
Rice Science ›› 2020, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 237-245.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2020.04.006
• Research Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuexiong Zhang1,2, Gang Qin2, Qianqian Ma1, Minyi Wei2, Xinghai Yang2, Zengfeng Ma2, Haifu Liang2, Chi Liu2, Zhenjing Li2, Fang Liu1, Dahui Huang2( ), Rongbai Li1(
), Rongbai Li1( )
)
Received:2019-02-20
Accepted:2019-04-26
Online:2020-05-28
Published:2020-01-17
About author:# These authors contributed equally to this work
Yuexiong Zhang, Gang Qin, Qianqian Ma, Minyi Wei, Xinghai Yang, Zengfeng Ma, Haifu Liang, Chi Liu, Zhenjing Li, Fang Liu, Dahui Huang, Rongbai Li. Identification of Major Locus Bph35 Resistance to Brown Planthopper in Rice[J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(3): 237-245.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
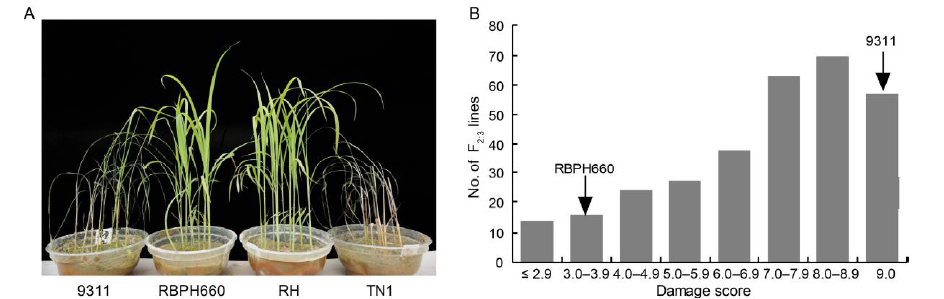
Fig. 1. Brown planthopper (BPH) resistance evaluation of two parents and F2:3 population. A, Resistance evaluation of parents, RBPH660 and 9311, along with resistant and susceptible controls Rathu Heenati (RH) and Taichung Native 1 (TN1) to BPH. B, Frequency distribution of BPH damage score in 9311/RBPH660 F2:3 population.
| Marker | Physical position (bp) | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSM15 | 7 093 839-7 093 993 | AAAGACTGGACATGAAGTCG | TCTTGCCATAAAAAGACCAC |
| PSM11 | 7 307 740-7 307 835 | AGCAGCTTGTAGTCCAGGTA | TTAGGAGCGTTTGTAGGAAG |
| PSM19 | 6 481 834-6 481 973 | CGTTTGAAGTTGAAGGATTC | TAGATAAAAATTGGCCGAAG |
| PSM16 | 5 290 425-5 290 710 | AATCACCATTGGCTTTTATCCC | ACCGTGTGCTGGACGAGGA |
| PSM20 | 6 938 563-6 938 767 | GCAGAGAATGGAAGTAAAGCA | CAATGGACCTCAGGAATGTG |
| PSM8 | 13 819 492-13 819 703 | CCACTGGAACAACAAATCAAA | TGTCAACTATTCAGAAACCTACC |
| PSM23 | 15 890 765-15 891 107 | AGATGTTTATCCTCTTGCGGG | ATACCACAAAGTGCGATGATTC |
Table 1 InDel markers used for fine mapping of Bph35 locus.
