
Rice Science ›› 2023, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 426-436.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2023.02.004
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Tan Jingyi, Zhang Xiaobo, Shang Huihui, Li Panpan, Wang Zhonghao, Liao Xinwei, Xu Xia, Yang Shihua, Gong Junyi( ), Wu Jianli(
), Wu Jianli( )
)
Received:2022-12-19
Accepted:2023-02-21
Online:2023-09-28
Published:2023-08-14
Contact:
Wu Jianli (About author:First author contact:#These authors contributed equally to this work
Tan Jingyi, Zhang Xiaobo, Shang Huihui, Li Panpan, Wang Zhonghao, Liao Xinwei, Xu Xia, Yang Shihua, Gong Junyi, Wu Jianli. ORYZA SATIVA SPOTTED-LEAF 41 (OsSPL41) Negatively Regulates Plant Immunity in Rice[J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 426-436.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
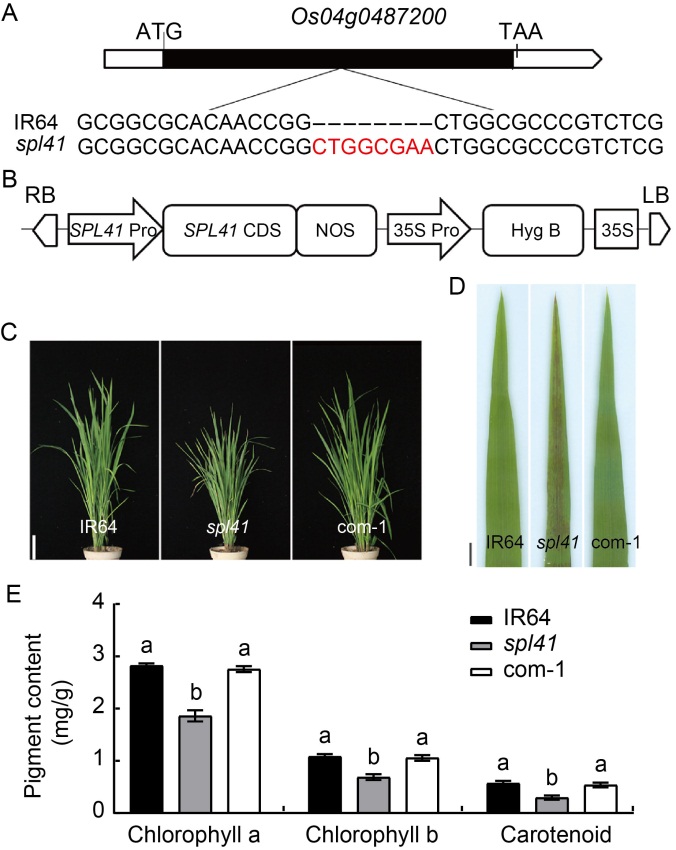
Fig. 1. Identification and functional validation of OsSPL41. A, An 8-bp insertion (red letters) was detected in the mutant allele of Os04g0487200. ATG and TAA refer to initiation codon and termination codon, respectively. B, Structure of complementary construct p1300-OsSPL41-com. RB, Right border; LB, Left border; Pro, Promoter; CDS, Coding sequence; Hyg, Hygromycin; NOS, Terminator. C, Phenotypes of IR64, spl41 and complementary line (com-1) at the tillering stage. Scale bar, 10 cm. D, Leaf phenotypes of IR64, spl41 and complementary line (com-1) at the tillering stage. Scale bar, 1 cm. E, Contents of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoid in IR64, spl41 and complementary line (com-1) at the tillering stage.
