
Rice Science ›› 2018, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (1): 1-18.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2017.07.001
• Orginal Article • Next Articles
Nayak Parsuram( ), Kumar Mukherjee Arup, Pandit Elssa, Kumar Pradhan Sharat
), Kumar Mukherjee Arup, Pandit Elssa, Kumar Pradhan Sharat
Received:2017-05-15
Accepted:2017-07-07
Online:2018-01-28
Published:2017-11-16
Nayak Parsuram, Kumar Mukherjee Arup, Pandit Elssa, Kumar Pradhan Sharat. Application of Statistical Tools for Data Analysis and Interpretation in Rice Plant Pathology[J]. Rice Science, 2018, 25(1): 1-18.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
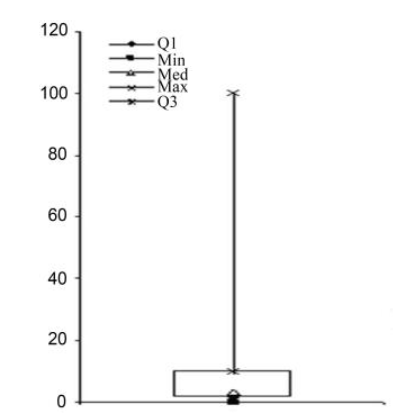
Fig. 2. Box plot depicting the distribution properties of disease severity among 42 rice genotypes across 9 seasons of testing (Mukherjee et al, 2013b).Min, Minimum; Med, Median; Max, Maximum; Q1, The first quartile; Q3, The third quartile.
| [1] | Abamu F J, Akinsola E A, Alluri K.1998. Applying the AMMI models to understand genotype-by-environment (GE) interactions in rice reaction to blast disease in Africa.Int J Pest Manag, 44(4): 239-245. |
| [2] | Adeyanju A, Little C, Yu J M, Tesso T.2015. Genome-wide association study on resistance to stalk rot diseases in grain sorghum.G3-Genes Genom Genet, 5(6): 1165-1175. |
| [3] | Adhikari T B, Mew T W, Teng P S.1994. Phenotypic diversity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in Nepal.Plant Dis, 78: 68-72. |
| [4] | Adhikari T B, Cruz C, Zhang Q, Nelson R J, Skinner D Z, Mew T W, Leach J E.1995. Genetic diversity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in Asia.Appl Environ Microb, 61(3): 966-971. |
| [5] | Adhikari T B, Mew T W, Leach J E.1999. Genotypic and pathotypic diversity in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in Nepal.Phytopathology, 89(8): 687-694. |
| [6] | Ahn S W, Ou S H.1982. Quantitative resistance of rice blast disease.Phytopathology, 72(3): 279-282. |
| [7] | Analytis S.1973. Zur Methodik der Analyse von Epidemien Dargestellt am Apfelschorf (Venturia inaequalis(Cooke) Aderh.).Acta Phytomed, 1: 1-76. |
| [8] | Annicchiarico P.1997. Joint regression vs. AMMI analysis of genotypes environment interactions for cereals in Italy.Euphytica, 94(1): 53-62. |
| [9] | Austin M P, Orloci L.1975. Multivariate analysis in vegetation research.J Ecol, 68(1): 276. |
| [10] | Bastien M, Sonah H, François B.2014. Genome wide association mapping of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum resistance in soybean with a genotyping-by-sequencing approach.Plant Genome, 7(1): 1-13. |
| [11] | Becker H C, Leon J.1988. Stability analysis in plant breeding.Plant Breeding, 101(1): 1-23. |
| [12] | Berger R D, Mishoe J W.1976. GSMP simulation of several growth functions to describe epidemic progress.Proc Am Phytopathol Soc, 3: 217. |
| [13] | Bharadwaj C L, Singh B M.1983. The stability of resistance to Pyricularia oryzae Cav. in rice. Ind Phytopathol, 36: 422-426. |
| [14] | Bradbury P J, Zhang Z, Kroon D E, Casstevens T M, Ramdoss Y, Buckler E S.2007. TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples.Bioinformatics, 23: 2633-2635. |
| [15] | Campbell C L, Madden L V, Pennypacker S P.1980. Structural characterization of bean root rot epidemics.Phytopathology, 70(2): 152-155. |
| [16] | Campbell C L, Madden L V.1990. Introduction to Plant Disease Epidemiology. New York: John Wiley & Sons. |
| [17] | Carlson G A.1969. Bayesian analysis of pesticide use. In: Proceedings of the American Statistic Association. Business and Economic Statistics Section: 411-416. |
| [18] | Carlson G A.1970. A decision theoretic approach to crop disease prediction and control.Am J Agric Econ, 52(2): 216-223. |
