei C L, Zhu S S, Pan T, Wang Y F, Zhang H, Wang F, Tan Y Q, Wang Y P, Jin X, Luo S, Zhou C L, Zhang X, Liu J L, Wang S, Meng L Z, Wang Y H, Chen X, Lin Q B, Zhang X, Guo X P, Cheng Z J, Wang J L, Tian Y L, Liu S J, Jiang L, Wu C Y, Wang E T, Zhou J M, Wang Y F, Wang H Y, Wan J M. 2019. A cyclic nucleotide-gated channel mediates cytoplasmic calcium elevation and disease resistance in rice. Cell Res, 29(10): 820-831. |
| [72] | Wang J J, Zhang L X, Wang L Y, Zhang L H, Zhu C N, He Z H, Jin Q S, Fan H H, Yu X. 2010. Response to illumination induction and effect of temperature on lesion formation of lrd (lesion resembling disease) in rice. Sci Agric Sin, 43(10): 2039-2044. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [73] | Wang L J, Pei Z Y, Tian Y C, He C Z. 2005. OsLSD1, a rice zinc finger protein, regulates programmed cell death and callus differentiation. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact, 18(5): 375-384. |
| [74] | Wang S, Lei C L, Wang J L, Ma J, Tang S, Wang C L, Zhao K J, Tian P, Zhang H, Qi C Y, Cheng Z J, Zhang X, Guo X P, Liu L L, Wu C Y, Wan J M. 2017. SPL33, encoding an eEF1A-like protein, negatively regulates cell death and defense responses in rice. J Exp Bot, 68(5): 899-913. |
| [75] | Wang X J, Gan P F, Tang C L, Kang Z S. 2020. Plant disease resistance and disease green prevention and control: Major Scientific issues and future research directions. Bull Natl Nat Sci Found China, 34(4): 381-392. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [76] | Wang Y Q, Teng Z F, Li H, Wang W, Xu F, Sun K, Chu J F, Qian Y W, Loake G J, Chu C C, Tang J Y. 2023. An activated form of NB-ARC protein RLS1 functions with cysteine-rich receptor- like protein RMC to trigger cell death in rice. Plant Commun, 4(2): 100459. |
| [77] | White R F. 1979. Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) induces resistance to tobacco mosaic virus in tobacco. Virology, 99(2): 410-412. |
| [78] | Xia S S, Liu H, Cui Y J, Yu H P, Rao Y C, Yan Y P, Zeng D L, Hu J, Zhang G H, Gao Z Y, Zhu L, Shen L, Zhang Q, Li Q, Dong G J, Guo L B, Qian Q, Ren D Y. 2022. UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase enhances rice survival at high temperature. New Phytol, 233(1): 344-359. |
| [79] | Xu G J, Zhong X H, Shi Y L, Liu Z, Jiang N, Liu J, Ding B, Li Z Q, Kang H X, Ning Y S, Liu W D, Guo Z J, Wang G L, Wang X L. 2020. A fungal effector targets a heat shock-dynamin protein complex to modulate mitochondrial dynamics and reduce plant immunity. Sci Adv, 6: eabb7719. |
| [80] | Yamaguchi T, Kuroda M, Yamakawa H, Ashizawa T, Hirayae K, Kurimoto L, Shinya T, Shibuya N. 2009. Suppression of a phospholipase D gene, OsPLDβ1, activates defense responses and increases disease resistance in rice. Plant Physiol, 150(1): 308-319. |
| [81] | Yamamura C, Mizutani E, Okada K, Nakagawa H, Fukushima S, Tanaka A, Maeda S, Kamakura T, Yamane H, Takatsuji H, Mori M. 2015. Diterpenoid phytoalexin factor, a bHLH transcription factor, plays a central role in the biosynthesis of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice. Plant J, 84(6): 1100-1113. |
| [82] | Yan J J, Fang Y X, Xue D W. 2022. Advances in the genetic basis and molecular mechanism of lesion mimic formation in rice. Plants, 11(16): 2169. |
| [83] | Yao Y, Zhou J H, Cheng C, Niu F, Zhang A P, Sun B, Tu R J, Wan J N, Li Y, Huang Y W, Xie K Z, Dai Y T, Zhang H, Hong J H, Pan X H, Zhu J J, Zhou H, Liu Z H, Cao L M, Chu H W. 2021. A conserved clathrin-coated vesicle component, OsSCYL2, regulates plant innate immunity in rice. Plant Cell Environ, 45(2): 542-555. |
