
Rice Science ›› 2018, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (2): 82-93.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2018.02.001
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Kamarul Zaman Nadzariah1, Yusoff Abdullah Mohd1( ), Othman Sariam2, Kamarul Zaman Nadzirah1(
), Othman Sariam2, Kamarul Zaman Nadzirah1( )
)
Received:2017-05-31
Accepted:2017-08-23
Online:2018-03-28
Published:2017-12-22
Kamarul Zaman Nadzariah, Yusoff Abdullah Mohd, Othman Sariam, Kamarul Zaman Nadzirah. Growth and Physiological Performance of Aerobic and Lowland Rice as Affected by Water Stress at Selected Growth Stages[J]. Rice Science, 2018, 25(2): 82-93.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Month | Temperature (ºC) | Rainfall | Relative humidity (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Maximum | (mm) | ||
| Aug-15 | 24.7 | 31.8 | 410.2 | 82.8 |
| Sep-15 | 24.6 | 31.8 | 113 | 83.9 |
| Oct-15 | 24.4 | 32.6 | 244 | 82.7 |
| Nov-15 | 24.6 | 32.4 | 217 | 85.9 |
| Dec-15 | 24.5 | 32.4 | 275.6 | 83.5 |
| Jan-16 | 25.2 | 33.3 | 122.4 | 81 |
Table 1 Climatic factors during experimental period.
| Month | Temperature (ºC) | Rainfall | Relative humidity (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Maximum | (mm) | ||
| Aug-15 | 24.7 | 31.8 | 410.2 | 82.8 |
| Sep-15 | 24.6 | 31.8 | 113 | 83.9 |
| Oct-15 | 24.4 | 32.6 | 244 | 82.7 |
| Nov-15 | 24.6 | 32.4 | 217 | 85.9 |
| Dec-15 | 24.5 | 32.4 | 275.6 | 83.5 |
| Jan-16 | 25.2 | 33.3 | 122.4 | 81 |
| Treatment | Growth stage | Variety | Imposition of water stress a (d) | Stress |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| period (d) | ||||
| T2 | Panicle initiation | MA1 | 44-53 | 10 |
| MR253 | 56-71 | 16 | ||
| T3 | Flowering | MA1 | 56-71 | 16 |
| MR253 | 77-92 | 16 | ||
