
Rice Science ›› 2023, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (2): 104-112.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2023.01.003
• Research Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Van Quoc Giang1, Huynh Ky1( ), Nguyen Chau Thanh Tung1, Nguyen Loc Hien1, Nguyen van Manh1, Nguyen Nhut Thanh2, Vo Cong Thanh1, Swee Keong Yeap3(
), Nguyen Chau Thanh Tung1, Nguyen Loc Hien1, Nguyen van Manh1, Nguyen Nhut Thanh2, Vo Cong Thanh1, Swee Keong Yeap3( )
)
Received:2022-03-12
Accepted:2022-05-22
Online:2023-03-28
Published:2022-11-11
Contact:
Huynh Ky (hky@ctu.edu.vn);Swee Keong Yeap (skyeap@xmu.edu.my)
Van Quoc Giang, Huynh Ky, Nguyen Chau Thanh Tung, Nguyen Loc Hien, Nguyen van Manh, Nguyen Nhut Thanh, Vo Cong Thanh, Swee Keong Yeap. Novel Deletion in Exon 7 of Betaine Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 (BADH2)[J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(2): 104-112.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
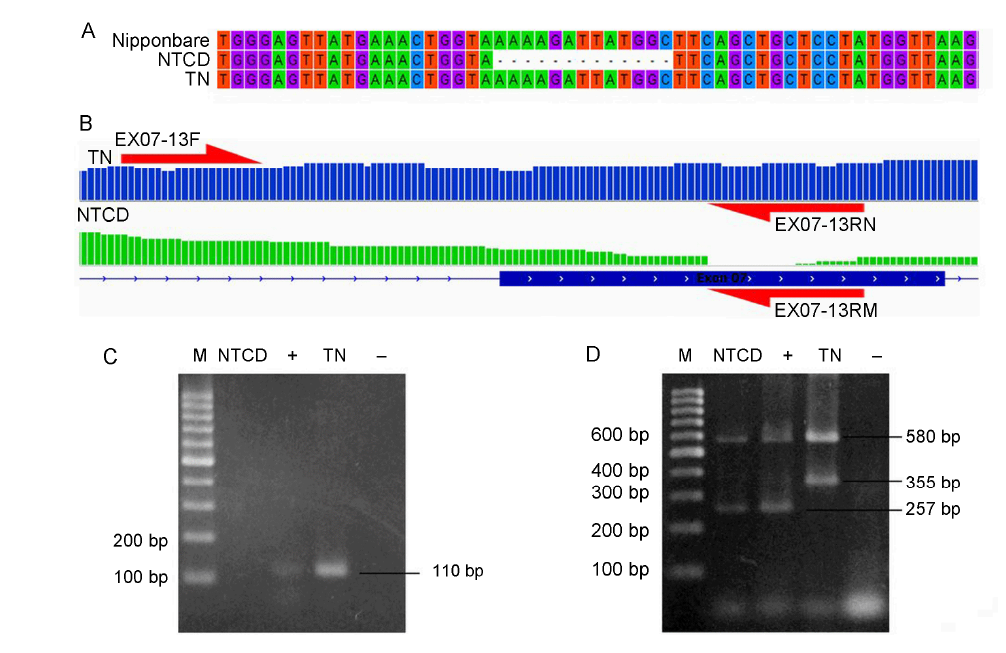
Fig. 2. Sequencing data validation in exon 7 in BADH2 gene. A, Validation of BADH2 gene by Sanger method. B, Primer design for allele specific amplification in exon 7 of BADH2 gene. C, Testing of EX07-13F with EX07- 13RN (normal) and EX07-13RM (mutant) primers for NTCD’s allele specific amplification. D, Fragrance analysis for NTCD and TN using four primers from Bradbury et al (2005). M, Thermo ladder 100 bp; NTCD, Nang Thom Cho Dao; TN, Tai Nguyen; ‘+’, Positive control MTL676; ‘-’, Negative control.
