
Rice Science ›› 2021, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (2): 133-145.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2021.01.003
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Mishra Rukmini1, Zheng Wei2, Kumar Joshi Raj3, Kaijun Zhao2( )
)
Received:2020-04-10
Accepted:2020-08-04
Online:2021-03-28
Published:2021-03-28
Mishra Rukmini, Zheng Wei, Kumar Joshi Raj, Kaijun Zhao. Genome Editing Strategies Towards Enhancement of Rice Disease Resistance[J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(2): 133-145.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
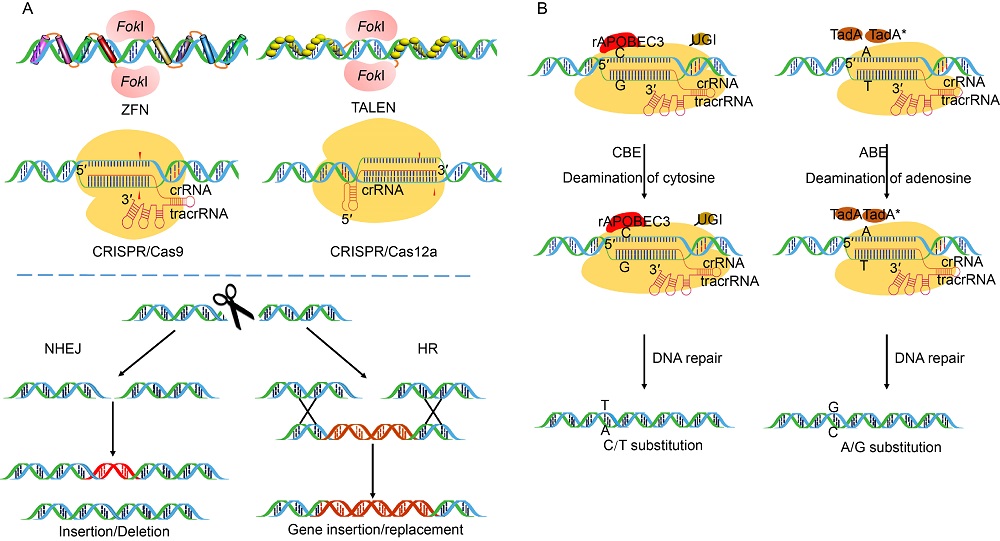
Fig. 1. Sequence specific nucleases used for genome editing. A, Sequence specific nucleases including zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs), transcriptional activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/Cas9 or CRISPR/Cas12a create double-stranded breaks (DSBs) at the target site which is subsequently repaired either by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or homologous recombination (HR) by cellular system leading to gene disruption by insertion/deletion, gene addition or replacement, respectively. The cleavage of the targeted DNA is facilitated by FokI endonuclease in ZFNs and TALENs and Cas endonucleases in CRISPR/Cas9 and CRISPR/Cas12a. CRISPR/Cas9 makes use of a 100 nt single guide (sgRNA) comprising of crisprRNA (crRNA) and trans-acting crispr RNA (tracrRNA) while CRISPR/Cas12a requires only a 40-45 nt long crRNA to facilitate gene editing. B, Base editing platforms used for target specific single base modification. Cytidine base editor (CBE) uses Cas9 nickase together with a cytidine deaminase rAPOBEC3 and an uracil DNA glycosylase inhibitor (UGI) to facilitate cytosine to thymine conversions. Adenine base editor (ABE) consists of Cas9 nickase fused with E. coli derived ecTadA(WT)-ecTadA* heterodimer to facilitate adenosine to guanine conversions.
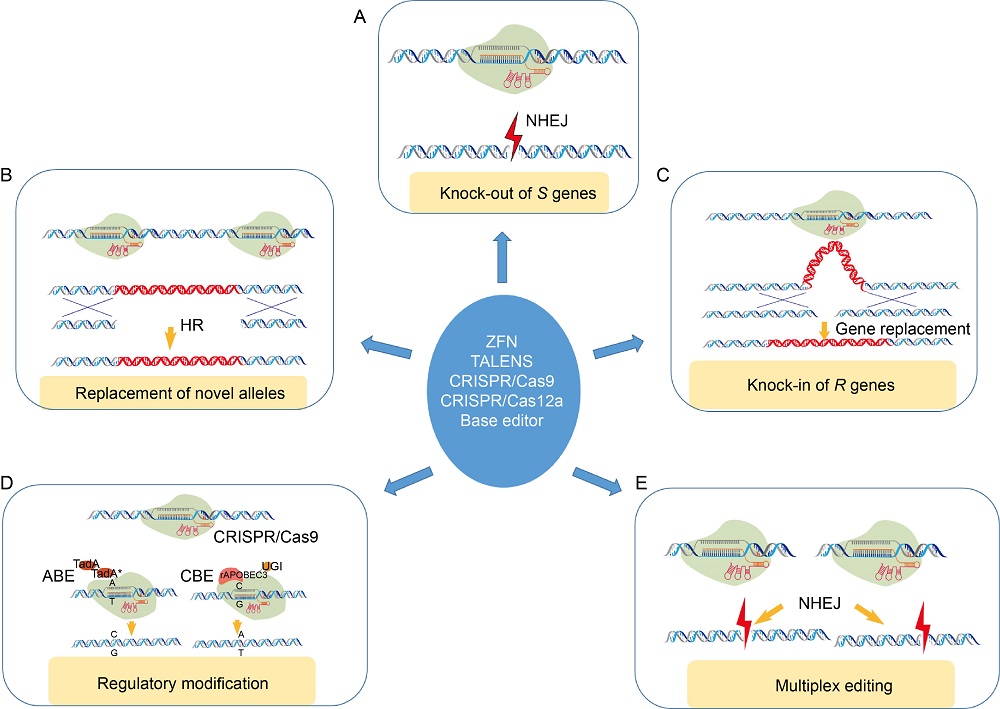
Fig. 2. Genome editing strategies towards disease resistance in plants. Multiple genome editing platforms can facilitate disease resistance through knock-out of susceptibility (S) genes (A), homology directed replacement of novel alleles (B), knock-in of resistance (R) genes (C), regulatory modification of R/S gene expression (D) and multiplex editing of resistance and susceptibility factors (E). HR, Homologous recombination; ZFN, Zinc finger nuclease; NHEJ, Non-homologous end joining; ABE, Adenine base editor; CBE, Cytidine base editor; UGI, Uracil DNA glycosylase.
