
Rice Science ›› 2018, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 279-285.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2018.04.005
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hongyan Liu1,2, Weiqin Wang1, Aibin He1, Lixiao Nie1,3( )
)
Received:2018-01-04
Accepted:2018-04-17
Online:2018-09-28
Published:2018-06-11
Hongyan Liu, Weiqin Wang, Aibin He, Lixiao Nie. Correlation of Leaf and Root Senescence During Ripening in Dry Seeded and Transplanted Rice[J]. Rice Science, 2018, 25(5): 279-285.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
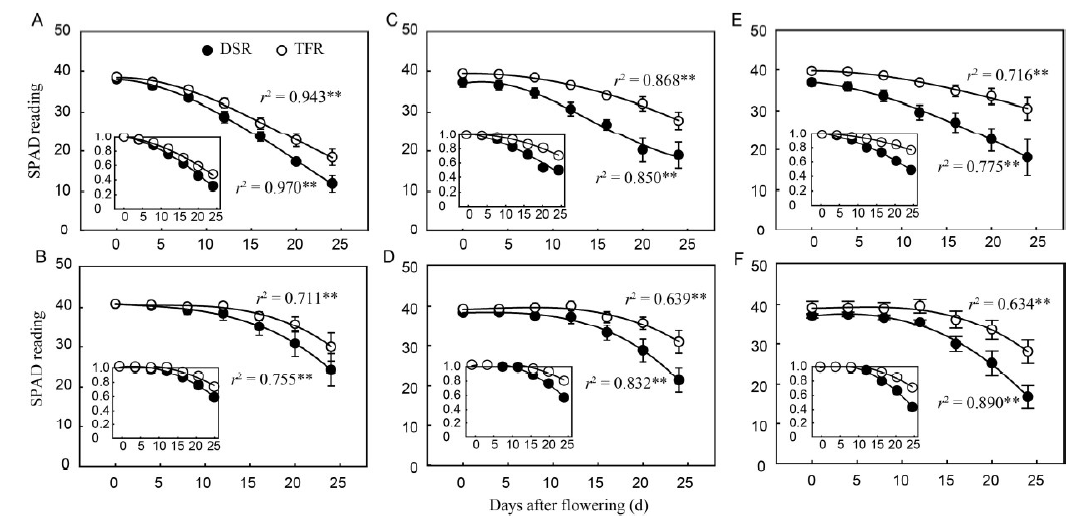
Fig. 1. Relationship between SPAD value and days after flowering under DSR and TFR in 2012 (Main graph: Cubic fitting) and the dynamic changes (Inset: Quadratic fitting) in relative SPAD value after flowering (normalized by SPAD value at flowering) under DSR and TFR. A, Huanghuazhan for flag leaf; B, Yangliangyou 6 for flag leaf; C, Huanghuazhan for top second leaf; D, Yangliangyou 6 for top second leaf; E, Huanghuazhan for top third leaf; F, Yangliangyou 6 for top third leaf. SPAD, Soil and plant analyzer development; DSR, Dry seeded flooded rice; TFR, Transplanted flooded rice.**, Significant difference at the 0.01 level. Data in main graphs are shown as mean ± standard error, and the data in inset graphs are means.
