
Rice Science ›› 2024, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 14-32.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2023.08.005
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Masoumeh Kordi1, Naser Farrokhi1( ), Martin I. Pech-Canul2, Asadollah Ahmadikhah1
), Martin I. Pech-Canul2, Asadollah Ahmadikhah1
Received:2023-05-25
Accepted:2023-08-31
Online:2024-01-28
Published:2024-02-06
Contact:
Naser Farrokhi (Masoumeh Kordi, Naser Farrokhi, Martin I. Pech-Canul, Asadollah Ahmadikhah. Rice Husk at a Glance: From Agro-Industrial to Modern Applications[J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(1): 14-32.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
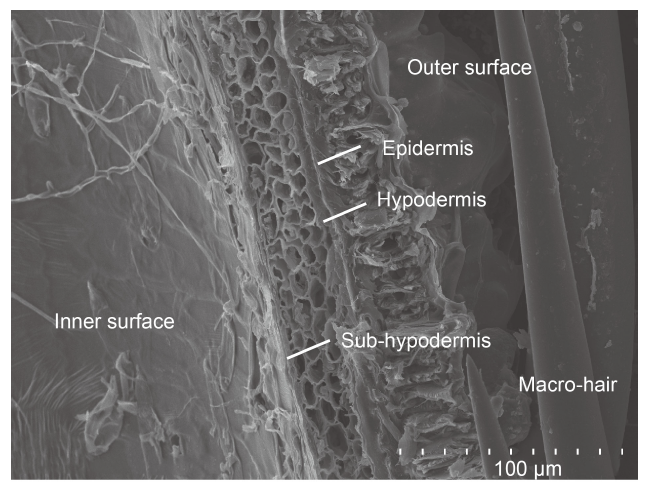
Fig. 2. Scanning electron micrograph of cross section of rice husk. Outer surface, inner surface, macro-hair, epidermis, hypodermis, and sub-hypodermis are shown.
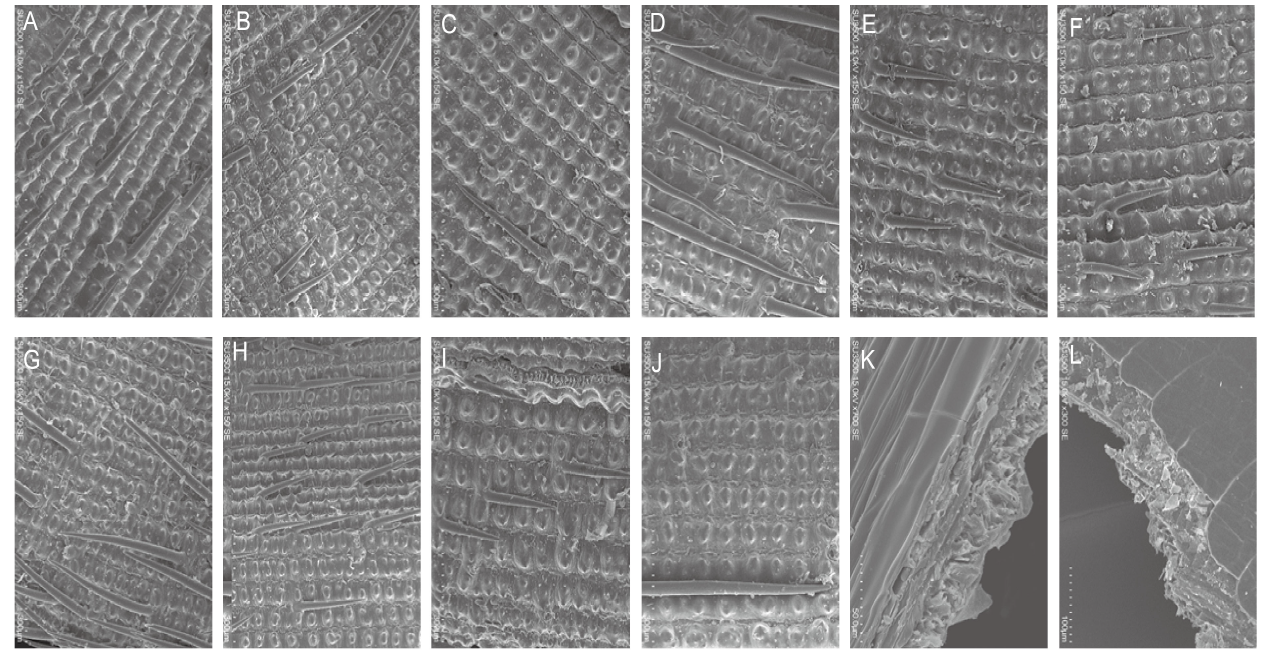
Fig. 3. Scanning electron microscope images taken from rice husk outer (A-J) and inner (K and L) surfaces of 10 rice genotypes. A, ARC 7229 (India); B, JAMIR (Bangladesh); C, BUL ZO (South Korea); D, DOBLE CAROLINA RINALDO BARSANI (Uruguay); E, DAWEBYAN (Myanmar); F, RATHUWEE (Sri Lanka); G, MELANOTRIX (Tajikistan); H, FORTUNA (the United States); I, BLACK GORA (India); J, SRI MALAYSIA DUA (Malaysia); K, ARC 7229 (India); L, DAWEBYAN (Myanmar). Genotypes used in these photographs were obtained from the International Rice Research Institute. A wide diversity of surface protrusions and macro-hairs are evident and inner surfaces of rice husk have a relatively smooth exterior (K and L). The magnifications are indicated on the edge of each photograph (A-J, 300 µm; K, 50 µm; and L, 100 µm).