| Pathogenic perspective | Target gene | Editing tool | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance to bacterial infection | OsSWEET13 | TALENs | Enhanced resistance to BLB | |
| OsSWEET13 | TALENs | Enhanced resistance to BLB | ||
| OsSWEET13 | TALENs | Enhanced resistance to BLB | ||
| Os09g29100 | TALENs | Enhanced resistance to BLB | ||
| Os8N3 (OsSWEET11) | CRISPR/Cas9 | Enhanced resistance to BLB | ||
| OsSWEET11 and OsSWEET14 | CRISPR/Cas9 | Broad spectrum resistance to BLB | ||
| OsSWEET11, OsSWEET13 and OsSWEET14 | CRISPR/Cas9 | Broad spectrum resistance to BLB | ||
| Resistance to fungal infection | OsERF922 | CRISPR/Cas9 | Enhanced resistance to blast disease | |
| OsSEC3A | CRISPR/Cas9 | Enhanced resistance to blast disease | ||
| OsPFT1 | CRISPR/Cas9 | Resistance to rice sheath blight | ||
| Resistance to viral infection | eIF4G | CRISPR/Cas9 | Enhanced resistance to tungro disease |
Table 1. List of genes targeted by genome editing tools for rice disease resistance.
| Pathogenic perspective | Target gene | Editing tool | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance to bacterial infection | OsSWEET13 | TALENs | Enhanced resistance to BLB | |
| OsSWEET13 | TALENs | Enhanced resistance to BLB | ||
| OsSWEET13 | TALENs | Enhanced resistance to BLB | ||
| Os09g29100 | TALENs | Enhanced resistance to BLB | ||
| Os8N3 (OsSWEET11) | CRISPR/Cas9 | Enhanced resistance to BLB | ||
| OsSWEET11 and OsSWEET14 | CRISPR/Cas9 | Broad spectrum resistance to BLB | ||
| OsSWEET11, OsSWEET13 and OsSWEET14 | CRISPR/Cas9 | Broad spectrum resistance to BLB | ||
| Resistance to fungal infection | OsERF922 | CRISPR/Cas9 | Enhanced resistance to blast disease | |
| OsSEC3A | CRISPR/Cas9 | Enhanced resistance to blast disease | ||
| OsPFT1 | CRISPR/Cas9 | Resistance to rice sheath blight | ||
| Resistance to viral infection | eIF4G | CRISPR/Cas9 | Enhanced resistance to tungro disease |
| [1] | Antony G, Zhou J H, Huang S, Li T, Liu B, White F, Yang B.2010. Rice xa13 recessive resistance to bacterial blight is defeated by induction of the disease susceptibility gene Os-11N3.Plant Cell, 22(11): 3864-3876. |
| [2] | Bäckström S, Elfving N, Nilsson R, Wingsle G, Björklund S.2007. Purification of a plant mediator from Arabidopsis thaliana identifies PFT1 as the Med25 subunit.Mol Cell, 26(5): 717-729. |
| [3] | Baltes N J, Hummel A W, Konecna E, Cegan R, Bruns A N, Bisaro D M, Voytas D F.2015. Conferring resistance to Gemini viruses with the CRISPR-Cas prokaryotic immune system.Nat Plants, 1: 15145. |
| [4] | Banakar R, Schubert M, Collingwood M, Vakulskas C, Eggenberger A L, Wang K.2020. Comparison of CRISPR-Cas9/Cas12a ribonucleoprotein complexes for genome editing efficiency in the rice Phytoene Desaturase (OsPDS) gene.Rice, 13(1): 4. |
| [5] | Bastet A, Robaglia C, Gallois J L.2017. eIF4E resistance: Natural variation should guide gene editing.Trends Plant Sci, 22(5): 411-419. |
| [6] | Blanvillain-Baufume S, Reschke M, Sole M, Auguy F, Doucoure H, Szurek B, Meynard D, Portefaix M, Cunnac S, Guiderdoni E, Boch J, Koebnik R.2017. Targeted promoter editing for rice resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae reveals differential activities for SWEET14-inducing TAL effectors.Plant Biotechnol J, 15(3): 306-317. |
| [7] | Bloch D, Pleskot R, Pejchar P, Potocký M, Trpkošová P, Cwiklik L, Vukašinović N, Sternberg H, Yalovsky S, Žárský V.2016. Exocyst SEC3 and phosphoinositides define sites of exocytosis in pollen tube initiation and growth.Plant Physiol, 172(2): 980-1002. |
| [8] | Bogdanove A J, Schornack S, Lahaye T.2010. TAL effectors: Finding plant genes for disease and defense.Curr Opin Plant Biol, 13(4): 394-401. |
| [9] | Bogdanove A J, Voytas D F.2011. TAL Effectors: Customizable proteins for DNA targeting.Science, 333: 1843-1846. |