| Marker | Physical position (bp) | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSM15 | 7 093 839-7 093 993 | AAAGACTGGACATGAAGTCG | TCTTGCCATAAAAAGACCAC |
| PSM11 | 7 307 740-7 307 835 | AGCAGCTTGTAGTCCAGGTA | TTAGGAGCGTTTGTAGGAAG |
| PSM19 | 6 481 834-6 481 973 | CGTTTGAAGTTGAAGGATTC | TAGATAAAAATTGGCCGAAG |
| PSM16 | 5 290 425-5 290 710 | AATCACCATTGGCTTTTATCCC | ACCGTGTGCTGGACGAGGA |
| PSM20 | 6 938 563-6 938 767 | GCAGAGAATGGAAGTAAAGCA | CAATGGACCTCAGGAATGTG |
| PSM8 | 13 819 492-13 819 703 | CCACTGGAACAACAAATCAAA | TGTCAACTATTCAGAAACCTACC |
| PSM23 | 15 890 765-15 891 107 | AGATGTTTATCCTCTTGCGGG | ATACCACAAAGTGCGATGATTC |
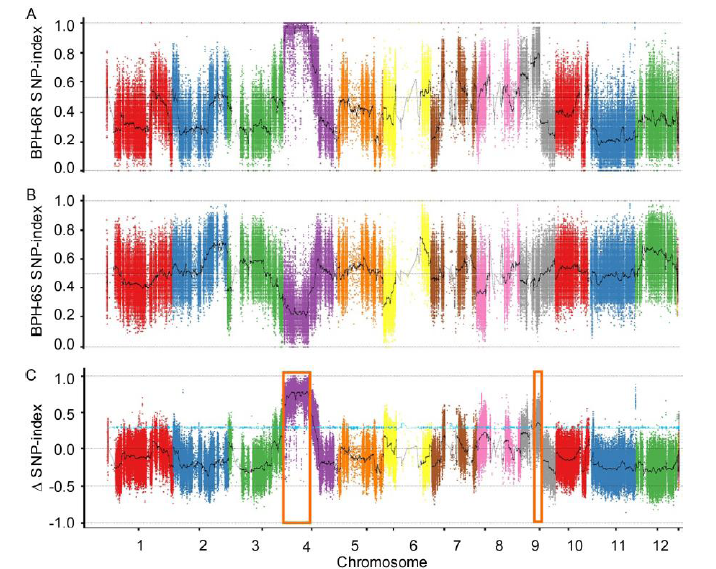
Fig. 2. SNP-index graphs of BPH-6R bulk (A), BPH-6S bulk (B) and Δ(SNP-index) (C) from BSA-seq analysis. X-axis represents the position of the 12 chromosomes in rice and Y-axis represents the SNP-index. The black curve shows the average value of SNP-index, and the blue line shows the association threshold at the 95% confidence level. Two associated genomic regions (orange box) with brown planthopper (BPH) resistance were identified on chromosomes 4 and 9, respectively.
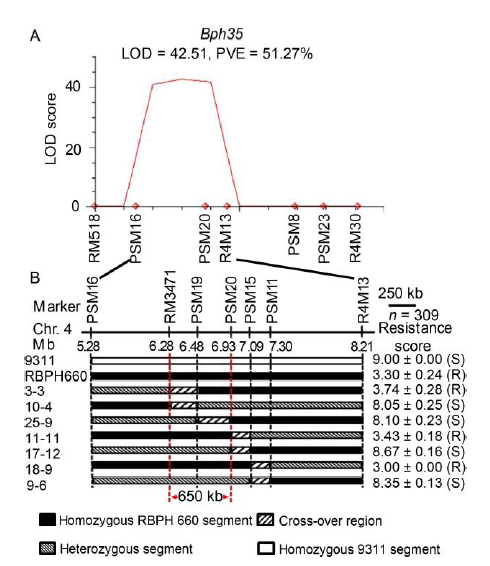
Fig. 3. Mapped of a major resistance locus Bph35 to BPH on chromosome 4. A, Bph35 was detected between PSM16 and R4M13 in an F2:3 population by using QTL IciMapping 4.1, accounted for 51.27% of the phenotypic variation with a LOD score of 42.51. PVE, Phenotypic variation explanation. B, Further narrow down the genomic region of Bph35 to 650 kb by substitution mapping of recombinant plants.
