
Rice Science ›› 2020, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 405-413.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2019.12.010
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuyu Chen1,2, Aike Zhu3, Pao Xue1, Xiaoxia Wen1, Yongrun Cao1, Beifang Wang1, Yue Zhang1, Liaqat Shah1, Shihua Cheng1, Liyong Cao1( ), Yingxin Zhang1(
), Yingxin Zhang1( )
)
Received:2019-09-09
Accepted:2019-12-31
Online:2020-09-28
Published:2020-09-28
Contact:
Liyong Cao, Yingxin Zhang
Yuyu Chen, Aike Zhu, Pao Xue, Xiaoxia Wen, Yongrun Cao, Beifang Wang, Yue Zhang, Liaqat Shah, Shihua Cheng, Liyong Cao, Yingxin Zhang. Effects of GS3 and GL3.1 for Grain Size Editing by CRISPR/Cas9 in Rice[J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(5): 405-413.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Primer | Sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| sgRNA-GS3-F | GGCAAGTGACATGGCAATGGCGG |
| SgRNA-GS3-R | AAACCCGCCATTGCCATGTCACT |
| SgRNA-GL3.1-F | GGCAGGAGCTACCGTGGGCGTCCC |
| SgRNA-GL3.1-R | AAACGGGACGCCCACGGTAGCTCC |
| Hyg-F | ACGGTGTCGTCCATCACAGTTTGCC |
| Hyg-R | TTCCGGAAGTGCTTGACATTGGGGA |
| GS3-F | CCATTGACTTCCTATTCGATC |
| GS3-R | CTCCATCTCCATGTGCTCTT |
| GL3.1-F | GTACGGATCCCAGCACTG |
| GL3.1-R | ACTCTAGGAGGGGTGGGG |
Supplemental Table 1 Primers used in this study.
| Primer | Sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| sgRNA-GS3-F | GGCAAGTGACATGGCAATGGCGG |
| SgRNA-GS3-R | AAACCCGCCATTGCCATGTCACT |
| SgRNA-GL3.1-F | GGCAGGAGCTACCGTGGGCGTCCC |
| SgRNA-GL3.1-R | AAACGGGACGCCCACGGTAGCTCC |
| Hyg-F | ACGGTGTCGTCCATCACAGTTTGCC |
| Hyg-R | TTCCGGAAGTGCTTGACATTGGGGA |
| GS3-F | CCATTGACTTCCTATTCGATC |
| GS3-R | CTCCATCTCCATGTGCTCTT |
| GL3.1-F | GTACGGATCCCAGCACTG |
| GL3.1-R | ACTCTAGGAGGGGTGGGG |
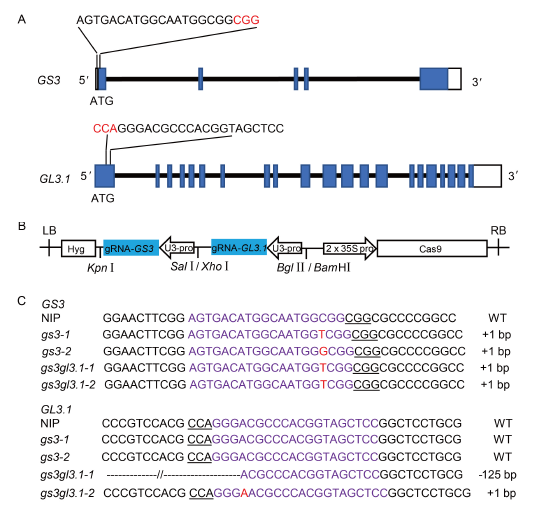
Fig. 1. Orientation mutations in GS3 and GL3.1 using CRISPR/Cas9- mediated multiplex genome editing system.A, Schematic diagram of the targeted sites in GS3 and GL3.1. UTRs, exons and introns are indicated by blank rectangles, blue rectangles and black lines, respectively. The target sequence is labelled on top of each schematic gene structure, and the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) is highlighted in red. B, Structure of the GS3 and GL3.1 gene editing system. LB, Left border; RB, Right border. C, Sequencing results of targeted regions of GS3 and GL3.1 in four T0 transgenic plants. The target sequence is shown in purple. PAM is underlined. The insertion nucleotide is shown in red. The deletion sequence is shown by dashed line.