| [10] | Cai C Q, Doyon Y, Ainley W M, Miller J C, Dekelver R C, Moehle E A, Rock J M, Lee Y L, Garrison R, Schulenberg L, Blue R, Worden A, Baker L, Faraji F, Zhang L, Holmes M C, Rebar E J, Collingwood T N, Rubin-Wilson B, Gregory P D, Urnov F D, Petolino J F.2009. Targeted transgene integration in plant cells using designed zinc finger nucleases.Plant Mol Biol, 69: 699-709. |
| [11] | Cai L L, Cao Y Y, Xu Z Y, Ma W X, Zakria M, Zou L F, Cheng Z Q, Chen G Y.2017. A transcription activator-like effector Tal7 of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola activates rice gene Os09g29100 to suppress rice immunity.Sci Rep, 7(1): 5089. |
| [12] | Carroll D.2011. Genome engineering with zinc finger nucleases.Genetics, 188(4): 773-782. |
| [13] | Chancellor T C B, Holt J, Villareal S, Tiongco E R, Venn J.2006. Spread of plant virus disease to new plantings: A case study of rice tungro disease.Adv Virus Res, 66: 1-29. |
| [14] | Chandrasekaran J, Brumin M, Wolf D, Leibman D, Klap C, Pearlsman M, Sherman A, Arazi T, Gal-On A.2016. Development of broad virus resistance in non-transgenic cucumber using CRISPR/Cas9 technology.Mol Plant Pathol, 17(7): 1140-1153. |
| [15] | Chu Z H, Yuan M, Yao L L, Ge X J, Yuan B, Xu C G, Li X H, Fu B Y, Li Z K, Bennetzen J L, Zhang Q F, Wang S P.2006. Promoter mutations of an essential gene for pollen development result in disease resistance in rice.Genes Dev, 20(10): 1250-1255. |
| [16] | Cohn M, Bart R S, Shybut M, Dahlbeck D, Gomez M, Morbitzer R, Hou B H, Frommer W B, Lahaye T, Staskawicz B J.2014. Xanthomonas axonopodis virulence is promoted by a transcription activator-like effector-mediated induction of a SWEET sugar transporter in cassava.Mol Plant-Microbe Intreact, 27(11): 1186-1198. |
| [17] | Cox D B T, Gootenberg J S, Abudayyeh O O, Franklin B, Kellner M J, Joung J, Zhang F.2017. RNA editing with CRISPR-Cas13.Science, 358: 1019-1027. |
| [18] | Cui H T, Tsuda K, Parker J E.2015. Effector-triggered immunity: From pathogen perception to robust defense.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 66: 487-511. |
| [19] | Deng Y W, Zhai K R, Xie Z, Yang D Y, Zhu X D, Liu J Z, Wang X, Qin P, Yang Y Z, Zhang G M, Li Q, Zhang J F, Wu S Q, Milazzo J, Mao B Z, Wang E, Xie H, Tharreau D, He Z H.2017. Epigenetic regulation of antagonistic receptors confers rice blast resistance with yield balance.Science, 355: 962-965. |
| [20] | Endo A, Masafumi M, Kaya H, Toki S.2016. Efficient targeted mutagenesis of rice and tobacco genomes using Cpf1 from Francisella novicida.Sci Rep, 6: 38169. |
| [21] | FAO.2017. The Future of Food and Agriculture: Trends and Challenges. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. |
| [22] | Gao L Y, Cox D B T, Yan W X, Manteiga J C, Schneider M W, Yamano T, Nishimasu H, Nureki O, Crosetto N, Zhang F.2017. Engineered Cpf1 variants with altered PAM specificities.Nat Biotechnol, 35: 789-792. |
| [23] | Giraud T, Gladieux P, Gavrilets S.2010. Linking the emergence of fungal plant diseases with ecological speciation.Trends Ecol Evol, 25(7): 387-395. |
| [24] | He L, Li X F, Xu Y, Liu H L, He M L, Tian X J, Wang Z Y, Wu X J, Bu Q Y, Yang J.2020. High-efficiency reduction of rice amylose content via CRISPR/Cas9-mediated base editing.Rice Sci, 27(16): 445-448. |
| [25] | Hibino H, Cabauatan P Q.1987. Infectivity neutralization of rice tungro associated viruses acquired by vector leafhoppers.Phytopathology, 77: 473-476. |
| [26] | Hsu P D, Lander E S, Zhang F.2014. Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering.Cell, 157(6): 1262-1278. |
| [27] | Hu J H, Miller S M, Geurts M H, Tang W X, Chen L W, Sun N, Zeina C M, Gao X, Rees H A, Liu D R.2018. Evolved Cas9 variants with broad PAM compatibility and high DNA specificity.Nature, 556: 57-63. |