| Number | Gene | Putative function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Os04g0191400 | Expressed protein |
| 2 | Os04g0191800 | OsFBX118-F-box domain containing protein, expressed |
| 3 | Os04g0193200 | Methyl-CpG binding domain containing protein, expressed |
| 4 | Os04g0193950 | NB-ARC, leucine-rich repeat family protein, expressed |
| 5 | Os04g0194000 | OsFBX120-F-box domain containing protein, expressed |
| 6 | Os04g0194400 | Hypothetical protein |
| 7 | Os04g0194433 | Hypothetical gene |
| 8 | Os04g0194500 | Similar to ABC transporter-like protein |
| 9 | Os04g0194600 | TCP family transcription factor, putative, expressed |
| 10 | Os04g0195000 | WD domain, G-beta repeat domain containing protein, expressed |
| 11 | Os04g0195400 | Transposon protein, putative, unclassified, expressed |
| 12 | Os04g0196200 | O-methyltransferase, putative, expressed |
| 13 | Os04g0196600 | Glycosyltransferase, putative, expressed |
| 14 | Os04g0196850 | Similar to OSIGBa0132I10.3 protein |
| 15 | Os04g0197100 | Retrotransposon protein, putative, unclassified, expressed |
| 16 | Os04g0197500 | UDP-glucuronosyl/UDP-glucosyltransferase family protein |
| 17 | Os04g0201200 | Pumilio-family RNA binding repeat containing protein, expressed |
| 18 | Os04g0201800 | Amino acid transporter protein, putative, expressed |
Table 2 Functional annotation of 18 candidate genes in Bph35 genomic region.
| Number | Gene | Putative function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Os04g0191400 | Expressed protein |
| 2 | Os04g0191800 | OsFBX118-F-box domain containing protein, expressed |
| 3 | Os04g0193200 | Methyl-CpG binding domain containing protein, expressed |
| 4 | Os04g0193950 | NB-ARC, leucine-rich repeat family protein, expressed |
| 5 | Os04g0194000 | OsFBX120-F-box domain containing protein, expressed |
| 6 | Os04g0194400 | Hypothetical protein |
| 7 | Os04g0194433 | Hypothetical gene |
| 8 | Os04g0194500 | Similar to ABC transporter-like protein |
| 9 | Os04g0194600 | TCP family transcription factor, putative, expressed |
| 10 | Os04g0195000 | WD domain, G-beta repeat domain containing protein, expressed |
| 11 | Os04g0195400 | Transposon protein, putative, unclassified, expressed |
| 12 | Os04g0196200 | O-methyltransferase, putative, expressed |
| 13 | Os04g0196600 | Glycosyltransferase, putative, expressed |
| 14 | Os04g0196850 | Similar to OSIGBa0132I10.3 protein |
| 15 | Os04g0197100 | Retrotransposon protein, putative, unclassified, expressed |
| 16 | Os04g0197500 | UDP-glucuronosyl/UDP-glucosyltransferase family protein |
| 17 | Os04g0201200 | Pumilio-family RNA binding repeat containing protein, expressed |
| 18 | Os04g0201800 | Amino acid transporter protein, putative, expressed |
| [1] | Abe A, Kosugi S, Yoshida K, Natsume S, Takagi H, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Yoshida K, Mitsuoka C, Tamiru M, Innan H, Cano L, Kamoun S, Terauchi R.2012. Genome sequencing reveals agronomically important loci in rice using MutMap.Nat Biotechnol, 30(2): 174-178. |
| [2] | Cabauatan P Q, Cabunagan R C, Choi I R.2009. Rice viruses transmitted by the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Stål. In: Heong K L, Hardy B. Planthoppers: New Threats to the Sustainability of Intensive Rice Production Systems in Asia. Los Baños, the Philippine: International Rice Research Institute: 357-368. |
