
Rice Science ›› 2015, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 89-98.DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6308(14)60281-X
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles
N. Padhy Rabindra( ), Rath Shakti
), Rath Shakti
Received:2014-03-31
Accepted:2014-09-30
Online:2015-03-10
Published:2015-01-27
N. Padhy Rabindra, Rath Shakti. Probit Analysis of Carbamate-Pesticide-Toxicity at Soil-Water Interface to N2-Fixing Cyanobacterium Cylindrospermum sp[J]. Rice Science, 2015, 22(2): 89-98.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.org/EN/10.1016/S1672-6308(14)60281-X
| Pesticide | Medium | Liquid culture | Agar medium | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GEC | NOEC | Partial lethal range | LC100 | HPC | LC100 | ||||
| MIC | HPC | ||||||||
| Carbaryl | C-N | NO | 10 | 20 | 80 | 100 | 80 | 100 | |
| C+N | NO | 10 | 20 | 100 | 120 | 80 | 100 | ||
| Carbofuran | C-N | 25 | 50 | 100 | 1 500 | 2 000 | 500 | 600 | |
| C+N | 25 | 50 | 100 | 2 000 | 3 000 | 500 | 600 | ||
| Ziram | C-N | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.5 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.17 | |
| C+N | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.5 | 0.13 | 0.2 | 0.15 | 0.17 | ||
| Zineb | C-N | NO | 0.5 | 1 | 15 | 25 | 5 | 10 | |
| C+N | NO | 0.5 | 5 | 20 | 30 | 5 | 10 | ||
| Mancozeb | C-N | NO | 0.5 | 1 | 7 | 9 | 5 | 7 | |
| C+N | NO | 0.5 | 1 | 7 | 9 | 5 | 7 | ||
Table 1 Toxic ranges of Cylindrospermum sp. due to carbamate pesticides in liquid and agar media. (µg/mL)
| Pesticide | Medium | Liquid culture | Agar medium | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GEC | NOEC | Partial lethal range | LC100 | HPC | LC100 | ||||
| MIC | HPC | ||||||||
| Carbaryl | C-N | NO | 10 | 20 | 80 | 100 | 80 | 100 | |
| C+N | NO | 10 | 20 | 100 | 120 | 80 | 100 | ||
| Carbofuran | C-N | 25 | 50 | 100 | 1 500 | 2 000 | 500 | 600 | |
| C+N | 25 | 50 | 100 | 2 000 | 3 000 | 500 | 600 | ||
| Ziram | C-N | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.5 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.17 | |
| C+N | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.5 | 0.13 | 0.2 | 0.15 | 0.17 | ||
| Zineb | C-N | NO | 0.5 | 1 | 15 | 25 | 5 | 10 | |