| [19] | Chiang K S, Huang Y T.2005. Analysis of the spatial pattern of rice leaf blast.Plant Prot Bull Taipei, 47(2): 129-142. |
| [20] | Choi W J.1987. A computer simulation model for rice leaf blast. Suweon: Korea Seoul National University. |
| [21] | Collett D.1991. Modelling Binary Data. London: Chapman & Hall. |
| [22] | Crossa J, Gauch H G J, Zobel R W.1990. Additive main effects and multiplicative interaction analysis of two international maize cultivar trials.Crop Sci, 30(3): 493-500. |
| [23] | Debibakas S, Rocher S, Garsmeur O, Toubi L, Roques D, D’hont A, Hoarau J Y, Davgrois J H.2014. Prospecting sugarcane resistance to sugarcane yellow leaf virus by genome-wide association.Theor Appl Genet, 127(8): 1719-1732. |
| [24] | de Silva N H, Gea L, Lowe R.2014. Genetic analysis of resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae(Psa) in a kiwifruit progeny test: An application of generalised linear mixed models (GLMMs).Springer Plus, 3: 547. |
| [25] | Dewey D R, Lu K H.1959. A correlation and path-coefficient analysis of components of crested wheat grass seed production.Agron J, 51(9): 515-518. |
| [26] | Eberhart S A, Russell W A.1966. Stability parameters for comparing varieties.Crop Sci, 6(1): 36-40. |
| [27] | Eskridge K M.1995. Statistical analysis of disease reaction data using nonparametric methods.Hort Sci, 30(3): 478-480. |
| [28] | Ezuka A, Horino O.1974. Classification of rice varieties and Xanthomonas oryzae strains on the basis of their differential interaction.Bull Tokai Kinki Natl Agric Exp Stat, 27: 1-19. (in Japanese) |
| [29] | Faris M A, de A Lara M, de S Leao Veiga A F.1979. Stability of sorghum midge resistance.Crop Sci, 19(5): 577-580. |
| [30] | Fisher R A.1925. Statistical Methods for Research Workers. Edinburgh, UK: Oliver and Boyd: 239. |
| [31] | Fisher R A.1936. The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems.Ann Human Geset, 7(2): 179-188. |
| [32] | Flores F, Moreno M T, Martinez A, Cubero J I.1996. Genotype-environment interaction in faba bean: Comparison of AMMI and principal coordinate models.Field Crops Res, 47: 117-127. |
| [33] | Folman L B, Postma J, Veen J A.2003. Inability to find consistent bacterial biocontrol agents of Pythium aphanidermatum in cucumber using screens based on ecophysiological traits.Microbiol Ecol, 45(1): 72-87. |
| [34] | Forbes G A, Chacon M G, Kirk H G, Huarte M A, van Damme M, Distel S, Mackay G R, Stewart H E, Lowe R, Duncan J M, Mayton H S, Fry W E, Andrivon D, Ellisseche D, Pelie R, Platt H W, MacKenzie G, Tan T R, Colon L T, Budding D J, Lozoya-Saldana H, Harnandez-Vilchis A, Capezio S.2005. Stability of resistance to Phytophthora infestans in potato: An international evaluation.Plant Pathol, 54(3): 364-372. |
| [35] | Gabriel K R.1971. The biplot graphic display of matrices with application to principal component analysis.Biometrika, 58(3): 453-467. |
| [36] | Gao L, Turner M K, Chao S, James K, Anderson J A.2016. Genome-wide association study of seedling and adult plant leaf rust resistance in elite spring wheat breeding lines. PLoS One, doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0148671. |
| [37] | Garrett K A, Madden L V, Hughes G, Pfender W F.2004. New application of statistical tools in plant pathology.Phytopathology, 94(9): 999-1003. |
| [38] | Golinski P, Kacmarek Z, Kiccana I, Wisniewska H, Kaptur P, Kostecki M, Chelkowski J.2002. Fusarium head blight of common Polish winter wheat cultivars: Comparison of effects of Fusarium avenaceum and Fusarium culmorum on yield components.J Phytopathol, 150(3): 135-141. |
