
Rice Science ›› 2023, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 405-416.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2023.04.002
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ammara Latif1( ), Sun Ying1, Pu Cuixia1, Noman Ali2
), Sun Ying1, Pu Cuixia1, Noman Ali2
Received:2022-12-27
Accepted:2023-04-23
Online:2023-09-28
Published:2023-08-14
Contact:
Ammara Latif (Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress[J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Crop | Water required | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth (cm) | Quantity (L/kg) | Depth (cm) | Depth (cm) | Quantity (L/plant) | |
| Rice | 95‒100 | 2 497 | 182 | 90‒250 | 23.95 |
| Wheat | ‒ | 1 350 | 75 | 45‒65 | 6.91 |
| Maize | 40‒45 | 1 222 | 84 | 50‒80 | ‒ |
| Potato | ‒ | 287 | 88 | 50‒70 | 30.11 |
| Cotton | 60‒75 | 10 000 | ‒ | 70‒130 | ‒ |
| Groundnut | 60‒65 | ‒ | ‒ | 50‒70 | 17.84 |
Table 1. Rice water requirements compared with main crops reported in the preceding decade.
| Crop | Water required | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth (cm) | Quantity (L/kg) | Depth (cm) | Depth (cm) | Quantity (L/plant) | |
| Rice | 95‒100 | 2 497 | 182 | 90‒250 | 23.95 |
| Wheat | ‒ | 1 350 | 75 | 45‒65 | 6.91 |
| Maize | 40‒45 | 1 222 | 84 | 50‒80 | ‒ |
| Potato | ‒ | 287 | 88 | 50‒70 | 30.11 |
| Cotton | 60‒75 | 10 000 | ‒ | 70‒130 | ‒ |
| Groundnut | 60‒65 | ‒ | ‒ | 50‒70 | 17.84 |
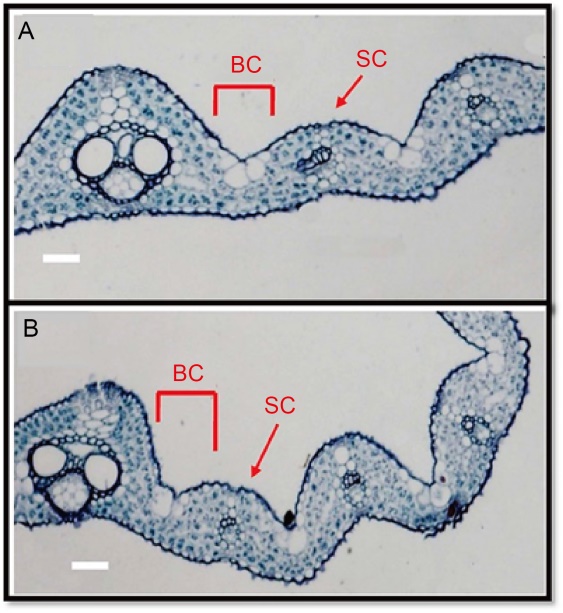
Fig. 2. Comparison of rice leaf anatomy under normal (A) and drought stress conditions (B) (Sun et al, 2020). BC and SC represent bulliform cells and sclerenchyma cells, respectively. Scale bars, 20 μm.
| Gene abbreviation | Gene full name | Transcription factor/ Gene regulator | Functional role in leaf rolling | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADL1 | ADAXIALIZED LEAF1 | Calpain-like cysteine protease | Involved in abaxial leaf rolling | Hibara et al, |
| SLL1 | SHALLOT-LIKE1 | MYB family transcriptional factor class SHAQKYF | Controls the growth of sclerenchyma cells | Zhang et al, |
| ACL1 | abaxially curled leaf 1 | Unidentified protein | Determines the development of leaves | Li et al, |
| NRL1 | NARROW AND ROLLED LEAF 1 | Cellulose synthase like protein D4 | Regulates cell formation | Hu et al, |
| CFL1 | CURLY FLAG LEAF1 | A homeodomain transcription factor class IV | Governs cuticle development | Wu et al, |
| ROC5 | Rice outermost cell-specific gene5 | A homeodomain leucine zipper class IV transcriptional factor | Regulates the formation of bulliform cells | Zou et al, |
| RL14 | Rolling-leaf14 | 2OG-Fe (II) oxygenase | Controls the secondary cell wall formation | Fang et al, |
| LC1 | LEAF INCLINATION1 | T-DNA insert in LOC_Os07g38664 | Directs cell division | Zhao et al, |
| OsZHD1 | zinc finger homeodomain 1 | ZF-HD transcription factor | Participates in abaxial rolling | Xu et al, |
| SLL2 | SHALLOT-LIKE2 | Unidentified plant-specific protein | Controls the size and shape of bulliform cell | Zhang et al, |
| REL1 | Rolled and Erect Leaf 1 | Unknown protein | Positive regulator of leaf rolling | Chen et al, |
| OsI-BAK1 | Brassinosteroid Insensitive 1-Associated Kinase 1 | Unknown | Involved in BR signaling pathway | Khew et al, |
| OsARF18 | AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR18 | Target of mirna160 | Involved in auxin signaling | Huang et al, |
| REL2 | Rolled and Erect Leaf 2 | An unknown protein containing DUF630 and DUF632 domains | Defines the leaf shape | Yang et al, |
| OsLBD3-7 | lateral organ boundary domain 3-7 | DUF260 domain protein | Serves as an activator of transcription | Pina et al, |
| CLD1/SRL1 | CURLED LEAF AND DWARF 1 | GPI anchored protein | Controls osmotic adjustment and cell wall integrity | Li et al, |
| OsRRK1 | Rop-interesting receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase 1 | Unidentified | Causes adaxial rolling by controlling the size of bulliform cells | Ma et al, |
| RFS | Rolled Fine Striped | CHD3/Mi-2 | Regulates leaf polarity | Cho et al, |
| OSHB4 | HOMEODOMAIN CONTAINING PROTEIN 4 | HD-ZIP class III gene | Responsible for adaxial curling due to a decrease in number of bulliform cells | Zhang et al, |