| T4 | Early ripening | MA1 | 77-88 | 12 |
| MR253 | 95-105 | 11 |
Table 2 Water stress imposition period based on crop age and water stress period at various growth stages.
| Treatment | Growth stage | Variety | Imposition of water stress a (d) | Stress |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| period (d) | ||||
| T2 | Panicle initiation | MA1 | 44-53 | 10 |
| MR253 | 56-71 | 16 | ||
| T3 | Flowering | MA1 | 56-71 | 16 |
| MR253 | 77-92 | 16 | ||
| T4 | Early ripening | MA1 | 77-88 | 12 |
| MR253 | 95-105 | 11 |
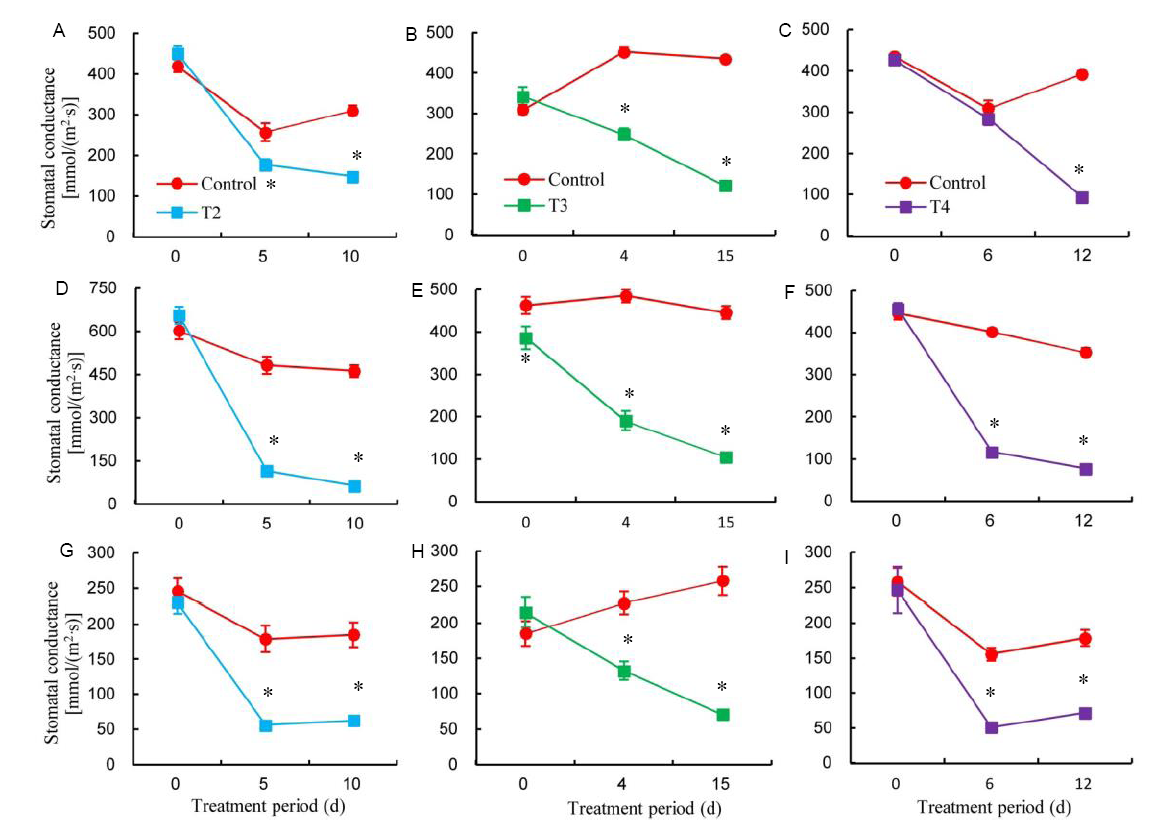
Fig. 1. Changes in diurnal stomatal conductance (gs) during water stress period of MA1 as affected by water stress at selected growth stages.A, Morning gs under treatment 2 (T2, water stress at the panicle initiation stage); B, Morning gs under treatment 3 (T3, water stress at the flowering stage); C, Morning gs under treatment 4 (T4, water stress at the ripening stage); D, Midday gs under T2; E, Midday gs under T3; F, Midday gs under T4; G, Evening gs under T2; H, Evening gs under T3; I, Evening gs under T4. * represents significant difference between treatments at P ≤ 0.05. Bars are standard errors (n = 12).
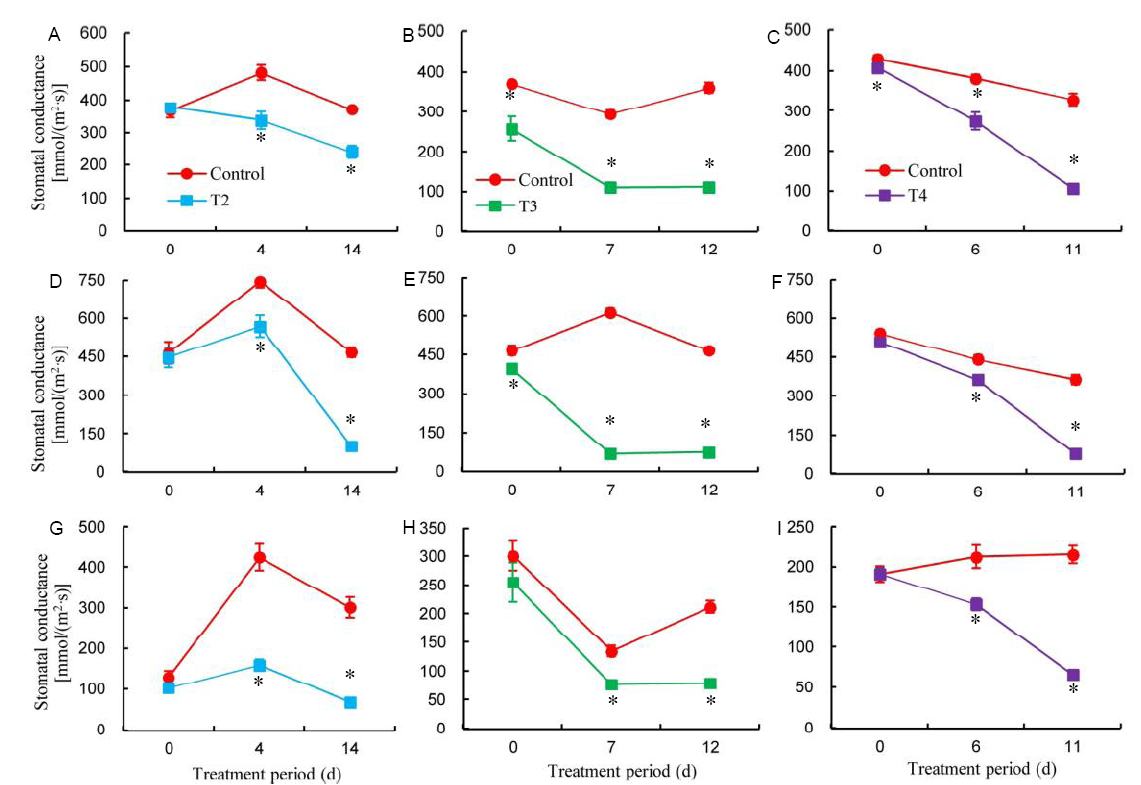
Fig. 2. Changes in diurnal stomatal conductance (gs) during water stress period of MR253 as affected by water stress at selected growth stages.A, Morning gs under treatment 2 (T2, water stress at the panicle initiation stage); B, Morning gs under treatment 3 (T3, water stress at the flowering stage); C, Morning gs under treatment 4 (T4, water stress at the ripening stage); D, Midday gs under T2; E, Midday gs under T3; F, Midday gs under T4; G, Evening gs under T2; H, Evening gs under T3; I, Evening gs under T4. * represents significant difference between treatments at P ≤ 0.05 (n = 12).
