
Rice Science ›› 2022, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (3): 216-224.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2021.08.003
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yang Ziyi1, Xu Zhijian2, Yang Qingwen1( ), Qiao Weihua1(
), Qiao Weihua1( )
)
Received:2021-04-20
Accepted:2021-08-02
Online:2022-05-28
Published:2022-03-10
Contact:
Yang Qingwen, Qiao Weihua
Yang Ziyi, Xu Zhijian, Yang Qingwen, Qiao Weihua. Conservation and Utilization of Genetic Resources of Wild Rice in China[J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(3): 216-224.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
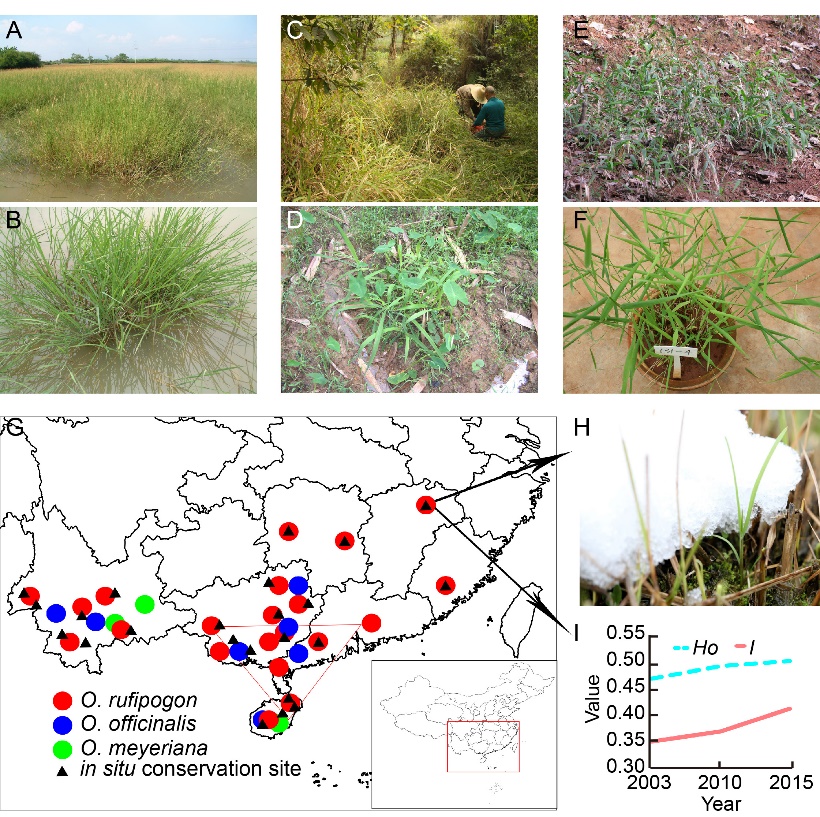
Fig. 1. Wild rice species and distributions in China. A-F, Chinese wild rice in its original habitats. A, O. rufipogon population; B, O. rufipogon single plant; C, O. officinalis population; D, O. officinalis single plant; E, O. meyeriana population; F, O. meyeriana single plant. G, Distribution map of three species of Chinese wild rice, 23 critically endangered wild rice populations in in situ conservation sites are shown as black triangle, and the red inverted triangle represents for diversity center of Chinese wild rice. Pu’er wild rice population in Yunnan Province, and Dongxiang wild rice population in Jiangxi Province grow at the highest altitude (1 068 m) of O. meyeriana and the northernmost location (28º14′ N) of O. rufipogon in the world, respectively. H, Dongxiang wild rice shows extreme cold tolerance. I, Assessment of in situ conservation of Dongxiang wild rice. Ho, Observed heterozygosity; I, Shannon’s information index.