| [1] | Abazari A, Navidshad B, Aghjehgheshlagh F M, Nikbin S. 2016. The effect of rice husk as an insoluble dietary fiber source on intestinal morphology and Lactobacilli and Escherichia coli populations in broilers. Iran J Vet Med, 10: 217-224. |
| [2] | Abdul Wahab R A, Mohd Zaid M H, Aziz S H A, Amin Matori K, Fen Y W, Yaakob Y. 2020. Effects of sintering temperature variation on synthesis of glass-ceramic phosphor using rice husk ash as silica source. Materials, 13(23): 5413. |
| [3] | Abigail M E A, Samuel S M, Chidambaram R. 2016. Application of rice husk nanosorbents containing 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicide to control weeds and reduce leaching from soil. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng, 63: 318-326. |
| [4] | Adeniji A A, Oluwafemi R A, Akinpelu O B. 2014. The feeding value of rice husk with or without probiotics and enzyme supplementation in replacing groundnut cake in the diets of juvenile snails (Archanchatina marginata). Int J Livest Res, 4(9): 15-27. |
| [5] | Adnan M, Asif M, Khalid M, Abbas B, Hayyat M S, Raza A, Khan B A, Hassan M, Khan M A B, Hanif M S. 2020. Role of mulches in agriculture: A review. Int J Bot Stud, 3: 309-314. |
| [6] | Affandi S, Setyawan H, Winardi S, Purwanto A, Balgis R. 2009. A facile method for production of high-purity silica xerogels from bagasse ash. Adv Powder Technol, 20(5): 468-472. |
| [7] | Afjeh M S, Marandi G B, Zohuriaan-Mehr M J. 2020. Nitrate removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto hydrogel- rice husk biochar composite. Water Environ Res, 92(6): 934-947. |
| [8] | Ahmadabadi Z, Zarei M, Yasrebi J, Ronaghi A, Ghasemi R, Sadegh Kasmaei L, Bloem E, Schnug E. 2019. How can organic amendments help to bind sulfadiazine in the soil? An Iranian soil study. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal, 50(19): 2397-2410. |
| [9] | Akinyemi B A, Kolajo T E, Adedolu O. 2022. Blended formaldehyde adhesive bonded particleboards made from groundnut shell and rice husk wastes. Clean Technol Environ Policy, 24(6): 1653-1662. |
| [10] | Ali Farid S, Zaheer M M. 2023. Production of new generation and sustainable concrete using rice husk ash (RHA): A review. Mater Today Proc. (in press) |
| [11] | Ali M S, Azmah Hanim M A, Tahir S M, Jaafar C N A, Mazlan N, Amin Matori K. 2017. The effect of commercial rice husk ash additives on the porosity, mechanical properties, and microstructure of alumina ceramics. Adv Mater Sci Eng, 2017: 1-10. |
| [12] | Ali Qureshi L, Ali B, Ali A. 2020. Combined effects of supplementary cementitious materials (silica fume, GGBS, fly ash and rice husk ash) and steel fiber on the hardened properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr Build Mater, 263: 120636. |
| [13] | Amiri M J, Bahrami M, Beigzadeh B, Gil A. 2018. A response surface methodology for optimization of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid removal from synthetic and drainage water: A comparative study. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 25(34): 34277-34293. |
| [14] | Ansari S, Mousavi A, Safarnejad M R, Farrokhi N, Alavi S M, Schillberg S, Nölke G. 2021. Selection and characterization of two monoclonal antibodies specific for the Aspergillus flavus major antigenic cell wall protein Aflmp1. Fungal Biol, 125(8): 621-629. |
| [15] | Anyakorah C I, Dike E N. 2013. Comparison of sawdust and rice husk as casing materials for Pleurotus pulmonarius propagation on cassava peel substrate. Agric Biol J North Am, 4(5): 552-554. |
| [16] | Aprilia S, Rosnelly C M, Zuhra, Fitriani F, Haffiz Akbar E, Raqib M, Rahmah K, Amin A, Baity R A. 2023. Synthesis of amorphous silica from rice husk ash using the sol-gel method: Effect of alkaline and alkaline concentration. Mater Today Proc. (in press) |
| [17] | Arjmandi R, Hassan A, Majeed K, Zakaria Z. 2015. Rice husk filled polymer composites. Int J Polym Sci, 2015: 1-32. |
| [18] | Asadi H, Ghorbani M, Rezaei-Rashti M, Abrishamkesh S, Amirahmadi E, Chen C R, Gorji M. 2021. Application of rice husk biochar for achieving sustainable agriculture and environment. Rice Sci, 28(4): 325-343. |
| [19] | Ataie F F. 2021. Utilization of treated agricultural residue ash as sodium silicate in alkali activated slag systems. Materials, 14(2): 329. |
| [20] | Athinarayanan J, Periasamy V S, Alshatwi A A. 2014. Biogenic silica-metal phosphate (metal = Ca, Fe or Zn) nanocomposites: Fabrication from rice husk and their biomedical applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Med, 25(7): 1637-1644. |
| [21] | Azat S, Korobeinyk A V, Moustakas K, Inglezakis V J. 2019. Sustainable production of pure silica from rice husk waste in Kazakhstan. J Clean Prod, 217: 352-359. |
| [22] | Badar R, Qureshi S A. 2014. Composted rice husk improves the growth and biochemical parameters of sunflower plants. J Bot, 2014: 1-6. |
| [23] | Bahrami A, Pech-Canul M I, Gutiérrez C A, Soltani N. 2015a. Effect of rice-husk ash on properties of laminated and functionally graded Al/SiC composites by one-step pressureless infiltration. J Alloys Compd, 644: 256-266. |
| [24] | Bahrami A, Pech-Canul M I, Gutiérrez C A, Soltani N. 2015b. Wetting and reaction characteristics of crystalline and amorphous SiO2 derived rice-husk ash and SiO2/SiC substrates with Al-Si- Mg alloys. Appl Surf Sci, 357: 1104-1113. |
| [25] | Bahrami A, Simon U, Soltani N, Zavareh S, Schmidt J, Pech-Canul M I, Gurlo A. 2017. Eco-fabrication of hierarchical porous silica monoliths by ice-templating of rice husk ash. Green Chem, 19(1): 188-195. |
| [26] | Bakaev V A, Pantano C G. 2009. Inverse reaction chromatography: 2. Hydrogen/deuterium exchange with silanol groups on the surface of fumed silica. J Phys Chem C, 113(31): 13894-13898. |
| [27] | Balarak D, Mostafapour F K, Azarpira H. 2016. Adsorption isotherm studies of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solutions by maize stalks as a cheap biosorbent. Int J Pharm Technol, 8: 16664-16675. |
| [28] | Balarak D, Mostafapour F K. 2019. Photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin using UV/synthesized NiO from pharmaceutical wastewater. Indones J Chem, 19(1): 211-218. |
| [29] | Balarak D, Bandani F, Shehu Z, Ahmed N J. 2020. Adsorption properties of thermally treated rice husk for removal of sulfamethazine antibiotic from pharmaceutical wastewater. J Pharm Res Int, 32: 84-92. |
| [30] | Balo F. 2015. Feasibility study of ‘green’ insulation materials including tall oil: Environmental, economical and thermal properties. Energy Build, 86: 161-175. |
| [31] | Basu P. 2018. Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis and Torrefaction:Practical Design and Theory. 3rd edn. San Diego, CA, USA: Academic Press. |
| [32] | Batagarawa S M, Ajibola A K. 2019. Comparative evaluation for the adsorption of toxic heavy metals on to millet, corn and rice husks as adsorbents. J Anal Pharm Res, 8(3): 119-125. |
| [33] | Berktas I, Chaudhari O, Ghafar A N, Menceloglu Y, Okan B S. 2021. Silanization of SiO2 decorated carbon nanosheets from rice husk ash and its effect on workability and hydration of cement grouts. Nanomaterials, 11(3): 655. |