| [39] | Gu K, Tian D, Yang F, Wu L, Sreekala C, Wang D, Wang G L, Yin Z.2004. High resolution genetic mapping of Xa27(t), a new bacterial blight resistance gene in rice, Oryza sativa L.Theor Appl Genet, 108: 800-807. |
| [40] | Gunther H.1986. Simulation of the Epidemiology of Pyricularia oryzae in Rice: A First Attempt. Wageningen, the Netherlands Department of Theoretical Production Ecology, Wageningen Agricultural University: 80. |
| [41] | Gurung S, Mamidi S, Bonman J M, Xiong M, Brown-Guedira G, Adhikari T B.2014. Genome-wide association study reveals novel quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to multiple leaf spot diseases of spring wheat.PLoS One, 9(9): e108179. |
| [42] | Hannessy G G, de Milliano W A J, McLaren C G.1990. Influence of primary weather variables on sorghum leaf blight severity in southern Africa.Phytopathology, 80(10): 943-945. |
| [43] | Hashimoto A, Matsumoto K, Adachi T.1982. Some trials for forecasting rice leaf blast epidemics by application of the computer simulation.Annu Rep Soc Pl Prot North Jpn, 33: 12-14. |
| [44] | Hashimoto A, Hirano K, Matsumoto K.1984. Studies on the forecasting of rice blast development by application of the computer simulation.Sp Bull Fukushima Pref Agric Exp Stn, 2: 1-104. |
| [45] | Hau B, Kranz J.1977. A comparsion of different transformations of progress curves.Phytopathol Z, 88: 53-68. |
| [46] | Hazel L N.1943. The genetic basis for constructing selection indices.Genetics, 28(6): 476-490. |
| [47] | Hughes G, Madden L V.1995. Some methods allowing for aggregated patterns of disease incidence in the analysis of data from designed experiments.Plant Pathol, 44(6): 927-943. |
| [48] | Indira S, Rana B S, Reddy B B, Rao N G P.1983. Stability of host plant resistance to sorghum charcoal rot. Ind Phytopathol, 36(3): 473-479. |
| [49] | IRRI (International Rice Research Institute). 2002. Standard Evaluation System for Rice. Manila, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| [50] | Ishiguro K.1986. Composing a simulation model for epidemics of rice panicle blast.J Agric Sci (Japan), 41: 491-495. |
| [51] | Ishiguro K, Hashimoto A.1988. Development of a simulation model for rice panicle blast epidemics: Composition of basic model.Bull Fukishima Pref Agric Res Stn, 27: 1-19. |
| [52] | Ishiguro K, Hashimoto A.1990. Development of a simulation model for rice [Oryza sativa] panicle blast epidemics: 2. Its verification and sensitive analysis. Bull Fukis Pref Agric Res Stn, 29: 15-70. |
| [53] | Jeger M J.1986. The potential of analytic compared with simulation approaches to modeling in plant disease epidemiology. In: Leonard K, Fry W. Plant Disease Epidemiology, Population Dynamics and Management. Macmillan,New York, USA: 255-281. |
| [54] | Jeger M J, van Den Bosch F, Madden L V, Holt J.1998. A model for analyzing plant-virus transmission characteristics and epdemic development.IMA J Math Appl Med, 15: 1-18. |
| [55] | Jeger M J.2000. Theory and plant epidemiology.Plant Pathol, 49(6): 651-658. |
| [56] | Jeger M J, Viljanen-Rollinson S L H.2001. The use of the area under disease progresscurve (AUDPC) to assess quantitative disease resistance in crop cultivars.Theor Appl Genet, 102(1): 32-40. |
| [57] | Jeger M J.2004. Analysis of disease progress as a basis of evaluating disease management practices.Annu Rev Phytopathol, 42: 61-82. |
| [58] | Johnson D A, Alldredge J R, Vakoch D L.1996. Potato late blight forecasting models for semiarid environment of south-central Washington.Phytopathology, 86(5): 480-484. |
| [59] | Jowett D, Browning J A, Haning B C.1974. Non-linear disease progress curves. In: Kranz J. Epidemics of Plant Diseases. Berlin: Springer-Verlag: 115-136. |