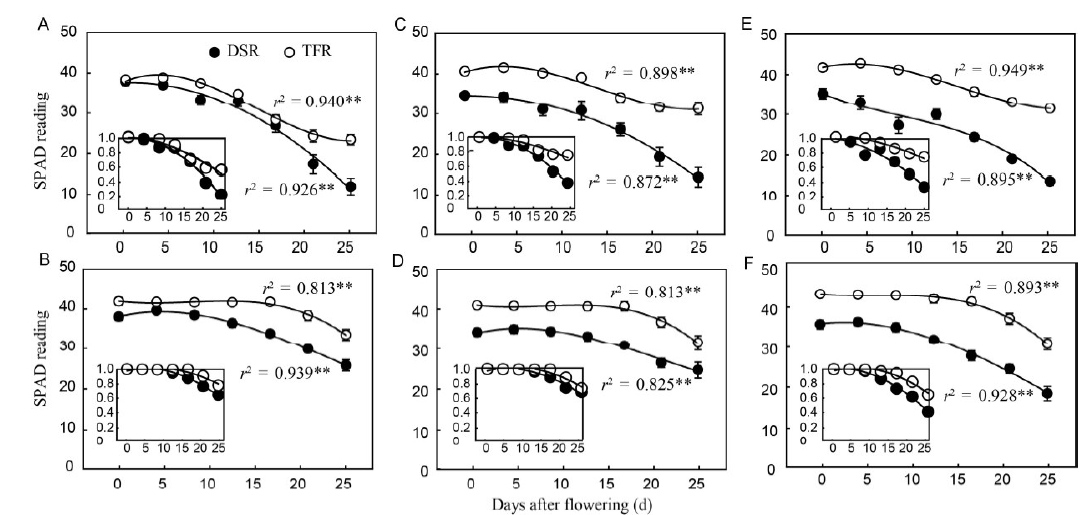
Fig. 2. Relationship between SPAD value and days after flowering under DSR and TFR in 2013 (Main graphs: Cubic fitting) and the dynamic changes (Inset: Quadratic fitting) in relative SPAD value after flowering (normalized by SPAD value at flowering) under DSR and TFR.A, Huanghuazhan for flag leaf; B, Yangliangyou 6 for flag leaf; C, Huanghuazhan for top second leaf; D, Yangliangyou 6 for top second leaf; E, Huanghuazhan for top third leaf; F, Yangliangyou 6 for top third leaf. SPAD, Soil and plant analyzer development; DSR, Dry seeded flooded rice; TFR, Transplanted flooded rice.**, Significant difference at the 0.01 level. Data in main graphs are shown as mean ± standard error, and the data in inset graphs are means.
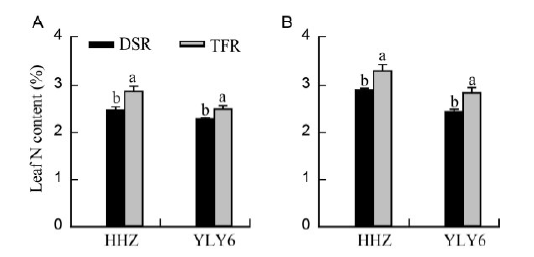
Fig. 3. Leaf nitrogen (N) content of Huanghuazhan (HHZ) and Yangliangyou 6 (YLY6) in DSR and TFR at the flowering stage in 2012 (A) and 2013 (B).DSR, Dry seeded flooded rice; TFR, Transplanted flooded rice.Data are shown as mean ± standard error. Different lowercase letters represent significant difference at the 0.05 level.
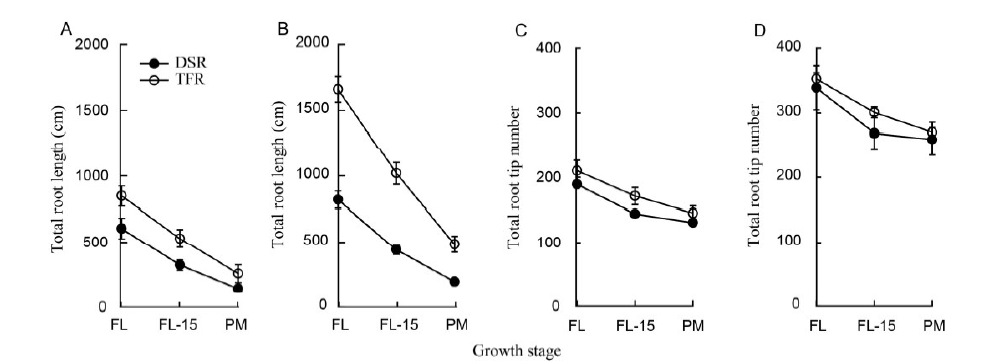
Fig. 4. Total root lengthand tip number of Huanghuazhan (A and C) and Yangliangyou 6 (B and D) in DSR and TFR at different growth stages.DSR, Dry seeded flooded rice; TFR, Transplanted flooded rice; FL, Flowering stage; FL-15, Mid-grain filling; PM, Physiological maturity stage.Root data were collected from 0-45 cm below soil surface in 2013. Data are shown as mean ± standard error.