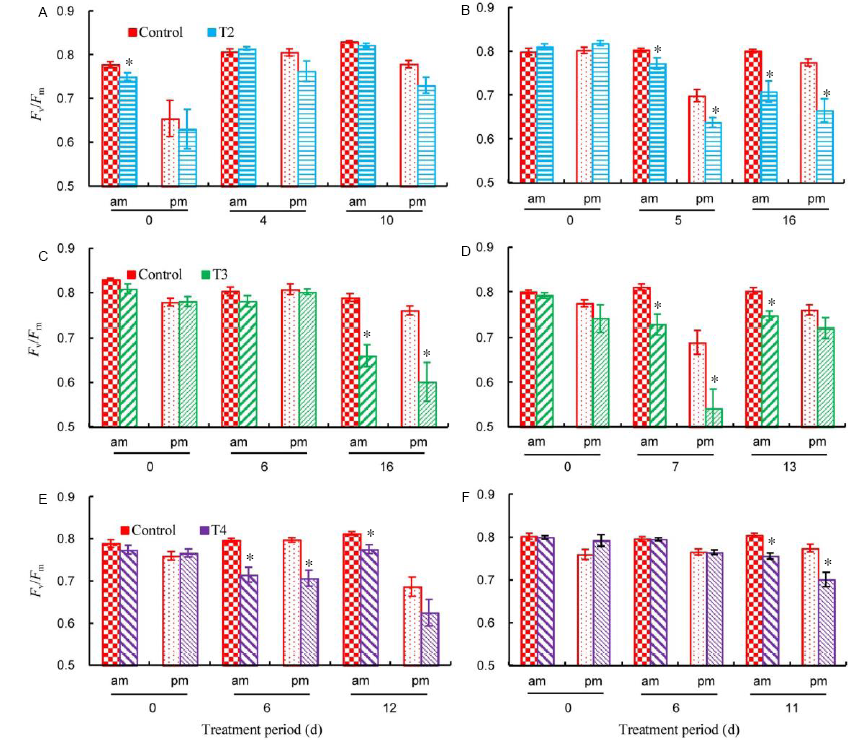
Fig. 3. Changes in chlorophyll a fluorescence (Fv/Fm) during water stress period of the two varieties as affected by water stress at selected growth stages.* represents significant difference between treatments at P ≤ 0.05 (n = 12).A, MA1 at the panicle initiation stage; B, MR253 at the panicle initiation stage; C, MA1 at the flowering stage; D, MR253 at the flowering stage; E, MA1 at the ripening stage; F, MR253 at the ripening stage.
| Variety | Stage | Treatment | SMC (%) | Leaf RWC (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base | Middle | End | Base | Middle | End | ||||
| MA1 | Panicle initiation | Control | 22.92 ± 2.82 ns | 15.57 ± 1.32 ns | 12.60 ± 0.40 a | 80.81 ± 2.36 b | 95.47 ± 0.76 a | 92.09 ± 1.39 a | |
| Water stress | 22.13 ± 2.53 ns | 15.50 ± 1.19 ns | 6.57 ± 0.35 b | 92.49 ± 1.09 a | 83.92 ± 0.94 b | 58.21 ± 1.34 b | |||
| Flowering | Control | 12.60 ± 0.40 ns | 19.69 ± 1.39 a | 24.78 ± 0.44 a | 90.01 ± 2.43 ns | 87.64 ± 1.91 ns | 87.55 ± 1.40 a | ||
| Water stress | 13.89 ± 0.87 ns | 10.49 ± 0.70 b | 3.67 ± 0.34 b | 93.61 ± 1.16 ns | 83.69 ± 1.04 ns | 56.85 ± 0.91 b | |||
| Ripening | Control | 24.78 ± 0.44 ns | 27.00 ± 0.43 a | 24.01 ± 1.06 a | 87.55 ± 1.40 ns | 86.32 ± 1.49 a | 84.46 ± 1.29 a | ||
| Water stress | 24.06 ± 0.55 ns | 9.63 ± 0.23 b | 7.30 ± 0.29 b | 90.64 ± 1.19 ns | 81.11 ± 1.30 b | 53.16 ± 0.93 b | |||
| MR253 | Panicle initiation | Control | 14.91 ± 0.72 b | 21.67 ± 1.49 a | 22.24 ± 2.30 a | 91.02 ± 1.22 ns | 89.42 ± 1.34 a | 91.93 ± 1.07 a | |
| Water stress | 21.17 ± 1.71 a | 15.16 ± 1.37 b | 3.53 ± 0.28 b | 92.10 ± 0.98 ns | 79.08 ± 1.54 b | 56.41 ± 1.10 b | |||
| Flowering | Control | 22.24 ± 2.30 ns | 18.42 ± 0.65 a | 22.06 ± 0.40 a | 91.93 ± 1.07 ns | 88.46 ± 0.96 a | 87.91 ± 0.81 a | ||
| Water stress | 23.18 ± 2.07 ns | 9.03 ± 0.18 b | 7.76 ± 0.26 b | 89.65 ± 0.58 ns | 78.07 ± 1.44 b | 53.25 ± 0.61 b | |||
| Ripening | Control | 12.66 ± 0.49 ns | 14.52 ± 0.56 a | 13.59 ± 0.79 a | 75.34 ± 2.22 ns | 83.31 ± 2.28 a | 78.44 ± 1.11 a | ||
| Water stress | 12.51 ± 0.17 ns | 8.37 ± 0.47 b | 6.59 ± 0.26 b | 76.20 ± 1.20 ns | 63.49 ± 1.39 b | 51.37 ± 2.59 b | |||
Table 3 Soil moisture content (SMC) and leaf relative water content (leaf RWC) during water stress period at selected growth stages.