| OsCHR4 | Chromatin remodeling factor 4 | CHD3 chromatin modeler | Encourages thin and curled leaf phenotype with thicker cuticular wax | Guo et al, |
| PSL1 | PHOTO-SENSITIVE LEAF ROLLING 1 | Cell wall-localized polygalacturonase | Enhances drought tolerance by modifying the cell wall and leaf rolling phenotype | Zhang et al, |
| SRL3 | SEMI-ROLLED LEAF 3 | Novel gene with unknown protein | Responsible for abnormal development of bulliform and sclerenchyma cells | Yu X Q et al, |
| ditl1 | Drought insensitive TILLING line 1 | Deletion of one nucleotide on LOC_Os05g48260 gene | Decreases water loss and leaf rolling by accumulating cuticular wax at epidermal cells | Choi et al, |
| OsMLP423 | Major latex protein 423 | Belongs to major latex protein family | Heightens drought tolerance by curling leaves | Zhou et al, |
Table 2. List of genes/transcription factors responsible for adaxial and abaxial leaf rolling in rice.
| Gene abbreviation | Gene full name | Transcription factor/ Gene regulator | Functional role in leaf rolling | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADL1 | ADAXIALIZED LEAF1 | Calpain-like cysteine protease | Involved in abaxial leaf rolling | Hibara et al, |
| SLL1 | SHALLOT-LIKE1 | MYB family transcriptional factor class SHAQKYF | Controls the growth of sclerenchyma cells | Zhang et al, |
| ACL1 | abaxially curled leaf 1 | Unidentified protein | Determines the development of leaves | Li et al, |
| NRL1 | NARROW AND ROLLED LEAF 1 | Cellulose synthase like protein D4 | Regulates cell formation | Hu et al, |
| CFL1 | CURLY FLAG LEAF1 | A homeodomain transcription factor class IV | Governs cuticle development | Wu et al, |
| ROC5 | Rice outermost cell-specific gene5 | A homeodomain leucine zipper class IV transcriptional factor | Regulates the formation of bulliform cells | Zou et al, |
| RL14 | Rolling-leaf14 | 2OG-Fe (II) oxygenase | Controls the secondary cell wall formation | Fang et al, |
| LC1 | LEAF INCLINATION1 | T-DNA insert in LOC_Os07g38664 | Directs cell division | Zhao et al, |
| OsZHD1 | zinc finger homeodomain 1 | ZF-HD transcription factor | Participates in abaxial rolling | Xu et al, |
| SLL2 | SHALLOT-LIKE2 | Unidentified plant-specific protein | Controls the size and shape of bulliform cell | Zhang et al, |
| REL1 | Rolled and Erect Leaf 1 | Unknown protein | Positive regulator of leaf rolling | Chen et al, |
| OsI-BAK1 | Brassinosteroid Insensitive 1-Associated Kinase 1 | Unknown | Involved in BR signaling pathway | Khew et al, |
| OsARF18 | AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR18 | Target of mirna160 | Involved in auxin signaling | Huang et al, |
| REL2 | Rolled and Erect Leaf 2 | An unknown protein containing DUF630 and DUF632 domains | Defines the leaf shape | Yang et al, |
| OsLBD3-7 | lateral organ boundary domain 3-7 | DUF260 domain protein | Serves as an activator of transcription | Pina et al, |
| CLD1/SRL1 | CURLED LEAF AND DWARF 1 | GPI anchored protein | Controls osmotic adjustment and cell wall integrity | Li et al, |
| OsRRK1 | Rop-interesting receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase 1 | Unidentified | Causes adaxial rolling by controlling the size of bulliform cells | Ma et al, |
| RFS | Rolled Fine Striped | CHD3/Mi-2 | Regulates leaf polarity | Cho et al, |
| OSHB4 | HOMEODOMAIN CONTAINING PROTEIN 4 | HD-ZIP class III gene | Responsible for adaxial curling due to a decrease in number of bulliform cells | Zhang et al, |
| OsCHR4 | Chromatin remodeling factor 4 | CHD3 chromatin modeler | Encourages thin and curled leaf phenotype with thicker cuticular wax | Guo et al, |
| PSL1 | PHOTO-SENSITIVE LEAF ROLLING 1 | Cell wall-localized polygalacturonase | Enhances drought tolerance by modifying the cell wall and leaf rolling phenotype | Zhang et al, |
| SRL3 | SEMI-ROLLED LEAF 3 | Novel gene with unknown protein | Responsible for abnormal development of bulliform and sclerenchyma cells | Yu X Q et al, |
| ditl1 | Drought insensitive TILLING line 1 | Deletion of one nucleotide on LOC_Os05g48260 gene | Decreases water loss and leaf rolling by accumulating cuticular wax at epidermal cells | Choi et al, |