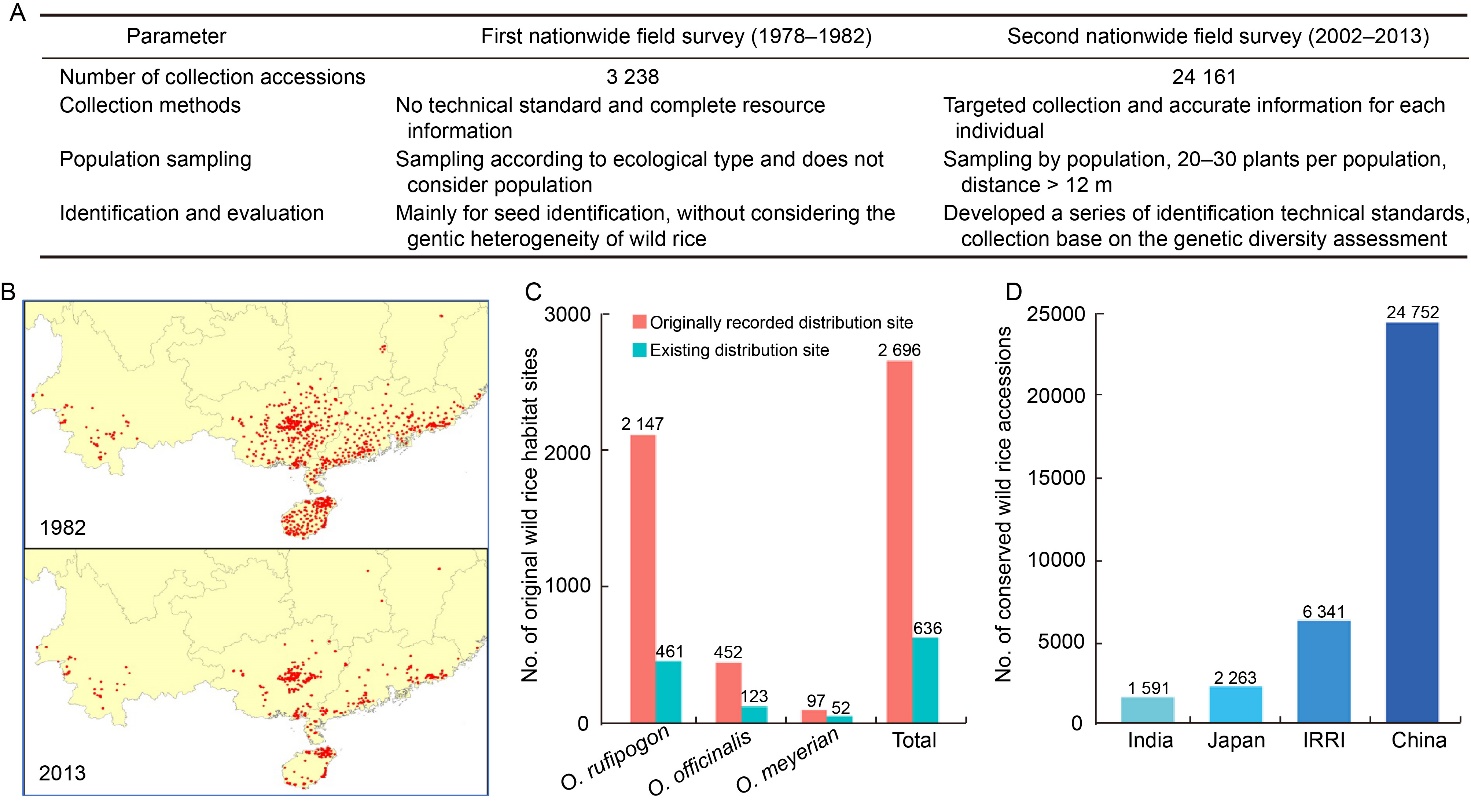
Fig. 2. Status of Chinese wild rice conservation. A, Comparison of the first and the second nationwide wild rice field survey programs. B, Wild rice distribution sites in China in 1982 and 2013. Red circles indicate each wild rice distribution site. C, Comparison of numbers of original wild rice habitat sites between the first (original recorded) and the second (existing) nationwide field surveys. D, Number of wild rice resources conserved by China, other countries and the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI).