| [28] | Hua K, Tao X P, Yuan F T, Wang D, Zhu J K.2018. Precise AT to GC base editing in the rice genome.Mol Plant, 11(4): 627-630. |
| [29] | Hua K, Tao X P, Zhu J K.2019. Expanding the base editing scope in rice by using Cas9 variants.Plant Biotechnol J, 17(2): 499-504. |
| [30] | Hull R.1996. Molecular biology of rice tungro viruses.Annu Rev Phytopathol, 34: 275-297. |
| [31] | Hutin M, Sabot F, Ghesquière A, Koebnik R, Szurek B.2015. A knowledge-based molecular screen uncovers a broad-spectrum OsSWEET14 resistance allele to bacterial blight from wild rice.Plant J, 84(4): 694-703. |
| [32] | Jones H D.2015. Regulatory uncertainty over genome editing.Nat Plants, 1: 14011. |
| [33] | Khush G S, Angeles E, Virk P S, Brar D S.2004. Breeding rice for resistance to tungro virus at IRRI.SABRAO J Breed Genet, 36(2): 101-106. |
| [34] | Kim Y A, Moon H, Park C J.2019. CRISPR/Cas9-targeted mutagenesis of Os8N3 in rice to confer resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae.Rice, 12: 67. |
| [35] | Kleinstiver B P, Prew M S, Tsai S Q, Topkar V V, Nguyen N T, Zheng Z L, Gonzales A P W, Li Z Y, Peterson R T, Yeh J R J, Aryee M J, Joung J K.2015. Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases with altered PAM specificities.Nature, 523: 481-485. |
| [36] | Komor A C, Kim Y B, Packer M S, Zuris J A, Liu D R.2016. Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double stranded DNA cleavage.Nature, 533: 420-424. |
| [37] | Lee J H, Muhsin M, Atienza G A, Kwak D Y, Kim S M, De Leon T B, Angeles E R, Coloquio E, Kondoh H, Satoh K, Cabunagan R C, Cabauatan P Q, Kikuchi S, Leung H, Choi I R.2010. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in a gene for translation initiation factor (eIF4G) of rice (Oryza sativa) associated with resistance to rice tungro spherical virus.Mol Plant-Microbe Interact, 23(1): 29-38. |
| [38] | Li C, Zong Y, Wang Y P, Jin S, Zhang D B, Song Q N, Zhang R, Gao C X.2018. Expanded base editing in rice and wheat using a Cas9-adenosine deaminase fusion.Genome Biol, 19: 59. |
| [39] | Li S F, Shen L, Hu P, Liu Q, Zhu X D, Qian Q, Wang K J, Wang Y X.2019. Developing disease-resistant thermosensitive male sterile rice by multiplex gene editing.J Integr Plant Biol, 61(12): 1201-1205. |
| [40] | Li S Y, Zhang X, Wang W S, Guo X P, Wu Z C, Du W M, Zhao Y D, Xia L Q.2018. Expanding the scope of CRISPR/Cpf1 mediated genome editing in rice.Mol Plant, 11(7): 995-998. |
| [41] | Li T, Liu B, Spalding M H, Weeks D P, Yang B.2012. High-efficiency TALEN-based gene editing produces disease- resistant rice.Nat Biotechnol, 30: 390-392. |
| [42] | Li T, Liu B, Chen C Y, Yang B.2016. TALEN-mediated homologous recombination produces site-directed DNA base change and herbicide-resistant rice.J Genet Genom, 43(5): 297-305. |
| [43] | Li W, Deng Y W, Ning Y S, He Z H, Wang G L.2020. Exploiting broad-spectrum disease resistance in crops: From molecular dissection to breeding.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 29: 575-603. |
| [44] | Li W T, Zhu Z W, Chern M, Yin J J, Yang C, Ran L, Cheng M P, He M, Wang K, Wang J, Zhou X G, Zhu X B, Chen Z X, Wang J C, Zhao W, Ma B T, Qin P, Chen L H, Wang Y P, Liu J L, Wang W M, Wu X J, Li P, Wang J R, Zhu L H, Li S G, Chen X W.2017. A natural allele of a transcription factor in rice confers broad-spectrum blast resistance.Cell, 170(1): 114-126. |
| [45] | Li Y, Xiao J H, Chen L L, Huang X H, Cheng Z K, Han B, Zhang Q F, Wu C Y.2016. Rice functional genomics research: Past decade and future.Mol Plant, 11(3): 359-380. |
| [46] | Liang Z, Chen K L, Li T D, Zhang Y, Wang Y P, Zhao Q, Liu J X, Zhang H W, Liu C M, Ran Y D, Gao C X.2017. Efficient DNA-free genome editing of bread wheat using CRISPR/Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complexes.Nat Commun, 8: 14261. |
| [47] | Lu Y M, Zhu J K.2017. Precise editing of a target base in the rice genome using a modified CRISPR/Cas9 system.Mol Plant, 10(3): 523-525. |
