
Rice Science ›› 2023, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 207-221.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2023.03.005
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Long Xinkang, Guan Chunmin, Wang Lin, Jia Liting, Fu Xiangjin, Lin Qinlu, Huang Zhengyu, Liu Chun( )
)
Received:2022-07-11
Accepted:2023-01-16
Online:2023-05-28
Published:2023-03-13
Contact:
Liu Chun (chunliu@csuft.edu.cn; liuchunxl@163.com)
Long Xinkang, Guan Chunmin, Wang Lin, Jia Liting, Fu Xiangjin, Lin Qinlu, Huang Zhengyu, Liu Chun. Rice Storage Proteins: Focus on Composition, Distribution, Genetic Improvement and Effects on Rice Quality[J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(3): 207-221.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Rice fraction | Albumin | Globulin | Prolamin | Glutelin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice bran | 37 | 36 | 5 | 22 |
| Fine bran | 30 | 14 | 5 | 51 |
| Milled rice | 5 | 9 | 3 | 83 |
Table 1. Distributions of albumin, globulin, prolamin and glutelin (Ren et al, 2002). %
| Rice fraction | Albumin | Globulin | Prolamin | Glutelin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice bran | 37 | 36 | 5 | 22 |
| Fine bran | 30 | 14 | 5 | 51 |
| Milled rice | 5 | 9 | 3 | 83 |
| Rice | Crude protein content (g) |
|---|---|
| Brown rice | 7.1-8.3 |
| Milled rice | 6.3-7.1 |
| Rice bran | 11.3-14.9 |
| Rice hull | 2.0-2.8 |
Table 2. Proximate protein contents of rough rice and its milling fractions (Juliano, 1993).
| Rice | Crude protein content (g) |
|---|---|
| Brown rice | 7.1-8.3 |
| Milled rice | 6.3-7.1 |
| Rice bran | 11.3-14.9 |
| Rice hull | 2.0-2.8 |
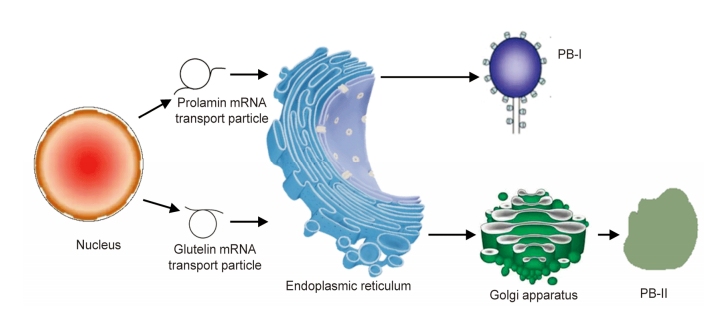
Fig. 3. Biosynthesis of prolamin and glutelin. PB-I, Spherical type I protein body with concentric-sheet structure; PB-II, Ellipsoid type II protein body without sheet structure.
| QTL | Chromosome | Marker interval | Crossing parent | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qPC-6 | 6 | C952-Wx | Zhenshan 97/Minghui 63 | Tan et al, |
| qPC-7 | 7 | R1245-RM234 | Zhenshan 97/Minghui 63 | Tan et al, |
| Pro1 | 1 | RM226-RM297 | Caiapo/IRGC103544 | Aluko et al, |
| Pro2 | 2 | RM6-RM112 | Caiapo/IRGC103544 | Aluko et al, |
| Pro6 | 6 | RM190-RM253 | Caiapo/IRGC103544 | Aluko et al, |
| Pro11 | 11 | RM209-RM229 | Caiapo/IRGC103544 | Aluko et al, |
| RPC-1 | 1 | RG811-BP127 | Gui 630/02428 | Hu et al, |
| RPC-4 | 4 | C22-RG449d | Gui 630/02428 | Hu et al, |
| RPC-5 | 5 | RG435-RG172a | Gui 630/02428 | Hu et al, |
| RPC-6 | 6 | RG171-RG119a | Gui 630/02428 | Hu et al, |
| RPC-7 | 7 | ZG34B-G20 | Gui 630/02428 | Hu et al, |
| cpb1, cph1 | 1 | E14M61.325 | Cypress/Panda | Kepiro et al, |
| cpb4, cph4 | 4 | E12M61.256 | Cypress/Panda | Kepiro et al, |
| cph2 | 2 | E16M51.240 | Cypress/Panda | Kepiro et al, |
| qALB-1 | 1 | R3203-XNpb113 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qALB-2 | 2 | XNpb349-V83B | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qGLB-1 | 1 | XNpb113-XNpb93 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qGLB-2.1, qGLT-2 | 2 | XNpb89-3eC1470 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qGLB-2.2 | 2 | XNpb250-C560 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qGLB-5 | 5 | XNpb81-G1103 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qPLA-1 | 1 | R210-C1211 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qPLA-3 | 3 | XNpb48-C393B | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qPLA-10, qGLT-10 | 10 | C16-C797 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qGLT-11 | 11 | XNpb320-C496 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qGLT-12, qCP-12 | 12 | XNpb193-C562B | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qCP-2 | 2 | XNpb204-R418 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qCP-7 | 7 | R1245-R1789 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qPC-6 | 6 | RM588-RM540 | Chuan 7/Nanyangzhan | Lou et al, |
| qPC-7 | 7 | RM5436-RM6776 | Chuan 7/Nanyangzhan | Lou et al, |
| qPC-3 | 3 | RM251-RM282 | Xieqingzao B/Milyang 46 | Yu et al, |
| qPC-4 | 4 | RG214-RG620 | Xieqingzao B/Milyang 46 | Yu et al, |
| qPC-5 | 5 | RG470-RZ70 | Xieqingzao B/Milyang 46 | Yu et al, |
| qPC-6 | 6 | RM190-RZ516 | Xieqingzao B/Milyang 46 | Yu et al, |
| qPC-10 | 10 | RM184-RM3229B | Xieqingzao B/Milyang 46 | Yu et al, |
| qPC-1 | 1 | R886-R1485 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-3.1 | 3 | XNpb212-G1318 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-3.2 | 3 | R758-XNpb15 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-3.3 | 3 | C606-XNpb238 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-4 | 4 | R1854-R2373 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-6 | 6 | C1003-C688 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-7.1 | 7 | XNpb338-C796 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-7.2 | 7 | XNpb268-R411 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-8 | 8 | C483-C259G | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-9 | 9 | R265B-XNpb36 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-10 | 10 | C16-C809 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-12 | 12 | XNpb24-C562 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-1a, qPC-1b | 1 | R1982, XNpb113 | Asominori/IR24 | Liu et al, |
| qPC-2 | 2 | XNpb67 | Asominori/IR24 | Liu et al, |
| qPC-3 | 3 | C563 | Asominori/IR24 | Liu et al, |
| qPC-6 | 6 | C688 | Asominori/IR24 | Liu et al, |
| qPC-8a, qPC-8b | 8 | G1149, XNpb41 | Asominori/IR24 | Liu et al, |
| qPC-11 | 11 | C1350 | Asominori/IR24 | Liu et al, |
| qPC7 | 7 | RM8261 | Cheongcheong/Nagdong | Bruno et al, |
