
Rice Science ›› 2020, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 101-112.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2019.04.007
• Research Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wenlei Cao1, Xinxin Cao2, Jianhua Zhao1, Zhaoyang Zhang2, Zhiming Feng1,4, Shouqiang Ouyang1,2,3( ), Shimin Zuo1,4(
), Shimin Zuo1,4( )
)
Received:2018-12-12
Accepted:2019-04-26
Online:2020-03-28
Published:2019-11-28
About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work
Wenlei Cao, Xinxin Cao, Jianhua Zhao, Zhaoyang Zhang, Zhiming Feng, Shouqiang Ouyang, Shimin Zuo. Comprehensive Characteristics of MicroRNA Expression Profile Conferring to Rhizoctonia solani in Rice[J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(2): 101-112.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
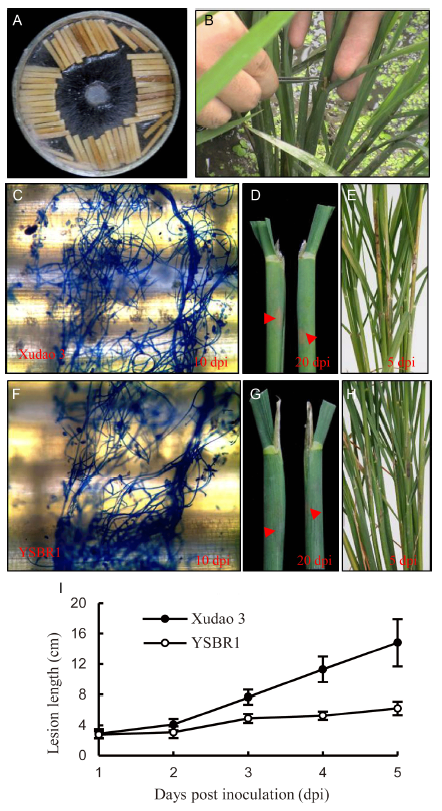

Fig. 1. R. solani inoculum and disease severity of susceptible cultivar Xudao 3 and resistant cultivar YSBR1 in greenhouse. A, The inoculum used in the present study. B, Indication of inoculation site in rice. C, Stained by lacto-phenol cotton blue for Xudao 3 at 10 d post inoculation (dpi). D, Lesion in rice sheath indicated by red arrow for Xudao 3 at 20 dpi. E, Lesion in rice sheath for Xudao 3 at 5 dpi. F, Stained by lacto-phenol cotton blue for YSBR1 at 10 dpi. G, Lesion in rice sheath indicated by red arrow for YSBR1 at 20 dpi. H, Lesion in rice sheath indicated for YSBR1 at 5 dpi. I, Statistics of lesion length in Xudao 3 and YSBR1. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 2).
| Library | Total read | High quality | 3′ adapter null | Insert null | 5′ adapter contaminant | Smaller than 18 nt | polyA | Clean read | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Count | % | Count | % | Count | % | Count | % | Count | % | Count | % | Count | % | ||
| XC5 | 32 799 952 | 32 287 444 | 100 | 159 708 | 0.49 | 14 595 | 0.05 | 30 643 | 0.09 | 3 035 094 | 9.40 | 360 | 0.00 | 29 047 044 | 89.96 | |
| XC10 | 31 289 810 | 30 793 396 | 100 | 186 452 | 0.61 | 4 137 | 0.05 | 18 544 | 0.06 | 2 056 543 | 6.68 | 232 | 0.00 | 28 517 488 | 92.61 | |
| XC20 | 28 181 536 | 27 748 448 | 100 | 121 045 | 0.44 | 26 104 | 0.09 | 27 422 | 0.10 | 3 140 979 | 11.32 | 289 | 0.00 | 24 432 609 | 88.05 | |
| XT5 | 27 616 282 | 27 182 187 | 100 | 148 168 | 0.55 | 22 745 | 0.08 | 15 564 | 0.06 | 1 554 941 | 5.72 | 341 | 0.00 | 25 440 428 | 93.59 | |
| XT10 | 28 651 787 | 28 266 164 | 100 | 249120 | 0.88 | 51 729 | 0.18 | 24 077 | 0.09 | 2 284 965 | 8.08 | 248 | 0.00 | 25 656 025 | 90.77 | |
| XT20 | 32 747 097 | 32 299 479 | 100 | 218 084 | 0.68 | 44 324 | 0.14 | 24 153 | 0.07 | 2 488 524 | 7.70 | 309 | 0.00 | 29 524 085 | 91.41 | |
| YC5 | 30 759 202 | 30 341 902 | 100 | 184 708 | 0.61 | 47 254 | 0.16 | 34 138 | 0.11 | 3 415 914 | 11.26 | 214 | 0.00 | 26 659 674 | 87.86 | |
| YC10 | 27 189 430 | 26 824 480 | 100 | 157 101 | 0.59 | 45 378 | 0.17 | 18 941 | 0.07 | 1 628 709 | 6.07 | 211 | 0.00 | 24 974 140 | 93.10 | |
| YC20 | 27 268 095 | 26 892 808 | 100 | 202 043 | 0.75 | 65 279 | 0.24 | 34 931 | 0.13 | 2 768 115 | 10.29 | 229 | 0.00 | 23 822 211 | 88.58 | |
| YT5 | 30 414 313 | 29 998 079 | 100 | 216 264 | 0.72 | 35 100 | 0.12 | 38 493 | 0.13 | 3 363 923 | 11.21 | 200 | 0.00 | 26 344 099 | 87.82 | |
| YT10 | 27 931 541 | 27 555 540 | 100 | 210 300 | 0.76 | 53 864 | 0.20 | 30 147 | 0.11 | 2 737 133 | 9.93 | 151 | 0.00 | 24 523 945 | 89.00 | |
| YT20 | 26 721 361 | 26 354 686 | 100 | 147 538 | 0.56 | 39 329 | 0.15 | 30 794 | 0.12 | 2 958 468 | 11.23 | 154 | 0.00 | 23 178 403 | 87.95 | |
| Total | 351 570 406 | 319 720 133 | 2 200 531 | 449 838 | 327 847 | 31 433 308 | 2 938 | 312 120 151 | ||||||||
Supplemental Table 1. Summary of reads collected by RNA-seq from twelve libraries.
| Library | Total read | High quality | 3′ adapter null | Insert null | 5′ adapter contaminant | Smaller than 18 nt | polyA | Clean read | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Count | % | Count | % | Count | % | Count | % | Count | % | Count | % | Count | % | ||
| XC5 | 32 799 952 | 32 287 444 | 100 | 159 708 | 0.49 | 14 595 | 0.05 | 30 643 | 0.09 | 3 035 094 | 9.40 | 360 | 0.00 | 29 047 044 | 89.96 | |
| XC10 | 31 289 810 | 30 793 396 | 100 | 186 452 | 0.61 | 4 137 | 0.05 | 18 544 | 0.06 | 2 056 543 | 6.68 | 232 | 0.00 | 28 517 488 | 92.61 | |
| XC20 | 28 181 536 | 27 748 448 | 100 | 121 045 | 0.44 | 26 104 | 0.09 | 27 422 | 0.10 | 3 140 979 | 11.32 | 289 | 0.00 | 24 432 609 | 88.05 | |
| XT5 | 27 616 282 | 27 182 187 | 100 | 148 168 | 0.55 | 22 745 | 0.08 | 15 564 | 0.06 | 1 554 941 | 5.72 | 341 | 0.00 | 25 440 428 | 93.59 | |
| XT10 | 28 651 787 | 28 266 164 | 100 | 249120 | 0.88 | 51 729 | 0.18 | 24 077 | 0.09 | 2 284 965 | 8.08 | 248 | 0.00 | 25 656 025 | 90.77 | |
| XT20 | 32 747 097 | 32 299 479 | 100 | 218 084 | 0.68 | 44 324 | 0.14 | 24 153 | 0.07 | 2 488 524 | 7.70 | 309 | 0.00 | 29 524 085 | 91.41 | |
| YC5 | 30 759 202 | 30 341 902 | 100 | 184 708 | 0.61 | 47 254 | 0.16 | 34 138 | 0.11 | 3 415 914 | 11.26 | 214 | 0.00 | 26 659 674 | 87.86 | |
| YC10 | 27 189 430 | 26 824 480 | 100 | 157 101 | 0.59 | 45 378 | 0.17 | 18 941 | 0.07 | 1 628 709 | 6.07 | 211 | 0.00 | 24 974 140 | 93.10 | |
| YC20 | 27 268 095 | 26 892 808 | 100 | 202 043 | 0.75 | 65 279 | 0.24 | 34 931 | 0.13 | 2 768 115 | 10.29 | 229 | 0.00 | 23 822 211 | 88.58 | |
| YT5 | 30 414 313 | 29 998 079 | 100 | 216 264 | 0.72 | 35 100 | 0.12 | 38 493 | 0.13 | 3 363 923 | 11.21 | 200 | 0.00 | 26 344 099 | 87.82 | |
| YT10 | 27 931 541 | 27 555 540 | 100 | 210 300 | 0.76 | 53 864 | 0.20 | 30 147 | 0.11 | 2 737 133 | 9.93 | 151 | 0.00 | 24 523 945 | 89.00 | |
| YT20 | 26 721 361 | 26 354 686 | 100 | 147 538 | 0.56 | 39 329 | 0.15 | 30 794 | 0.12 | 2 958 468 | 11.23 | 154 | 0.00 | 23 178 403 | 87.95 | |
| Total | 351 570 406 | 319 720 133 | 2 200 531 | 449 838 | 327 847 | 31 433 308 | 2 938 | 312 120 151 | ||||||||
| Library | miRNA | rRNA | Repeat | snRNA | snoRNA | tRNA | Unannotation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XC5 | 7 078 | 0.17% | 671 405 | 16.02% | 2 141 | 0.05% | 12 063 | 0.29% | 9 575 | 0.23% | 51 491 | 1.23% | 2 607 435 | 62.23% |
| XC10 | 6 790 | 0.16% | 702 101 | 16.37% | 2 102 | 0.05% | 13 433 | 0.31% | 11 867 | 0.28% | 47 947 | 1.12% | 2 706 094 | 63.09% |
| XC20 | 6 654 | 0.16% | 558 686 | 13.49% | 2 040 | 0.05% | 12 297 | 0.30% | 10 539 | 0.25% | 50 108 | 1.21% | 2 719 682 | 65.68% |
| XT5 | 7 012 | 0.16% | 583 595 | 13.55% | 2 270 | 0.05% | 12 214 | 0.28% | 10 942 | 0.25% | 43 689 | 1.01% | 2 802 198 | 65.04% |
| XT10 | 6 384 | 0.16% | 624 579 | 15.83% | 1 873 | 0.05% | 11 641 | 0.29% | 9 409 | 0.24% | 43 291 | 1.10% | 2 517 937 | 63.80% |
| XT20 | 7 323 | 0.15% | 679 675 | 13.74% | 2 400 | 0.05% | 13 356 | 0.27% | 12 086 | 0.24% | 55 485 | 1.12% | 3 294 453 | 66.58% |
| YC5 | 5 997 | 0.15% | 539 626 | 13.27% | 2 250 | 0.06% | 7 605 | 0.19% | 9 924 | 0.24% | 36 877 | 0.91% | 2 800 361 | 68.88% |
| YC10 | 5 556 | 0.14% | 576 120 | 14.31% | 2 181 | 0.05% | 7 888 | 0.20% | 9 264 | 0.23% | 36 218 | 0.90% | 2 781 134 | 69.06% |
| YC20 | 4 890 | 0.15% | 548 609 | 16.81% | 1 770 | 0.05% | 8 298 | 0.25% | 9 517 | 0.29% | 36 568 | 1.12% | 2 098 698 | 64.30% |
| YT5 | 5 628 | 0.15% | 597 566 | 16.43% | 1 969 | 0.05% | 8 058 | 0.22% | 8 766 | 0.24% | 37 700 | 1.04% | 2 388 685 | 65.68% |
| YT10 | 5 351 | 0.15% | 564 840 | 15.75% | 1 921 | 0.05% | 8 072 | 0.23% | 9 744 | 0.27% | 41 557 | 1.16% | 2 379 169 | 66.34% |
| YT20 | 5 509 | 0.16% | 487 539 | 14.12% | 2 119 | 0.06% | 7 464 | 0.22% | 8 455 | 0.24% | 29 764 | 0.86% | 2 318 216 | 67.16% |
Supplemental Table 2. Exploring miRNA regulation in rice responding to R. solani invasion.