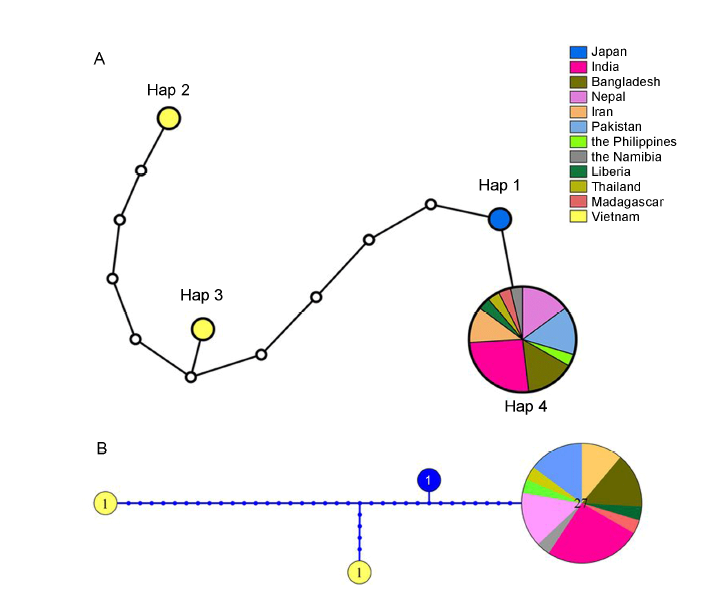
Fig. 3. Haplotype networks inferred from 30 sequences from 12 countries representing relationship of nucleotide deletion in exon 7 of BADH2 gene. A, TCS (Templeton, Crandall, and Sing) haplotype network generated from 30 sequences using maximum parsimony. Nang Thom Cho Dao and Tai Nguyen from Vietnam, 1 reference genome and 27 aromatic rice varieties from 3 000 Rice Genomes Project were used. B, Haplotype network inferred from Bayesian analysis.
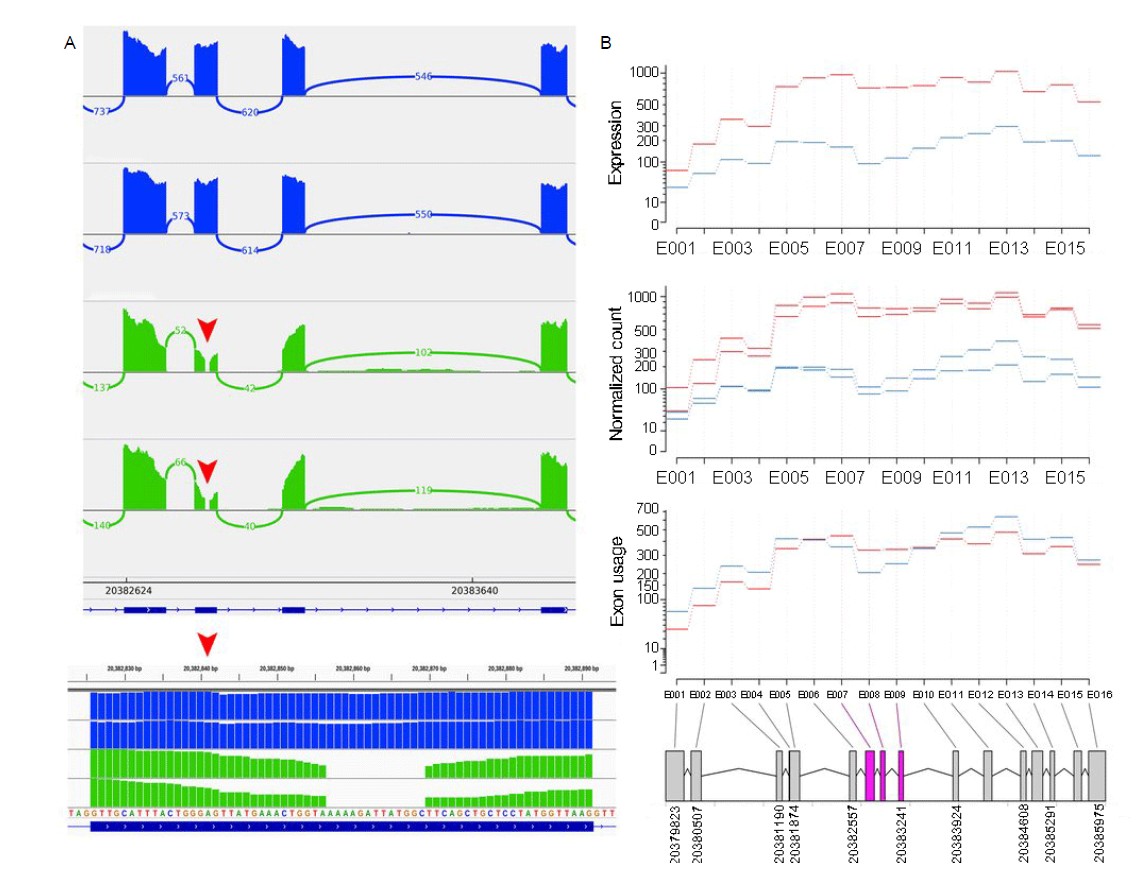
Fig. 5. RNA-Seq analysis of TN (Tai Nguyen, non-aromatic rice) and NTCD (Nang Thom Cho Dao, aromatic rice) derived from Vietnam. A, Visualization of RNA-Seq data generated by Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) program. Red arrows show the location of novel deletion. Alleles shown in blue are from TN, and alleles shown in green are from NTCD. B, Differential exon usage of RNA-Seq data between TN and NTCD in BADH2 gene. Boxes shown in pink are the exon that showed significant differential exon usage (false discovery rate < 0.05).
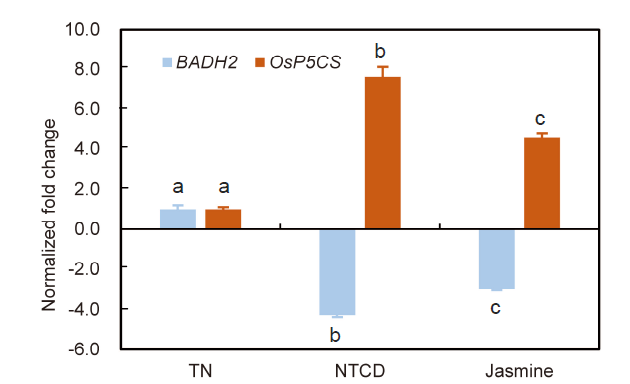
Fig. 6. Transcription levels of BADH2 and OsP5CS in leaves of Nang Thom Cho Dao (NTCD), Tai Nguyen (TN) and Jasmine. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between the samples (P < 0.05).
