
Rice Science ›› 2019, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (6): 416-424.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2019.06.001
• Research Paper • Previous Articles
Yaobin Liu1,#, Lin Qin3,#, Fengbo Li1,2, Xiyue Zhou1, Chunchun Xu1, Long Ji1, Zhongdu Chen1, Jinfei Feng1( ), Fuping Fang1(
), Fuping Fang1( )
)
Received:2019-04-03
Accepted:2019-06-24
Online:2019-11-28
Published:2019-08-19
Contact:
Yaobin Liu, Lin Qin
About author: These authors contributed equally to this work
Yaobin Liu, Lin Qin, Fengbo Li, Xiyue Zhou, Chunchun Xu, Long Ji, Zhongdu Chen, Jinfei Feng, Fuping Fang. Impact of Rice-Catfish/Shrimp Co-culture on Nutrients Fluxes Across Sediment-Water Interface in Intensive Aquaculture Ponds[J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(6): 416-424.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Parameter | YC-R | YC | FS-R | FS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.45 a | 7.81 b | 7.72 b | 7.98 c |
| BOD (mg/L) | 4.69 ab | 6.26 c | 4.12 a | 5.06 b |
| COD (mg/L) | 209.50 a | 276.70 b | 196.10 a | 185.40 a |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 81.90 c | 112.90 d | 35.80 a | 54.40 b |
| TSS (mg/L) | 312.60 a | 382.60 c | 297.30 a | 341.90 b |
| TN (mg/L) | 2.53 b | 4.16 c | 1.70 a | 2.22 b |
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | 0.45 b | 0.87 d | 0.33 a | 0.54 c |
| NO3--N (mg/L) | 1.27 a | 1.50 b | 1.16 a | 1.38 b |
| NO2--N (mg/L) | 0.03 a | 0.05 b | 0.02 a | 0.05 b |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.27 b | 0.39 c | 0.16 a | 0.30 b |
| OP (μmg/L) | 4.40 a | 5.80 b | 4.80 a | 7.80 c |
Table 1 Water properties of monoculture and co-culture ponds.
| Parameter | YC-R | YC | FS-R | FS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.45 a | 7.81 b | 7.72 b | 7.98 c |
| BOD (mg/L) | 4.69 ab | 6.26 c | 4.12 a | 5.06 b |
| COD (mg/L) | 209.50 a | 276.70 b | 196.10 a | 185.40 a |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 81.90 c | 112.90 d | 35.80 a | 54.40 b |
| TSS (mg/L) | 312.60 a | 382.60 c | 297.30 a | 341.90 b |
| TN (mg/L) | 2.53 b | 4.16 c | 1.70 a | 2.22 b |
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | 0.45 b | 0.87 d | 0.33 a | 0.54 c |
| NO3--N (mg/L) | 1.27 a | 1.50 b | 1.16 a | 1.38 b |
| NO2--N (mg/L) | 0.03 a | 0.05 b | 0.02 a | 0.05 b |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.27 b | 0.39 c | 0.16 a | 0.30 b |
| OP (μmg/L) | 4.40 a | 5.80 b | 4.80 a | 7.80 c |
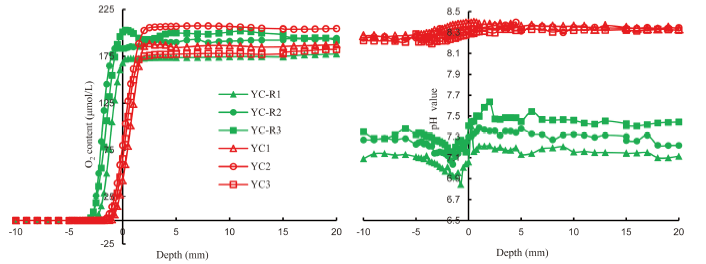
Fig. 2. Micro-profiles of oxygen (O2) and pH value across sediment-water interface in rice-catfish co-culture and catfish monoculture ponds.YC1 to YC3, Three profiles of yellow catfish monoculture; YC-R1 to YC-R3, Three profiles of yellow catfish-rice co-culture.