| Gene/QTL | Chr | ID | Agronomic trait | Germplasm with superior allele | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xa23 | 11 | Os11g0586701 | Broad-spectrum disease resistance | O. rufipogon | Wang et al, |
| Xa29(t) | 1 | - | Resistant to bacterial blight | O. officinalis | Tan et al, |
| Xa30(t) | 11 | - | Resistant to bacterial blight | O. rufipogon | Jin et al, |
| xa32(t) | 12 | - | Resistant to bacterial blight | O. meyeriana | Ruan et al, |
| Pi-gx(t) | 2 | - | Rice blast resistance | O. rufipogon | Yan et al, |
| bls1 | 6 | - | Bacterial leaf streak resistance | O. rufipogon | He et al, |
| bph20(t) | 6 | - | Resistant to brown planthopper | O. rufipogon | Yang et al, |
| bph21(t) | 4 | - | Resistant to brown planthopper | O. rufipogon | Yang et al, |
| bph22(t) | 4 | - | Resistant to brown planthopper | O. rufipogon | Hou et al, |
| bph23(t) | 8 | - | Resistant to brown planthopper | O. rufipogon | Hou et al, |
| Bph27 | 4 | - | Resistant to brown planthopper | O. rufipogon | Li C B et al, |
| An-1 | 4 | Os04g0350700 | Regulate awn development, grain size and grain number | O. rufipogon | Luo et al, |
| GAD1 | 8 | Os08g0485500 | Regulate grain number, grain length and awn development | O. rufipogon | Jin et al, |
| OsLG1 | 4 | Os04g0656500 | Inflorescence architecture, closed panicle | O. rufipogon | Zhu et al, |
| LABA1/An-2 | 4 | Os04g0518800 | Awn development | O. rufipogon | Hua et al, |
| NOG1 | 1 | Os01g0752200 | Increase the grain yield of rice | O. rufipogon | Huo et al, |
| GIF1 | 4 | Os04g0413500 | Grain size | O. rufipogon | Wang et al, |
| COLD1 | 4 | Os04g0600800 | Cold tolerance | O. rufipogon | Ma et al, |
| bZIP73 | 9 | Os09g0474000 | Cold tolerance | O. rufipogon | Liu et al, |
| CTB4a | 4 | Os04g0132500 | Cold tolerance | O. rufipogon | Zhang et al, |
Table 1. Status of excavation of elite genes in Chinese wild rice.
| Gene/QTL | Chr | ID | Agronomic trait | Germplasm with superior allele | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xa23 | 11 | Os11g0586701 | Broad-spectrum disease resistance | O. rufipogon | Wang et al, |
| Xa29(t) | 1 | - | Resistant to bacterial blight | O. officinalis | Tan et al, |
| Xa30(t) | 11 | - | Resistant to bacterial blight | O. rufipogon | Jin et al, |
| xa32(t) | 12 | - | Resistant to bacterial blight | O. meyeriana | Ruan et al, |
| Pi-gx(t) | 2 | - | Rice blast resistance | O. rufipogon | Yan et al, |
| bls1 | 6 | - | Bacterial leaf streak resistance | O. rufipogon | He et al, |
| bph20(t) | 6 | - | Resistant to brown planthopper | O. rufipogon | Yang et al, |
| bph21(t) | 4 | - | Resistant to brown planthopper | O. rufipogon | Yang et al, |
| bph22(t) | 4 | - | Resistant to brown planthopper | O. rufipogon | Hou et al, |
| bph23(t) | 8 | - | Resistant to brown planthopper | O. rufipogon | Hou et al, |
| Bph27 | 4 | - | Resistant to brown planthopper | O. rufipogon | Li C B et al, |