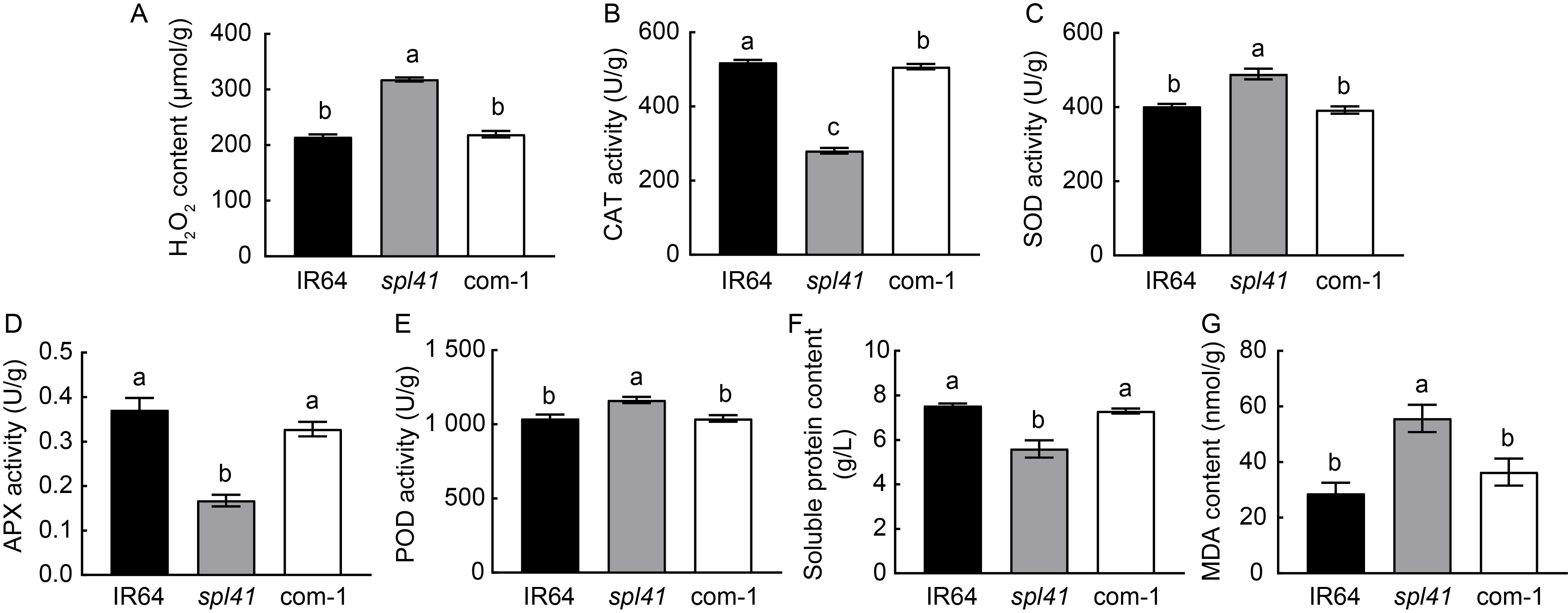
Fig. 2. Physiological parameters in IR64, spl41 and complementary line (com-1). A?G, Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) content (A), catalase (CAT) activity (B), superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity (C), ascorbate peroxidase (APX) activity (D), peroxidase (POD) activity (E), total soluble protein content (F) and malondialdehyde (MDA) content (G) in IR64 (wild type), spl41 and complementary line (com-1). Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). Different lowercase letters above the bars indicate significant differences by the Duncan’s multiple test (P < 0.05).
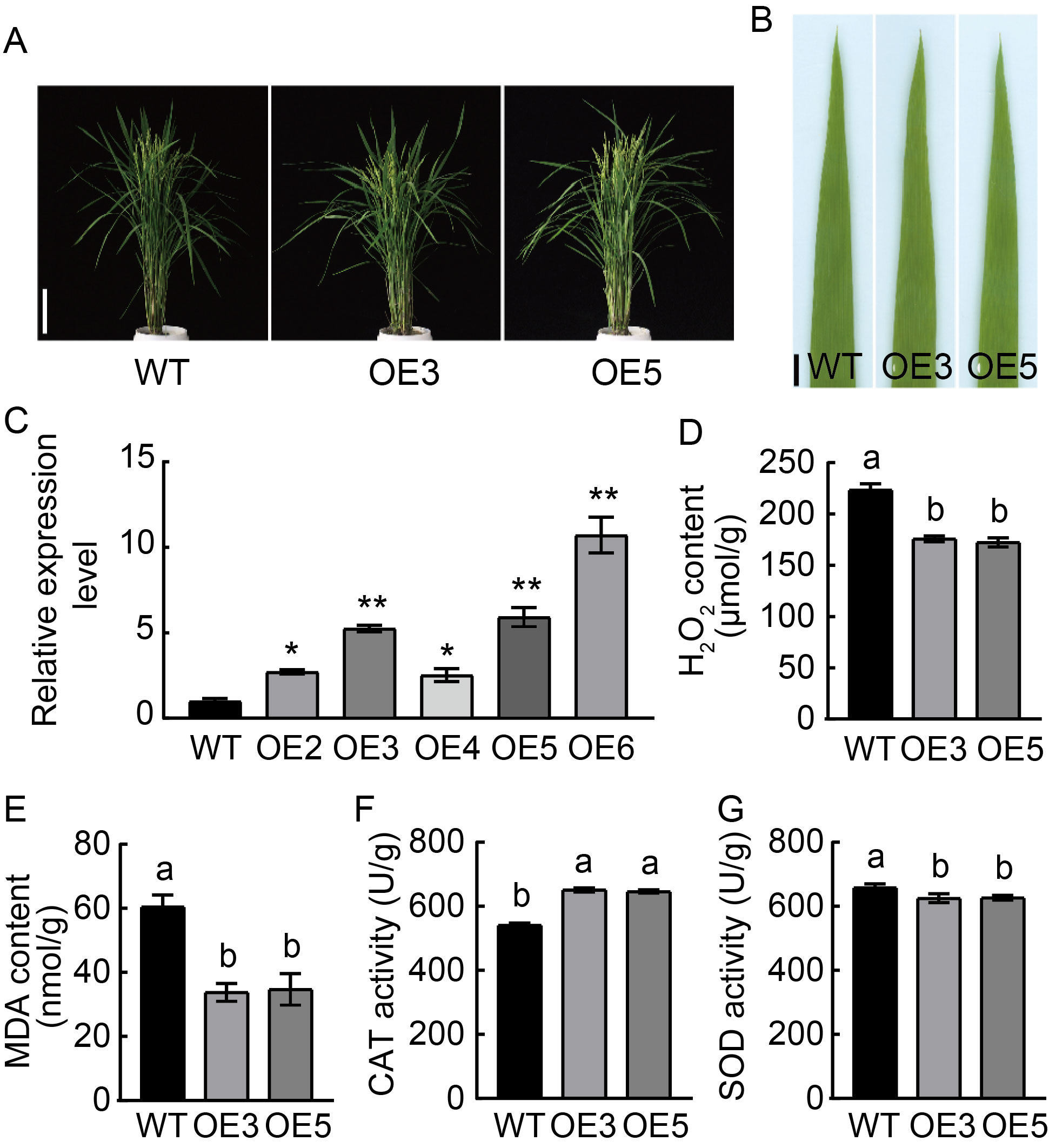
Fig. 3. Characterization of over-expression lines at the heading stage. A, Phenotypes of wild type (WT) Nipponbare and over-expression lines OE3 and OE5. Scale bar, 15 cm. B, Leaf phenotypes of WT and over-expression lines OE3 and OE5. Scale bar, 1 cm. C, Relative expression of OsSPL41 in WT and over-expression lines. * and ** indicate significant differences at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 by the Student’s t-test, respectively. The first leaves from the top