
Rice Science ›› 2024, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 62-76.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2023.10.002
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Gao Ningning1,2,#, Ye Shuifeng3,#, Zhang Yu2,4, Zhou Liguo2, Ma Xiaosong2, Yu Hanxi1,2, Li Tianfei2, Han Jing2, Liu Zaochang1,2( ), Luo Lijun1,2(
), Luo Lijun1,2( )
)
Received:2023-06-12
Accepted:2023-10-10
Online:2024-01-28
Published:2024-02-06
Contact:
Luo Lijun (About author:First author contact:#These authors contributed equally to this work
Gao Ningning, Ye Shuifeng, Zhang Yu, Zhou Liguo, Ma Xiaosong, Yu Hanxi, Li Tianfei, Han Jing, Liu Zaochang, Luo Lijun. A β-Carotene Ketolase Gene NfcrtO from Subaerial Cyanobacteria Confers Drought Tolerance in Rice[J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(1): 62-76.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
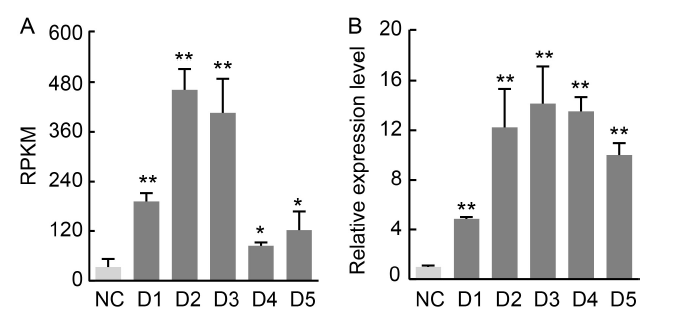
Fig. 1. Transcriptome and NfcrtO expression profile analyses of Nostoc flagelliforme under drought stress. A, Reads per kilobase per million mapped reads (RPKM) data of NfcrtO from a transcriptome analysis of N. flagelliforme under drought stress. B, Expression profile analysis of NfcrtO under drought stress. NC, Normal conditions; D1-D5, RNA sequencing of N. flagelliforme under water loss levels of 10%, 30%, 50%, 70%, and 90%. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, by the Student’s t-test.
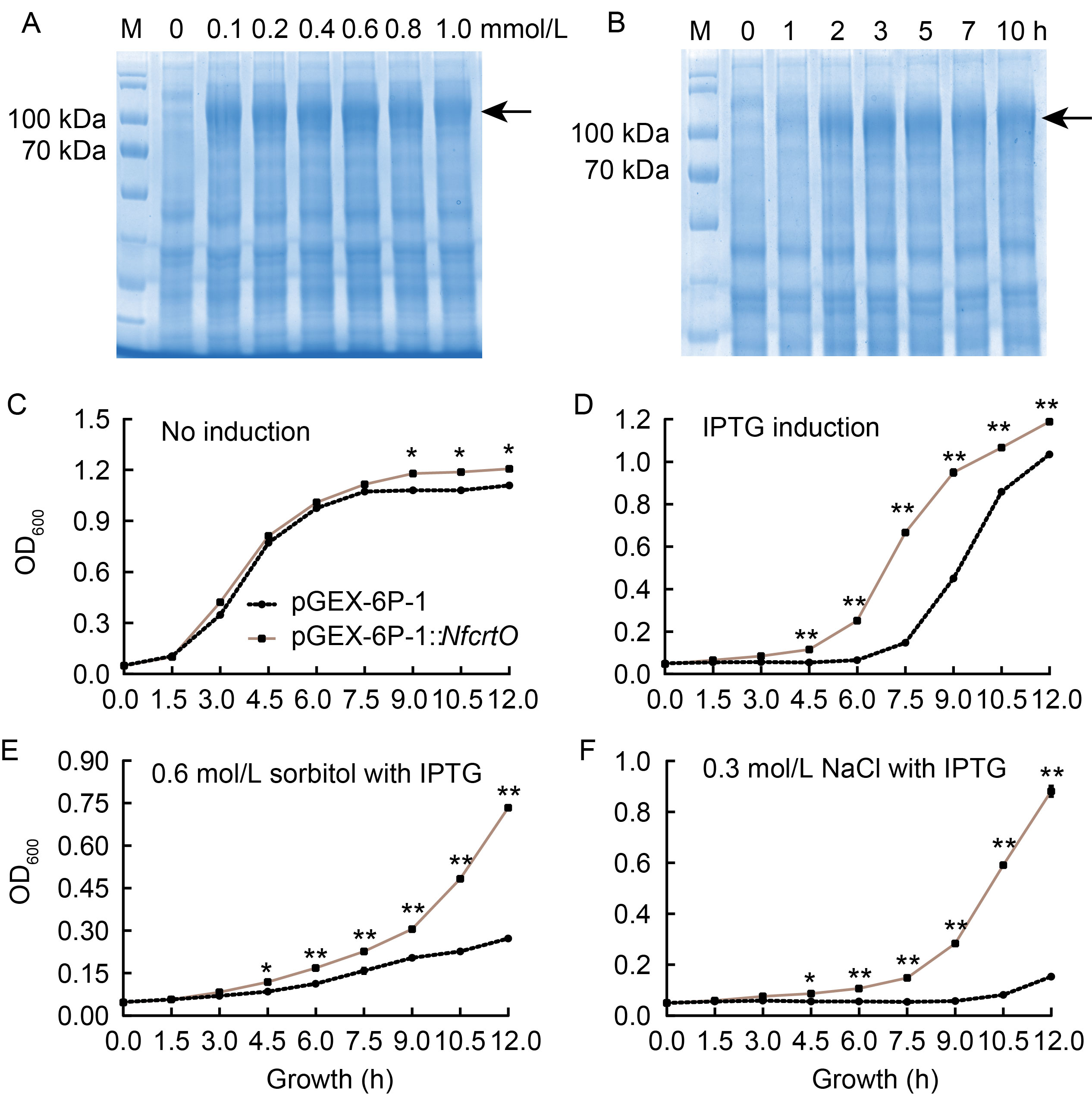
Fig. 2. Heterologous expression of NfcrtO in Escherichia coli. A and B, Protein expression of NfcrtO under different concentrations (A) and times (B) of isopropyl- β-d-1-thiogalactopyranosid (IPTG) induction. Arrow indicates expressed NfcrtO. C-F, Growth charts of NfcrtO-expressing E. coli under normal conditions (C), 0.4 mmol/L IPTG induction (D), 0.6 mol/L sorbitol treatment and 0.4 mmol/L IPTG induction (E), and 0.3 mol/L NaCl treatment and 0.4 mmol/L IPTG induction (F). Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, by the Student’s t-test.