| Library | miRNA | rRNA | Repeat | snRNA | snoRNA | tRNA | Unannotation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XC5 | 7 078 | 0.17% | 671 405 | 16.02% | 2 141 | 0.05% | 12 063 | 0.29% | 9 575 | 0.23% | 51 491 | 1.23% | 2 607 435 | 62.23% |
| XC10 | 6 790 | 0.16% | 702 101 | 16.37% | 2 102 | 0.05% | 13 433 | 0.31% | 11 867 | 0.28% | 47 947 | 1.12% | 2 706 094 | 63.09% |
| XC20 | 6 654 | 0.16% | 558 686 | 13.49% | 2 040 | 0.05% | 12 297 | 0.30% | 10 539 | 0.25% | 50 108 | 1.21% | 2 719 682 | 65.68% |
| XT5 | 7 012 | 0.16% | 583 595 | 13.55% | 2 270 | 0.05% | 12 214 | 0.28% | 10 942 | 0.25% | 43 689 | 1.01% | 2 802 198 | 65.04% |
| XT10 | 6 384 | 0.16% | 624 579 | 15.83% | 1 873 | 0.05% | 11 641 | 0.29% | 9 409 | 0.24% | 43 291 | 1.10% | 2 517 937 | 63.80% |
| XT20 | 7 323 | 0.15% | 679 675 | 13.74% | 2 400 | 0.05% | 13 356 | 0.27% | 12 086 | 0.24% | 55 485 | 1.12% | 3 294 453 | 66.58% |
| YC5 | 5 997 | 0.15% | 539 626 | 13.27% | 2 250 | 0.06% | 7 605 | 0.19% | 9 924 | 0.24% | 36 877 | 0.91% | 2 800 361 | 68.88% |
| YC10 | 5 556 | 0.14% | 576 120 | 14.31% | 2 181 | 0.05% | 7 888 | 0.20% | 9 264 | 0.23% | 36 218 | 0.90% | 2 781 134 | 69.06% |
| YC20 | 4 890 | 0.15% | 548 609 | 16.81% | 1 770 | 0.05% | 8 298 | 0.25% | 9 517 | 0.29% | 36 568 | 1.12% | 2 098 698 | 64.30% |
| YT5 | 5 628 | 0.15% | 597 566 | 16.43% | 1 969 | 0.05% | 8 058 | 0.22% | 8 766 | 0.24% | 37 700 | 1.04% | 2 388 685 | 65.68% |
| YT10 | 5 351 | 0.15% | 564 840 | 15.75% | 1 921 | 0.05% | 8 072 | 0.23% | 9 744 | 0.27% | 41 557 | 1.16% | 2 379 169 | 66.34% |
| YT20 | 5 509 | 0.16% | 487 539 | 14.12% | 2 119 | 0.06% | 7 464 | 0.22% | 8 455 | 0.24% | 29 764 | 0.86% | 2 318 216 | 67.16% |
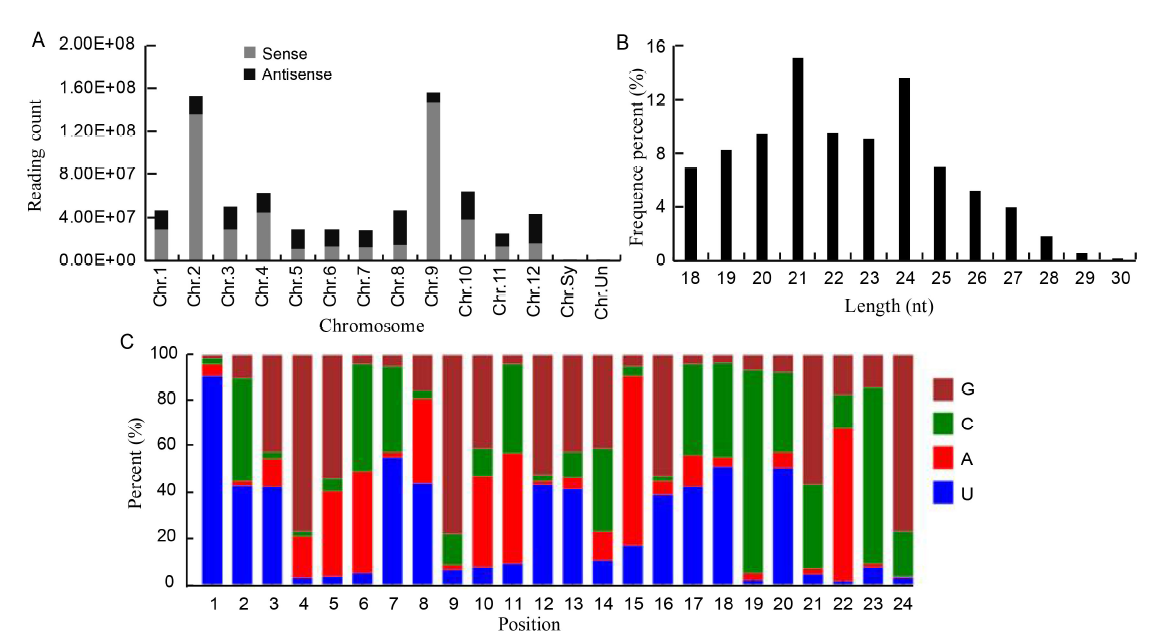
Fig. 2. Properties of sRNAs expressed in resistant and susceptible rice cultivars treated with water or fungal pathogen R. solani. A, Distribution of sRNAs in chromosome. Chr.Sy and Chr.Un are unassemble to pseudomolecule sequences. B, Sequence length percentage of sRNAs. C, miRNA nucleotide bias at each position.
| Library | Known miRNA | Novel miRNA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA | miRNA-5P | miRNA-3P | Target gene number | miRNA | Target gene number | ||
| XC5 | 450 | 81 | 80 | 2 690 | 450 | 9 648 | |
| XC10 | 441 | 81 | 68 | 2 296 | 487 | 8 213 | |
| XC20 | 415 | 73 | 72 | 1 524 | 557 | 9 653 | |
| XT5 | 444 | 76 | 79 | 2 132 | 495 | 8 794 | |
| XT10 | 427 | 76 | 72 | 1 929 | 509 | 12 010 | |
| XT20 | 454 | 79 | 75 | 1 579 | 617 | 11 257 | |
| YC5 | 411 | 74 | 68 | 2 584 | 581 | 4 857 | |
| YC10 | 405 | 69 | 70 | 1 846 | 539 | 8 177 | |
| YC20 | 402 | 75 | 61 | 1 804 | 457 | 6 881 | |
| YT5 | 420 | 77 | 70 | 2 303 | 515 | 7 737 | |
| YT10 | 403 | 74 | 70 | 1 888 | 571 | 8 974 | |
| YT20 | 406 | 72 | 69 | 1 834 | 560 | 5 542 | |
Supplemental Table 3. Number of known/novel miRNAs and target genes from each library.