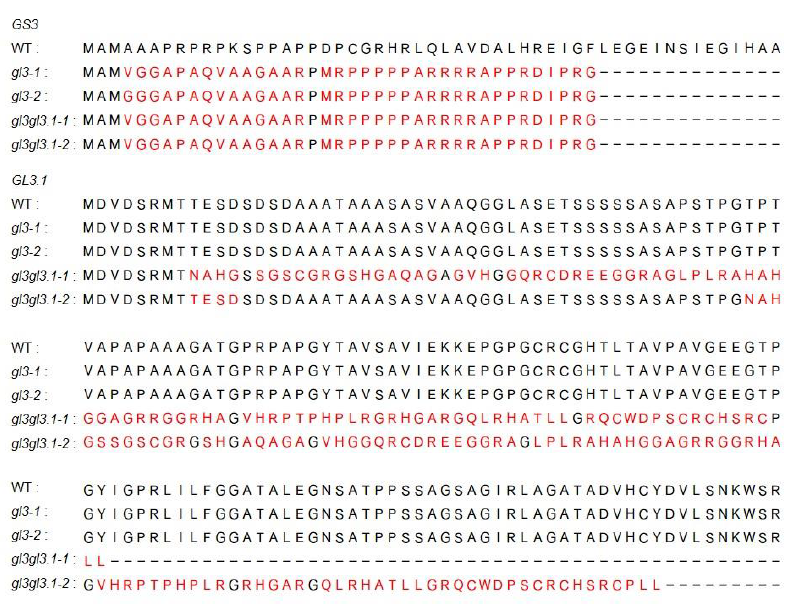
Supplemental Fig. 1. Parts amino acid sequences alignment between NIP and mutation lines at rice GS3 and GL3.1 gene respectively.The variant sequences are highlighted in yellow background. The deletion sequences of mutation lines shown by dashed line.
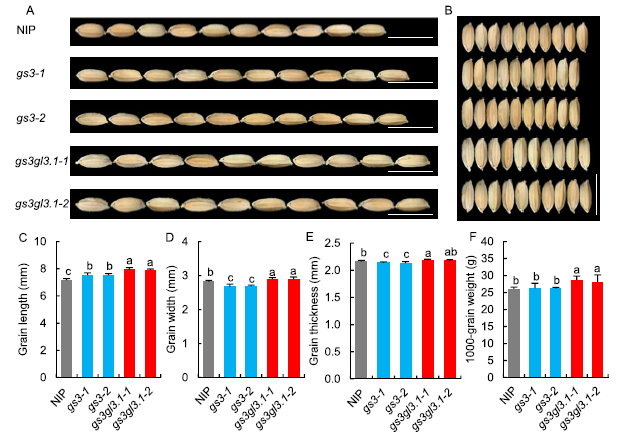
Fig. 2. Grain morphology analysis of Nipponbare (NIP) and T1 lines.A and B, Mature grain phenotypes. Scale bars, 10 mm. C, Grain length. D, Grain width. E, Grain thickness. F, 1000-grain weight.Error bars indicate the standard deviation (n = 10). The same lowercase letters denote no significant differences by the Duncan’s multiple range test at the 0.05 level.
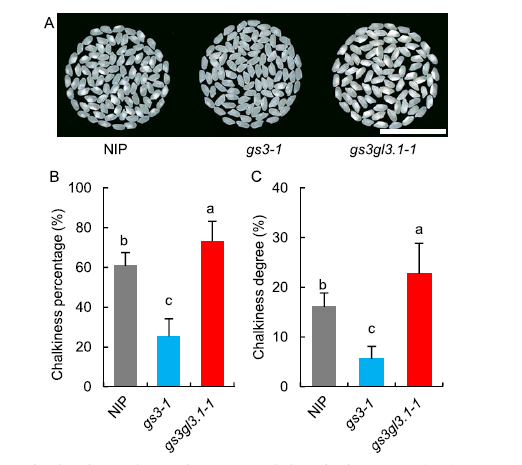
Fig. 3. Rice grain quality characteristics of Nipponbare (NIP), gs3-1 and gs3gl3.1-1.A, Milled rice morphology. Scale bar, 25 mm. B, Chalkiness percentage. C, Chalkiness degree.Error bars indicate the standard deviation (n = 20). The different lowercase letters denote significant differences by the Duncan’s multiple range test at the 0.05 level.
