
Rice Science ›› 2023, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 247-256.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2023.03.008
• Research Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhou Longfei1, Meng Ran1,4( ), Yu Xing2, Liao Yigui1, Huang Zehua1, Lü Zhengang1, Xu Binyuan1, Yang Guodong2, Peng Shaobing2, Xu Le2,3(
), Yu Xing2, Liao Yigui1, Huang Zehua1, Lü Zhengang1, Xu Binyuan1, Yang Guodong2, Peng Shaobing2, Xu Le2,3( )
)
Received:2022-08-20
Accepted:2022-11-30
Online:2023-05-28
Published:2023-03-13
Contact:
Meng Ran (mengran@mail.hzau.edu.cn); Xu Le (Le.Xu@mail.hzau.edu.cn)
Zhou Longfei, Meng Ran, Yu Xing, Liao Yigui, Huang Zehua, Lü Zhengang, Xu Binyuan, Yang Guodong, Peng Shaobing, Xu Le. Improved Yield Prediction of Ratoon Rice Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-Based Multi-Temporal Feature Method[J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(3): 247-256.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
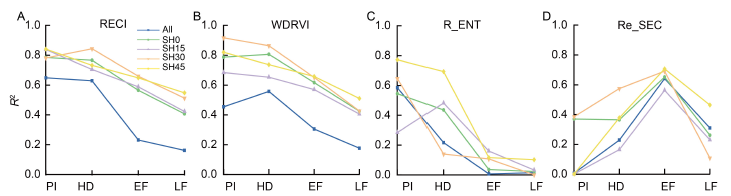
Fig. 2. Determination coefficients of vegetation indices (VIs) (A and B) and texture feature (C and D) for yield prediction of ratoon rice yield at different stubble heights. PI, Panicle initiation; HD, Heading; EF, Early filling; LF, Late filling; All represents all stubble height; SH0, SH15, SH30 and SH45 represent stubble heights of 0, 15, 30 and 45 cm, respectively.RECI, Red-edge chlorophyll index; WDRVI, Wide dynamic range vegetation index; R_ENT, Red_entropy; RE_SEC, Red-edge_second moment.
| Stage | Feature | No. of features | R2 | RMSE | RRMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panicle initiation | VIs | 2 | 0.611 | 0.459 | 0.115 |
| Tex | 2 | 0.576 | 0.472 | 0.118 | |
| VIs + API | 3 | 0.685 | 0.417 | 0.104 | |
| Tex + API | 3 | 0.564 | 0.477 | 0.119 | |
| VIs & Tex | 4 | 0.700 | 0.412 | 0.103 | |
| VIs & Tex + API | 5 | 0.732 | 0.406 | 0.101 | |
| Heading | VIs | 2 | 0.618 | 0.334 | 0.083 |
| Tex | 1 | 0.603 | 0.341 | 0.085 | |
| VIs + API | 3 | 0.654 | 0.317 | 0.079 | |
| Tex + API | 3 | 0.587 | 0.349 | 0.087 | |
| VIs & Tex | 3 | 0.690 | 0.302 | 0.075 | |
| VIs & Tex + API | 4 | 0.705 | 0.295 | 0.073 | |
| Early filling | VIs | 2 | 0.491 | 0.480 | 0.118 |
| Tex | 2 | 0.582 | 0.432 | 0.107 | |
| VIs + API | 3 | 0.478 | 0.486 | 0.120 | |
| Tex + API | 3 | 0.599 | 0.424 | 0.105 | |
| VIs & Tex | 4 | 0.606 | 0.420 | 0.104 | |
| VIs & Tex + API | 5 | 0.611 | 0.417 | 0.103 | |
| Late filling | VIs | 1 | 0.006 | 0.776 | 0.190 |
| Tex | 1 | 0.365 | 0.551 | 0.134 | |
| VIs + API | 2 | 0.257 | 0.597 | 0.146 | |
| Tex + API | 2 | 0.422 | 0.523 | 0.128 | |
| VIs & Tex | 2 | 0.244 | 0.606 | 0.148 | |
| VIs & Tex + API | 3 | 0.502 | 0.499 | 0.122 | |
| Multi-temporal | VIs | 2 | 0.780 | 0.296 | 0.072 |
| Tex | 3 | 0.702 | 0.345 | 0.084 | |
| VIs + API | 3 | 0.768 | 0.304 | 0.074 | |
| Tex + API | 4 | 0.730 | 0.334 | 0.081 | |
| VIs & Tex | 5 | 0.795 | 0.298 | 0.072 | |
| VIs & Tex + API | 6 | 0.794 | 0.300 | 0.073 |
Table 1. Validation of ratoon rice yield models based on different feature sets.