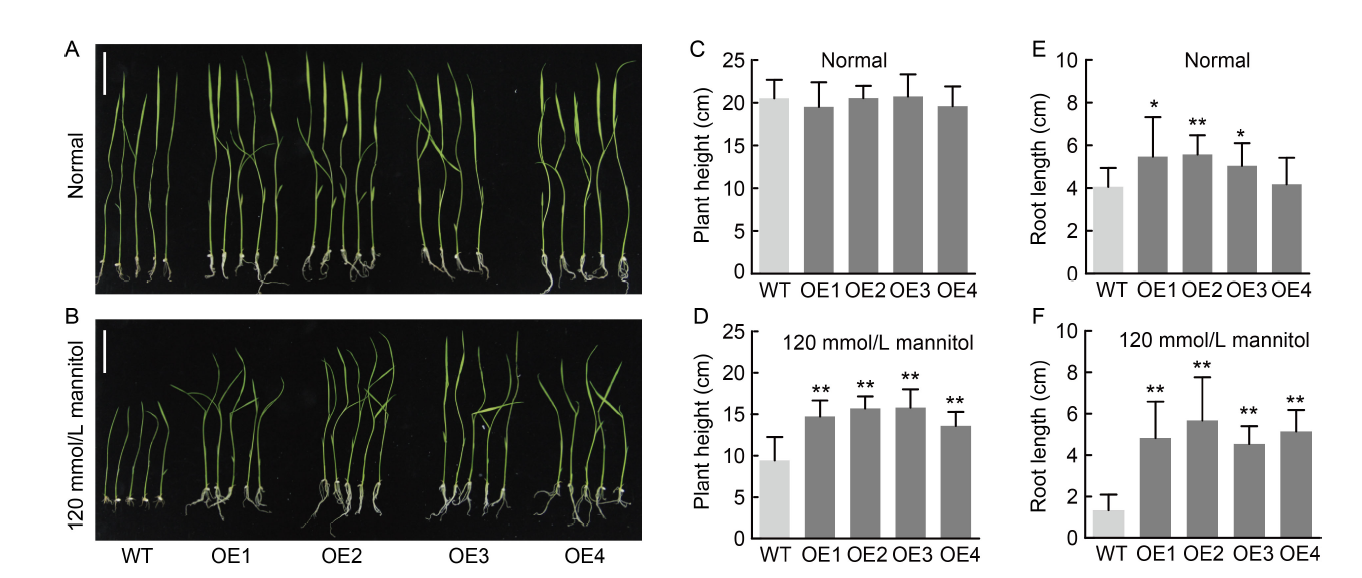
Fig. 3. NfcrtO-overexpressing rice seedlings on ½ Murashige and Skoog (MS) solid medium under mannitol treatment. A and B, Phenotypes of NfcrtO-overexpression (OE1-OE4) and wild type (WT) lines under normal (A) and 120 mmol/L mannitol (B) treatments on ½ MS solid medium. Scale bars, 5 cm. C and D, Seedling plant heights of NfcrtO-overexpression and WT lines under normal (C) and 120 mmol/L mannitol (D) treatments on ½ MS solid medium. E and F, Seedling root lengths of NfcrtO-overexpression and WT lines under normal (E) and 120 mmol/L mannitol (F) treatments on ½ MS solid medium. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, by the Student’s t-test.
