
Rice Science ›› 2023, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 181-185.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2023.03.003
• Letter • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ayotunde A. Adeosun, Adam H. Price, Gareth J. Norton( )
)
Received:2022-05-25
Accepted:2022-07-23
Online:2023-05-28
Published:2023-03-13
Contact:
Gareth J. Norton (g.norton@abdn.ac.uk)
Ayotunde A. Adeosun, Adam H. Price, Gareth J. Norton. Cadmium Tolerance and Accumulation in Wild Rice Species[J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(3): 181-185.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
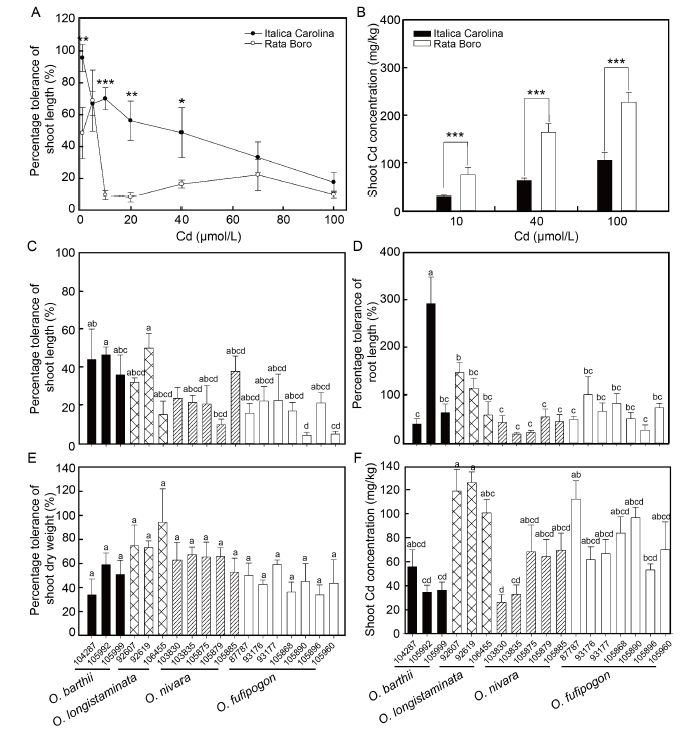
Fig. 1. Responses of Oryza sativa (A and B) and wild rice accessions (C-F) grown in a hydroponic system to different cadmium (Cd) concentration treatments. A, Percentage tolerance of shoot length in O. sativa; B, Shoot Cd concentration in O. sativa; C, Percentage tolerance of shoot length in wild rice accessions. D, Percentage tolerance of root length in wild rice accessions; E, Percentage tolerance of shoot dry weight in wild rice accessions. F, Shoot Cd concentration in wild rice accessions.Data are Mean ± SE (n = 3 or 4). In A and B, *, ** and *** represent significant differences between the two rice cultivars at the 0.05, 0.01 and 0.001 levels, respectively. In C-F, the different lowercase letters are significantly different by one-way analysis of variance followed by the Fisher’s LSD test (P < 0.05). The numbers in x axis represent the wild rice accession.
| [1] | Arao T, Ae N. 2003. Genotypic variations in cadmium levels of rice grain. Soil Sci Plant Nutr, 49(4): 473-479. |
| [2] | ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry). 2008. Draft toxicological profile for cadmium [2021-11-20]. http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp5.pdf. |
| [3] | Atwell B J, Wang H, Scafaro A P. 2014. Could abiotic stress tolerance in wild relatives of rice be used to improve Oryza sativa? Plant Sci, 215/216: 48-58. |
| [4] |
Brar D S, Khush G S. 1997. Alien introgression in rice. Plant Mol Biol, 35: 35-47.
PMID |
| [5] | Brar D S, Khush G S. 2003. Utilization of wild species of genus Oryza in rice improvement. In: Nanda J S, Sharma S D. Monograph on Genus Oryza. New Hampshire, USA: Science Publisher: 283-309. |
| [6] | Commission Regulation. 2006. Setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs: EC No. 1881/2006 [2021-11-20]. http://extwprlegs1.fao.org/docs/pdf/eur68134original.pdf. |
| [7] |
Gill S S, Tuteja N. 2011. Cadmium stress tolerance in crop plants: Probing the role of sulfur. Plant Signal Behav, 6(2): 215-222.