| [84] | Yin Z C, Chen J, Zeng L R, Goh M, Leung H, Khush G S, Wang G L. 2000. Characterizing rice lesion mimic mutants and identifying a mutant with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact, 13(8): 869-876. |
| [85] | You Q Y, Zhai K R, Yang D L, Yang W B, Wu J N, Liu J Z, Pan W B, Wang J J, Zhu X D, Jian Y K, Liu J Y, Zhang Y Y, Deng Y W, Li Q, Lou Y G, Xie Q, He Z H. 2016. An E3 ubiquitin ligase- BAG protein module controls plant innate immunity and broad- spectrum disease resistance. Cell Host Microbe, 20(6): 758-769. |
| [86] | Yuan Y X, Zhong S H, Li Q, Zhu Z R, Lou Y G, Wang L Y, Wang J J, Wang M Y, Li Q L, Yang D L, He Z H. 2007. Functional analysis of rice NPR1-like genes reveals that OsNPR1/NH1 is the rice orthologue conferring disease resistance with enhanced herbivore susceptibility. Plant Biotechnol J, 5(2): 313-324. |
| [87] | Zavafer A, González-Solís A, Palacios-Bahena S, Saucedo-García M, Tapia de Aquino C, Vázquez-Santana S, King-Díaz B, Gavilanes-Ruiz M. 2020. Organized disassembly of photosynthesis during programmed cell death mediated by long chain bases. Sci Rep, 10: 10360. |
| [88] | Zhang H H, Wang F M, Song W Q, Yang Z H, Li L L, Ma Q, Tan X X, Wei Z Y, Li Y J, Li J M, Yan F, Chen J P, Sun Z T. 2023. Different viral effectors suppress hormone-mediated antiviral immunity of rice coordinated by OsNPR1. Nat Commun, 14(1): 3011. |
| [89] | Zhang P, Ma X D, Liu L N, Mao C J, Hu Y K, Yan B X, Guo J, Liu X Y, Shi J X, Lee G S, Pan X W, Deng Y W, Zhang Z G, Kang Z S, Qiao Y L. 2023. MEDIATOR SUBUNIT 16 negatively regulates rice immunity by modulating PATHOGENESIS RELATED 3 activity. Plant Physiol, 192(2): 1132-1150. |
| [90] | Zhang X B, Feng B H, Wang H M, Xu X, Shi Y F, He Y, Chen Z, Sathe A P, Shi L, Wu J L. 2018. A substitution mutation in OsPELOTA confers bacterial blight resistance by activating the salicylic acid pathway. J Integr Plant Biol, 60(2): 160-172. |
| [91] | Zhang Y, Liu Q E, Zhang Y X, Chen Y Y, Yu N, Cao Y R, Zhan X D, Cheng S H, Cao L Y. 2019. LMM24 encodes receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase 109, which regulates cell death and defense responses in rice. Int J Mol Sci, 20(13): 3243. |
| [92] | Zhao J Y, Liu P C, Li C R, Wang Y Y, Guo L Q, Jiang G H, Zhai W X. 2017. LMM5.1 and LMM5.4, two eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1A-like gene family members, negatively affect cell death and disease resistance in rice. J Genet Genomics, 44(2): 107-118. |
| [93] | Zhao X S, Qiu T C, Feng H J, Yin C F, Zheng X M, Yang J, Peng Y L, Zhao W S. 2021. A novel glycine-rich domain protein, GRDP1, functions as a critical feedback regulator for controlling cell death and disease resistance in rice. J Exp Bot, 72(2): 608-622. |
| [94] | Zhao Y, Zhu X B, Chen X W, Zhou J M. 2022. From plant immunity to crop disease resistance. J Genet Genomics, 49(8): 693-703. |
| [95] | Zhu X B, Yin J J, Liang S H, Liang R H, Zhou X G, Chen Z X, Zhao W, Wang J, Li W T, He M, Yuan C, Miyamoto K, Ma B T, Wang J C, Qin P, Chen W L, Wang Y P, Wang W M, Wu X J, Yamane H, Zhu L H, Li S G, Chen X W. 2016. The multivesicular bodies (MVBs)-localized AAA ATPase LRD6-6 inhibits immunity and cell death likely through regulating MVBs-mediated vesicular trafficking in rice. PLoS Genet, 12(9): e1006311. |
| [96] | Zhu X B, Ze M, Mawsheng C, Chen X W, Wang J. 2020. Deciphering rice lesion mimic mutants to understand molecular network governing plant immunity and growth. Rice Sci, 27(4): 278-288. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||