
Rice Science ›› 2020, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 162-174.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2020.01.007
• Research Paper • Previous Articles
Chunmei Xu, Liping Chen, Song Chen, Guang Chu, Danying Wang( ), Xiufu Zhang(
), Xiufu Zhang( )
)
Received:2018-09-08
Accepted:2019-04-26
Online:2020-03-28
Published:2019-11-28
Chunmei Xu, Liping Chen, Song Chen, Guang Chu, Danying Wang, Xiufu Zhang. Rhizosphere Aeration Improves Nitrogen Transformation in Soil, and Nitrogen Absorption and Accumulation in Rice Plants[J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(2): 162-174.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Soil characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Soil organic matter (g/kg) | 34.20 ± 1.80 |
| Total N (g/kg) | 2.51 ± 0.32 |
| Available N (mg/kg) | 318.40 ± 12.00 |
| Available P (mg/kg) | 11.40 ± 1.30 |
| Available K (mg/kg) | 72.00 ± 0.90 |
| pH | 6.04 ± 0.04 |
| Gravimetric soil moisture content (kg/kg) | 0.17 ± 0.05 |
| Bulk density (g/cm3) | 1.24 ± 0.20 |
Table 1 Characteristics of tested pot soils.
| Soil characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Soil organic matter (g/kg) | 34.20 ± 1.80 |
| Total N (g/kg) | 2.51 ± 0.32 |
| Available N (mg/kg) | 318.40 ± 12.00 |
| Available P (mg/kg) | 11.40 ± 1.30 |
| Available K (mg/kg) | 72.00 ± 0.90 |
| pH | 6.04 ± 0.04 |
| Gravimetric soil moisture content (kg/kg) | 0.17 ± 0.05 |
| Bulk density (g/cm3) | 1.24 ± 0.20 |
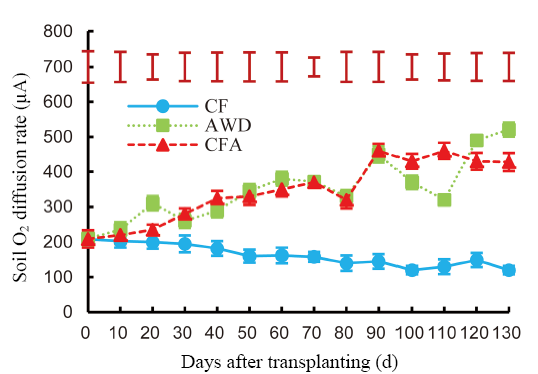
Fig. 1. Oxygen (O2) diffusion rate in the pots under different soil O2 conditions during rice-growing seasons in Hangzhou, China. CF, Continuous flooding; AWD, Alternate wetting and drying; CFA, Continuous flooding and aeration.Error bars represent the standard deviation (n = 3). Vertical bars with caps represent LSD0.05 for the oxygen diffusion rate of soil under different soil oxygen treatments.
| Treatment | Tillering stage | Heading stage | Maturity stage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf area (cm2/hill) | TDMA (g/hill) | Leaf area (cm2/hill) | TDMA (g/hill) | TDMA (g/hill) | |||
| Xiushui 09 | |||||||
| CF (Control) | 355.62 ± 6.20 c | 4.42 ± 0.15 a | 831.56 ± 26.10 b | 18.05 ± 0.92 b | 27.41 ± 0.15 c | ||
| AWD | 397.40 ± 11.70 b | 4.53 ± 0.33 a | 804.36 ± 12.98 b | 22.13 ± 1.50 a | 36.61 ± 0.74 a | ||
| CFA | 435.62 ± 10.81 a | 4.05 ± 0.30 a | 887.38 ± 18.31 a | 18.74 ± 0.99 b | 31.86 ± 0.52 b | ||
| Chunyou 84 | |||||||
| CF (Control) | 901.52 ± 17.98 b | 9.44 ± 0.38 a | 2 661.08 ± 46.47 a | 47.20 ± 1.33 b | 80.61 ± 0.80 b | ||
| AWD | 756.96 ± 11.98 c | 8.43 ± 0.84 a | 2 316.09 ± 63.67 b | 56.12 ± 0.97 a | 78.56 ± 1.00 c | ||
| CFA | 959.77 ± 10.78 a | 9.59 ± 0.82 a | 2 790.18 ± 36.96 a | 55.09 ± 1.87 a | 82.62 ± 0.93 a | ||
Table 2 Effects of different soil oxygen conditions on rice leaf area and biomass accumulation at the different rice growth stages.
