
Rice Science ›› 2022, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (5): 451-461.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2022.07.005
• Research Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Du Shuanglin1,#, Wang Zhongwei2,#, Chen Yun1,#, Tan Yao1, Li Xiang1, Zhu Wenping1, He Guanghua3, Lei Kairong2( ), Guo Longbiao4(
), Guo Longbiao4( ), Zhang Yi1(
), Zhang Yi1( )
)
Received:2021-09-08
Accepted:2022-02-18
Online:2022-09-28
Published:2022-07-14
Contact:
Lei Kairong, Guo Longbiao, Zhang Yi
About author:First author contact:# These authors contributed equally to this work
Du Shuanglin, Wang Zhongwei, Chen Yun, Tan Yao, Li Xiang, Zhu Wenping, He Guanghua, Lei Kairong, Guo Longbiao, Zhang Yi. Coleoptile Purple Line Regulated by A-P Gene System Is a Valuable Marker Trait for Seed Purity Identification in Hybrid Rice[J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(5): 451-461.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX

Fig. 1. Phenotypic characteristics of coleoptile purple line and coleoptile non-purple line on R25 and YR25 at the germination stage. A and C, Phenotypes of coleoptile purple line in R25. B and D, Phenotypes of coleoptile non-purple line in YR25. Coleoptile purple line and non-purple line are indicated by black and white arrows, respectively. Scale bars, 1 mm.
| Line | Cl | Sh | In | Au | L | St | Ap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R25 | + | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| YR25 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| II-32 A | + | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| II-32 B | + | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| YII-32 A | - | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| YII-32 B | - | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| Zhongjiu A | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Zhongjiu B | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| NJ7B | - | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| 2081A | - | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| 2081B | - | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| 06A2066 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Luhui 17 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| R30 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| R287 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| R725 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Table 1. Purple organs in different rice materials used in this study.