| qPC2 | 2 | S2_24197424 | 258 accessions from 3 K Rice Genome Project | Wang et al, |
| qPC10 | 10 | S10_17723490 | 258 accessions from 3 K Rice Genome Project | Wang et al, |
| TGP12 | 12 | RM1880-RM2935 | Koshihikari/Nona Bokra | Kashiwagi and Munakata, |
| qGPC-1 | 1 | RM7124 | Habataki/Sasanishiki | Yang et al, |
| qGPC-10 | 10 | RM7217 | Habataki/Sasanishiki | Yang et al, |
| qPro9 | 9 | 9851330-9848867 | Hwayeong/Wandoaengmi 6 | Park et al, |
Table 3. Mapped QTLs related with rice storage proteins.
| QTL | Chromosome | Marker interval | Crossing parent | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qPC-6 | 6 | C952-Wx | Zhenshan 97/Minghui 63 | Tan et al, |
| qPC-7 | 7 | R1245-RM234 | Zhenshan 97/Minghui 63 | Tan et al, |
| Pro1 | 1 | RM226-RM297 | Caiapo/IRGC103544 | Aluko et al, |
| Pro2 | 2 | RM6-RM112 | Caiapo/IRGC103544 | Aluko et al, |
| Pro6 | 6 | RM190-RM253 | Caiapo/IRGC103544 | Aluko et al, |
| Pro11 | 11 | RM209-RM229 | Caiapo/IRGC103544 | Aluko et al, |
| RPC-1 | 1 | RG811-BP127 | Gui 630/02428 | Hu et al, |
| RPC-4 | 4 | C22-RG449d | Gui 630/02428 | Hu et al, |
| RPC-5 | 5 | RG435-RG172a | Gui 630/02428 | Hu et al, |
| RPC-6 | 6 | RG171-RG119a | Gui 630/02428 | Hu et al, |
| RPC-7 | 7 | ZG34B-G20 | Gui 630/02428 | Hu et al, |
| cpb1, cph1 | 1 | E14M61.325 | Cypress/Panda | Kepiro et al, |
| cpb4, cph4 | 4 | E12M61.256 | Cypress/Panda | Kepiro et al, |
| cph2 | 2 | E16M51.240 | Cypress/Panda | Kepiro et al, |
| qALB-1 | 1 | R3203-XNpb113 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qALB-2 | 2 | XNpb349-V83B | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qGLB-1 | 1 | XNpb113-XNpb93 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qGLB-2.1, qGLT-2 | 2 | XNpb89-3eC1470 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qGLB-2.2 | 2 | XNpb250-C560 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qGLB-5 | 5 | XNpb81-G1103 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qPLA-1 | 1 | R210-C1211 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qPLA-3 | 3 | XNpb48-C393B | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qPLA-10, qGLT-10 | 10 | C16-C797 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qGLT-11 | 11 | XNpb320-C496 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qGLT-12, qCP-12 | 12 | XNpb193-C562B | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qCP-2 | 2 | XNpb204-R418 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qCP-7 | 7 | R1245-R1789 | Asominori/IR24 | Zhang et al, |
| qPC-6 | 6 | RM588-RM540 | Chuan 7/Nanyangzhan | Lou et al, |
| qPC-7 | 7 | RM5436-RM6776 | Chuan 7/Nanyangzhan | Lou et al, |
| qPC-3 | 3 | RM251-RM282 | Xieqingzao B/Milyang 46 | Yu et al, |
| qPC-4 | 4 | RG214-RG620 | Xieqingzao B/Milyang 46 | Yu et al, |
| qPC-5 | 5 | RG470-RZ70 | Xieqingzao B/Milyang 46 | Yu et al, |
| qPC-6 | 6 | RM190-RZ516 | Xieqingzao B/Milyang 46 | Yu et al, |
| qPC-10 | 10 | RM184-RM3229B | Xieqingzao B/Milyang 46 | Yu et al, |
| qPC-1 | 1 | R886-R1485 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-3.1 | 3 | XNpb212-G1318 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-3.2 | 3 | R758-XNpb15 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-3.3 | 3 | C606-XNpb238 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-4 | 4 | R1854-R2373 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-6 | 6 | C1003-C688 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-7.1 | 7 | XNpb338-C796 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-7.2 | 7 | XNpb268-R411 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-8 | 8 | C483-C259G | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-9 | 9 | R265B-XNpb36 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-10 | 10 | C16-C809 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-12 | 12 | XNpb24-C562 | Asominori/IR24 | Zheng et al, |
| qPC-1a, qPC-1b | 1 | R1982, XNpb113 | Asominori/IR24 | Liu et al, |
| qPC-2 | 2 | XNpb67 | Asominori/IR24 | Liu et al, |
| qPC-3 | 3 | C563 | Asominori/IR24 | Liu et al, |
| qPC-6 | 6 | C688 | Asominori/IR24 | Liu et al, |
| qPC-8a, qPC-8b | 8 | G1149, XNpb41 | Asominori/IR24 | Liu et al, |
| qPC-11 | 11 | C1350 | Asominori/IR24 | Liu et al, |
| qPC7 | 7 | RM8261 | Cheongcheong/Nagdong | Bruno et al, |
| qPC2 | 2 | S2_24197424 | 258 accessions from 3 K Rice Genome Project | Wang et al, |
| qPC10 | 10 | S10_17723490 | 258 accessions from 3 K Rice Genome Project | Wang et al, |
| TGP12 | 12 | RM1880-RM2935 | Koshihikari/Nona Bokra | Kashiwagi and Munakata, |
| qGPC-1 | 1 | RM7124 | Habataki/Sasanishiki | Yang et al, |
| qGPC-10 | 10 | RM7217 | Habataki/Sasanishiki | Yang et al, |
| qPro9 | 9 | 9851330-9848867 | Hwayeong/Wandoaengmi 6 | Park et al, |
| Analytical detection technique | Detectable indicator | Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Sensory evaluation method | Odor, appearance structure, palatability, taste, texture, etc. | Sensory evaluation of rice odor, palatability, taste, appearance, texture and other indexes |
| Iodo blue colorimetry | Amylose content (AC) | Amylose reacts with iodine turned blue, and amylopectin reacts with iodine turned red (Olivares Díaz et al, |
| Potassium hydroxide assay | Gel consistency | Rice starch is hot gelatinized into rice gum by dilute alkali and extends to some extent in a test tube placed horizontally after cooling, and the length of rice gum after extension is measured (Bhattacharya, |
| Alkali spreading value | Gelatinization temperature (GT) | Alkali spreading value is just opposite to GT, with high alkali spreading values corresponding to low GTs. GT is indirectly determined (Bhattacharya, |