PMID |
| [8] | He J Y, Zhu C, Ren Y F, Yan Y P, Jiang D A. 2006. Genotypic variation in grain cadmium concentration of lowland rice. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci, 169(5): 711-716. |
| [9] |
Ishikawa S, Ae N, Yano M. 2005. Chromosomal regions with quantitative trait loci controlling cadmium concentration in brown rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol, 168(2): 345-350.
PMID |
| [10] |
Kovach M J, McCouch S R. 2008. Leveraging natural diversity: Back through the bottleneck. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 11(2): 193-200.
PMID |
| [11] | Ma X, Fu Y C, Zhao X H, Jiang L Y, Zhu Z F, Gu P, Xu W Y, Su Z, Sun C Q, Tan L B. 2016. Genomic structure analysis of a set of Oryza nivara introgression lines and identification of yield-associated QTLs using whole-genome resequencing. Sci Rep, 6: 27425. |
| [12] | McCouch S R, Sweeney M, Li J, Jiang H, Thomson M, Septiningsih E, Edwards J, Moncada P, Mahmoud A A, Sukumar S, Krishnan H B. 2008. Interspecific rice hybrid of Oryza sativa × Oryza nivara reveals a significant increase in seed protein content. J Agric Food Chem, 56: 476-482. |
| [13] |
Meharg A A, Norton G, Deacon C, Williams P, Adomako E E, Price A, Zhu Y G, Li G, Zhao F J, McGrath S, Villada A, Sommella A,de Silva P M C S, Brammer H, Dasgupta T, Islam M R. 2013. Variation in rice cadmium related to human exposure. Environ Sci Technol, 47(11): 5613-5618.
PMID |
| [14] | National Food Industry Standardization Technical Committee. 2013. National food safety standard food microbiological examination: Commercial sterility:GB 4789. 26-2013 [2021-11-20]. https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF.aspx/GB4789.26-2013. |
| [15] | Nie Y Y, Xia H, Ma X S, Lou Q J, Liu Y, Zhang A L, Cheng L, Yan L A, Luo L J. 2022. Dissecting genetic basis of deep rooting in dongxiang wild rice. Rice Sci, 29(3): 277-287. |
| [16] |
Norton G J, Travis A, Ruang-areerate P, Nicol G W, Adeosun A A, Hossain M, Islam M R, Douglas A, Price A H. 2021. Genetic loci regulating cadmium content in rice grains. Euphytica, 217(3): 35.
PMID |
| [17] |
Palmgren M G, Edenbrandt A K, Vedel S E, Andersen M M, Landes X, Østerberg J T, Falhof J, Olsen L I, Christensen S B, Sandøe P, Gamborg C, Kappel K, Thorsen B J, Pagh P. 2015. Are we ready for back-to-nature crop breeding? Trends Plant Sci, 20(3): 155-164.
PMID |
| [18] | Ramos I, Esteban E, Lucena J J, Gárate A. 2002. Cadmium uptake and subcellular distribution in plants of Lactuca sp. Cd-Mn interaction. Plant Sci, 162(5): 761-767. |
| [19] | Shi Z Y, Carey M, Meharg C, Williams P N, Signes-Pastor A J, Triwardhani E A, Pandiangan F I, Campbell K, Elliott C, Marwa E M, Xiao J J, Farias J G, Nicoloso F T, Silva P M C S, Lu Y, Norton G, Adomako E, Green A J, Moreno-Jiménez E, Zhu Y G,Carbonell-Barrachina Á A, Haris P I, Lawgali Y F, Sommella A, Pigna M, Brabet C, Montet D, Njira K, Watts M J, Hossain M, Islam M R, Tapia Y, Oporto C, Meharg A A. 2020. Rice grain cadmium concentrations in the global supply-chain. Expo Health, 12(4): 869-876. |
| [20] | Song W E, Chen S B, Liu J F, Chen L, Song N N, Li N, Liu B. 2015. Variation of Cd concentration in various rice cultivars and derivation of cadmium toxicity thresholds for paddy soil by species-sensitivity distribution. J Integr Agric, 14(9): 1845-1854. |
| [21] | Stebbins G L. 1981. Coevolution of grasses and herbivores. Ann Mo Bot Gard, 68(1): 75-86. |
| [22] | Sun C Q, Wang X K, Li Z C, Yoshimura A, Iwata N. 2001. Comparison of the genetic diversity of common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) and cultivated rice (O. sativa L.) using RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet, 102(1): 157-162. |
| [23] | Swamy B P M, Kaladhar K, Shobha Rani N, Prasad G S V, Viraktamath B C, Reddy G A, Sarla N. 2012. QTL analysis for grain quality traits in 2 BC2F2 populations derived from crosses between Oryza sativa cv. Swarna and 2 accessions of O. nivara. J Hered, 103(3): 442-452. |
| [24] | Swamy B P M, Kaladhar K, Reddy G A, Viraktamath B C, Sarla N. 2014. Mapping and introgression of QTL for yield and related traits in two backcross populations derived from Oryza sativa cv. Swarna and two accessions of O. nivara. J Genet, 93(3): 643-654. |
| [25] | Swamy B P M, Kaladhar K, Anuradha K, Batchu A K, Longvah T, Sarla N. 2018. QTL analysis for grain iron and zinc concentrations in two O. nivara derived backcross populations. Rice Sci, 25(4): 197-207. |
| [26] |
Ueno D, Kono I, Yokosho K, Ando T, Yano M, Ma J F. 2009. A major quantitative trait locus controlling cadmium translocation in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol, 182(3): 644-653.