| Variety | Stage | Treatment | SMC (%) | Leaf RWC (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base | Middle | End | Base | Middle | End | ||||
| MA1 | Panicle initiation | Control | 22.92 ± 2.82 ns | 15.57 ± 1.32 ns | 12.60 ± 0.40 a | 80.81 ± 2.36 b | 95.47 ± 0.76 a | 92.09 ± 1.39 a | |
| Water stress | 22.13 ± 2.53 ns | 15.50 ± 1.19 ns | 6.57 ± 0.35 b | 92.49 ± 1.09 a | 83.92 ± 0.94 b | 58.21 ± 1.34 b | |||
| Flowering | Control | 12.60 ± 0.40 ns | 19.69 ± 1.39 a | 24.78 ± 0.44 a | 90.01 ± 2.43 ns | 87.64 ± 1.91 ns | 87.55 ± 1.40 a | ||
| Water stress | 13.89 ± 0.87 ns | 10.49 ± 0.70 b | 3.67 ± 0.34 b | 93.61 ± 1.16 ns | 83.69 ± 1.04 ns | 56.85 ± 0.91 b | |||
| Ripening | Control | 24.78 ± 0.44 ns | 27.00 ± 0.43 a | 24.01 ± 1.06 a | 87.55 ± 1.40 ns | 86.32 ± 1.49 a | 84.46 ± 1.29 a | ||
| Water stress | 24.06 ± 0.55 ns | 9.63 ± 0.23 b | 7.30 ± 0.29 b | 90.64 ± 1.19 ns | 81.11 ± 1.30 b | 53.16 ± 0.93 b | |||
| MR253 | Panicle initiation | Control | 14.91 ± 0.72 b | 21.67 ± 1.49 a | 22.24 ± 2.30 a | 91.02 ± 1.22 ns | 89.42 ± 1.34 a | 91.93 ± 1.07 a | |
| Water stress | 21.17 ± 1.71 a | 15.16 ± 1.37 b | 3.53 ± 0.28 b | 92.10 ± 0.98 ns | 79.08 ± 1.54 b | 56.41 ± 1.10 b | |||
| Flowering | Control | 22.24 ± 2.30 ns | 18.42 ± 0.65 a | 22.06 ± 0.40 a | 91.93 ± 1.07 ns | 88.46 ± 0.96 a | 87.91 ± 0.81 a | ||
| Water stress | 23.18 ± 2.07 ns | 9.03 ± 0.18 b | 7.76 ± 0.26 b | 89.65 ± 0.58 ns | 78.07 ± 1.44 b | 53.25 ± 0.61 b | |||
| Ripening | Control | 12.66 ± 0.49 ns | 14.52 ± 0.56 a | 13.59 ± 0.79 a | 75.34 ± 2.22 ns | 83.31 ± 2.28 a | 78.44 ± 1.11 a | ||
| Water stress | 12.51 ± 0.17 ns | 8.37 ± 0.47 b | 6.59 ± 0.26 b | 76.20 ± 1.20 ns | 63.49 ± 1.39 b | 51.37 ± 2.59 b | |||
| Parameter | gs | Fv/Fm | Leaf RWC | SMC | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morning | Midday | Pooled data | Morning | Midday | Pooled data | Morning | Midday | Pooled data | Morning | Midday | Pooled data | ||||
| gs | - | - | - | 0.51** | 0 | -0.12 | 0.39* | 0.57** | 0.45** | 0.23 | 0.45* | 0.33* | |||
| Fv/Fm | -0.22 | -0.18 | -0.25 | - | - | - | 0.35 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.19 | 0.03 | 0.05 | |||
| Leaf RWC | 0.47* | 0.57** | 0.51*** | 0.27 | 0.51** | 0.36** | - | - | - | 0.74*** | 0.74*** | 0.74*** | |||
| SMC | 0.69*** | 0.58** | 0.60*** | -0.38 | -0.25 | -0.26 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33* | - | - | - | |||
Table 4 Correlation coefficients of various physiological parameters during water stress period.