| C+N | NO | 0.5 | 5 | 20 | 30 | 5 | 10 | ||
| Mancozeb | C-N | NO | 0.5 | 1 | 7 | 9 | 5 | 7 | |
| C+N | NO | 0.5 | 1 | 7 | 9 | 5 | 7 | ||
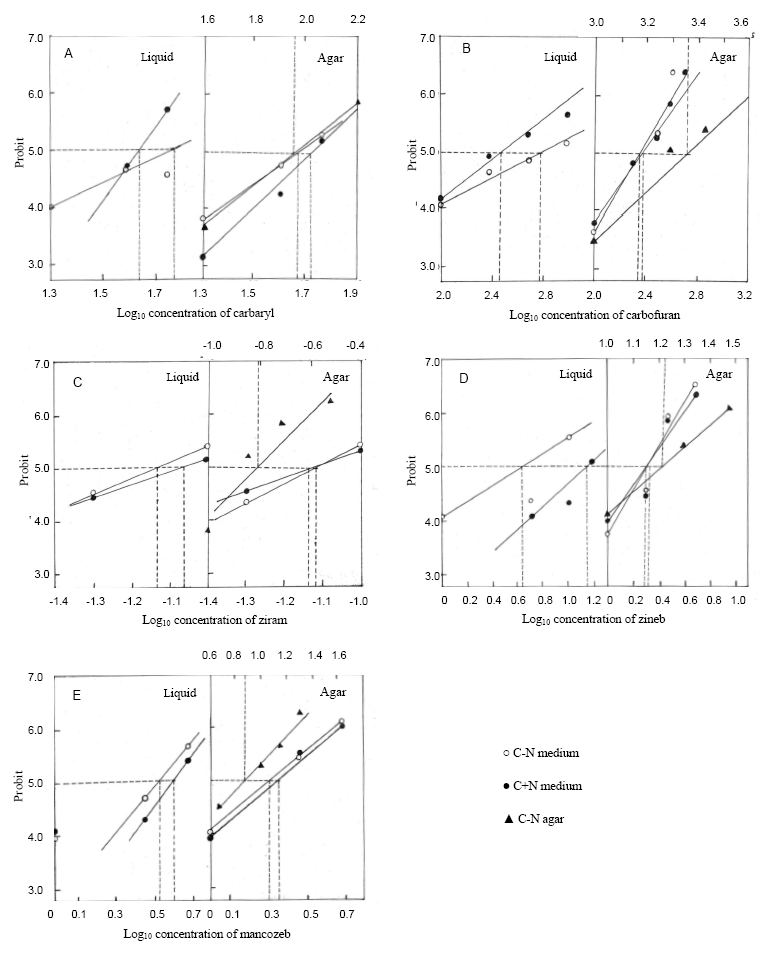
Fig. 1. Probits of percent lethality plotted against log10 concentrations of five pesticides carbaryl, carbofuran, ziram, zineb and mancozeb in toxicity studies of Cylindrospermum sp. in liquid medium and agar medium. Values of LC25, LC50 (extrapolation by broken lines) and LC75 were extrapolated from the respective lines drawn for connecting probit points. The upper-side scale of log10 concentration was the data of soil-water interface.
| Pesticide | Medium | Lethal range in liquid medium | Lethal range in agar medium | Lethality in soil-water interface | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC25 | LC50 | LC75 | LC100 | LC25 | LC50 | LC75 | LC100 | LC50 | LC100 | ||||
| Carbaryl | C-N | 28.2 (1.45) | 56.2 (1.75) | 58.9 (1.77) | 100 | 27.5 (1.44) | 44.7 (1.65) | 67.6 (1.83) | 100 | 91.2 | 200 | ||
| C+N | 33.9 (1.53) | 43.7 (1.64) | - | 120 | 34.7 (1.54) | 55.0 (1.74) | 70.8 (1.85) | 100 | - | - | |||
| Carbofuran | C-N | 158.5 (2.20) | 588.8 (2.77) | - | 1 500.0 | 147.9 (2.17) | 239.9 (2.38) | 363.1 (2.56) | 600 | 2 317.0 (3.36) | 6 000.0 | ||
| C+N | 123.0 (2.09) | 288.4 (2.46) | 758.8 (2.88) | 2 000.0 | 147.9 (2.17) | 223.9 (2.35) | 338.8 (2.53) | 600 | - | - | |||
| Ziram | C-N | 0.05 (-1.35) | 0.07 (-1.15) | - | 0.17 | 0.05 (-1.29) | 0.07 (-1.12) | - | 0.17 | 0.15 (-0.82) | 0.5 | ||
| C+N | 0.04 (-1.35) | 0.08 (-1.06) | - | 0.2 | 0.04 (-1.38) | 0.07 (-1.12) | - | 0.17 | - | - | |||
| Zineb | C-N | 1.6 (0.20) | 4.2 (0.62) | 13.5 (1.13) | 25 | 1.5 (0.16) | 1.8 (0.25) | 3.2 (0.50) | 10 | 16.4 (1.21) | 50 | ||
| C+N | - | 13.4 (1.13) | - | 30 | 1.5 (0.17) | 1.8 (0.26) | 3.0 (0.47) | 10 | - | - | |||
| Mancozeb | C-N | 2.3 (0.37) | 3.4 (0.53) | 4.8 (0.68) | 9 | 0.9 (0.09) | 2.3 (0.37) | 3.3 (0.52) | 7 | 7.2 (0.86) | 25 | ||
| C+N | 2.6 (0.42) | 4.2 (0.62) | 5.6 (0.75) | 9 | 1.3 (0.10) | 2.0 (0.31) | 3.0 (0.47) | 7 | - | - | |||
Table 2 Toxic ranges of Cylindrospermum sp. of two insecticides and three fungicides in liquid and agar C-N and C+N media as well as toxicity at soil-water interface monitored on C-N agar media.