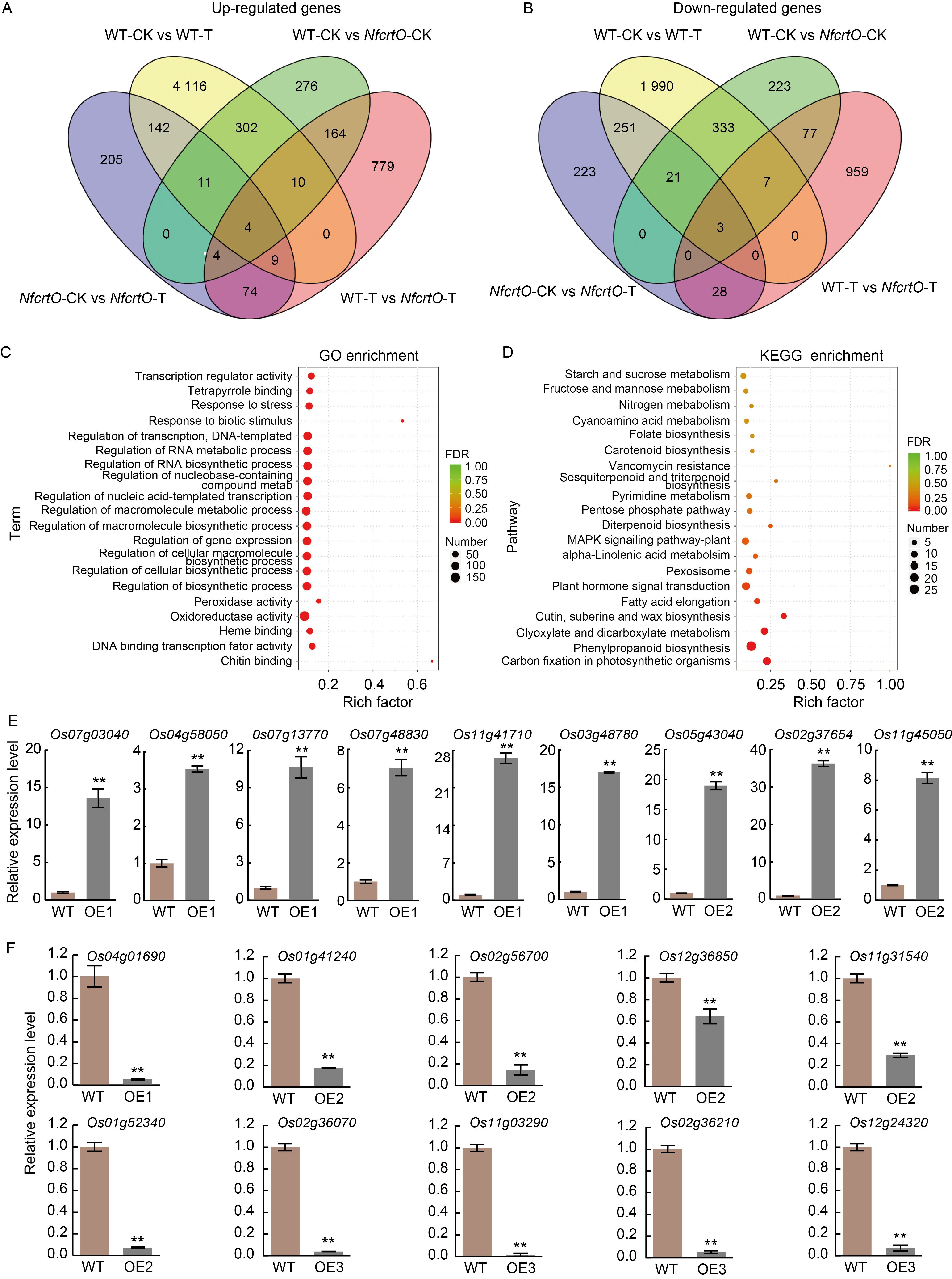
Fig. 4. RNA-sequencing of NfcrtO-overexpression seedlings in rice on ½ Murashige and Skoog (MS) solid medium under mannitol stress. A and B, Up-regulated (A) and down-regulated (B) genes as determined by comparative transcriptome analysis between the wild type (WT) and overexpression (NfcrtO) lines. WT-CK, NfcrtO-CK, WT-T, and NfcrtO-T represent WT and overexpression lines under normal conditions (CK) and mannitol stress treatment (T), respectively. C, Enriched Gene Ontology (GO) terms in the comparative transcriptome analysis between the WT and NfcrtO-overexpression lines. FDR, False discovery rate. D, Enriched Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways in the comparative transcriptome analysis between the WT and NfcrtO- overexpression lines. E and F, Validation by qRT-PCR of up-regulated (E) and down-regulated (F) genes. Leaves of rice seedlings on ½ MS culture flasks with and without 120 mmol/L mannitol for 7 d were sampled for transcriptome sequencing analysis. RNA was used for qRT-PCR, and Actin gene was used as the reference gene to normalize the target gene expression. OE1, OE2, and OE3 represent NfcrtO-overexpression lines. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). **, P < 0.01, by the Student’s t-test.
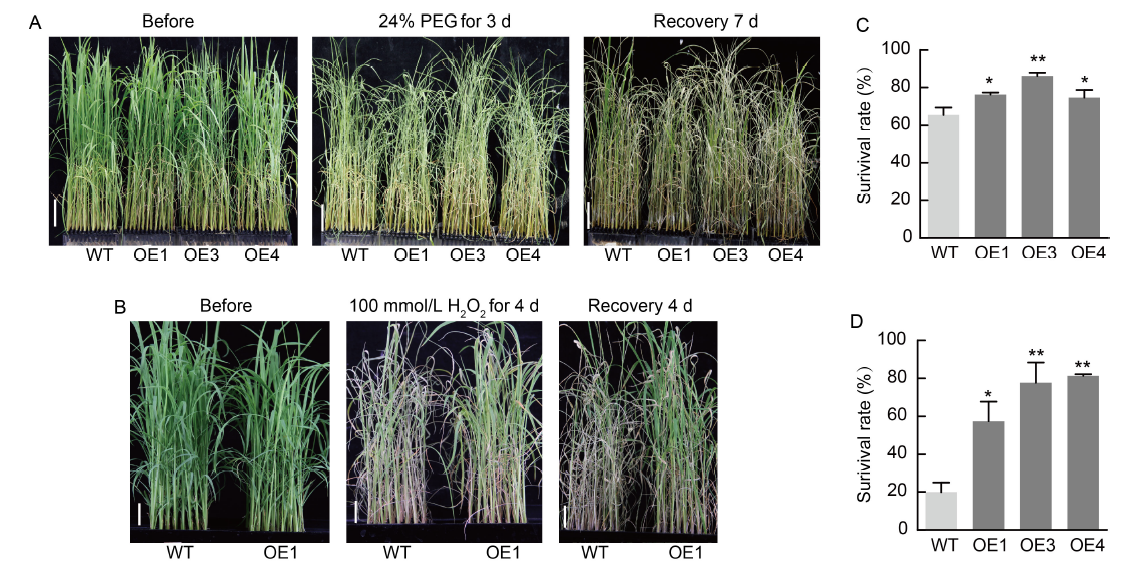

Fig. 5. NfcrtO-overexpression lines of rice under polyethylene glycol (PEG) and H2O2 stresses. A and B, Phenotypes of rice NfcrtO-overexpression (OE1, OE3, and OE4) and wild type (WT) lines under 24% PEG (A) and 100 mmol/L H2O2 (B) treatments. Scale bars, 5 cm. C and D, Survival rates of NfcrtO-overexpression and WT lines under 24% PEG (C) and 100 mmol/L H2O2 (D) treatments. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, by the Student’s t-test.