| Rapid viscosity analyzer | Viscosity, pasting properties, etc. | A controlled deformation or strain is applied at a given time, and the final force response is measured to obtain the relevant mechanical parameters (Martínez, |
| Raman spectroscopy | Compositional structure analysis, variety discrimination, quality testing, etc. | Scattered light is used to obtain relevant information about molecular vibrations providing information about their structure, symmetry, electronic environment, and the molecules to which they are bound (Wei et al, |
| Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance | Moisture content and moisture distribution | A specific pulse sequence is used to excite nuclei with a fixed magnetic moment in the sample, which then produces a series of detectable sensing signals with strong attenuation (Ezeanaka et al, |
| Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry | Volatile components and their contents | Separation, qualitative and quantitative detection technology combining high separation ability of chromatography and high identification ability of mass spectrometry (Likić, |
| Texture analyzer | Hardness, chewiness, cohesion, cohesion, elasticity, etc. | Reaction force of the sample on the probe is sensed, and the mechanical signal is transformed into numbers and graphics (Rolle et al, |
| Colorimeter | Chroma | Color parameters are determined by detecting the spectral components of the sample (Wang C B et al, |
| Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) | AC, protein content (PC), amino acid content, fat content, etc. | NIRS mainly reflects the frequency doubling, spectral frequency, as well as the superimposed absorption of the vibration of hydrogen containing groups (C-H, O-H, N-H, etc.) in samples, and contains information about sample composition state, molecular structure, and so on (Osborne, |
| Computer vision technology | Chalkiness, grain type, head rice yield, PC, AC, etc. | Using computer simulations of human macroscopic visual function (Meng et al, |
| Electronic nose | Odor properties | Using metal oxides and biofilms, aroma is judged by the small changes in membrane potential caused by molecular contact of the odorant (Zhong, |
Table 4. Analytical techniques for detecting rice quality.
| Analytical detection technique | Detectable indicator | Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Sensory evaluation method | Odor, appearance structure, palatability, taste, texture, etc. | Sensory evaluation of rice odor, palatability, taste, appearance, texture and other indexes |
| Iodo blue colorimetry | Amylose content (AC) | Amylose reacts with iodine turned blue, and amylopectin reacts with iodine turned red (Olivares Díaz et al, |
| Potassium hydroxide assay | Gel consistency | Rice starch is hot gelatinized into rice gum by dilute alkali and extends to some extent in a test tube placed horizontally after cooling, and the length of rice gum after extension is measured (Bhattacharya, |
| Alkali spreading value | Gelatinization temperature (GT) | Alkali spreading value is just opposite to GT, with high alkali spreading values corresponding to low GTs. GT is indirectly determined (Bhattacharya, |
| Rapid viscosity analyzer | Viscosity, pasting properties, etc. | A controlled deformation or strain is applied at a given time, and the final force response is measured to obtain the relevant mechanical parameters (Martínez, |
| Raman spectroscopy | Compositional structure analysis, variety discrimination, quality testing, etc. | Scattered light is used to obtain relevant information about molecular vibrations providing information about their structure, symmetry, electronic environment, and the molecules to which they are bound (Wei et al, |
| Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance | Moisture content and moisture distribution | A specific pulse sequence is used to excite nuclei with a fixed magnetic moment in the sample, which then produces a series of detectable sensing signals with strong attenuation (Ezeanaka et al, |
| Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry | Volatile components and their contents | Separation, qualitative and quantitative detection technology combining high separation ability of chromatography and high identification ability of mass spectrometry (Likić, |
| Texture analyzer | Hardness, chewiness, cohesion, cohesion, elasticity, etc. | Reaction force of the sample on the probe is sensed, and the mechanical signal is transformed into numbers and graphics (Rolle et al, |
| Colorimeter | Chroma | Color parameters are determined by detecting the spectral components of the sample (Wang C B et al, |
| Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) | AC, protein content (PC), amino acid content, fat content, etc. | NIRS mainly reflects the frequency doubling, spectral frequency, as well as the superimposed absorption of the vibration of hydrogen containing groups (C-H, O-H, N-H, etc.) in samples, and contains information about sample composition state, molecular structure, and so on (Osborne, |
| Computer vision technology | Chalkiness, grain type, head rice yield, PC, AC, etc. | Using computer simulations of human macroscopic visual function (Meng et al, |
| Electronic nose | Odor properties | Using metal oxides and biofilms, aroma is judged by the small changes in membrane potential caused by molecular contact of the odorant (Zhong, |
| Quality criterion | Protein content |
|---|---|
| Aroma | -0.324 |
| Flavour | -0.718** |
| Tenderness | -0.382 |
| Cohesiveness | -0.310 |
| Colour | 0.704** |
| Gloss | -0.343 |
Table 5. Correlation between eating quality scores and protein content of 23 samples of milled non-waxy rice (Bhattacharya, 2011).