| OsMLP423 | Major latex protein 423 | Belongs to major latex protein family | Heightens drought tolerance by curling leaves | Zhou et al, |
| [1] | Ahmad M S A, Javed F, Ashraf M. 2007. Iso-osmotic effect of NaCl and PEG on growth, cations and free proline accumulation in callus tissue of two indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. Plant Growth Regul, 53(1): 53-63. |
| [2] | Amal B A, Said M, Abdelaziz B, Mouhammed M, Nasser E N,Bouhmadi Keltoum E. 2020. Relationship between leaf rolling and some physiological parameters in durum wheat under water stress. Afr J Agric Res, 16(7): 1061-1068. |
| [3] | Anjum S A, Xie X Y, Wang L C, Saleem M F, Man C, Lei W. 2011. Morphological, physiological and biochemical responses of plants to drought stress. Afr J Agric Res, 6(9): 2026-2032. |
| [4] |
Baret F, Madec S, Irfan K, Lopez J, Comar A, Hemmerlé M, Dutartre D, Praud S, Tixier M H. 2018. Leaf-rolling in maize crops: From leaf scoring to canopy-level measurements for phenotyping. J Exp Bot, 69(10): 2705-2716.
PMID |
| [5] | Barik S R, Pandit E, Pradhan S K, Mohanty S P, Mohapatra T. 2019. Genetic mapping of morpho-physiological traits involved during reproductive stage drought tolerance in rice. PLoS One, 14(12): e0214979. |
| [6] | Bharteey P K, Singh Y V, Deka B, Dutta M. 2020. Assessment of water requirement for major crops of Mirzapur district in eastern Uttar Pradesh. Ann Plant Res Soil, 22(1): 100-106. |
| [7] | Bouman B A M, Lampayan R M, Tuong T P. 2007. Water Management in Irrigated Rice: Coping with Water Scarcity. Los Banos, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| [8] | Cal A J, Sanciangco M, Rebolledo M C, Luquet D, Torres R O, McNally K L, Henry A. 2019. Leaf morphology, rather than plant water status, underlies genetic variation of rice leaf rolling under drought. Plant Cell Environ, 42(5): 1532-1544. |
| [9] |
Canales C, Grigg S, Tsiantis M. 2005. The formation and patterning of leaves: Recent advances. Planta, 221(6): 752-756.
PMID |
| [10] | Chaves M M, Flexas J, Pinheiro C. 2009. Photosynthesis under drought and salt stress: Regulation mechanisms from whole plant to cell. Ann Bot, 103(4): 551-560. |
| [11] | Chen F, Aqeel M, Khalid N, Irshad M K, Farhat F, Nazir A, Ma J, Akhtar M S, Eldesoky G E, Aljuwayid A M, Noman A. 2023. Glutathione treatment suppresses the adverse effects of microplastics in rice. Chemosphere, 322: 138079. |
| [12] | Chen Q L, Xie Q J, Gao J, Wang W Y, Sun B, Liu B H, Zhu H T, Peng H F, Zhao H B, Liu C H, Wang J, Zhang J L, Zhang G Q, Zhang Z M. 2015. Characterization of Rolled and Erect Leaf 1 in regulating leave morphology in rice. J Exp Bot, 66(19): 6047-6058. |
| [13] | Cho S H, Lee C H, Gi E, Yim Y, Koh H J, Kang K, Paek N C. 2018. The rice rolled fine striped (RFS) CHD3/Mi-2 chromatin remodeling factor epigenetically regulates genes involved in oxidative stress responses during leaf development. Front Plant Sci, 9: 364. |
| [14] | Choi S Y, Lee Y J, Seo H U, Kim J H, Jang C S. 2022. Physio- biochemical and molecular characterization of a rice drought- insensitive TILLING line 1 (ditl1) mutant. Physiol Plant, 174(3): e13718. |
| [15] | Crang R, Lyons-Sobaski S, Wise R. 2018. Plant Anatomy: A Concept-Based Approach to the Structure of Seed Plants. Springer Nature Swetzerland AG: Springer: 181-213. |
| [16] | De Rybel B, Mähönen A P, Helariutta Y, Weijers D. 2016. Plant vascular development: From early specification to differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 17(1): 30-40. |
| [17] | Dharminder C, Singh R K, Kumar V, Devedee A K, Mruthyunjaya M, Reshu B. 2019. The clean water: The basic need of human and agriculture. Int J Chem Stud, 7(2): 1994-1998. |
| [18] | Fang J J, Guo T T, Xie Z W, Chun Y, Zhao J F, Peng L X, Zafar S A, Yuan S J, Xiao L T, Li X Y. 2021. The URL1-ROC5-TPL2 transcriptional repressor complex represses the ACL1 gene to modulate leaf rolling in rice. Plant Physiol, 185(4): 1722-1744. |
| [19] |
Fang L K, Zhao F M, Cong Y F, Sang X C, Du Q, Wang D Z, Li Y F, Ling Y H, Yang Z L, He G H. 2012. Rolling-leaf14 is a 2OG-Fe (II) oxygenase family protein that modulates rice leaf rolling by affecting secondary cell wall formation in leaves. Plant Biotechnol J, 10(5): 524-532.
