
Rice Science ›› 2016, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (4): 203-209.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2016.06.003
收稿日期:2015-06-28
接受日期:2015-09-14
出版日期:2016-07-28
发布日期:2016-04-11
. [J]. Rice Science, 2016, 23(4): 203-209.
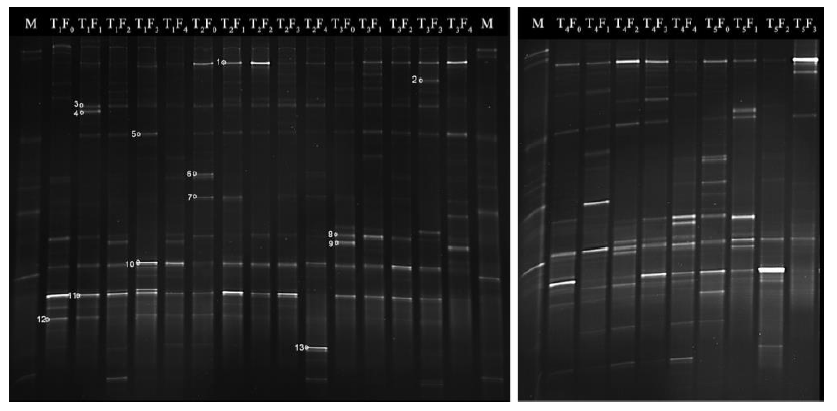
Fig. 1. Denatured gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) profile of 16S rDNA V3 fragments of bacteria associated with generations of A. nilaparvatae cultured under different temperatures. M, Marker; T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 corresponding to 22 °C, 25 °C, 28 °C, 31 °C and 34 °C, respectively; F0 to F4 corresponding to 0 to 4th generations. All marked bands were analyzed by sequence analysis.
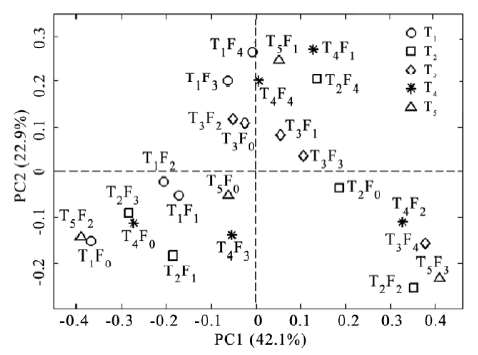
Fig. 2. Principal component analysis of denatured gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) profiles. Plots indicate the bacterial community structure of samples; Legends showed the different temperatures and generations.T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 corresponding to 22 °C, 25 °C, 28 °C, 31 °C and 34 °C, respectively; F0 to F4 corresponding to 0 to 4th generations.
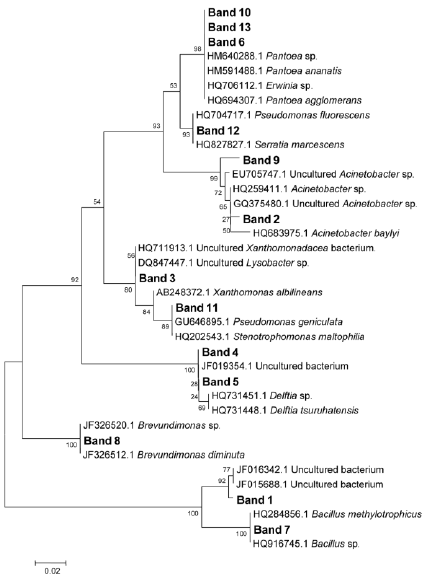
Fig. 3. Phylogenetic tree of bacteria associated with generations of A. nilaparvatae cultured under different temperatures. Distances were calculated using the maximum-likelihood method, and the tree was constructed using neighbor-jonining method.
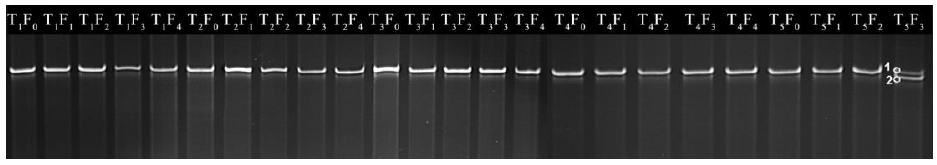
Fig. 4. Denatured gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) profile of wsp gene fragments of Wolbachia in generations of A. nilaparvatae cultured under different temperatures. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 corresponding to 22 °C, 25 °C, 28 °C, 31 °C and 34 °C, respectively; F0 to F4 corresponding to 0 to 4th generations. All marked bands were analyzed by sequence analysis.