| An-1 | 4 | Os04g0350700 | Regulate awn development, grain size and grain number | O. rufipogon | Luo et al, |
| GAD1 | 8 | Os08g0485500 | Regulate grain number, grain length and awn development | O. rufipogon | Jin et al, |
| OsLG1 | 4 | Os04g0656500 | Inflorescence architecture, closed panicle | O. rufipogon | Zhu et al, |
| LABA1/An-2 | 4 | Os04g0518800 | Awn development | O. rufipogon | Hua et al, |
| NOG1 | 1 | Os01g0752200 | Increase the grain yield of rice | O. rufipogon | Huo et al, |
| GIF1 | 4 | Os04g0413500 | Grain size | O. rufipogon | Wang et al, |
| COLD1 | 4 | Os04g0600800 | Cold tolerance | O. rufipogon | Ma et al, |
| bZIP73 | 9 | Os09g0474000 | Cold tolerance | O. rufipogon | Liu et al, |
| CTB4a | 4 | Os04g0132500 | Cold tolerance | O. rufipogon | Zhang et al, |
| [1] | A X X, Qin F L, Tang C F, Zhang F F, Dong C, Yang Y Y, Zhang D P, Dai L Y. 2021. Diversity of resistance to bacterial blight and geographical distribution of 29 populations of wild rice [Oryza meyeriana (Zoll. & Moritzi) Baill.] in Yunnan, China. Genet Resour Crop Evol, 68: 513-527. |
| [2] | Aggarwal R K, Brar D S, Khush G S. 1997. Two new genomes in the Oryza complex identified on the basis of molecular divergence analysis using total genomic DNA hybridization. Mol Gen Genet, 254(1): 1-12. |
| [3] | Chang T T. 1987. The origins and early cultures of the cereal grains and food legumes. Agric Archaeol, 68(132): 1-18. (in Chinese) |
| [4] | Chen Q Q, Yu S B, Li C H, Mou T M. 2008. Localization analysis of heat tolerance QTL in rice heading and flowering stage. Sci Agric Sin, 41(2): 315-321. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Choi J Y, Purugganan M D. 2018. Multiple origin but single domestication led to Oryza sativa. Genes Genomes Genet, 8(3): 797-803. |
| [6] | Civáň P, Craig H, Cox C J, Brown T A. 2015. Three geographically separate domestications of Asian rice. Nat Plants, 1: 15164. |
| [7] | He W A, Huang D H, Li R B, Qiu Y F, Song J D, Yang H N, Zheng J X, Huang Y Y, Li X Q, Liu C, Zhang Y X, Ma Z F, Yang Y. 2012. Identification of a resistance gene bls1 to bacterial leaf streak in wild rice Oryza rufipogon Griff. J Integr Agric, 11: 962-969. |
| [8] | Hou L Y, Yu P, Xu Q, Yuan X P, Yu H Y, Wang Y P, Wang C H, Wan G, Tang S X, Peng S T, Wei X H. 2011. Genetic analysis and preliminary mapping of two recessive resistance genes to brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stål in rice. Rice Sci, 18(3): 238-242. |
| [9] | Hua L, Wang D R, Tan L B, Fu Y C, Liu F X, Xiao L T, Zhu Z F, Fu Q, Sun X Y, Gu P, Cai H W, McCouch S R, Sun C Q. 2015. LABA1, a domestication gene associated with long, barbed awns in wild rice. Plant Cell, 27(7): 1875-1888. |
| [10] |
Huang D, Qiu Y, Zhang Y, Huang F, Meng J, Wei S, Li R, Chen B. 2013. Fine mapping and characterization of BPH27, a brown planthopper resistance gene from wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff). Theor Appl Genet, 126(1): 219-229.