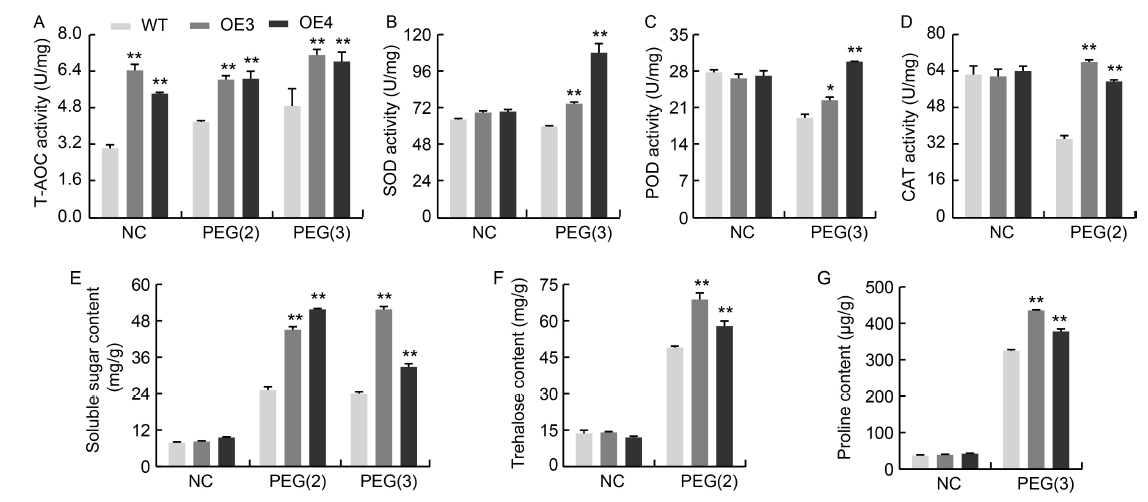
Fig. 6. Physiological indices of NfcrtO-overexpression lines of rice under 20% polyethylene glycol (PEG) treatment. A, Total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) activity. B, Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. C, Peroxidase (POD) activity. D, Catalase (CAT) activity. E, Soluble sugar content. F, Trehalose content. G, Proline content. NC, Normal conditions; PEG(2) and PEG(3), PEG osmotic stress for 2 and 3 d, respectively; WT, Wild type; OE3 and OE4, NfcrtO-overexpression lines. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, by the Student’s t-test.
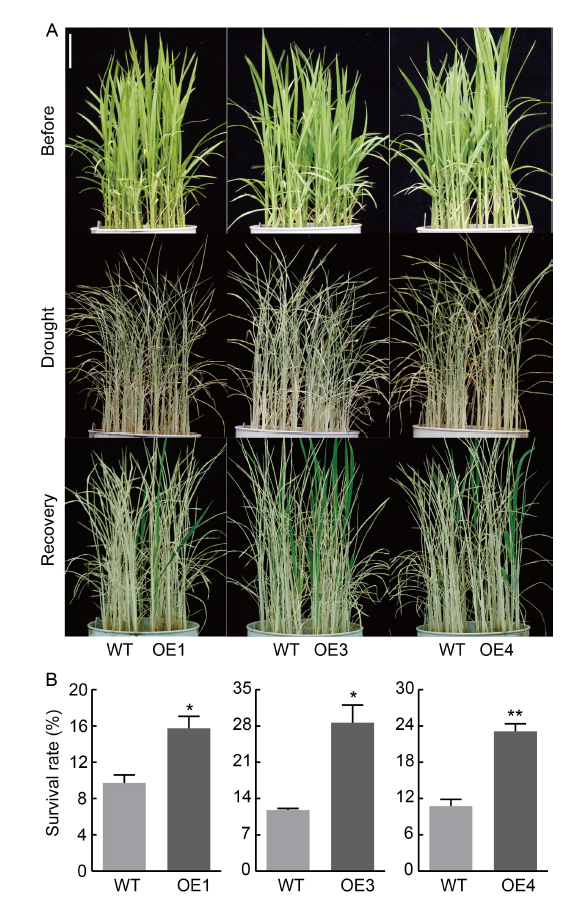
Fig. 7. Rice seedlings of NfcrtO-overexpression lines at the seedling stage in soil under drought treatment. A, Phenotypes of NfcrtO-overexpression rice seedlings (OE1, OE3, and OE4) in soil under drought stress. Scale bar, 5 cm. B, Survival rates of NfcrtO-overexpression rice seedlings under drought stress. WT, Wild type. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, by the Student’s t-test.