| Stage | Feature | No. of features | R2 | RMSE | RRMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panicle initiation | VIs | 2 | 0.611 | 0.459 | 0.115 |
| Tex | 2 | 0.576 | 0.472 | 0.118 | |
| VIs + API | 3 | 0.685 | 0.417 | 0.104 | |
| Tex + API | 3 | 0.564 | 0.477 | 0.119 | |
| VIs & Tex | 4 | 0.700 | 0.412 | 0.103 | |
| VIs & Tex + API | 5 | 0.732 | 0.406 | 0.101 | |
| Heading | VIs | 2 | 0.618 | 0.334 | 0.083 |
| Tex | 1 | 0.603 | 0.341 | 0.085 | |
| VIs + API | 3 | 0.654 | 0.317 | 0.079 | |
| Tex + API | 3 | 0.587 | 0.349 | 0.087 | |
| VIs & Tex | 3 | 0.690 | 0.302 | 0.075 | |
| VIs & Tex + API | 4 | 0.705 | 0.295 | 0.073 | |
| Early filling | VIs | 2 | 0.491 | 0.480 | 0.118 |
| Tex | 2 | 0.582 | 0.432 | 0.107 | |
| VIs + API | 3 | 0.478 | 0.486 | 0.120 | |
| Tex + API | 3 | 0.599 | 0.424 | 0.105 | |
| VIs & Tex | 4 | 0.606 | 0.420 | 0.104 | |
| VIs & Tex + API | 5 | 0.611 | 0.417 | 0.103 | |
| Late filling | VIs | 1 | 0.006 | 0.776 | 0.190 |
| Tex | 1 | 0.365 | 0.551 | 0.134 | |
| VIs + API | 2 | 0.257 | 0.597 | 0.146 | |
| Tex + API | 2 | 0.422 | 0.523 | 0.128 | |
| VIs & Tex | 2 | 0.244 | 0.606 | 0.148 | |
| VIs & Tex + API | 3 | 0.502 | 0.499 | 0.122 | |
| Multi-temporal | VIs | 2 | 0.780 | 0.296 | 0.072 |
| Tex | 3 | 0.702 | 0.345 | 0.084 | |
| VIs + API | 3 | 0.768 | 0.304 | 0.074 | |
| Tex + API | 4 | 0.730 | 0.334 | 0.081 | |
| VIs & Tex | 5 | 0.795 | 0.298 | 0.072 | |
| VIs & Tex + API | 6 | 0.794 | 0.300 | 0.073 |
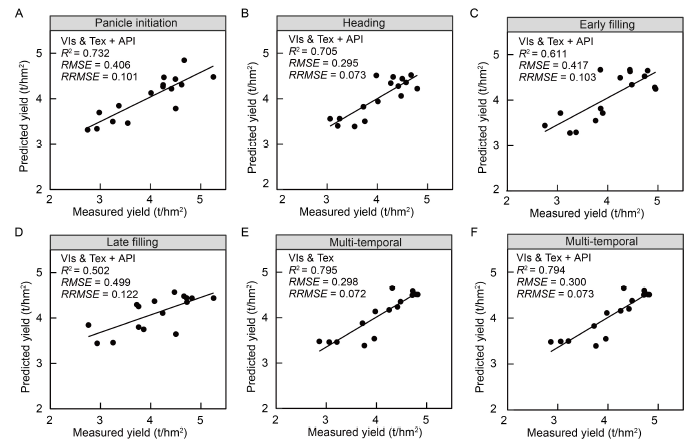
Fig. 3. Validated scatter plot of measured and predicted yields of ratoon rice. A-D, Optimal prediction results for growth period at panicle initiation (A), heading (B), early filling (C) and late filling (D). E and F, Yield prediction results for the best multi-phase model without (E) and with API (F).VIs, Vegetation indices; Tex, Texture; API, Agronomic practice information; R2, Coefficient of determination; RMSE, Root mean square error; RRMSE, Relative root mean square error.