| Treatment | Tillering stage | Heading stage | Maturity stage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf area (cm2/hill) | TDMA (g/hill) | Leaf area (cm2/hill) | TDMA (g/hill) | TDMA (g/hill) | |||
| Xiushui 09 | |||||||
| CF (Control) | 355.62 ± 6.20 c | 4.42 ± 0.15 a | 831.56 ± 26.10 b | 18.05 ± 0.92 b | 27.41 ± 0.15 c | ||
| AWD | 397.40 ± 11.70 b | 4.53 ± 0.33 a | 804.36 ± 12.98 b | 22.13 ± 1.50 a | 36.61 ± 0.74 a | ||
| CFA | 435.62 ± 10.81 a | 4.05 ± 0.30 a | 887.38 ± 18.31 a | 18.74 ± 0.99 b | 31.86 ± 0.52 b | ||
| Chunyou 84 | |||||||
| CF (Control) | 901.52 ± 17.98 b | 9.44 ± 0.38 a | 2 661.08 ± 46.47 a | 47.20 ± 1.33 b | 80.61 ± 0.80 b | ||
| AWD | 756.96 ± 11.98 c | 8.43 ± 0.84 a | 2 316.09 ± 63.67 b | 56.12 ± 0.97 a | 78.56 ± 1.00 c | ||
| CFA | 959.77 ± 10.78 a | 9.59 ± 0.82 a | 2 790.18 ± 36.96 a | 55.09 ± 1.87 a | 82.62 ± 0.93 a | ||
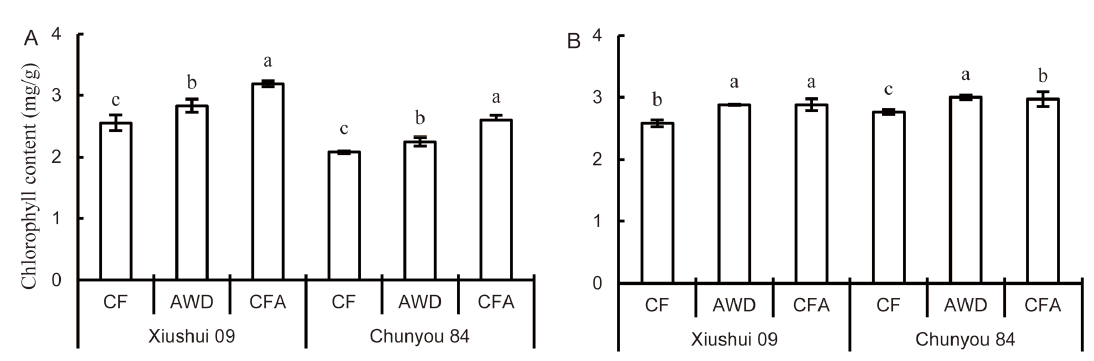
Fig. 2. Leaf chlorophyll content at the tillering (A) and heading (B) stages under different soil oxygen conditions.CF, Continuous flooding; AWD, Alternate wetting and drying; CFA, Continuous flooding and aeration.Data represent Mean ± SD (n = 3). Different letters above the column indicate differences between the soil oxygen conditions for the same rice cultivar at the 0.05 level.
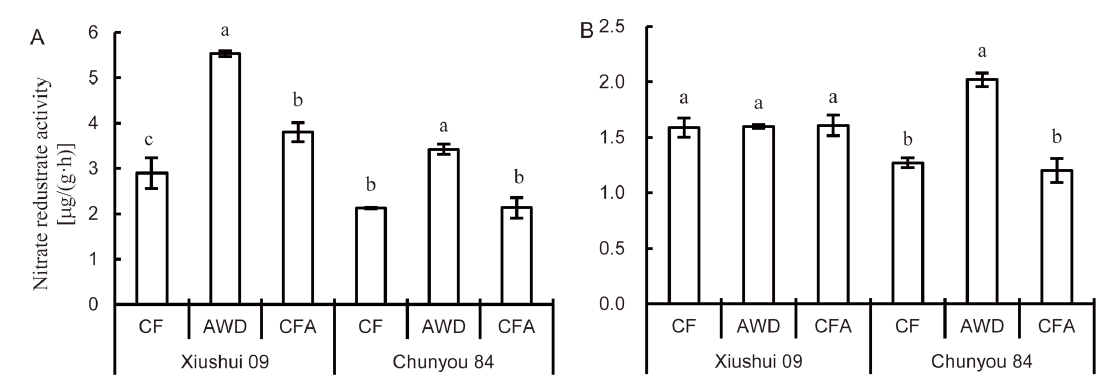
Fig. 3. Leaf nitrate reductase activity at the tillering (A) and heading (B) stages under different soil oxygen conditions.CF, Continuous flooding; AWD, Alternate wetting and drying; CFA, Continuous flooding and aeration.Data represent Mean ± SD (n = 3). Different lowercase letters above the column indicate differences between the soil oxygen conditions for the same rice cultivar at the 0.05 level.