| Parameter | gs | Fv/Fm | Leaf RWC | SMC | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morning | Midday | Pooled data | Morning | Midday | Pooled data | Morning | Midday | Pooled data | Morning | Midday | Pooled data | ||||
| gs | - | - | - | 0.51** | 0 | -0.12 | 0.39* | 0.57** | 0.45** | 0.23 | 0.45* | 0.33* | |||
| Fv/Fm | -0.22 | -0.18 | -0.25 | - | - | - | 0.35 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.19 | 0.03 | 0.05 | |||
| Leaf RWC | 0.47* | 0.57** | 0.51*** | 0.27 | 0.51** | 0.36** | - | - | - | 0.74*** | 0.74*** | 0.74*** | |||
| SMC | 0.69*** | 0.58** | 0.60*** | -0.38 | -0.25 | -0.26 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33* | - | - | - | |||
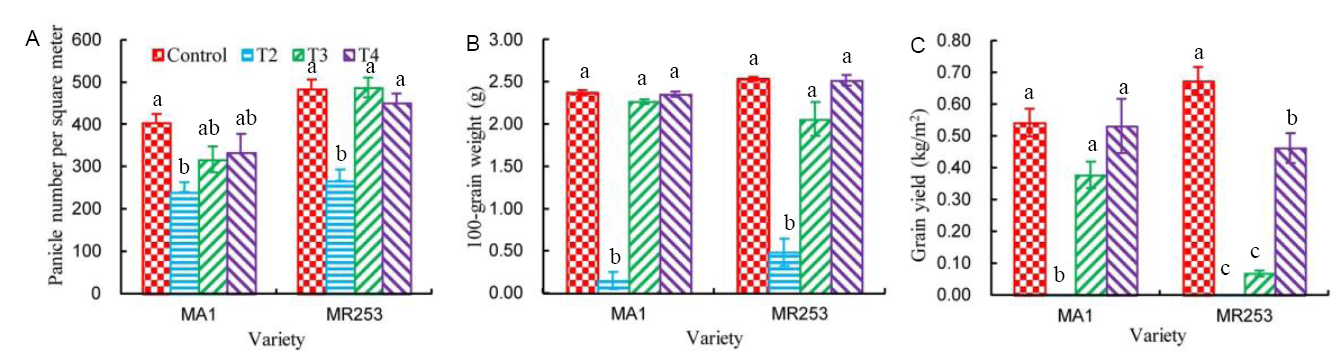
Fig. 4. Panicle number, 100-grain weight and grain yield of the two varieties as affected by water stress (n = 6).T2, Water stress at the panicle initiation stage; T3, Water stress at the flowering stage; T4, Water stress at the ripening stage.Different letters mean significant difference between treatments at the 0.05 level.
| [1] | Abou-Khalifa A A B.2010. Response of some rice varieties to irrigation withholding under different sowing dates.Agric Biol J North Am, 1(1): 56-64. |
| [2] | Anjum S A, Xie X Y, Wang L C, Saleem M F, Man C, Lei W.2011. Morphological, physiological and biochemical responses of plants to drought stress.Afr J Agric Res, 6(9): 2026-2032. |
| [3] | Bakul M R A, Akter M S, Islam M N, Chowdhury M M A A, Amin M H A.2009. Water stress effect on morphological characters and yield attributes in some mutants T-Aman rice lines.Bangl Res Public J, 3(2): 934-944. |
| [4] | Björkman O, Demmig B.1987. Photon yield of O2 evolution and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics at 77K among vascular plants of diverse origin.Planta, 170(4): 489-504. |
| [5] | Black C A.1965. Methods of Soil Analysis: I. Physical and Mineralogical Properties. Wisconsin: American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America. |
| [6] | Boonjung H, Fukai S.1996. Effects of soil water deficit at different growth stages on rice growth and yield under upland conditions: 2. Phenology, biomass production and yield.Field Crops Res, 48(1): 47-55. |
| [7] | Bouman B A M, Hengsdijk H, Hardy B, Bindraban P S, Tuong T P, Ladha J K.2002. Water-wise rice production. In: Proceedings of the International Workshop on Water-Wise Rice Production. 8-11 April 2002. Los Baños, the Phillipines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| [8] | Bunnag S, Pongthai P.2013. Selection of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars tolerant to drought stress at the vegetative stage under field conditions. Am J Plant Sci, 4(9): 1701-1708. |
| [9] | Chan C S, Zainudin H, Saad A, Azmi M.2012. Productive water use in aerobic rice cultivation.J Trop Agric Food Sci, 49(1): 117-126. |
| [10] | Chauhan B S, Abugho S B.2013. Effect of water stress on the growth and development of Amaranthus spinosus, Leptochloa chinensis, and rice. Am J Plant Sci, 4: 989-998. |
| [11] | Cha-um S, Yooyongwech S, Supaibulwatana K.2010. Water deficit stress in the reproductive stage of four indica rice(Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. J Bot, 42(5): 3387-3398. |
| [12] | Cha-um S, Yooyongwech S, Supaibulwatana K.2012. Water-deficit tolerant classification in mutant lines of indica rice. Sci Agric, 69(2): 135-141. |
| [13] | Chen D Q, Wang S W, Cao B B, Cao D, Leng G H, Li H B, Yin L N, Shan L, Deng X P.2015. Genotypic variation in growth and physiological response to drought stress and re-watering reveals the critical role of recovery in drought adaptation in maize seedlings.Front Plant Sci, 6: 1241. |
| [14] | Davatgar N, Neishabouri M R, Sepaskhah A R, Soltani A.2009. Physiological and morphological responses of rice (Oryza sativa L.) to varying water stress management strategies. Int J Plant Prod, 3(4): 19-32. |