| Quality criterion | Protein content |
|---|---|
| Aroma | -0.324 |
| Flavour | -0.718** |
| Tenderness | -0.382 |
| Cohesiveness | -0.310 |
| Colour | 0.704** |
| Gloss | -0.343 |
| Physical characteristic | Albumin | Globulin | Prolamin | Glutelin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensory quality | -0.273 | -0.091 | -0.549 | -0.226 |
| Gel consistency (mm) | -0.768 | 0.208 | -0.874* | -0.360 |
| Hardness (N) | -0.706 | 0.280 | -0.831* | -0.355 |
| Viscosity (N·s) | -0.274 | -0.502 | 0.284 | 0.528 |
| Cohesion | -0.832* | 0.476 | -0.786 | -0.041 |
| Elastic | -0.597 | 0.468 | -0.968* | -0.772 |
| Gumminess (N) | -0.851* | 0.487 | -0.882** | -0.169 |
| Chewiness (N) | -0.847* | 0.533 | -0.921** | -0.259 |
Table 6. Correlation coefficients between protein components and physical and sensory properties of cooked rice (Wang P Y et al, 2016).
| Physical characteristic | Albumin | Globulin | Prolamin | Glutelin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensory quality | -0.273 | -0.091 | -0.549 | -0.226 |
| Gel consistency (mm) | -0.768 | 0.208 | -0.874* | -0.360 |
| Hardness (N) | -0.706 | 0.280 | -0.831* | -0.355 |
| Viscosity (N·s) | -0.274 | -0.502 | 0.284 | 0.528 |
| Cohesion | -0.832* | 0.476 | -0.786 | -0.041 |
| Elastic | -0.597 | 0.468 | -0.968* | -0.772 |
| Gumminess (N) | -0.851* | 0.487 | -0.882** | -0.169 |
| Chewiness (N) | -0.847* | 0.533 | -0.921** | -0.259 |
| [1] | Al-Doury M K W, Hettiarachchy N S, Horax R. 2018. Rice-endosperm and rice-bran proteins: A review. J Am Oil Chem Soc, 95(8): 943-956. |
| [2] | Ali M M, Hashim N, Abd Aziz S, Lasekan O. 2020. Principles and recent advances in electronic nose for quality inspection of agricultural and food products. Trends Food Sci Technol, 99: 1-10. |
| [3] | Aluko G, Martinez C, Tohme J, Castano C, Bergman C, Oard J H. 2004. QTL mapping of grain quality traits from the interspecific cross Oryza sativa × O. glaberrima. Theor Appl Genet, 109(3): 630-639. |
| [4] | Amagliani L, O’Regan J, Kelly A L, O’Mahony J A. 2016. Chemistry, structure, functionality and applications of rice starch. J Cereal Sci, 70: 291-300. |
| [5] | Amagliani L, O’Regan J, Kelly A L, O’Mahony J A. 2017. The composition, extraction, functionality and applications of rice proteins: A review. Trends Food Sci Technol, 64: 1-12. |
| [6] | Bhattacharya K R. 2011. Rice Quality: A Guide to Rice Properties and Analysis. Woodhead Publishing. |
| [7] | Birla D S, Malik K, Sainger M, Chaudhary D, Jaiwal R, Jaiwal P K. 2017. Progress and challenges in improving the nutritional quality of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 57(11): 2455-2481. |
| [8] | Bruno E, Choi Y S, Chung I K, Kim K M. 2017. QTLs and analysis of the candidate gene for amylose, protein, and moisture content in rice (Oryza sativa L.). 3 Biotech, 7(1): 40. |
| [9] | Champagne E T, Bett-Garber K L, Thomson J L, Fitzgerald M A. 2009. Unraveling the impact of nitrogen nutrition on cooked rice flavor and texture. Cereal Chem J, 86(3): 274-280. |
| [10] | Chattopadhyay K, Sharma S G, Bagchi T B, Molla K A, Sarkar S, Marndi B C, Sarkar A, Dash S K, Singh O N. 2018. Development of recombinant high yielding lines with improved protein content in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Agric Sci, 156(2): 241-257. |
| [11] | Chen J Y, Miao Y L, Sato S, Zhang H. 2008. Near infrared spectroscopy for determination of the protein composition of rice flour. Food Sci Technol Res, 14(2): 132-138. |
| [12] | Chen P F, Gu J R, Qiao Z Y, Zhao B H, Ji H J, Dong M H. 2018. Study on rice quality of main japonica rice varieties in Jiangsu Province. Southwest China J Agric Sci, 31(5): 877-883. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Chen R Z, Deng Y W, Ding Y L, Guo J X, Qiu J, Wang B, Wang C S, Xie Y Y, Zhang Z H, Chen J X, Chen L T, Chu C C, He G C, He Z H, Huang X H, Xing Y Z, Yang S H, Xie D X, Liu Y G, Li J Y. 2022. Rice functional genomics: Decades’ efforts and roads ahead. Sci China Life Sci, 65(1): 33-92. |
| [14] | Chen Y, Wang M, Ouwerkerk P B F. 2012. Molecular and environmental factors determining grain quality in rice. Food Energy Secur, 1(2): 111-132. |
| [15] | Chen Z H, Du H X, Tao Y J, Xu Y, Wang F Q, Li B, Zhu Q H, Niu H B, Yang J. 2022. Efficient breeding of low glutelin content rice germplasm by simultaneous editing multiple glutelin genes via CRISPR/Cas9. Plant Sci, 324: 111449. |
| [16] | Chrastil J. 1990. Protein-starch interactions in rice grains: Influence of storage on oryzenin and starch. J Agric Food Chem, 38(9): 1804-1809. |
| [17] | Cui J, Zhang X, Cui Z Q, Kusutani A, Ito S, Matsue Y. 2016. Correlation between evaluation of palatability by sensory test and physicochemical properties in Chinese japonica-type rice. J Fac Agric Kyushu Univ, 61(1): 53-58. |
| [18] | Detchewa P, Prasajak P, Phungamngoen C, Sriwichai W, Naivikul O, Moongngarm A. 2022. Substitution of rice flour with rice protein improved quality of gluten-free rice spaghetti processed using single screw extrusion. LWT, 153: 112512. |