were sampled at the tillering stage. Ubiquitin gene was used as a reference gene. D?G, Contents of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (D) and malondialdehyde (MDA) (E) as well as activities of catalase (CAT) (F) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) (G) in WT and over-expression lines (OE3 and OE5). Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). Different lowercase letters above the bars indicate significant differences by the Duncan’s multiple test (P < 0.05).
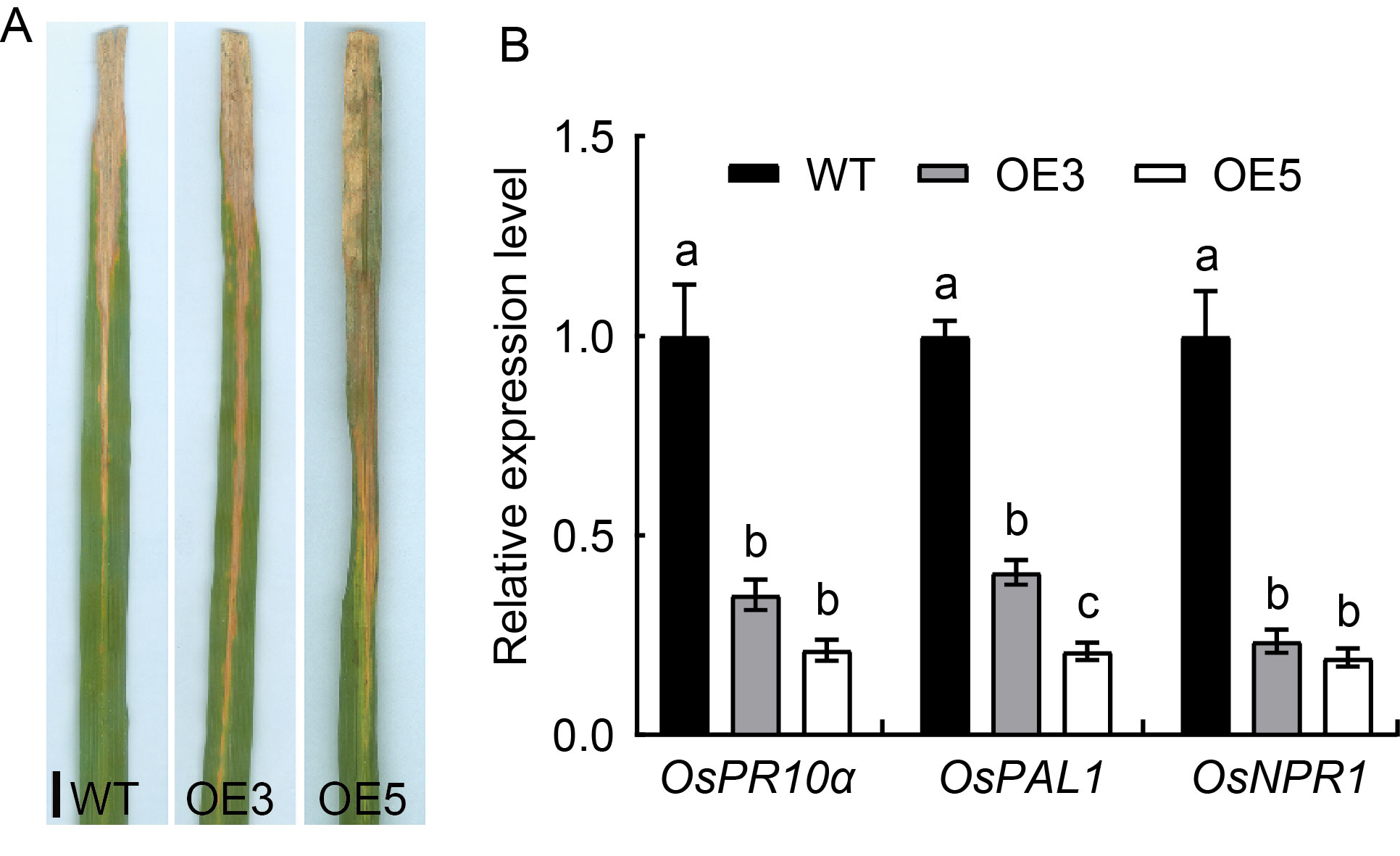
Fig. 4. Responses of OsSPL41 over-expression to bacterial blight pathogen race PXO280. A, Lesion length in reaction to bacterial blight race PXO280. Scale bar, 1 cm. B, Relative expression of defense genes in Nipponbare (Wild type, WT) and over-expression lines (OE3 and OE5) inoculated with bacterial blight race PXO280. The first leaves from the top sampled at the tillering stage were used for the gene expression analysis. Ubiquitin gene was used as a reference gene. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). Different lowercase letters above the bars indicate significant differences by the Duncan’s multiple test (P < 0.05).