| [60] | Kleinn C, Jovel J, Hilje L.1999. A model for assessing the effect of distance on disease spread in crop fields.Crop Prot, 18(9): 609-617. |
| [61] | Koizumi S, Kato H.1990. Distribution of rice blast lesions and susceptible tissues in rice canopy.Bull Natl Agric Res Cent Tsukuba, 19: 1-15. |
| [62] | Kranz J, Mogk M, Stumpf A.1973. EPIVEN: Ein simulator fur Apfelschort.Z Pflanzenk Pflanze, 80: 181-187. |
| [63] | Kranz J.1974a. Comparison of epidemics.Ann Rev Phytopathol, 12(1): 355-374. |
| [64] | Kranz J.1974b. The role and scope of mathematical analysis and modeling in epidemiology. In: Kranz, J. Epidemics of Plant Diseases. Berlin, Springer-Verlag: 7-54. |
| [65] | Kranz J.1978. Comparative anatomy of epidemics. In: Horsfall J G, Cowling E B. Plant Disease. New York, USA: Academic Press: 33-62. |
| [66] | Leach J E, Rhoads M L, Vera Cruz C M, White F F, Mew T W.1992. Assessment of genetic diversity and population structure of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae with a repetitive DNA element.Appl Environ Microbiol, 58(7): 2188-2195. |
| [67] | Lebeda A, Jendrulek T.1987a. Application of cluster analysis for establishment of genetic similarity in gene-for-gene host parasite relationships.J Phytopathol, 119(2): 131-141. |
| [68] | Lebeda A, Jendrulek T.1987b. Cluster analysis as a method for evaluation of genetic similarity in specific host-parasite interaction ( Lectuca sativa-Bremia lactucae).Theor Appl Genet, 75(1): 194-199. |
| [69] | Lebeda A, Jendrulek T.1988. Application of methods of multivariate analysis in comparative epidemiology and research into field resistance.J Plant Dis Prot, 95(5): 495-505. |
| [70] | Lin C S, Bins M R, Lefkovitch L P.1986. Stability analysis: Where do we stand?Crop Sci, 26(5): 894-900. |
| [71] | Loreti S, Galleli A, Belisario A, Wajnberg E, Corazza L.2001. Investigation of genomic variability ofXanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis by AFLP analysis.Eur J Plant Pathol, 107(6): 583-591. |
| [72] | Madden L V, Pennypacker S P.1979. Principal component analysis of tomato early blight epidemics.J Phytopathol, 95(4): 364-369. |
| [73] | Madden L V, Hughes G.1994. BBD: Computer software for fitting the beta binomial distribution to disease incidence data.Plant Dis, 78(5): 536-540. |
| [74] | Madden L V, Turechek W W, Nita M.2002. Evaluation of generalized linear mixed models for analyzing disease incidence data obtained in designed experiments.Plant Dis, 86(3): 316-325. |
| [75] | Madden L V.2006. Botanical epidemiology: Some key advances and its continuing role in disease management.Eur J Plant Pathol, 115(1): 3-23. |
| [76] | Madden L V, Paul P A.2011. Meta-analysis for evidence synthesis in plant pathology: An overview.Phytopathology, 101(1): 16-30. |
| [77] | Maddison A C, Holt J, Jeger M J.1996. Spatial dynamics of a monocyclic disease in perennial crop.Ecol Model, 88: 45-52. |
| [78] | Mahuku G, Peters R D, Platt H W, Daayf F.2000. Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis of Phytophthora infestans isolates collected in Canada during 1994 to 1996.Plant Pathol, 49(2): 252-260. |
| [79] | Manibhushanrao K, Krishnan P.1991. Epidemiology of blast (EPIBLA): A simulation model and forecasting system for tropical rice in India. In: Rice Blast Modeling and Forecasting. Seoul, Korea Republic: International Rice Research Conference. 27-31. |
| [80] | Marchetti M A.1983. Dilatory resistance to rice blast in USA rice. Phytopathology, 73(5): 645-649. |
| [81] | Marchetti M A, Xianghua L.1986. Screening techniques to identify slow-blasting rice lines. In: Progress in Upland Rice Research. Manila, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute: 317-326. |