| [48] | Lusser M, Parisi C, Plan D, Rodriguez-Cerezo E.2012. Deployment of new biotechnologies in plant breeding.Nat Biotechnol, 30: 231-239. |
| [49] | Ma J, Chen J, Wang M, Ren Y L, Wang S, Lei C L, Cheng Z J, Sodmergen.2018. Disruption of OsSEC3A increases the content of salicylic acid and induces plant defense responses in rice.J Exp Bot, 69(5): 1051-1064. |
| [50] | Ma X L, Zhang Q Y, Zhu Q L, Liu W, Chen Y, Qiu R, Wang B, Yang Z F, Li H Y, Lin Y R, Xie Y Y, Shen R X, Chen S F, Wang Z, Chen Y L, Guo J X, Chen L T, Zhao X C, Dong Z C, Liu Y G.2015. A robust CRISPR/Cas9 system for convenient, high-efficiency multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants.Mol Plant, 8(8): 1274-1284. |
| [51] | Macovei A, Sevilla N R, Cantos C, Jonson G B, Slamet-Loedin I, Cermak T, Voytas D F, Choi I R, Chadha-Mohanty P.2018. Novel alleles of rice eIF4G generated by CRISPR/Cas9-targeted mutagenesis confer resistance to rice tungro spherical virus.Plant Biotechnol J, 16(11): 1918-1927. |
| [52] | Miah G, Rafii M Y, Ismail M R, Puteh A B, Rahim H A, Asfaliza R, Latif M A.2013. Blast resistance in rice: A review of conventional breeding to molecular approaches.Mol Biol Rep, 40: 2369-2388. |
| [53] | Mishra R, Joshi R K, Zhao K J.2018. Genome editing in rice: Recent advances, challenges, and future implications.Front Plant Sci, 9: 1361. |
| [54] | Mishra R, Joshi R K, Zhao K J.2020. Base editing in crops: Current advances, limitations and future implications.Plant Biotechnol J, 18(1): 20-31. |
| [55] | Nalley L, Tsiboe F, Durand-Morat A, Shew A, Thoma G.2016. Economic and environmental impact of rice blast pathogen ( Magnaporthe oryzae) alleviation in the United States.PLoS One, 11(12): e0167295. |
| [56] | Nishikura K.2010. Functions and regulation of RNA editing by ADAR deaminases.Annu Rev Biochem, 79: 321-349. |
| [57] | Olivia R, Ji C H, Atienza-Grande G, Huguet-Tapia J C, Perez- Quintero A, Li T, Eom J S, Li C H, Nguyen H, Liu B, Auguy F, Sciallano C, Luu V T, Dossa G S, Cunnac S, Schmidt S M, Samet-Loedin I H, Cruz C V, Szurek B, Frommer W B, White F F, Yang B.2019. Broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight in rice using genome editing.Nat Biotechnol, 37(11): 1344-1350. |
| [58] | Osakabe K, Osakabe Y, Toki S.2010. Site-directed mutagenesis in Arabidopsis using custom-designed zinc finger nucleases.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 107(26): 12034-1239. |
| [59] | Paques F, Duchateau P.2007. Meganucleases and DNA double- strand break-induced recombination: Perspectives for gene therapy.Curr Gene Ther, 7(1): 49-66. |
| [60] | Peng A H, Chen S C, Lei T G, Xu L Z, He Y R, Wu L, Yao L X, Zou X P.2017. Engineering canker-resistant plants through CRISPR/ Cas9-targeted editing of the susceptibility gene CsLOB1 promoter in citrus.Plant Biotechnol J, 15(12): 1509-1519. |
| [61] | Qin L, Li J Y, Wang Q Q, Xu Z P, Sun L, Alariqi M, Manghwar H, Wang G Y, Li B, Ding X, Rui H P, Huang H M, Lu T L, Lindsey K, Daniell H, Zhang X L, Jin S X.2019. High efficient and precise base editing of C∙G to T∙A in the allotetrapoid cotton ( Gossypium hirsutum) genome using a modified CRISPR/Cas9 system.Plant Biotechnol J, 1: 12. |
| [62] | Ren B, Yan F, Kuang Y J, Li N, Zhang D W,. Zhou X P, Lin H H, Zhou H B.2018. Improved base editor for efficiently inducing genetic variations in rice with CRISPR/Cas9-guided hyperactive hAID mutant.Mol Plant, 11(4): 623-626. |
| [63] | Rodriguez-Leal D, Lemmon Z H, Man J, Bartlett M E, Lippman Z B.2017. Engineering quantitative trait variation for crop improvement by genome editing.Cell, 171(2): 470-480. |
| [64] | Sander J D, Joung J K.2014. CRISPR-Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes.Nat Biotechnol, 32(4): 347-355. |