| Line | Cl | Sh | In | Au | L | St | Ap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R25 | + | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| YR25 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| II-32 A | + | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| II-32 B | + | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| YII-32 A | - | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| YII-32 B | - | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| Zhongjiu A | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Zhongjiu B | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| NJ7B | - | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| 2081A | - | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| 2081B | - | + | - | + | - | + | + |
| 06A2066 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Luhui 17 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| R30 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| R287 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| R725 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
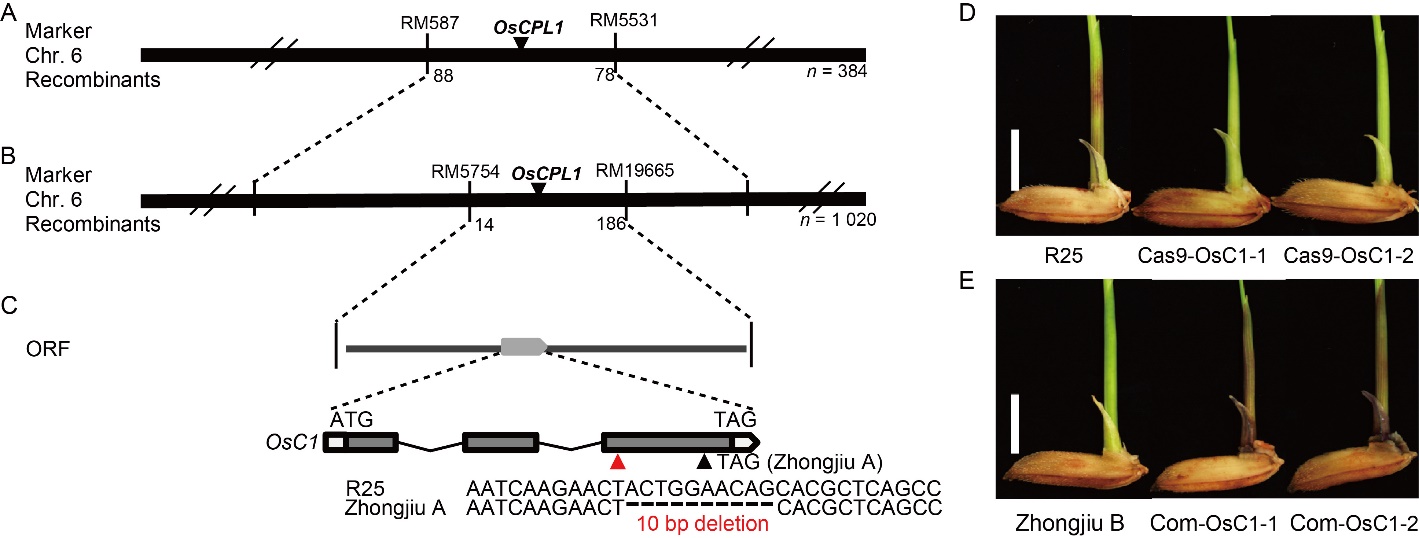
Fig. 2. Map-based cloning of OsCPL1. A, OsCPL1 locus is mapped to chromosome 6 (Chr. 6). B, OsCPL1 locus is narrowed down between markers RM5754 and RM19665. =C, Open reading frame (ORF) of candidate gene OsCPL1 in the mapped region. The mutation site is indicated by a red upright triangle, and the premature stop codon is indicated by a black triangle. D, Independent T1 mutants generated using a CRISPR/Cas9 system. The mutants (Cas9-OsC1-1 and -2) display non-purple color in coleoptile. R25, Wild type plants. Scale bar, 0.5 cm. E, Independent T1 complementary plants (Com-OsC1-1 and -2). The positive plants display purple color in coleoptile. Zhongjiu B is a Osc1 mutant. Scale bar, 0.5 cm.
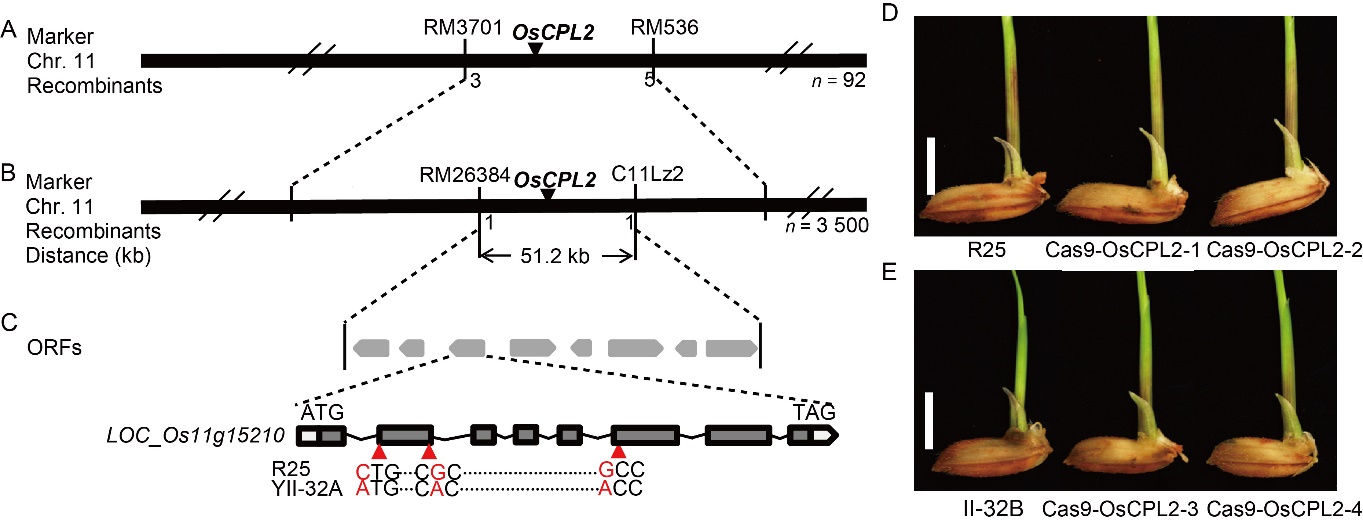
Fig. 3. Map-based cloning of OsCPL2. A, OsCPL2 locus was mapped to chromosome 11 (Chr. 11). B, OsCPL2 locus was narrowed down to a 51.2-kb interval. C, Open reading frames (ORFs) of the candidate gene LOC_Os11g15210 in the mapped region. The sense mutation sites are indicated by red upright triangles. D and E, Independent T1 mutants of R25 (D) and II-32B (E) generated using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. The mutants have non-purple line in the coleoptile. R25 and II-32B are wild type plants. Scale bars, 0.5 cm.