| [3] | Chen X, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho Y G, McCouch S R.1997. Development of a microsatellite framework map providing genome- wide coverage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet, 95(4): 553-567. |
| [4] | Cheng X Y, Zhu L L, He G C.2013. The understanding of molecular interaction between rice and brown planthopper.Mol Plant, 6: 621-634. |
| [5] | Deen R, Ramesh K, Gautam S K, Rao K Y, Lakshmi V J, Viraktamath B C, Brar D S, Ram T.2010. Identification of new gene for BPH resistance introgressed from O. rufipogon. Rice Genet Newsl, 25: 70-71. |
| [6] | Du B, Zhang W L, Liu B F, Hu J, Wei Z, Shi Z Y, He R F, Zhu L L, Chen R Z, Han B, He G C.2009. Identification and characterization ofBph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106: 22163-22168. |
| [7] | Guo J P, Xu C X, Wu D, Zhao Y, Qiu Y F, Wang X X, Ouyang Y D, Cai B D, Liu X, Jing S L, Shangguan X X, Wang H Y, Ma Y H, Hu L, Wu Y, Shi S J, Wang W L, Zhu L L, Xu X, Chen R Z, Feng Y Q, Du B, He G C.2018. Bph6 encodes an exocyst- localized protein and confers broad resistance to planthoppers in rice. Nat Genet, 50: 297-306. |
| [8] | Hou L Y, Yu P, Xu Q, Yan X P, Yu H Y, Wang Y P, Wang C H, Wan G, Tang S X, Peng S T, Wei X H.2011. Genetic analysis and preliminary mapping of two recessive resistance genes to brown planthopper,Nilaparvata lugens Stal in rice. Rice Sci, 18(3): 238-242. |
| [9] | Hu J, Xiao C, Cheng M X, Gao G J, Zhang Q L, He Y Q.2015a. Fine mapping and pyramiding of brown planthopper resistance genesQBph3 and QBph4 in an introgression line from wild rice O. officinalis. Mol Breeding, 35: 3-12. |
| [10] | Hu J, Xiao C, Cheng M X, Gao G J, Zhang Q L, He Y Q.2015b. A new finely mappedOryza australiensis derived QTL in rice confers resistance to brown planthopper. Gene, 561(1): 132-137. |
| [11] | Hu J, Xiao C, He Y Q.2016. Recent progress on the genetics and molecular breeding of brown planthopper resistance in rice.Rice, 9: 30. |
| [12] | Hu J, Chang X Y, Zou L, Tang W Q, Wu W R.2018. Identification and fine mapping ofBph33, a new brown planthopper resistance gene in rice(Oryza sativa L.). Rice, 11: 55. |
| [13] | Huang D, Qiu Y, Zhang Y, Huang F, Meng J, Wei S, Li R, Chen B.2013. Fine mapping and characterization ofBPH27, a brown planthopper resistance gene from wild rice(Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Theor Appl Genet, 126(1): 219-229. |
| [14] | Huang X H, Kurata N, Wei X H, Wang Z X, Wang A H, Zhao Q, Zhao Y, Liu K Y, Lu H Y, Li W J, Guo Y L, Lu Y Q, Zhou C C, Fan D L, Weng Q J, Zhu C R, Huang T, Zhang L, Wang Y C, Feng L, Furuumi H, Kubo T, Miyabayashi T, Yuan X P, Xu Q, Dong G J, Zhan Q L, Li C Y, Fujiyama A, Toyoda A, Lu T T, Feng Q, Qian Q, Li J Y, Han B.2012. A map of rice genome variation reveals the origin of cultivated rice.Nature, 490: 497-501. |
| [15] | Huang Z, He G C, Shu L H, Li X H, Zhang Q F.2001. Identification and mapping of two brown planthopper resistance genes in rice.Theor Appl Genet, 102: 929-934. |
| [16] | IRRI.1996. Standard Evaluation Systems for Rice. Manila, the Phillipines: IRRI. |
| [17] | Ishii T, Brar D S, Multani D S, Khush G S.1994. Molecular tagging of genes for brown planthopper resistance and earliness introgressed fromOryza australiensis into cultivated rice, O. sativa. Genome, 37(2): 217-221. |
