
Rice Science ›› 2017, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (1): 56-60.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2016.06.008
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles
Hong-zheng Sun, Ting Peng, Jing Zhang, Jun-zhou Li, Yan-xiu Du( ), Quan-zhi Zhao(
), Quan-zhi Zhao( )
)
Received:2016-04-10
Accepted:2016-06-06
Online:2017-01-10
Published:2016-11-01
Hong-zheng Sun, Ting Peng, Jing Zhang, Jun-zhou Li, Yan-xiu Du, Quan-zhi Zhao. Test of Small RNA Sequencing Repeatability in Rice[J]. Rice Science, 2017, 24(1): 56-60.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
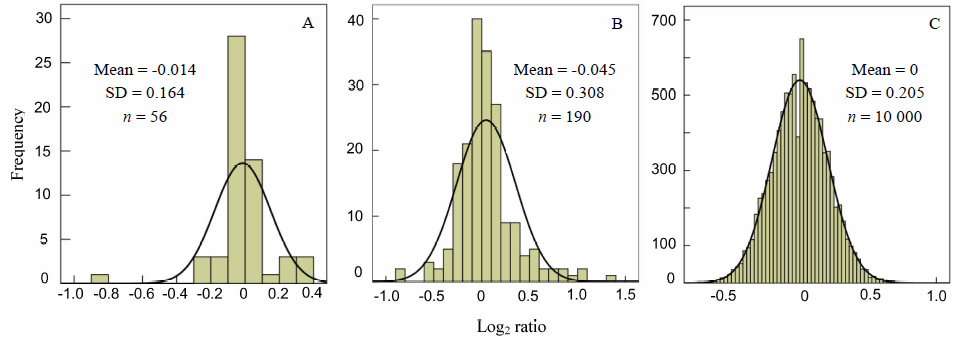
Fig. 1. Histogram of Log2 ratio frequency distribution of high abundance sRNAs. A, 56 miRNAs with expression level higher than 100 reads per million (RPM); B, 190 sRNAs with expression level higher than 100 RPM; C, Computer simulation of a sRNA population with 100 RPM.
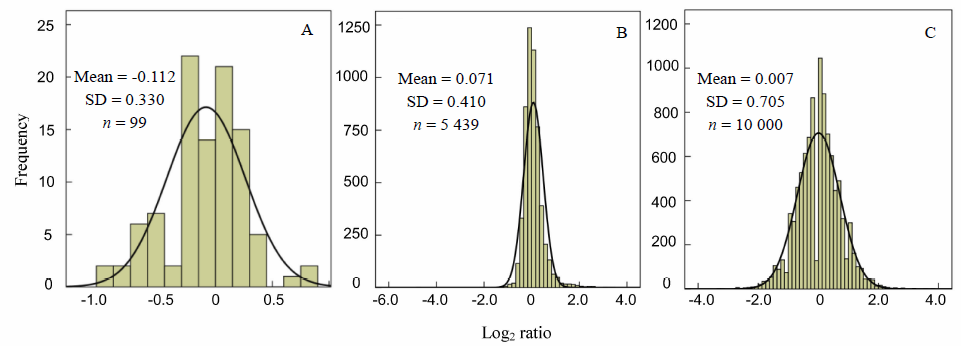
Fig. 2. Histogram of Log2 ratio frequency distribution of medium abundance sRNAs.A, 99 miRNAs with expression level of 10-100 reads per million (RPM); B, 5 439 sRNAs sequenced with expression level of 10-100 RPM; C, Computer simulation of a sRNA population with 10 RPM.