| [34] | Bernardo M M S, Madeira C A C, dos Santos Nunes N C L, Dias D A C M, Godinho D M B, de Jesus Pinto M F, do Nascimento Matos I A M, Carvalho A P B, de Figueiredo Ligeiro Fonseca I M. 2017. Study of the removal mechanism of aquatic emergent pollutants by new bio-based chars. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 24(28): 22698-22708. |
| [35] | Betiha M A, Moustafa Y M, El-Shahat M F, Rafik E. 2020. Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Aminopropyl-SBA-15 schiff Base hybrid for efficient removal of divalent heavy metal cations from wastewater. J Hazard Mater, 397: 122675. |
| [36] | Bhullar N K, Gruissem W. 2013. Nutritional enhancement of rice for human health: The contribution of biotechnology. Biotechnol Adv, 31(1): 50-57. |
| [37] | Bisht N, Gope P C, Rani N. 2020. Rice husk as a fibre in composites: A review. J Mech Behav Mater, 29(1): 147-162. |
| [38] | Biswas B, Pandey N, Bisht Y, Singh R, Kumar J, Bhaskar T. 2017. Pyrolysis of agricultural biomass residues: Comparative study of corn cob, wheat straw, rice straw and rice husk. Bioresour Technol, 237: 57-63. |
| [39] | Bodie A R, Micciche A C, Atungulu G G, Rothrock M J, Ricke S C. 2019. Current trends of rice milling byproducts for agricultural applications and alternative food production systems. Front Sustain Food Syst, 3: 47. |
| [40] | Brahmachary T K, Ahsan M K, Rokonuzzaman M. 2019. Impact of rice husk ash (RHA) and nylon fiber on the bearing capacity of organic soil. SN Appl Sci, 1(3): 1-13. |
| [41] | Budhy T I, Arundina I, Surboyo M D C, Halimah A N. 2021. The effects of rice husk liquid smoke in Porphyromonas gingivalis: Induced periodontitis. Eur J Dent, 15: 653-659. |
| [42] | Bushra B, Remya N. 2020. Biochar from pyrolysis of rice husk biomass: Characteristics, modification and environmental application. Biomass Conv Bioref, 2020: 1-12. |
| [43] | Cai J, Zhang D, Ding W P, Zhu Z Z, Wang G Z, He J R, Wang H B, Fei P, Si T L. 2020. Promising rice-husk-derived carbon/ Ni(OH)2 composite materials as a high-performing supercapacitor electrode. ACS Omega, 5(46): 29896-29902. |
| [44] | Campos P, Knicker H, Miller A Z, Velasco-Molina M, De la Rosa J M. 2021. Biochar ageing in polluted soils and trace elements immobilisation in a 2-year field experiment. Environ Pollut, 290: 118025. |
| [45] | Carmen S H, Mercedes S H, Rocio L R, Enrique E R, Agustin Hilario R R. 2017. Silica from rice as new drug delivery systems. In: Amanullah, Fahad S. Rice: Technology and Production. Croatia: InTech: 69. |
| [46] | Carmona V B, Oliveira R M, Silva W T L, Mattoso L H C, Marconcini J M. 2013. Nanosilica from rice husk: Extraction and characterization. Ind Crops Prod, 43: 291-296. |
| [47] | Carraro P M, Benzaquén T B, Eimer G A. 2021. Eco-friendly synthesis of nanostructured mesoporous materials from natural source rice husk silica for environmental applications. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 28(19): 23707-23719. |
| [48] | Carter C B, Norton M G. 2007. Ceramic Materials:Science and Engineering. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Springer. |
| [49] | Chaitanoo N, Aggarangsi P, Nitayavardhana S. 2021. Improvement of solid-state anaerobic digestion of broiler farm-derived waste via fungal pretreatment. Bioresour Technol, 332: 125146. |
| [50] | Chaiwong N, Pusadee T, Jamjod S, Prom-U-Thai C. 2022. Silicon application promotes productivity, silicon accumulation and upregulates silicon transporter gene expression in rice. Plants, 11(7): 989. |
| [51] | Chalapud M C, Herdt M, Nicolao E S, Ruseckaite R A, Ciannamea E M, Stefani P M. 2020. Biobased particleboards based on rice husk and soy proteins: Effect of the impregnation with tung oil on the physical and mechanical behavior. Constr Build Mater, 230: 116996. |
| [52] | Chandrasekhar S, Pramada P N, Majeed J. 2006. Effect of calcination temperature and heating rate on the optical properties and reactivity of rice husk ash. J Mater Sci, 41(23): 7926-7933. |
| [53] | Channa S H, Ali Mangi S, Bheel N, Soomro F A, Khahro S H. 2022. Short-term analysis on the combined use of sugarcane bagasse ash and rice husk ash as supplementary cementitious material in concrete production. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 29(3): 3555-3564. |
| [54] | Chariyakornkul A, Punvittayagul C, Taya S, Wongpoomchai R. 2019. Inhibitory effect of purple rice husk extract on AFB1- induced micronucleus formation in rat liver through modulation of xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes. BMC Complement Altern Med, 19(1): 1-11. |
| [55] | Chatveera B, Lertwattanaruk P. 2014. Evaluation of nitric and acetic acid resistance of cement mortars containing high-volume black rice husk ash. J Environ Manag, 133: 365-373. |
| [56] | Chaudhary N, Mohanty I, Saha P, Kumari R, Kumar Pandey A. 2023. Performance of resource saving agro-industrial wastes and their utilization in lightweight concrete: A review. Mater Today Proc. (in press) |
| [57] | Cheenmatchaya A, Kungwankunakorn S. 2014. Preparation of activated carbon derived from rice husk by simple carbonization and chemical activation for using as gasoline adsorbent. Int J Environ Sci Dev, 5: 171-175. |
| [58] | Chen R F, Congress S S C, Cai G J, Duan W, Liu S Y. 2021. Sustainable utilization of biomass waste-rice husk ash as a new solidified material of soil in geotechnical engineering:A review. Constr Build Mater, 292: 123219. |
| [59] | Chen R S, Ahmad S, Gan S, Tarawneh M A. 2020. High loading rice husk green composites: Dimensional stability, tensile behavior and prediction, and combustion properties. J Thermoplast Compos Mater, 33(7): 882-897. |
| [60] | Chen Y E, Zhu Y C, Wang Z C, Li Y, Wang L L, Ding L L, Gao X Y, Ma Y J, Guo Y P. 2011. Application studies of activated carbon derived from rice husks produced by chemical-thermal process: A review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci, 163(1): 39-52. |
| [61] | Cheng Y E, Lu M, Li J S, Su X Y, Pan S L, Jiao C A, Feng M H. 2012. Synthesis of MCM-22 zeolite using rice husk as a silica source under varying-temperature conditions. J Colloid Interface Sci, 369(1): 388-394. |
| [62] | Chien C C, Huang Y P, Sah J G, Cheng W J, Chang R Y, Lu Y S. 2011. Application of rice husk charcoal on remediation of acid soil. Mater Sci Forum, 685: 169-180. |
| [63] | Cho W C, Kim H J, Lee H I, Seo M W, Ra H W, Yoon S J, Mun T Y, Kim Y K, Kim J H, Kim B H, Kook J W, Yoo C Y, Lee J G, Choi J W. 2016. 5L-scale magnesio-milling reduction of nanostructured SiO2 for high capacity silicon anodes in lithium- ion batteries. Nano Lett, 16(11): 7261-7269. |
| [64] | Chockalingam E, Subramanian S. 2006. Studies on removal of metal ions and sulphate reduction using rice husk and Desulfotomaculum nigrificans with reference to remediation of acid mine drainage. Chemosphere, 62(5): 699-708. |
| [65] | Choudhary R, Venkatraman S K, Bulygina I, Senatov F, Kaloshkin S, Anisimova N, Kiselevskiy M, Knyazeva M, Kukui D, Walther F, Swamiappan S. 2021. Biomineralization, dissolution and cellular studies of silicate bioceramics prepared from eggshell and rice husk. Mater Sci Eng C, 118: 111456. |
| [66] | Chowdhury S, Mishra R, Saha P, Kushwaha P. 2011. Adsorption thermodynamics, kinetics and isosteric heat of adsorption of malachite green onto chemically modified rice husk. Desalination, 265: 159-168. |