| Sample | 2AP (µg/kg) |
|---|---|
| Tai Nguyen | Not detected |
| Jasmine | 13.250 ± 0.116 |
| Nang Thom Cho Dao | 16.263 ± 0.213 |
Table 1. Quantification of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline (2AP) using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
| Sample | 2AP (µg/kg) |
|---|---|
| Tai Nguyen | Not detected |
| Jasmine | 13.250 ± 0.116 |
| Nang Thom Cho Dao | 16.263 ± 0.213 |
| Marker | Sequence (5'-3') | Product type | Product (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EAP | AGTGCTTTACAAAGTCCCGC | EA-ES | 577 or 585 | Bradbury et al, |
| ESP | TTGTTTGGAGCTTGCTGATG | |||
| INSP | TGGTAAAAAGATTATGGCTTCA | IN-EA | 355 | |
| IFAP | CATAGGAGCAGCTGAAATATATACC | ES-IF | 257 (aromatic) | |
| EX07-13F | TACCCCATCAATGGAAATGA | 8 bp deletion with or without single nucleotide polymorphism (110 bp), while NTCD with 13 bp deletion without amplification | Developed in this study | |
| EX07-13RN (normal) | GCAGCTGAAGCCATAATCTTTT | |||
| EX07-13RM (mutant) | GCAGCTGAAGCCATAATCTATA | |||
Table 2. New functional markers for BADH2 were developed to discriminate Nang Thom Cho Dao (NTCD) from other fragrant rice varieties.