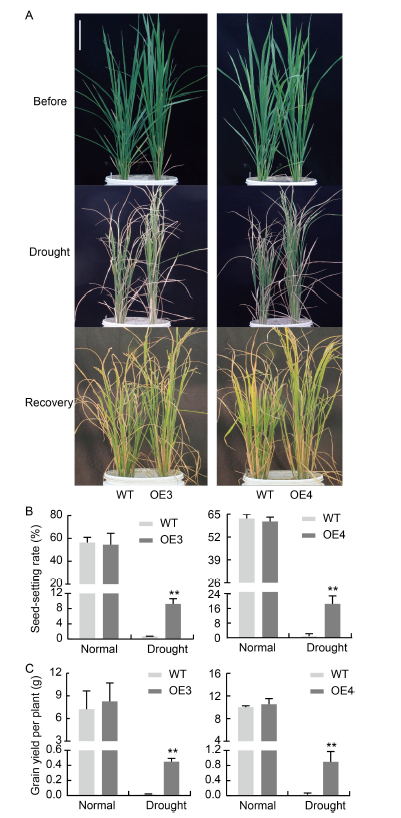
Fig. 8. NfcrtO-overexpression lines of rice at the booting stage under drought treatment. A, Phenotypes of NfcrtO-overexpression lines (OE3 and OE4) at the booting stage under drought treatment. Scale bar, 20 cm. B, Seed-setting rate of NfcrtO-overexpression lines. C, Grain yield per plant of NfcrtO-overexpression lines. WT, Wild type. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). **, P < 0.01, by the Student’s t-test.
| [1] | Ai Y F, Yang Y W, Gao X, Qiu B S. 2014a. Heterologous expression of three stress-responsive genes from Nostoc flagelliforme confers tolerance to abiotic stresses in Escherichia coli. J Appl Phycol, 26: 123-129. |
| [2] | Ai Y F, Yang Y W, Qiu B S, Gao X. 2014b. Unique WSPA protein from terrestrial macroscopic cyanobacteria can confer resistance to osmotic stress in transgenic plants. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 30(9): 2361-2369. |
| [3] | Arnon D I. 1949. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol, 24(1): 1-15. |
| [4] | Bar Eyal L, Ranjbar Choubeh R, Cohen E, Eisenberg I, Tamburu C, Dorogi M, Ünnep R, Appavou M S, Nevo R, Raviv U, Reich Z, Garab G, van Amerongen H, Paltiel Y, Keren N. 2017. Changes in aggregation states of light-harvesting complexes as a mechanism for modulating energy transfer in desert crust cyanobacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 114(35): 9481-9486. |
| [5] | Chen L J, Wuriyanghan H, Zhang Y Q, Duan K X, Chen H W, Li Q T, Lu X, He S J, Ma B, Zhang W K, Lin Q, Chen S Y, Zhang J S. 2013. An S-domain receptor-like kinase, OsSIK2, confers abiotic stress tolerance and delays dark-induced leaf senescence in rice. Plant Physiol, 163(4): 1752-1765. |
| [6] | Chen M Y, Teng W K, Zhao L, Hu C X, Zhou Y K, Han B P, Song L R, Shu W S. 2021. Comparative genomics reveals insights into cyanobacterial evolution and habitat adaptation. ISME J, 15(1): 211-227. |
| [7] | Chen S J, Xu K, Kong D Y, Wu L Y, Chen Q, Ma X S, Ma S Q, Li T F, Xie Q, Liu H Y, Luo L J. 2022. Ubiquitin ligase OsRINGzf1 regulates drought resistance by controlling the turnover of OsPIP2;1. Plant Biotechnol J, 20(9): 1743-1755. |
| [8] | Cui L J, Xu H Y, Zhu Z X, Gao X. 2017. The effects of the exopolysaccharide and growth rate on the morphogenesis of the terrestrial filamentous Cyanobacterium Nostoc flagelliforme. Biol Open, 6(9): 1329-1335. |
| [9] | Cui L J, Liu Y H, Yang Y W, Ye S F, Luo H Y, Qiu B S, Gao X. 2018. The drnf1 gene from the drought-adapted Cyanobacterium Nostoc flagelliforme improved salt tolerance in transgenic Synechocystis and Arabidopsis plant. Genes, 9(9): 441. |
| [10] | Dong J F, Zhou L, Feng A Q, Zhang S H, Fu H, Chen L, Zhao J L, Yang T F, Yang W, Ma Y M, Wang J, Zhu X Y, Liu Q, Liu B. 2021. The OsOXO2, OsOXO3 and OsOXO4 positively regulate panicle blast resistance in rice. Rice, 14(1): 51. |
| [11] | Fernández-González B, Sandmann G, Vioque A. 1997. A new type of asymmetrically acting β-carotene ketolase is required for the synthesis of echinenone in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. J Biol Chem, 272(15): 9728-9733. |
| [12] | Gao K S. 1998. Chinese studies on the edible blue-green Alga, Nostoc flagelliforme: A review. J Appl Phycol, 10(1): 37-49. |
| [13] | Gao X. 2017. Scytonemin plays a potential role in stabilizing the exopolysaccharidic matrix in terrestrial cyanobacteria. Microb Ecol, 73(2): 255-258. |
| [14] | Gao X, Xu H Y, Ye S F, Liang W Y. 2016. A proposal on the restoration of Nostoc flagelliforme for sustainable improvement in the ecology of arid steppes in China. Environments, 3(2): 14. |
| [15] | Gao X, Liu B, Ji B Y. 2019. Profiling of small molecular metabolites in Nostoc flagelliforme during periodic desiccation. Mar Drugs, 17(5): 298. |
| [16] | Gao X, Xu H Y, Zhu Z X, She Y, Ye S F. 2020. Improved production of echinenone and canthaxanthin in transgenic Nostoc sp. PCC 7120 overexpressing a heterologous crtO gene from Nostoc flagelliforme. Microbiol Res, 236: 126455. |
| [17] | Gao X, Zhu Z X, Xu H Y, Liu L T, An J, Ji B Y, Ye S F. 2021. Cold adaptation in drylands: Transcriptomic insights into cold-stressed Nostoc flagelliforme and characterization of a hypothetical gene with cold and nitrogen stress tolerance. Environ Microbiol, 23(2): 713-727. |
| [18] | Gong M Y, Bassi A. 2016. Carotenoids from microalgae: A review of recent developments. Biotechnol Adv, 34(8): 1396-1412. |
| [19] | Gong Z Z, Xiong L M, Shi H Z, Yang S H, Herrera-Estrella L R, Xu G H, Chao D Y, Li J R, Wang P Y, Qin F, Li J J, Ding Y L, Shi Y T, Wang Y, Yang Y Q, Guo Y, Zhu J K. 2020. Plant abiotic stress response and nutrient use efficiency. Sci China Life Sci, 63(5): 635-674. |