| [67] | Chungsangunsit T, Gheewala S H, Patumsawad S. 2005. Environmental assessment of electricity production from rice husk: A case study in Thailand. Int Energy J, 6(1): 47-55. |
| [68] | Cope C O, Webster D S, Sabatini D A. 2014. Arsenate adsorption onto iron oxide amended rice husk char. Sci Total Environ, 488/489: 554-561. |
| [69] | Crini G. 2006. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Bioresour Technol, 97(9): 1061-1085. |
| [70] | Cui J H, Yang Y H, Hu Y H, Li F B. 2015. Rice husk based porous carbon loaded with silver nanoparticles by a simple and cost- effective approach and their antibacterial activity. J Colloid Interface Sci, 455: 117-124. |
| [71] | Danewalia S S, Sharma G, Thakur S, Singh K. 2016. Agricultural wastes as a resource of raw materials for developing low- dielectric glass-ceramics. Sci Rep, 6: 24617. |
| [72] | Darabi S F S, Bahramifar N, Ali Khalilzadeh M. 2018. Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetics studies on adsorption of eosin Y and red X-GRL from aqueous solution by treated rice husk. J Appl Res Water Wastewater, 5(1): 392-398. |
| [73] | Debona D, Rodrigues F A, Datnoff L E. 2017. Silicon’s role in abiotic and biotic plant stresses. Annu Rev Phytopathol, 55: 85-107. |
| [74] | Deokar S K, Mandavgane S A, Kulkarni B D. 2016. Agro-industrial waste: A low cost adsorbent for effective removal of 4-chloro- 2-methylphenoxyacetic acid herbicide in batch and packed bed modes. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 23(16): 16164-16175. |
| [75] | Derakhshan-Nejad Z, Jung M C. 2019. Remediation of multi-metal contaminated soil using biochars from rice husk and maple leaves. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag, 21(3): 457-468. |
| [76] | Dey S, Haripavan N, Basha S R, Babu G V. 2021. Removal of ammonia and nitrates from contaminated water by using solid waste bio-adsorbents. Curr Res Che, 1: 100005. |
| [77] | Dhankhar P. 2014. Rice milling. IOSR J Eng, 4(5): 34-42. |
| [78] | Dhinasekaran D, Raj R, Rajendran A R, Purushothaman B, Subramanian B, Prakasarao A, Singaravelu G. 2020. Chitosan mediated 5-fluorouracil functionalized silica nanoparticle from rice husk for anticancer activity. Int J Biol Macromol, 156: 969-980. |
| [79] | Duan Y M, Yang J F, Song Y F, Chen F N, Li X F, Awasthi M K, Li H K, Zhang L S. 2021. Clean technology for biochar and organic waste recycling, and utilization in apple orchard. Chemosphere, 274: 129914. |
| [80] | Ebe S, Ohike T, Matsukawa T, Okanami M, Kajiyama S, Ano T. 2019. Promotion of lipopeptide antibiotic production by Bacillus sp. IA in the presence of rice husk biochar. J Pestic Sci, 44(1): 33-40. |
| [81] | Edrisi F, Salehi M, Ahmadi A, Fararoei M, Rusta F, Mahmoodianfard S. 2018. Effects of supplementation with rice husk powder and rice bran on inflammatory factors in overweight and obese adults following an energy-restricted diet: A randomized controlled trial. Eur J Nutr, 57(2): 833-843. |
| [82] | El-Sanhoury M. 2018. Efficiency of using rice husks in feeding growing rabbits as anti-aflatoxins. Egypt J Nutr Feeds, 21(1): 103-112. |
| [83] | Ewais E M M, Elsaadany R M, Ahmed A A, Shalaby N H, Al-Anadouli B E H. 2017. Insulating refractory bricks from water treatment sludge and rice husk ash. Refract Ind Ceram, 58(2): 136-144. |
| [84] | Fernández_Ledesma E, Rodríguez_Acosta C, Liva_Garrido M, Díaz_Polanco I, Cazanave_Guarnaluce D. 2015. Evaluation of rice husk as an excipient for the pharmaceutical industry. J Mater Environ Sci, 6(1): 114-118. |
| [85] | Firdus F, Samadi S, Muhammadar A A, Sarong M A, Muchlisin Z A, Sari W, Batubara A S. 2020. Gut and intestinal biometrics of the giant trevally, Caranx ignobilis, fed an experimental diet with difference sources of activated charcoal. F1000Research, 9: 444. |
| [86] | Frimpong-Manso J, Obodai M, Dzomeku M, Apertorgbor M M. 2011. Influence of rice husk on biological efficiency and nutrient content of Pleurotus ostreatus (Jacq. ex. Fr.) Kummer. Int Food Res J, 18(1): 249-254. |
| [87] | Fu J R, Zhu L X, Sun X T, Zhou D H, Ouyang L J, Bian J M, He H H, Xu J. 2015. Genetic analysis of grain shape and weight after cutting rice husk. Genet Mol Res, 14(4): 17739-17748. |
| [88] | Gao Y, Guo X B, Liu Y, Fang Z Q, Zhang M W, Zhang R F, You L J, Li T, Liu R H. 2018. A full utilization of rice husk to evaluate phytochemical bioactivities and prepare cellulose nanocrystals. Sci Rep, 8: 10482. |
| [89] | Garba J, Samsuri W A, Othman R, Ahmad Hamdani M S. 2019. Evaluation of adsorptive characteristics of cow dung and rice husk ash for removal of aqueous glyphosate and aminomethyl- phoshonic acid. Sci Rep, 9: 17689. |
| [90] | Ge X M, Xu F Q, Li Y B. 2016. Solid-state anaerobic digestion of lignocellulosic biomass: Recent progress and perspectives. Bioresour Technol, 205: 239-249. |
| [91] | Gopal P M, Sivaram N M, Barik D. 2019. Paper industry wastes and energy generation from wastes. In: Barik D. Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier: 83-97. |
| [92] | Gursel I V, Elbersen B, Meesters K P H, van Leeuwen M. 2022. Defining circular economy principles for biobased products. Sustainability, 14(19): 12780. |
| [93] | Hemnath A, Anbuchezhiyan G, NanthaKumar P, Senthilkumar N. 2021. Tensile and flexural behaviour of rice husk and sugarcane bagasse reinforced polyester composites. Mater Today Proc, 46: 3451-3454. |
| [94] | Hoerudin, Setyawan N, Suismono, Purwaningsih H, Apriliani N. 2022. Morphology, extraction yield, and properties of biogenic silica nanoparticles from Indonesian rice husk as influenced by solvent type and aging time. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci, 1024(1): 012076. |
| [95] | Hossain S S, Roy P K. 2019. Fabrication of sustainable insulation refractory: Utilization of different wastes. Bol Soc Esp Ceram Vidr, 58(3): 115-125. |
| [96] | Hossain S S, Bae C J, Roy P K. 2021. A replacement of traditional insulation refractory brick by a waste-derived lightweight refractory castable. Int J Appl Ceram Technol, 18(5): 1783-1791. |
| [97] | Hu L L, He Z, Zhang S P. 2020. Sustainable use of rice husk ash in cement-based materials: Environmental evaluation and performance improvement. J Clean Prod, 264: 121744. |
| [98] | Humphreys E, Gaydon D S, Eberbach P L. 2016. Evaluation of the effects of mulch on optimum sowing date and irrigation management of zero till wheat in central Punjab, India using APSIM. Field Crops Res, 197: 83-96. |
| [99] | Isinkaye E O, Shado A S, Sanya O T. 2015. Development and characterization of rice husk insulating bricks from two selected deposits in Ekiti State, Nigeria. Int J Sci Res, 6: 132-138. |
| [100] | Ismail H, Mohamad H. 2021. Bioactivity and biocompatibility properties of sustainable wollastonite bioceramics from rice husk ash/rice straw ash: A review. Materials, 14(18): 5193. |
| [101] | Jesudoss S K, Judith Vijaya J, Kaviyarasu K, Iyyappa Rajan P, Narayanan S, John Kennedy L. 2018. In-vitro anti-cancer activity of organic template-free hierarchical M (Cu, Ni)-modified ZSM-5 zeolites synthesized using silica source waste material. J Photochem Photobiol B, 186: 178-188. |
| [102] | Jing X, Wang T F, Yang J L, Wang Y L, Xu H F. 2018. Effects of biochar on the fate and toxicity of herbicide fenoxaprop-ethyl in soil. R Soc Open Sci, 5(5): 171875. |