| [19] | Ding D L, Zhang X, Zhao M, Yang X, Cui J, Shi L L, Wang S W. 2010. Relationships among quality traits of japonica rice varieties. Crops, 629(5): 60-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | Ding Y, Hua Z T, Wang F, Cai Z, Wang L, Guo D X. 2012. Effect of protein content on cooking and eating quality of japonica rice. Food Sci, 33(23): 42-46. |
| [21] | Doliente S S, Samsatli S. 2021. Integrated production of food, energy, fuels and chemicals from rice crops: Multi-objective optimisation for efficient and sustainable value chains. J Cleaner Product, 285: 124900. |
| [22] | Ezeanaka M C, Nsor-Atindana J, Zhang M. 2019. Online low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (LF-NMR) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for food quality optimization in food processing. Food Bioprocess Technol, 12(9): 1435-1451. |
| [23] | Fedorov F S, Yaqin A, Krasnikov D V, Kondrashov V A, Ovchinnikov G, Kostyukevich Y, Osipenko S, Nasibulin A G. 2021. Detecting cooking state of grilled chicken by electronic nose and computer vision techniques. Food Chem, 345: 128747. |
| [24] |
Furukawa S, Mizuma T, Kiyokawa Y, Masumura T, Tanaka K, Wakai Y. 2003. Distribution of storage proteins in low-glutelin rice seed determined using a fluorescent antibody. J Biosci Bioeng, 96(5): 467-473.
PMID |
| [25] | Furukawa S, Tanaka K, Masumura T, Ogihara Y, Kiyokawa Y, Wakai Y. 2006. Influence of rice proteins on eating quality of cooked rice and on aroma and flavor of sake. Cereal Chem J, 83(4): 439-446. |
| [26] | Gao Y, Liu C L, Li Y Y, Zhang A P, Dong G J, Xie L H, Zhang B, Ruan B P, Hong K, Xue D W, Zeng D L, Guo L B, Qian Q, Gao Z Y. 2016. QTL analysis for chalkiness of rice and fine mapping of a candidate gene for qACE9. Rice, 9(1): 41. |
| [27] | Gong T, Zhao S M, Xiong S B, Qu M Y. 2008. Effect of cooking technology on protein nutrition quality of cooked rice. J Chin Cereals Oils Assoc, 23(4): 14-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Goñi S M, Salvadori V O. 2017. Color measurement: Comparison of colorimeter vs. computer vision system. J Food Meas Charact, 11(2): 538-547. |
| [29] | Guo Y L, Fang L I, Hong Y, Liu Y. 2015. Study on the correlation between properties of rice and the quality of cooked rice. J Wuhan Polytech Univ, 34(3): 5-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Hamaker B R, Griffin V K. 1990. Changing the viscoelastic properties of cooked rice through protein disruption. Cereal Chem, 67(3): 261-264. |
| [31] | Hamaker B R, Griffin V K. 1993. Effect of disulfide bond-containing protein on rice starch gelatinization and pasting. Cereal Chem J, 70(4): 377-380. |
| [32] | He W, Wang L, Lin Q L, Yu F. 2021. Rice seed storage proteins: Biosynthetic pathways and the effects of environmental factors. J Integr Plant Biol, 63(12): 1999-2019. |
| [33] |
Hou X, Han M, Dai X H, Yang X F, Yi S G. 2013. A multi-residue method for the determination of 124 pesticides in rice by modified QuEChERS extraction and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem, 138: 1198-1205.
PMID |
| [34] | Hu Z L, Li P, Zhou M Q, Zhang Z H, Wang L X, Zhu L H, Zhu Y G. 2004. Mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for rice protein and fat content using doubled haploid lines. Euphytica, 135(1): 47-54. |
| [35] | Hua Z T, Ding Y, Wang F, Zhang Q. 2012. Study on protein components and microstructure of the japonica restorer line M119 with high protein content. Appl Mech Mater, 140: 441-445. |
| [36] | Huang M, Tang Q Y, Ao H J, Zou Y B. 2017. Yield potential and stability in super hybrid rice and its production strategies. J Integr Agric, 16(5): 1009-1017. |
| [37] | Huang S J, Zhao C F, Zhu Z, Zhou L H, Zheng Q H, Wang C L. 2020. Characterization of eating quality and starch properties of two Wx alleles japonica rice cultivars under different nitrogen treatments. J Integr Agric, 19(4): 988-998. |
| [38] | Jayaprakash G, Bains A, Chawla P, Fogarasi M, Fogarasi S. 2022. A narrative review on rice proteins: Current scenario and food industrial application. Polymers, 14(15): 3003. |
| [39] | Juliano B O. 1993. Rice in Human Nutrition. Manila, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute. |
| [40] | Kang M Y, Rico C W, Kim C E, Lee S C. 2011. Physicochemical properties and eating qualities of milled rice from different Korean elite rice varieties. Int J Food Prop, 14(3): 640-653. |
| [41] | Kashiwagi T, Munakata J. 2018. Identification and characteristics of quantitative trait locus for grain protein content, TGP12, in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica, 214(9): 1-15. |
| [42] |
Kawakatsu T, Yamamoto M P, Hirose S, Yano M, Takaiwa F. 2008. Characterization of a new rice glutelin gene GluD-1 expressed in the starchy endosperm. J Exp Bot, 59(15): 4233-4245.