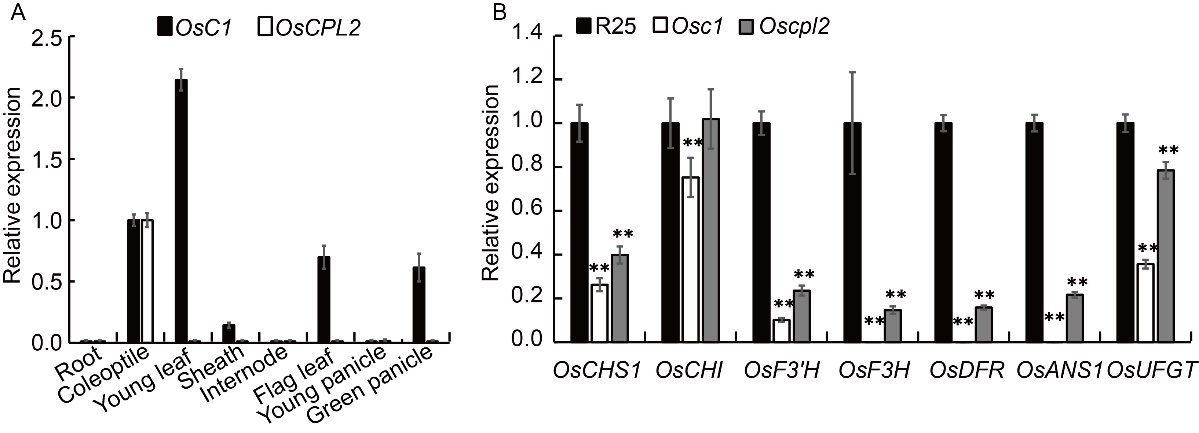
Fig. 4. Expression patterns of OsC1 and OsCPL2 and transcript expression analysis of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes in coleoptiles. A, Expression pattern analysis of OsC1 and OsCPL2 in various organs of wild type R25. B, Transcript expression analysis of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes in the coleoptiles of R25, the Osc1 mutant Zhongjiu B and the Oscpl2 mutant YII-32B. OsUbiquitin1 (Os03g0234200) was used as the internal control. Values are Mean ± SD with three biological replicates. The asterisks indicate statistical significance between R25 and the Osc1 or Oscpl2 mutant, as determined by the Student’s t-test (**, P < 0.01).
| Cross combination | Total number | Number of off-type seeds | Hybrid seed purity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2081A × 06A2066 | 1 000 | 26 | 97.4 |
| 2081A × R30 | 1 000 | 12 | 98.8 |
| 2081A × R287 | 1 000 | 12 | 98.8 |
| 2081A × R725 | 1 000 | 7 | 99.3 |
Table 2. Seed purity identification of hybrid rice seeds via coleoptile purple line.