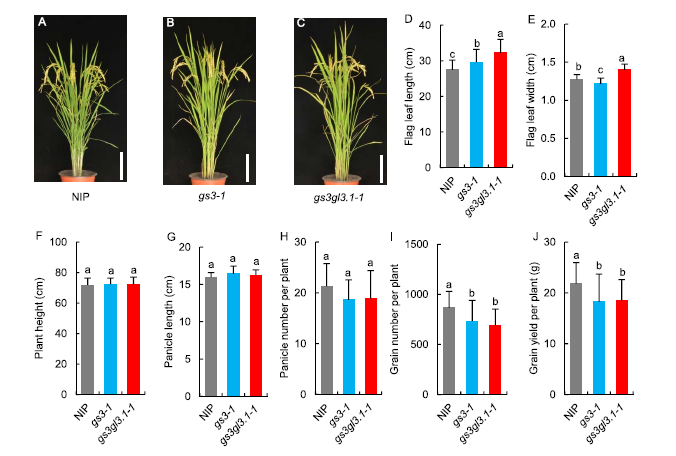
Fig. 4. Plant architecture and grain yield of Nipponbare (NIP), gs3-1 and gs3gl3.1-1.A, Representative plant of NIP at the maturity stage. B, Representative plant of gs3-1 at the maturity stage. C, Representative plant of gs3gl3.1-1 at the maturity stage. Scale bars, 15 cm in A, B and C. D, Flag leaf length. E, Flag leaf width. F, Plant height. G, Panicle length. H, Panicle number per plant. I, Grain number per plant. J, Grain yield per plant.Error bars indicate the standard deviation (n = 20). The different lowercase letters denote significant differences as by the Duncan’s multiple range test at the 0.05 level.
| [1] | Dong N Q, Sun Y W, Guo T, Shi C L, Zhang Y M, Kan Y, Xiang Y H, Zhang H, Yang Y B, Li Y C, Zhao H Y, Yu H X, Lu Z Q, Wang Y, Ye W W, Shan J X, Lin H X.2020. UDP- glucosyltransferase regulates grain size and abiotic stress tolerance associated with metabolic flux redirection in rice. Nat Commun, 11: 2629. |
| [2] | Che R H, Tong H N, Shi B H, Liu Y Q, Fang S R, Liu D P, Xiao Y H, Hu B, Liu L C, Wang H R, Zhao M F, Chu C C.2015. Control of grain size and rice yield by GL2-mediated brassinosteroid responses. Nat Plants, 2(1): 15195. |
| [3] | Chen K L, Wang Y P, Zhang R, Zhang H W, Gao C X.2019. CRISPR/Cas genome editing and precision plant breeding in agriculture. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 70: 667-697. |
| [4] | Fan C C, Xing Y Z, Mao H L, Lu T T, Han B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F.2006. GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet, 112: 1164-1171. |
| [5] | Gao X Y, Zhang X J, Lan H X, Huang J, Wang J F, Zhang H S.2015. The additive effects of GS3 and qGL3 on rice grain length regulation revealed by genetic and transcriptome comparisons. BMC Plant Biol, 15: 156. |
| [6] | Gao X Y, Zhang J Q, Zhang X J, Zhou J, Jiang Z S, Huang P, Tang Z B, Bao Y M, Cheng J P, Tang H J, Zhang W H, Zhang H S, Huang J.2019. Rice qGL3/OsPPKL1 functions with the GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase OsGSK3 to modulate brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Cell, 31(5): 1077-1093. |
| [7] | Hiei Y, Komari T, Kubo T.1997. Transformation of rice mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Mol Biol, 35: 205-218. |
| [8] | Hu J, Wang Y X, Fang Y X, Zeng L J, Xu J, Yu H P, Shi Z Y, Pan J J, Zhang D, Kang S J, Zhu L, Dong G J, Guo L B, Zeng D L, Zhang G H, Xie L H, Xiong G S, Li J Y, Qian Q.2015. A rare allele of GS2 enhances grain size and grain yield in rice. Mol Plant, 8(10): 1455-1465. |
| [9] | Ishimaru K, Hirotsu N, Madoka Y, Murakami N, Hara N, Onodera H, Kashiwagi T, Ujiie K, Shimizu B I, Onishi A, Miyagawa H, Katoh E.2013. Loss of function of the IAA-glucose hydrolase gene TGW6 enhances rice grain weight and increases yield. Nat Genet, 45(6): 707-711. |
| [10] | Li N, Xu R, Li Y H.2019. Molecular networks of seed size control in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 70: 435-463. |
| [11] | Li Y B, Fan C C, Xing Y Z, Jiang Y H, Luo L J, Sun L, Shao D, Xu C J, Li X H, Xiao J H, He Y Q, Zhang Q F.2011. Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat Genet, 43: 1266-1269. |
| [12] | Liu J F, Chen J, Zheng X M, Wu F Q, Li Q B, Heng Y Q, Tian P, Cheng Z J, Yu X W, Zhou K N, Zhang X, Guo X P, Wang J L, Wang H Y, Wan J M.2017. GW5 acts in the brassinosteroid signalling pathway to regulate grain width and weight in rice. Nat Plants, 3: 17043. |
| [13] | Liu Q, Han R X, Wu K, Zhang J Q, Ye Y F, Wang S S, Chen J F, Pan Y J, Li Q, Xu X P, Zhou J W, Tao D Y, Wu Y J, Fu X D.2018. G-protein βγ subunits determine grain size through interaction with MADS-domain transcription factors in rice. Nat Commun, 9(1): 852. |