| Pesticide | Medium | Lethal range in liquid medium | Lethal range in agar medium | Lethality in soil-water interface | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC25 | LC50 | LC75 | LC100 | LC25 | LC50 | LC75 | LC100 | LC50 | LC100 | ||||
| Carbaryl | C-N | 28.2 (1.45) | 56.2 (1.75) | 58.9 (1.77) | 100 | 27.5 (1.44) | 44.7 (1.65) | 67.6 (1.83) | 100 | 91.2 | 200 | ||
| C+N | 33.9 (1.53) | 43.7 (1.64) | - | 120 | 34.7 (1.54) | 55.0 (1.74) | 70.8 (1.85) | 100 | - | - | |||
| Carbofuran | C-N | 158.5 (2.20) | 588.8 (2.77) | - | 1 500.0 | 147.9 (2.17) | 239.9 (2.38) | 363.1 (2.56) | 600 | 2 317.0 (3.36) | 6 000.0 | ||
| C+N | 123.0 (2.09) | 288.4 (2.46) | 758.8 (2.88) | 2 000.0 | 147.9 (2.17) | 223.9 (2.35) | 338.8 (2.53) | 600 | - | - | |||
| Ziram | C-N | 0.05 (-1.35) | 0.07 (-1.15) | - | 0.17 | 0.05 (-1.29) | 0.07 (-1.12) | - | 0.17 | 0.15 (-0.82) | 0.5 | ||
| C+N | 0.04 (-1.35) | 0.08 (-1.06) | - | 0.2 | 0.04 (-1.38) | 0.07 (-1.12) | - | 0.17 | - | - | |||
| Zineb | C-N | 1.6 (0.20) | 4.2 (0.62) | 13.5 (1.13) | 25 | 1.5 (0.16) | 1.8 (0.25) | 3.2 (0.50) | 10 | 16.4 (1.21) | 50 | ||
| C+N | - | 13.4 (1.13) | - | 30 | 1.5 (0.17) | 1.8 (0.26) | 3.0 (0.47) | 10 | - | - | |||
| Mancozeb | C-N | 2.3 (0.37) | 3.4 (0.53) | 4.8 (0.68) | 9 | 0.9 (0.09) | 2.3 (0.37) | 3.3 (0.52) | 7 | 7.2 (0.86) | 25 | ||
| C+N | 2.6 (0.42) | 4.2 (0.62) | 5.6 (0.75) | 9 | 1.3 (0.10) | 2.0 (0.31) | 3.0 (0.47) | 7 | - | - | |||
| Pesticide | Pesticide (log10 concentration) (µg/mL) | Number of colonies on C-N agar | Probit of percent lethality | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Higher inoculation | Lower inoculation | |||
| Carbaryl | 0 | CG | 224 (0.0) | - |
| (inocula on filter paper: 3.6 × 103 and 1.8 × 103 CFU/mL) | 40 (1.60) | CG | 201 (10.3) | 3.7354 |
| 80 (1.90) | CG | 172 (23.3) | 4.271 | |
| 120 (2.08) | 258 | 83 (63.0) | 5.3319 | |
| 160 (2.20) | 106 | 41 (81.7) | 5.904 | |
| 180 (2.26) | 19 | 7 (96.9) | 6.8663 | |
| 200 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| Carbofuran | 0 | CG | 235 (0.0) | - |
| (inocula on filter paper: 4.0 × 103 and 2.0 × 103 CFU/mL) | 1 000 (3.00) | CG | 220 (6.4) | 3.478 |
| 2 000 (3.30) | CG | 117 (50.3) | 5.0075 | |
| 3 000 (3.48) | CG | 85 (63.9) | 5.3558 | |
| 4 000 (3.60) | 102 | 51 (78.3) | 5.7824 | |
| 4 500 (3.65) | 56 | 35 (85.2) | 6.045 | |
| 5 000 (3.70) | 12 | 2 (99.2) | - | |
| 6 000 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| Ziram | 0 | CG | 207 (0.0) | - |
| (inocula on filter paper: 3.8 × 103 and 1.4 × 103 CFU/mL) | 0.10 (-1.00) | CG | 183 (11.6) | 3.8048 |
| 0.15 (-0.82) | CG | 91 (56.1) | 5.1535 | |
| 0.20 (-0.70) | 78 | 43 (79.3) | 5.8169 | |
| 0.30 (-0.52) | 47 | 21 (89.9) | 6.2759 | |
| 0.40 (-0.40) | 3 | 0 | - | |
| 0.5 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| Zineb | 0 | CG | 221 (0.0) | - |
| (inocula on filter paper: 3.2 × 103 and 1.6 × 103 CFU/mL) | 10 (1.00) | CG | 179 (19.1) | 4.1258 |
| 20 (1.30) | 167 | 92 (58.4) | 5.2121 | |
| 30 (1.47) | 62 | 26 (88.3) | 6.1901 | |
| 40 (1.60) | 34 | 12 (94.6) | - | |
| 50 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| Mancozeb | 0 | CG | 243 (0.0) | - |
| (inocula on filter paper: 4.1 × 103 and 2.0 × 103 CFU/mL) | 5 (0.70) | CG | 158 (35.0) | 4.6147 |