| [20] | Graus D, Konrad K R, Bemm F, Patir Nebioglu M G, Lorey C, Duscha K, Güthoff T, Herrmann J, Ferjani A, Cuin T A, Roelfsema M R G, Schumacher K, Neuhaus H E, Marten I, Hedrich R. 2018. High V-PPase activity is beneficial under high salt loads, but detrimental without salinity. New Phytol, 219(4): 1421-1432. |
| [21] | Hagemann M. 2011. Molecular biology of cyanobacterial salt acclimation. FEMS Microbiol Rev, 35(1): 87-123. |
| [22] | Hu H H, Dai M Q, Yao J L, Xiao B Z, Li X H, Zhang Q F, Xiong L Z. 2006. Overexpressing a NAM, ATAF, and CUC (NAC) transcription factor enhances drought resistance and salt tolerance in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103(35): 12987-12992. |
| [23] | Karmakar S, Ali Molla K, Chanda P K, Sarkar S N, Datta S K, Datta K. 2016. Green tissue-specific co-expression of chitinase and oxalate oxidase 4 genes in rice for enhanced resistance against sheath blight. Planta, 243(1): 115-130. |
| [24] | Latif A, Sun Y, Pu C X, Ali N. 2023. Rice curled its leaves either adaxially or abaxially to combat drought stress. Rice Sci, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [25] | Li X X, Ding M M, Wang M, Yang S J, Ma X R, Hu J H, Song F, Wang L X, Liang W Y. 2022. Proteome profiling reveals changes in energy metabolism, transport and antioxidation during drought stress in Nostoc flagelliforme. BMC Plant Biol, 22(1): 162. |
| [26] | Liang W Y, Zhou Y W, Wang L X, You X R, Zhang Y P, Cheng C L, Chen W. 2012. Ultrastructural, physiological and proteomic analysis of Nostoc flagelliforme in response to dehydration and rehydration. J Proteomics, 75(18): 5604-5627. |
| [27] | Liu W, Cui L J, Xu H Y, Zhu Z X, Gao X. 2017. Flexibility-rigidity coordination of the dense exopolysaccharide matrix in terrestrial cyanobacteria acclimated to periodic desiccation. Appl Environ Microbiol, 83(22): e01619-17. |
| [28] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT Method. Methods, 25(4): 402-408. |
| [29] | Llewellyn C A, Airs R L, Farnham G, Greig C. 2020. Synthesis, regulation and degradation of carotenoids under low level UV-B radiation in the filamentous cyanobacterium Chlorogloeopsis fritschii PCC 6912. Front Microbiol, 11: 163. |
| [30] | Luo L J. 2010. Breeding for water-saving and drought-resistance rice (WDR) in China. J Exp Bot, 61(13): 3509-3517. |
| [31] | Luo L J, Mei H W, Yu X Q, Xia H, Chen L, Liu H Y, Zhang A N, Xu K, Wei H B, Liu G L, Wang F M, Liu Y, Ma X S, Lou Q J, Feng F J, Zhou L G, Chen S J, Yan M, Liu Z C, Bi J G, Li T F, Li M S. 2019. Water-saving and drought-resistance rice: From the concept to practice and theory. Mol Breed, 39: 145. |
| [32] | Peng Z, Huwanixi A, Wan C H. 2023. Identification of novel smORFs and microprotein acting in response to rehydration of Nostoc flagelliforme. Proteomics, 23(12): e2200473. |
| [33] | Sand-Jensen K. 2014. Ecophysiology of gelatinous Nostoc colonies: Unprecedented slow growth and survival in resource-poor and harsh environments. Ann Bot, 114(1): 17-33. |
| [34] | Scherer S, Ernst A, Chen T W, Böger P. 1984. Rewetting of drought-resistant blue-green algae: Time course of water uptake and reappearance of respiration, photosynthesis, and nitrogen fixation. Oecologia, 62(3): 418-423. |
| [35] | Shang J L, Chen M, Hou S W, Li T, Yang Y W, Li Q, Jiang H B, Dai G Z, Zhang Z C, Hess W R, Qiu B S. 2019. Genomic and transcriptomic insights into the survival of the subaerial cyanobacterium Nostoc flagelliforme in arid and exposed habitats. Environ Microbiol, 21(2): 845-863. |
| [36] | Sinha R P, Klisch M, Walter Helbling E, Häder D P. 2001. Induction of mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) in cyanobacteria by solar ultraviolet-B radiation. J Photochem Photobiol B, 60(2/3): 129-135. |
| [37] | Sun Z T, Shen S C, Tian B, Wang H, Xu Z J, Wang L Y, Hua Y J. 2009. Functional analysis of γ-carotene ketolase involved in the carotenoid biosynthesis of Deinococcus radiodurans. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 301(1): 21-27. |
| [38] | Takenaka H, Yamaguchi Y, Sakaki S, Watarai K, Tanaka N, Hori M, Seki H, Tsuchida M, Yamada A, Nishimori T, Morinaga T. 1998. Safety evaluation of Nostoc flagelliforme (Nostocales, Cyanophyceae) as a potential food. Food Chem Toxicol, 36(12): 1073-1077. |
| [39] | Tamadaddi C, Sagar V, Verma A K, Afsal F, Sahi C. 2021. Expansion of the evolutionarily conserved network of J-domain proteins in the Arabidopsis mitochondrial import complex. Plant Mol Biol, 105(4/5): 385-403. |
| [40] | Tamadaddi C, Verma A K, Zambare V, Vairagkar A, Diwan D, Sahi C. 2022. J-like protein family of Arabidopsis thaliana: The enigmatic cousins of J-domain proteins. Plant Cell Rep, 41(6): 1343-1355. |
| [41] | Wada N, Sakamoto T, Matsugo S. 2013. Multiple roles of photosynthetic and sunscreen pigments in cyanobacteria focusing on the oxidative stress. Metabolites, 3(2): 463-483. |