PMID |
| [43] | Kawakatsu T, Yamamoto M P, Touno S M, Yasuda H, Takaiwa F. 2009. Compensation and interaction between RISBZ1 and RPBF during grain filling in rice. Plant J, 59(6): 908-920. |
| [44] | Kepiro J L, McClung A M, Chen M H, Yeater K M, Fjellstrom R G. 2008. Mapping QTLs for milling yield and grain characteristics in a tropical japonica long grain cross. J Cereal Sci, 48(2): 477-485. |
| [45] | Kim H, Kim O W, Kwak H S, Kim S S, Lee H J. 2017. Prediction model of rice eating quality using physicochemical properties and sensory quality evaluation. J Sens Stud, 32(4): e12273. |
| [46] | Kubota M, Saito Y, Masumura T, Kumagai T, Watansbe R, Fujimura S, Kadowaki M. 2010. Improvement in the in vivo digestibility of rice protein by alkali extraction is due to structural changes in prolamin/protein body-I particle. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 74(3): 614-619. |
| [47] |
Kusano M, Yang Z, Okazaki Y, Nakabayashi R, Fukushima A, Saito K. 2015. Using metabolomic approaches to explore chemical diversity in rice. Mol Plant, 8(1): 58-67.
PMID |
| [48] | Lang G H, Kagiya Y, Ohnishi-Kameyama M, Kitta K. 2013. Evaluation of extraction solutions for biochemical analyses of the proteins in rice grains. Biosci, Biotechnol Biochem, 77(1): 126-131. |
| [49] | Lee J Y, Kang J W, Jo S M, Kwon Y H, Lee S M, Lee S B, Shin D J, Park D S, Lee J H, Ko J M, Cho J H. 2021. Screening and breeding for biofortification of rice with protein and high lysine contents. Plant Breed Biotechnol, 9(3): 199-212. |
| [50] | Li J Y, Xu S B, Yang L J, Zhou Y, Fan S J, Zhang W. 2009. Breeding elite japonica-type soft rice with high protein content through the introduction of the anti-waxy gene. Afr J Biotechnol, 8: 161-166. |
| [51] | Li S H, Song Y Y, Dong M S, Li T P. 2017. Analysis of correlations between physicochemical properties and eating quality of rice. Food Res Develop, 38(23): 26-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [52] | Liang C G, Liu J, Wang Y, Xiong D, Ding C B, Li T. 2015. Low light during grain filling stage deteriorates rice cooking quality, but not nutritional value. Rice Sci, 22(4): 197-206. |
| [53] |
Likić V A. 2009. Extraction of pure components from overlapped signals in gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). BioData Min, 2(1): 6.
PMID |
| [54] |
Liu F, Ren Y L, Wang Y H, Peng C, Zhou K N, Lv J, Guo X P, Zhang X, Zhong M S, Zhao S L, Jiang L, Wang H Y, Bao Y Q, Wan J M. 2013. OsVPS9A functions cooperatively with OsRAB5A to regulate post-Golgi dense vesicle-mediated storage protein trafficking to the protein storage vacuole in rice endosperm cells. Mol Plant, 6(6): 1918-1932.
PMID |
| [55] | Liu Q Q, Zhou L H, Wang H M, Gu M H. 2008. Advances on biosynthesis of rice seed storage proteins in molecular biology. Mol Plant Breed, 6(1): 1-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [56] | Liu Y X, Cao M J, Liu G M. 2019. Texture analyzers for food quality evaluation. In: Zhong J, Wang X C. Evaluation Technologies for Food Quality. Amsterdam, the Netherland: Elsevier: 441-463. |
| [57] | Lou J, Chen L, Yue G H, Lou Q J, Mei H W, Xiong L, Luo L J. 2009. QTL mapping of grain quality traits in rice. J Cereal Sci, 50(2): 145-151. |
| [58] | Lu D D, Yong M L, Tao Y, Ye M, Zhang Z J. 2022. Characteristics of grain protein accumulation and Its response to nitrogen level in good taste rice varieties. Chin J Rice Sci, 36(5): 520-530. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [59] | Mandal S, Mandal R K. 2000. Seed storage proteins and approaches for improvement of their nutritional quality by genetic engineering. Curr Sci, 79(5): 576-589. |
| [60] | Mariotti M, Fongaro L, Catenacci F. 2010. Alkali spreading value and image analysis. J Cereal Sci, 52(2): 227-235. |
| [61] | Marshall W E, Wadsworth J I. 1994. Rice science and technology. Science, 214: 495-495. |
| [62] | Martin M, Fitzgerald M A. 2002. Proteins in rice grains influence cooking properties! J Cereal Sci, 36(3): 285-294. |
| [63] | Martínez M M. 2015. Applications of the rapid visco analyser (RVA) in the food industry: A broader view. Perten Sci World, (11): 14-19. |
| [64] | Matsue Y, Odahara K, Hiramatsu M. 1995. Differences in amylose content, amylographic characteristics and storage proteins of grains on primary and secondary Rachis branches in rice. Jpn J Crop Sci, 64(3): 601-606. |
| [65] | Meng N, Liu M, Liu Y X, Zan X M, Sun Y, Zhang P Y, Tan B. 2019. Application and prospect of nondestructive testing technology in rice quality detection. Sci Technol Cereals Oils Foods, 27(6): 98-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [66] |
Miura K, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M. 2011. The role of QTLs in the breeding of high-yielding rice. Trends Plant Sci, 16(6): 319-326.