| [18] | Jena K K, Jeung J U, Lee J H, Choi H C, Brar D S.2006. High resolution mapping of a new brown planthopper (BPH) resistance gene,Bph18(t), and marker-assisted selection for BPH resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet, 112(2): 288-297. |
| [19] | Ji H, Kim S R, Kim Y H, Suh J P, Park H M, Sreenivasulu N, Misra G, Kim S M, Hechanova S L, Kim H, Lee G S, Yoon U H, Kim T H, Lim H, Suh S C, Yang J, An G, Jena K K.2016. Map-based cloning and characterization of theBPH18 gene from wild rice conferring resistance to brown planthopper (BPH) insect pest. Sci Rep, 6: 34376. |
| [20] | Jiang H Y, Zeng G, Hao M, Huang X G, Xiao Y H.2019. Identification of brown planthopper resistance genes in broad-spectrum blast resistant rice germplasm 75-1-127 and its molecular marker-assisted selection breeding.Chin J Rice Sci, 33(3): 227-234. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Jing S L, Zhao Y, Du B, Chen R Z, Zhu L L, He G C.2017. Genomics of interaction between the brown planthopper and rice.Curr Opin Insect Sci, 19: 82-87. |
| [22] | Khush G S, Karim A R, Angeles E R.1985. Genetics of resistance of rice cultivar ARC10550 to Bangladesh brown planthopper biotype.J Genet, 64(2): 121-125. |
| [23] | Kumar K, Sarao P S, Bhatia D, Neelam K, Kaur A, Mangat G S, Brar D S, Singh K.2018. High resolution genetic mapping of a novel brown planthopper resistance locus,Bph34 in Oryza sativa L. × Oryza nivara(Sharma & Shastry) derived interspecific F2 population. Theor Appl Genet, 131(5): 1163-1171. |
| [24] | Li H, Durbin R.2009. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform.Bioinformatics, 25(14): 1754-1760. |
| [25] | Liu G Q, Yan H H, Fu Q, Qian Q, Zhang Z T, Zhai W X, Zhu L H.2001. Mapping of a new gene for brown planthopper resistance in cultivated rice introgressed fromOryza eichingeri. Chin Sci Bull, 46: 1459-1462. |
| [26] | Liu Y Q, Wu H, Chen H, Liu Y L, He J, Kang H Y, Sun Z Q, Pan G, Wang Q, Hu J L, Zhou F, Zhou K N, Zheng X M, Ren Y L, Chen L M, Wang Y H, Zhao Z G, Lin Q B, Wu F Q, Zhang X, Guo X P, Cheng X N, Jiang L, Wu C Y, Wang H Y, Wan J M.2015. A gene cluster encoding lectin receptor kinases confers broad-spectrum and durable insect resistance in rice.Nat Biotechnol, 33(3): 334-335. |
| [27] | Lv W T, Du B, Shangguan X X, Zhao Y, PanY F, Zhu L L, He Y Q, He G C.2014. BAC and RNA sequencing reveal the brown planthopper resistance geneBPH15 in a recombination cold spot that mediates a unique defense mechanism. BMC Genom, 15(1): 674. |
| [28] | McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler S, Daly M, DePristo M A.2010. The genome analysis toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data.Genom Res, 20(9): 1297-1303. |
| [29] | Meng L, Li H H, Zhang L Y, Wang J K.2015. QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations.Crop J, 3: 269-283. |
| [30] | Min S, Lee S W, Choi B R, Lee S H, Kwon D H.2014. Insecticide resistance monitoring and correlation analysis to select appropriate insecticides againstNilaparvata lugens(Stål), a migratory pest in Korea. J Asia Pac Entomol, 17(4): 711-716. |
| [31] | Naik S B, Divya D, Sahu N, Sundaram R M, Sarao P S, Singh K, Lakshmi V J, Bentur J S.2018. A new gene Bph33(t) conferring resistance to brown planthopper (BPH), Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) in rice line RP2068-18-3-5. Euphytica, 214: 53. |
| [32] | Nemoto H, Ikeda R, Kaneda C.1989. New gene for resistance to brown planthopper,Nilaparvata lugens Stål, in rice. Jpn J Breeding, 39: 23-28. |