| Cross combination | Total number | Number of off-type seeds | Hybrid seed purity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2081A × 06A2066 | 1 000 | 26 | 97.4 |
| 2081A × R30 | 1 000 | 12 | 98.8 |
| 2081A × R287 | 1 000 | 12 | 98.8 |
| 2081A × R725 | 1 000 | 7 | 99.3 |
| [1] | Cao L Y, Qian Q, Zhu X D, Zeng D L, Min S K, Xiong Z M. 1999. Breeding of a photo-thermo sensitive genie male sterile indica rice Zhongzi S with a purple-leaf marker and the hoterosis of its hybrid rice produced with it. Acta Agron Sin, 25(1): 44-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [2] | Chin H S, Wu Y P, Hour A L, Hong C Y, Lin Y R. 2016. Genetic and evolutionary analysis of purple leaf sheath in rice. Rice, 9(1): 8. |
| [3] | Dong F G, Zhu X D, Xiong Z M, Cheng S H, Sun Z X, Min S K. 1995. Breeding of a photo-thermoperiod sensitive genic male sterile indica rice with a pale-green-leaf marker. Chin J Rice Sci, 9(2): 65-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Fan F J, Fan Y Y, Du J H, Zhuang J Y. 2008. Fine mapping of C (chromogen for anthocyanin) gene in rice. Rice Sci, 15(1): 1-6. |
| [5] |
Furukawa T, Maekawa M, Oki T, Suda I, Iida S, Shimada H, Takamure I, Kadowaki K I. 2007. The Rc and Rd genes are involved in proanthocyanidin synthesis in rice pericarp. Plant J, 49(1): 91-102.
PMID |
| [6] | Gao D Y, He B, Zhou Y H, Sun L H. 2011. Genetic and molecular analysis of a purple sheath somaclonal mutant in japonica rice. Plant Cell Rep, 30(5): 901-911. |
| [7] |
Hichri I, Barrieu F, Bogs J, Kappel C, Delrot S, Lauvergeat V. 2011. Recent advances in the transcriptional regulation of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. J Exp Bot, 62(8): 2465-2483.
PMID |
| [8] |
Hiei Y, Komari T. 2008. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of rice using immature embryos or calli induced from mature seed. Nat Protoc, 3(5): 824-834.
PMID |
| [9] | Hu W, Zhou T H, Han Z M, Tan C, Xing Y Z. 2020. Dominant complementary interaction between OsC1 and two tightly linked genes, Rb1 and Rb2, controls the purple leaf sheath in rice. Theor Appl Genet, 133(9): 2555-2566. |
| [10] | Kinoshita T. 1984. Gene analysis and linkage map. In: Tsunoda S, Takahashi N. Biology of Rice. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier: 187-274. |
| [11] | Kondo A. 1963. Fundamental studies on rice breeding through hybridization between Japanese and foreign varieties: VII. Identification of the gene system controlling anthocyanin coloration in Japanese and foreign varieties. Jpn J Breed, 13: 92-98. |
| [12] | Lev-Yadun S, Gould K S. 2009. Role of anthocyanins in plant defence. In: Winefield C, Davies K, Gould K. Anthocyanins: Biosynthesis, Functions, and Applications. New York, USA: Springer: 21-48. |
| [13] | Li S Q, Yang D C, Zhu Y G. 2007. Characterization and use of male sterility in hybrid rice breeding. J Integr Plant Biol, 49(6): 791-804. |
| [14] |
Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCTmethod. Methods, 25(4): 402-408.
PMID |
| [15] | Ludwig S R, Habera L F, Dellaporta S L, Wessler S R. 1989. Lc, a member of the maize R gene family responsible for tissue- specific anthocyanin production, encodes a protein similar to transcriptional activators and contains the myc-homology region. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 86(18): 7092-7096. |
| [16] | Maeda H, Yamaguchi T, Omoteno M, Takarada T, Fujita K, Murata K, Iyama Y, Kojima Y, Morikawa M, Ozaki H, Mukaino N, Kidani Y, Ebitani T. 2014. Genetic dissection of black grain rice by the development of a near isogenic line. Breed Sci, 64(2): 134-141. |
| [17] |
Meng L Z, Qi C Y, Wang C H, Wang S, Zhou C L, Ren Y L, Cheng Z J, Zhang X, Guo X P, Zhao Z C, Wang J, Lin Q B, Zhu S S, Wang H Y, Wang Z H, Lei C L, Wan J M. 2021. Determinant factors and regulatory systems for anthocyanin biosynthesis in rice apiculi and stigmas. Rice, 14(1): 37.