| [42] | Wang B, Yang L, Zhang Y Q, Chen S L, Gao X, Wan C H. 2019. Investigation of the dynamical expression of Nostoc flagelliforme proteome in response to rehydration. J Proteomics, 192: 160-168. |
| [43] | Wang L K, Feng Z X, Wang X, Wang X W, Zhang X G. 2010. DEGseq: An R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics, 26(1): 136-138. |
| [44] | Wang L X, Lei X T, Yang J, Wang S P, Liu Y, Liang W Y. 2018. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals that photosynthesis contributes to drought tolerance of Nostoc flagelliforme (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria). Phycologia, 57(1): 113-120. |
| [45] | Wang L X, Wang S P, Li X X, Wang M, Zhang Z, Shi J, Xu T T, Liang W Y. 2020. Overexpression of cphA gene from Nostoc flagelliforme improves the drought tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana. S Afr J Bot, 132: 127-131. |
| [46] | Wang L X, Li X X, Wang M, Ma X R, Song F, Hu J H, Liang W L, Liang W Y. 2022. Carbon metabolism and the ROS scavenging system participate in Nostoc flagelliforme’s adaptive response to dehydration conditions through protein acetylation. J Proteome Res, 21(2): 482-493. |
| [47] | Wang M, Zhu Q, Li X X, Hu J H, Song F, Liang W L, Ma X R, Wang L X, Liang W Y. 2022. Effect of drought stress on degradation and remodeling of membrane lipids in Nostoc flagelliforme. Foods, 11(12): 1798. |
| [48] | Wu S J, Yu K Q, Li L, Wang L X, Liang W Y. 2021. Enhancement of exopolysaccharides production and reactive oxygen species level of Nostoc flagelliforme in response to dehydration. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 28(26): 34300-34308. |
| [49] | Xia H, Zhang X X, Liu Y, Bi J G, Ma X S, Zhang A N, Liu H Y, Chen L, Zhou S, Gao H, Xu K, Wei H B, Liu G L, Wang F M, Zhao H Y, Luo X X, Hou D P, Lou Q J, Feng F J, Zhou L G, Chen S J, Yan M, Li T F, Li M S, Wang L, Liu Z C, Yu X Q, Mei H W, Luo L J. 2022. Blue revolution for food security under carbon neutrality: A case from the water-saving and drought- resistance rice. Mol Plant, 15(9): 1401-1404. |
| [50] | Xiang Y, Tang N, Du H, Ye H Y, Xiong L Z. 2008. Characterization of OsbZIP23 as a key player of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family for conferring abscisic acid sensitivity and salinity and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol, 148(4): 1938-1952. |
| [51] | Xiao L H, Yang G, Zhang L C, Yang X H, Zhao S, Ji Z Z, Zhou Q, Hu M, Wang Y, Chen M, Xu Y, Jin H J, Xiao X, Hu G P, Bao F, Hu Y, Wan P, Li L G, Deng X, Kuang T Y, Xiang C B, Zhu J K, Oliver M J, He Y K. 2015. The resurrection genome of Boea hygrometrica: A blueprint for survival of dehydration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 112(18): 5833-5837. |
| [52] | Xu H F, Dai G Z, Ye D M, Shang J L, Song W Y, Shi H Z, Qiu B S. 2020. Dehydration-induced DnaK2 chaperone is involved in PSII repair of a desiccation-tolerant cyanobacterium. Plant Physiol, 182(4): 1991-2005. |
| [53] | Xu H F, Raanan H, Dai G Z, Oren N, Berkowicz S, Murik O, Kaplan A, Qiu B S. 2021. Reading and surviving the harsh conditions in desert biological soil crust: The cyanobacterial viewpoint. FEMS Microbiol Rev, 45(6): fuab036. |
| [54] | Xue Y, He Q F. 2015. Cyanobacteria as cell factories to produce plant secondary metabolites. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 3: 57. |
| [55] | Yan L, Gong Y Y, Luo Q, Dai G X, Teng Z N, He Y, Wu X X, Liu C, Tang D Y, Ye N H, Deng G F, Lin J Z, Liu X M. 2021. Heterologous expression of fungal AcGDH alleviates ammonium toxicity and suppresses photorespiration, thereby improving drought tolerance in rice. Plant Sci, 305: 110769. |
| [56] | Yang Y W, Yin Y C, Li Z K, Huang D, Shang J L, Chen M, Qiu B S. 2019. Orange and red carotenoid proteins are involved in the adaptation of the terrestrial cyanobacterium Nostoc flagelliforme to desiccation. Photosynth Res, 140(1): 103-113. |
| [57] | Ye S F, Gao X. 2015. Excavating abiotic stress-related gene resources of terrestrial macroscopic cyanobacteria for crop genetic engineering: Dawn and challenge. Bioengineered, 6(6): 313-315. |
| [58] | Yu S B, Ali J, Zhou S C, Ren G J, Xie H A, Xu J L, Yu X Q, Zhou F S, Peng S B, Ma L Y, Yuan D Y, Li Z F, Chen D Z, Zheng R F, Zhao Z G, Chu C C, You A Q, Wei Y, Zhu S S, Gu Q Y, He G C, Li S G, Liu G F, Liu C H, Zhang C P, Xiao J H, Luo L J, Li Z K, Zhang Q F. 2022. From Green Super Rice to green agriculture: Reaping the promise of functional genomics research. Mol Plant, 15(1): 9-26. |
| [59] | Yuan X L, An J, Zheng T, Liu W J. 2022. Exogenous melatonin improves salt tolerance mainly by regulating the antioxidant system in cyanobacterium Nostoc flagelliforme. PeerJ, 10: e14479. |