| [65] | Savary S, Willocquet L, Elazegui F A, Castilla N P, Teng P S.2000. Rice pest constraints in tropical Asia: Quantification of yield losses due to rice pests in a range of production situations.Plant Dis, 84(3): 357-369. |
| [66] | Shah P R, Varanavasiappan S, Kokiladevi E, Ramanathan A, Kumar K K.2019. Genome editing of rice PFT1 gene to study its role in rice sheath blight disease resistance.Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci, 8(6): 2356-2364. |
| [67] | Sharma T R, Rai A K, Gupta S K, Vijayan J, Devanna B N, Ray S.2012. Rice blast management through host plant resistance: Retrospect and prospects.Agric Res, 1(1): 37-52. |
| [68] | Shukla V K, Doyon Y, Miller J C, Dekelver R C, Moehle E A, Worden S E, Mitchell J C, Arnold N L, Gopalan S, Meng X D, Choi V M, Rock J M, Wu Y Y, Katibah G E, Gao Z F, McCaskill D, Simpson M A, Blakeslee B, Greenwalt S A, Butler H J, Hinkley S J, Zhang L, Rebar E J, Gregory P D, Urnov F D.2009. Precise genome modification in the crop species Zea mays using zinc finger nucleases.Nature, 459: 437-441. |
| [69] | Silva N V, Patron N J.2017. CRISPR-based tools for plant genome engineering.Emerg Top Life Sci, 1(2): 135-149. |
| [70] | Stafforst T, Schneider M F.2012. An RNA-deaminase conjugate selectively repairs point mutations.Angew Chem Int Ed E, 51: 11166-11169. |
| [71] | Sun Y W, Jiao G A, Liu Z P, Zhang X, Li J Y, Guo X P, Du W M, Du J L, Francis F, Zhao Y D, Xia L Q.2017. Generation of high- amylose rice through CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis of starch branching enzymes.Front Plant Sci, 8: 298. |
| [72] | Svitashev S, Schwartz C, Lenderts B, Young J K, Cigan M A.2016. Genome editing in maize directed by CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins complexes.Nat Commun, 7: 13274. |
| [73] | Tang X, Ren Q R, Yang L J, Bao Y, Zhong Z H, He Y,Liu S S, Qi C Y, Liu B L, Wang Y, Sretenovic S, Zhang Y X, Zheng X L, Zhang T, Qi Y P, Zhang Y.2019. Single transcript unit CRISPR 2.0 systems for robust Cas9 and Cas12a mediated plant genome editing.Plant Biotechnol J, 17(7): 1431-1445. |
| [74] | Thatcher L F, Manners J M, Kazan K.2009. Fusarium oxysporum hijacks COI1-mediated jasmonate signaling to promote disease development in Arabidopsis. Plant J, 58(6): 927-939. |
| [75] | Toda E, Koiso N, Takebayashi A, Ichikawa M, Kiba T, Osakabe K, Osakabe Y, Sakakibara H, Kato N, Okamoto T.2019. An efficient DNA- and selectable-marker-free genome-editing system using zygotes in rice.Nat Plants, 5: 363-368. |
| [76] | Tomlinson L, Yang Y, Emenecker R, Smoker M, Taylor J, Perkins S, Smith J, MacLean D, Olszewski N E, Jones J D G.2019. Using CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing in tomato to create a gibberellin- responsive dominant dwarf DELLA allele.Plant Biotechnol J, 17: 132-140. |
| [77] | Ul Haq I, Ijaz S.2020. Plant Disease Management Strategies for Sustainable Agriculture Through Traditional and Modern Approached. Springer. |
| [78] | van Schie C C N, Takken F L W.2014. Susceptibility genes 101: How to be a good host.Annu Rev Phytopathol, 52: 551-581. |
| [79] | Varshney R K, Godwin I D, Mohapatra T, Jones J D G, McCouch S R.2019. A SWEET solution to rice blight.Nat Biotechnol, 37: 1280-1282. |
| [80] | Veillet F, Perrot L, Guyon-Debast A, Kermarrec M P, Chauvin L, Chauvin J E, Gallois J L, Mazier M, Nogue F.2020. Expanding the CRISPR toolbox in P. patens using SpCAS-NG variant and application for gene and base editing in Solanaceae crops.Int J Mol Sci, 21: 1024. |
| [81] | Voytas D F.2013. Plant genome engineering with sequence- specific nucleases.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 64: 327-350. |
| [82] | Voytas D F, Gao C X.2014. Precision genome engineering and agriculture: Opportunities and regulatory challenges.PLoS Biol, 12(6): e1001877. |