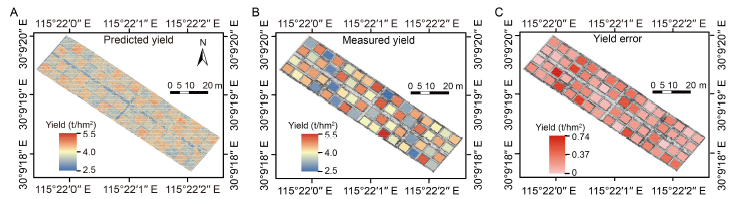
Fig. 4. Ratoon rice yield prediction map based on multi-temporal model (A), actual measured yield (B) and yield error between prediction and actual measured yields (C).
| [1] | Bahar F A, de Datta S K. 1977. Prospects of increasing tropical rice production through ratooning. Agron J, 69(4): 536-540. |
| [2] | Colomina I, Molina P. 2014. Unmanned aerial systems for photogrammetry and remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens, 92: 79-97. |
| [3] | Crusiol L G T, Sun L, Sibaldelli R N R, Junior V F, Furlaneti W X, Chen R, Sun Z, Wuyun D, Chen Z, Nanni M R, Furlanetto R H, Cezar E, Nepomuceno A L, Farias J R B. 2022. Strategies for monitoring within-field soybean yield using Sentinel-2 Vis-NIR-SWIR spectral bands and machine learning regression methods. Precis Agric, 23(3): 1093-1123. |
| [4] | Dimo D, Uhl J H, Löw F, Seboka G N. 2022. Sugarcane yield estimation through remote sensing time series and phenology metrics. Smart Agric Technol, 2: 100046 |
| [5] | Duan B, Fang S H, Gong Y, Peng Y, Wu X T, Zhu R S. 2021. Remote estimation of grain yield based on UAV data in different rice cultivars under contrasting climatic zone. Field Crops Res, 267: 108148. |
| [6] | Erten E, Lopez-Sanchez J M, Yuzugullu O, Hajnsek I. 2016. Retrieval of agricultural crop height from space: A comparison of SAR techniques. Remote Sens Environ, 187: 130-144. |
| [7] | Feng A J, Zhou J F, Vories E D, Sudduth K A, Zhang M N. 2020. Yield estimation in cotton using UAV-based multi-sensor imagery. Biosyst Eng, 193: 101-114. |
| [8] | Gao F, Anderson M, Daughtry C, Johnson D. 2018. Assessing the variability of corn and soybean yields in central Iowa using high spatiotemporal resolution multi-satellite imagery. Remote Sens, 10(9): 1489. |
| [9] | Ge H X, Ma F, Li Z W, Du C W. 2021. Grain yield estimation in rice breeding using phenological data and vegetation indices derived from UAV images. Agronomy, 11(12): 2439. |
| [10] | Geipel J, Link J, Claupein W. 2014. Combined spectral and spatial modeling of corn yield based on aerial images and crop surface models acquired with an unmanned aircraft system. Remote Sens, 6(11): 10335-10355. |
| [11] | Ghimire B, Timsina D, Nepal J. 2015. Analysis of chlorophyll content and its correlation with yield attributing traits on early varieties of maize (Zea mays L.). J Maize Res Dev, 1(1): 134-145. |
| [12] | Gitelson A A, Vina A, Masek J G, Verma S B, Suyker A E. 2008. Synoptic monitoring of gross primary productivity of maize using Landsat data. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett, 5(2): 133-137. |
| [13] |
Gong Y, Yang K L, Lin Z H, Fang S H, Wu X T, Zhu R S, Peng Y. 2021. Remote estimation of leaf area index (LAI) with unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) imaging for different rice cultivars throughout the entire growing season. Plant Methods, 17(1): 88.
PMID |
| [14] | Harrell D L, Bond J A, Blanche S. 2009. Evaluation of main-crop stubble height on ratoon rice growth and development. Field Crops Res, 114(3): 396-403. |
| [15] | Hlatshwayo S T, Mutanga O, Lottering R T, Kiala Z, Ismail R. 2019. Mapping forest aboveground biomass in the reforested Buffelsdraai landfill site using texture combinations computed from SPOT-6 pan-sharpened imagery. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinformation, 74: 65-77. |
| [16] | Huete A, Didan K, Miura T, Rodriguez E P, Gao X, Ferreira L G. 2002. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens Environ, 83(1/2): 195-213. |
| [17] | Johnson M D, Hsieh W W, Cannon A J, Davidson A, Bédard F. 2016. Crop yield forecasting on the Canadian Prairies by remotely sensed vegetation indices and machine learning methods. Agric For Meteorol, 218/219: 74-84. |
| [18] | Li B, Xu X M, Zhang L, Han J W, Bian C S, Li G C, Liu J G, Jin L P. 2020. Above-ground biomass estimation and yield prediction in potato by using UAV-based RGB and hyperspectral imaging. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens, 162: 161-172. |
| [19] | Ling X X, Zhang T Y, Deng N Y, Yuan S, Yuan G H, He W J, Cui K H, Nie L X, Peng S B, Li T, Huang J L. 2019. Modelling rice growth and grain yield in rice ratooning production system. Field Crops Res, 241: 107574. |
| [20] | Liu K Z, Zhang C X, Guan B B, Yang R, Liu K, Wang Z Z, Li X, Xue K Y, Yin L J, Wang X Y. 2021. The effect of different sowing dates on dry matter and nitrogen dynamics for winter wheat: An experimental simulation study. PeerJ, 9: e11700. |
| [21] | Lv Z G, Meng R, Man J G, Zeng L L, Wang M, Xu B Y, Gao R J, Sun R, Zhao F. 2021. Modeling of winter wheat fAPAR by integrating unmanned aircraft vehicle-based optical, structural and thermal measurement. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf, 102: 102407. |
| [22] |
Maes W H, Steppe K. 2019. Perspectives for remote sensing with unmanned aerial vehicles in precision agriculture. Trends Plant Sci, 24(2): 152-164.