| [60] | Zhang H, Li Y Y, Zhu J K. 2018. Developing naturally stress- resistant crops for a sustainable agriculture. Nat Plants, 4(12): 989-996. |
| [61] | Zhang H, Zhao Y, Zhu J K. 2020. Thriving under stress: How plants balance growth and the stress response. Dev Cell, 55(5): 529-543. |
| [62] | Zhang H M, Zhu J H, Gong Z Z, Zhu J K. 2022. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat Rev Genet, 23(2): 104-119. |
| [63] | Zhang Q F. 2007. Strategies for developing green super rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104(42): 16402-16409. |
| [64] | Zhang Z C, Wang K, Hao F H, Shang J L, Tang H R, Qiu B S. 2021. New types of ATP-grasp ligase are associated with the novel pathway for complicated mycosporine-like amino acid production in desiccation-tolerant cyanobacteria. Environ Microbiol, 23(11): 6420-6432. |
| [65] | Zhu J K. 2016. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell, 167(2): 313-324. |
| [66] | Zhu X Y, Xiong L Z. 2013. Putative megaenzyme DWA1 plays essential roles in drought resistance by regulating stress-induced wax deposition in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 110(44): 17790-17795. |
| [1] | Liu Dan, Zhao Huibo, Wang Zi’an, Xu Jing, Liu Yiting, Wang Jiajia, Chen Minmin, Liu Xiong, Zhang Zhihai, Cen Jiangsu, Zhu Li, Hu Jiang, Ren Deyong, Gao Zhenyu, Dong Guojun, Zhang Qiang, Shen Lan, Li Qing, Qian Qian, Hu Songping, Zhang Guangheng. Leaf Morphology Genes SRL1 and RENL1 Co-Regulate Cellulose Synthesis and Affect Rice Drought Tolerance [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(1): 103-117. |
| [2] | Wei Huanhe, Geng Xiaoyu, Zhang Xiang, Zhu Wang, Zhang Xubin, Chen Yinglong, Huo Zhongyang, Zhou Guisheng, Meng Tianyao, Dai Qigen. Grain Yield, Biomass Accumulation, and Leaf Photosynthetic Characteristics of Rice under Combined Salinity-Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(1): 118-128. |
| [3] | Masoumeh Kordi, Naser Farrokhi, Martin I. Pech-Canul, Asadollah Ahmadikhah. Rice Husk at a Glance: From Agro-Industrial to Modern Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(1): 14-32. |
| [4] | Tian Yu, Sun Jing, Li Jiaxin, Wang Aixia, Nie Mengzi, Gong Xue, Wang Lili, Liu Liya, Wang Fengzhong, Tong Litao. Effects of Milling Methods on Rice Flour Properties and Rice Product Quality: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(1): 33-46. |
| [5] | Norhashila Hashim, Maimunah Mohd Ali, Muhammad Razif Mahadi, Ahmad Fikri Abdullah, Aimrun Wayayok, Muhamad Saufi Mohd Kassim, Askiah Jamaluddin. Smart Farming for Sustainable Rice Production: An Insight into Application, Challenge, and Future Prospect [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(1): 47-61. |
| [6] | Li Qianlong, Feng Qi, Wang Heqin, Kang Yunhai, Zhang Conghe, Du Ming, Zhang Yunhu, Wang Hui, Chen Jinjie, Han Bin, Fang Yu, Wang Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 552-565. |
| [7] | Ji Dongling, Xiao Wenhui, Sun Zhiwei, Liu Lijun, Gu Junfei, Zhang Hao, Matthew Tom Harrison, Liu Ke, Wang Zhiqin, Wang Weilu. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 598-612. |
| [8] | Prathap V, Suresh Kumar, Nand Lal Meena, Chirag Maheshwari, Monika Dalal, Aruna Tyagi. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through Combined Physiological, Biochemical, and Proteome Analyses [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 613-631. |
| [9] | Serena Reggi, Elisabetta Onelli, Alessandra Moscatelli, Nadia Stroppa, Matteo Dell’Anno, Kiril Perfanov, Luciana Rossi. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Engineered Rice Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 587-597. |
| [10] | Sundus Zafar, Xu Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 523-536. |
| [11] | Kankunlanach Khampuang, Nanthana Chaiwong, Atilla Yazici, Baris Demirer, Ismail Cakmak, Chanakan Prom-U-Thai. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 632-640. |
| [12] | Fan Fengfeng, Cai Meng, Luo Xiong, Liu Manman, Yuan Huanran, Cheng Mingxing, Ayaz Ahmad, Li Nengwu, Li Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 577-586. |
| [13] | Lin Shaodan, Yao Yue, Li Jiayi, Li Xiaobin, Ma Jie, Weng Haiyong, Cheng Zuxin, Ye Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 652-660. |
| [14] | Md. Forshed Dewan, Md. Ahiduzzaman, Md. Nahidul Islam, Habibul Bari Shozib. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and Southeast Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 537-551. |
| [15] | Raja Chakraborty, Pratap Kalita, Saikat Sen. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Pigmented Black Rice Variety Chakhao poireiton in High-Fat High-Sugar Induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 641-651. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||