| Treatment | Tillering stage | Heading stage | Maturity stage | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stem | Leaf | Stem | Leaf | Panicle | Stem | Leaf | Panicle | |||
| Xiushui 09 | ||||||||||
| CF | 1.52 ± 0.07 b | 3.30 ± 0.14 c | 0.65 ± 0.00 b | 1.31 ± 0.14 c | 1.23 ± 0.03 ab | 0.52 ± 0.02 a | 0.76 ± 0.05 ab | 1.20 ± 0.06 a | ||
| AWD | 1.78 ± 0.07 a | 3.64 ± 0.04 b | 0.68 ± 0.02 ab | 2.02 ± 0.09 b | 1.20 ± 0.04 b | 0.51 ± 0.00 a | 0.69 ± 0.04 b | 1.32 ± 0.04 a | ||
| CFA | 1.87 ± 0.10 a | 3.98 ± 0.12 a | 0.70 ± 0.02 a | 2.34 ± 0.12 a | 1.32 ± 0.05 a | 0.53 ± 0.01 a | 0.83 ± 0.04 a | 1.19 ± 0.07 a | ||
| Chunyou 84 | ||||||||||
| CF | 1.35 ± 0.10 b | 3.02 ± 0.06 b | 0.53 ± 0.01 b | 1.54 ± 0.03 c | 1.11 ± 0.05 a | 0.44 ± 0.02 b | 0.75 ± 0.05 c | 1.18 ± 0.07 ab | ||
| AWD | 2.09 ± 0.05 a | 3.28 ± 0.21 ab | 0.72 ± 0.00 a | 1.73 ± 0.07 b | 1.19 ± 0.05 a | 0.43 ± 0.02 b | 0.89 ± 0.03 a | 1.26 ± 0.03 a | ||
| CFA | 1.46 ± 0.05 b | 3.59 ± 0.18 a | 0.54 ± 0.03 b | 1.92 ± 0.07 a | 1.12 ± 0.06 a | 0.58 ± 0.00 a | 0.82 ± 0.03 b | 1.14 ± 0.00 b | ||
Table 3 Nitrogen concentrations under different soil oxygen conditions at different sampling stages. mg/g
| Treatment | Tillering stage | Heading stage | Maturity stage | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stem | Leaf | Stem | Leaf | Panicle | Stem | Leaf | Panicle | |||
| Xiushui 09 | ||||||||||
| CF | 1.52 ± 0.07 b | 3.30 ± 0.14 c | 0.65 ± 0.00 b | 1.31 ± 0.14 c | 1.23 ± 0.03 ab | 0.52 ± 0.02 a | 0.76 ± 0.05 ab | 1.20 ± 0.06 a | ||
| AWD | 1.78 ± 0.07 a | 3.64 ± 0.04 b | 0.68 ± 0.02 ab | 2.02 ± 0.09 b | 1.20 ± 0.04 b | 0.51 ± 0.00 a | 0.69 ± 0.04 b | 1.32 ± 0.04 a | ||
| CFA | 1.87 ± 0.10 a | 3.98 ± 0.12 a | 0.70 ± 0.02 a | 2.34 ± 0.12 a | 1.32 ± 0.05 a | 0.53 ± 0.01 a | 0.83 ± 0.04 a | 1.19 ± 0.07 a | ||
| Chunyou 84 | ||||||||||
| CF | 1.35 ± 0.10 b | 3.02 ± 0.06 b | 0.53 ± 0.01 b | 1.54 ± 0.03 c | 1.11 ± 0.05 a | 0.44 ± 0.02 b | 0.75 ± 0.05 c | 1.18 ± 0.07 ab | ||
| AWD | 2.09 ± 0.05 a | 3.28 ± 0.21 ab | 0.72 ± 0.00 a | 1.73 ± 0.07 b | 1.19 ± 0.05 a | 0.43 ± 0.02 b | 0.89 ± 0.03 a | 1.26 ± 0.03 a | ||
| CFA | 1.46 ± 0.05 b | 3.59 ± 0.18 a | 0.54 ± 0.03 b | 1.92 ± 0.07 a | 1.12 ± 0.06 a | 0.58 ± 0.00 a | 0.82 ± 0.03 b | 1.14 ± 0.00 b | ||
| Treatment | Tillering stage | Heading stage | Maturity stage | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stem | Leaf | Stem | Leaf | Panicle | Stem | Leaf | Panicle | |||
| Xiushui 09 | ||||||||||
| CF | 3.82 ± 0.46 a | 62.29 ± 3.26 b | 68.57 ± 5.47 b | 62.61 ± 3.61 c | 33.40 ± 2.83 a | 60.82 ± 0.97 a | 34.65 ± 1.50 a | 152.97 ± 5.73 c | ||
| AWD | 4.34 ± 0.18 a | 75.75 ± 4.15 a | 75.67 ± 3.50 ab | 110.38 ± 5.61 b | 30.36 ± 1.71 a | 50.26 ± 0.46 b | 34.24 ± 1.20 a | 260.79 ± 8.15 a | ||
| CFA | 4.14 ± 0.28 a | 73.12 ± 1.73 a | 78.66 ± 4.81 a | 118.08 ± 3.34 a | 32.98 ± 3.16 a | 51.08 ± 2.86 b | 31.92 ± 2.19 a | 230.20 ± 3.46 b | ||
| Chunyou 84 | ||||||||||
| CF | 7.28 ± 0.52 b | 122.33 ± 6.58 b | 138.56 ± 6.07 c | 208.38 ± 10.19 c | 83.40 ± 3.21 b | 126.16 ± 1.58 a | 101.55 ± 8.97 b | 469.45 ± 12.36 b | ||