PMID |
| [23] | Maimaitijiang M, Ghulam A, Sidike P, Hartling S, Maimaitiyiming M, Peterson K, Shavers E, Fishman J, Peterson J, Kadam S, Burken J, Fritschi F. 2017. Unmanned aerial system (UAS)-based phenotyping of soybean using multi-sensor data fusion and extreme learning machine. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens, 134: 43-58. |
| [24] | Maimaitijiang M, Sagan V, Sidike P, Hartling S, Esposito F, Fritschi F B. 2020. Soybean yield prediction from UAV using multimodal data fusion and deep learning. Remote Sens Environ, 237: 111599. |
| [25] | Meng R, Dennison P E, Zhao F, Shendryk I, Rickert A, Hanavan R P, Cook B D, Serbin S P. 2018. Mapping canopy defoliation by herbivorous insects at the individual tree level using bi-temporal airborne imaging spectroscopy and LiDAR measurements. Remote Sens Environ, 215: 170-183. |
| [26] | Qiu Z C, Ma F, Li Z W, Xu X B, Ge H X, Du C W. 2021. Estimation of nitrogen nutrition index in rice from UAV RGB images coupled with machine learning algorithms. Comput Electron Agric, 189: 106421. |
| [27] | Santos A B, Fageria N K, Prabhu A S. 2003. Rice ratooning management practices for higher yields. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal, 34(5/6): 881-918. |
| [28] | Shen X, Zhang L, Zhang J B. 2021. Ratoon rice production in central China: Environmental sustainability and food production. Sci Total Environ, 764: 142850. |
| [29] | Skakun S, Vermote E, Roger J C, Franch B. 2017. Combined use of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2A images for winter crop mapping and winter wheat yield assessment at regional scale. AIMS Geosci, 3(2): 163-186. |
| [30] | Takai T, Matsuura S, Nishio T, Ohsumi A, Shiraiwa T, Horie T. 2006. Rice yield potential is closely related to crop growth rate during late reproductive period. Field Crops Res, 96(2/3): 328-335. |
| [31] | Tao H L, Feng H K, Xu L J, Miao M K, Yang G J, Yang X D, Fan L L. 2020. Estimation of the yield and plant height of winter wheat using UAV-based hyperspectral images. Sensors, 20(4): E1231. |
| [32] | Teoh C C, Mohd N, Mohd J, Izani I, Faizal K, Shukry H B. 2016. Rice yield estimation using below cloud remote sensing images acquired by unmanned airborne vehicle system. Int J Adv Sci Eng Inf Technol, 6(4): 516. |
| [33] | Thenkabail P S. 2003. Biophysical and yield information for precision farming from near-real-time and historical Landsat TM images. Int J Remote Sens, 24(14): 2879-2904. |
| [34] | Viña A. 2012. Evaluating vegetation indices for assessing productivity along a tropical rain forest chronosequence in Western Amazonia. Isr J Plant Sci, 60(1/2): 123-133. |
| [35] | Wan L, Cen H Y, Zhu J P, Zhang J F, Zhu Y M, Sun D W, Du X Y, Zhai L, Weng H Y, Li Y J, Li X R, Bao Y D, Shou J Y, He Y. 2020. Grain yield prediction of rice using multi-temporal UAV-based RGB and multispectral images and model transfer: A case study of small farmlands in the south of China. Agric For Meteorol, 291: 108096. |
| [36] | Wang F M, Yao X P, Xie L L, Zheng J Y, Xu T Y. 2021. Rice yield estimation based on vegetation index and florescence spectral information from UAV hyperspectral remote sensing. Remote Sens, 13(17): 3390. |
| [37] | Wang L G, Tian Y C, Yao X, Zhu Y, Cao W X. 2014. Predicting grain yield and protein content in wheat by fusing multi-sensor and multi-temporal remote-sensing images. Field Crops Res, 164: 178-188. |
| [38] | Wang X Y, Yang G D, Pan X C, Xiang H S, Peng S B, Xu L. 2022. Feasibility of improving unmanned aerial vehicle-based seeding efficiency by using rice varieties with low seed weight. Rice Sci, 29(4): 299-303. |