Fig. 5. Histochemical and gene expression analysis of cell death. A, Trypan blue staining of IR64 (left, before staining; right, after staining), spl41 (left, before staining; right, after staining) and complementary plants (left, before staining; right, after staining) at the late-tillering stage. Scale bar, 1 cm. B, TDT-mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) assay of IR64 and spl41 leaves, blue fluorescence represents 4’,6-diamino-phenylindole (DAPI) staining, green fluorescence represents positive TUNEL signal. Scale bar, 50 μm. C, Relative expression levels of metascaspase (MC) genes by qRT- PCR. The first leaves from the top sampled at the tillering stage were used for the gene expression analysis. Ubiquitin gene was used as a reference gene. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). * and ** represent significant differences at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 by the Student’s t-test, respectively.
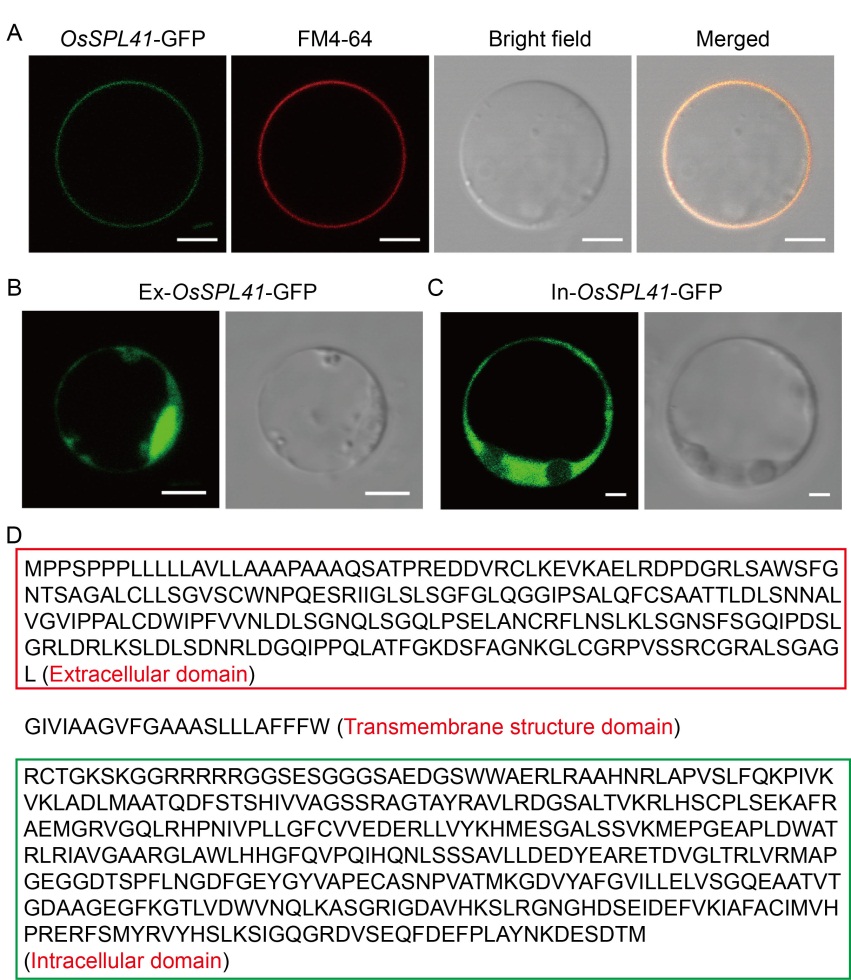
Fig. 6. Subcellular localization of OsSPL41. A, Subcellular localization of OsSPL41-GFP fusion proteins. FM4-64, Cell membrane specific dye. Scale bar, 5 μm. B, Subcellular localization of extracellular domain. Scale bar, 5 μm. C, Subcellular localization of intracellular domain. Scale bar, 2 μm. D, Structural identification of OsSPL41 amino acid sequence. Red and green boxes indicate the extracellular and intracellular domains, respectively.