| [14] | Liu W Z, Xie X R, Ma X L, Li J, Chen J H, Liu Y G.2015. DSDecode: A web-based tool for decoding of sequencing chromatograms for genotyping of targeted mutations. Mol Plant, 8(9): 1431-1433. |
| [15] | Mao H L, Sun S Y, Yao J L, Wang C R, Yu S B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F.2010. Linking differential domain functions of the GS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 107(45): 19579-19584. |
| [16] | Murray M G, Thompson W F.1980. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucl Acids Res, 8: 4321-4325. |
| [17] | Qi P, Lin Y S, Song X J, Shen J B, Huang W, Shan J X, Zhu M Z, Jiang L W, Gao J P, Lin H X.2012. The novel quantitative trait locus GL3.1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating Cyclin-T1;3. Cell Res, 22(12): 1666-1680. |
| [18] | Ruan B P, Shang L G, Zhang B, Hu J, Wang Y X, Lin H, Zhang A P, Liu C L, Peng Y L, Zhu L, Ren D Y, Shen L, Dong G J, Zhang G H, Zeng D L, Guo L B, Qian Q, Gao Z Y.2020. Natural variation in the promoter of TGW2 determines grain width and weight in rice. New Phytol, 227(2): 629-640. |
| [19] | Shen L, Wang C, Fu Y P, Wang J J, Liu Q, Zhang X M, Yan C J, Qian Q, Wang K J.2016. QTL editing confers opposing yield performance in different rice varieties. J Integr Plant Biol, 60(2): 89-93. |
| [20] | Shomura A, Izawa T, Ebana K, Ebitani T, Kanegae H, Konishi S, Yano M.2008. Deletion in a gene associated with grain size increased yields during rice domestication. Nat Genet, 40(8): 1023-1028. |
| [21] | Si L Z, Chen J Y, Huang X H, Gong H, Luo J H, Hou Q Q, Zhou T Y, Lu T T, Zhu J J, Shangguan Y Y, Chen E W, Gong C X, Zhao Q, Jing Y F, Zhao Y, Li Y, Cui L L, Fan D L, Lu Y Q, Weng Q J, Wang Y C, Zhan Q L, Liu K Y, Wei X H, An K S, An G H, Han B.2016. OsSPL13 controls grain size in cultivated rice. Nat Genet, 48: 447-456. |
| [22] | Song X J, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu M Z, Lin H X.2007. A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet, 39(5): 623-630. |
| [23] | Song X J, Kuroha T, Ayano M, Furuta T, Nagai K, Komeda N, Segami S, Miura K, Ogawa D, Kamura T, Suzuki T, Higashiyama T, Yamasaki M, Mori H, Inukai Y, Wu J Z, Kitano H, Sakakibara H, Jacobsen S E, Ashikari M.2015. Rare allele of a previously unidentified histone H4 acetyltransferase enhances grain weight, yield, and plant biomass in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 112(1): 76-81. |
| [24] | Sun S Y, Wang L, Mao H L, Shao L, Li X H, Xiao J H, Ouyang Y D, Zhang Q F.2018. A G-protein pathway determines grain size in rice. Nat Commun, 9: 851. |
| [25] | Wang A H, Hou Q Q, Si L Z, Huang X H, Luo J H, Lu D F, Zhu J J, Shangguan Y Y, Miao J S, Xie Y F, Wang Y C, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhou C C, Li Y, Fan D L, Lu Y Q, Tian Q L, Wang Z X, Han B.2019. The PLATZ transcription factor GL6 affects grain length and number in rice. Plant Physiol, 180(4): 2077-2090. |
| [26] | Wang C, Shen L, Fu Y P, Yan C J, Wang K J.2015. A simple CRISPR/Cas9 system for multiplex genome editing in rice. J Genet Genom, 42(12): 703-706. |
| [27] | Wang S K, Wu K, Yuan Q B, Liu X Y, Liu Z B, Lin X Y, Zeng R Z, Zhu H T, Dong G J, Qian Q, Zhang G Q, Fu X D.2012. Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet, 44: 905-954. |
| [28] | Wang S K, Li S, Liu Q, Wu K, Zhang J Q, Wang S S, Wang Y, Chen X B, Zhang Y, Gao C X, Wang F, Huang H X, Fu X D.2015. The OsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rices yield and grain quality. Nat Genet, 47: 949-954. |
| [29] | Wang Y X, Xiong G S, Hu J, Jiang L, Yu H, Xu J, Fang Y X, Zeng L J, Xu E B, Xu J, Ye W J, Meng X B, Liu R F, Chen H Q, Jing Y H, Wang Y Y, Zhu X D, Li J Y, Qian Q.2015. Copy number variation at the GL7 locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice. Nat Genet, 47(8): 944-948. |