| Library | Known miRNA | Novel miRNA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA | miRNA-5P | miRNA-3P | Target gene number | miRNA | Target gene number | ||
| XC5 | 450 | 81 | 80 | 2 690 | 450 | 9 648 | |
| XC10 | 441 | 81 | 68 | 2 296 | 487 | 8 213 | |
| XC20 | 415 | 73 | 72 | 1 524 | 557 | 9 653 | |
| XT5 | 444 | 76 | 79 | 2 132 | 495 | 8 794 | |
| XT10 | 427 | 76 | 72 | 1 929 | 509 | 12 010 | |
| XT20 | 454 | 79 | 75 | 1 579 | 617 | 11 257 | |
| YC5 | 411 | 74 | 68 | 2 584 | 581 | 4 857 | |
| YC10 | 405 | 69 | 70 | 1 846 | 539 | 8 177 | |
| YC20 | 402 | 75 | 61 | 1 804 | 457 | 6 881 | |
| YT5 | 420 | 77 | 70 | 2 303 | 515 | 7 737 | |
| YT10 | 403 | 74 | 70 | 1 888 | 571 | 8 974 | |
| YT20 | 406 | 72 | 69 | 1 834 | 560 | 5 542 | |
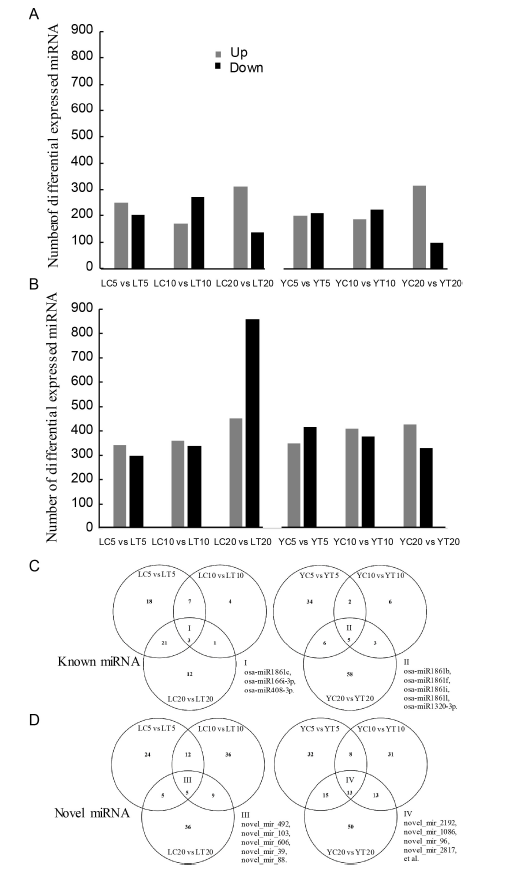
Supplemental Fig. 2. Properties of differential expressed miRNAs in resistant and susceptible rice cultivars treated with water or the fungal pathogen R. solani. A, B Differential expressed known/novel miRNAs, respectively. C, D Venn diagrams presented for the miRNAs in 5 dpi, 10 dpi and 20 dpi respectively for known/novel miRNAs from two rice varieties, respectively.
| miRNA | Compared libraries | Co-expressed miRNAs ID in three time points in Venn |
|---|---|---|
| Known miRNA | XC/XT (3) | osa-miR1861c, osa-miR166i-3p, osa-miR408-3p |
| YC/YT (5) | osa-miR1861b, osa-miR1861f, osa-miR1861i, osa-miR1861l, osa-miR1320-3p | |
| XT/YT (66) | osa-miR5340, osa-miR531a, osa-miR531b, osa-miR531c, osa-miR530-5p, osa-miR3980a-5p, osa-miR3980b-5p, osa-miR398b, osa-miR3980a-3p, osa-miR3980b-3p, osa-miR408-3p, osa-miR812g, osa-miR1861e, osa-miR1861k, osa-miR1861m, osa-miR1863c, osa-miR812h, osa-miR812i, osa-miR1860-3p, osa-miR1881, osa-miR444a-3p.2, osa-miR444e, osa-miR1861h, osa-miR1861j, osa-miR1876, osa-miR397b, osa-miR528-5p, osa-miR397a, osa-miR408-5p, osa-miR2880, osa-miR1846a-5p, osa-miR1846b-5p, osa-miR5814, osa-miR2871b, osa-miR167e-3p, osa-miR167i-3p, osa-miR5337a, osa-miR156d, osa-miR156f-5p, osa-miR156h-5p, osa-miR156j-5p, osa-miR535-3p, osa-miR1846c-5p, osa-miR5788, osa-miR156b-5p, osa-miR156c-5p, osa-miR156g-5p, osa-miR156a, osa-miR156e, osa-miR156i, osa-miR1846a-3p, osa-miR2106, osa-miR1874-3p, osa-miR1846b-3p, osa-miR5149, osa-miR1883a, osa-miR1883b, osa-miR1856, osa-miR1862c, osa-miR1862b, osa-miR1862a, osa-miR5807, osa-miR169i-5p.2, osa-miR5827, osa-miR2877, osa-miR1873 | |
| Novel miRNA | XC/XT (5) | novel_mir_492, novel_mir_103, novel_mir_606, novel_mir_39, novel_mir_88 |
| YC/YT (13) | novel_mir_2192, novel_mir_1086, novel_mir_96, novel_mir_2817, novel_mir_370, novel_mir_2307, novel_mir_2162, novel_mir_2598, novel_mir_1968, novel_mir_1228, novel_mir_2595, novel_mir_2720, novel_mir_1576 | |
| XT/YT (45) | novel_mir_1950, novel_mir_2064, novel_mir_1962, novel_mir_2242, novel_mir_2088, novel_mir_2006, novel_mir_2225, novel_mir_735, novel_mir_1956, novel_mir_2598, novel_mir_2048, novel_mir_2817, novel_mir_2338, novel_mir_2067, novel_mir_2101, novel_mir_2164, novel_mir_1957, novel_mir_1086, novel_mir_26, novel_mir_37, novel_mir_348, novel_mir_177, novel_mir_50, novel_mir_322, novel_mir_287, novel_mir_229, novel_mir_469, novel_mir_781, novel_mir_577, novel_mir_1228, novel_mir_438, novel_mir_1872, novel_mir_478, novel_mir_316, novel_mir_328, novel_mir_468, novel_mir_717, novel_mir_492, novel_mir_174, novel_mir_553, novel_mir_137, novel_mir_273, novel_mir_113, novel_mir_810, novel_mir_382 |
Supplemental Table 4. Details of co-expressed known and novel miRNAs from different libraries in three time points in Venn.
| miRNA | Compared libraries | Co-expressed miRNAs ID in three time points in Venn |
|---|---|---|
| Known miRNA | XC/XT (3) | osa-miR1861c, osa-miR166i-3p, osa-miR408-3p |
| YC/YT (5) | osa-miR1861b, osa-miR1861f, osa-miR1861i, osa-miR1861l, osa-miR1320-3p | |
| XT/YT (66) | osa-miR5340, osa-miR531a, osa-miR531b, osa-miR531c, osa-miR530-5p, osa-miR3980a-5p, osa-miR3980b-5p, osa-miR398b, osa-miR3980a-3p, osa-miR3980b-3p, osa-miR408-3p, osa-miR812g, osa-miR1861e, osa-miR1861k, osa-miR1861m, osa-miR1863c, osa-miR812h, osa-miR812i, osa-miR1860-3p, osa-miR1881, osa-miR444a-3p.2, osa-miR444e, osa-miR1861h, osa-miR1861j, osa-miR1876, osa-miR397b, osa-miR528-5p, osa-miR397a, osa-miR408-5p, osa-miR2880, osa-miR1846a-5p, osa-miR1846b-5p, osa-miR5814, osa-miR2871b, osa-miR167e-3p, osa-miR167i-3p, osa-miR5337a, osa-miR156d, osa-miR156f-5p, osa-miR156h-5p, osa-miR156j-5p, osa-miR535-3p, osa-miR1846c-5p, osa-miR5788, osa-miR156b-5p, osa-miR156c-5p, osa-miR156g-5p, osa-miR156a, osa-miR156e, osa-miR156i, osa-miR1846a-3p, osa-miR2106, osa-miR1874-3p, osa-miR1846b-3p, osa-miR5149, osa-miR1883a, osa-miR1883b, osa-miR1856, osa-miR1862c, osa-miR1862b, osa-miR1862a, osa-miR5807, osa-miR169i-5p.2, osa-miR5827, osa-miR2877, osa-miR1873 | |
| Novel miRNA | XC/XT (5) | novel_mir_492, novel_mir_103, novel_mir_606, novel_mir_39, novel_mir_88 |
| YC/YT (13) | novel_mir_2192, novel_mir_1086, novel_mir_96, novel_mir_2817, novel_mir_370, novel_mir_2307, novel_mir_2162, novel_mir_2598, novel_mir_1968, novel_mir_1228, novel_mir_2595, novel_mir_2720, novel_mir_1576 | |
| XT/YT (45) | novel_mir_1950, novel_mir_2064, novel_mir_1962, novel_mir_2242, novel_mir_2088, novel_mir_2006, novel_mir_2225, novel_mir_735, novel_mir_1956, novel_mir_2598, novel_mir_2048, novel_mir_2817, novel_mir_2338, novel_mir_2067, novel_mir_2101, novel_mir_2164, novel_mir_1957, novel_mir_1086, novel_mir_26, novel_mir_37, novel_mir_348, novel_mir_177, novel_mir_50, novel_mir_322, novel_mir_287, novel_mir_229, novel_mir_469, novel_mir_781, novel_mir_577, novel_mir_1228, novel_mir_438, novel_mir_1872, novel_mir_478, novel_mir_316, novel_mir_328, novel_mir_468, novel_mir_717, novel_mir_492, novel_mir_174, novel_mir_553, novel_mir_137, novel_mir_273, novel_mir_113, novel_mir_810, novel_mir_382 |
| Species | MIR821 | MIR1428 | MIR169_5 | MIR1435 | MIR1437 | MIR1440 | MIR1846 | MIR1858 | MIR2118 | MIR1861 | MIR1862 | MIR1878 | MIR1882 | MIR1883 | MIR1319 | MIR827 | MIR2121 | MIR2275 | MIR2863 | MIR2871 | MIR2873 | MIR1863 | MIR396_2 | MIR2907 | MIR3980 | MIR5079 | MIR5143 | MIR5148 | MIR5157 | MIR5160 | MIR5179 | MIR5512 | MIR5516 | MIR5534 | MIR5539 | MIR806 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oryza_sativa | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Arabidopsis_thaliana | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Zea_mays | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Sorghum_bicolor | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Medicago_truncatula | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Saccharum_officinarum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Glycine_max | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Populus_trichocarpa | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Physcomitrella_patens | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_hirsutum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_raimondii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_herbaceum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Chlamydomonas_reinhardtii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brassica_napus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pinus_taeda | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Selaginella_moellendorffii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Triticum_aestivum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Carica_papaya | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brassica_oleracea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brassica_rapa | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Vitis_vinifera | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Solanum_lycopersicum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Lotus_japonicus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Vigna_unguiculata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Malus_domestica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Phaseolus_vulgaris | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brachypodium_distachyon | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Aquilegia_caerulea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Populus_euphratica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_trifoliata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_sinensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_clementina | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_reticulata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ricinus_communis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_arboreum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Arabidopsis_lyrata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Arachis_hypogaea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Glycine_soja | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Picea_abies | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Hordeum_vulgare | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Triticum_turgidum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Festuca_arundinacea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bruguiera_gymnorhiza | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bruguiera_cylindrica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Theobroma_cacao | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Rehmannia_glutinosa | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cucumis_melo | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Saccharum_sp. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Acacia_auriculiformis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Acacia_mangium | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Salvia_sclarea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Digitalis_purpurea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Nicotiana_tabacum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Solanum_tuberosum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Elaeis_guineensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Manihot_esculenta | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cynara_cardunculus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Linum_usitatissimum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Panax_ginseng | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Hevea_brasiliensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Prunus_persica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pinus_densata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_annuus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_ciliaris | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_tuberosus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_argophyllus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_paradoxus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_petiolaris | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_exilis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cunninghamia_lanceolata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Avicennia_marina | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Amborella_trichopoda | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Aegilops_tauschii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Species | MIR821 | MIR1428 | MIR169_5 | MIR1435 | MIR1437 | MIR1440 | MIR1846 | MIR1858 | MIR2118 | MIR1861 | MIR1862 | MIR1878 | MIR1882 | MIR1883 | MIR1319 | MIR827 | MIR2121 | MIR2275 | MIR2863 | MIR2871 | MIR2873 | MIR1863 | MIR396_2 | MIR2907 | MIR3980 | MIR5079 | MIR5143 | MIR5148 | MIR5157 | MIR5160 | MIR5179 | MIR5512 | MIR5516 | MIR5534 | MIR5539 | MIR806 |
| Oryza_sativa | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Arabidopsis_thaliana | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Zea_mays | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Sorghum_bicolor | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Medicago_truncatula | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Saccharum_officinarum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Glycine_max | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Populus_trichocarpa | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Physcomitrella_patens | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_hirsutum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_raimondii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_herbaceum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Chlamydomonas_reinhardtii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brassica_napus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pinus_taeda | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Selaginella_moellendorffii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Triticum_aestivum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Carica_papaya | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brassica_oleracea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brassica_rapa | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Vitis_vinifera | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Solanum_lycopersicum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Lotus_japonicus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Vigna_unguiculata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Malus_domestica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Phaseolus_vulgaris | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brachypodium_distachyon | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Aquilegia_caerulea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Populus_euphratica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_trifoliata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_sinensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_clementina | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_reticulata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ricinus_communis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_arboreum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Arabidopsis_lyrata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Arachis_hypogaea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Glycine_soja | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Picea_abies | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Hordeum_vulgare | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Triticum_turgidum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Festuca_arundinacea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bruguiera_gymnorhiza | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bruguiera_cylindrica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Theobroma_cacao | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Rehmannia_glutinosa | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cucumis_melo | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Saccharum_sp. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Acacia_auriculiformis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Acacia_mangium | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Salvia_sclarea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Digitalis_purpurea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Nicotiana_tabacum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Solanum_tuberosum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Elaeis_guineensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Manihot_esculenta | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cynara_cardunculus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Linum_usitatissimum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Panax_ginseng | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Hevea_brasiliensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Prunus_persica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pinus_densata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_annuus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_ciliaris | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_tuberosus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_argophyllus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_paradoxus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_petiolaris | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_exilis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cunninghamia_lanceolata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Avicennia_marina | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Amborella_trichopoda | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Aegilops_tauschii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Supplemental Table 5. GO miRNA family analysis.
| Species | MIR821 | MIR1428 | MIR169_5 | MIR1435 | MIR1437 | MIR1440 | MIR1846 | MIR1858 | MIR2118 | MIR1861 | MIR1862 | MIR1878 | MIR1882 | MIR1883 | MIR1319 | MIR827 | MIR2121 | MIR2275 | MIR2863 | MIR2871 | MIR2873 | MIR1863 | MIR396_2 | MIR2907 | MIR3980 | MIR5079 | MIR5143 | MIR5148 | MIR5157 | MIR5160 | MIR5179 | MIR5512 | MIR5516 | MIR5534 | MIR5539 | MIR806 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oryza_sativa | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Arabidopsis_thaliana | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Zea_mays | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Sorghum_bicolor | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Medicago_truncatula | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Saccharum_officinarum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Glycine_max | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Populus_trichocarpa | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Physcomitrella_patens | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_hirsutum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_raimondii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_herbaceum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Chlamydomonas_reinhardtii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brassica_napus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pinus_taeda | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Selaginella_moellendorffii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Triticum_aestivum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Carica_papaya | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brassica_oleracea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brassica_rapa | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Vitis_vinifera | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Solanum_lycopersicum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Lotus_japonicus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Vigna_unguiculata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Malus_domestica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Phaseolus_vulgaris | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brachypodium_distachyon | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Aquilegia_caerulea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Populus_euphratica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_trifoliata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_sinensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_clementina | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_reticulata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ricinus_communis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_arboreum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Arabidopsis_lyrata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Arachis_hypogaea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Glycine_soja | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Picea_abies | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Hordeum_vulgare | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Triticum_turgidum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Festuca_arundinacea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bruguiera_gymnorhiza | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bruguiera_cylindrica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Theobroma_cacao | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Rehmannia_glutinosa | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cucumis_melo | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Saccharum_sp. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Acacia_auriculiformis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Acacia_mangium | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Salvia_sclarea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Digitalis_purpurea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Nicotiana_tabacum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Solanum_tuberosum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Elaeis_guineensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Manihot_esculenta | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cynara_cardunculus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Linum_usitatissimum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Panax_ginseng | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Hevea_brasiliensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Prunus_persica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pinus_densata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_annuus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_ciliaris | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_tuberosus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_argophyllus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_paradoxus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_petiolaris | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_exilis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cunninghamia_lanceolata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Avicennia_marina | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Amborella_trichopoda | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Aegilops_tauschii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Species | MIR821 | MIR1428 | MIR169_5 | MIR1435 | MIR1437 | MIR1440 | MIR1846 | MIR1858 | MIR2118 | MIR1861 | MIR1862 | MIR1878 | MIR1882 | MIR1883 | MIR1319 | MIR827 | MIR2121 | MIR2275 | MIR2863 | MIR2871 | MIR2873 | MIR1863 | MIR396_2 | MIR2907 | MIR3980 | MIR5079 | MIR5143 | MIR5148 | MIR5157 | MIR5160 | MIR5179 | MIR5512 | MIR5516 | MIR5534 | MIR5539 | MIR806 |
| Oryza_sativa | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Arabidopsis_thaliana | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Zea_mays | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Sorghum_bicolor | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Medicago_truncatula | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Saccharum_officinarum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Glycine_max | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Populus_trichocarpa | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Physcomitrella_patens | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_hirsutum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_raimondii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_herbaceum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Chlamydomonas_reinhardtii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brassica_napus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pinus_taeda | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Selaginella_moellendorffii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Triticum_aestivum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Carica_papaya | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brassica_oleracea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brassica_rapa | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Vitis_vinifera | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Solanum_lycopersicum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Lotus_japonicus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Vigna_unguiculata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Malus_domestica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Phaseolus_vulgaris | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brachypodium_distachyon | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Aquilegia_caerulea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Populus_euphratica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_trifoliata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_sinensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_clementina | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Citrus_reticulata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ricinus_communis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gossypium_arboreum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Arabidopsis_lyrata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Arachis_hypogaea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Glycine_soja | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Picea_abies | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Hordeum_vulgare | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Triticum_turgidum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Festuca_arundinacea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bruguiera_gymnorhiza | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bruguiera_cylindrica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Theobroma_cacao | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Rehmannia_glutinosa | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cucumis_melo | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Saccharum_sp. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Acacia_auriculiformis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Acacia_mangium | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Salvia_sclarea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Digitalis_purpurea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Nicotiana_tabacum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Solanum_tuberosum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Elaeis_guineensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Manihot_esculenta | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cynara_cardunculus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Linum_usitatissimum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Panax_ginseng | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Hevea_brasiliensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Prunus_persica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pinus_densata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_annuus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_ciliaris | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_tuberosus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_argophyllus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_paradoxus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_petiolaris | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Helianthus_exilis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cunninghamia_lanceolata | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Avicennia_marina | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Amborella_trichopoda | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Aegilops_tauschii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| miRNA family | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| miR531 | Involved in MAP kinase signaling cascade | [57] |
| miR810 | Response to drought stress | [49] |
| miR812 | Response to H2O2 stress | [50] |
| miR814 | Response to drought stress | [51] |
| miR815 | Response to drought stress | [52] |
| miR820 | Response to salt stress | [53] |
| miR1846 | Response to low-N stress | [54] |
| miR1861 | Developmental and signaling pathways | [55] |
| miR1862 | Response to H2O2 stress | [50] |
| miR2863 | Response to fungal elicitors | [22] |
| miR2871 | Response to drought, cold and salt stress | [56] |
| miR1863 | Required for silencing heterochromatin by methylation in rice | [58] |
Supplemental Table 6. Functions of miRNA families specially present in rice.