PMID |
| [18] | Oikawa T, Maeda H, Oguchi T, Yamaguchi T, Tanabe N, Ebana K, Yano M, Ebitani T, Izawa T. 2015. The birth of a black rice gene and its local spread by introgression. Plant Cell, 27(9): 2401-2414. |
| [19] |
Petroni K, Tonelli C. 2011. Recent advances on the regulation of anthocyanin synthesis in reproductive organs. Plant Sci, 181(3): 219-229.
PMID |
| [20] | Reddy V, Scheffler B E, Wienand U, Wessler S R, Reddy A R. 1998. Cloning and characterization of the rice homologue of the maize C1 anthocyanin regulatory gene. Plant Mol Biol, 36(3): 497-498. |
| [21] |
Saitoh K, Onishi K, Mikami I, Thidar K, Sano Y. 2004. Allelic diversification at the C (OsC1) locus of wild and cultivated rice: Nucleotide changes associated with phenotypes. Genetics, 168(2): 997-1007.
PMID |
| [22] |
Sakamoto W, Ohmori T, Kageyama K, Miyazaki C, Saito A, Murata M, Noda K, Maekawa M. 2001. The Purple leaf (Pl) locus of rice: The Plw allele has a complex organization and includes two genes encoding basic helix-loop-helix proteins involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol, 42(9): 982-991.
PMID |
| [23] | Shen Y J, Jiang H, Jin J P, Zhang Z B, Xi B, He Y Y, Wang G, Wang C, Qian L, Li X, Yu Q B, Liu H J, Chen D H, Gao J H, Huang H, Shi T L, Yang Z N. 2004. Development of genome- wide DNA polymorphism database for map-based cloning of rice genes. Plant Physiol, 135(3): 1198-1205. |
| [24] |
Shih C H, Chu H, Tang L K, Sakamoto W, Maekawa M, Chu I K, Wang M F, Lo C. 2008. Functional characterization of key structural genes in rice flavonoid biosynthesis. Planta, 228(6): 1043-1054.
PMID |
| [25] | Shih-Cheng L, Loung P Y. 1980. Hybrid rice breeding in China. In: Innovative Approaches to Rice Breeding: Selected Papers from the 1979 International Rice Research Conference. Los Banos, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute: 35-51. |
| [26] | Shu Q Y, Chen S F, Wu D X, Shen S Q, Cui H R, Xia Y W. 2001. Studies on breeding of a new type of cytoplasmic male sterile rice line Quanlong A. Sci Agric Sin, 34(4): 349-354. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Song K B, Song Z G. 2007. Discovery and preliminary research of the yellowish leaf mutant Annongbiao 810S in rice. Hybrid Rice, 22(6): 71-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Song K B, Xiao J P. 2012. Progress in breeding of male sterile lines with recessive yellowish leaf color marker in rice. Hybrid Rice, 27 (2): 15-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Sun X M, Zhang Z Y, Chen C, Wu W, Ren N N, Jiang C H, Yu J P, Zhao Y, Zheng X M, Yang Q W, Zhang H L, Li J J, Li Z C. 2018. The C-S-A gene system regulates hull pigmentation and reveals evolution of anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway in rice. J Exp Bot, 69(7): 1485-1498. |
| [30] | Takahashi M E. 1957. Analysis on apiculus color genes essential to anthocyanin coloration rice. J Fac Agric, 50(3): 266-362. |
| [31] | Wang Z W, Lv J, Xie S Z, Zhang Y, Qiu Z N, Chen P, Cui Y T, Niu Y F, Hu S K, Jiang H Z, Ge S Z, Trinh H, Lei K R, Bai W Q, Zhang Y, Guo L B, Ren D Y. 2018. OsSLA4 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein essential for early chloroplast development and seedling growth in rice. Plant Growth Regul, 84(2): 249-260. |