PMID |
| [11] | Huang X H, Kurata N, Wei X H, Wang Z X, Wang A H, Zhao Q, Zhao Y, Liu K Y, Lu H Y, Li W J, Guo Y L, Lu Y Q, Zhou C C, Fan D L, Weng Q J, Zhu C R, Huang T, Zhang L, Wang Y C, Feng L, Furuumi H, Kubo T, Miyabayashi T, Yuan X P, Xu Q, Dong G J, Zhan Q L, Li C Y, Fujiyama A, Toyoda A, Lu T T, Feng Q, Qian Q, Li J Y, Han B. 2012. A map of rice genome variation reveals the origin of cultivated rice. Nature, 490: 497-501. |
| [12] | Huo X, Wu S, Zhu Z F, Liu F X, Fu Y C, Cai H W, Sun X Y, Gu P, Xie D X, Tan L B, Sun C Q. 2017. NOG1 increases grain production in rice. Nat Commun, 8(1): 1497. |
| [13] | Ishii T, Numaguchi K, Miura K, Yoshida K, Thanh P T, Htun T M, Yamasaki M, Komeda N, Matsumoto T, Terauchi R, Ishikawa R, Ashikari M. 2013. OsLG1 regulates a closed panicle trait in domesticated rice. Nat Genet, 45: 462-465. |
| [14] | Jin J, Hua L, Zhu Z F, Tan L B, Zhao X H, Zhang W F, Liu F X, Fu Y C, Cai H W, Sun X Y, Gu P, Xie D X, Sun C Q. 2016. GAD1 encodes a secreted peptide that regulates grain number, grain length, and awn development in rice domestication. Plant Cell, 28(10): 2453-2463. |
| [15] | Jin X W, Wang C L, Yang Q, Jiang Q X, Zhao K J. 2007. Breeding of near isogenic line CBB30 and molecular mapping of Xa30(t), a new resistance gene to bacterial blight in rice. Sci Agric Sin, 40(6): 1094-1100. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Kui L M, Tan L B, Tu J, Lu Y X, Sun C Q. 2008. Heat-resistant QTL mapping of wild rice in Yunnan Yuanjiang during heading and flowering stage. J Agric Biotechnol, 16(3): 461-464. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Li C B, Zhou A L, Sang T. 2006. Rice domestication by reducing shattering. Science, 311: 1936-1939. |
| [18] | Li R B, Zhang X J, Li X Y, Yang X Q, Wei Y W, Li L S, Wei S M, Chen Y Z, Bai D L, Yang L, Huang F K, Lü W L. 2006. The evaluation and utilization of new genes for brown planthopper resistance in common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Mol Plant Breed, 4: 365-371. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Li W, Li K, Huang Y, Shi C, Hu W S, Zhang Y, Zhang Q J, Xia E H, Hutang G R, Zhu X G, Liu Y L, Liu Y, Tong Y, Zhu T, Huang H, Zhang D, Zhao Y, Jiang W K, Yuan J, Niu Y C, Gao C W, Gao L Z. 2020. SMRT sequencing of the Oryza rufipogon genome reveals the genomic basis of rice adaptation. Commun Biol, 3(1): 167. |
| [20] | Liu C T, Ou S J, Mao B G, Tang J Y, Wang W, Wang H R, Cao S Y, Schläppi M R, Zhao B R, Xiao G Y, Wang X P, Chu C C. 2018. Early selection of bZIP73 facilitated adaptation of japonica rice to cold climates. Nat Commun, 9: 3302. |
| [21] | Liu C T, Schläppi M R, Mao B G, Wang W, Wang A J, Chu C C. 2019. The bZIP73 transcription factor controls rice cold tolerance at the reproductive stage. Plant Biotechnol J, 17(9): 1834-1849. |
| [22] | Liu S, Zheng X M, Yu L Q, Feng L, Wang J R, Gong T T, Liang X X, Qi L, Su L, Ding Y B, Xu R, Qiao W H, Cheng Y L, Zhang L F, Yang Q W. 2017. Comparison of the genetic structure between In situ and ex situ populations of Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogan Griff). Crop Sci, 57(6): 3075-3084. |
| [23] | Lu B R. 1999. Taxonomy of the genus Oryza (Poaceae): Historical perspective and current status. Int Rice Res Notes, 24: 4-8. |
| [24] | Luo J H, Liu H, Zhou T Y, Gu B G, Huang X H, Shangguan Y Y, Zhu J J, Li Y, Zhao Y, Wang Y C, Zhao Q, Wang A H, Wang Z Q, Sang T, Wang Z X, Han B. 2013. An-1 encodes a basic helix-loop-helix protein that regulates awn development, grain size, and grain number in rice. Plant Cell, 25(9): 3360-3376. |