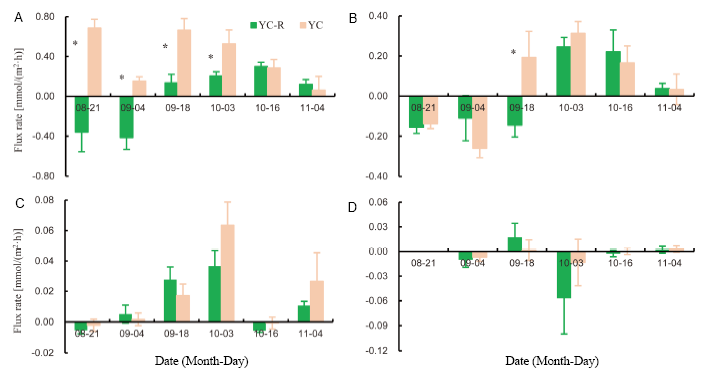
Fig. 3. Flux rates of NH4+ (A), NO3- (B), NO2- (C) and PO43- (D) across the sediment-water interface in the rice-catfish co-culture and catfish monoculture ponds.YC, Yellow catfish monoculture; YC-R, Yellow catfish-rice co-culture.Values are Mean ± SE (n = 3). * indicates significant differences at the 0.05 level.
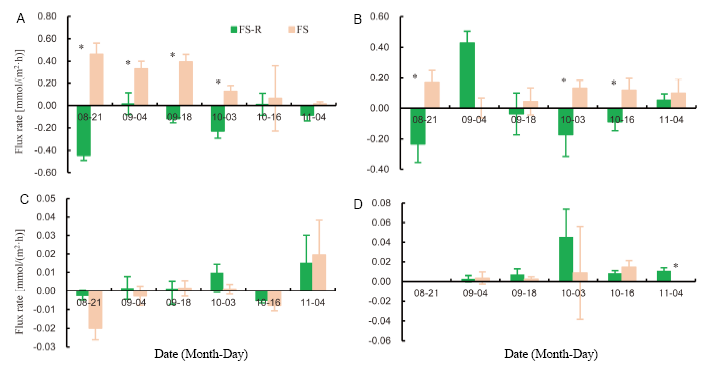
Fig. 4. Flux rates of NH4+ (A), NO3- (B), NO2- (C) and PO43- (D) across the sediment-water interface in the rice-shrimp co-culture and shrimp monoculture ponds.FS, Freshwater shrimp monoculture; FS-R, Freshwater shrimp-rice co-culture. Values are Mean ± SE (n = 3). * indicates significant differences at the 0.05 level.
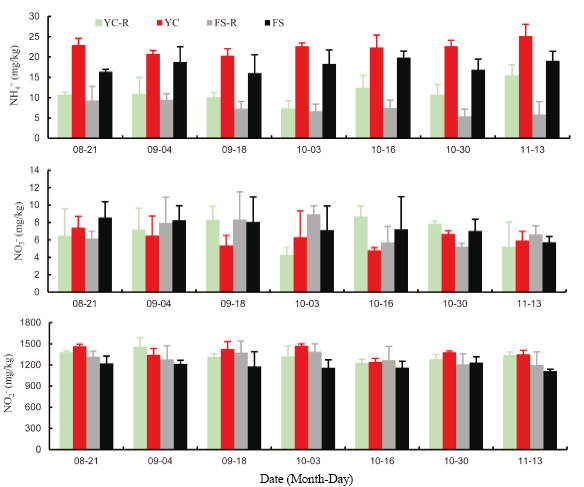
Fig. 5. Fractions of N in the sediment of co-culture and monoculture ponds.YC, Yellow catfish monoculture; YC-R, Yellow catfish-rice co-culture; FS, Freshwater shrimp monoculture; FS-R, Freshwater shrimp-rice co-culture.Data are Mean ± SE (n = 3).
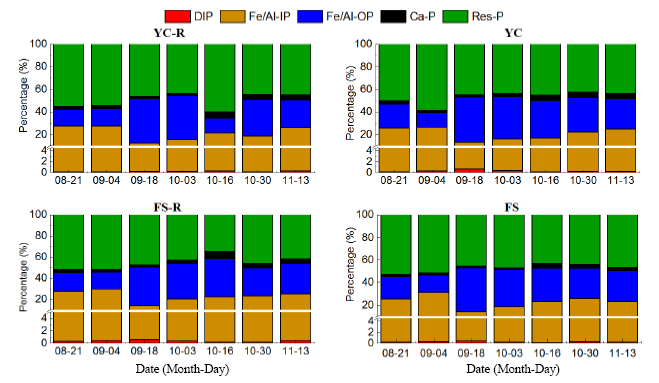
Fig. 6. Fractions of P in the sediment of co-culture and monoculture ponds. YC, Yellow catfish monoculture; YC-R, Yellow catfish-rice co-culture; FS, Freshwater shrimp monoculture; FS-R, Freshwater shrimp-rice co-culture; DIP, Dissolved inorganic phosphorus; Fe/Al-IP, Fe- and Al-bound inorganic phosphorus; Fe/Al-OP, Fe- and Al-bound organic phosphorus; Res-P, Residual phosphorus; Ca-P, Ca-bound phosphorus.