| [83] | Wang F J, Wang C L, Liu P Q, Lei P L, Hao W, Gao Y, Liu Y G, Zhao K J.2016. Enhanced rice blast resistance by CRISPR/ Cas9-targeted mutagenesis of the ERF transcription factor gene OsERF922.PLoS One, 11(4): e0154027. |
| [84] | Wang M G, Mao Y F, Lu Y M, Tao X P, Zhu J K.2017. Multiplex gene editing in rice using the CRISPR-Cpf1 system.Mol Plant, 10(7): 1011-1013. |
| [85] | Wang Y P, Cheng X, Shan Q W, Zhang Y, Liu J X, Gao C X, Qiu J L.2014. Simultaneous editing of three homoeoalleles in hexaploid bread wheat confers heritable resistance to powdery mildew.Nat Biotechnol, 32: 947-951. |
| [86] | Woo J W, Kim J, Kwon S I, Corvalán C, Cho S W, Kim H, Kim S G, Kim S T, Choe S, Kim J S.2015. DNA-free genome editing in plants with preassembled CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins.Nat Biotechnol, 33(11): 1162-1164. |
| [87] | Xiao W M, Yang Q Y, Huang M, Guo T, Liu Y Z, Wang J F, Yang G L, Zhou J Y, Yang J Y, Zhu X Y, Chen Z Q, Wang H.2019. Improvement of rice blast resistance by developing monogenic lines, two-gene pyramids and three-gene pyramid through MAS.Rice, 12(1): 78. |
| [88] | Xu R F, Yang Y C, Qin R Y, Li H, Qiu C H, Li L, Wei P C.2016. Rapid improvement of grain weight via highly efficient CRISPR/Cas9-mediated multiplex genome editing in rice.J Genet Genom, 43(8): 529-532. |
| [89] | Xu Z Y, Xu X M, Gong Q, Li Z Y, Li Y, Wang S, Yang Y Y, Ma W X, Liu L Y, Zhu B, Zou L F, Chen G Y.2019. Engineering broad-spectrum bacterial blight resistance by simultaneously disrupting variable TALE-binding elements of multiple susceptibility genes in rice.Mol Plant, 12(11): 1434-1446. |
| [90] | Yin K Q, Qiu J L.2019. Genome editing for plant disease resistance: Applications and perspectives.Phil Trans R Soc B, 374: 20180322. |
| [91] | Yin X J, Biswal A K, Dionora J, Perdigon K M, Balahadia C P, Mazumdar S, Chater C, Lin H C, Coe R A, Kretzschmar T, Gray J E, Quick P W, Bandyopadhyay A.2017. CRISPR-Cas9 and CRISPR-Cpf1 mediated targeting of a stomatal developmental gene EPFL9 in rice.Plant Cell Rep, 36(5): 745-757. |
| [92] | Zaidi S S E A, Tashkandi M, Mansoor S, Mahfouz M M.2016. Engineering plant immunity: Using CRISPR/Cas9 to generate virus resistance.Front Plant Sci, 7: 1673. |
| [93] | Zaidi S S E A, Mahfouz M M, Mansoor S.2017. CRISPR-Cpf1: A new tool for plant genome editing.Trends Plant Sci, 22(7): 550-553. |
| [94] | Zaidi S S E A, Mukhtar M S, Mansoor S.2018. Genome editing: Targeting susceptibility genes for plant disease resistance.Trends Biotechnol, 36(9): 898-906. |
| [95] | Zetsche B, Gootenberg J S, Abudayyeh O O, Slaymaker I M, Makarova K S, Essletzbichler P, Volz S E, Joung J, van der Oost J, Regev A, Koonin E V, Zhang F.2015. Cpf1 is a single RNA- guided endonuclease of a class 2 CRISPR-Cas system.Cell, 163(3): 759-771. |
| [96] | Zhang Q W, Yin K Q, Liu G W, Li S N, Li M G, Qiu J L.2020. Fusing T5 exonuclease with Cas9 and Cas12a increases the frequency and size of deletion at target sites.Sci Chin: Life Sci, 63: 1-10. |
| [97] | Zhang Y, Massel K, Godwin I D, Gao C X.2018. Applications and potential of genome editing in crop improvement.Genome Biol, 19(1): 210. |
| [98] | Zhang Y, Pribil M, Palmgren M, Gao C X.2020. A CRISPR way for accelerating improvement of food crops.Nat Food, 1: 200-205. |
| [99] | Zhou J H, Peng Z, Long J Y, Sosso D, Liu B, Eom J S, Huang S, Liu S Z, Cruz C V, Frommer W B, White F F, Yang B.2015. Gene targeting by the TAL effector PthXo2 reveals cryptic resistance gene for bacterial blight of rice.Plant J, 82(4): 632-643. |
| [100] | Zong Y, Wang Y P, Li C, Zhang R, Chen K L, Ran Y D, Qiu J L, Wang D W, Gao C X.2017. Precise base editing in rice, wheat and maize with a Cas9-cytidine deaminase fusion.Nat Biotechnol, 35: 438-440. |
| [101] | Zong Y, Song Q N, Li C, Jin S, Zhang D B, Wang Y P, Qiu J L, Gao C X.2018. Efficient C to T base editing in plants using a fusion of nCas9 and human APOBEC3A.Nat Biotechnol, 36: 950-953. |