| [15] | Fan X L, Zhang Z S, Gao H Y, Yang C, Liu M J, Li Y T, Li P M.2014. Photoinhibition-like damage to the photosynthetic apparatus in plant leaves induced by submergence treatment in the dark.PLoS One, 9(2): e89067. |
| [16] | Farquhar G D, Sharkey T D.1982. Stomatal conductance and photosynthesis.Annu Rev Plant Physiol, 33(1): 317-345. |
| [17] | Gauthami P, Subrahmanyam D, Padma V, Kiran T V, Rao Y V, Rao P R, Voleti S R.2014. Variation in leaf photosynthetic response of rice genotypes to post-anthesis water deficit.Ind J Plant Physiol, 19(2): 127-137. |
| [18] | Glimn-Lacy J, Kaufman P B.2006. Botany Illustrated: Introduction to Plants, Major Groups, Flowering Plant Families. 2nd edn. USA: Springer. |
| [19] | González L, González-Vilar M.2001. Determination of relative water content. In: Roger M J R. Handbook of Plant Ecophysiology Techniques. Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Springer: 207-212. |
| [20] | Govindarasu R, Paramasivam K, Nadaradjan S, Shashidhara N, Vengatesh M.2015. Aerobic rice: A production system for water scarceness.AE Int J Sci Technol, 3(6): 2348-6732. |
| [21] | Guimarães C M, Stone L F, Rangel P H N, Silva A C D L.2013. Tolerance of upland rice genotypes to water deficit.Rev Bras Eng Agric Ambient, 17(8): 805-810. |
| [22] | Jones H G.1992. Plants and Microclimate: A Quantitative Approach to Environmental Plant Physiology. 2nd edn. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [23] | Kato Y, Okami M.2011. Root morphology, hydraulic conductivity and plant water relations of high-yielding rice grown under aerobic conditions.Ann Bot, 108(3): 575-583. |
| [24] | Li R H, Guo P G, Baum M, Grando S, Ceccarelli S.2006. Evaluation of chlorophyll content and fluorescence parameters as indicators of drought tolerance in barley.Agric Sci China, 5(10): 751-757. |
| [25] | Liang Z S, Zhang F S, Shao M G, Zhang J H.2002. The relations of stomatal conductance, water consumption, growth rate to leaf water potential during soil drying and rewatering cycle of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Bot Bull Acad Sin, 43: 187-192. |
| [26] | Liu J H, Shen J Q, Xu Y, Li X H, Xiao J H, Xiong L Z.2016. Ghd2, a CONSTANS-like gene, confers drought sensitivity through regulation of senescence in rice. J Exp Bot, 67(19): 5785-5798. |
| [27] | Long S P, Zhu X G, Naidu S L, Ort D R.2006. Can improvement in photosynthesis increase crop yields?Plant Cell Environ, 29(3): 315-330. |
| [28] | Lu G, Cabangon R, Tuong T P, Belder P, Bouman B A M, Castillo E.2002. The effects of irrigation management on yield and water productivity of inbred, hybrid and aerobic rice varieties. In: Bouman B A M, Hengsdijk H, Hardy B, Bindraban P S, Tuong T P, Ladha J K. Proceedings of the International Workshop on Water-Wise Rice Production. 8-11 April 2002. Los Baños, the Phillipines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| [29] | Mahmod I F, Barakbah S S, Osman N, Omar O.2014. Physiological response of local rice varieties to aerobic condition.Int J Agric Biol, 16(4): 738-744. |
| [30] | MARDI (Malaysian Agricultural Research and Development Institute). 2009. Paddy Grow: Sustainable Rice Cultivation Technology Manual. MARDI Press. (in Malay) |
| [31] | MARDI (Malaysian Agricultural Research and Development Institute). 2014. MARDI New Popular Varieties. Kuala Lumpur: MARDI Press. (in Malay) |
| [32] | Na Y W, Jeong H J, Lee S Y, Choi H G, Kim S H, Rho I R.2014. Chlorophyll fluorescence as a diagnostic tool for abiotic stress tolerance in wild and cultivated strawberry species.Hort Environ Biotechnol, 55(4): 280-286. |
| [33] | O’Neill S D.1983. Role of osmotic potential gradients during water stress and leaf senescence in Fragaria virginiana. Plant Physiol, 72(4): 931-937. |
| [34] | Panda D.2011. Diurnal variations in gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence in rice leaves: The cause for midday depression in CO2 photosynthetic rate.J Stress Physiol Biochem, 7(4): 175-186. |