PMID |
| [20] |
Fang Y J, Xiong L Z. 2015. General mechanisms of drought response and their application in drought resistance improvement in plants. Cell Mol Life Sci, 72(4): 673-689.
PMID |
| [21] | Farooq M, Wahid A, Kobayashi N, Fujita D, Basra S M A. 2009. Plant drought stress: Effects, mechanisms and management. Agron Sustain Dev, 29: 185-212. |
| [22] | Fischer T R, Byerlee D, Edmeades G O. 2009. Can technology deliver on the yield challenge to 2050? In: Conforti P. Looking Ahead in World Food and Agriculture: Perspectives to 2050 FAO: Agricultural Development Economics Division Economic and Social Development Department. |
| [23] |
Fujino K, Matsuda Y, Ozawa K, Nishimura T, Koshiba T, Fraaije M W, Sekiguchi H. 2008. NARROW LEAF 7 controls leaf shape mediated by auxin in rice. Mol Genet Genomics, 279(5): 499-507.
PMID |
| [24] | Guo T T, Wang D F, Fang J J, Zhao J F, Yuan S J, Xiao L T, Li X Y. 2019. Mutations in the rice OsCHR4 gene, encoding a CHD3 family chromatin remodeler, induce narrow and rolled leaves with increased cuticular wax. Int J Mol Sci, 20(10): 2567. |
| [25] |
Hellal F A, El-Shabrawi H M, Abd El-Hady M, Khatab I A, El-Sayed S A, Abdelly C. 2018. Influence of PEG induced drought stress on molecular and biochemical constituents and seedling growth of Egyptian barley cultivars. J Genet Eng Biotechnol, 16(1): 203-212.
PMID |
| [26] | Hibara K I, Obara M, Hayashida E, Abe M, Ishimaru T, Satoh H, Itoh J I, Nagato Y. 2009. The ADAXIALIZED LEAF1gene functions in leaf and embryonic pattern formation in rice. Dev Biol, 334(2): 345-354. |
| [27] |
Hsiao T C, O’Toole J C, Yambao E B, Turner N C. 1984. Influence of osmotic adjustment on leaf rolling and tissue death in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Physiol, 75(2): 338-341.
PMID |
| [28] | Hu J, Zhu L, Zeng D L, Gao Z Y, Guo L B, Fang Y X, Zhang G H, Dong G J, Yan M X, Liu J, Qian Q. 2010. Identification and characterization of NARROW AND ROLLED LEAF 1, a novel gene regulating leaf morphology and plant architecture in rice. Plant Mol Biol, 73(3): 283-292. |
| [29] |
Huang J, Li Z Y, Zhao D Z. 2016. Deregulation of the OsmiR160 target gene OsARF18 causes growth and developmental defects with an alteration of auxin signaling in rice. Sci Rep, 6: 29938.
PMID |
| [30] | Irshad M K, Ibrahim M, Noman A, Shang J Y, Mahmood A, Mubashir M, Khoo K S, Ng H S, Show P L. 2022. Elucidating the impact of goethite-modified biochar on arsenic mobility, bioaccumulation in paddy rice (Oryza sativa L.) along with soil enzyme activities. Process Saf Environ Prot, 160: 958-967. |
| [31] | Islam M M, Kayesh E, Zaman E, Urmi T A, Haque M M. 2018. Evaluation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes for drought tolerance at germination and early seedling stage. Agriculturists, 16(1): 44-54. |
| [32] | Itoh J I, Nonomura K I, Ikeda K, Yamaki S, Inukai Y, Yamagishi H, Kitano H, Nagato Y. 2005. Rice plant development: From zygote to spikelet. Plant Cell Physiol, 46(1): 23-47. |
| [33] |
Juarez M T, Twigg R W, Timmermans M C. 2004. Specification of adaxial cell fate during maize leaf development. Development, 131(18): 4533-4544.