| [32] | Xi J M. 1997. The discovery and primary research of coleoptile purple lines in rice. Hybrid Rice, (6): 41. (in Chinese) |
| [33] | Yang X H, Wang J R, Xia X Z, Zhang Z Q, He J, Nong B X, Luo T P, Feng R, Wu Y Y, Pan Y H, Xiong F Q, Zeng Y, Chen C, Guo H, Xu Z J, Li D T, Deng G F. 2021. OsTTG1, a WD40 repeat gene, regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in rice. Plant J, 107(1): 198-214. |
| [34] | Yu X Q, Wu P L, Zhao F S, Jin W K, Chen H S. 2003. Improvement of recessive purple leaf rice and its utilization. Guizhou Agric Sci, 31(3): 3-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [35] | Zeng Y H. 1996. Studies on the verification of the truth and purith of hybrid seeds of Hsier-type rice. Acta Agric Univ Jiangxi, 18(1): 119-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [36] | Zhang F, Chen W. 2004. Review of methods for the purity identification of hybrid rice. Seed, 23(9): 55-58. (in Chinese) |
| [37] | Zhang G C, Liu Z M, Liu Y H, Kuya N, Hua Y C, Shi H R, Zhao W L, Han Y Q, Yamamoto T, Chen W F, Sun J. 2021. iTRAQ-based proteomics investigation of critical response proteins in embryo and coleoptile during rice anaerobic germination. Rice Sci, 28(4): 391-401. |
| [38] | Zhang Y, Li Y F, Liu X F, Lin M X, Shen F C, He G H, Yang Z L, Yang G W. 2004a. Analysis on the inheritance of coleoptile purple line in rice. Sci Agric Sin, 37(11): 1693-1698. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [39] | Zhang Y, Shen F C, Yang G W, He G H, Zhang Z S, Yang Z L. 2004b. Analysis on the inheritance of inhibition and anti-inhibition of coleoptile purple line in rice and the SSR location of Ai(t) gene. Acta Genet Sin, 31(8): 830-835. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [40] |
Zhao D Q, Tao J. 2015. Recent advances on the development and regulation of flower color in ornamental plants. Front Plant Sci, 6: 261.
PMID |
| [41] | Zhao H J, Wu D X, Shu Q Y, Shen S Q, Ma C X. 2004. Breeding and characteristics of photo-thermo sensitive genic male sterile rice Yutu S labeled with green-revertible albino leaf marker. Chin J Rice Sci, 18(6): 515-521. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [42] | Zhao S S, Wang C H, Ma J, Wang S, Tian P, Wang J L, Cheng Z J, Zhang X, Guo X P, Lei C L. 2016. Map-based cloning and functional analysis of the chromogen gene C in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Plant Biol, 59(5): 496-505. |
| [43] |
Zheng J, Wu H, Zhu H B, Huang C Y, Liu C, Chang Y S, Kong Z C, Zhou Z H, Wang G W, Lin Y J, Chen H. 2019. Determining factors, regulation system, and domestication of anthocyanin biosynthesis in rice leaves. New Phytol, 223(2): 705-721.
PMID |
| [1] | Suchila Utasee, Sansanee Jamjod, Sittisavet Lordkaew, Chanakan Prom-U-Thai. Improve Anthocyanin and Zinc Concentration in Purple Rice by Nitrogen and Zinc Fertilizer Application [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(5): 435-450. |
| [2] | Yamuangmorn Supaporn, Dell Bernard, Prom-u-thai Chanakan. Effects of Cooking on Anthocyanin Concentration and Bioactive Antioxidant Capacity in Glutinous and Non-Glutinous Purple Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2018, 25(5): 270-278. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||