| [39] | Xie H A. 2010. Studies on high-yielding cultivation characteristics of super hybrid rice grown as ratoon rice. Hybrid Rice, 25: 17-26. |
| [40] | Xu F X, Zhang L, Zhou X B, Guo X Y, Zhu Y C, Liu M, Xiong H, Jiang P. 2021. The ratoon rice system with high yield and high efficiency in China: Progress, trend of theory and technology. Field Crops Res, 272: 108282. |
| [41] | Xu L, Zhan X W, Yu T T, Nie L X, Huang J L, Cui K H, Wang F, Li Y, Peng S B. 2018. Yield performance of direct-seeded, double-season rice using varieties with short growth durations in central China. Field Crops Res, 227: 49-55. |
| [42] | Xu L, Zhou L F, Meng R, Zhao F, Lv Z G, Xu B Y, Zeng L L, Yu X, Peng S B. 2022. An improved approach to estimate ratoon rice aboveground biomass by integrating UAV-based spectral, textural and structural features. Precis Agric, 23(4): 1276-1301. |
| [43] | Yang D S, Peng S B, Zheng C, Xiang H S, Huang J L, Cui K H, Wang F. 2021. Effects of nitrogen fertilization for bud initiation and tiller growth on yield and quality of rice ratoon crop in central China. Field Crops Res, 272: 108286. |
| [44] | Yang D S, Peng S B, Zheng C, Xiong Z, Yang G D, Deng S, Wang F. 2022. Stubble height affects the grain yield of ratoon rice under rainfed conditions. Agric Water Manag, 272: 107815. |
| [45] | Yang Q, Shi L S, Han J Y, Zha Y Y, Zhu P H. 2019. Deep convolutional neural networks for rice grain yield estimation at the ripening stage using UAV-based remotely sensed images. Field Crops Res, 235: 142-153. |
| [46] | Yang W, Peng S B, Laza R C, Visperas R M, Dionisio-Sese M L. 2008. Yield gap analysis between dry and wet season rice crop grown under high-yielding management conditions. Agron J, 100(5): 1390-1395. |
| [47] | Yu D Y, Zha Y Y, Shi L S, Jin X L, Hu S, Yang Q, Huang K, Zeng W Z. 2020. Improvement of sugarcane yield estimation by assimilating UAV-derived plant height observations. Eur J Agron, 121: 126159. |
| [48] | Yuan S, Cassman K G, Huang J L, Peng S B, Grassini P. 2019. Can ratoon cropping improve resource use efficiencies and profitability of rice in central China? Field Crops Res, 234: 66-72. |
| [49] | Zeng L L, Peng G Z, Meng R, Man J G, Li W B, Xu B Y, Lv Z G, Sun R. 2021. Wheat yield prediction based on unmanned aerial vehicles-collected red-green-blue imagery. Remote Sens, 13: 2937. |
| [50] |
Zhang J Y, Zhang N, Liu Y X, Zhang X N, Hu B, Qin Y, Xu H R, Wang H, Guo X X, Qian J M, Wang W, Zhang P F, Jin T, Chu C C, Bai Y. 2018. Root microbiota shift in rice correlates with resident time in the field and developmental stage. Sci China Life Sci, 61(6): 613-621.
PMID |
| [51] | Zhang J Y, Qiu X L, Wu Y T, Zhu Y, Cao Q, Liu X J, Cao W X. 2021. Combining texture, color, and vegetation indices from fixed-wing UAS imagery to estimate wheat growth parameters using multivariate regression methods. Comput Electron Agric, 185: 106138. |
| [52] | Zhao Y, Chen X P, Cui Z L, Lobell D B. 2015. Using satellite remote sensing to understand maize yield gaps in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res, 183: 31-42. |
| [53] | Zhao Y, Potgieter A B, Zhang M, Wu B F, Hammer G L. 2020. Predicting wheat yield at the field scale by combining high-resolution Sentinel-2 satellite imagery and crop modelling. Remote Sens, 12(6): 1024. |
| [54] | Zhou X, Zheng H B, Xu X Q, He J Y, Ge X K, Yao X, Cheng T, Zhu Y, Cao W X, Tian Y C. 2017. Predicting grain yield in rice using multi-temporal vegetation indices from UAV-based multispectral and digital imagery. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens, 130: 246-255. |
| [1] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||