| [103] | Jittin V, Bahurudeen A, Ajinkya S D. 2020. Utilisation of rice husk ash for cleaner production of different construction products. J Clean Prod, 263: 121578. |
| [104] | Kadam A A, Telke A A, Lade H S, Saratale R G, Saratale G D. 2023. Agro-industrial waste biomass utilization via solid-state fermentation for textile wastewater treatment. In: Larroche C, Sanroman M A, Du G C, Pandey A. Current Developments in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier: 253-277. |
| [105] | Kalderis D, Bethanis S, Paraskeva P, Diamadopoulos E. 2008. Production of activated carbon from bagasse and rice husk by a single-stage chemical activation method at low retention times. Bioresour Technol, 99(15): 6809-6816. |
| [106] | Kalderis D, Kotti M S, Méndez A, Gascó G. 2014. Characterization of hydrochars produced by hydrothermal carbonization of rice husk. Solid Earth, 5(1): 477-483. |
| [107] | Kandanelli R, Meesala L, Kumar J, Raju C S K, Rao Peddy V C, Gandham S, Kumar P. 2018. Cost effective and practically viable oil spillage mitigation: Comprehensive study with biochar. Mar Pollut Bull, 128: 32-40. |
| [108] | Kaniapan S, Pasupuleti J, Patma Nesan K, Abubackar H N, Umar H A, Oladosu T L, Bello S R, Rene E R. 2022. A review of the sustainable utilization of rice residues for bioenergy conversion using different valorization techniques, their challenges, and techno-economic assessment. Int J Environ Res Public Heath, 19(6): 3427. |
| [109] | Karatai T R, Kaluli J W, Kabubo C, Thiong’o G. 2017. Soil stabilization using rice husk ash and natural lime as an alternative to cutting and filling in road construction. J Constr Eng Manage, 143(5): 04016127. |
| [110] | Kaur D, Reddy M S, Pandey O P. 2020. In-vitro bioactivity of silicate-phosphate glasses using agriculture biomass silica. J Mater Sci: Mater Med, 31(8): 65. |
| [111] | Kaur R, Singh H. 2017. Bio-ethanol production from rice-husk using simultaneous saccharification and fermentation and optimization of pre-treatment methods. Der Pharma Chemica, 9(7): 1-7. |
| [112] | Khat-udomkiri N, Toejing P, Sirilun S, Chaiyasut C, Lailerd N. 2020. Antihyperglycemic effect of rice husk derived xylooligo- saccharides in high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rat model. Food Sci Nutr, 8(1): 428-444. |
| [113] | Kim Y Y, Lee B J, Saraswathy V, Kwon S J. 2014. Strength and durability performance of alkali-activated rice husk ash geopolymer mortar. Sci World J, 2014: 1-10. |
| [114] | Kiran B R, Prasad M N V. 2019. Biochar and rice husk ash assisted phytoremediation potentials of Ricinus communis L. for lead- spiked soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 183: 109574. |
| [115] | Kolar P, Jin H. 2019. Baseline characterization data for raw rice husk. Data Brief, 25: 104219. |
| [116] | Koskin A P, Zibareva I V, Vedyagin A A. 2020. Conversion of rice husk and nutshells into gaseous, liquid, and solid biofuels. In: Nanda S, Vo D V N, Sarangi K. Biorefinery of Alternative Resources: Targeting Green Fuels and Platform Chemicals. Singapore: Springer: 171-194. |
| [117] | Kumar D C, Vasanthi P, Devaraju A. 2022. Development of agro- industrial wastes in material production. In: Palani I A, Sathiya P, Palanisamy D. Recent Advances in Materials and Modern Manufacturing. Singapore: Springer: 973-981. |
| [118] | Kumar S, Sangwan P, Dhankhar R M V, Bidra S. 2013. Utilization of rice husk and their ash: A review. Res J Chem Env Sci, 1: 126-129. |
| [119] | Lacey L A, Grzywacz D, Shapiro-Ilan D I, Frutos R, Brownbridge M, Goettel M S. 2015. Insect pathogens as biological control agents: Back to the future. J Invertebr Pathol, 132: 1-41. |
| [120] | Laidlaw M A S, Filippelli G M, Brown S, Paz-Ferreiro J, Reichman S M, Netherway P, Truskewycz A, Ball A S, Mielke H W. 2017. Case studies and evidence-based approaches to addressing urban soil lead contamination. Appl Geochem, 83: 14-30. |
| [121] | Lalruatsangi E, Hazarika B N, Raja P. 2018. Effect of paddy straw and rice husk mulching on soil microbial population in acid lime (Citrus Aurantifolia Swingle). Indian J Agric Sci, 77: 241-243. |
| [122] | Lertwattanaruk P, Makul N. 2021. Influence of ground calcium carbonate waste on the properties of green self-consolidating concrete prepared by low-quality bagasse ash and rice husk ash. Materials, 14(15): 4232. |
| [123] | Li X X, Wang X L, Chen Y D, Yang X Y, Cui Z J. 2019. Optimization of combined phytoremediation for heavy metal contaminated mine tailings by a field-scale orthogonal experiment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 168: 1-8. |
| [124] | Li Y, Hagos F M, Chen R R, Qian H X, Mo C X, Di J, Gai X K, Yang R Q, Pan G X, Shan S D. 2021. Rice husk hydrochars from metal chloride-assisted hydrothermal carbonization as biosorbents of organics from aqueous solution. Bioresour Bioprocess, 8(1): 1-15. |
| [125] | Li Y N, Wang R, Chen Z X, Zhao X P, Luo X H, Wang L, Li Y F, Teng F. 2020. Preparation of magnetic mesoporous silica from rice husk for aflatoxin B1 removal: Optimum process and adsorption mechanism. PLoS One, 15(9): e0238837. |
| [126] | Li Z M, Song Z L, Cornelis J T. 2014. Impact of rice cultivar and organ on elemental composition of phytoliths and the release of bio-available silicon. Front Plant Sci, 5: 529. |
| [127] | Liang Y C, Nikolic M, Bélanger R, Gong H J, Song A L. 2015. Silicon-mediated tolerance to metal toxicity. In: Liang Y C, Nikolic M, Bélanger R, Gong H J, Song A L. Silicon in Agriculture: From Theory to Practice. Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Springer: 83-122. |
| [128] | Liu X Y, Yang L, Zhao H T, Wang W. 2020. Pyrolytic production of zerovalent iron nanoparticles supported on rice husk-derived biochar: Simple, in situ synthesis and use for remediation of Cr(VI)-polluted soils. Sci Total Environ, 708: 134479. |
| [129] | Lourith N, Kanlayavattanakul M. 2013. Appraisal of Thai glutinous rice husk for health promotion products. J Cereal Sci, 57(3): 343-347. |
| [130] | Mahmad-Toher A S, Govender N, Dorairaj D, Wong M Y. 2022. Comparative evaluation on calcium silicate and rice husk ash amendment for silicon-based fertilization of Malaysian rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. J Plant Nutr, 45(9): 1336-1347. |
| [131] | Majeed K, Arjmandi R, Al-Maadeed M A, Hassan A, Ali Z, Khan A U, Khurram M S, Inuwa I M, Khanam P N. 2017. Structural properties of rice husk and its polymer matrix composites. In: Jawaid M, Tahir P M, Saba N. Lignocellulosic Fibre and Biomass-Based Composite Materials. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier: 473-490. |
| [132] | Maki M L, Idrees A, Leung K T, Qin W S. 2012. Newly isolated and characterized bacteria with great application potential for decomposition of lignocellulosic biomass. Microb Physiol, 22(3): 156-166. |
| [133] | Mandal A, Singh N, Purakayastha T J. 2017. Characterization of pesticide sorption behaviour of slow pyrolysis biochars as low cost adsorbent for atrazine and imidacloprid removal. Sci Total Environ, 577: 376-385. |
| [134] | Manpetch P, Singhapong W, Jaroenworaluck A. 2022. Synthesis and characterization of a novel composite of rice husk-derived graphene oxide with titania microspheres (GO-RH/TiO2) for effective treatment of cationic dye methylene blue in aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 29(42): 63917-63935. |