| Marker | Sequence (5'-3') | Product type | Product (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EAP | AGTGCTTTACAAAGTCCCGC | EA-ES | 577 or 585 | Bradbury et al, |
| ESP | TTGTTTGGAGCTTGCTGATG | |||
| INSP | TGGTAAAAAGATTATGGCTTCA | IN-EA | 355 | |
| IFAP | CATAGGAGCAGCTGAAATATATACC | ES-IF | 257 (aromatic) | |
| EX07-13F | TACCCCATCAATGGAAATGA | 8 bp deletion with or without single nucleotide polymorphism (110 bp), while NTCD with 13 bp deletion without amplification | Developed in this study | |
| EX07-13RN (normal) | GCAGCTGAAGCCATAATCTTTT | |||
| EX07-13RM (mutant) | GCAGCTGAAGCCATAATCTATA | |||
| [1] | Addison C K, Angira B, Kongchum M, Harrell D L, Baisakh N, Linscombe S D, Famoso A N. 2020. Characterization of haplotype diversity in the BADH2 aroma gene and development of a KASP SNP assay for predicting aroma in U.S. rice. Rice, 13(1): 47. |
| [2] |
Ahn S N, Bollich C N, Tanksley S D. 1992. RFLP tagging of a gene for aroma in rice. Theor Appl Genet, 84: 825-828.
PMID |
| [3] | Amarawathi Y, Singh R, Singh A K, Singh V P, Mohapatra T, Sharma T R, Singh N K. 2008. Mapping of quantitative trait loci for Basmati quality traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed, 21(1): 49-65. |
| [4] |
Anders S, Reyes A, Huber W. 2012. Detecting differential usage of exons from RNA-Seq data. Genome Res, 22(10): 2008-2017.
PMID |
| [5] | Begum H, Spindel J E, Lalusin A, Borromeo T, Gregorio G, Hernandez J, Virk P, Collard B, McCouch S R. 2015. Genome- wide association mapping for yield and other agronomic traits in an elite breeding population of tropical rice (Oryza sativa). PLoS One, 10(3): e0119873. |
| [6] | Bergman C J, Delgado J T, Bryant R, Grimm C, Cadwallader K R, Webb B D. 2000. Rapid gas chromatographic technique for quantifying 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline and hexanal in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Cereal Chem J, 77(4): 454-458. |
| [7] | Bindusree G, Natarajan P, Kalva S, Madasamy P. 2017. Whole genome sequencing of Oryza sativa L. cv. Seeragasamba identifies a new fragrance allele in rice. PLoS One, 12(11): e0188920. |
| [8] | Bligh H F J. 2000. Detection of adulteration of Basmati rice with non-premium long-grain rice. Int J Food Sci Tech, 35(3): 257-265. |
| [9] | Bouckaert R, Heled J, Kühnert D, Vaughan T, Wu C H, Xie D, Suchard M A, Rambaut A, Drummond A J. 2014. BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput Biol, 10(4): e1003537. |
| [10] | Bouckaert R, Vaughan T G, Barido-Sottani J, Duchêne S, Fourment M, Gavryushkina A, Heled J, Jones G, Kühnert D, de Maio N, Matschiner M, Mendes F K, Müller N F, Ogilvie H A, du Plessis L, Popinga A, Rambaut A, Rasmussen D, Siveroni I, Suchard M A, Wu C H, Xie D, Zhang C, Stadler T, Drummond A J. 2019. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput Biol, 15(4): e1006650. |
| [11] |
Bourgis F, Guyot R, Gherbi H, Tailliez E, Amabile I, Salse J, Lorieux M, Delseny M, Ghesquière A. 2008. Characterization of the major fragance gene from an aromatic japonica rice and analysis of its diversity in Asian cultivated rice. Theor Appl Genet, 117(3): 353-368.
PMID |
| [12] |
Bradbury L M T, Fitzgerald T L, Henry R J, Jin Q S, Waters D L E. 2005. The gene for fragrance in rice. Plant Biotechnol J, 3(3): 363-370.
PMID |
| [13] |
Chen S F, Zhou Y Q, Chen Y R, Gu J. 2018. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics, 34(17): 884-890.