Fig. 5. Phylogenetic tree of wsp gene of Wolbachia in generations of A. nilaparvatae cultured under different temperatures.Distances were calculated using the maximum-likelihood method, and the tree was constructed using neighbor-jonining method.
| 1 | Anbutsu H, Goto S, Fukatsu T.2008. High and low temperatures differently affect infection density and vertical transmission of male-killing spiroplasma symbionts in drosophila hosts.Appl Environ Microb, 74(19): 6053-6059. |
| 2 | Bandi C, McCall J W, Genchi C, Corona S, Venco L, Sacchi L.1999. Effects of tetracycline on the filarial worms Brugia pahangi and Dirofilaria immitis and their bacterial endosymbionts Wolbachia.Int J Parasitol, 29(2): 357-364. |
| 3 | Bottrell D G, Schoenly K G.2012. Resurrecting the ghost of the green revolution: The brown planthopper as a recurring threat to high-yielding rice production in tropical Asia.J Asia-Pac Entomol, 15(1): 122-140. |
| 4 | Braig H R, Zhou W G, Dobson S L, O’Neill S L.1998. Cloning and characterization of a gene encoding the major surface protein of the bacterial endosymbiont Wolbachia pipientis.J Bacteriol, 180(9): 2373-2378. |
| 5 | Brummel T, Ching A, Seroude L, Simon A F, Benzer S, Affiliations A.2004. Drosophila lifespan enhancement by exogenous bacteria.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 101(35): 12974-12979. |
| 6 | Chiappini E, Lin N Q.1998. Anagrus (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) of China, with descriptions of nine new species.Ann Entomol Soc Am, 91(5): 549-571. |
| 7 | Cook J M, Butcher R D J.1999. The transmission and effects of Wolbachia bacteria in parasitoids.Res Popul Ecol, 41(1): 15-28. |
| 8 | Copeland C S, Matthews R W, Gonzalez J M, Aluja M, Sivinski J.2008. Wolbachia in two populations of Melittobia digitata dahms (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae).Neotrop Entomol, 37(6): 633-640. |
| 9 | Cui B Y, Qian H T, Dong H, Cong B, Li X H.2007. Effect of high temperature shock on Trichogramma dendrolimi infected by wolbachia.Chin Bull Entomol, 44(5): 694-697. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 10 | de Almeida R P, van Lenteren J C, Stouthamer R.2010. Does Wolbachia infection affect Trichogramma atopovirilia behaviour.Braz J Biol, 70(2): 435-442. |
| 11 | de Almeida R P.2004. Trichogramma and its relationship with Wolbachia: Identification of Trichogramma species, phylogeny, transfer and costs of Wolbachia symbionts. The Netherlands: Wagenignen University. |
| 12 | Dillon R J, Dillon V M.2004. The gut bacteria of insects: Nonpathogenic interactions.Ann Rev Entomol, 49(1): 71-92. |
| 13 | Don R H, Cox P T, Wainwright B J, Baker K, Mattick J S.1991. ‘Touchdown’ PCR to circumvent spurious priming during gene amplification.Nucl Acids Res, 19(14): 4008. |
| 14 | Floate K D, Kyei-poku G K, Coghlin P C.2006. Overview and relevance of Wolbachia bacteria in biocontrol research.Biocontrol Sci Technol, 16(8): 767-788. |
| 15 | Gurr G M, Liu J, Read D M Y, Catindig J L A, Cheng J A, Lan L P, Heong K L.2011. Parasitoids of Asian rice planthopper (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) pests and prospects for enhancing biological control by ecological engineering.Ann Appl Biol, 158(2): 149-176. |
| 16 | Huigens M E, Hohmann C L, Luck R F, Gort G, Stouthamer R.2004. Reduced competitive ability due to Wolbachia infection in the parasitoid wasp Trichogramma kaykai.Entomol Exp Appl, 110(2): 115-123. |
| 17 | Kaltenpoth M, Gǒttler W, Herzner G, Strohm E.2005. Symbiotic bacteria protect wasp larvae from fungal infestation.Curr Biol, 15(5): 475-479. |
| 18 | Liu S P, Xu H X, Zheng X S, Lu Z X.2011. The research progress in Wolbachia bacteria in the parasitic wasps.J Environ Entomol, 33(1): 107-116. |
| 19 | Liu S P, Zheng X S, Yang Y J, Xu H X, Lu Z X.2012. Impact of temperature on the ecological fitness of successive generation of Anagrus nilaparvatae Pang et Wang (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae).Chin J Biol Control, 28(1): 20-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 20 | Lou Y G, Du M H, Turlings T C J, Cheng J A, Shen W F.2005. Exogenous application of jasmonic acid induces volatile emissions in rice and enhances parasitism of Nilaparvata lugens eggs by the parasitoid Anagrus nilaparvatae.J Chem Ecol, 31(9): 1985-2002. |
| 21 | Mao R Q, Gu D X, Zhang G R, Zhang W Q.2002. A preliminary investigation on structure and dynamics of egg parasitoid community on the brown planthopper in rice field.Act Entomol Sin, 45(3): 408-412. |