| [1] | Yong Yang, Qiujun Lin, Xinyu Chen, Weifang Liang, Yuwen Fu, Zhengjin Xu, Yuanhua Wu, Xuming Wang, Jie Zhou, Chulang Yu, Chengqi Yan, Qiong Mei, Jianping Chen. Characterization and Proteomic Analysis of Novel Rice Lesion Mimic Mutant with Enhanced Disease Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(5): 466-478. |
| [2] | Yanchang Luo, Tingchen Ma, Teo Joanne, Zhixiang Luo, Zefu Li, Jianbo Yang, Zhongchao Yin. Marker-Assisted Breeding of Thermo-Sensitive Genic Male Sterile Line 1892S for Disease Resistance and Submergence Tolerance [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(1): 89-98. |
| [3] | Yuyu Chen, Aike Zhu, Pao Xue, Xiaoxia Wen, Yongrun Cao, Beifang Wang, Yue Zhang, Liaqat Shah, Shihua Cheng, Liyong Cao, Yingxin Zhang. Effects of GS3 and GL3.1 for Grain Size Editing by CRISPR/Cas9 in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(5): 405-413. |
| [4] | B. ANGELES-SHIM Rosalyn, P. REYES Vincent, M. del VALLE Marilyn, S. LAPIS Ruby, SHIM Junghyun, SUNOHARA Hidehiko, K. JENA Kshirod, ASHIKARI Motoyuki, DOI Kazuyuki. Marker-Assisted Introgression of Quantitative Resistance Gene pi21 Confers Broad Spectrum Resistance to Rice Blast [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(2): 113-123. |
| [5] | Ting Chen, Zheng Chen, Prakash Sathe Atul, Zhihong Zhang, Liangjian Li, Huihui Shang, Shaoqing Tang, Xiaobo Zhang, Jianli Wu. Characterization of a Novel Gain-of-Function Spotted-Leaf Mutant with Enhanced Disease Resistance in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(6): 372-383. |
| [6] | Jiehua Qiu, Shuai Meng, Yizhen Deng, Shiwen Huang, Yanjun Kou. Ustilaginoidea virens: A Fungus Infects Rice Flower and Threats World Rice Production [J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(4): 199-206. |
| [7] | Srivastava Deepti, Shamim Md, Kumar Mahesh, Mishra Anurag, Pandey Pramila, Kumar Deepak, Yadav Prashant, Harrish Siddiqui Mohammed, Narayan Singh Kapildeo. Current Status of Conventional and Molecular Interventions for Blast Resistance in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2017, 24(6): 299-321. |
| [8] | Tao Chen, Hao Wu, Ya-dong Zhang, Zhen Zhu, Qi-yong Zhao, Li-hui Zhou, Shu Yao, Ling Zhao, Xin Yu, Chun-fang Zhao, Cai-lin Wang. Genetic Improvement of Japonica Rice Variety Wuyujing 3 for Stripe Disease Resistance and Eating Quality by Pyramiding Stv-bi and Wx-mq [J]. Rice Science, 2016, 23(2): 69-77. |
| [9] | YAO Shu1, 2, CHEN Tao1, ZHANG Ya-dong1, ZHU Zhen1, ZHAO Ling1, ZHAO Qing-yong1, . Transferring Translucent Endosperm Mutant Gene Wx-mq and Rice Stripe Disease Resistance Gene Stv-bi by Marker-Assisted Selection in Rice (Oryza sativa) [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2011, 18(2): 102-109. |
| [10] | HUANG Qi-na, YANG Yang, SHI Yong-feng, CHEN Jie, WU Jian-li. Spotted-Leaf Mutants of Rice (Oryza sativa) [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2010, 17(4): 247-256 . |
| [11] | CHEN De-xi, CHEN Xue-wei, LEI Cai-lin, MA Bing-tian, WANG Yu-ping, LI Shi-gui. Rice Blast Resistance of Transgenic Rice Plants with Pi-d2 Gene [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2010, 17(3): 179-184 . |
| [12] | WANG Zhong-hua, JIA Yu-lin, LIN Hui, Adair INTERN, Barbara VALENT, J. Neil RUTGER . Host Active Defense Responses Occur within 24 Hours after Pathogen Inoculation in the Rice Blast System [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2007, 14(4): 302-310 . |
| [13] | CAO Li-yong, ZHUANG Jie-yun, YUAN Shou-jiang, ZHAN Xiao-deng, ZHENG Kang-le, CHENG Shi-hua. Hybrid Rice Resistant to Bacterial Leaf Blight Developed By Marker Assisted Selection [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2003, 11(1-2): 68-70 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||