| AWD | 9.74 ± 0.48 a | 124.46 ± 5.22 b | 235.56 ± 7.74 a | 251.16 ± 4.07 b | 103.30 ± 6.46 a | 87.38 ± 2.02 c | 135.06 ± 5.62 a | 551.88 ± 16.59 a | ||
| CFA | 7.35 ± 0.66 b | 162.28 ± 8.94 a | 177.98 ± 4.45 b | 292.94 ± 2.05 a | 99.19 ± 2.60 a | 103.16 ± 2.37 b | 104.43 ± 6.73 b | 545.77 ± 12.43 a | ||
Table 4 Nitrogen accumulation under different soil oxygen conditions at different rice growth stages. mg/hill
| Treatment | Tillering stage | Heading stage | Maturity stage | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stem | Leaf | Stem | Leaf | Panicle | Stem | Leaf | Panicle | |||
| Xiushui 09 | ||||||||||
| CF | 3.82 ± 0.46 a | 62.29 ± 3.26 b | 68.57 ± 5.47 b | 62.61 ± 3.61 c | 33.40 ± 2.83 a | 60.82 ± 0.97 a | 34.65 ± 1.50 a | 152.97 ± 5.73 c | ||
| AWD | 4.34 ± 0.18 a | 75.75 ± 4.15 a | 75.67 ± 3.50 ab | 110.38 ± 5.61 b | 30.36 ± 1.71 a | 50.26 ± 0.46 b | 34.24 ± 1.20 a | 260.79 ± 8.15 a | ||
| CFA | 4.14 ± 0.28 a | 73.12 ± 1.73 a | 78.66 ± 4.81 a | 118.08 ± 3.34 a | 32.98 ± 3.16 a | 51.08 ± 2.86 b | 31.92 ± 2.19 a | 230.20 ± 3.46 b | ||
| Chunyou 84 | ||||||||||
| CF | 7.28 ± 0.52 b | 122.33 ± 6.58 b | 138.56 ± 6.07 c | 208.38 ± 10.19 c | 83.40 ± 3.21 b | 126.16 ± 1.58 a | 101.55 ± 8.97 b | 469.45 ± 12.36 b | ||
| AWD | 9.74 ± 0.48 a | 124.46 ± 5.22 b | 235.56 ± 7.74 a | 251.16 ± 4.07 b | 103.30 ± 6.46 a | 87.38 ± 2.02 c | 135.06 ± 5.62 a | 551.88 ± 16.59 a | ||
| CFA | 7.35 ± 0.66 b | 162.28 ± 8.94 a | 177.98 ± 4.45 b | 292.94 ± 2.05 a | 99.19 ± 2.60 a | 103.16 ± 2.37 b | 104.43 ± 6.73 b | 545.77 ± 12.43 a | ||
| Treatment | Tillering stage | Heading stage | Maturing stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xiushui 09 | |||
| CF | 62.27 ± 0.35 a | 106.17 ± 1.75 b | 110.39 ± 0.37 a |
| AWD | 56.56 ± 1.13 b | 113.65 ± 3.12 a | 104.43 ± 2.42 b |
| CFA | 52.48 ± 1.12 c | 84.81 ± 1.11 c | 109.21 ± 1.26 a |
| Chunyou 84 | |||
| CF | 72.88 ± 0.91 a | 109.69 ± 0.46 a | 107.46 ± 1.96 b |
| AWD | 66.73 ± 1.64 b | 95.11 ± 1.33 c | 103.39 ± 0.72 b |
| CFA | 56.78 ± 1.08 c | 101.62 ± 0.86 b | 113.24 ± 2.11 a |
Table 5 Nitrogen use efficiency under different soil oxygen conditions at different sampling stages.
| Treatment | Tillering stage | Heading stage | Maturing stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xiushui 09 | |||
| CF | 62.27 ± 0.35 a | 106.17 ± 1.75 b | 110.39 ± 0.37 a |
| AWD | 56.56 ± 1.13 b | 113.65 ± 3.12 a | 104.43 ± 2.42 b |
| CFA | 52.48 ± 1.12 c | 84.81 ± 1.11 c | 109.21 ± 1.26 a |
| Chunyou 84 | |||
| CF | 72.88 ± 0.91 a | 109.69 ± 0.46 a | 107.46 ± 1.96 b |
| AWD | 66.73 ± 1.64 b | 95.11 ± 1.33 c | 103.39 ± 0.72 b |
| CFA | 56.78 ± 1.08 c | 101.62 ± 0.86 b | 113.24 ± 2.11 a |
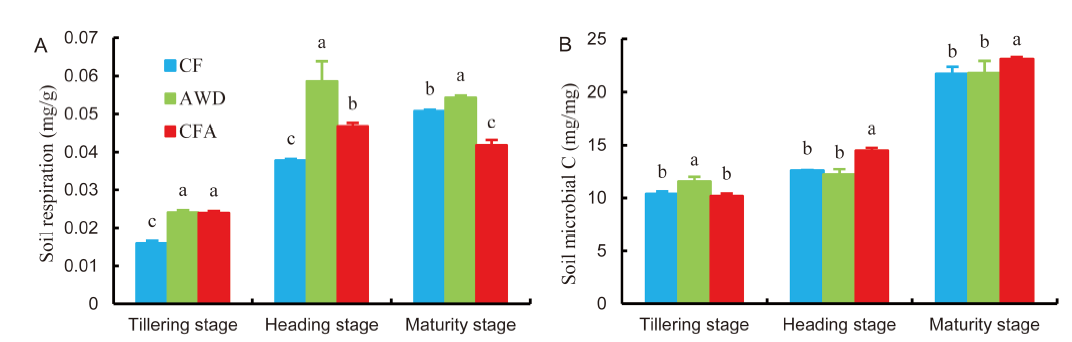
Fig. 4. Soil respiration (A) and microbial biomass carbon (B) under different soil oxygen conditions at different sampling stages.CF, Continuous flooding; AWD, Alternate wetting and drying; CFA, Continuous flooding and aeration.Data represent Mean ± SD (n = 3). Different letters indicate differences between the soil oxygen conditions for the same sampling stage at the 0.05 level level.