PMID |
| [34] | Kadioglu A, Terzi R. 2007. A dehydration avoidance mechanism: Leaf rolling. Bot Rev, 73(4): 290-302. |
| [35] | Kadioglu A, Saruhan N, Sağlam A, Terzi R, Acet T. 2011. Exogenous salicylic acid alleviates effects of long term drought stress and delays leaf rolling by inducing antioxidant system. Plant Growth Regul, 64(1): 27-37. |
| [36] |
Kadioglu A, Terzi R, Saruhan N, Saglam A. 2012. Current advances in the investigation of leaf rolling caused by biotic and abiotic stress factors. Plant Sci, 182: 42-48.
PMID |
| [37] | Kahlown M A, Kemper W D. 2007. Factors affecting success and failure of trickle irrigation systems in Balochistan, Pakistan. Irrig Sci, 26(1): 71-79. |
| [38] | Khew C Y, Teo C J, Chan W S, Wong H L, Namasivayam P, Ho C L. 2015. Brassinosteroid insensitive 1-associated kinase 1 (OsI- BAK1) is associated with grain filling and leaf development in rice. J Plant Physiol, 182: 23-32. |
| [39] | Lafitte H R, Blum A, Atlin G. 2003. Using secondary traits to help identify drought-tolerant genotypes. In: Fischer K S, Lafitte R, Fukai S, Atlin G, Hardy B. Breeding Rice for Drought-Prone Environments, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute: 37-48. |
| [40] | Lang Y Z, Zhang Z J, Gu X Y, Yang J C, Zhu Q S. 2004. Physiological and ecological effects of crimpy leaf character in rice (Oryza sativa L.): II. Acta Agron Sin, 30(9): 883-887. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [41] | Li C, Zou X H, Zhang C Y, Shao Q H, Liu J, Liu B, Li H Y, Zhao T. 2016. OsLBD3-7 overexpression induced adaxially rolled leaves in rice. PLoS One, 11(6): e0156413. |
| [42] | Li L, Shi Z Y, Li L, Shen G Z, Wang X Q, An L S, Zhang J L. 2010. Overexpression of ACL1 (abaxially curled leaf 1) increased bulliform cells and induced abaxial curling of leaf blades in rice. Mol Plant, 3(5): 807-817. |
| [43] | Li M, Li X Z, Zhu L, Xue P B, Bao J L, Zhou B B, Jin J, Wang J. 2022. Genome-wide transcriptomic analysis reveals the gene regulatory network controlled by SRL1 in regulating rice leaf rolling. J Plant Growth Regul, 41(6): 2292-2304. |
| [44] | Li S X, Wang Z H, Malhi S S, Li S Q, Gao Y J, Tian X H. 2009. Chapter 7: Nutrient and water management effects on crop production, and nutrient and water use efficiency in dryland areas of China. Adv Agron, 102: 223-265. |
| [45] | Li W Q, Zhang M J, Gan P F, Qiao L, Yang S Q, Miao H, Wang G F, Zhang M M, Liu W T, Li H F, Shi C H, Chen K M. 2017. CLD1/SRL1 modulates leaf rolling by affecting cell wall formation, epidermis integrity and water homeostasis in rice. Plant J, 92(5): 904-923. |
| [46] |
Liu F, Wang P D, Zhang X B, Li X F, Yan X H, Fu D H, Wu G. 2018. The genetic and molecular basis of crop height based on a rice model. Planta, 247(1): 1-26.
PMID |
| [47] | Ma J, Aqeel M, Khalid N, Nazir A, Alzuaibr F M, Al-Mushhin A A M, Hakami O, Iqbal M F, Chen F, Alamri S, Hashem M, Noman A. 2022. Effects of microplastics on growth and metabolism of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Chemosphere, 307: 135749. |
| [48] | Ma Y H, Zhao Y, Shangguan X X, Shi S J, Zeng Y, Wu Y, Chen R Z, You A Q, Zhu L L, Du B, He G C. 2017. Overexpression of OsRRK1 changes leaf morphology and defense to insect in rice. Front Plant Sci, 8: 1783. |
| [49] | Maclean J L, Dawe D C, Hardy B, Hettel G P. 2002. Rice Almanac: Source Book for the Most Important Economic Activity on Earth. Wallingford: CABI. |
| [50] | Mahmood T, Abdullah M, Ahmar S, Yasir M, Iqbal M S, Yasir M, Ur Rehman S, Ahmed S, Rana R M, Ghafoor A, Nawaz Shah M K, Du X M, Mora-Poblete F. 2020. Incredible role of osmotic adjustment in grain yield sustainability under water scarcity conditions in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plants, 9(9): 1208. |
| [51] | Mangena P. 2018. Water stress: Morphological and anatomical changes in soybean (Glycine max L.) plants. In: Andjelkovic V. Plant, Abiotic Stress and Responses to Climate Change. IntechOpen: 9-31. |
| [52] | Matschi S, Vasquez M F, Bourgault R, Steinbach P, Chamness J, Kaczmar N, Gore M A, Molina I, Smith L G. 2020. Structure- function analysis of the maize bulliform cell cuticle and its potential role in dehydration and leaf rolling. Plant Direct, 4(10): e00282. |
| [53] |
Matsumoto H, Yasui Y, Kumamaru T, Hirano H Y. 2018. Characterization of a half-pipe-like leaf1 mutant that exhibits a curled leaf phenotype. Genes Genet Syst, 92(6): 287-291.