| [82] | Maxwell A E.1961. Recent trends in factor analysis.J Roy Statis Soc A, 124: 49-59. |
| [83] | McCoy R E.1976. MYCOS, a computer simulator of ascochyta blight of Chrysanthemum.Proc Fla State Hort Soc, 89: 296-299. |
| [84] | Mersha Z, Hau B.2008. Effect of bean rust (Uromyces appendiculatus) epidemics of host dynamics of common beans(Phaseolus bulgaris). Plant Pathol, 57(4): 674-686. |
| [85] | Mila A L, Carriquiry A L.2004. Bayesian analysis in plant pathology.Phytopathology, 94(9): 1027-1030. |
| [86] | Mohammadi Z, Sabouri A, Mousanejad S.2015. Association analysis for traits associated with powdery mildew tolerance in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) using AFLP markers. J Plant Mol Breeding, 3(1): 1-17. |
| [87] | Mohapatra N K, Mukherjee A K, Mishra A K, Nayak P.1997. Dispertion statistics and sequential sampling plan for rice blast disease.Oryza, 34: 367-371. |
| [88] | Mohapatra N K, Mukherjee A K, Suriya Rao A V, Nayak P.2008. Disease progress curves in the rice blast pathosystem compared with the logistic and Gompertz models.J Agric Biol Sci, 3(1): 28-37. |
| [89] | Mohapatra N K, Mukherjee A K, Suriya Rao A V, Jambhulkar N N, Nayak P.2014. Comparison of different parameters for evaluation of partial resistance to rice blast disease.Am J Exp Agric, 4(1): 58-79. |
| [90] | Mukherjee A K, De R N, Nayak P.1995. Identification of slow-blasting resistance in early rice.Oryza, 32(2): 101-103. |
| [91] | Mukherjee A K, Mohapatra N K, Nayak P.1996. The use of selection indices for identification of slow-blasting rice genotypes.Int J Trop Plant Dis, 14: 179-187. |
| [92] | Mukherjee A K, Nayak P.1997. Association among the components of slow-blasting resistance in rice.J Mycol Plant Pathol, 27: 175-183. |
| [93] | Mukherjee A K, Suriya Rao A V, Nayak P.1998. Stable slow-blasting resistance in rice.Ann Plant Prot Sci, 6(1): 11-18. |
| [94] | Mukherjee A K, Suriya Rao A V, De R N, Nayak P.1999. Genetic diversity among slow-blasting rice genotypes.Oryza, 36(1): 70-73. |
| [95] | Mukherjee A K, Mohapatra N K, Suriya Rao A V, Nayak P.2005. Effect of nitrogen fertilization on the expression of slow-blasting resistance in rice.J Agric Sci, 143: 385-393. |
| [96] | Mukherjee A K, Mohapatra N K, Nayak P.2010. Estimation of area under the disease progress curves in a rice blast pathosystem from two data points.Eur J Plant Pathol, 127(1): 33-39. |
| [97] | Mukherjee A K, Mohapatra N K, Nayak P.2013a. Identification of slow-blasting rice genotypes through multivariate analysis of components of resistance.J Agric Biol Sci, 8(2): 125-138. |
| [98] | Mukherjee A K, Mohapatra N K, Bose L K, Jambhulkar N N, Nayak P.2013b. Additive main effects and multiplicative interaction (AMMI) analysis of G × E interactions in rice-blast pathosystems to identify stable resistant genotypes.Afr J Agric Res, 8(44): 5492-5507. |
| [99] | Nayak D, Bose L K, Singh U D, Singh S, Nayak P.2008a. Measurement of genetic diversity of virulence in populations ofXanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in India. Commun Biom Crop Sci, 3(1): 16-28. |
| [100] | Nayak D, Bose L K, Singh S, Nayak P.2008b. Additive main effects and multiplicative interaction analysis of host-pathogen relationship in rice-bacterial blight pathosystem.Plant Pathol J, 24(3): 337-351. |
| [101] | Nayak P, Chakrabarti N K.1986. Stable resistance to bacterial blight disease in rice.Ann Appl Biol, 109(1): 179-186. |
| [102] | Nayak P, Reddy P R.1987. The pattern of bacterial leaf blight disease development and spread in rice.J Phytopathol, 119(3): 255-261. |