PMID |
| [14] |
Chen S H, Yang Y, Shi W W, Ji Q, He F, Zhang Z D, Cheng Z K, Liu X N, Xu M L. 2008. Badh2, encoding betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase, inhibits the biosynthesis of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, a major component in rice fragrance. Plant Cell, 20(7): 1850-1861.
PMID |
| [15] |
Clement M, Posada D, Crandall K A. 2000. TCS: A computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol Ecol, 9(10): 1657-1659.
PMID |
| [16] | Cordeiro G M, Christopher M J, Henry R J, Reinke R F. 2002. Identification of microsatellite markers for fragrance in rice by analysis of the rice genome sequence. Mol Breed, 9: 245-250. |
| [17] |
Darriba D, Taboada G L, Doallo R, Posada D. 2012. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat Methods, 9(8): 772.
PMID |
| [18] |
Drummond A J, Rambaut A. 2007. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol Biol, 7: 214.
PMID |
| [19] |
Drummond A J, Suchard M A, Xie D, Rambaut A. 2012. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST1.7. Mol Biol Evol, 29(8): 1969-1973.
PMID |
| [20] |
Ganopoulos I, Argiriou A, Tsaftaris A. 2011. Adulterations in Basmati rice detected quantitatively by combined use of microsatellite and fragrance typing with High Resolution Melting (HRM) analysis. Food Chem, 129(2): 652-659.
PMID |
| [21] | Giraud G. 2013. The world market of fragrant rice, main issues and perspectives. Int Food Agribus Man, 16: 1-20. |
| [22] | Hinge V, Patil H, Nadaf A. 2016. Comparative characterization of aroma volatiles and related gene expression analysis at vegetative and mature stages in Basmati and non-Basmati rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. Appl Biochem Biotechnol, 178(4): 619-639. |
| [23] | Hoffmann J F, Bassinello P Z, Colombari Filho J M, Lindemann I S, Elias M C, Takeoka G R, Vanier N L. 2019. Volatile compounds profile of Brazilian aromatic brown rice genotypes and its cooking quality characteristics. Cereal Chem, 96(2): 292-301. |
| [24] | Huang T C, Teng C S, Chang J L, Chuang H S, Ho C T, Wu M L. 2008. Biosynthetic mechanism of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline and its relationship with delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid and methylglyoxal in aromatic rice (Oryza sativa L.) callus. J Agric Food Chem, 56(16): 7399-7404. |
| [25] |
Huang X H, Wei X H, Sang T, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhao Y, Li C Y, Zhu C R, Lu T T, Zhang Z W, Li M, Fan D L, Guo Y L, Wang A H, Wang L, Deng L W, Li W J, Lu Y Q, Weng Q J, Liu K Y, Huang T, Zhou T Y, Jing Y F, Li W, Lin Z, Buckler E S, Qian Q, Zhang Q F, Li J Y, Han B. 2010. Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces. Nat Genet, 42(11): 961-967.
PMID |
| [26] | Huang X H, Zhao Y, Wei X H, Li C Y, Wang A H, Zhao Q, Li W J, Guo Y L, Deng L W, Zhu C R, Fan D L, Lu Y Q, Weng Q J, Liu K Y, Zhou T Y, Jing Y F, Si L Z, Dong G J, Huang T, Lu T T, Feng Q, Qian Q, Li J Y, Han B. 2012. Genome-wide association study of flowering time and grain yield traits in a worldwide collection of rice germplasm. Nat Genet, 44(1): 32-39. |
| [27] | Jin Q S, Waters D, Cordeiro G M, Henry R J, Reinke R F. 2003. A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) marker linked to the fragrance gene in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci, 165(2): 359-364. |
| [28] | Khandagale K S, Chavhan R, Nadaf A B. 2020. RNAi-mediated down regulation of BADH2 gene for expression of 2-acetyl-1- pyrroline in non-scented indica rice IR-64 (Oryza sativa L.). 3 Biotech, 10(4): 145. |
| [29] | Khanh T D, Duong V X, Nguyen P C, Xuan T D, Trung N T, Trung K H, Gioi D H, Hoang N H, Tran H D, Trung D M, Huong B T T. 2021. Rice breeding in Vietnam: Retrospects, challenges and prospects. Agriculture, 11: 397. |
| [30] | Khush G S. 1996. Rice Genetics III:Proceedings of the Third International Rice Genetics Symposium. Manila, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| [31] | Kovach M J, Calingacion M N, Fitzgerald M A, McCouch S R. 2009. The origin and evolution of fragrance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106: 14444-14449. |
| [32] | Kraithong S, Lee S, Rawdkuen S. 2018. Effect of red jasmine rice replacement on rice flour properties and noodle qualities. Food Sci Biotechnol, 28(1): 25-34. |
| [33] | Li W B, Zeng X H, Li S L, Chen F B, Gao J. 2020. Development and application of two novel functional molecular markers of BADH2 in rice. Electron J Biotechnol, 46: 1-7. |
| [34] |
Liao Y, Smyth G K, Shi W. 2014. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics, 30(7): 923-930.