PMID |
| [67] | Nascimento L Á, Abhilasha A, Singh J, Elias M C, Colussi R. 2022. Rice germination and its impact on technological and nutritional properties: A review. Rice Sci, 29(3): 201-215. |
| [68] | Ning H F, Qiao J F, Liu Z H, Lin Z M, Li G H, Wang Q S, Wang S H, Ding Y F. 2010. Distribution of proteins and amino acids in milled and brown rice as affected by nitrogen fertilization and genotype. J Cereal Sci, 52(1): 90-95. |
| [69] | Okadome H, Toyoshima H, Ohtsubo K. 1999. Multiple measurements of physical properties of individual cooked rice grains with a single apparatus. Cereal Chem J, 76(6): 855-860. |
| [70] |
Olivares Díaz E, Kawamura S, Matsuo M, Kato M, Koseki S. 2019. Combined analysis of near-infrared spectra, colour, and physicochemical information of brown rice to develop accurate calibration models for determining amylose content. Food Chem, 286: 297-306.
PMID |
| [71] | Olson R A, Frey K J. 1987. Nutritional Quality of Cereal Grains: Genetic and Agronomic Improvement. Madison, WI, USA: John Wiley & Sons. |
| [72] | Osborne B G. 2006. Near-infrared spectroscopy in food analysis. In: Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry: Applications, Theory and Instrumentation. Madison, USA: John Wiley & Sons. |
| [73] | Park S G, Park H S, Baek M K, Jeong J M, Cho Y C, Lee G M, Lee C M, Suh J P, Kim C S, Kim S M. 2019. Improving the glossiness of cooked rice, an important component of visual rice grain quality. Rice, 12(1): 87. |
| [74] | Pellegrini N, Agostoni C. 2015. Nutritional aspects of gluten-free products. J Sci Food Agric, 95(12): 2380-2385. |
| [75] |
Peng B, Kong H L, Li Y B, Wang L Q, Zhong M, Sun L, Gao G J, Zhang Q L, Luo L J, Wang G W, Xie W B, Chen J X, Yao W, Peng Y, Lei L, Lian X M, Xiao J H, Xu C G, Li X H, He Y Q. 2014. OsAAP6 functions as an important regulator of grain protein content and nutritional quality in rice. Nat Commun, 5: 4847.
PMID |
| [76] | Qiang L, Tian J Z, Li J J. 2012. Described the relationship between the characteristics of rice protein and the quality of rice. J Wheat Res, 33(1): 29-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [77] | Reche M, Pascual C, Fiandor A, Polanco I, Rivero-Urgell M, Chifre R, Johnston S, Martín-Esteban M. 2010. The effect of a partially hydrolysed formula based on rice protein in the treatment of infants with cow’s milk protein allergy. Pediatr Allergy Immunol, 21: 577-585. |
| [78] | Ren S, Wang S. 2002. Distribution and nutritional analysis of rice proteins. J Chin Cereals Oils Assoc, 17: 35-538. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [79] | Ren Y L, Wang Y H, Liu F, Zhou K N, Ding Y, Zhou F, Wang Y, Liu K, Gan L, Ma W W, Han X H, Zhang X, Guo X P, Wu F Q, Cheng Z J, Wang J L, Lei C L, Lin Q B, Jiang L, Wu C Y, Bao Y Q, Wang H Y, Wan J M. 2014. GLUTELIN PRECURSOR ACCUMULATION3 encodes a regulator of post-Golgi vesicular traffic essential for vacuolar protein sorting in rice endosperm. Plant Cell, 26(1): 410-425. |
| [80] | Ren Y L, Wang Y H, Pan T, Wang Y L, Wang Y F, Gan L, Wei Z Y, Wang F, Wu M M, Jing R N, Wang J C, Wan G X, Bao X H, Zhang B L, Zhang P C, Zhang Y, Ji Y, Lei C L, Zhang X, Cheng Z J, Lin Q B, Zhu S S, Zhao Z C, Wang J, Wu C Y, Qiu L J, Wang H Y, Wan J M. 2020. GPA5 encodes a Rab5a effector required for post-Golgi trafficking of rice storage proteins. Plant Cell, 32(3): 758-777. |
| [81] | Rolle L, Siret R, Segade S R, Maury C, Gerbi V, Jourjon F. 2012. Instrumental texture analysis parameters as markers of table-grape and winegrape quality: A review. Am J Enol Vitic, 63(1): 11-28. |
| [82] | Ruan Y S, Duan S E, Zhao W M. 2001. A quick method of analysis of protein subunits by two dimensional electrophoresis. Acta Bot Boreal Occident Sin, 21(1): 175-179. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [83] | Saito Y, Shigemitsu T, Yamasaki R, Sasou A, Goto F, Kishida K, Kuroda M, Tanaka K, Morita S, Satoh S, Masumura T. 2012. Formation mechanism of the internal structure of type I protein bodies in rice endosperm: Relationship between the localization of prolamin species and the expression of individual genes. Plant J, 70(6): 1043-1055. |
| [84] | Sattari A, Mahdinezhad N, Fakheri B, Noroozi M, Beheshtizadeh H. 2015. Improvement of the eating and cooking qualities of rice: A review. Intl J Farm Alli Sci, 4(2): 153-160. |
| [85] | Schaeffer G W, Sharpe F T. 1997. Electrophoretic profiles and amino acid composition of rice endosperm proteins of a mutant with enhanced lysine and total protein after backcrosses for germplasm improvements. Theor Appl Genet, 95: 230-235. |
| [86] | Sharma G, Upadyay A K, Biradar H, Sonia, Hittalmani S. 2019. OsNAC-like transcription factor involved in regulating seed-storage protein content at different stages of grain filling in rice under aerobic conditions. J Genet, 98: 18. |
| [87] | Tan Y F, Sun M, Xing Y Z, Hua J P, Sun X L, Zhang Q F, Corke H. 2001. Mapping quantitative trait loci for milling quality, protein content and color characteristics of rice using a recombinant inbred line population derived from an elite rice hybrid. Theor Appl Genet, 103: 1037-1045. |
| [88] | Tanaka K, Sugimoto T, Ogawa M, Kasai Z. 1980. Isolation and characterization of two types of protein bodies in the rice endosperm. Agric Biol Chem, 44(7): 1633-1639. |