| [30] | Wang Z K, Zeng D D, Qin R, Liu J L, Shi C H, Jin X L.2018. A novel and pleiotropic factor SLENDER GRAIN3 is involved in regulating grain size in rice. Rice Sci, 25(3): 132-141. |
| [31] | Wu W G, Liu X Y, Wang M H, Meyer R S, Luo X J, Ndjiondjop M N, Tan L, Zhang J W, Wu J Z, Cai H W, Sun C Q, Wang X K, Wing R A, Zhu Z F.2017. A single-nucleotide polymorphism causes smaller grain size and loss of seed shattering during African rice domestication. Nat Plants, 3(6): 17064. |
| [32] | Xia D, Zhou H, Liu R J, Dan W H, Li P B, Wu B, Chen J X, Wang L Q, Gao G J, Zhang Q L, He Y Q.2018. GL3.3, a novel QTL encoding a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase, epistatically interacts with GS3 to form extra-long grains in rice. Mol Plant, 11(5): 754-756. |
| [33] | Xu R F, Yang Y C, Qin R Y, Li H, Qiu C H, Li L, Wei P C, Yang J B.2016. Rapid improvement of grain weight via highly efficient CRISPR/Cas9-mediated multiplex genome editing in rice. J Genet Genom, 43(8): 529-532. |
| [34] | Ying J Z, Ma M, Bai C, Huang X H, Liu J L, Fan Y Y, Song X J.2018. TGW3, a major QTL that negatively modulates grain length and weight in rice. Mol Plant, 11(5): 750-753. |
| [35] | Yu J P, Xiong H Y, zhu X Y, Zhang H L, Li H H, Miao J L, Wang W S, Tang Z S, Zhang Z Y, Yao G X, Zhang Q, Pan Y H, Wang X, Rashid M A R, Li J J, Gao Y M, Li Z K, Yang W C, Fu X D, Li Z C.2017. OsLG3 contributing to rice grain length and yield was mined by Ho-LAMap. BMC Biol, 15(1): 28. |
| [36] | Yu J P, Miao J L, Zhang Z Y, Xiong H Y, Zhu X Y, Sun X M, Pan Y H, Liang Y T, Zhang Q, Abdul Rehman R M, Li J J, Zhang H L, Li Z C.2018. Alternative splicing of OsLG3b controls grain length and yield in japonica rice. Plant Biotechnol J, 16(9): 1667-1678. |
| [37] | Zhang X J, Wang J F, Huang J, Lan H X, Wang C L, Yin C F, Wu Y Y, Tang H J, Qian Q, Li J Y, Zhang H S.2012. Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 109: 21534-21539. |
| [38] | Zhao D S, Li Q F, Zhang C Q, Zhang C, Yang Q Q, Pan L X, Ren X Y, Lu J, Gu M H, Liu Q Q.2018. GS9 acts as a transcriptional activator to regulate rice grain shape and appearance quality. Nat Commun, 9(1): 1240. |
| [1] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [2] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [3] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [4] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [5] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [6] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [7] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [8] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [9] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [10] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [11] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [12] | Tan Jingyi, Zhang Xiaobo, Shang Huihui, Li Panpan, Wang Zhonghao, Liao Xinwei, Xu Xia, Yang Shihua, Gong Junyi, Wu Jianli. ORYZA SATIVA SPOTTED-LEAF 41 (OsSPL41) Negatively Regulates Plant Immunity in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 426-436. |
| [13] | Monica Ruffini Castiglione, Stefania Bottega, Carlo Sorce, Carmelina SpanÒ. Effects of Zinc Oxide Particles with Different Sizes on Root Development in Oryza sativa [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 449-458. |
| [14] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [15] | Liu Qiao, Qiu Linlin, Hua Yangguang, Li Jing, Pang Bo, Zhai Yufeng, Wang Dekai. LHD3 Encoding a J-Domain Protein Controls Heading Date in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 437-448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||