| Treatment | DIP | Fe/Al-IP | Fe/Al-OP | Ca-P | Res-P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YC-R | 0.85 a | 115.5 a | 139.4 a | 19.3 a | 276.0 a |
| YC | 1.43 b | 113.9 a | 158.3 b | 18.9 a | 267.3 a |
| FS-R | 1.82 c | 130.2 ab | 154.6 b | 21.3 a | 253.1 a |
| FS | 1.18 b | 132.3 b | 157.1 b | 14.2 a | 275.6 a |
Table 2 Mean contents of different phosphorus (P) fractions in the sediment of co-culture and monoculture ponds.
| Treatment | DIP | Fe/Al-IP | Fe/Al-OP | Ca-P | Res-P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YC-R | 0.85 a | 115.5 a | 139.4 a | 19.3 a | 276.0 a |
| YC | 1.43 b | 113.9 a | 158.3 b | 18.9 a | 267.3 a |
| FS-R | 1.82 c | 130.2 ab | 154.6 b | 21.3 a | 253.1 a |
| FS | 1.18 b | 132.3 b | 157.1 b | 14.2 a | 275.6 a |
| [1] | Adámek Z, Maršálek B.2013. Bioturbation of sediments by benthic macroinvertebrates and fish and its implication for pond ecosystems: A review.Aquacult Int, 21: 1-17. |
| [2] | Akinbile C O, Yusoff M S.2011. Assessing water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassopes) and lettuce (Pistia stratiotes) effectivesness in aquaculture wasterwater treatment. Int J Phytorem, 14(3): 201-211. |
| [3] | Andersen T, Andersen F O, Pedersen O.2006. Increased CO2 in the water aroundLittorella uniflora raises the sediment O2 concentration. Aquat Bot, 84: 294-300. |
| [4] | Arandia-Gorostidi N, Weber P K, Alonso-Sáez L, Morán X A G, Mayali X.2016. Elevated temperature increases carbon and nitrogen fluxes between phytoplankton and heterotrophic bacteria through physical attachment.ISME J, 11: 641. |
| [5] | Avnimelech Y, Ritvo G.2003. Shrimp and fish pond soils: Processes and management.Aquaculture, 220: 549-567. |
| [6] | Bolan N S.1991. A critical review on the role of mycorrhizal fungi in the uptake of phosphorus by plants.Plant Soil, 134(2): 189-207. |
| [7] | Bosma R H, Verdegem M C J.2011. Sustainable aquaculture in ponds: Principles, practices and limits.Livest Sci, 139: 58-68. |
| [8] | Boynton W R, Ceballos M A C, Bailey E M, Hodgkins C L S, Humphrey J L, Testa J M.2018. Oxygen and nutrient exchanges at the sediment-water interface: A global synthesis and critique of estuarine and coastal data.Estuar Coast, 41(2): 301-333. |
| [9] | Briggs M R P, Fvnge-Smith S J.1994. A nutrient budget of some intensive marine shrimp ponds in Thailand.Aquac Res, 25: 789-811. |
| [10] | Bryant L D, Gantzer P A, Little J C.2011. Increased sediment oxygen uptake caused by oxygenation-induced hypolimnetic mixing.Water Res, 45: 3692-3703. |
| [11] | Cheng X J, Zeng Y X, Guo Z R, Zhu L S.2014. Diffusion of nitrogen and phosphorus across the sediment-water interface and in seawater at aquaculture areas of Daya Bay, China.Int J Environ Res Pubic Health, 11(2): 1557-1572. |
| [12] | Colmer T D, Cox M C H, Voesenek L A C JJ. 2006. Root aeration in rice (Oryza sativa): Evaluation of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and ethylene as possible regulators of root acclimatizations. New Phytol, 170: 767-778. |
| [13] | Dai Y R, Cheng S P, Liang W, Wu Z B.2015. Submerged macrophyteCeratophyllum demersum affects phosphorus exchange at the sediment-water interface. Water Sci Technol, 71(6): 913-921. |
| [14] | Dien L D, Hiep L H, Hao N V, Sammut J, Burford M A.2018. Comparing nutrient budgets in integrated rice-shrimp ponds and shrimp grow-out ponds.Aquaculture, 484: 250-258. |
| [15] | Feng J F, Li F B, Zhou X Y, Xu C C, Fang F P.2016. Nutrient removal ability and economical benefit of a rice-fish co-culture system in aquaculture pond.Ecol Eng, 94: 315-319. |
| [16] | Ferdoushi Z, Haque F, Khan S, Haque M M.2008. The effects of two aquatic floating macrophytes (Lemna and Azolla) as biofilters of nitrogen and phosphate in fish ponds. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci, 8: 253-258. |