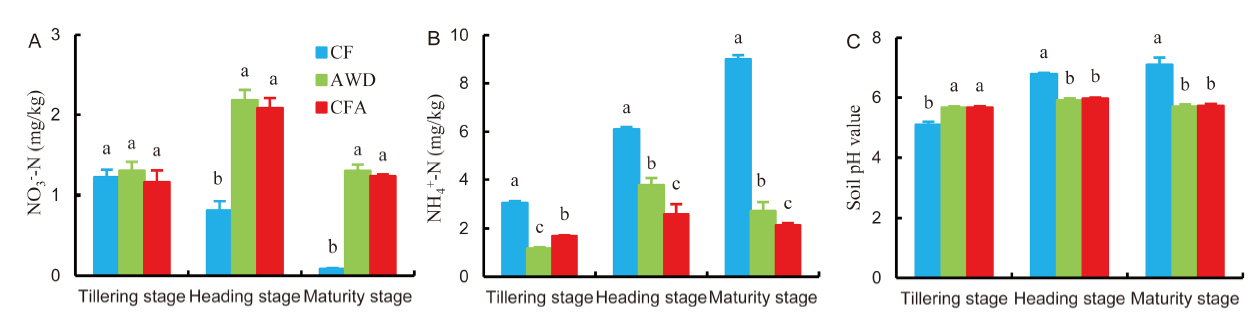
Fig. 5. Soil nitrate-nitrogen (NO3--N) concentration (A), ammonium-nitrogen (NH4+-N) concentration (B) and pH value (C) under different soil oxygen conditions at different sampling stages.CF, Continuous flooding; AWD, Alternate wetting and drying; CFA, Continuous flooding and aeration.Data represent Mean ± SD (n = 3). Different letters indicate differences between the soil oxygen conditions for the same sampling stage at the 0.05 level.
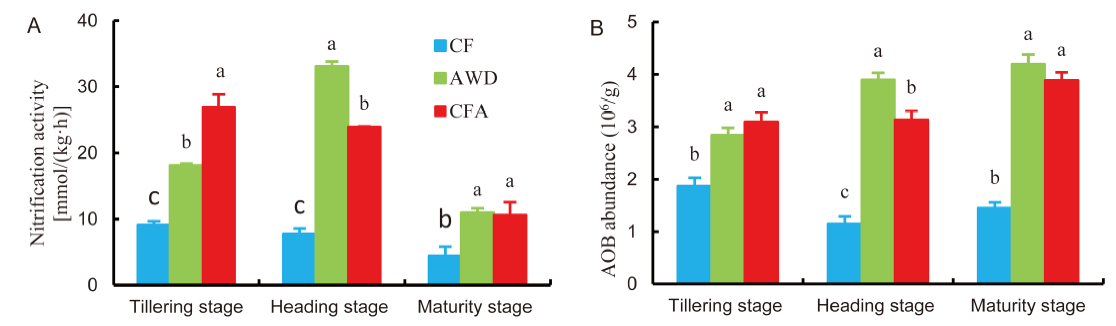
Fig. 6. Soil nitrification activity (A) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) abundance (B) measured under different soil oxygen conditions at different sampling stages.CF, Continuous flooding; AWD, Alternate wetting and drying; CFA, Continuous flooding and aeration.Data represent Mean ± SD (n = 3). Different letters indicate differences between the soil oxygen conditions for the same sampling stage at the 0.05 level.
| Growth stage | Parameter | Total nitrogen accumulation | Nitrification activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tillering stage | Soil respiration | 0.612 | - |
| Nitrification activity | 0.806** | 1.000 | |
| AOB abundance | 0.742* | 0.913** | |
| Heading stage | Soil respiration | 0.850** | - |
| Nitrification activity | 0.927** | 1.000 | |
| AOB abundance | 0.848** | 0.949** | |
| Maturity stage | Soil respiration | 0.117 | - |
| Nitrification activity | 0.650* | 1.000 | |
| AOB abundance | 0.715* | 0.826** |
Table 6 Correlation coefficients for both treatments between total nitrogen accumulation, nitrification activity, and ammonia- oxidizing bacteria (AOB) abundance.
| Growth stage | Parameter | Total nitrogen accumulation | Nitrification activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tillering stage | Soil respiration | 0.612 | - |
| Nitrification activity | 0.806** | 1.000 | |
| AOB abundance | 0.742* | 0.913** | |
| Heading stage | Soil respiration | 0.850** | - |
| Nitrification activity | 0.927** | 1.000 | |
| AOB abundance | 0.848** | 0.949** | |
| Maturity stage | Soil respiration | 0.117 | - |
| Nitrification activity | 0.650* | 1.000 | |
| AOB abundance | 0.715* | 0.826** |
| [1] | Belder P, Bouman B A M, Cabangon R, Lu G, Quilang E J P, Li Y H, Spiertz J H J, Tuong T P. 2004. Effect of water saving irrigation on rice yield and water use in typical lowland conditions in Asia. Agric Water Manage, 65(3): 193-210. |
| [2] | Bhat A K. 2013. Preserving microbial diversity of soil ecosystem: A key to sustainable productivity. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci, 2(8): 85-101. |
| [3] | Brady N C. 2002. The nature and properties of soils. J Range Manage, 5(6): 333. |
| [4] | Bremner J M. 1960. Determination of nitrogen in soil by the Kjeldahl method. J Agric Sci, 55(1): 11-33. |
| [5] | Cai Z C. 2002. Ammonium transformation in paddy soil affected by the presence of nitrate. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys, 63(2): 267-274. |
| [6] | Cammeron K C, Di H J, Moir J L. 2013. Nitrogen losses from the soil/plant system: A review. Ann Appl Biol, 162(2): 145-173. |
| [7] | Canfield D E, Glazer A N, Falkowshi P G. 2010. The evolution and future of earth’s nitrogen cycle. Science, 330: 192-196. |
| [8] | Cao X C, Li X Y, Zhu L F, Zhang J H, Yu S M, Wu L H, Jin Q Y. 2016. Effects of water management on rice nitrogen utilization. Acta Ecol Sin, 36(13): 3882-3890. |
| [9] | Cao Y, Fan X R, Sun S B, Xu G H, Hu J, Shen Q R. 2008. Effect of nitrate on activities and transcript levels of nitrate reductase and glutamine synthetase in rice. Pedosphere, 18(5): 664-673. |
| [10] | Chen D, Suter H, Islam A, Edis R, Freney J R, Walker C N. 2008. Prospects of improving efficiency of fertiliser nitrogen in Australian agriculture: A review of enhanced efficiency fertilisers. Soil Res, 46: 289-301. |
| [11] | Chu H Y, Morimoto S, Fujii T, Yagi K, Nishimura S. 2009. Soil ammonia-oxidizing bacterial communities in paddy rice fields as affected by upland conversion history. Soil Sci Soc Am J, 73(6): 2026-2031. |
| [12] | Dash C J, Sarangi A, Singh D K, Singh A K, Adhikary P P. 2015. Prediction of root zone water and nitrogen balance in an irrigated rice field using a simulation model. Paddy Water Environ, 13(3): 281-290. |
| [13] | De-Boer W, Klein-Gunnewiek P J A, Troelstra S R. 1990. Nitrification in Dutch heathland soils: II. Characteristics of nitrate production. Plant Soil, 127(2): 193-200. |