PMID |
| [54] | Matsumoto H, Yasui Y, Ohmori Y, Tanaka W, Ishikawa T, Numa H, Shirasawa K, Taniguchi Y, Tanaka J, Suzuki Y, Hirano H Y. 2020. CURLED LATER1 encoding the largest subunit of the Elongator complex has a unique role in leaf development and meristem function in rice. Plant J, 104(2): 351-364. |
| [55] | Nar H, Saglam A, Terzi R, Várkonyi Z, Kadioglu A. 2009. Leaf rolling and photosystem II efficiency in Ctenanthe setosa exposed to drought stress. Photosynthetica, 47(3): 429-436. |
| [56] | Nikolaeva M K, Maevskaya S N, Shugaev A G, Bukhov N G. 2010. Effect of drought on chlorophyll content and antioxidant enzyme activities in leaves of three wheat cultivars varying in productivity. Russ J Plant Physiol, 57(1): 87-95. |
| [57] |
Osakabe Y, Osakabe K, Shinozaki K, Tran L S P. 2014. Response of plants to water stress. Front Plant Sci, 5: 86.
PMID |
| [58] |
Pina A L C B, Zandavalli R B, Oliveira R S, Martins F R, Soares A A. 2016. Dew absorption by the leaf trichomes of Combretum leprosum in the Brazilian semiarid region. Funct Plant Biol, 43(9): 851-861.
PMID |
| [59] | Praharaj C S, Singh U, Singh S S, Singh N P, Shivay Y S. 2016. Supplementary and life-saving irrigation for enhancing pulses production, productivity and water-use efficiency in India. Ind J Agron, 61: S249-S261. |
| [60] | Rahaman M M, Shehab M K. 2018. Is the propensity of increasing the rice production a sustainable approach? Experiences from India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh. J Water Resour Eng Manag, 5(2): 12-28. |
| [61] | Rahman H, Ramanathan V, Nallathambi J, Duraialagaraja S, Muthurajan R. 2016. Over-expression of a NAC 67 transcription factor from finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.) confers tolerance against salinity and drought stress in rice. BMC Biotechnol, 16(Suppl 1): 35. |
| [62] | Rodriguez R E, Debernardi J M, Palatnik J F. 2014. Morphogenesis of simple leaves: Regulation of leaf size and shape. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol, 3(1): 41-57. |
| [63] |
Rontein D, Dieuaide-Noubhani M, Dufourc E J, Raymond P, Rolin D. 2002. The metabolic architecture of plant cells: Stability of central metabolism and flexibility of anabolic pathways during the growth cycle of tomato cells. J Biol Chem, 277(46): 43948-43960.
PMID |
| [64] |
Saijo Y, Hata S, Kyozuka J, Shimamoto K, Izui K. 2000. Over- expression of a single Ca2+-dependent protein kinase confers both cold and salt/drought tolerance on rice plants. Plant J, 23(3): 319-327.
PMID |
| [65] |
Sakurai N, Katayama Y, Yamaya T. 2001. Overlapping expression of cytosolic glutamine synthetase and phenylalanine ammonia- lyase in immature leaf blades of rice. Physiol Plant, 113(3): 400-408.
PMID |
| [66] | Salehi-Lisar S Y, Bakhshayeshan-Agdam H. 2016. Drought stress in plants:Causes, consequences, and tolerance. In: Hossain M A, Wani S H, Bhattacharjee S, Burritt D J, Tran L P. Drought Stress Tolerance in Plants:Vol. 1. Physiology and Biochemistry. Spring Nature Swetzerland AG: Springer Cham. |
| [67] | Sarkar S, Islam A K M A, Barma N C D, Ahmed J U. 2021. Tolerance mechanisms for breeding wheat against heat stress: A review. S Afr J Bot, 138: 262-277. |
| [68] | Seleiman M F, Al-Suhaibani N, Ali N, Akmal M, Alotaibi M, Refay Y, Dindaroglu T, Abdul-Wajid H H, Battaglia M L. 2021. Drought stress impacts on plants and different approaches to alleviate its adverse effects. Plants, 10(2): 259. |
| [69] | Singh B, Reddy K R, Diaz Redoña E, Walker T. 2017. Screening of rice cultivars for morpho-physiological responses to early- season soil moisture stress. Rice Sci, 24(6): 322-335. |
| [70] |
Singh S, Koyama H, Bhati K K, Alok A. 2021. The biotechnological importance of the plant-specific NAC transcription factor family in crop improvement. J Plant Res, 134: 475-495.