| [17] | Guo Y J, Shen Y P, Wang F, Zhang Z D.2013. Nutrient fluxes across sediment-water interface in different grass carp polyculture enclosures.Acta Hydrobiol Sin, 37(4): 595-605. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Hargreaves J A.1998. Nitrogen biogeochemistry of aquaculture ponds.Aquaculture, 166: 181-212. |
| [19] | Helali M A, Zaaboub N, Oueslati W, Added A, Aleya L.2016. Nutrient exchange and oxygen demand at the sediment-water interface during dry and wet seasons off the Medjerda River Delta (Tunis Gulf, Tunisia).Environ Earth Sci, 75: 25. |
| [20] | Henry-Silva G G, Camargo A F M.2006. Efficiency of aquatic macrophytes to treat Nile tilapia pond effluents.Sci Agric, 63: 433-438. |
| [21] | Hu B, Tan L J, Wang J T.2017. Study on the diffusion fluxes of dissolved inorganic nitrogen phosphorus and urea across sediment-water interface in scallop culture area of Changli coastal waters.Marine Environ Sci, 36(6): 864-870. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [22] | Jackson C, Preston N, Thompson P J, Michele B.2003. Nitrogen budget and effluent nitrogen components at an intensive shrimp farm. Aquaculture, 218: 397-411. |
| [23] | Jescovitch L N.2014. Water Surface Area Ratio for Aquaculture Ponds. Alabama: Auburn University. |
| [24] | Jiang Z J, Cui Y, Chen B J.2007. Diffusive fluxes of dissolved inorganic nitrogen across sediment-water interface in net-cage culture area of Tangdao Bay.Environ Sci, 28(5): 1001-1005. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Kapanen G.2008. Phosphorus fractionation in lake sediments.Est J Ecol, 57(4): 244-255. |
| [26] | Koschorreck M, Brookland I, Matthias A.2003. Biogeochemistry of the sediment-water interface in the littoral of an acidic mining lake studied with microsensors and gel-probes. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol, 285-286: 71-84. |
| [27] | Lei P, Zhang H, Wang C, Pan K.2018. Migration and diffusion for pollutants across the sediment-water interface in lakes: A review.J Lake Sci, 30(6): 1489-1508. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Li F B, Sun Z P, Qi H Y, Zhou X Y, Xu C C, Wu D X, Fang F P, Feng J F, Zhang N.2019. Effects of rice-fish co-culture on oxygen consumption in intensive aquaculture pond.Rice Sci, 26(1): 50-59. |
| [29] | Li X P, Li J R, Wang Y B, Fu L L, Fu Y Y, Li B Q, Jiao B H.2011. Aquaculture industry in China: Current state, challenges, and outlook.Rev Fish Sci, 19(3): 187-200. |
| [30] | Liao H F, Zheng Z M, Regan N, Zhu J Y.2016. Study on nutrient fluxes of sediment-water interface in cage culture zone of large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea in Xiangshan Bay. J Marine Sci, 34: 84-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Lin X B, Lin X, Yan Y Y, He S, Jiang L L, Zeng C S.2013. Inorganic nitrogen exchange fluxes at the sediment-water interface in saline-fresh water wetland of Min River estuary.J Soil Water Conserv, 27(5): 260-266. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Liu J G, Qian M, Cai G L, Zhu Q S, Wong M H.2007. Variations between rice cultivars in root secretion of organic acids and the relationship with plant cadmium uptake.Environ Geochem Health, 29(3): 189-195. |
| [33] | Lu R. 2000. Methods of nitrogen and phosphorus analysis. In: Soil and Agro-chemical Analysis Methods. Agricultural Science and Beijing: Technology Press. |
| [34] | Martinez-Porchas M, Martinez-Cordova L R. 2012. World aquaculture: Environmental impacts and troubleshooting alternatives.Sci World J, 2012: 389623. |
| [35] | Mu D, Yuan D K, Feng H, Xing F W, Teo F Y, Li S Z.2017. Nutrient fluxes across sediment-water interface in Bohai Bay Coastal Zone, China.Mar Pollut Bull, 114(2): 705-714. |
| [36] | Mügler C, Rabouille C, Bombled B, Montarnal P.2012. Impact of spatial heterogeneities on oxygen consumption in sediments: Experimental observations and 2D numerical modeling.J Geochem Explor, 112: 76-83. |