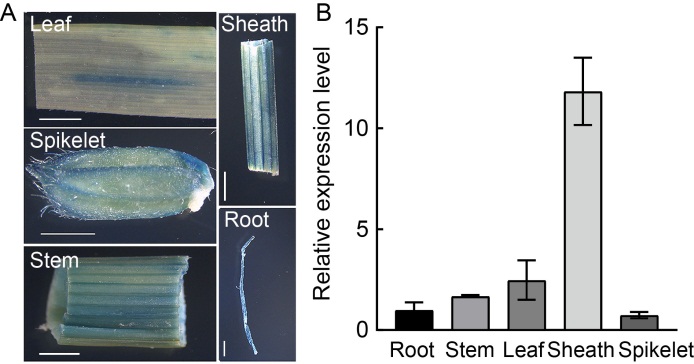
Fig. 7. Spatial-temporal expression pattern of OsSPL41. A, β-glucuronidase (GUS) transient expression driven by OsSPL41 promoter in root, stem, leaf, sheath and spikelet of Nipponbare. Scale bar, 0.2 cm. B, Relative expression levels of OsSPL41 in roots, stems, leaves, sheaths and spikelets of IR64 at the heading stage. Ubiquitin gene was used as a reference gene. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3).
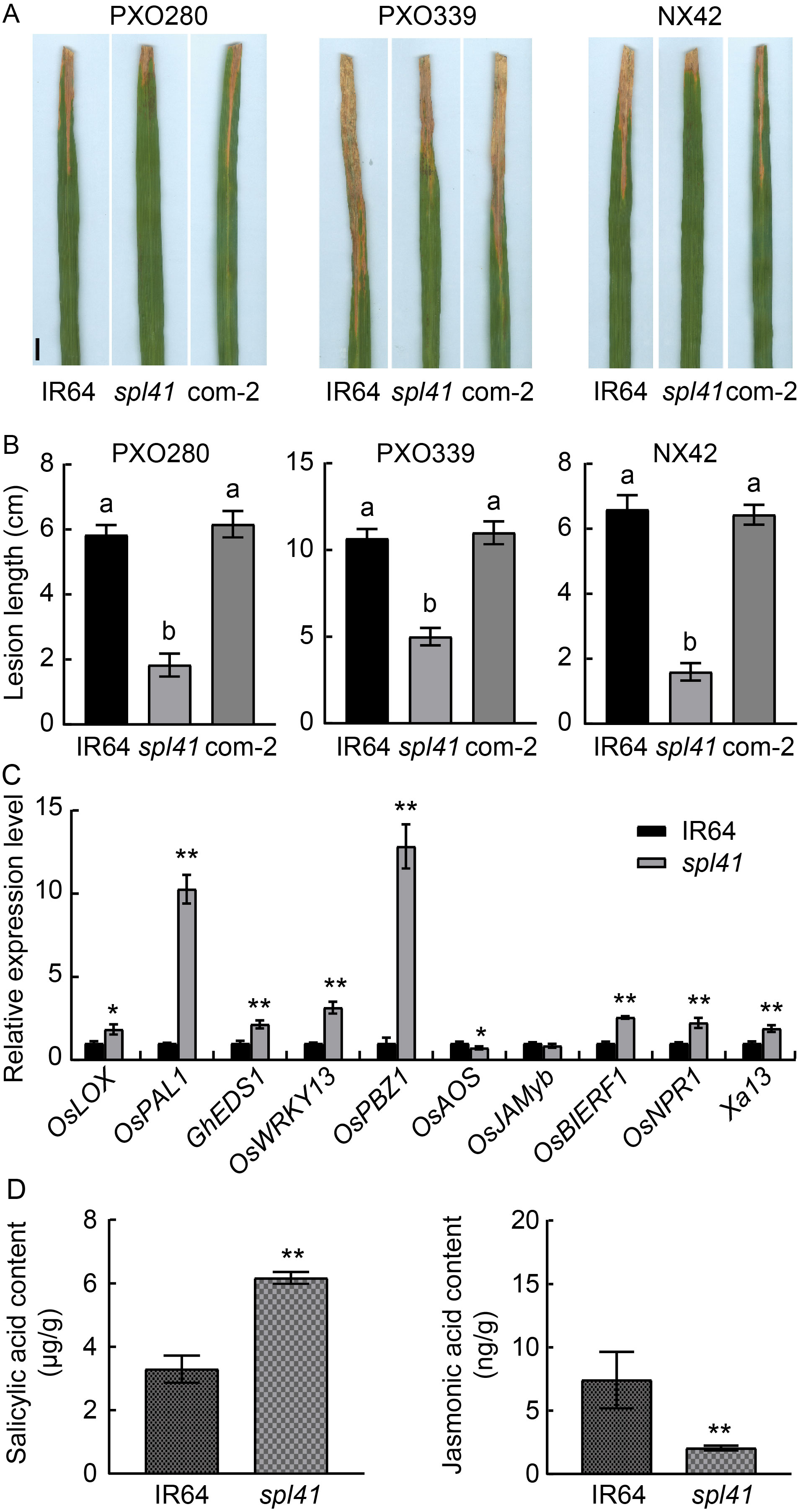
Fig. 8. Disease evaluation, gene defense genes in IR64 and spl41. The first leaves from the top sampled at the tillering stage were used for the gene expression analysis. Ubiquitin gene was used as a reference gene. D, Hormone levels in IR64 and spl41. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). Different lowercase letters above the bars indicate significant differences by the Duncan’s test (P < 0.05). * and ** represent significant differences at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 by the Student’s t-test, respectively.