| [135] | Marinković S, Carević V. 2019. Comparative studies of the life cycle analysis between conventional and recycled aggregate concrete. In: de Brito J, Agrela F. New Trends in Eco-efficient and Recycled Concrete. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier: 257-291. |
| [136] | Melendez-Rodriguez B, Torres-Giner S, Aldureid A, Cabedo L, Lagaron J M. 2019. Reactive melt mixing of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate)/ rice husk flour composites with purified biosustainably produced poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate). Materials, 12(13): 2152. |
| [137] | Memon M J, Jhatial A A, Murtaza A, Raza M S, Phulpoto K B. 2021. Production of eco-friendly concrete incorporating rice husk ash and polypropylene fibres. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 28(29): 39168-39184. |
| [138] | Mopoung S, Udeye V, Viruhpintu S, Yimtragool N, Unhong V. 2020. Water treatment for fish aquaculture system by biochar- supplemented planting panel system. Sci World J, 2020: 1-8. |
| [139] | Morpurgo M, Teoli D, Pignatto M, Attrezzi M, Spadaro F, Realdon N. 2010. The effect of Na2CO3, NaF and NH4OH on the stability and release behavior of sol-gel derived silica xerogels embedded with bioactive compounds. Acta Biomater, 6(6): 2246-2253. |
| [140] | Mostafa S A, Faried A S, Farghali A A, El-Deeb M M, Tawfik T A, Majer S, Abd Elrahman M. 2020. Influence of nanoparticles from waste materials on mechanical properties, durability and microstructure of UHPC. Materials, 13(20): 4530. |
| [141] | Motaung T E, Luyt A S. 2010. Effect of maleic anhydride grafting and the presence of oxidized wax on the thermal and mechanical behaviour of LDPE/silica nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng A, 527(3): 761-768. |
| [142] | Mujtaba M, Fraceto L F, Fazeli M, Mukherjee S, Savassa S M, de Medeiros G A, Santo Pereira A D S, Mancini S D, Lipponen J, Vilaplana F. 2023. Lignocellulosic biomass from agricultural waste to the circular economy: A review with focus on biofuels, biocomposites and bioplastics. J Clean Prod, 402: 136815. |
| [143] | Muntohar S A, Hantoro G. 2000. Influence of rice husk ash and lime on engineering properties of a clayey subgrade. Electron J Geotech Eng, 5: 1-13. |
| [144] | Muscat A, de Olde E M, Ripoll-Bosch R, van Zanten H H E, Metze T A P, Termeer C J A M, van Ittersum M K, de Boer I J M. 2021. Principles, drivers and opportunities of a circular bioeconomy. Nat Food, 2(8): 561-566. |
| [145] | Nair R K, Sawant M R. 2006. Effect of the coating of the polymer blend (polyacrylamide/PEG 6000) on the efficiency of rice husk as a pesticide carrier. J Dispersion Sci Technol, 27(7): 1021-1025. |
| [146] | Naseer R, Hashmi A S H, Hassan Z U, Rehman H, Naveed S, Masood F, Tayyab M. 2017. Assessment of feeding value of processed rice husk for lohi sheep in growing phase. Pak J Zool, 49(5): 1725-1729. |
| [147] | Nayak R K, Athira V G, Selvan D, Kumar S S. 2017. Rice husk as an alternate fuel. 2017 IEEE Technological Innovations in ICT for Agriculture and Rural Development (TIAR). April 7-8, 2017. Chennai, India: IEEE: 126-129. |
| [148] | Nguyen T A H, Ngo H H, Guo W S, Zhang J, Liang S, Yue Q Y, Li Q, Nguyen T V. 2013. Applicability of agricultural waste and by-products for adsorptive removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Bioresour Technol, 148: 574-585. |
| [149] | Nighojkar A, Patidar M K, Nighojkar S. 2019. Pectinases: production and applications for fruit juice beverages. In: Grumezescu A M, Holban A M. Processing and Sustainability of Beverages. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier: 235-273. |
| [150] | Nizamuddin S, Baloch H A, Siddiqui M T H, Mubarak N M, Tunio M M, Bhutto A W, Jatoi A S, Griffin G J, Srinivasan M P. 2018. An overview of microwave hydrothermal carbonization and microwave pyrolysis of biomass. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol, 17(4): 813-837. |
| [151] | Nizamuddin S, Jadhav A, Qureshi S S, Baloch H A, Siddiqui M T H, Mubarak N M, Griffin G, Madapusi S, Tanksale A, Ahamed M I. 2019. Synthesis and characterization of polylactide/rice husk hydrochar composite. Sci Rep, 9: 5445. |
| [152] | O’Connor D, Peng T Y, Li G H, Wang S X, Duan L, Mulder J, Cornelissen G, Cheng Z L, Yang S M, Hou D Y. 2018. Sulfur- modified rice husk biochar: A green method for the remediation of mercury contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ, 621: 819-826. |
| [153] | OECD. 2016. OECD Factbook 2015-2016: Economic, Environmental and Social Statistics. [2023-02-15]. https://www.oecd.org/sdd/oecd-factbook-18147364.htm. |
| [154] | Ogaji I J, Nep E I, Audu-Peter J D. 2012. Advances in natural polymers as pharmaceutical excipients. Pharm Anal Acta, 3(1): 146. |
| [155] | Ota K, Mitsushima S, Matsuzawa K, Ishihara A. 2014. Assessing the environmental impact of hydrogen energy production. In: Basile A, Lulianelli A. Advances in Hydrogen Production, Storage and Distribution. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier: 32-42. |
| [156] | Oviedo L R, Muraro P C L, Pavoski G, Espinosa D C R, Ruiz Y P M, Galembeck A, Rhoden C R B, da Silva W L. 2022. Synthesis and characterization of nanozeolite from (agro) industrial waste for application in heterogeneous photocatalysis. Environ Sci Pollu Res, 29: 3794-3807. |
| [157] | Pang S S. 2019. Advances in thermochemical conversion of woody biomass to energy, fuels and chemicals. Biotechnol Adv, 37(4): 589-597. |
| [158] | Pérez-Marín A B, Ballester A, González F, Blázquez M L, Muñoz J A, Sáez J, Zapata V M. 2008. Study of cadmium, zinc and lead biosorption by orange wastes using the subsequent addition method. Bioresour Technol, 99(17): 8101-8106. |
| [159] | Pham T D, Bui T T, Nguyen V T, van Bui T K, Tran T T, Phan Q C, Pham T D, Hoang T H. 2018. Adsorption of polyelectrolyte onto nanosilica synthesized from rice husk: Characteristics, mechanisms, and application for antibiotic removal. Polymers, 10(2): 220. |
| [160] | Pham T D, Vu T N, Nguyen H L, Le P H P, Hoang T S. 2020. Adsorptive removal of antibiotic ciprofloxacin from aqueous solution using protein-modified nanosilica. Polymers, 12(1): 57. |
| [161] | Phuong N T K, Khoi C M, van Sinh N, Chiem N H, Toyota K. 2019. Effects of rice husk biochar and calcium amendment on remediation of saline soil from rice-shrimp cropping system in Vietnamese Mekong delta. J Exp Agric Int, 39(2): 1-12. |
| [162] | Phuong N T K, Khoi C M, Ritz K, Linh T B, Minh D D, Duc T A, Van Sinh N, Linh T T, Toyota K. 2020. Influence of rice husk biochar and compost amendments on salt contents and hydraulic properties of soil and rice yield in salt-affected fields. Agronomy, 10(8): 1101. |
| [163] | Pode R. 2016. Potential applications of rice husk ash waste from rice husk biomass power plant. Renew Sustain Energy Rev, 53: 1468-1485. |
| [164] | Porrang S, Rahemi N, Davaran S, Mahdavi M, Hassanzadeh B. 2021. Preparation and in-vitro evaluation of mesoporous biogenic silica nanoparticles obtained from rice and wheat husk as a biocompatible carrier for anti-cancer drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Sci, 163: 105866. |