| miRNA family | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| miR531 | Involved in MAP kinase signaling cascade | [57] |
| miR810 | Response to drought stress | [49] |
| miR812 | Response to H2O2 stress | [50] |
| miR814 | Response to drought stress | [51] |
| miR815 | Response to drought stress | [52] |
| miR820 | Response to salt stress | [53] |
| miR1846 | Response to low-N stress | [54] |
| miR1861 | Developmental and signaling pathways | [55] |
| miR1862 | Response to H2O2 stress | [50] |
| miR2863 | Response to fungal elicitors | [22] |
| miR2871 | Response to drought, cold and salt stress | [56] |
| miR1863 | Required for silencing heterochromatin by methylation in rice | [58] |
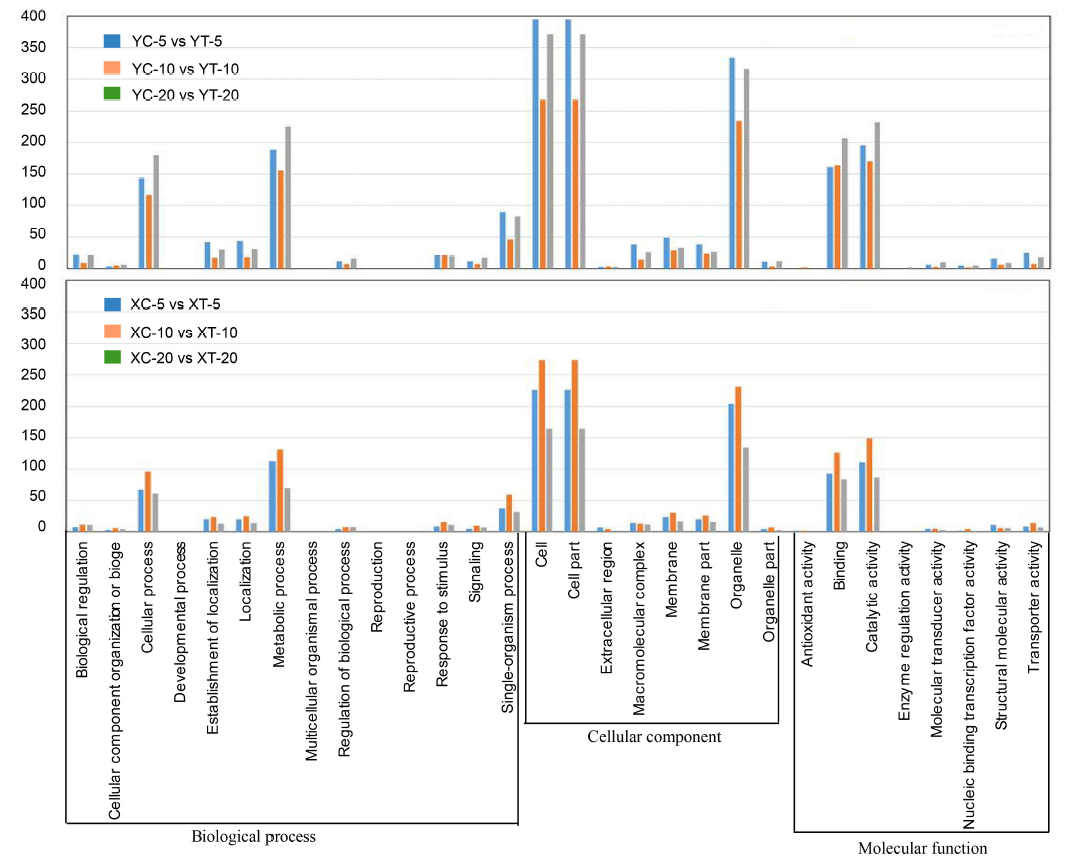
Fig. 3. Gene ontology analysis with frequencies more than 1% found for coding regions of unigenes derived from water and pathogen treatments at different time points. XC, Xudao 3 treated with water; XT, Xudao 3 treated with R. solani; YC, YSBR1 treated with water; YT, YSBR1 treated with R. solani. The upper panel for susceptible cultivar Xudao 3, and the lower panel for resistant cultivar YSBR1.
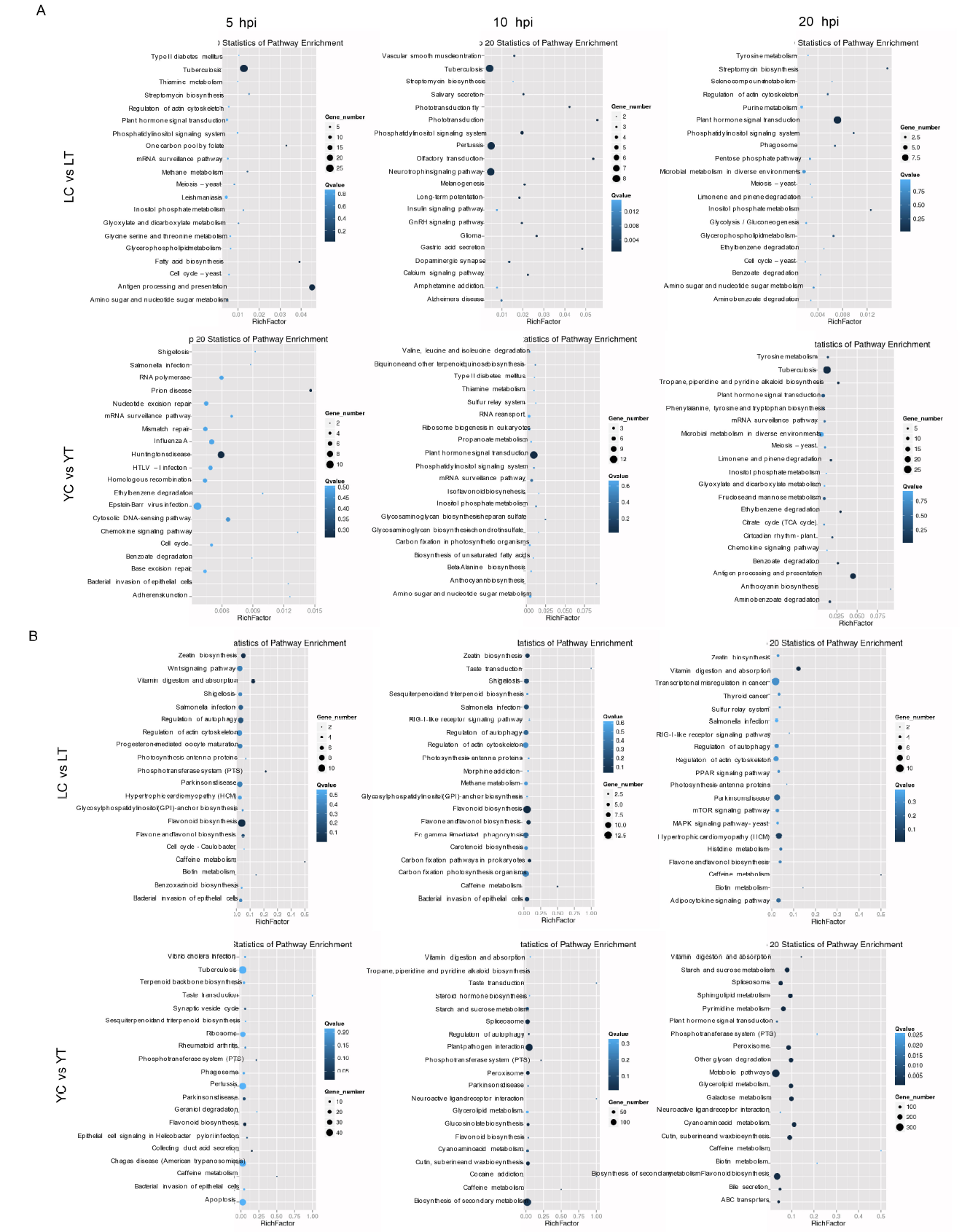
Supplemental Fig. 4. KEGG pathway based on GO terms classification of enrichment analysis unigenes differentially expressed between the water and pathogen treatment at different time point. A, Known miRNAs from Lemond libraries (upper panel) and YSBR1 (bottom panel). B, Novel miRNAs from Lemond libraries (upper panel) and YSBR1 (bottom panel).