| [1] | Arase S. 2005. Studies on fungal pathogenicity and host resistance in rice blast disease using a lesion mimic mutant of rice. J Gen Plant Pathol, 71(6): 448-450. |
| [2] | Arnon D I. 1949. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol, 24(1): 1-15. |
| [3] |
Campbell M A, Ronald P C. 2005. Characterization of four rice mutants with alterations in the defence response pathway. Mol Plant Pathol, 6(1): 11-21.
PMID |
| [4] | Chen P P, Ye S H, Zhao N C, Lu Y T, Liu H J, Yang L, Jin Q S, Zhang X M. 2010. Characteristics and genetic mapping of a lesion mimic mutant spl(t) in japonica rice variety Zhejing 22. J Nucl Agric Sci, 24(1): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Chu Z H, Yuan M, Yao J L, Ge X J, Yuan B, Xu C G, Li X H, Fu B Y, Li Z K, Bennetzen J L, Zhang Q F, Wang S P. 2006. Promoter mutations of an essential gene for pollen development result in disease resistance in rice. Genes Dev, 20(10): 1250-1255. |
| [6] |
Fan J B, Bai P F, Ning Y S, Wang J Y, Shi X T, Xiong Y H, Zhang K, He F, Zhang C Y, Wang R Y, Meng X Z, Zhou J G, Wang M, Shirsekar G, Park C H, Bellizzi M, Liu W D, Jeon J S, Xia Y, Shan L B, Wang G L. 2018. The monocot-specific receptor-like kinase SDS2 controls cell death and immunity in rice. Cell Host Microbe, 23(4): 498-510.
PMID |
| [7] |
Fujiwara T, Maisonneuve S, Isshiki M, Mizutani M, Chen L T, Wong H L, Kawasaki T, Shimamoto K. 2010. Sekiguchi lesion gene encodes a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase that catalyzes conversion of tryptamine to serotonin in rice. J Biol Chem, 285(15): 11308-11313.
PMID |
| [8] | Greene E A, Codomo C A, Taylor N E, Henikoff J G, Till B J, Reynolds S H, Enns L C, Burtner C, Johnson J E, Odden A R, Comai L, Henikoff S. 2003. Spectrum of chemically induced mutations from a large-scale reverse-genetic screen in Arabidopsis. Genetics, 164(2): 731-740. |
| [9] | He X, Jiang J S, Wang C Q, Dehesh K. 2017. ORA59 and EIN3 interaction couples jasmonate-ethylene synergistic action to antagonistic salicylic acid regulation of PDF expression. J Integr Plant Biol, 59(4): 275-287. |
| [10] | Hiei Y, Komari T. 2008. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of rice using immature embryos or calli induced from mature seed. Nat Protoc, 3(5): 824-834. |
| [11] | Huang L M, Sun Q W, Qin F J, Li C, Zhao Y, Zhou D X. 2007. Down-regulation of a SILENT INFORMATION REGULATOR2- related histone deacetylase gene, OsSRT1, induces DNA fragmentation and cell death in rice. Plant Physiol, 144(3): 1508-1519. |
| [12] | Huang Q N, Yang Y, Shi Y F, Chen J, Wu J L. 2010. Spotted-leaf mutants of rice (Oryza sativa). Rice Sci, 17(4): 247-256. |
| [13] | Huang Q N, Shi Y F, Yang Y, Feng B H, Wei Y L, Chen J, Baraoidan M, Leung H, Wu J L. 2011. Characterization and genetic analysis of a light- and temperature-sensitive spotted-leaf mutant in rice. J Integr Plant Biol, 53(8): 671-681. |
| [14] | Huang Q N, Shi Y F, Zhang X B, Song L X, Feng B H, Wang H M, Xu X, Li X H, Guo D, Wu J L. 2016. Single base substitution in OsCDC48 is responsible for premature senescence and death phenotype in rice. J Integr Plant Biol, 58(1): 12-28. |
| [15] |
Jambunathan N, Siani J M, McNellis T W. 2001. A humidity- sensitive Arabidopsis copine mutant exhibits precocious cell death and increased disease resistance. Plant Cell, 13(10): 2225-2240.