| [165] | Prabha S, Durgalakshmi D, Rajendran S, Lichtfouse E. 2021. Plant- derived silica nanoparticles and composites for biosensors, bioimaging, drug delivery and supercapacitors: A review. Environ Chem Lett, 19(2): 1667-1691. |
| [166] | Prabhakaran P, Ranganathan R, Kumar V M, Rajasekar R, Devakumar L, Pal S K. 2017. Review on parameters influencing the rice breakage and rubber roll wear in sheller. Arch Metall Mater, 62(3): 1875-1880. |
| [167] | Prapagdee S, Piyatiratitivorakul S, Petsom A. 2016. Physico-chemical activation on rice husk biochar for enhancing of cadmium removal from aqueous solution. Asian J Water Environ Pollut, 13(1): 27-34. |
| [168] | Prasara-A J, Gheewala S H. 2017. Sustainable utilization of rice husk ash from power plants: A review. J Clean Prod, 167: 1020-1028. |
| [169] | Puppe D, Leue M, Sommer M, Schaller J, Kaczorek D. 2022. Auto- fluorescence in phytoliths: A mechanistic understanding derived from microscopic and spectroscopic analyses. Front Environ Sci, 10: 915947. |
| [170] | Putranto A W, Abida S H, Sholeh A B, Azfa H T. 2021. The potential of rice husk ash for silica synthesis as a semiconductor material for monocrystalline solar cell: A review. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci, 733(1): 012029. |
| [171] | Qu J H, Yuan Y H, Meng Q J, Zhang G S, Deng F X, Wang L, Tao Y E, Jiang Z, Zhang Y. 2020. Simultaneously enhanced removal and stepwise recovery of atrazine and Pb(II) from water using β-cyclodextrin functionalized cellulose: Characterization, adsorptive performance and mechanism exploration. J Hazard Mater, 400: 123142. |
| [172] | Rea R S, Islam M R, Rahman M M, Nath B, Mix K. 2022. Growth, nutrient accumulation, and drought tolerance in crop plants with silicon application: A review. Sustainability, 14(8): 4525. |
| [173] | Reaño R L. 2020. Assessment of environmental impact and energy performance of rice husk utilization in various biohydrogen production pathways. Bioresour Technol, 299: 122590. |
| [174] | Rongchapo W, Sophiphun O, Rintramee K, Prayoonpokarach S, Wittayakun J. 2013. Paraquat adsorption on porous materials synthesized from rice husk silica. Water Sci Technol, 68(4): 863-869. |
| [175] | Rosa S M L, Rehman N, de Miranda M I G, Nachtigall S M B, Bica C I D. 2012. Chlorine-free extraction of cellulose from rice husk and whisker isolation. Carbohydr Polym, 87(2): 1131-1138. |
| [176] | Rowe R C, Sheskey P J, Quinn M E. 2009. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients. 6th edn. London, England: Pharmaceutical Press: 637. |
| [177] | Roy A. 2014. Soil stabilization using rice husk ash and cement. Int J Civil Eng Res, 5: 49-54. |
| [178] | Sala A, Artola A, Sánchez A, Barrena R. 2020. Rice husk as a source for fungal biopesticide production by solid-state fermentation using B. bassiana and T. harzianum. Bioresour Technol, 296: 122322. |
| [179] | Sala A, Vittone S, Barrena R, Sánchez A, Artola A. 2021. Scanning agro-industrial wastes as substrates for fungal biopesticide production: Use of Beauveria bassiana and Trichoderma harzianum in solid-state fermentation. J Environ Manag, 295: 113113. |
| [180] | Salavati-Niasari M, Javidi J, Dadkhah M. 2013. Ball milling synthesis of silica nanoparticle from rice husk ash for drug delivery application. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen, 16(6): 458-462. |
| [181] | Salisu J, Gao N B, Quan C. 2021. Techno-economic assessment of co-gasification of rice husk and plastic waste as an off-grid power source for small scale rice milling: An aspen plus model. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 158: 105157. |
| [182] | Salman A D, Juzsakova T, Jalhoom M G, Le Phuoc C, Mohsen S, Adnan Abdullah T, Zsirka B, Cretescu I, Domokos E, Stan C D. 2020. Novel hybrid nanoparticles: Synthesis, functionalization, characterization, and their application in the uptake of scandium (III) ions from aqueous media. Materials, 13(24): 5727. |
| [183] | Samaddar P, Ok Y S, Kim K H, Kwon E E, Tsang D C W. 2018. Synthesis of nanomaterials from various wastes and their new age applications. J Clean Prod, 197: 1190-1209. |
| [184] | Scaglioni P T, Badiale-Furlong E. 2016. Rice husk as an adsorbent: A new analytical approach to determine aflatoxins in milk. Talanta, 152: 423-431. |
| [185] | Sekifuji R, Tateda M. 2019. Study of the feasibility of a rice husk recycling scheme in Japan to produce silica fertilizer for rice plants. Sustain Environ Res, 29(1): 1-9. |
| [186] | Shaaban M. 2021. Properties of concrete with binary binder system of calcined dolomite powder and rice husk ash. Heliyon, 7(2): e06311. |
| [187] | Shak K P Y, Wu T Y, Lim S L, Lee C A. 2014. Sustainable reuse of rice residues as feedstocks in vermicomposting for organic fertilizer production. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 21(2): 1349-1359. |
| [188] | Shamsollahi Z, Partovinia A. 2019. Recent advances on pollutants removal by rice husk as a bio-based adsorbent: A critical review. J Environ Manag, 246: 314-323. |
| [189] | Shen Y F, Zhao P T, Shao Q F. 2014. Porous silica and carbon derived materials from rice husk pyrolysis char. Microporous Mesoporous Mat, 188: 46-76. |
| [190] | Shi J X, Fan X L, Tsang D C W, Wang F, Shen Z T, Hou D Y, Alessi D S. 2019. Removal of lead by rice husk biochars produced at different temperatures and implications for their environmental utilizations. Chemosphere, 235: 825-831. |
| [191] | Shibata K, Yamaguchi T, Hokkirigawa K. 2014. Tribological behavior of RH ceramics made from rice husk sliding against stainless steel, alumina, silicon carbide, and silicon nitride. Tribol Int, 73: 187-194. |
| [192] | Shuib F N S, Husaini A, Zulkharnain A, Roslan H A, Guan T M. 2016. Optimization of physiochemical parameters during bioremediation of synthetic dye by Marasmius cladophyllus UMAS MS8 using statistical approach. Sci World J, 2016: 1-7. |
| [193] | Smith J S, Winston R J, Tirpak R A, Wituszynski D M, Boening K M, Martin J F. 2020. The seasonality of nutrients and sediment in residential stormwater runoff: Implications for nutrient- sensitive waters. J Environ Manag, 276: 111248. |
| [194] | Soccol C R, da Costa E S F, Letti L A, Karp S G, Woiciechowski A L, de Souza Vandenberghe L P. 2017. Recent developments and innovations in solid state fermentation. Biotechnol Res Innov, 1(1): 52-71. |
| [195] | Soltani N, Bahrami A, Pech-Canul M I, González L A. 2015. Review on the physicochemical treatments of rice husk for production of advanced materials. Chem Eng J, 264: 899-935. |
| [196] | Soltani N, Simon U, Bahrami A, Wang X F, Selve S, Epping J D, Pech-Canul M I, Bekheet M F, Gurlo A. 2017. Macroporous polymer-derived SiO2/SiOC monoliths freeze-cast from polysiloxane and amorphous silica derived from rice husk. J Eur Ceram Soc, 37(15): 4809-4820. |
| [197] | Suhot M A, Hassan M Z, Aziz S A, Md Daud M Y. 2021. Recent progress of rice husk reinforced polymer composites: A review. Polymers, 13(15): 2391. |
| [198] | Sun X, Liu Q, Tang T T, Chen X A, Luo X A. 2019. Silicon fertilizer application promotes phytolith accumulation in rice plants. Front Plant Sci, 10: 425. |
| [199] | Sundaramahalingam B, Mahboob S, Jain C, Marimuthu N, Manickaraj P, Al-Ghanim K A, Al-Misned F, Ahmed Z. 2020. Design and development of porous terracotta disc: An eco-friendly novel control agent for mosquito larvae. Exp Parasitol, 218: 107988. |