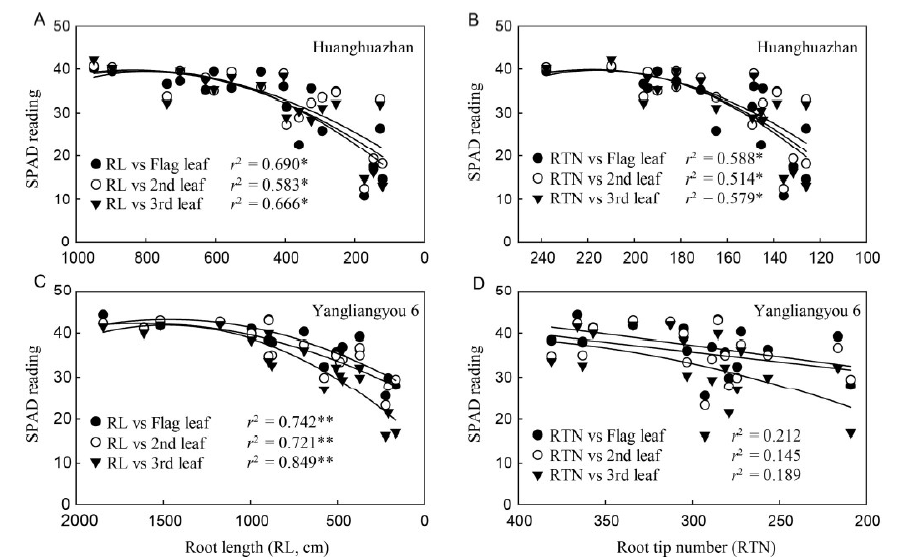
Fig. 5. Relationship between SPAD value of top three leaves and root amount at flowering stage (FL), mid-grain filling stage (FL-15) and physiological maturity (PM) stages in Huanghuazhan and Yangliangyou 6 under both DSR and TFR in 2013. DSR, Dry seeded flooded rice; TFR, Transplanted flooded rice; 2nd, The top 2nd leaf; 3rd, The top 3rd leaf.* and **, Significant difference at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively.
| 1 | Beyrouty C A, Wells B R, Norman R J, Marvel J N, Pillow J A.1988. Root growth dynamics of a rice cultivar grown at two locations.Agron J, 80: 1001-1004. |
| 2 | Beyrouty C A, Norman R J, Wells B R, Gbur E E, Grigg B, Teo Y H.1992. Water management and location effects on root and shoot growth of irrigated lowland rice.J Plant Nutr, 15: 737-752. |
| 3 | Cairns J E, Impa S M, O’Toole J C, Jagadish S V K, Price A H.2011. Influence of the soil physical environment on rice (Oryza sativa L.) response to drought stress and its implications for drought research.Field Crop Res, 121(3): 303-310. |
| 4 | Cassman K G, Whitney A S, Stockinger K R.1980. Root growth and dry matter distribution of soybean as affected by phosphorus stress, nodulation, and nitrogen source.Crop Sci, 20: 239-244. |
| 5 | Colmer T D.2003. Long-distance transport of gases in plants: A perspective on internal aeration and radial oxygen loss from roots.Plant Cell Environ, 26(1): 17-36. |
| 6 | Fu J D, Yan Y F, Lee B W.2009. Physiological characteristics of a functional stay-green rice ‘SNU-SG1’ during grain-filling period.J Crop Sci Biotechnol, 12(1): 47-52. |
| 7 | Gong Y H, Ji X H, Gao J F.2009. Grain sink strength related to carbon staying in the leaves of hybrid wheat XN901.Agr Sci China, 8(5): 546-555. |
| 8 | Humphreys E, Freney J R, Muirhead W A, Denmead O T, Simpson J R, Leuning R, Trevitt A C F, Obcemea W N, Wetselaar R, Cai G X.1988. Loss of ammonia after application of urea at different times to dry-seeded, irrigated rice.Nutr Cycl Agroeco, 16(1): 47-57. |
| 9 | Johnson M G, Tingey D T, Phillips D L, Storm M J.2001. Advancing fine root research with minirhizotrons.Environ Exp Bot, 45(3): 263-289. |
| 10 | Kato Y, Kamoshita A, Yamagishi J, Imoto H, Abe J.2007. Growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars under upland conditions with different levels of water supply: 3. Root system development, soil moisture change and plant water status.Plant Prod Sci, 10: 3-13. |
| 11 | Kato Y, Okami M.2010. Root growth dynamics and stomatal behaviour of rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown under aerobic and flooded conditions.Field Crop Res, 117(1): 9-17. |
| 12 | Katsura K, Maeda S, Horie T, Shiraiwa T.2007. Analysis of yield attributes and crop physiological traits of Liangyoupeijiu, a hybrid rice recently bred in China.Field Crop Res, 103(3): 170-177. |