| [14] | Dewi W S, Wahyuningsih G I, Syamsiyah J, Mujiyo.2018. Dynamics of N-NH4+, N-NO3-, and total soil nitrogen in paddy field with azolla and biochar. Earth Environ Sci, 142(1): 012014. |
| [15] | Dong D, Feng Q B, Mcgrouther K, Yang M, Wang H L, Wu W X. 2015. Effects of biochar amendment on rice growth and nitrogen retention in a waterlogged paddy field. J Soils Sedim, 15(1): 153-162. |
| [16] | Dotaniya M L, Meena V D. 2015. Rhizosphere effect on nutrient availability in soil and its uptake by plants: A review. Proc Natl Acad Sci Ind B, 85(1): 1-12. |
| [17] | Duan Y H, Zhang Y L, Shen Q R. 2004. Nitrification in rice rhizosphere and the nitrate nutrition of rice. Acta Pedolog Sin, 41(5): 803-809. (in Chinese) |
| [18] | Duan Y H, Zhang Y L, Shen Q R, Wang S W. 2006. Nitrate effect on rice growth and nitrogen absorption and assimilation at different growth stages. Pedosphere, 16(6): 707-717. |
| [19] | Fierer N, Schimel J P. 2002. Effect of drying-rewetting frequency on soil carbon and nitrogen transformations. Soil Biol Biochem, 34(6): 777-787. |
| [20] | Galib M. 2015. Effect of flooding on nitrate reductase activities of seedling of some Indonesian local rice varieties. Int J Adv Res Eng Appl Sci, 4(5): 26-31. |
| [21] | Geng J B, Chen J Q, Sun Y B, Zheng W K, Tian X F, Yang Y C, Li C L, Zhang M. 2016. Controlled release urea improved nitrogen use efficiency and yield of wheat and corn. Agron J, 108(4): 1666-1673. |
| [22] | Guo J H, Peng Y Z, Wang S Y, Zheng Y N, Huang H J, Wang Z W. 2009. Long-term effect of dissolved oxygen on partial nitrification performance and microbial community structure. Biores Technol, 100(11): 2796-2802. |
| [23] | Haefele S M, Jabbar S M A, Siopongco J D L C,, Tirol-Padre A, Amarante S T, Sta Cruz P C, Cosico W C. 2008. Nitrogen use efficiency in selected rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes under different water regimes and nitrogen levels. Field Crops Res, 107(2): 137-146. |
| [24] | Hageman R H, Reed A J. 1980. Nitrate reductase from higher plants. Methods Enzymol, 69: 270-280. |
| [25] | Hamilton E W, Ftank D A. 2001. Can plants stimulate soil microbes and their own nutrient supply? Evidence from a grazing tolerant grass. Ecology, 82(9): 2397-2402. |
| [26] | Hao X Y, Chang C, Travis G R, Zhang F R. 2003. Soil carbon and nitrogen response to 25 annual cattle manure applications. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci, 166(2): 239-245. |
| [27] | Henriques F S. 1989. Effects of copper deficiency on the photosynthetic apparatus of sugar beet (Beta vulgatis L.). J Plant Physiol, 135(4): 453-458. |
| [28] | Hiinninghaus M, Koller R, Kramer S, Marhan S, Ellen K, Bonkowski M. 2017. Changes in bacterial community composition and soil respiration indicate rapid successions of protest grazers during mineralization of maize crop residues. Pedobiologia, 62: 1-8. |
| [29] | Hodge A, Berta G, Doussan C, Merchan F, Crespi M. 2009. Plant root growth, architecture and function. Plant Soil, 321: 153-187. |
| [30] | Ishii S, Ikeda S, Minamisawa K, Senoo K. 2011. Nitrogen cycling in rice paddy environments: Past achievements and future challenges. Microbes Environ, 26(4): 282-292. |
| [31] | Islam S M M, Gaihre Y K, Shah A L, Singh U, Sarkar M I U, Satter M A, Sanabria J, Biswas J C. 2016. Rice yields and nitrogen use efficiency with different fertilizers and water management under intensive lowland rice cropping systems in Bangladesh. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys, 106(2): 1-14. |
| [32] | Jackson M B, Ismail A M. 2015. Introduction to the special issue: Electrons, water and rice fields: Plant response and adaptation to flooding and submergence stress. AoB Plants, 7: plv078. |
| [33] | Kaiser W M, Huber S C. 2001. Post-translational regulation of nitrate reductase: Mechanism, physiological relevance and environmental triggers. J Exp Bot, 52: 1981-1989. |
| [34] | Kirk G J D, Greenway H, Atwell B J, Ismail A M, Colmer T D. 2014. Adaptation of rice to flooded soils. In: Lttge U, Beyschlag W, Cushman J. Progress in Botany. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer: 75: 215-253. |
| [35] | Kögel-Knabner I, Amelung W, Cao Z H, Fiedler S, Frenzel P, Jahn R, Kalbitz K, Kölbl A, Schloter M. 2010. Biogeochemistry of paddy soils. Geoderma, 157(1): 1-14. |