| [37] | Nicholaus R, Zheng Z M.2014. The effects of bioturbation by the Venus clamCyclina sinensis on the fluxes of nutrients across the sediment-water interface in aquaculture ponds. Aquacult Intl, 22(2): 913-924. |
| [38] | Niencheski L F, Jahnke R A.2002. Benthic respiration and inorganic nutrient fluxes in the estuarine region of Patos Lagoon (Brazil).Aquat Geochem, 8(3): 135-152. |
| [39] | Nowlin W H, Evarts J L, Vanni M J.2005. Release rates and potential fates of nitrogen and phosphorus from sediments in a eutrophic reservoir. Freshwater Biol, 50(2): 301-322. |
| [40] | Petranich E, Covelli S, Acquavita A, de Vittor C, Faganeli J, Contin M.2018. Benthic nutrient cycling at the sediment-water interface in a lagoon fish farming system (northern Adriatic Sea, Italy).Sci Total Environ, 644: 137-149. |
| [41] | Qiu H M, Geng J J, Ren H Q, Xu Z Y.2016. Phosphite flux at the sediment-water interface in northern Lake Taihu.Sci Total Environ, 543: 67-74. |
| [42] | Santschi P, Höhener P, Benoit G, Buchholtz-ten Brink M.1990. Chemical processes at the sediment-water interface.Mar Chem, 30: 269-315. |
| [43] | SEPA. 2002. Monitor and Analysis Methods of Water and Wastewater. Beijing, China. |
| [44] | Sun Z P, Qin L, Liu Y B, Li F B, Feng J F, Wu D X, Fang F P.2018. Advances in restoration effects of rice growing on eutrophic water.Chin J Rice Sci, 32(5): 509-518. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [45] | Tian C C, Wang C B, Li Q, Xiao B D.2013. Effects of Hydrilla verticillata on physical and chemical variables of the microprofiles at sediment-water interface. J Lake Sci, 25(5): 715-722. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [46] | Wang J F, Chen J A, Zeng Y, Yang Y Q, Yang H Q, Ji Y X.2013b. Application of microelectrode measurement system in research on biogeochemical processed across the water-sediment Interface in Hongfeng Lake.Earth Environ, 41(1): 65-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [47] | Wang L T, Liu L, Qian B, Xia Q, Chen L Y.2013a. Changes in environmental chemistry at water-sediment interface before and after dredging of Dazong Lake in Yancheng City.Water Resour Prot, 29(2): 33-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [48] | Wang S R, Jin X C, Zhao H C, Zhou X N, Wu F C.2007. Effects of Hydrilla verticillata on phosphorus retention and release in sediments. Water Air Soil Poll, 181: 329-339. |
| [49] | Wenzhöfer F, Holby O, Glud R N, Nielsen H K, Gundersen J K.2000. In situ microsensor studies of a shallow water hydrothermal vent at Milos, Greece. Mar Chem, 69: 43-54. |
| [50] | Yahel G, Yahel R, Katz T, Lazar B, Herut B, Tunnicliffe V.2008. Fish activity: A major mechanism for sediment resuspension and organic matter remineralization in coastal marine sediments.Marine MAR Ecol Prog Ser, 372: 195-209. |
| [51] | Yang P, Lai D Y F, Jin B, Bastviken D, Tan L S, Tong C.2017. Dynamics of dissolved nutrients in the aquaculture shrimp ponds of the Min River estuary, China: Concentrations, fluxes and environmental loads. Sci Total Environ, 603-604: 256-267. |
| [52] | Zhang K, Xie J, Yu D G, Wang G J, Yu E M, Gong W B, Li Z F, Wang C C, Xia Y.2018. A comparative study on the budget of nitrogen and phosphorus in polyculture systems of snakehead with bighead carp.Aquaculture, 483: 69-75. |
| [53] | Zhong D S, Wang F, Dong S L, Li L.2015. Impact of Litopenaeus vannamei bioturbation on nitrogen dynamics and benthic fluxes at the sediment-water interface in pond aquaculture. Aquacult Intl, 23(4): 967-980. |
| [1] | Fengbo Li, Zhiping Sun, Hangying Qi, Xiyue Zhou, Chunchun Xu, Dianxin Wu, Fuping Fang, Jinfei Feng, Ning Zhang. Effects of Rice-Fish Co-culture on Oxygen Consumption in Intensive Aquaculture Pond [J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(1): 50-49. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||