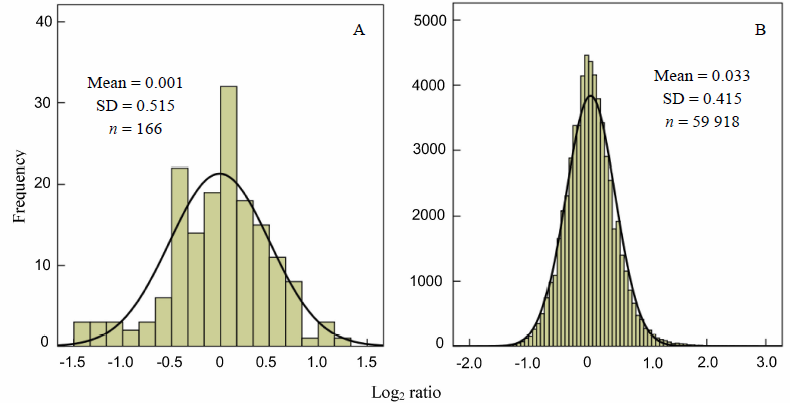
Fig. 3. Histogram of Log2 ratio frequency distribution of low abundance sRNAs. A, 166 miRNAs with expression level of 1-10 reads per million (RPM); B, 59 918 sRNAs sequenced with expression level of 1-10 RPM.
| 1 | Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J.1990. Basic local alignment search tool.J Mol Biol, 215(3): 403-410. |
| 2 | An F X, Liang Y, Li J F, Chen X L, Han H, Li F H.2014. Construction and significance analysis of the microRNA expression profile of hemerocallis fulva at low temperature.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 78(3): 378-383. |
| 3 | Benjamini Y, Yekutieli D.2005. Quantitative trait loci analysis using the false discovery rate. Genetics, 171(2): 783-790. |
| 4 | Bonnet E, van de Peer Y, Rouze P.2006. The small RNA world of plants.New Phytol, 171(3): 451-468. |
| 5 | Brautigam A, Gowik U.2010. What can next generation sequencing do for you? Next generation sequencing as a valuable tool in plant research.Plant Biol (Stuttg), 12(6): 831-841. |
| 6 | Carrington J C, Ambros V.2003. Role of microRNAs in plant and animal development.Science, 301: 336-338. |
| 7 | Cheah B H, Nadarajah K, Divate M D, Wickneswari R.2015. Identification of four functionally important microRNA families with contrasting differential expression profiles between drought-tolerant and susceptible rice leaf at vegetative stage.BMC Genom, 16(1): 692. |
| 8 | Groszmann M, Greaves I K, Albertyn Z I, Scofield G N, Peacock W J, Dennis E S.2011. Changes in 24-nt siRNA levels in Arabidopsis hybrids suggest an epigenetic contribution to hybrid vigor.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 108(6): 2617-2622. |
| 9 | He L, Hannon G J.2004. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation.Nat Rev Genet, 5(7): 522-531. |
| 10 | Huang J M, Ju Z H, Li Q L, Wang C F, Hou Q L, Li J B, Li R L, Wang L L, Sun T, Hang S Q, Gao Y D, Hou M H, Zhong J F.2011. Solexa sequencing of novel and differentially expressed microRNAs in testicular and ovarian tissues in Holstein cattle.Int J Biol Sci, 7(7): 1016-1026. |
| 11 | Khraiwesh B, Arif M A, Seumel G I, Ossowski S, Weigel D, Reski R, Frank W.2010. Transcriptional control of gene expression by microRNAs.Cell, 140(1): 111-122. |
| 12 | Kim V N.2005. Small RNAs: Classification, biogenesis, and function. Mol Cells, 19(1): 1-15. |
| 13 | Kumar R R, Pathak H, Sharma S K, Kala Y K, Nirjal M K, Singh G P, Goswami S, Rai R D.2015. Novel and conserved heat-responsive microRNAs in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Funct Integr Genom, 15(3): 323-348. |
| 14 | Liu H, Searle I R., Watson-Haigh N S, Baumann U, Mather D E, Able A J, Able J A.2015. Genome-wide identification of microRNAs in leaves and the developing head of four durum genotypes during water deficit stress.PLoS One, 10(11): e0142799. |
| 15 | Mallory A C, Vaucheret H.2006. Functions of microRNAs and related small RNAs in plants.Nat Genet, 38: S31-836. |
| 16 | Peng T, Lv Q, Zhang J, Li J Z, Du Y X, Zhao Q Z.2011. Differential expression of the microRNAs in superior and inferior spikelets in rice (Oryza sativa).J Exp Bot, 62(14): 4943-4954. |
| 17 | Peng T, Sun H Z, Du Y X, Zhang J, Li J Z, Liu Y X, Zhao Y F, Zhao Q Z.2013. Characterization and expression patterns of microRNAs involved in rice grain filling.PLoS One, 8(1): e54148. |