| [36] | Konishi H, Ishiguro K, Komatsu S. 2015. A proteomics approach towards understanding blast fungus infection of rice grown under different levels of nitrogen fertilization. Proteomics, 1(9): 1162-1171. |
| [37] | Koutroubas S D, Ntanos D A. 2003. Genotypic differences for grain yield and nitrogen utilization in indica and japonica rice under Mediterranean conditions. Field Crops Res, 83(3): 251-260. |
| [38] | Kronzucker H J, Siddiqi M Y, Glass A D M, Kirk G J D. 1999. Nitrate-ammonium synergism in rice: A subcellular flux analysis. Plant Physiol, 119(3): 1041-1046. |
| [39] | Ladha J K, Tirol-Padre A, Reddy C K, Cassman K G, Verma S, Powlson D S, van Kessel C, de B Richter D, Chakraborty D, Pathak H. 2016. Global nitrogen budgets in cereals: A 50-year assessment for maize, rice, and wheat production systems. Sci Rep, 6: 19355. |
| [40] | Li F D, Yu Z N, He S J. 1996. Agricultural Microbiological Experimental Technique. Beijing, China: China Agriculture Press: 34-36. |
| [41] | Li Y L, Fan X R, Shen Q R. 2008. The relationship between rhizosphere nitrification and nitrogen-use efficiency in rice plants. Plant Cell Environ, 31(1): 73-85. |
| [42] | Li Y L, Wang X X. 2013. Root-induced changes in radial oxygen loss, rhizosphere oxygen profile, and nitrification of two rice cultivars in Chinese red soil regions. Plant Soil, 365: 115-126. |
| [43] | Limami A M, Diab H, Lothier J. 2014. Nitrogen metabolism in plants under low oxygen stress. Planta, 239(3): 531-541. |
| [44] | Lu R K. 2000. Soil Agricultural Chemical Analysis Methods. Beijing, China: Agricultural Science and Technology Press. |
| [45] | Mishra A, Salokhe V M. 2010. The effects of planting pattern and water regime on root morphology, physiology and grain yield of rice. J Agron Crop Sci, 196(5): 368-378. |
| [46] | Ollivier J, Töwe S, Bannert A, Hai B, Kastl E M, Meyer A, Su M X, Kleineidam K, Schloter M. 2011. Nitrogen turnover in soil and global change. FEMS Microbiol Ecol, 78(1): 3-16. |
| [47] | Ponnamperuma F N. 1972. The chemistry of submerged soils. Adv Agron, 24: 29-96. |
| [48] | Qian X Q, Shen Q R, Xu G H, Wang J J, Zhou M Y. 2004. Nitrogen form effects on yield and nitrogen uptake of rice crop grown in aerobic soil. J Plant Nutr, 27(6): 1061-1076. |
| [49] | Reddy K R, Gretz D A. 1998. Carbon and nitrogen dynamics in wetland soils. In: Hook D D, McKee Jr W H, Smith H K, Gregory J, Burrell Jr V G, DeVoe M R, Sojka R E, Gilbert S, Banks R, Stolzy L H, Brooks C, Matthews T D, Shear T H. The Ecology and Management of Wetlands. Volume 1: Ecology of wetlands. New York, USA: Springer: 307-318. |
| [50] | Rejesus R M, Palis F G, Rodriguez D G P, Lampayan R M, Bouman B A M. 2011. Impact of the alternate wetting and drying (AWD) water-saving irrigation technique: Evidence from rice producers in the Philippines. Food Policy, 36(2): 280-288. |
| [51] | Ruan J Y, Gerendás J, Härdter R, Sattelmacher B. 2007. Effect of nitrogen form and root-zone pH on growth and nitrogen uptake of tea (Camellia sinensis) plants. Ann Bot, 99(2): 301-310. |
| [52] | Schlemmer M, Gitelson A, Schepers J, Ferguson R, Peng Y, Shanahan J, Rundquist D. 2013. Remote estimation of nitrogen and chlorophyll contents in maize at leaf and canopy levels. Int J Appl Earth Obs, 25: 47-54. |
| [53] | Schlesinger W J.1991. Biogeochemisity: An analysis of global change. San Diego, USA: Academic Press: 443. |
| [54] | Sooksa-nguan T, Thies J E, Gypmantasiri P, Boonkerd N, Teaumroong N. 2009. Effect of rice cultivation systems on nitrogen cycling and nitrifying bacterial community structure. Appl Soil Ecol, 43(1): 139-149. |
| [55] | Spiertz J H J. 2010. Nitrogen, sustainable agriculture and food security: A review. Agron Sustain Dev, 30(1): 43-55. |
| [56] | Sun H J, Zhang H L, Powlson D, Min J, Shi W M. 2015. Rice production, nitrous oxide emission and ammonia volatilization as impacted by the nitrification inhibitor 2-chloro-6- (trichloromethy1)-pyridine. Field Crops Res, 173: 1-7. |
| [57] | Swift M J, Heal O W, Anderson J M. 1979. Decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. Stud Ecol, 5(14): 2272-2774. |
| [58] | Tan X Z, Shao D G, Liu H H, Yang F S, Xiao C, Yang H D. 2013. Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on percolation and nitrogen leaching in paddy fields. Paddy Water Environ, 11: 381-395. |