| [200] | Suwan T, Khongkhunthian S, Okonogi S. 2018. Green synthesis and inhibitory effects against oral pathogens of silver nanoparticles mediated by rice extracts. Drug Discov Ther, 12(4): 189-196. |
| [201] | Swarnalakshmi K S, Chinnaiyan P, Nivetha S, Nair A S. 2018. Use of rice husk ash as an adsorbent to remove contaminants in water and comparison with advanced oxidation process: A study. Mater Today, 5(11): 24248-24257. |
| [202] | Tabata T, Yoshiba Y, Takashina T, Hieda K, Shimizu N. 2017. Bioethanol production from steam-exploded rice husk by recombinant Escherichia coli KO11. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 33(3): 47. |
| [203] | Tan G C, Wang H Y, Xu N, Liu H B, Zhai L M. 2018. Biochar amendment with fertilizers increases peanut N uptake, alleviates soil N2O emissions without affecting NH3 volatilization in field experiments. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 25(9): 8817-8826. |
| [204] | Teng F Y, Zhang Y X, Wang D Q, Shen M C, Hu D F. 2020. Iron-modified rice husk hydrochar and its immobilization effect for Pb and Sb in contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater, 398: 122977. |
| [205] | Thiyageshwari S, Gayathri P, Krishnamoorthy R, Anandham R, Paul D. 2018. Exploration of rice husk compost as an alternate organic manure to enhance the productivity of blackgram in typic haplustalf and typic rhodustalf. Int J Environ Res Public Heath, 15(2): 358. |
| [206] | Tsegaye Z, Tefera G. 2017. Cultivation of oyster mushroom (Pleurotusostreatus Kumm, 1871) using agro-industrial residues. J Appl Microb Res, 1: 1-6. |
| [207] | Ugheoke B I, Onche E O, Namessan O N, Asikpo G A. 2006. Property optimization of kaolin-rice husk insulating fire-bricks. Leonardo Electron J Pract Technol, 9: 167-178. |
| [208] | Ugwu C E, Chime S A, Isha C E. 2019. Evaluation of excipient potentials of alpha-cellulose extracted from rice husk in metronidazole compressed tablets: Colon targeted drug delivery and in vitro characterizations. J Chem Pharm Res, 11: 92-116. |
| [209] | Uwaezuoke O J, Bamiro O A, Ngwuluka N C, Ajalla O T, Okinbaloye A O. 2014. Comparative evaluation of the disintegrant properties of rice husk cellulose, corn starch and Avicel in metronidazole tablet formulation. J Appl Pharm Sci, 4(12): 112-117. |
| [210] | Vadivelan V, Kumar K V. 2005. Equilibrium, kinetics, mechanism, and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk. J Colloid Interface Sci, 286(1): 90-100. |
| [211] | Vadiveloo J, Nurfariza B, Fadel J G. 2009. Nutritional improvement of rice husks. Anim Feed Sci Technol, 151(3/4): 299-305. |
| [212] | Vaz M G, Pereira A G B, Fajardo A R, Azevedo A C N, Rodrigues F H A. 2017. Methylene blue adsorption on chitosan-g-poly (acrylic acid)/rice husk ash superabsorbent composite: Kinetics, equilibrium, and thermodynamics. Water Air Soil Pollut, 228(1): 14. |
| [213] | Wan Ismail W N, Umairah Mokhtar S. 2020. Various methods for removal, treatment, and detection of emerging water contaminants. Emerging Contaminants. In: Nuro A. Emerging Contaminants. London, UK: IntechOpen: 1-27. |
| [214] | Wang F, Wang H K, Sun C, Yan Z. 2021. Conventional bioretention column with Fe-hydrochar for stormwater treatment: Nitrogen removal, nitrogen behaviour and microbial community analysis. Bioresour Technol, 334: 125252. |
| [215] | Wang J, Shi L, Zhang X Z, Zhao X, Zhong K C, Wang S X, Zou J W, Shen Z G, Chen Y H. 2019. Earthworm activities weaken the immobilizing effect of biochar as amendment for metal polluted soils. Sci Total Environ, 696: 133729. |
| [216] | Wang L W, Bolan N S, Tsang D C W, Hou D Y. 2020. Green immobilization of toxic metals using alkaline enhanced rice husk biochar: Effects of pyrolysis temperature and KOH concentration. Sci Total Environ, 720: 137584. |
| [217] | Wang Z F, Smith A T, Wang W X, Sun L Y. 2018. Versatile nanostructures from rice husk biomass for energy applications. Angew Chem Int Ed, 57(42): 13722-13734. |
| [218] | Wei B G, Yang L S. 2010. A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem J, 94(2): 99-107. |
| [219] | Wibowo D E, Ramadhan D A, Endaryanta, Prayuda H. 2023. Soil stabilization using rice husk ash and cement for pavement subgrade materials. Rev Constr, 22(1): 192-202. |
| [220] | Win K T, Okazaki K, Ookawa T, Yokoyama T, Ohwaki Y. 2019. Influence of rice-husk biochar and Bacillus pumilus strain TUAT-1 on yield, biomass production, and nutrient uptake in two forage rice genotypes. PLoS One, 14(7): e0220236. |
| [221] | Wisetkomolmat J, Arjin C, Hongsibsong S, Ruksiriwanich W, Niwat C, Tiyayon P, Jamjod S, Yamuangmorn S, Prom-U-Thai C, Sringarm K. 2023. Antioxidant activities and characterization of polyphenols from selected northern thai rice husks: relation with seed attributes. Rice Sci, 30(2): 148-159. |
| [222] | Wu S C, Hsu H C, Hsiao S H, Ho W F. 2009. Preparation of porous 45S5 Bioglass®-derived glass-ceramic scaffolds by using rice husk as a porogen additive. J Mater Sci: Mater Med, 20(6): 1229-1236. |
| [223] | Yang B W, Dai J W, Zhao Y, Wu J W, Ji C Y, Zhang Y H. 2022. Advances in preparation, application in contaminant removal, and environmental risks of biochar-based catalysts: A review. Biochar, 4(1): 51. |
| [224] | Yavari S, Sapari N B, Malakahmad A, Yavari S,. 2019. Degradation of imazapic and imazapyr herbicides in the presence of optimized oil palm empty fruit bunch and rice husk biochars in soil. J Hazard Mater, 366: 636-642. |
| [225] | Yi S Z, Gao B, Sun Y Y, Wu J C, Shi X Q, Wu B J, Hu X. 2016. Removal of levofloxacin from aqueous solution using rice-husk and wood-chip biochars. Chemosphere, 150: 694-701. |
| [226] | Yuan Q, Zuo S H, L Z M, Shi C J, Wu Q H. 2021. Optimizing three-dimensional printing binder composed of ordinary Portland cement and calcium sulfoaluminate cement with retarders. ACI Mater J, 118(6): 155-165. |
| [227] | Zhan D, Luo W, Kraatz H B, Fehse M, Li Y Q, Xiao Z A, Brougham D F, Simpson A J, Wu B. 2019. Facile approach for synthesizing high-performance MnO/C electrodes from rice husk. ACS Omega, 4(20): 18908-18917. |
| [228] | Zhang H L, Chen S, Jia X R, Huang Y X, Ji R, Zhao L J. 2021. Comparation of the phytotoxicity between chemically and green synthesized silver nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ, 752: 142264. |
| [229] | Zhang X G, Wang Y, Cai J M, Wilson K, Lee A F. 2020. Bio/hydrochar sorbents for environmental remediation. Energy Environ Mater, 3(4): 453-468. |
| [230] | Zhang Y, Zhang P, Song X L, Shen H J, Kong X D, Xu H M. 2020. Low-cost 3D porous sea-hedgehog-like NiCo2O4/C as anode for Li-ion battery. Nanotechnology, 31(41): 415704. |
| [231] | Zheng X J, Chen M, Wang J F, Liu Y, Liao Y Q, Liu Y C. 2020. Assessment of zeolite, biochar, and their combination for stabilization of multimetal-contaminated soil. ACS Omega, 5(42): 27374-27382. |
| [1] | Asadi Hossein, Ghorbani Mohammad, Rezaei-Rashti Mehran, Abrishamkesh Sepideh, Amirahmadi Elnaz, Chengrong Chen, Gorji Manouchehr. Application of Rice Husk Biochar for Achieving Sustainable Agriculture and Environment [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(4): 325-343. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||