| [25] | Ma Y, Dai X Y, Xu Y Y, Luo W, Zheng X M, Zeng D L, Pan Y J, Lin X L, Liu H H, Zhang D J, Xiao J, Guo X Y, Xu S J, Niu Y D, Jin J B, Zhang H, Xu X, Li L G, Wang W, Qian Q, Ge S, Chong K. 2015. COLD1 confers chilling tolerance in rice. Cell, 160(6): 1209-1221. |
| [26] | Molina J, Sikora M, Garud N, Flowers J M, Rubinstein S, Reynolds A, Huang P, Jackson S, Schaal B A, Bustamante C D, Boyko A R, Purugganan M D. 2011. Molecular evidence for a single evolutionary origin of domesticated rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 108: 8351-8356. |
| [27] | Oka H I. 1988. Origin of Cultivated Rice. Elsevier, the Netherlands: 935. |
| [28] | Qi L, Ding Y B, Zheng X M, Xu R, Zhang L Z, Wang Y Y, Wang X N, Zhang L F, Cheng Y L, Qiao W H, Yang Q W. 2018. Fine mapping and identification of a novel locus qGL12.2 control grain length in wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Theor Appl Genet, 131: 1497-1508. |
| [29] | Qiao W H, Qi L, Cheng Z J, Su L, Li J, Sun Y, Ren J F, Zheng X M, Yang Q W. 2016. Development and characterization of chromosome segment substitution lines derived from Oryza rufipogon in the genetic background of O. sativa spp. indica cultivar 9311. BMC Genomics, 17: 580. |
| [30] | Quan R D, Wang J, Hui J, Bai H B, Lyu X L, Zhu Y X, Zhang H W, Zhang Z J, Li S H, Huang R F. 2018. Improvement of salt tolerance using wild rice genes. Front Plant Sci, 8: 2269. |
| [31] | Ruan H H, Yan C Q, An D R, Liu R H, Chen J P. 2008. Identifying and mapping new gene xa32(t) for resistance to bacterial blight (Xanthomonas oryzae pv oryzae, Xoo) from Oryza meyeriana L. Acta Agric Boreal Sin, 17(6): 170-174. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Tan G X, Ren X, Weng Q M, Shi Z Y, Zhu L L, He G C. 2004. Mapping of a new resistance gene to bacterial blight in rice line introgressed from Oryza officinalis. Acta Genet Sin, 31(7): 724-729. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [33] | Tan L B, Liu F X, Xue W, Wang G J, Ye S, Zhu Z F, Fu Y C, Wang X K, Sun C Q. 2007. Development of Oryza rufipogon and O. sativa introgression lines and assessment for yield-related quantitative trait loci. J Integr Plant Biol, 49(6): 871-884. |
| [34] | Tan L B, Li X R, Liu F X, Sun X Y, Li C G, Zhu Z F, Fu Y C, Cai H W, Wang X K, Xie D X, Sun C Q. 2008. Control of a key transition from prostrate to erect growth in rice domestication. Nat Genet, 40: 1360-1364. |
| [35] |
Tanksley S D, McCouch S R. 1997. Seed banks and molecular maps: Unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science, 277: 1063-1066.
PMID |
| [36] | Tian F, Li D J, Fu Q, Zhu Z F, Fu Y C, Wang X K, Sun C Q. 2006. Construction of introgression lines carrying wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) segments in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) background and characterization of introgressed segments associated with yield-related traits. Theor Appl Genet, 112: 570-580. |
| [37] | Wang C L, Zhang X P, Fan Y L, Gao Y, Zhu Q L, Zheng C K, Qin T F, Li Y F, Che J Y, Zhang M W, Yang B, Liu Y G, Zhao K J. 2015. XA23 is an executor R protein and confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Mol Plant, 8(2): 290-302. |
| [38] | Wang E T, Wang J J, Zhu X D, Hao W, Wang L Y, Li Q, Zhang L X, He W, Lu B R, Lin H X, Ma H, Zhang G Q, He Z H. 2008. Control of rice grain-filling and yield by a gene with a potential signature of domestication. Nat Genet, 40: 1370-1374. |