PMID |
| [71] | Subashri M, Robin S, Vinod K K, Rajeswari S, Mohanasundaram K, Raveendran T S. 2009. Trait identification and QTL validation for reproductive stage drought resistance in rice using selective genotyping of near flowering RILs. Euphytica, 166(2): 291-305. |
| [72] | Sun J, Cui X A, Teng S Z, Zhao K N, Wang Y W, Chen Z H, Sun X H, Wu J X, Ai P F, Quick W P, Lu T G, Zhang Z G. 2020. HD-ZIP IV gene Roc8 regulates the size of bulliform cells and lignin content in rice. Plant Biotechnol J, 18(12): 2559-2572. |
| [73] | Tee E E. 2020. Journey and destination: KORRIGAN1 subcellular localization dynamically changes during plant growth and stress tolerance. Plant Cell, 32(2): 291-292. |
| [74] | Ullah H, Santiago-Arenas R, Ferdous Z, Attia A, Datta A. 2019. Improving water use efficiency, nitrogen use efficiency, and radiation use efficiency in field crops under drought stress: A review. Adv Agron, 156: 109-157. |
| [75] | Upadhyaya A. 2019. Multi-objective fuzzy linear programming for land allocation under different crops in bhagwanpur distributary. J AgriSearch, 6(4): 188-193. |
| [76] |
Valliyodan B, Nguyen H T. 2006. Understanding regulatory networks and engineering for enhanced drought tolerance in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 9(2): 189-195.
PMID |
| [77] | Venuprasad R, Bool M E, Quiatchon L, Sta Cruz M T, Amante M, Atlin G N. 2012. A large-effect QTL for rice grain yield under upland drought stress on chromosome 1. Mol Breed, 30(1): 535-547. |
| [78] | Wang L, Xu J, Nian J Q, Shen N W, Lai K K, Hu J, Zeng D L, Ge C W, Fang Y X, Zhu L, Qian Q, Zhang G H. 2016. Characterization and fine mapping of the rice gene OsARVL4 regulating leaf morphology and leaf vein development. Plant Growth Regul, 78(3): 345-356. |
| [79] | Wu R H, Li S B, He S, Wassmann F, Yu C H, Qin G J, Schreiber L, Qu L J, Gu H Y. 2011. CFL1, a WW domain protein, regulates cuticle development by modulating the function of HDG1, a class IV homeodomain transcription factor, in rice and Arabidopsis Plant Cell, 23(9): 3392-3411. |
| [80] | Xiang J J, Zhang G H, Qian Q, Xue H W. 2012. SEMI-ROLLED LEAF1 encodes a putative glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein and modulates rice leaf rolling by regulating the formation of bulliform cells. Plant Physiol, 159(4): 1488-1500. |
| [81] |
Xu P Z, Ali A, Han B L, Wu X J. 2018. Current advances in molecular basis and mechanisms regulating leaf morphology in rice. Front Plant Sci, 9: 1528.
PMID |
| [82] | Xu Y, Wang Y H, Long Q Z, Huang J X, Wang Y L, Zhou K N, Zheng M, Sun J, Chen H, Chen S H, Jiang L, Wang C M, Wan J M. 2014. Overexpression of OsZHD1, a zinc finger homeodomain class homeobox transcription factor, induces abaxially curled and drooping leaf in rice. Planta, 239(4): 803-816. |
| [83] |
Xu Y, Kong W Y, Wang F Q, Wang J, Tao Y J, Li W Q, Chen Z H, Fan F J, Jiang Y J, Zhu Q H, Yang J. 2021. Heterodimer formed by ROC8 and ROC5 modulates leaf rolling in rice. Plant Biotechnol J, 19(12): 2662-2672.
PMID |
| [84] |
Xue D W, Zhang X Q, Lu X L, Chen G, Chen Z H. 2017. Molecular and evolutionary mechanisms of cuticular wax for plant drought tolerance. Front Plant Sci, 8: 621.
PMID |
| [85] | Yang S Q, Li W Q, Miao H, Gan P F, Qiao L, Chang Y L, Shi C H, Chen K M. 2016. REL2, a gene encoding an unknown function protein which contains DUF630 and DUF632 domains controls leaf rolling in rice. Rice, 9(1): 37. |
| [86] |
Young T E, Meeley R B, Gallie D R. 2004. ACC synthase expression regulates leaf performance and drought tolerance in maize. Plant J, 40(5): 813-825.
PMID |
| [87] | Yu N, Liang Y P, Wang Q P, Peng X X, He Z H, Hou X W. 2022. Transcriptomic analysis of OsRUS1 overexpression rice lines with rapid and dynamic leaf rolling morphology. Sci Rep, 12(1): 6736. |
| [88] |
Yu S, Tian L. 2018. Breeding major cereal grains through the lens of nutrition sensitivity. Mol Plant, 11(1): 23-30.