| 13 | Laza M R C, Peng S B, Sanico A L, Visperas R M, Akita S.2001. Higher leaf area growth rate contributes to greater vegetative growth of F1 rice hybrids in the tropics.Plant Prod Sci, 4(3): 184-188. |
| 14 | Liang J S, Cao X Z.1993. Studies on the relationship between several physiological characteristics of leaf and bleeding rate of roots in hybrid rice (O. sativa L.).J Jiangsu Agric Coll, 14(3): 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 15 | Liu H Y, Hussain S, Zheng M M, Peng S B, Huang J L, Cui K H, Nie L X.2015. Dry seeded rice as an alternative to transplanted- flooded rice in Central China.Agron Sustain Dev, 35: 285-294. |
| 16 | Mae T, Ohiro K.1981. The remobilization of nitrogen related to leaf growth and senescence in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.).Plant Cell Physiol, 22(6): 1067-1074. |
| 17 | Mae T, Hoshino T.1985. Proteinase activities and loss of nitrogen in the senescing leaves of field-grown rice (Oryza sativa L.).Soil Sci Plant Nutr, 31(4): 589-600. |
| 18 | Mae T.1997. Physiological nitrogen efficiency in rice: Nitrogen utilization, photosynthesis, and yield potential.Plant Soil, 196(2): 201-210. |
| 19 | Majdi H.1996. Root sampling methods-applications and limitations of the minirhizotron technique.Plant Soil, 185(2): 255-258. |
| 20 | Park J H, Lee B W.2003. Genotypic difference in leaf senescence during grain filling and its relation to grain yield of rice.Kor J Crop Sci, 48(3): 216-223. |
| 21 | Peng S B, García F V, Laza R C, Cassman K G.1993. Adjustment for specific leaf weight improves chlorophyll meter’s estimate of rice leaf nitrogen concentration.Agron J, 85(5): 987-990. |
| 22 | Peng S B, Cassman K G, Kropff M J.1995. Relationship between leaf photosynthesis and nitrogen content of field-grown rice in tropics.Crop Sci, 35: 1627-1630. |
| 23 | Peng S B, Garcia F V, Laza R C, Sanico A L, Visperas R M, Cassman K G.1996. Increased N-use efficiency using a chlorophyll mete on high-yielding irrigated rice.Field Crop Res, 47: 243-252. |
| 24 | Ramasamy S, Ten Berge H F M, Purushothaman S.1997. Yield formation in rice in response to drainage and nitrogen application.Field Crop Res, 51: 65-82. |
| 25 | Rao A N, Johnson D E, Sivaprasad B, Ladha J K, Mortimer A M.2007. Weed management in seeded rice.Adv Agron, 93: 153-255. |
| 26 | Ray S, Mondal W A, Choudhuri M A.1983. Regulation of leaf senescence, grain-filling and yield of rice by kinetin and abscisicacid.Physiol Plantarum, 59(3): 343-346. |
| 27 | Richardson-Calfee L E.2004. Post-Transplant Root Production, Mortality, and Periodicity of Landscape-Sized Shade Trees. [Master Thesis]. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University. |
| 28 | Sakaigaichi T, Morita S, Abe J, Yamaguchi T.2007. Diurnal and phenological changes in the rate of nitrogen transportation monitored by bleeding in field-grown rice plants (Oryza sativa L.).Plant Prod Sci, 10: 270-276. |