| 10 (1.00) | 214 | 93 (61.8) | 5.3002 | |
| 15 (1.18) | 105 | 63 (74.1) | 5.6464 | |
| 20 (1.30) | 23 | 17 (93.1) | 6.3469 | |
| 25 | 0 | 0 | - | |
Table 3 Colony-counts on C-N agar plates of Cylindrospermum sp. after contact of filaments with wet soil (soil-water interface) with individual pesticides.
| Pesticide | Pesticide (log10 concentration) (µg/mL) | Number of colonies on C-N agar | Probit of percent lethality | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Higher inoculation | Lower inoculation | |||
| Carbaryl | 0 | CG | 224 (0.0) | - |
| (inocula on filter paper: 3.6 × 103 and 1.8 × 103 CFU/mL) | 40 (1.60) | CG | 201 (10.3) | 3.7354 |
| 80 (1.90) | CG | 172 (23.3) | 4.271 | |
| 120 (2.08) | 258 | 83 (63.0) | 5.3319 | |
| 160 (2.20) | 106 | 41 (81.7) | 5.904 | |
| 180 (2.26) | 19 | 7 (96.9) | 6.8663 | |
| 200 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| Carbofuran | 0 | CG | 235 (0.0) | - |
| (inocula on filter paper: 4.0 × 103 and 2.0 × 103 CFU/mL) | 1 000 (3.00) | CG | 220 (6.4) | 3.478 |
| 2 000 (3.30) | CG | 117 (50.3) | 5.0075 | |
| 3 000 (3.48) | CG | 85 (63.9) | 5.3558 | |
| 4 000 (3.60) | 102 | 51 (78.3) | 5.7824 | |
| 4 500 (3.65) | 56 | 35 (85.2) | 6.045 | |
| 5 000 (3.70) | 12 | 2 (99.2) | - | |
| 6 000 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| Ziram | 0 | CG | 207 (0.0) | - |
| (inocula on filter paper: 3.8 × 103 and 1.4 × 103 CFU/mL) | 0.10 (-1.00) | CG | 183 (11.6) | 3.8048 |
| 0.15 (-0.82) | CG | 91 (56.1) | 5.1535 | |
| 0.20 (-0.70) | 78 | 43 (79.3) | 5.8169 | |
| 0.30 (-0.52) | 47 | 21 (89.9) | 6.2759 | |
| 0.40 (-0.40) | 3 | 0 | - | |
| 0.5 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| Zineb | 0 | CG | 221 (0.0) | - |
| (inocula on filter paper: 3.2 × 103 and 1.6 × 103 CFU/mL) | 10 (1.00) | CG | 179 (19.1) | 4.1258 |
| 20 (1.30) | 167 | 92 (58.4) | 5.2121 | |
| 30 (1.47) | 62 | 26 (88.3) | 6.1901 | |
| 40 (1.60) | 34 | 12 (94.6) | - | |
| 50 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| Mancozeb | 0 | CG | 243 (0.0) | - |
| (inocula on filter paper: 4.1 × 103 and 2.0 × 103 CFU/mL) | 5 (0.70) | CG | 158 (35.0) | 4.6147 |
| 10 (1.00) | 214 | 93 (61.8) | 5.3002 | |
| 15 (1.18) | 105 | 63 (74.1) | 5.6464 | |
| 20 (1.30) | 23 | 17 (93.1) | 6.3469 | |
| 25 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| 1 | Bambaradeniya C N B, Amerasinghe F P.2003. Biodiversity Associated with the Rice Field Agroecosystem in Asian Countries: A Brief Review. Colombo, Sri Lanka: International Water Management Institute, Working Paper 63. |
| 2 | Bhunia A K, Roy D, Banerjee S K.1993. Carbaryl-induced effects on glutathione content, glutathione reductase and superoxide dismutase activity of the cyanobacteriumNostoc muscorum. Lett Appl Microbiol, 16: 10-13. |
| 3 | Brusslan J, Haselkorn R.1988. Molecular genetics of herbicide resistance in cyanobacteria.Photosynth Res, 17: 115-124. |
| 4 | Dean R, VanKan J A L, Pretorius Z A, Hammond-Kosack K E, Di Pietro A, Spanu P D, Rudd J J, Dickman M, Kahmann R, Ellis J, Foster G D.2012. The top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology.Mol Plant Pathol, 13: 414-430. |
| 5 | Debnath M, Mandal N C, Ray S.2012. Effect of fungicides and insecticides on growth and enzyme activity of four cyanobacteria.Ind J Microbiol, 52: 275-280. |