| Pathway | Annotation | Target genes involved in the pathway |
|---|---|---|
| Plant-pathogen interaction (RNA-seq) | WRKY protein (6 genes) | LOC_Os01g08710.1, LOC_Os01g08710.2, LOC_Os02g43560.1, LOC_Os06g05380.1, LOC_Os11g45750.1, LOC_Os11g45750.2. |
| NB domain containing protein (42 genes) | LOC_Os01g16390.1, LOC_Os02g19750.1, LOC_Os06g06390.1, LOC_Os06g06400.1, LOC_Os07g09940.1, LOC_Os07g40810.1, LOC_Os08g10430.1, LOC_Os08g10440.1, LOC_Os08g30660.1, LOC_Os08g42710.1, LOC_Os09g34150.1, LOC_Os09g34150.2, LOC_Os11g11550.1, LOC_Os11g11550.2, LOC_Os11g11790.1, LOC_Os11g11810.1, LOC_Os11g27430.1, LOC_Os11g34970.1, LOC_Os11g39160.1, LOC_Os11g39260.1, LOC_Os11g39320.1, LOC_Os11g45790.1, LOC_Os11g45930.1, LOC_Os11g45970.1, LOC_Os11g46080.1, LOC_Os11g46210.1, LOC_Os12g06920.1, LOC_Os12g09710.1, LOC_Os12g10410.1, LOC_Os12g13550.1, LOC_Os12g17410.1, LOC_Os12g18374.2, LOC_Os12g28100.1, LOC_Os03g46550.1, LOC_Os11g15190.1, LOC_Os12g37760.1, LOC_Os12g37770.1, LOC_Os05g40150.1, LOC_Os10g22484.1, LOC_Os10g22484.2, LOC_Os10g22484.3, LOC_Os11g45780.1. | |
| Retrotransposon protein (32 genes) | LOC_Os01g16500.1, LOC_Os01g29270.1, LOC_Os02g17820.1, LOC_Os02g18290.1, LOC_Os02g22040.1, LOC_Os02g32090.1, LOC_Os02g32880.1, LOC_Os02g41702.1, LOC_Os02g43260.1, LOC_Os02g47270.1, LOC_Os03g30990.1, LOC_Os03g62040.1, LOC_Os04g03120.1, LOC_Os04g14770.1, LOC_Os04g45420.1, LOC_Os05g31860.1, LOC_Os05g51320.1, LOC_Os06g24670.1, LOC_Os06g30110.1, LOC_Os06g39310.1, LOC_Os07g14800.1, LOC_Os07g24810.1, LOC_Os07g31170.1, LOC_Os07g40050.1, LOC_Os07g43090.1, LOC_Os07g49170.1, LOC_Os08g16530.1, LOC_Os09g14720.1, LOC_Os10g32250.1, LOC_Os11g43230.1, LOC_Os12g23374.1, LOC_Os12g25510.1. | |
| Stripe rust resistance protein (7 genes) | LOC_Os01g23380.1, LOC_Os07g09910.1, LOC_Os10g04342.1, LOC_Os11g15500.1, LOC_Os11g32170.1, LOC_Os11g34920.1, LOC_Os12g17490.1. | |
| Disease resistance protein (12 genes) | LOC_Os01g57870.1, LOC_Os01g57870.2, LOC_Os04g11760.1, LOC_Os08g07774.1, LOC_Os08g07920.1, LOC_Os08g07940.1, LOC_Os08g28470.1, LOC_Os11g12040.1, LOC_Os11g16510.1, LOC_Os11g29030.1, LOC_Os12g28250.1, LOC_Os02g17304.1. | |
| Resistance protein (10 genes) | LOC_Os04g11780.1, LOC_Os06g06850.1, LOC_Os07g27370.1, LOC_Os08g29809.1, LOC_Os08g42670.1, LOC_Os08g42670.2, LOC_Os08g42700.1, LOC_Os11g11920.1, LOC_Os11g14380.1, LOC_Os12g37290.1. | |
| Mla (9 genes) | LOC_Os06g06860.1, LOC_Os08g31780.1, LOC_Os10g22510.1, LOC_Os11g13410.1, LOC_Os11g16470.1, LOC_Os11g16470.2, LOC_Os11g16470.3, LOC_Os12g17480.1, LOC_Os10g04110.1. | |
| Receptor kinase (3 genes) | LOC_Os10g32990.1, LOC_Os11g35660.1, LOC_Os11g47160.1. |
Supplemental Table 7 Details of target genes involved in the plant-pathogen interaction pathway.
| Pathway | Annotation | Target genes involved in the pathway |
|---|---|---|
| Plant-pathogen interaction (RNA-seq) | WRKY protein (6 genes) | LOC_Os01g08710.1, LOC_Os01g08710.2, LOC_Os02g43560.1, LOC_Os06g05380.1, LOC_Os11g45750.1, LOC_Os11g45750.2. |
| NB domain containing protein (42 genes) | LOC_Os01g16390.1, LOC_Os02g19750.1, LOC_Os06g06390.1, LOC_Os06g06400.1, LOC_Os07g09940.1, LOC_Os07g40810.1, LOC_Os08g10430.1, LOC_Os08g10440.1, LOC_Os08g30660.1, LOC_Os08g42710.1, LOC_Os09g34150.1, LOC_Os09g34150.2, LOC_Os11g11550.1, LOC_Os11g11550.2, LOC_Os11g11790.1, LOC_Os11g11810.1, LOC_Os11g27430.1, LOC_Os11g34970.1, LOC_Os11g39160.1, LOC_Os11g39260.1, LOC_Os11g39320.1, LOC_Os11g45790.1, LOC_Os11g45930.1, LOC_Os11g45970.1, LOC_Os11g46080.1, LOC_Os11g46210.1, LOC_Os12g06920.1, LOC_Os12g09710.1, LOC_Os12g10410.1, LOC_Os12g13550.1, LOC_Os12g17410.1, LOC_Os12g18374.2, LOC_Os12g28100.1, LOC_Os03g46550.1, LOC_Os11g15190.1, LOC_Os12g37760.1, LOC_Os12g37770.1, LOC_Os05g40150.1, LOC_Os10g22484.1, LOC_Os10g22484.2, LOC_Os10g22484.3, LOC_Os11g45780.1. | |
| Retrotransposon protein (32 genes) | LOC_Os01g16500.1, LOC_Os01g29270.1, LOC_Os02g17820.1, LOC_Os02g18290.1, LOC_Os02g22040.1, LOC_Os02g32090.1, LOC_Os02g32880.1, LOC_Os02g41702.1, LOC_Os02g43260.1, LOC_Os02g47270.1, LOC_Os03g30990.1, LOC_Os03g62040.1, LOC_Os04g03120.1, LOC_Os04g14770.1, LOC_Os04g45420.1, LOC_Os05g31860.1, LOC_Os05g51320.1, LOC_Os06g24670.1, LOC_Os06g30110.1, LOC_Os06g39310.1, LOC_Os07g14800.1, LOC_Os07g24810.1, LOC_Os07g31170.1, LOC_Os07g40050.1, LOC_Os07g43090.1, LOC_Os07g49170.1, LOC_Os08g16530.1, LOC_Os09g14720.1, LOC_Os10g32250.1, LOC_Os11g43230.1, LOC_Os12g23374.1, LOC_Os12g25510.1. | |
| Stripe rust resistance protein (7 genes) | LOC_Os01g23380.1, LOC_Os07g09910.1, LOC_Os10g04342.1, LOC_Os11g15500.1, LOC_Os11g32170.1, LOC_Os11g34920.1, LOC_Os12g17490.1. | |
| Disease resistance protein (12 genes) | LOC_Os01g57870.1, LOC_Os01g57870.2, LOC_Os04g11760.1, LOC_Os08g07774.1, LOC_Os08g07920.1, LOC_Os08g07940.1, LOC_Os08g28470.1, LOC_Os11g12040.1, LOC_Os11g16510.1, LOC_Os11g29030.1, LOC_Os12g28250.1, LOC_Os02g17304.1. | |
| Resistance protein (10 genes) | LOC_Os04g11780.1, LOC_Os06g06850.1, LOC_Os07g27370.1, LOC_Os08g29809.1, LOC_Os08g42670.1, LOC_Os08g42670.2, LOC_Os08g42700.1, LOC_Os11g11920.1, LOC_Os11g14380.1, LOC_Os12g37290.1. | |
| Mla (9 genes) | LOC_Os06g06860.1, LOC_Os08g31780.1, LOC_Os10g22510.1, LOC_Os11g13410.1, LOC_Os11g16470.1, LOC_Os11g16470.2, LOC_Os11g16470.3, LOC_Os12g17480.1, LOC_Os10g04110.1. | |
| Receptor kinase (3 genes) | LOC_Os10g32990.1, LOC_Os11g35660.1, LOC_Os11g47160.1. |
| miRNA | Sequence (5′-3′) | Probe (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| miR444b.2 | UGCAGUUGUUGUCUCAAGCUU | AAGCTTGAGACAACAACTGCA |
| miR531a | CUCGCCGGGGCUGCGUGCCGCCAU | ATGGCGGCACGCAGCCCCGGCGAG |
| miR1861i | CGGUCUUGAGGCAGGAACUGAG | CTCAGTTCCTGCCTCAAGACCG |
| Novel_miR1956 | UGUAUAUCUAAGAAGUAACUU | AAGTTACTTCTTAGATATACA |
| Novel_miR135 | UUCAUCUAGUAUGAGGACGUG | CACGTCCTCATACTAGATGAA |
| U6 | - | GGGGCCATGCTAATCTTCTCTG |
Supplemental Table 8. Primers used for Northern blot analysis in this study.
| miRNA | Sequence (5′-3′) | Probe (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| miR444b.2 | UGCAGUUGUUGUCUCAAGCUU | AAGCTTGAGACAACAACTGCA |
| miR531a | CUCGCCGGGGCUGCGUGCCGCCAU | ATGGCGGCACGCAGCCCCGGCGAG |
| miR1861i | CGGUCUUGAGGCAGGAACUGAG | CTCAGTTCCTGCCTCAAGACCG |
| Novel_miR1956 | UGUAUAUCUAAGAAGUAACUU | AAGTTACTTCTTAGATATACA |
| Novel_miR135 | UUCAUCUAGUAUGAGGACGUG | CACGTCCTCATACTAGATGAA |
| U6 | - | GGGGCCATGCTAATCTTCTCTG |
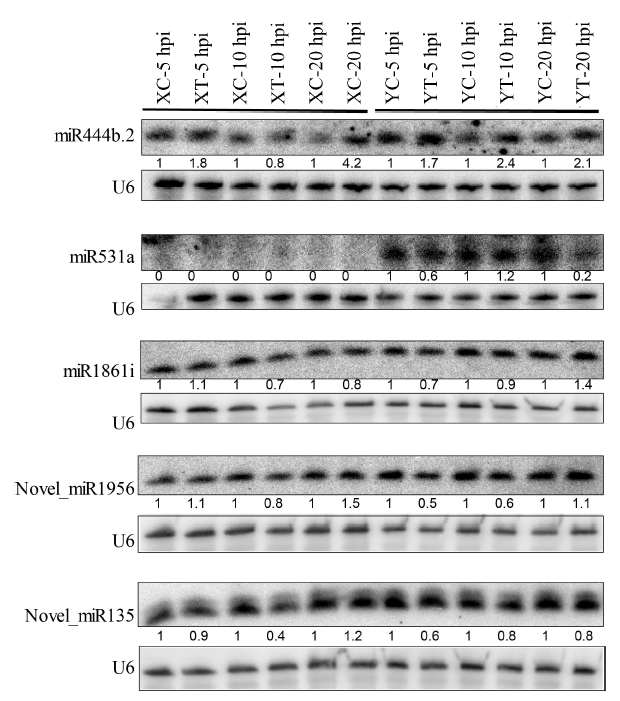
Fig. 4. Expression validation of selected miRNAs by Northern blot analysis. XC, Xudao 3 treated with water; XT, Xudao 3 treated with R. solani; YC, YSBR1 treated with water; YT, YSBR1 treated with R. solani; hpi, Hours post inoculation.The lower sections of the blot for each miRNA were used for the loading control using a U6 oligonucleotide probe. The numbers below each blot present the relative enrichment of individual miRNA in each treatment normalized to the corresponding water-treated control.