| [103] | Nelson S C.1995. STCLASS: Spatiotemporal distance class analysis software for the personal computer.Plant Dis, 79(6): 643-648. |
| [104] | Ngugi H K, Esker P D, Scherm H.2011. Meta-analysis to determine the effect of plant disease management measures: Review and case studies on soybean and apple.Phytopathology, 101(1): 31-41. |
| [105] | Noe J P, Barker K R.1985. Relation of within field spatial variation of plant parasitic nematode population densities and edaphic factors.Phytopathology, 75(2): 247-252. |
| [106] | Nutter F F W.2007. The role of plant disease epidemiology in developing successful integrated disease management programmes. In: Ciancio A, Mukerji G. General Concepts in Integrated Pest and Disease Management. Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Springer: 45-79. |
| [107] | Ochiai H, Horino O, Miyajima K, Kaku H.2000. Genetic diversity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae strains from Sri Lanka.Phytopathology, 90(4): 415-421. |
| [108] | Onasanya A, Sere Y, Nwilene F, Abo M E, Akator K.2004. Reactions and resistance status of differential rice genotypes to rice yellow mottle virus, Genus Sobemovirus in Cote d’ Ivoire. Asian J Plant Sci, 3(6): 718-723. |
| [109] | Parlevliet J E.1979. Components of resistance that reduce the rate of epidemic development.Annu Rev Phytopathol, 17: 203-222. |
| [110] | Piepho H P.1999. Analyzing disease incidence data from designed experiments by generalized linear mixed models.Plant Pathol, 48(5): 668-674. |
| [111] | Rao C R.1952. Advanced Statistical Methods in Biometrical Research. New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. |
| [112] | Rao S A V, Mukherjee A K, Mohapatra N K, Nayak P.2007. Spatial distribution of rice blast disease under natural field epidemics.Res J Agric Biol Sci, 3(6): 615-620. |
| [113] | Rees R G, Thompson J P, Goward E A.1979. Slow-rusting and tolerance to rust in wheat: II. The progress and effects of epidemics of Puccinia recondite tritici in selected wheat cultivars.Aust J Agric Res, 30(3): 421-432. |
| [114] | Richards F J.1959. A flexible growth function for empirical use.J Exp Bot, 10(2): 290-301. |
| [115] | Richards F J.1969. The quantitative analysis of growth. In: Steward F C. Plant Physiology. New York, USA: Academic Press: 3-76. |
| [116] | Robinson J, Jalli M.1999. Sensitivity of resistance to net blotch of barley.J Phytopathol, 147(4): 235-241. |
| [117] | Rodriguez M, Gálvez G E.1975. Indications of partial resistance of rice to the fungus Pyricularia oryzae Cav. Int Biodeter Bull, 15(2): 218-219. |
| [118] | Sah D A, Madden L V.2004. Nonparametric analysis of ordinal data in designed factorial experiments.Phytopathology, 94(1): 33-43. |
| [119] | Sandland R L, McGilchrist C A.1979. Stochastic growth curve analysis.Biometrics, 35(1): 255-271. |
| [120] | Sanogo S, Yang X B.2004. Overview of selected multivariate statistical methods and their use in phytopatholgical research.Phytopathology, 94(9): 1004-1006. |
| [121] | Savary S, Willocquet L, Elazegui F A, Castilla N P, Teng P S.2000. Rice pest constraints in topical Asia: Quantification of yield losses due to rice pests in a range of production situations.Plant Dis, 84(3): 357-369. |
| [122] | Scherm H, Ngugi H K, Ojiambo P S.2006. Trends in theoretical plant epidemiology.Eur J Plant Pathol, 115: 61-73. |
| [123] | Schlosser I, Kranz J, Bonman J M.2000. Characterization of plant type and epidemiological development in the pathosystem “upland rice/rice blast” (Pyricularia grisea) by means of multivariate statistical methods. J Plant Dis Prot, 107(1): 12-32. |