| [33] | Prahalada G D, Shivakumar N, Lohithaswa H C, Sidde Gowda D K, Ramkumar G, Kim S R, Ramachandra C, Hittalmani S, Mohapatra T, Jena K K.2017. Identification and fine mapping of a new gene,BPH31 conferring resistance to brown planthopper biotype 4 of India to improve rice, Oryza sativa L. Rice, 10: 41. |
| [34] | Qi L, Ding Y B, Zheng X M, Xu R, Zhang L Z, Wang Y Y, Wang X N, Zhang L F, Cheng Y L, Qiao W H, Yang Q W.2018. Fine mapping and identification of a novel locusqGL12.2 control grain length in wild rice(Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Theor Appl Genet, 131(7): 1497-1508. |
| [35] | Rahman M L, Jiang W Z, Chu S H, Qiao Y L, Ham T H, Woo M O, Lee J, Khanam M S, Chin J H, Jeung J U, Brar D S, Jena K K, Koh H J.2009. High-resolution mapping of two rice brown planthopper resistance genes,High-resolution mapping of two rice brown planthopper resistance genes, Bph20(t) and Bph21(t) originating from Oryza minuta. Theor Appl Genet, 119(7): 1237-1246. |
| [36] | Ram T, Deen R, Gautam S K, Ramesh K, Rao Y K, Brar D S.2010. Identification of new genes for brown planthopper resistance in rice introgressed fromO. glaberrima and O. minuta. Rice Genet Newsl, 25: 67-69. |
| [37] | Ren J S, Gao F Y, Wu X T, Lu X J, Zeng L H, Lv J Q, Su X W, Luo H, Ren G J.2016. Bph32, a novel gene encoding an unknown SCR domain-containing protein, confers resistance against the brown planthopper in rice. Sci Rep, 6: 37645. |
| [38] | Renganayaki K, Fritz A K, Sadasivam S, Pammi S, Harrington S E, McCouch S R, Kumar S M, Reddy A S.2002. Mapping and progress toward map-based cloning of brown planthopper biotype-4 resistance gene introgressed fromOryz officinalis into cultivated rice, O. sativa. Crop Sci, 42: 2112-2117. |
| [39] | Sarao P S, Sahi G K, Neelam K, Mangat G S, Patra B C, Singh K.2016. Donors for resistance to brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens(Stål) from wild rice species. Rice Sci, 23(4): 219-224. |
| [40] | Shen Y J, Jiang H, Jin J P, Zhang Z B, Xi B, He Y Y, Wang G, Wang C, Qian L, Li X, Yu Q B, Liu H J, Chen D H, Gao J H, Huang H, Shi T L, Yang Z N.2004. Development of genome- wide DNA polymorphism database for map-based cloning of rice genes.Plant Physiol, 135(3): 1198-1205. |
| [41] | Sun J, Yang L M, Wang J G, Liu H L, Zheng H L, Xie D W, Zhang M H, Feng M F, Jia Y, Zhao H W, Zou D T.2018. Identification of a cold-tolerant locus in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using bulked segregant analysis with a next-generation sequencing strategy. Rice, 11: 24. |
| [42] | Takagi H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kosugi S, Natsume S, Mitsuoka C, Uemura A, Utsushi H, Tamiru M, Takuno S, Innan H, Cano L M, Kamoun S, Terauchi R.2013. QTL-seq: Rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations.Plant J, 74(1): 174-183. |
| [43] | Tamura Y, Hattori M, Yoshioka H, Yoshioka M, Takahashi A, Wu J Z, Sentoku N, Yasui H.2014. Map-based cloning and characterization of a brown planthopper resistance geneBPH26 from Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica cultivar ADR52. Sci Rep, 4: 5872. |
| [44] | Tanaka K, Endo S, Kazano H.2000. Toxicity of insecticides to predators of rice planthoppers: Spiders, the mired bug and the dryinid wasp.Appl Entomol Zool, 35: 177-187. |