| 18 | Peng T, Sun H Z, Qiao M M, Zhao Y F, Du Y X, Zhang J, Li J Z, Tang G L, Zhao Q Z.2014. Differentially expressed microRNA cohorts in seed development may contribute to poor grain filling of inferior spikelets in rice.BMC Plant Biol, 14: 196. |
| 19 | Ruiz-Ferrer V, Voinnet O.2009. Roles of plant small RNAs in biotic stress responses.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 60: 485-510. |
| 20 | Secco D, Jabnoune M, Walker H, Shou H X, Wu P, Poirier Y, Whelan J.2013. Spatio-temporal transcript profiling of rice roots and shoots in response to phosphate starvation and recovery.Plant Cell, 25(11): 4285-4304. |
| 21 | Voinnet O.2009. Origin, biogenesis, and activity of plant microRNAs.Cell, 136(4): 669-687. |
| 22 | Wang F D, Li H Y, Zhang Y H, Li J J, Li L B, Liu L F, Wang L H, Wang C H, Gao J W.2013. MicroRNA expression analysis of rosette and folding leaves in Chinese cabbage using high-throughput Solexa sequencing.Gene, 532(2): 222-229. |
| 23 | Wang J Y, Yang X D, Xu H B, Chi X Y, Zhang M, Hou X L.2012. Identification and characterization of microRNAs and their target genes in Brassica oleracea.Gene, 505(2): 300-308. |
| 24 | Wu X Y, Ding D, Shi C N, Xue Y D, Zhang Z H, Tang G L, Tang J H.2016. MicroRNA-dependent gene regulatory networks in maize leaf senescence.BMC Plant Biol, 16(1): 73. |
| 25 | Zhao Y T, Wang M, Fu S X, Yang W C, Qi C K, Wang X J.2012. Small RNA profiling in two Brassica napus cultivars identifies microRNAs with oil production- and development-correlated expression and new small RNA classes.Plant Physiol, 158(2): 813-823. |
| 26 | Zhu F, Wang Z, Sun B Z.2016. Differential expression of microRNAs in shrimp Marsupenaeus japonicus in response to Vibrio alginolyticus infection.Dev Comp Immunol, 55: 76-79. |
| 27 | Zhu Q H, Spriggs A, Matthew L, Fan L J, Kennedy G, Gubler F, Helliwell C.2008. A diverse set of microRNAs and microRNA-like small RNAs in developing rice grains.Genom Res, 18(9): 1456-1465. |
| [1] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [2] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [3] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [4] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [5] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [6] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [7] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [8] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [9] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [10] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [11] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [12] | Monica Ruffini Castiglione, Stefania Bottega, Carlo Sorce, Carmelina SpanÒ. Effects of Zinc Oxide Particles with Different Sizes on Root Development in Oryza sativa [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 449-458. |
| [13] | Tan Jingyi, Zhang Xiaobo, Shang Huihui, Li Panpan, Wang Zhonghao, Liao Xinwei, Xu Xia, Yang Shihua, Gong Junyi, Wu Jianli. ORYZA SATIVA SPOTTED-LEAF 41 (OsSPL41) Negatively Regulates Plant Immunity in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 426-436. |
| [14] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [15] | Liu Qiao, Qiu Linlin, Hua Yangguang, Li Jing, Pang Bo, Zhai Yufeng, Wang Dekai. LHD3 Encoding a J-Domain Protein Controls Heading Date in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 437-448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||