| [39] | Wang H R, Vieira F G, Crawford J E, Chu C C, Nielsen R. 2017. Asian wild rice is a hybrid swarm with extensive gene flow and feralization from domesticated rice. Genome Res, 27: 1029-1038. |
| [40] | Wang J X, Chen Y T, Huang J, Qiao W H, Zhang W X, Yang Q W. 2009. Comparison of genetic diversity between in-situ conserved and non-conserved Oryza rufipogon populations in China. Acta Agron Sin, 35(8): 1474-1482. (in Chinese) |
| [41] | Wei X, Qiao W H, Chen Y T, Wang R S, Cao L R, Zhang W X, Yuan N N, Li Z C, Zeng H L, Yang Q W. 2012. Domestication and geographic origin of Oryza sativa in China: Insights from multi-locus analysis of nucleotide variation of O. sativa and O. rufipogon. Mol Ecol, 21: 5073-5087. |
| [42] | Wu T, Li X, Huang D R, Huang F L, Xiao Y L, Hu B L. 2020. QTL analysis for yield traits related to low nitrogen tolerance using backcrossing recombinant inbred lines derived from Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Chin J Rice Sci, 34(6): 499-511. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [43] | Wu Z G, Fang D M, Yang R, Gao F, An X Y, Zhuo X X, Li Y F, Yi C D, Zhang T, Liang C Z, Cui P, Cheng Z K, Luo Q. 2018. De novo genome assembly of Oryza granulata reveals rapid genome expansion and adaptive evolution. Commun Biol, 1: 84. |
| [44] | Xie X R, Du H L, Tang H W, Tang J N, Tan X Y, Liu W Z, Li T, Lin Z S, Liang C Z, Liu Y G. 2020. A chromosome-level genome assembly of the wild rice Oryza rufipogon facilitates tracing the origins of Asian cultivated rice. Sci China: Life Sci, 64(2): 282-293. |
| [45] | Xu Z J, Wang J L, Zheng X M, Fang Z L, Tang C F, Wang X H, Liu W Q, Zhu Y B, Yang Q W. 2020. Investigation, collection and protection of wild rice germplasm resources in China. J Plant Genet Res, 21(6): 1337-1343. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [46] | Yan Q, Pan Y H, Qin X Y, Gao H L, Li D Y, Feng R, Guo H, Zhu R C. 2012. Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of a rice blast resistance gene Pi-gx(t) derived from common wild rice. J Southern Agric, 43: 1433-1437. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [47] | Yang L, Li R B, Li Y R, Huang F K, Chen Y Z, Huang S S, Huang L F, Liu C, Ma Z F, Huang D H, Jiang J J. 2012. Genetic mapping of bph20(t) and bph21(t) loci conferring brown planthopper resistance to Nilaparvata lugens Stal in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica, 183: 161-171. |
| [48] | Yang Q W, Zhang W X, He D X, Chen D Z, Dai L Y, Chen C B, Huang K D. 2003. Studies on in situ conservation methods of wild rice in China. J Plant Genet Res, 4(1): 63-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [49] | Yang Q W, Qin W B, Zhang W X, Qiao W H, Yu S N, Guo Q. 2013. In situ conservation practices and future development of wild relatives of crops in China. J Plant Genet Res, 14(1): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [50] | Zhang W X, Yang Q W. 2003. Collecting, evaluation and conservation of wild rice resources in China. J Plant Genet Res, 4(4): 369-373. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [51] | Zhang Z Y, Li J J, Pan Y H, Li J L, Zhou L, Shi H L, Zeng Y W, Guo H F, Yang S M, Zheng W W, Yu J P, Sun X M, Li G L, Ding Y L, Ma L, Shen S Q, Dai L Y, Zhang H L, Yang S H, Guo Y, Li Z C. 2017. Natural variation in CTB4a enhances rice adaptation to cold habitats. Nat Commun, 8: 14788. |
| [52] |
Zheng J, Wu H, Zhu H B, Huang C Y, Liu C, Chang Y S, Kong Z C, Zhou Z H, Wang G W, Lin Y J, Chen H. 2019. Determining factors, regulation system, and domestication of anthocyanin biosynthesis in rice leaves. New Phytol, 223(2): 705-721.