| [35] | Panda D, Sarkar R K.2013. Natural leaf senescence: Probed by chlorophyll fluorescence, CO2 photosynthetic rate and antioxidant enzyme activities during grain filling in different rice cultivars.Physiol Mol Biol Plants, 19(1): 43-51. |
| [36] | Pandey P, Bhandari H.2007. Drought: An overview. In: Pandey P, Bhandari H, Hardy B. Economic Costs of Drought and Rice Farmers’ Coping Mechanisms: A Cross-Country Comparative Analysis. Los Baños, the Phillipines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| [37] | Parthasarathi T, Vanitha K, Lakshamanakumar P, Kalaiyarasi D.2012. Aerobic rice-mitigating water stress for the future climate change.Int J Agron Plant Prod, 3(7): 241-254. |
| [38] | Pask A J D, Pietragalla J.2012. Stomatal conductance. In: Pask A J D, Pietragalla J, Mullan D M, Reynolds M P. Physiological Breeding: II. A Field Guide to Wheat Phenotyping. Mexico: CIMMYT: 15-17. |
| [39] | Pirdashti H, Sarvestani Z T, Bahmanyar M A.2009. Comparison of physiological responses among four contrast rice cultivars under drought stress conditions.Proc World Acad Sci Engin Technol, 49: 52-53. |
| [40] | Roohi E, Tahmasebi-Sarvestani Z, Modarres-Sanavy S A M, Siosemardeh A.2013. Comparative study on the effect of soil water stress on photosynthetic function of triticale, bread wheat, and barley.J Agric Sci Technol, 15: 215-225. |
| [41] | Saragih A A, Puteh A B, Ismail M R, Mondal M M A.2013. Pollen quality traits of cultivated (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica) and weedy(Oryza sativa var. nivara) rice to water stress at reproductive stage. Aust J Crop Sci, 7(8): 1106-1112. |
| [42] | Sariam O, Zainudin P M D H, Chan C S, Azmi M, Rosniyana A, Badrulhadza A.2014. Aerobic rice for water shortage problem.J Technol, 70(6): 65-68. (in Malay) |
| [43] | Sariam O, Azmi M, Chan C S, Badrulhadza A, Mohd Khusairy K, Mohd Fitri M, Alicia A J, Rosnani H, Shamsul A S.2015. Aerobic Rice Manual. Kuala Lumpur: MARDI Press. (in Malay) |
| [44] | Shahruddin S, Puteh A, Juraimi A S.2014. Responses of source and sink manipulations on yield of selected rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. J Adv Agric Technol, 1(2): 125-131. |
| [45] | Shimono H, Okada M, Inoue M, Nakamura H, Kobayashi K, Hasegawa T.2010. Diurnal and seasonal variations in stomatal conductance of rice at elevated atmospheric CO2 under fully open-air conditions.Plant Cell Environ, 33(3): 322-331. |
| [46] | Sikuku P A, Netondo G W, Onyango J C, Musyimi D M.2010. Effects of water deficit on physiology and morphology of three varieties of Nerica rainfed rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Agric Biol Sci, 5(1): 23‒28. |
| [47] | Sikuku P A, Onyango J C, Netondo G W.2012. Physiological and biochemical responses of five nerica rice varieties (Oryza sativa L.) to water deficit at vegetative and reproductive stage. Agric Biol J North Am, 3(3): 93‒104. |
| [48] | Sokoto M B, Muhammad A.2014. Response of rice varieties to water stress in Sokoto, Sudan Savannah, Nigeria.J Biosci Med, 2: 68-74. |
| [49] | Sunian E, Azlan S, Zainudin P M D H, Saad A, Alias I, Othman O, Rani M N F A, Muhamad H, Asfaliza R, Mohamad Najib M Y, Nurkhairani A B, Amirrudin M, Maisarah M S, Shahida H, Siti Norsuha M.2012. MR253: New rice varieties resistant to blast disease and suitable for planting on marginal soil.Bull Technol MARDI, 1: 23-31. (in Malay) |
| [50] | Turner N C.1981. Techniques and experimental approaches for the measurement of the plant water status.Plant Soil, 58: 339-366. |
| [51] | Uyprasert S, Toojinda T, Udomprasert N, Tragoonrung S, Vanavichit A.2004. Root responses to water deficit under rain-fed lowland rice.Kasetsart J (Nat Sci), 38: 448-456. |
| [52] | Wopereis M C S, Kropff M J, Maligaya A R, Tuong T P.1996. Drought-stress responses of two lowland rice cultivars to soil water status.Field Crops Res, 46(1): 21-39. |