| 6 | Ferrero A, Tinarelli A.2007. Rice cultivation in the E.U. ecological conditions and agronomical practices. In: Capri E, Karpouzas D G. Pesticide Risk Assessment in Rice Paddies: Theory and Practice. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier: 1-24. |
| 7 | Galhano V, Gomes L, Eduardo F V, Videira R, Peixoto F.2011. Impact of herbicides on non-target organisms in sustainable irrigated rice production systems: State of knowledge and future Prospects. In: Kortekamp A. Herbicides and Environment. Croatia: Intech: 45-72. |
| 8 | Gray J S.2002. Biomagnification in marine systems: The perspective of an ecologist.Mar Pollut Bull, 45: 46-52. |
| 9 | Habib K, Kumar S, Manikar N, Zutshi S, Fatma T.2011. Biochemical effect of carbaryl on oxidative stress, antioxidant enzymes and osmolytes of cyanobacterium Calothrix brevissima.Bull Environ Contam Toxicol, 87: 615-620. |
| 10 | Kar S, Singh P K.1978. Toxicity of carbofuran to blue-green alga Nostoc muscorum.Bull Environ Contam Toxicol, 20: 707-714. |
| 11 | Kim J D, Lee C G.2006. Diversity of heterocystous filamentous cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) from rice paddy fields and their differential susceptibility to ten fungicides used in Korea.J Microbiol Biotech, 16: 240-246. |
| 12 | Koenig F.2001. Eukaryotic algae, cyanobacteria and pesticides. In: Rai L C, Gaur J P. Algal Adaptation to Environmental Stresses: Physiological, Biochemical and Molecular Mechanisms. Berlin: Springer: 389-406. |
| 13 | Ma J Y.2005. Differential sensitivity of three cyanobacterial and five green algal species to organotins and pyrethroids pesticides.Sci Total Environ, 341: 109-117. |
| 14 | Ma J Y, Lu N H, Qin W D, Xu R F, Wang Y B, Chen X N.2006. Differential responses of eight cyanobacterial and green algal species, to carbamate insecticides.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 63: 268-274. |
| 15 | Megharaj M, Rao A P, Rao A S, Venkateswarlu K.1990. Interaction effects of carbaryl and its hydrolysis product, 1-naphthol, towards three isolates of microalgae from rice soil.Agric Ecosys Environ, 31: 293-300. |
| 16 | Megharaj M, Venkateswarlu K, Naidu R.2011. Effects of carbaryl and 1-naphthol on soil population of cyanobacteria and microalgae and select cultures of diazotrophic cyanobacteria.Bull Environ Contam Toxicol, 87: 324-329. |
| 17 | Millner P D, Olenchock S A, Epstein E, Haines R J, Walker L, Ooi B L, Horne E, Maritato M.1994. Bioaerosols associated with composting facilities.Compost Sci Util, 2: 6-47. |
| 18 | Mishra M, Maharana S, Padhy R N.2005. Monitoring of chemical fertilizers on toxicity of carbamate fungicides to the cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermum sp.Fresenius Environ Bull, 14: 788-794. |
| 19 | Nirmal Kumar J I, Bora A, Amb M K, Kumar R N.2011. An evaluation of pesticide stress induced proteins in three cyanobacterial species Anabaena fertilissima, Aulosira fertilissima and Westiellopsis prolifica using SDS-PAGE.Adv Environ Biol, 5: 739-745. |
| 20 | Nirmal Kumar J I, Bora A, Kumar R N, Amb M K.2012. Differential effects of agricultural pesticides endosulfan and tebuconazole on photosynthetic pigments, metabolism and assimilating enzymes of three heterotrophic, filamentous cyanobacteria.J Biol Environ Sci, 6: 67-75. |