PMID |
| [16] | Kauffman H E, Reddy A, Hsieh S, Merca S. 1973. An improved technique for evaluating resistance of rice varieties to Xanthomonas oryzae. Plant Dis Rep, 57: 537-541. |
| [17] |
Kim J A, Cho K, Singh R, Jung Y H, Jeong S H, Kim S H, Lee J E, Cho Y S, Agrawal G K, Rakwal R, Tamogami S, Kersten B, Jeon J S, An G, Jwa N S. 2009. Rice OsACDR1 (Oryza sativa accelerated cell death and resistance 1) is a potential positive regulator of fungal disease resistance. Mol Cells, 28(5): 431-439.
PMID |
| [18] | Li X H, Shi Y F, Zhang X B, Feng B H, Song L X, Wang H M, Xu X, Huang Q N, Guo D, Wu J L. 2015. Identification and gene mapping of a spotted-leaf mutant hm197 in rice. Chin J Rice Sci, 29(5): 447-456. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Liu J L, Park C H, He F, Nagano M, Wang M, Bellizzi M, Zhang K, Zeng X S, Liu W D, Ning Y S, Kawano Y, Wang G L. 2015. The RhoGAP SPIN6 associates with SPL11 and OsRac1 and negatively regulates programmed cell death and innate immunity in rice. PLoS Pathog, 11(2): e1004629. |
| [20] |
Lu D P, Wu S J, Gao X Q, Zhang Y L, Shan L B, He P. 2010. A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase, BIK1, associates with a flagellin receptor complex to initiate plant innate immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 107(1): 496-501.
PMID |
| [21] |
Macho A P, Zipfel C. 2014. Plant PRRs and the activation of innate immune signaling. Mol Cell, 54: 263-272.
PMID |
| [22] | Nanda A K, Andrio E, Marino D, Pauly N, Dunand C. 2010. Reactive oxygen species during plant-microorganism early interactions. J Integr Plant Biol, 52(2): 195-204. |
| [23] | Qiao Y L, Jiang W Z, Lee J, Park B, Choi M S, Piao R H, Woo M O, Roh J H, Han L Z, Paek N C, Seo H S, Koh H J. 2010. SPL28 encodes a clathrin-associated adaptor protein complex 1, medium subunit micro 1 (AP1M1) and is responsible for spotted leaf and early senescence in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol, 185(1): 258-274. |
| [24] | Recio L, Steen A M, Pluta L J, Meyer K G, Saranko C J. 2001. Mutational spectrum of 1,3-butadiene and metabolites 1, 2-epoxybutene and 1, 2, 3, 4-diepoxybutane to assess mutagenic mechanisms. Chem Biol Interact, 135/136: 325-341. |
| [25] | Sathe A P, Su X N, Chen Z, Chen T, Wei X J, Tang S Q, Zhang X B, Wu J L. 2019. Identification and characterization of a spotted-leaf mutant spl40 with enhanced bacterial blight resistance in rice. Rice, 12(1): 68. |
| [26] | Shang H H, Li P P, Zhang X B, Xu X, Gong J Y, Yang S H, He Y Q, Wu J L. 2022. The gain-of-function mutation, OsSpl26, positively regulates plant immunity in rice. Int J Mol Sci, 23(22): 14168. |
| [27] | Shen X L, Liu H B, Yuan B, Li X H, Xu C G, Wang S P. 2011. OsEDR1 negatively regulates rice bacterial resistance via activation of ethylene biosynthesis. Plant Cell Environ, 34(2): 179-191. |
| [28] |
Shi H, Ishitani M, Kim C, Zhu J K. 2000. The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 97(12): 6896-6901.
PMID |
| [29] | Shi L, Zhang X B, Shi Y F, Xu X, He Y Q, Shao G S, Huang Q N, Wu J L. 2019. OsCDC48/48E complex is required for plant survival in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol, 100(1/2): 163-179. |
| [30] | Song Y J, Niu R F, Yu H L, Guo J, Du C H, Zhang Z L, Wei Y, Li J X, Zhang S Q. 2022. OsSLA1 functions in leaf angle regulation by enhancing the interaction between OsBRI1 and OsBAK1 in rice. Plant J, 110(4): 1111-1127. |
| [31] |
Sun C H, Liu L C, Tang J Y, Lin A H, Zhang F T, Fang J, Zhang G F, Chu C C. 2011. RLIN1, encoding a putative coproporphyrinogen III oxidase, is involved in lesion initiation in rice. J Genet Genomics, 38(1): 29-37.