| [53] | Yang X, Wang H, Wang Z, Zhao J, Chen B, Bouman B A M.2002. Yield of aerobic rice (Han Dao) under different water regimes in North China. In: Bouman B A M, Hengsdijk H, Hardy B, Bindraban P S, Tuong T P, Ladha J K. Proceedings of the International Workshop on Water-Wise Rice Production. 8-11 April 2002. Los Baños, the Phillipines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| [54] | Yan W M, Zhong Y Q, Shangguan Z P.2016. A meta-analysis of leaf gas exchange and water status responses to drought.Sci Rep, 6: 20917. |
| [55] | Yoshida S.1981. Growth and Development of the Rice Plant: Fundamentals of Rice Crop Science. Los Baños, the Phillipines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| [56] | Yu S M, Lo S F, Ho T H.2015. Source-sink communication: Regulated by hormone, nutrient, and stress cross-signaling.Trends Plant Sci, 20(12): 844-857. |
| [57] | Zain N A M, Ismail M R, Mahmood M, Puteh A, Ibrahim M H.2014. Alleviation of water stress effects on MR220 rice by application of periodical water stress and potassium fertilization.Molecules, 19(2): 1795-1819. |
| [58] | Zhang W H, Kokubun M.2004. Historical changes in grain yield and photosynthetic rate of rice cultivars released in the 20th century in Tohoku Region.Plant Prod Sci, 7(1): 36-44. |
| [59] | Zulkarnain W M, Ismail M R, Ashrafuzzaman M, Mohd Saud H M, Haroun I C.2009. Growth, physiological and biochemical responses of Malaysia rice cultivars to water stress.Pertanika J Trop Agric Sci, 32(2): 323-333. |
| [1] | Kartika Kartika, Sakagami Jun-Ichi, Lakitan Benyamin, Yabuta Shin, Wijaya Andi, Kadir Sabaruddin, Ilman Widuri Laily, Siaga Erna, Nakao Yoshihiro. Morpho-Physiological Response of Oryza glaberrima to Gradual Soil Drying [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(1): 67-74. |
| [2] | Amanullah, Hidayatullah. Influence of Organic and Inorganic Nitrogen on Grain Yield and Yield Components of Hybrid Rice in Northwestern Pakistan [J]. Rice Science, 2016, 23(6): 326-333. |
| [3] | Sekiya Nobuhito, Cyril Shayo Aristarick, Kaozya Jacob Mathew, Oizumi Nobuaki, Tomitaka Motonori, Araki Hideki. Performance of Four Rice Cultivars Transplanted Monthly over Full Year under Irrigated Conditions in Tanzania [J]. Rice Science, 2015, 22(2): 71-80. |
| [4] | N. Manikanda BOOPATHI1, Gat SWAPNASHRI1, P. KAVITHA1, S. SATHISH1, R. NITHYA1, Wickneswari RATNAM2, Arvind KUMAR3. Evaluation and Bulked Segregant Analysis of Major Yield QTL qtl12.1 Introgressed into Indigenous Elite Line for Low Water Availability under Water Stress [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2013, 20(1): 25-30. |
| [5] | B. P. MALLIKARJUNA SWAMY1,,K. KALADHAR, M. S. RAMESHA, B. C. VIRAKTAMATH, N. SARLA. Molecular Mapping of QTLs for Yield and Related Traits in Oryza sativa cv Swarna x O. nivara (IRGC81848) Backcross Population [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2011, 18(3): 178-186. |
| [6] | FU Guan-fu, SONG Jian, LI Yu-rong, YUE Ming-kai, XIONG Jie, TAO Long-xing. Alterations of Panicle Antioxidant Metabolism and Carbohydrate Content and Pistil Water Potential Involved in Spikelet Sterility in Rice under Water-Deficit Stress [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2010, 17(4): 303-310 . |
| [7] | Suriyan CHA-UM, Kanyaratt SUPAIBULWATTANA, Chalermpol KIRDMANEE. Comparative Effects of Salt Stress and Extreme pH Stress Combined on Glycinebetaine Accumulation, Photosynthetic Abilities and Growth Characters of Two Rice Genotypes [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2009, 16(4): 274-282 . |
| [8] | LIU Shi-ping, NIE Xin-tao, DAI Qi-gen, HUO Zhong-yang, XU Ke. Effect of Interplanting with Zero Tillage and Straw Manure on Rice Growth and Rice Quality [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2007, 14(3): 204-210 . |
| [9] | ZHANG Wen-zhong, HAN Ya-dong, DU Hong-juan. Relationship Between Canopy Temperature at Flowering Stage and Soil Water Content, Yield Components in Rice [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2007, 14(1): 67-70 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||