| [59] | Tian C, Zhou X, Xie G X, Liu Q, Rong X M, Zhang Y P, Tan L Z, Peng J W. 2018. Ammonia volatilization loss and nitrogen use efficiency in double-cropping rice field as affected by decreasing controlled-release urea application level. Chin J Rice Sci, 32(4): 387-397. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [60] | Wang Z Q, Zhang W Y, Beebout S S, Zhang H, Liu L J, Yang J C, Zhang J H. 2016. Grain yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of rice as influenced by irrigation regimes and their interaction with nitrogen rates. Field Crops Res, 193: 54-69. |
| [61] | Warrington R. 1878. On nitrification. J Chem Soc Pak, 33: 44-51. |
| [62] | Wu L L, Shen Y, Huang L Y, Sun F, Zhu G L, Li G H, Fahad S, Peng S B, Wang F. 2016. Physiological mechanisms underlying the high-grain yield and high-nitrogen use efficiency of elite rice varieties under a low rate of nitrogen application in China. Front Plant Sci, 7(7): 1024. |
| [63] | Yan J, Wu Q X, Zhu J Q, Zhang L P. 2019 Effects of nitrogen application on rice photosynthetic characteristics, nitrogen uptake and grain yield formation under rainfall-adapted water management. Chin J Rice Sci, 33(4): 347-356. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [64] | Yan X, Jin J Y, He P, Liang M Z. 2008. Recent advances in technology of increasing fertilizer use efficiency. Sci Agric Sin, 41(2): 450-459. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [65] | Yang Y J, Zhang J B, Cai Z C. 2016. Nitrification activities and N mineralization in paddy soils are insensitive to oxygen concentration. Acta Agric Scand, Section B: Soil Plant Sci, 66(3): 272-281. |
| [66] | Yoichiro K, Midori O. 2010. Root growth dynamics and stomatal behaviour of rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown under aerobic and flooded conditions. Field Crops Res, 117(1): 9-17. |
| [67] | Zhang J P, Zhou X H, Chen L, Cheng Z G, Chu J Y, Li Y M. 2016. Comparison of the abundance and community structure of ammonia oxidizing prokaryotes in rice rhizosphere under three different irrigation cultivation modes. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 32: 85. |
| [68] | Zhang Y L, Dong Y Y, Shen Q R, Duan Y H. 2004. Characteristics of NH4+ and NO3- uptake by rice of different genotypes. Acta Pedol Sin, 41(6): 918-923. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [69] | Zhao F, Wang D Y, Xu C M, Zhang W J, Zhang X F. 2009. Progress in research on physiological and ecological response of rice to oxygen nutrition and its environment effects. Chin J Rice Sci, 23(4): 335-341. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [70] | Zhao X Q, Zhao S P, Shi W M. 2008. Enhancement of NH4+ uptake by NO3- in relation to expression of nitrate-induced genes in rice (Oryza sativa) roots. Pedosphere, 18(1): 86-91. |
| [71] | Zhou M H, Butterbach-Bah K. 2014. Assessment of nitrate leaching loss on a yield-scaled basis from maize and wheat cropping systems. Plant Soil, 374: 977-991. |
| [72] | Zhu L F, Yu S M, Jin Q Y. 2012. Effects of aerated irrigation on leaf senescence at late growth stage and grain yield of rice. Rice Sci, 19(1): 44-48. |
| [1] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [2] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [3] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [4] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [5] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [6] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [7] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [8] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [9] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [10] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [11] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [12] | Monica Ruffini Castiglione, Stefania Bottega, Carlo Sorce, Carmelina SpanÒ. Effects of Zinc Oxide Particles with Different Sizes on Root Development in Oryza sativa [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 449-458. |
| [13] | Tan Jingyi, Zhang Xiaobo, Shang Huihui, Li Panpan, Wang Zhonghao, Liao Xinwei, Xu Xia, Yang Shihua, Gong Junyi, Wu Jianli. ORYZA SATIVA SPOTTED-LEAF 41 (OsSPL41) Negatively Regulates Plant Immunity in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 426-436. |
| [14] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [15] | Liu Qiao, Qiu Linlin, Hua Yangguang, Li Jing, Pang Bo, Zhai Yufeng, Wang Dekai. LHD3 Encoding a J-Domain Protein Controls Heading Date in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 437-448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||