PMID |
| [32] | Wang G D, Ellendorff U, Kemp B, Mansfield J W, Forsyth A, Mitchell K, Bastas K, Liu C M, Woods-Tör A, Zipfel C, de Wit P J G M, Jones J D G, Tör M, Thomma B P H J. 2008. A genome-wide functional investigation into the roles of receptor- like proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 147(2): 503-517. |
| [33] | Wang S H, Lim J H, Kim S S, Cho S H, Yoo S C, Koh H J, Sakuraba Y, Paek N C. 2015. Mutation of SPOTTED LEAF3 (SPL3) impairs abscisic acid-responsive signalling and delays leaf senescence in rice. J Exp Bot, 66(22): 7045-7059. |
| [34] | Wellburn A R. 1994. The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J Plant Physiol, 144(3): 307-313. |
| [35] |
Wu C J, Bordeos A, Madamba M R S, Baraoidan M, Ramos M, Wang G L, Leach J E, Leung H. 2008. Rice lesion mimic mutants with enhanced resistance to diseases. Mol Genet Genomics, 279(6): 605-619.
PMID |
| [36] | Wu Y, Zhou J M. 2013. Receptor-like kinases in plant innate immunity. J Integr Plant Biol, 55(12): 1271-1286. |
| [37] |
Yamaguchi K, Yamada K, Ishikawa K, Yoshimura S, Hayashi N, Uchihashi K, Ishihama N, Kishi-Kaboshi M, Takahashi A, Tsuge S, Ochiai H, Tada Y, Shimamoto K, Yoshioka H, Kawasaki T. 2013. A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase targeted by a plant pathogen effector is directly phosphorylated by the chitin receptor and mediates rice immunity. Cell Host Microbe, 13(3): 347-357.
PMID |
| [38] |
Yamanouchi U, Yano M, Lin H X, Ashikari M, Yamada K. 2002. A rice spotted leaf gene, Spl7, encodes a heat stress transcription factor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 99(11): 7530-7535.
PMID |
| [39] | Yin Z C, Chen J, Zeng L R, Goh M, Leung H, Khush G S, Wang G L. 2000. Characterizing rice lesion mimic mutants and identifying a mutant with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight. Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 13(8): 869-876. |
| [40] | Yuan Y X, Zhong S H, Li Q, Zhu Z R, Lou Y G, Wang L Y, Wang J J, Wang M Y, Li Q L, Yang D L, He Z H. 2007. Functional analysis of rice NPR1-like genes reveals that OsNPR1/NH1 is the rice orthologue conferring disease resistance with enhanced herbivore susceptibility. Plant Biotechnol J, 5(2): 313-324. |
| [41] | Zeng L R, Qu S H, Bordeos A, Yang C W, Baraoidan M, Yan H Y, Xie Q, Nahm B H, Leung H, Wang G L. 2004. Spotted leaf11, a negative regulator of plant cell death and defense, encodes a U-box/armadillo repeat protein endowed with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Plant Cell, 16(10): 2795-2808. |
| [42] |
Zhang J, Li W, Xiang T T, Liu Z X, Laluk K, Ding X J, Zou Y, Gao M H, Zhang X J, Chen S, Mengiste T, Zhang Y L, Zhou J M. 2010. Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases integrate signaling from multiple plant immune receptors and are targeted by a Pseudomonas syringae effector. Cell Host Microbe, 7(4): 290-301.
PMID |
| [43] | Zhang X B, Feng B H, Wang H M, Xu X, Shi Y F, He Y, Chen Z, Sathe A P, Shi L, Wu J L. 2018. A substitution mutation in OsPELOTA confers bacterial blight resistance by activating the salicylic acid pathway. J Integr Plant Biol, 60(2): 160-172. |
| [44] |
Zhang Y, Gao Y H, Liang Y B, Dong Y J, Yang X F, Qiu D W. 2019. Verticillium dahliae PevD1, an Alt a 1-like protein, targets cotton PR5-like protein and promotes fungal infection. J Exp Bot, 70(2): 613-626.
PMID |
| [45] | Zhu X B, Ze M, Chern M, Chen X W, Wang J. 2020. Deciphering rice lesion mimic mutants to understand molecular network governing plant immunity and growth. Rice Sci, 27(4): 278-288. |
| [46] |
Zipfel C, Kunze G, Chinchilla D, Caniard A, Jones J D G, Boller T, Felix G. 2006. Perception of the bacterial PAMP EF-Tu by the receptor EFR restricts Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Cell, 125(4): 749-760.
PMID |
| [1] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [2] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [3] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [4] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [5] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [6] | XIA Xiaodong, ZHANG Xiaobo, WANG Zhonghao, CHENG Benyi, Sun Huifeng, XU Xia, GONG Junyi, YANG Shihua, WU Jianli, SHI Yongfeng, XU Rugen. Mapping and Functional Analysis of LE Gene in a Lethal Etiolated Rice Mutant at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 13-. |
| [7] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [8] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [9] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [10] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [11] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [12] | Jiang Changjie, Liang Zhengwei, Xie Xianzhi. Priming for Saline-Alkaline Tolerance in Rice: Current Knowledge and Future Challenges [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 417-425. |
| [13] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [14] | Monica Ruffini Castiglione, Stefania Bottega, Carlo Sorce, Carmelina SpanÒ. Effects of Zinc Oxide Particles with Different Sizes on Root Development in Oryza sativa [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 449-458. |
| [15] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||