| 29 | Seiler G J.1998. Influence of temperature on primary and lateral root growth of sunflower seedlings.Environ Exp Bot, 40(2): 135-146. |
| 30 | Siopongco J D L C, Yamauchi A, Salekdeh H, Bennett J, Wade L J.2006. Growth and water use response of doubled-haploid rice lines to drought and rewatering during the vegetative stage.Plant Prod Sci, 9: 141-151. |
| 31 | Sudhir-Yadav, Gill G, Humphreys E, Kukal S S, Walia U S.2011. Effect of water management on dry seeded and puddled transplanted rice: Part 1. Crop performance.Field Crop Res, 120(1): 112-122. |
| 32 | Tao Y, Chen Q, Peng S B, Wang W Q, Nie L X.2016. Lower global warming potential and higher yield of wet seeded rice in central China.Agron Sust Dev, 36(2): 1-9. |
| 33 | Watanabe S, Hatanaka Y, Inada K.1980. Development of a digital chlorophyll meter: I. Structure and performance.Jpn J Crop Sci, 49: 89-90. |
| 34 | Yoshida S.1972. Physiological aspect of grain yield.Ann Rev Plant Physiol, 23(1): 437-464. |
| 35 | Yoshida S.1981. Fundamentals of Rice Crop Science. Los Baños, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| 36 | Zhang C F, Peng S B, Laza R C.2003. Senescence of top three leaves in field-grown rice plants.J Plant Nutr, 26: 2453-2468. |
| 37 | Zhang H, Xue Y G, Wang Z Q, Yang J C, Zhang J H.2009. Morphological and physiological traits of roots and their relationships with shoot growth in “super” rice.Field Crop Res, 113(1): 31-40. |
| 38 | Zhang W J, Wu L M, Ding Y F, Weng F, Wu X R, Li G H, Liu Z H, Tang S, Ding C Q, Wang S H.2016. Top-dressing nitrogen fertilizer rate contributes to decrease culm physical strength by reducing structural carbohydrate content in japonica rice.J Int Agric, 15(5): 992-1004. |
| 39 | Zhang Y B, Tang Q Y, Zou Y B, Li D Q, Qin J Q, Yang S H, Chen L J, Xia B, Peng S B.2009. Yield potential and radiation use efficiency of ‘super’ hybrid rice grown under subtropical conditions. Field Crop Res, 114(1): 91-98. |
| [1] | Zhaowei Li, Qian Zhao, Fangmin Cheng. Sugar Starvation Enhances Leaf Senescence and Genes Involved in Sugar Signaling Pathways Regulate Early Leaf Senescence in Mutant Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(3): 201-214. |
| [2] | WANG Chong-qing1, WANG Tao1, MU Ping2, LI Zi-chao2, YANG Ling1. Quantitative Trait Loci for Mercury Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2013, 20(3): 238-242. |
| [3] | HE Jun-yu, REN Yan-fang, ZHU Cheng, JIANG De-an. Effects of Cadmium Stress on Seed Germination, Seedling Growth and Seed Amylase Activities in Rice (Oryza sativa) [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2008, 15(4): 319-325 . |
| [4] |
FAN Jin-juan, LI Xue-mei , XU Zheng-jin, ZHANG Li-jun.
Relationship Between Changes in Leaf Endogenous Hormone Contents and Senescence During Grain Filling Stage of a Rice Hybrid and its Parents [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2004, 11(4): 200-204 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||