| 22 | Muyzer G, de Waal E C, Uitterlinden A G.1993. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA.Appl Environ Microbiol, 59(3): 695-700. |
| 23 | Muyzer G, Brinkhoff T, Nübel U, Santegoeds C, Schäfer H, Wawer C.2004. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) in microbial ecology. In: Kowalchuk G A, de Bruijn F J, Head I M, Akkermans A D L, Elsas J D. Molecular Microbial Ecology Manual. Dordrecht, Kluwer Academic Publishers: 743-769. |
| 24 | Oliver K M, Moran N A, Hunter M S.2005. Variation in resistance to parasitism in aphids is due to symbionts not host genotype.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 102(36): 12795-12800. |
| 25 | Pintureau B, Pizzol J, Bolland P.2003. Effects of endosymbiotic Wolbachia on the diapause in Trichogramma hosts and effects of the diapause on Wolbachia.Entomol Exp Appl, 106(3): 193-200. |
| 26 | Prado S S, Hung K Y, Daugherty M P, Almeida R P P.2010. Indirect effects of temperature on stink bug fitness, via maintenance of gut-associated symbionts.Appl Environ Microb, 76(4): 1261-1266. |
| 27 | Riemann L, Steward G F, Fandino L B, Campbell L, Landry M R, Azam F.1999. Bacterial community composition during two consecutive NE monsoon periods in the Arabian Sea studied by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) of rRNA genes.Deep Sea Res Pt II Top Stud Ocean, 46(8/9): 1791-1811. |
| 28 | Serbus L R, Casper-Lindley C, Landmann F, Sullivan W.2008. The genetics and cell biology of Wolbachia-host interactions.Ann Rev Genet, 42(1): 683-707. |
| 29 | Stouthamer R, Luck R F, Hamilton W D.1990. Antibiotics cause parthenogenetic Trichogramma (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) to revert to sex.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 87(7): 2424-2427. |
| 30 | Unckless R L, Boelio L M, Herren J K, Jaenike J.2009. Wolbachia as populations within individual insects: Causes and consequences of density variation in natural populations.Proc Roy Soc B: Biol Sci, 276: 2805-2811. |
| 31 | Vasquez C J, Stouthamer R, Jeong G, Morse J G.2011. Discovery of a CI-inducing Wolbachia and its associated fitness costs in the biological control agent Aphytis melinus DeBach (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae).Biol Control, 58(3): 192-198. |
| 32 | Walther G R, Post E, Convey P, Menzel A, Parmesan C, Beebee T J C, Fromentin J M, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Bairlein F.2002. Ecological responses to recent climate change.Nature, 416: 389-395. |
| 33 | Wang H, Jin L, Zhang H.2011. Comparison of the diversity of the bacterial communities in the intestinal tract of adult Bactrocera dorsalis from three different populations.J Appl Microbiol, 110(6): 1390-1401. |
| 34 | Werren J H, Windsor D, Guo L R.1995. Distribution of Wolbachia among neotropical arthropods.Proc Roy Soc B: Biol Sci, 262: 197-204. |
| 35 | Wiwatanaratanabutr I, Kittayapong P.2009. Effects of crowding and temperature on Wolbachia infection density among life cycle stages of Aedes albopictus.J Invertebr Pathol, 102(3): 220-224. |
| 36 | Xiang H, Huang Y P.2008. Symbiosis between gut microbiota and insects.Chin Bull Entomol, 45(5): 687-693. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 37 | Xiang Y, Shen Z R, Wang W J, Huang D Z, Li R J.2006. Effect of wasp symbionts Wolbachia on the thelytokous parthenogenesis of Trichogramma cacoeciae.Chin Bull Entomol, 43: 219-222. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 38 | Yu X P, Barrion A T, Lu Z X.2001. A taxonomic investigation on egg parasitoid, Anagrus of rice planthopper in Zhejiang Province.Chin Rice Res News Lett, 9(3): 8-9. |
| 39 | Zhou S X, Li Y, Zhang F.2009. Influences of high temperature shock on the reproduction and development of the Wolbachia- induced parthenogenetic parasitoid wasp, Encarsia formosa (Gahan).Acta Ecol Sin, 29: 4732-4737. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 40 | Zhou W G, Rousset F, O’Neill S.1998. Phylogeny and PCR-based classification of Wolbachia strains using wsp gene sequences.Proc Roy Soc B: Biol Sci, 265: 509-515. |
| 41 | Zhu Z R, Cheng J A, Chen X.1991. Influence of temperature and food on development, survival and fecundity of Anagrus nilaparvatae (Pang et wang).Acta Ecol Sin, 11: 66-72. |
| 42 | Zhuo W X, Zhao S X, Luo X N.1992. Influence of temperature on experimental population of the egg parasitoid, Anagrus nilaparvatae (Pang et wang).Entomol J East China, (1): 61-66. (in Chinese) |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||