PMID |
| [35] | Lin Z W, Griffith M E, Li X R, Zhu Z F, Tan L B, Fu Y C, Zhang W X, Wang X K, Xie D X, Sun C Q. 2007. Origin of seed shattering in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Planta, 226(1): 11-20. |
| [36] | Love M I, Huber W, Anders S. 2014. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-Seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol, 15(12): 550. |
| [37] | Luo H W, He L X, Du B, Pan S G, Mo Z W, Yang S Y, Zou Y B, Tang X R. 2022. Epoxiconazole improved photosynthesis, yield formation, grain quality and 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline biosynthesis of fragrant rice. Rice Sci, 29(2): 189-196. |
| [38] | Mahajan G, Matloob A, Singh R, Singh V P, Chauhan B S. 2018. Basmati rice in the Indian subcontinent: Strategies to boost production and quality traits. Adv Agron, 151: 159-213. |
| [39] |
Maleki C, Oliver P, Lewin S, Liem G, Keast R. 2020. Preference mapping of different water-to-rice ratios in cooked aromatic white jasmine rice. J Food Sci, 85(5): 1576-1585.
PMID |
| [40] | Mansueto L, Fuentes R R, Borja F N, Detras J, Abriol-Santos J M, Chebotarov D, Sanciangco M, Palis K, Copetti D, Poliakov A, Dubchak I, Solovyev V, Wing R A, Hamilton R S, Mauleon R, McNally K L, Alexandrov N. 2017. Rice SNP-seek database update: New SNPs, indels, and queries. Nucleic Acids Res, 45(D1): D1075-D1081. |
| [41] |
Múrias dos Santos A, Cabezas M P, Tavares A I, Xavier R, Branco M. 2016. tcsBU: A tool to extend TCS network layout and visualization. Bioinformatics, 32(4): 627-628.
PMID |
| [42] | Muthayya S, Sugimoto J D, Montgomery S, Maberly G F. 2014. An overview of global rice production, supply, trade, and consumption. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 1324: 7-14. |
| [43] | Okpala N E, Mo Z W, Duan M Y, Tang X R. 2019. The genetics and biosynthesis of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline in fragrant rice. Plant Physiol Biochem, 135: 272-276. |
| [44] | Prodhan Z H, Shu Q Y. 2020. Rice aroma: A natural gift comes with price and the way forward. Rice Sci, 27(2): 86-100. |
| [45] | Rambaut A, Drummond A J, Xie D, Baele G, Suchard M A. 2018. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Systemat Biol, 67: 901-904. |
| [46] |
Rensink W A, Buell C R. 2004. Arabidopsis to rice: Applying knowledge from a weed to enhance our understanding of a crop species. Plant Physiol, 135(2): 622-629.