| [1] | Arikit S, Zhai J X, Meyers B C. 2013. Biogenesis and function of rice small RNAs from non-coding RNA precursors. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 16(2): 170-179. |
| [2] | Aukerman M J, Sakai H. 2003. Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a microRNA and its APETALA2-like target genes. Plant Cell, 15(11): 2730-2741. |
| [3] | Axtell M J. 2013. Classification and comparison of small RNAs from plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 64: 137-159. |
| [4] | Baldrich P, Campo S, Wu M T, Liu T T, Hsing Y L, San Segundo B. 2015. MicroRNA-mediated regulation of gene expression in the response of rice plants to fungal elicitors. RNA Biol, 12(8): 847-863. |
| [5] | Barrera-Figueroa B E, Gao L, Wu Z G, Zhou X F, Zhu J H, Jin H L, Liu R Y, Zhu J K. 2012. High throughput sequencing reveals novel and abiotic stress-regulated microRNAs in the inflorescences of rice. BMC Plant Biol, 12: 132. |
| [6] | Bartel D P. 2004. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell, 116(2): 281-297. |
| [7] | Baulcombe D. 2004. RNA silencing in plants. Nature, 431: 356-363. |
| [8] | Boccara M, Sarazin A, Thiebeauld O, Jay F, Voinnet O, Navarro L, Colot V. 2014. The Arabidopsis miR472-RDR6 silencing pathway modulates PAMP- and effector-triggered immunity through the post-transcriptional control of disease resistance genes. PLoS Pathog, 10(1): e1003883. |
| [9] | Boller T, Felix G. 2009. A renaissance of elicitors: Perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Ann Rev Plant Biol, 60: 379-406. |
| [10] | Brodersen P, Sakvarelidze-Achard L, Bruun-Rasmussen M, Dunoyer P, Yamamoto Y Y, Sieburth L, Voinnet O. 2008. Widespread translational inhibition by plant miRNAs and siRNAs. Science, 320: 1185-1190. |
| [11] | Campo S, Peris-Peris C, Sire C, Moreno A B, Donaire L, Zytnicki M, Notredame C, Llave C, San Segundo B. 2013. Identification of a novel microRNA (miRNA) from rice that targets an alternatively spliced transcript of the Nramp6 (Natural resistance-associated macrophage protein 6) gene involved in pathogen resistance. New Phytol, 199(1): 212-227. |
| [12] | Cao S J, Zhu Q H, Shen W X, Jiao X M, Zhao X C, Wang M B, Liu L X, Singh S P, Liu Q. 2013. Comparative profiling of miRNA expression in developing seeds of high linoleic and high oleic safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) plants. Front Plant Sci, 4: 489. |
| [13] | Carthew R W, Sontheimer E J. 2009. Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell, 136(4): 642-655. |
| [14] | Cheah B H, Nadarajah K, Divate M D, Wickneswari R. 2015. Identification of four functionally important microRNA families with contrasting differential expression profiles between drought-tolerant and susceptible rice leaf at vegetative stage. BMC Genom, 16(1): 692. |
| [15] | Chen F, Li Q, He Z H. 2007. Proteomic analysis of rice plasma membrane-associated proteins in response to chitooligo- saccharide elicitors. J Integr Plant Biol, 49(6): 863-870. |
| [16] | Chen X J, Chen Y, Zhang L N, Xu B, Zhang J H, Chen Z X, Tong Y H, Zuo S M, Xu J Y. 2016. Overexpression of OsPGIP1 enhances rice resistance to sheath blight. Plant Dis, 100(2): 388-395. |
| [17] | Fei Q L, Xia R, Meyers B C. 2013. Phased, secondary, small interfering RNAs in posttranscriptional regulatory networks. Plant Cell, 25(7): 2400-2415. |
| [18] | Ghildiyal M, Zamore P D. 2009. Small silencing RNAs: An expanding universe. Nat Rev Genet, 10(2): 94-108. |
| [19] | Ito T M, Polido P B, Rampim M C, Kaschuk G, Souza S G H. 2014. Genome-wide identification and phylogenetic analysis of the AP2/ERF gene superfamily in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis). Genet Mol Res, 13(3): 7839-7851. |
| [20] | Jiang S F, Wang C J Z, Shu C W, Zhou E X. 2018. Cloning and expression analysis of RsPhm gene in Rhizoctonia solani AG-1IA of rice sheath blight pathogen. Chin J Rice Sci, 32(2): 111-118. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Jones J D G, Dangl J L. 2006. The plant immune system. Nature, 444: 323-329. |
| [22] | Jones-Rhoades M W, Bartel D P. 2004. Computational identification of plant microRNAs and their targets, including a stress-induced miRNA. Mol Cell, 14(6): 787-799. |
| [23] | Karmakar S, Molla K A, Chanda P K, Sarkar S N, Datta S K, Datta K. 2016. Green tissue-specific co-expression of chitinase and oxalate oxidase 4 genes in rice for enhanced resistance against sheath blight. Planta, 243(1): 115-130. |
| [24] | Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S. 2014. miRBase: Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucl Acids Res, 42: D68-D73. |
| [25] | Li T, Li H, Zhang Y X, Liu J Y. 2011. Identification and analysis of seven H2O2-responsive miRNAs and 32 new miRNAs in the seedlings of rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp indica). Nucl Acids Res, 39(7): 2821-2833. |
| [26] | Li Z Y, Xia J, Chen Z, Yu Y, Li Q F, Zhang Y C, Zhang J P, Wang C Y, Zhu X Y, Zhang W, Chen Y Q. 2016. Large-scale rewiring of innate immunity circuitry and microRNA regulation during initial rice blast infection. Sci Rep, 6: 25493. |
| [27] | Lin R M, He L Y, He J Y, Qin P G, Wang Y R, Deng Q M, Yang X T, Li S C, Wang S Q, Wang W M, Liu H N, Li P, Zheng A P. 2016. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA-seq and target mRNAs of rice sheath blight pathogen provides new insights into pathogenic regulatory mechanisms. DNA Res, 23(5): 415-425. |
| [28] | Liu W D, Liu J L, Triplett L, Leach J E, Wang G L. 2014. Novel insights into rice innate immunity against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Ann Rev Phytopathol, 52: 213-241. |
| [29] | Llave C, Kasschau K D, Rector M A, Carrington J C. 2002a. Endogenous and silencing-associated small RNAs in plants. Plant Cell, 14(7): 1605-1619. |
| [30] | Llave C, Xie Z X, Kasschau K D, Carrington J C. 2002b. Cleavage of scarecrow-like mRNA targets directed by a class of Arabidopsis miRNA. Science, 297: 2053-2056. |
| [31] | Manavella P A, Koenig D, Weigel D. 2012. Plant secondary siRNA production determined by microRNA-duplex structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 109(7): 2461-2466. |
| [32] | Matzke M A, Mosher R A. 2014. RNA-directed DNA methylation: An epigenetic pathway of increasing complexity. Nat Rev Genet, 15(6): 394-408. |
| [33] | Merico D, Isserlin R, Stueker O, Emili A, Bader G D. 2010. Enrichment map: A network-based method for gene-set enrichment visualization and interpretation. PLoS One, 5(11): e13984. |
| [34] | Mi S J, Cai T, Hu Y G, Chen Y M, Hodges E, Ni F R, Wu L, Li S, Zhou H Y, Long C Z, Chen S, Hannon G J, Qi Y J. 2008. Sorting of small RNAs into Arabidopsis argonaute complexes is directed by the 5'-terminal nucleotide. Cell, 133(1): 116-127. |
| [35] | Montgomery T A, Howell M D, Cuperus J T, Li D W, Hansen J E, Alexander A L, Chapman E J, Fahlgren N, Allen E, Carrington J C. 2008. Specificity of ARGONAUTE7-miR390 interaction and dual functionality in TAS3 trans-acting siRNA formation. Cell, 133(1): 128-141. |
| [36] | Mutum R D, Kumar S, Balyan S, Kansal S, Mathur S, Raghuvanshi S. 2016. Identification of novel miRNAs from drought tolerant rice variety Nagina 22. Sci Rep, 6: 30786. |
| [37] | Navarro L, Dunoyer P, Jay F, Arnold B, Dharmasiri N, Estelle M, Voinnet O, Jones J D. 2006. A plant miRNA contributes to antibacterial resistance by repressing auxin signaling. Science, 312: 436-439. |
| [38] | Nischal L, Mohsin M, Khan I, Kardam H, Wadhwa A, Abrol Y P, Iqbal M, Ahmad A. 2012. Identification and comparative analysis of microRNAs associated with low-N tolerance in rice genotypes. PLoS One, 7(12): e50261. |
| [39] | Ouyang S Q, Park G, Atamian H S, Han C S, Stajich J E, Kaloshian I, Borkovich K A. 2014. MicroRNAs suppress NB domain genes in tomato that confer resistance to Fusarium oxysporum. PLoS Pathog, 10(10): e1004464. |
| [40] | Padmanabhan C, Zhang X M, Jin H L. 2009. Host small RNAs are big contributors to plant innate immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 12(4): 465-472. |
| [41] | Palatnik J F, Allen E, Wu X, Schommer C, Schwab R, Carrington J C, Weigel D. 2003. Control of leaf morphogenesis by microRNAs. Nature, 425: 257-263. |
| [42] | Park W, Li J J, Song R T, Messing J, Chen X M. 2002. CARPEL FACTORY, a dicer homolog, and HEN1, a novel protein, act in microRNA metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Biol, 12(17): 1484-1495. |
| [43] | Peng T, Sun H Z, Qiao M M, Zhao Y F, Du Y X, Zhang J, Li J Z, Tang G L, Zhao Q Z. 2014. Differentially expressed microRNA cohorts in seed development may contribute to poor grain filling of inferior spikelets in rice. BMC Plant Biol, 14: 196. |
| [44] | Peng X X, Hu Y J, Tang X K, Zhou P L, Deng X B, Wang H H, Guo Z J. 2012. Constitutive expression of rice WRKY30 gene increases the endogenous jasmonic acid accumulation, PR gene expression and resistance to fungal pathogens in rice. Planta, 236(5): 1485-1498. |