| [124] | Schneider J H M, van den Boogert P H J F, Zadoks J C.1999. Exploring differential interactions betweenRhizoctonia solani AG 2-t isolates and tulip cultivars. Plant Dis, 83(5): 474-481. |
| [125] | Searle S R, Casella G, McCulloch C E.1992. Variance components. New York, USA: John Wiley Sons, Inc. |
| [126] | Shaner G, Finney R E.1977. The effect of nitrogen fertilization on the expression of slow-mildewing resistance in knox wheat.Phytopathology, 67: 1051-1056. |
| [127] | Shaw D V, Larson K D.1999. A Meta-analysis of strawberry yield response to replant soil fumigation with combinations of methyl Bromide-chloropicrin and four alternative systems.HortScience, 34(5): 839-845. |
| [128] | Shew B B, Beute M K, Campbell C L.1984. Spatial pattern of southern stem rot caused byScleritium riflsii in six North Carolina peanut fields. Phytopathology, 74(6): 730-735. |
| [129] | Shinada H, Yamamoto T, Sato H, Yamamoto E, Hori K, Yonemaru J, Sato T, Fujino K.2015. Quantitative trait loci for rice blast resistance detected in a local rice breeding population by genome-wide association mapping.Breeding Sci, 65(5): 388-395. |
| [130] | Shrum R D.1975. Simulation of wheat stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis West) using EPIDEMIC, a flexible plant disease simulator. Prog Rep Pa Agric Exp Stn: 347. |
| [131] | Singh R K.1972. Selection index: Yes or No?Vistas Pl Sci, 2: 111-140. |
| [132] | Singh R K, Chaudhary B D.1985. Biometrical Methods in Quantitative Genetic Analysis. New Delhi Ludhiana: Kalyani Publishers: 318. |
| [133] | Singh S P, Jetwani M G, Rana B S, Rao N G P.1978. Stability of host plant resistance to sorghum shootfly,Antherigona soccata(Rondam). Ind J Ent, 40: 376-383. |
| [134] | Smith H F.1936. A discriminant function for plant selection.Ann Hum Genet, 7(3): 240-250. |
| [135] | Sneath P H A, Sokal R R.1973. Numerical Taxonomy: The Principles and Practice of Numerical Classification. San Francisco: W H Freeman and Company: 573. |
| [136] | Snedecor G W, Cochran W G.1976. Statistical Methods. 6th edn. Ames: Iowa State University Press. |
| [137] | Sprent P, Smeeton N C.2001. Applied Nonparametric Statistical Methods. Boca Raton, FL: Chapman Hall. |
| [138] | Thompson J P, Rees R G.1979. Pattern analysis in epidemiological evaluation of cultivar resistance.Phytopathology, 69(6): 545-549. |
| [139] | Torres C Q.1986. Effect of plant age on the expression of resistance to Pyricularia oryzae Cav. in upland rice varieties. Los Banos, Laguna, the Philippines: University of the Philippines: 82. |
| [140] | Tukey J W.1977. Exploratory data analysis.Addison-Wesley Pub Co., 26: 163-182. |
| [141] | van den Bosch F, Zadoks J C, Metz J A J.1988. Focus expansion in plant disease: I. The constant rate focus expansion.Phytopathology, 78: 55-58. |
| [142] | van der Plank J E. 1963. Plant Diseases: Epidemics and Control. New York: Academic Press: 349. |
| [143] | Villareal R L, MacKenzie D R, Nelson R R, Coffman W R.1980. Apparent infection rates of Pyricularia oryzae on different rice cultivars. Phytopathology, 70(12): 1224-1226. |
| [144] | Waggoner P E, Horsfall J G.1969. EPIDEM: A simulator of plant disease written for a computer. Connecticut. Agricultural Experimental Bulletin, USA: 698. |
| [145] | Waggoner P E, Horsfall J G, Lukens R J.1969. Epimay: A Simulator of Southern Corn Leaf Blight. New Haven, USA: Bulletin of the Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station. |
| [146] | Wang C H, Yang Y L, Yuan X P, Xu Q, Feng Y, Yu H Y, Wang Y P, Wei X H.2014. Genome-wide association study of blast resistance in indica rice. BMC Plant Biol, 14(1): 311. |
| [147] | Wang Z M, Mackill D J, Bonman J M.1989. Inheritance of partial resistance to blast in indica rice cultivars. Crop Sci, 29(4): 848-853. |