PMID |
| [47] | Roy S, Banerjee A, Mawkhlieng B, Misra A K, Pattanayak A, Harish G D, Singh S K, Ngachan S V, Bansal K C. 2015. Genetic diversity and population structure in aromatic and quality rice (Oryza sativa L.) landraces from north-eastern India. PLoS One, 10(6): e0129607. |
| [48] | Shao G N, Tang A, Tang S Q, Luo J, Jiao G A, Wu J L, Hu P S. 2011. A new deletion mutation of fragrant gene and the development of three molecular markers for fragrance in rice. Plant Breed, 130(2): 172-176. |
| [49] | Shao G N, Tang S Q, Chen M L, Wei X J, He J W, Luo J, Jiao G A, Hu Y C, Xie L H, Hu P S. 2013. Haplotype variation at Badh2, the gene determining fragrance in rice. Genomics, 101(2): 157-162. |
| [50] | Shi W W, Yang Y, Chen S H, Xu M L. 2008. Discovery of a new fragrance allele and the development of functional markers for the breeding of fragrant rice varieties. Mol Breed, 22(2): 185-192. |
| [51] | Shi Y Q, Zhao G C, Xu X L, Li J Y. 2014. Discovery of a new fragrance allele and development of functional markers for identifying diverse fragrant genotypes in rice. Mol Breed, 33(3): 701-708. |
| [52] | Srivong P, Wangsomnuk P, Pongdontri P. 2008. Characterization of a fragrant gene and enzymatic activity of betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase in aromatic and nonaromatic Thai rice cultivars. KKU Sci J, 36(4): 290-301. |
| [53] | Sun S X, Gao F Y, Lu X J, Wu X J, Wang X D, Ren G J, Luo H. 2008. Genetic analysis and gene fine mapping of aroma in rice (Oryza sativa L. Cyperales, Poaceae). Genet Mol Biol, 31(2): 532-538. |
| [54] | Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. 2013. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol, 30(12): 2725-2729. |
| [55] |
Templeton A R, Crandall K A, Sing C F. 1992. A cladistic analysis of phenotypic associations with haplotypes inferred from restriction endonuclease mapping and DNA sequence data: III. Cladogram estimation. Genetics, 132(2): 619-633.
PMID |
| [56] |
Tyagi A K, Khurana J P, Khurana P, Raghuvanshi S, Gaur A, Kapur A, Gupta V, Kumar D, Ravi V, Vij S, Khurana P, Sharma S. 2004. Structural and functional analysis of rice genome. J Genet, 83(1): 79-99.
PMID |
| [57] | Wang H, Nussbaum-Wagler T, Li B L, Zhao Q, Vigouroux Y, Faller M, Bomblies K, Lukens L, Doebley J F. 2005. The origin of the naked grains of maize. Nature, 436: 714-719. |
| [1] | Luo Haowen, He Longxin, Du Bin, Pan Shenggang, Mo Zhaowen, Yang Shuying, Zou Yingbin, Tang Xiangru. Epoxiconazole Improved Photosynthesis, Yield Formation, Grain Quality and 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline Biosynthesis of Fragrant Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(2): 189-196. |
| [2] | K. Hajira S., M. Sundaram R., S. Laha G., Yugander A., M. Balachandran S., C. Viraktamath B., Sujatha K., H. Balachiranjeevi C., Pranathi K., Anila M., Bhaskar S., Abhilash V., K. Mahadevaswamy H., Kousik M., Dilip Kumar T., Harika G., Rekha G.. A Single-Tube, Functional Marker-Based Multiplex PCR Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Major Bacterial Blight Resistance Genes Xa21, xa13 and xa5 in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2016, 23(3): 144-151. |
| [3] | CHEN Tao, TIAN Meng-xiang, ZHANG Ya-dong, ZHU Zhen, ZHAO Ling, ZHAO Qing-yong, LIN Jing, ZHOU Li-hui, WANG Cai-lin. Development of Simple Functional Markers for Low Glutelin Content Gene 1 (Lgc1) in Rice (Oryza sativa) [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2010, 17(3): 173-178 . |
| [4] | XIA Zhi-hui, HAN Fei, GAO Li-fen, YUAN Qian-hua, ZHAI Wen-xue, LIU Di, LUO Yue-hua. Application of Functional Markers to Identify Genes for Bacterial Blight Resistance in Oryza rufipogon [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2010, 17(1): 73-76 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||