PMID |
| [53] | Zhu Z F, Tan L B, Fu Y C, Liu F X, Cai H W, Xie D X, Wu F, Wu J Z, Matsumoto T, Sun C Q. 2013. Genetic control of inflorescence architecture during rice domestication. Nat Commun, 4: 2200. |
| [1] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [2] | Si Fengfeng, Fan Fengfeng, Wei Xiao, He Shihao, Li Xianlong, Peng Xiaojue, Li Shaoqing. Quantitative Trait Locus Mapping of High Photosynthetic Efficiency and Biomass in Oryza longistaminata [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(6): 569-576. |
| [3] | Nie Yuanyuan, Xia Hui, Ma Xiaosong, Lou Qiaojun, Liu Yi, Zhang Anling, Cheng Liang, Yan Longan, Luo Lijun. Dissecting Genetic Basis of Deep Rooting in Dongxiang Wild Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(3): 277-287. |
| [4] | Weidong Qi, Hongping Chen, Zuozhen Yang, Biaolin Hu, Xiangdong Luo, Bing Ai, Yuan Luo, Yu Huang, Jiankun Xie, Fantao Zhang. Systematic Characterization of Long Non-Coding RNAs and Their Responses to Drought Stress in Dongxiang Wild Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(1): 21-31. |
| [5] | P. M. Swamy B., Kaladhar K., Anuradha K., K. Batchu Anil, Longvah T., Sarla N.. QTL Analysis for Grain Iron and Zinc Concentrations in Two O. nivara Derived Backcross Populations [J]. Rice Science, 2018, 25(4): 197-207. |
| [6] | Fantao Zhang, Yuan Luo, Meng Zhang, Yi Zhou, Hongping Chen, Biaolin Hu, Jiankun Xie. Identification and Characterization of Drought Stress- Responsive Novel microRNAs in Dongxiang Wild Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2018, 25(4): 175-184. |
| [7] | Haritha G., P. M. Swamy B., L. Naik M., Jyothi B., Divya B., Malathi S., Sarla N.. Yield Traits and Associated Marker Segregation in Elite Introgression Lines Derived from O. sativa × O. nivara [J]. Rice Science, 2018, 25(1): 19-31. |
| [8] | SHEN Xian-hua, YAN Song, HUANG Ren-liang, ZHU Shan, XIONG Hong-liang, SHEN Lin-jun. Development of Novel Cytoplasmic Male Sterile Source from Dongxiang Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon) [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2013, 20(5): 379-382. |
| [9] | CHENG Zai-quan1, YING Fu-you1, LI Ding-qing1, YU Teng-qiong1, FU Jian1, YAN Hui-jun2, ZHONG Qiao-fang1, ZHANG Dun-yu1, LI Wei-jiao1, HUANG Xing-qi1, 2 . Genetic Diversity of Wild Rice Species in Yunnan Province of China [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2012, 19(1): 21-28. |
| [10] | FU Xue-lin, LU Yong-gen, LIU Xiang-dong, LI Jin-quan, ZHAO Xing-juan. Comparative Embryological Studies on Infertility of Interspecific Hybridizations Between Oryza sativa with Different Ploidy Levels and O. officinalis [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2009, 16(1): 58-64 . |
| [11] | YI Chuan-deng, CHENG Xu, WANG Bei-bei, LIANG Guo-hua, GONG Zhi-yun, TANG Shu-zhu, GU Ming-hong. Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis of Spontaneous Interspecific Hybrid Between Oryza sativa and Oryza minuta [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2008, 15(4): 283-288 . |
| [12] | FU Xue-lin, LU Yong-gen, LIU Xiang-dong, LI Jin-quan. Progress on Transferring Elite Genes from Non-AA Genome Wild Rice into Oryza sativa through Interspecific Hybridization [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2008, 15(2): 79-87 . |
| [13] | CHEN Xiao-rong, YANG Kong-song, FU Jun-ru, ZHU Chang-lan, PENG Xiao-song, HE Xiao-peng, HE Hao-hua . Identification and Genetic Analysis of Fertility Restoration Ability in Dongxiang Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon) [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2008, 15(1): 21-28 . |
| [14] | LIU Shi-ping, NIE Xin-tao, DAI Qi-gen, HUO Zhong-yang, XU Ke. Effect of Interplanting with Zero Tillage and Straw Manure on Rice Growth and Rice Quality [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2007, 14(3): 204-210 . |
| [15] | WAN Shu-qing, LIU Xiang-fa, FENG Guo-zhong, PAN Da-jian. Repellent Activity of Extracts of Wild Rice Species against Panonychus citri and Aphis citricola in Associated with Esterase Isoenzyme in Insests [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2006, 13(2): 146-148 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||