PMID |
| [89] | Yu X Q, Xie W, Liu H, Liu W, Zeng D L, Qian Q, Ren D Y. 2022. Characterization and fine mapping of a semi-rolled leaf mutant srl3 in rice. J Integr Agric, 21(11): 3103-3113. |
| [90] | Yuan S, Li Y, Peng S B. 2015. Leaf lateral asymmetry in morphological and physiological traits of rice plant. PLoS One, 10(6): e0129832. |
| [91] | Zhang G H, Xu Q, Zhu X D, Qian Q, Xue H W. 2009. SHALLOT- LIKE1 is a KANADI transcription factor that modulates rice leaf rolling by regulating leaf abaxial cell development. Plant Cell, 21(3): 719-735. |
| [92] | Zhang G H, Hou X, Wang L, Xu J, Chen J, Fu X, Shen N W, Nian J Q, Jiang Z Z, Hu J, Zhu L, Rao Y C, Shi Y F, Ren D Y, Dong G J, Gao Z Y, Guo L B, Qian Q, Luan S. 2021. PHOTO- SENSITIVE LEAF ROLLING 1encodes a polygalacturonase that modifies cell wall structure and drought tolerance in rice. New Phytol, 229(2): 890-901. |
| [93] | Zhang J J, Wu S Y, Jiang L, Wang J L, Zhang X, Guo X P, Wu C Y, Wan J M. 2015. A detailed analysis of the leaf rolling mutant sll2 reveals complex nature in regulation of bulliform cell development in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Biol, 17(2): 437-448. |
| [94] |
Zhang J S, Zhang H, Srivastava A K, Pan Y J, Bai J J, Fang J J, Shi H Z, Zhu J K. 2018. Knockdown of rice microRNA166 confers drought resistance by causing leaf rolling and altering stem xylem development. Plant Physiol, 176(3): 2082-2094.
PMID |
| [95] |
Zhang T P, Li C Y, Li D X, Liu Y, Yang X H. 2020. Roles of YABBY transcription factors in the modulation of morphogenesis, development, and phytohormone and stress responses in plants. J Plant Res, 133(6): 751-763.
PMID |
| [96] | Zhao S Q, Xiang J J, Xue H W. 2013. Studies on the rice LEAF INCLINATION1 (LC1), an IAA-amido synthetase, reveal the effects of auxin in leaf inclination control. Mol Plant, 6(1): 174-187. |
| [97] | Zhao S S, Zhao L, Liu F X, Wu Y Z, Zhu Z F, Sun C Q, Tan L B. 2016. NARROW AND ROLLED LEAF 2 regulates leaf shape, male fertility, and seed size in rice. J Integr Plant Biol, 58(12): 983-996. |
| [98] | Zhou L G, Liu Z C, Liu Y H, Kong D Y, Li T F, Yu S W, Mei H W, Xu X Y, Liu H Y, Chen L, Luo L J. 2016. A novel gene OsAHL1 improves both drought avoidance and drought tolerance in rice. Sci Rep, 6(1): 30264. |
| [99] | Zhou Z M, Fan J B, Zhang J, Yang Y M, Zhang Y F, Zan X F, Li X H, Wan J L, Gao X L, Chen R J, Huang Z J, Xu Z J, Li L H. 2022. OsMLP423 is a positive regulator of tolerance to drought and salt stresses in rice. Plants, 11(13): 1653. |
| [100] | Zoghi Z, Hosseini S M, Kouchaksaraei M T, Kooch Y, Guidi L. 2019. The effect of biochar amendment on the growth, morphology and physiology of Quercus castaneifolia seedlings under water- deficit stress. Eur J Forest Res, 138(6): 967-979. |
| [101] | Zou L P, Sun X H, Zhang Z G, Liu P, Wu J X, Tian C J, Qiu J L, Lu T G. 2011. Leaf rolling controlled by the homeodomain leucine zipper class IV gene Roc5 in rice. Plant Physiol, 156(3): 1589-1602. |
| [102] | Zou L P, Zhang Z G, Qi D F, Peng M, Lu T G. 2014. Cytological mechanisms of leaf rolling in rice. Crop Sci, 54(1): 198-209. |
| [103] | Zu X F, Lu Y K, Wang Q Q, Chu P F, Miao W, Wang H Q, La H G. 2017. A new method for evaluating the drought tolerance of upland rice cultivars. Crop J, 5(6): 488-498. |
| [1] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [2] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [3] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [4] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [5] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [6] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [7] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [8] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [9] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [10] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [11] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [12] | Monica Ruffini Castiglione, Stefania Bottega, Carlo Sorce, Carmelina SpanÒ. Effects of Zinc Oxide Particles with Different Sizes on Root Development in Oryza sativa [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 449-458. |
| [13] | Liu Qiao, Qiu Linlin, Hua Yangguang, Li Jing, Pang Bo, Zhai Yufeng, Wang Dekai. LHD3 Encoding a J-Domain Protein Controls Heading Date in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 437-448. |
| [14] | Lu Xuedan, Li Fan, Xiao Yunhua, Wang Feng, Zhang Guilian, Deng Huabing, Tang Wenbang. Grain Shape Genes: Shaping the Future of Rice Breeding [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 379-404. |
| [15] | Zhang Guomei, Li Han, Liu Shanshan, Zhou Xuming, Lu Mingyang, Tang Liang, Sun Lihua. Water Extract of Rice False Smut Balls Activates Nrf2/HO-1 and Apoptosis Pathways, Causing Liver Injury [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 473-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||