| [45] | Peng X X, Wang H H, Jang J C, Xiao T, He H H, Jiang D, Tang X K. 2016. OsWRKY80-OsWRKY4 module as a positive regulatory circuit in rice resistance against Rhizoctonia solani. Rice, 9: 63. |
| [46] | Pooja S, Sweta K, Mohanapriya A, Sudandiradoss C, Siva R, Gothandam K M, Babu S. 2015. Homotypic clustering of OsMYB4 binding site motifs in promoters of the rice genome and cellular-level implications on sheath blight disease resistance. Gene, 561(2): 209-218. |
| [47] | Qiao Y L, Liu L, Xiong Q, Flores C, Wong J, Shi J X, Wang X B, Liu X G, Xiang Q J, Jiang S S, Zhang F C, Wang Y C, Judelson H S, Chen X M, Ma W B. 2013. Oomycete pathogens encode RNA silencing suppressors. Nat Genet, 45(3): 330-333. |
| [48] | Raghuram B, Sheikh A H, Sinha A K. 2014. Regulation of MAP kinase signaling cascade by microRNAs in Oryza sativa. Plant Signal Behav, 9(10): e972130. |
| [49] | Reinhart B J, Slack F J, Basson M, Pasquinelli A E, Bettinger J C, Rougvie A E, Horvitz H R, Ruvkun G. 2000. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature, 403: 901-906. |
| [50] | Rubio-Somoza I, Cuperus J T, Weigel D, Carrington J C. 2009. Regulation and functional specialization of small RNA-target nodes during plant development. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 12(5): 622-627. |
| [51] | Ruepp A, Zollner A, Maier D, Albermann K, Hani J, Mokrejs M, Tetko I, Guldener U, Mannhaupt G, Munsterkotter M, Mewes H W. 2004. The FunCat, a functional annotation scheme for systematic classification of proteins from whole genomes. Nucl Acids Res, 32(18): 5539-5545. |
| [52] | Sharma N, Tripathi A, Sanan-Mishra N. 2015. Profiling the expression domains of a rice-specific microRNA under stress. Front Plant Sci, 6: 333. |
| [53] | Smoot M E, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang P L, Ideker T. 2011. Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics, 27(3): 431-432. |
| [54] | Stetson D B, Ko J S, Heidmann T, Medzhitov R. 2008. Trex1 prevents cell-intrinsic initiation of autoimmunity. Cell, 134(4): 587-598. |
| [55] | Sun Z T, He Y Q, Li J M, Wang X, Chen J P. 2015. Genome-wide characterization of rice black streaked dwarf virus-responsive microRNAs in rice leaves and roots by small RNA and degradome sequencing. Plant Cell Physiol, 56(4): 688-699. |
| [56] | Sunkar R, Kapoor A, Zhu J K. 2006. Posttranscriptional induction of two Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase genes in Arabidopsis is mediated by downregulation of miR398 and important for oxidative stress tolerance. Plant Cell, 18(8): 2051-2065. |
| [57] | Sunkar R, Chinnusamy V, Zhu J H, Zhu J K. 2007. Small RNAs as big players in plant abiotic stress responses and nutrient deprivation. Trends Plant Sci, 12(7): 301-309. |
| [58] | Taguchi-Shiobara F, Ozaki H, Sato H, Maeda H, Kojima Y, Ebitani T, Yano M. 2013. Mapping and validation of QTLs for rice sheath blight resistance. Breeding Sci, 63(3): 301-308. |
| [59] | Trapnell C, Salzberg S L. 2009. How to map billions of short reads onto genomes. Nat Biotechnol, 27(5): 455-457. |
| [60] | Trapnell C, Hendrickson D G, Sauvageau M, Goff L, Rinn J L, Pachter L. 2013. Differential analysis of gene regulation at transcript resolution with RNA-seq. Nat Biotechnol, 31(1): 46-53. |
| [61] | Vaucheret H. 2006. Post-transcriptional small RNA pathways in plants: Mechanisms and regulations. Genes Dev, 20(7): 759-771. |
| [62] | Wang H C, Jiao X M, Kong X Y, Hamera S, Wu Y, Chen X Y, Fang R X, Yan Y S. 2016. A signaling cascade from miR444 to RDR1 in rice antiviral RNA silencing pathway. Plant Physiol, 170(4): 2365-2377. |
| [63] | Wang H H, Meng J, Peng X X, Tang X K, Zhou P L, Xiang J H, Deng X B. 2015. Rice WRKY4 acts as a transcriptional activator mediating defense responses toward Rhizoctonia solani, the causing agent of rice sheath blight. Plant Mol Biol, 89: 157-171. |
| [64] | Wang R, Lu L X, Pan X B, Hu Z L, Ling F, Yan Y, Liu Y M, Lin Y J. 2015. Functional analysis of OsPGIP1 in rice sheath blight resistance. Plant Mol Biol, 87: 181-191. |
| [65] | Weiberg A, Wang M, Lin F M, Zhao H W, Zhang Z H, Kaloshian I, Huang H D, Jin H L. 2013. Fungal small RNAs suppress plant immunity by hijacking host RNA interference pathways. Science, 342: 118-123. |
| [66] | Wu J G, Yang R X, Yang Z R, Yao S Z, Zhao S S, Wang Y, Li P C, Song X W, Jin L, Zhou T, Lan Y, Xie L H, Zhou X P, Chu C C, Qi Y J, Cao X F, Li Y. 2017. ROS accumulation and antiviral defence control by microRNA528 in rice. Nat Plants, 3: 16203. |
| [67] | Xue X, Cao Z X, Zhang X T, Wang Y, Zhang Y F, Chen Z X, Pan X B, Zuo S M. 2016. Overexpression of OsOSM1 enhances resistance to rice sheath blight. Plant Dis, 100(8): 1634-1642. |
| [68] | Yadav S, Anuradha G, Kumar R R, Vemireddy L R, Sudhakar R, Donempudi K, Venkata D, Jabeen F, Narasimhan Y K, Marathi B, Siddiq E A. 2015. Identification of QTLs and possible candidate genes conferring sheath blight resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Springerplus, 4: 175. |
| [69] | Yan Y, Jia H H, Wang F, Wang C, Liu S C, Guo X Q. 2015. Overexpression of GhWRKY27a reduces tolerance to drought stress and resistance to Rhizoctonia solani infection in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana. Front Physiol, 6: 265. |
| [70] | Yang J, Zhang F, Li J, Chen J P, Zhang H M. 2016. Integrative analysis of the microRNAome and transcriptome illuminates the response of susceptible rice plants to rice stripe virus. PLoS One, 11(1): e0146946. |
| [71] | Zhai J X, Zhang H, Arikit S, Huang K, Nan G L, Walbot V, Meyers B C. 2015. Spatiotemporally dynamic, cell-type-dependent premeiotic and meiotic phasiRNAs in maize anthers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 112(10): 3146-3151. |
| [72] | Zhang N, Yang J W, Wang Z M, Wen Y K, Wang J, He W H, Liu B L, Si H J, Wang D. 2014. Identification of novel and conserved microRNAs related to drought stress in potato by deep sequencing. PLoS One, 9(4): e95489. |
| [73] | Zhao Y T, Wang M, Wang Z M, Fang R X, Wang X J, Jia Y T. 2015. Dynamic and coordinated expression changes of rice small RNAs in response to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. J Genet Genom, 42(11): 625-637. |
| [74] | Zuo S M, Zhang L, Wang H, Yin Y J, Zhang Y F, Chen Z X, Ma Y Y, Pan X B. 2008. Prospect of the QTL-qSB-9Tq utilized in molecular breeding program of japonica rice against sheath blight. J Genet Genom, 35(8): 499-505. |
| [75] | Zuo S M, Wang Z B, Chen X J, Gu F, Zhang Y F, Chen Z X, Pan X B, Pan C H. 2009. Evaluation of resistance of a novel rice line YSBR1 to sheath blight. Acta Agron Sin, 35(4): 608-614. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [76] | Zuo S M, Yin Y J, Pan C H, Chen Z X, Zhang Y F, Gu S L, Zhu L H, Pan X B. 2013. Fine mapping ofqSB-11(LE), the QTL that confers partial resistance to rice sheath blight. Theor Appl Genet, 126(5): 1257-1272. |
| [77] | Zuo S M, Zhang Y F, Yin Y J, Li G Z, Zhang G W, Wang H, Chen Z X, Pan X B. 2014a. Fine-mapping of qSB-9(TQ), a gene conferring major quantitative resistance to rice sheath blight. Mol Breeding, 34(4): 2191-2203. |
| [78] | Zuo S M, Zhu Y J, Yin Y J, Wang H, Zhang Y F, Chen Z X, Gu S L, Pan X B. 2014b. Comparison and confirmation of quantitative trait loci conferring partial resistance to rice sheath blight on chromosome 9. Plant Dis, 98(7): 957-964. |
| [1] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [2] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [3] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [4] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [5] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [6] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [7] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [8] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [9] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [10] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [11] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [12] | Tan Jingyi, Zhang Xiaobo, Shang Huihui, Li Panpan, Wang Zhonghao, Liao Xinwei, Xu Xia, Yang Shihua, Gong Junyi, Wu Jianli. ORYZA SATIVA SPOTTED-LEAF 41 (OsSPL41) Negatively Regulates Plant Immunity in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 426-436. |
| [13] | Monica Ruffini Castiglione, Stefania Bottega, Carlo Sorce, Carmelina SpanÒ. Effects of Zinc Oxide Particles with Different Sizes on Root Development in Oryza sativa [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 449-458. |
| [14] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [15] | Liu Qiao, Qiu Linlin, Hua Yangguang, Li Jing, Pang Bo, Zhai Yufeng, Wang Dekai. LHD3 Encoding a J-Domain Protein Controls Heading Date in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 437-448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||