| 21 | Nirmal Kumar J I, Bora A, Kumar R N, Amb M K, Khan S.2013. Toxicity analysis of pesticides on cyanobacterial species by 16S rDNA molecular characterization.Proc Int Acad Ecol Environ Sci, 3: 101-132. |
| 22 | Othma R, Naher U A, Yusoff S Z.2013. Effect of urea-N on growth and indole acetic acid production of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (Sb16) isolated from rice growing soils in Malaysia. Chilean J Agric Res, 73: 187-192. |
| 23 | Padhy R N.1985a. Cyanobacteria and pesticides.Resid Rev, 95: 1-44. |
| 24 | Padhy R N.1985b. Agriculture and environment: Cyanobacteria employed as fertilizers and waste disposers.Nature (London), 317: 475-476. |
| 25 | Padhy R N, Nayak N, Rath S.2014. Antagonism at combined effects of chemical fertilizer and carbamate insecticides on the rice field N2-fixing cyanobacterium Cylindrospermum sp. in vitro.Interdisc Toxicol, 7: 101-107. |
| 26 | Panigrahy K C, Padhy R N.2000. Toxicity of carbamate pesticides to cells, heterocysts and akinetes of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermum sp.Algol Stud, 99: 95-115. |
| 27 | Panigrahi S, Padhy S N, Padhy R N.2003. Toxicity of methyl parathion to cells, heterocysts and akinetes of cyanobacterium Cylindrospermum sp. and probit analysis of toxicity.Ann Appl Biol, 143: 195-202. |
| 28 | Pathak M D, Khan Z R.1994. Insect Pests of Rice. Phillipines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| 29 | Pattnaik U, Singh P K.1978. Effect of nitrate nitrogen of the growth, heterocyst differentiation and nitrogen fixation in rice blue-green alga Gloeotrichia sp.Algol Studies, 20: 318-327. |
| 30 | Pipe A E.1992. Pesticide effects on soil algae and cyanobacteria.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol, 127: 95-170. |
| 31 | Prasanna R, Sharma E, Sharma P, Kumar A, Kumar R, Gupta V, Pal R K, Shivay Y S, Nain L.2013. Soil fertility and establishment potential of inoculated cyanobacteria in rice crop grown under non-flooded conditions.Paddy Water Environ, 11: 175-183. |
| 32 | Rath S, Sahu M C, Dubey D, Debata N K, Padhy R N.2011. Which values should be used as the lethal concentration 50 (LC50) with bacteria?Inter-Disciplin Sci-Comput Life Sci, 3: 138-143. |
| 33 | Swaminathan M S.1984. Rice.Sci Am, 250: 81-93. |
| 34 | Subramanian G, Sekar S, Sampoornam S.1994. Biodegradation and utilization of organophosphorus pesticides by cyanobacteria.Int Biodegrad Biodetertor, 33: 129-143. |
| 35 | USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). 1999. The National Survey of Mercury Concentrations in Fish: Data Base Summary 1990-1995. EPA Publication 823-R-99-014, U.S. EPA: Washington, DC. www.epa.gov/waterscience/fish/mercurydata. html. |
| 36 | Ware G W, Whitacre D M.2004. The Pesticide Book. 6th ed. Cornell University, US: Meister Pro Information Resources: 1-488. |
| 37 | Whitton B A, Aziz A, Francis P, Rother J A, Simon J W, Tahmida Z N.1988. Ecology of deepwater rice-fields in Bangladesh: 1. Physical and chemical environment.Hidrobiol, 169: 3-67. |
| 38 | Zeigler R S, Barclay A.2008. The relevance of rice.Rice, 1: 3-10. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||