PMID |
| [27] |
Ueno D, Yamaji N, Kono I, Huang C F, Ando T, Yano M, Ma J F. 2010. Gene limiting cadmium accumulation in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 107(38): 16500-16505.
PMID |
| [28] |
Uraguchi S, Mori S, Kuramata M, Kawasaki A, Arao T, Ishikawa S. 2009. Root-to-shoot Cd translocation via the xylem is the major process determining shoot and grain cadmium accumulation in rice. J Exp Bot, 60(9): 2677-2688.
PMID |
| [29] | Wang X, Zhang Z W, Tu S H, Feng W Q, Xu F, Zhu F, Zhang D W, Du J B, Yuan S, Lin H H. 2013. Comparative study of four rice cultivars with different levels of cadmium tolerance. Biologia, 68(1): 74-81. |
| [30] | Wani P A, Khan M S, Zaidi A. 2007. Cadmium, chromium and copper in greengram plants. Agron Sustain Dev, 27(2): 145-153. |
| [31] | WHO (World Health Organization). 2008. Codex general standard for contaminants and toxins in foods and feed: CODEX STAN 193-1995 [2022-01-08]. http://www.codexalimentarius.net/download/standards/17/CXS_193e.pdf. |
| [32] | Xiao A W, Chen D T, Li W C, Ye Z H. 2021. Root morphology and anatomy affect cadmium translocation and accumulation in rice. Rice Sci, 28(6): 594-604. |
| [33] | Xu W H, Li Y R, He J P, Ma Q F, Zhang X J, Chen G Q, Wang H X, Zhang H B. 2010. Cd uptake in rice cultivars treated with organic acids and EDTA. J Environ Sci, 22(3): 441-447. |
| [34] | Yan Y F, Lestari P, Lee K J, Kim M Y, Lee S H, Lee B W. 2013. Identification of quantitative trait loci for cadmium accumulation and distribution in rice (Oryza sativa). Genome, 56(4): 227-232. |
| [35] | Zhang J, Sun W C, Li Z J, Liang Y C, Song A L. 2009. Cadmium fate and tolerance in rice cultivars. Agron Sustain Dev, 29(3): 483-490. |
| [36] |
Zhao J L, Yang W, Zhang S H, Yang T F, Liu Q, Dong J F, Fu H, Mao X X, Liu B. 2018. Genome-wide association study and candidate gene analysis of rice cadmium accumulation in grain in a diverse rice collection. Rice, 11(1): 61.
PMID |
| [37] | Zhou H, Zeng M, Zhou X, Liao B H, Peng P Q, Hu M, Zhu W, Wu Y J, Zou Z J. 2015. Heavy metal translocation and accumulation in iron plaques and plant tissues for 32 hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. Plant Soil, 386(1/2): 317-329. |
| [38] | Zhou Q, Shao G S, Zhang Y X, Dong Q, Wang H, Cheng S H, Cao L Y, Shen X H. 2017. The difference of cadmium accumulation between the indica and japonica sub species and the mechanism of it. Plant Growth Regul, 81(3): 523-532. |
| [39] | Zhu Q H, Zheng X M, Luo J C, Gaut B S, Ge S. 2007. Multilocus analysis of nucleotide variation of Oryza sativa and its wild relatives: Severe bottleneck during domestication of rice. Mol Biol Evol, 24(3): 875-888. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||