| [45] | Wang H Y, Shi S J, Guo Q, Nie L Y, Du B, Chen R Z, Zhu L L, He G C.2018. High-resolution mapping of a gene conferring strong antibiosis to brown planthopper and developing resistant near-isogenic lines in 9311 background.Mol Breeding, 38: 107. |
| [46] | Wang K, Li M Y, Hakonarson H.2010. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data.Nucl Acids Res, 38: e164. |
| [47] | Wang Y, Cao L M, Zhang Y X, Cao C X, Liu F, Huang F K, Qiu Y F, Li R B, Lou X J.2015. Map-based cloning and characterization ofBPH29, a B3 domain-containing recessive gene conferring brown planthopper resistance in rice. J Exp Bot, 66(19): 6035-6045. |
| [48] | Xiao C, Hu J, Ao Y T, Cheng M X, Gao G J, Zhang Q L, He G C, He Y Q.2016. Development and evaluation of near-isogenic lines for brown planthopper resistance in rice cv. 9311.Sci Rep, 6: 38159. |
| [49] | Yang H Y, Ren X, Weng Q M, Zhu L L, He G C.2002. Molecular mapping and genetic analysis of a rice brown planthopper (Nilarparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene. Hereditas, 136: 39-43. |
| [50] | Yang L, Li R B, Li Y R, Huang F K, Chen Y Z, Huang S S, Huang L F, Liu C, Ma Z F, Huang D H, Jiang J J.2012. Genetic mapping of bph20(t) and bph21(t) loci conferring brown planthopper resistance to Nilaparvata lugens Stål in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica, 183: 161-171. |
| [51] | Zhao Y, Huang J, Wang Z Z, Jing S L, Wang Y, Ouyang Y D, Cai B D, Xin X F, Liu X, Zhang C X, Pan Y F, Ma R, Li Q F, Jiang W H, Zeng Y, Shangguan X X, Wang H Y, Du B, Zhu L L, Xu X, Feng Y Q, He S Y, Chen R Z, Zhang Q F, He G C.2016. Allelic diversity in an NLR geneBPH9 enables rice to combat planthopper variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 113: 12850-12855. |
| [52] | Zheng W J, Wang Y, Wang L L, Ma Z B, Zhao J M, Wang P, Zhang L X, Liu Z H, Lu X C.2016. Genetic mapping and molecular marker development forPi65(t), a novel broad-spectrum resistance gene to rice blast using next-generation sequencing. Theor Appl Genet, 129(5): 1035-1044. |
| [1] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [2] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [3] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [4] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [5] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [6] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [7] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [8] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [9] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [10] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [11] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [12] | Monica Ruffini Castiglione, Stefania Bottega, Carlo Sorce, Carmelina SpanÒ. Effects of Zinc Oxide Particles with Different Sizes on Root Development in Oryza sativa [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 449-458. |
| [13] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [14] | Liu Qiao, Qiu Linlin, Hua Yangguang, Li Jing, Pang Bo, Zhai Yufeng, Wang Dekai. LHD3 Encoding a J-Domain Protein Controls Heading Date in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 437-448. |
| [15] | Lu Xuedan, Li Fan, Xiao Yunhua, Wang Feng, Zhang Guilian, Deng Huabing, Tang Wenbang. Grain Shape Genes: Shaping the Future of Rice Breeding [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 379-404. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||