| [148] | Williams W T.1976. Pattern analysis in agricultural science. Amsterdam, Oxford and New York: CSIRO, Melbourne and Elsevier, 331. |
| [149] | Xu X M, Ridout M S.1998. Effects of initial epidemic conditions, sporulation rate, and spore dispersal gradient on the spatio-temporal dynamics of plant disease epidemics.Phytopathology, 88(10): 1000-1012. |
| [150] | Xu X M, Ridout M S.2001. Effects of prevailing wind direction on spatial statistics of plant disease epidemics.J Phytopathol, 149: 155-166. |
| [151] | Xu X M.2006. Modeling and interpreting disease progress in time. In: Cooke B M, Gareth Jones D, Kaye B. The Epidemiology of Plant Disease. Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Springer: 215-238. |
| [152] | Yan W K, Hunt L A, Sheng Q L, Szlavnics Z.2000. Cultivar evaluation and mega-environment investigation based on the GGE biplot.Crop Sci, 40(3): 597-605. |
| [153] | Yang R C.2008. Why is MIXED analysis underutilised?Can J Plant Sci, 88: 563-567. |
| [154] | Yang R C.2010. Towards understansing and use of mixed-model analysis of agricultural experiments.Can J Plant Sci, 90(5): 605-630. |
| [155] | Yashitola J, Krishnaveni D, Reddy A P K, Sonti R V.1997. Genetic diversity within the population of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in India.Phytopathology, 87(7): 760-765. |
| [156] | Yi S Y, Lee H Y, Kim H A, Lim C J, Kim W B, Jang H A, Jeon J S, Kwon S Y.2013. Microarray analysis of bacterial blight resistance 1 mutant rice infected with Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae.Plant Breeding Biotechnol, 1(4): 354-365. |
| [157] | Yuen J.2003. Bayesian approaches to plant disease forecasting.Plant Health Progress, doi: 10.1094/PHP.2003-1113-06-RV. |
| [158] | Yuen J E, Hughes G.2002. Bayesian analysis of plant disease prediction.Plant Pathol, 51: 407-412. |
| [159] | Zadoks J C, Schein R D.1979. Epidemiology and Plant Disease Management. Oxford: Oxford University Press: 427. |
| [160] | Zhu L, Carlin B P, English P, Scalf R.2015. Hierarchical modeling of spatio-temporally misaligned data: Relating traffic density to pediatric asthma hospitalizations.Environmetrics, 11: 43-61. |
| [1] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [2] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [3] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [4] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [5] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [6] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [7] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [8] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [9] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [10] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [11] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [12] | Monica Ruffini Castiglione, Stefania Bottega, Carlo Sorce, Carmelina SpanÒ. Effects of Zinc Oxide Particles with Different Sizes on Root Development in Oryza sativa [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 449-458. |
| [13] | Tan Jingyi, Zhang Xiaobo, Shang Huihui, Li Panpan, Wang Zhonghao, Liao Xinwei, Xu Xia, Yang Shihua, Gong Junyi, Wu Jianli. ORYZA SATIVA SPOTTED-LEAF 41 (OsSPL41) Negatively Regulates Plant Immunity in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 426-436. |
| [14] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [15] | Liu Qiao, Qiu Linlin, Hua Yangguang, Li Jing, Pang Bo, Zhai Yufeng, Wang Dekai. LHD3 Encoding a J-Domain Protein Controls Heading Date in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 437-448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||