| [89] | Tang S, Chen W Z, Liu W Z, Zhou Q Y, Zhang H X, Wang S H, Ding Y F. 2018. Open-field warming regulates the morphological structure, protein synthesis of grain and affects the appearance quality of rice. J Cereal Sci, 84: 20-29. |
| [90] | Tian L H, Dai L L, Yin Z J, Fukuda M, Kumamaru T, Dong X B, Xu X P, Qu L Q. 2013. Small GTPase Sar1 is crucial for proglutelin and α-globulin export from the endoplasmic Reticulum in rice endosperm. J Exp Bot, 64(10): 2831-2845. |
| [91] | Tong C, Gao H Y, Luo S J, Liu L, Bao J S. 2019. Impact of postharvest operations on rice grain quality: A review. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf, 18(3): 626-640. |
| [92] | Wang C B, Qin L, Zhao L N, Ramp N. 2016. Preliminary comparison of the measurement results of the common color instrument. Modern Food, (3): 115-119. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [93] | Wang H C, Che G, Wan L, Liu M G, Sun W S. 2021. Experimental study on drying characteristics of rice by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. J Food Process Eng, 44(6): e13705. |
| [94] | Wang J X, Zhang Y J, Cheng A H, Lv B, Li X H, Zhao Y L, Liao H, Li D L, Li H, Ma W D, Huang X Q. 2008. Effects of protein subunits contents on eating quality in rice. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 24(1): 89-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [95] | Wang L F, Wang W, Zhang Y, Xu X Y, Pan S Y. 2009. Study on the relativity between characteristics of rice and quality of cooked rice. Sci Technol Food Ind, 30(8): 108-111. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [96] | Wang P Y, Shen Q X, Lu X H, Pang L J, Chen Z X. 2016. Relevance features of rice protein and its components to physical and sensory properties of cooked rice. Food Mach, 32(3): 24-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [97] |
Wang X Q, Pang Y L, Zhang J, Wu Z C, Chen K, Ali J, Ye G Y, Xu J L, Li Z K. 2017. Genome-wide and gene-based association mapping for rice eating and cooking characteristics and protein content. Sci Rep, 7(1): 17203.
PMID |
| [98] | Wang Y H, Ren Y L, Liu X, Jiang L, Chen L M, Han X H, Jin M N, Liu S J, Liu F, Lv J, Zhou K N, Su N, Bao Y Q, Wan J M. 2010. OsRab5a regulates endomembrane organization and storage protein trafficking in rice endosperm cells. Plant J, 64(5): 812-824. |
| [99] | Wang Y H, Liu F, Ren Y L, Wang Y L, Liu X, Long W H, Wang D, Zhu J P, Zhu X P, Jing R N, Wu M M, Hao Y Y, Jiang L, Wang C M, Wang H Y, Bao Y Q, Wan J M. 2016. GOLGI TRANSPORT 1B regulates protein export from the endoplasmic Reticulum in rice endosperm cells. Plant Cell, 28(11): 2850-2865. |
| [100] | Wang Y Z, Lin W F, Chen Z. 2011. Study on the correlation between characteristics of rice and the quality of cooked rice. Modern Food Sci Technol, 27(11): 1312-1315. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [101] | Wei N, Feng X Q, Zhang X F, Qi X H, Zou M Q, Wang M T. 2013. Research progress in Raman spectra and its test sample pretreatment. Spectrosc Spectr Anal, 33(3): 694-698. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [102] |
Wen T N, Luthe D S. 1985. Biochemical characterization of rice glutelin. Plant Physiol, 78(1): 172-177.
PMID |
| [103] |
Wong H W, Liu Q, Sun S S M. 2015. Biofortification of rice with lysine using endogenous histones. Plant Mol Biol, 87(3): 235-248.
PMID |
| [104] | Wu H K, Liu S J, Jiang L, Zhang W W, Wang Y H, Ren Y L, Han X H, Liu F. 2009. Relationship between protein composition and total protein content and starch RVA profile properties in rice. Chin J Rice Sci, 23(4): 421-426. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [105] | Xie L H, Luo J, Tang S Q, Chen N, Jiao G A, Shao G N, Wei X J, Hu P S. 2013. Proteins affect rice eating quality properties and its mechanism. Chin J Rice Sci, 27(1): 91-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [106] | Xu Y L, Xiong S B, Zhao S M. 2007. Effect of cooking technology and chemical components on stress-relaxation property of cooked rice. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng, 23(10): 235-240. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [107] |
Yamagata H, Sugimoto T, Tanaka K, Kasai Z. 1982. Biosynthesis of storage proteins in developing rice seeds. Plant Physiol, 70(4): 1094-1100.
PMID |
| [108] |
Yang W F, Liang J Y, Hao Q W, Luan X, Tan Q Y, Lin S W, Zhu H T, Liu G F, Liu Z P, Bu S H, Wang S K, Zhang G Q. 2021. Fine mapping of two grain chalkiness QTLs sensitive to high temperature in rice. Rice, 14(1): 33.
PMID |
| [109] |
Yang Y H, Guo M, Sun S Y, Zou Y L, Yin S Y, Liu Y N, Tang S Z, Gu M H, Yang Z F, Yan C J. 2019. Natural variation of OsGluA2 is involved in grain protein content regulation in rice. Nat Commun, 10(1): 1949.
PMID |
| [110] | Yang Y H, Shen Z Y, Li Y G, Xu C D, Xia H, Zhuang H, Sun S Y, Guo M, Yan C J. 2022. Rapid improvement of rice eating and cooking quality through gene editing toward glutelin as target. J Integr Plant Biol, 64(10): 1860-1865. |
| [111] |
Ye G Y, Liang S S, Wan J M. 2010. QTL mapping of protein content in rice using single chromosome segment substitution lines. Theor Appl Genet, 121(4): 741-750.
PMID |
| [112] | Yu Y H, Li G, Fan Y Y, Zhang K Q, Min J, Zhu Z W, Zhuang J Y. 2009. Genetic relationship between grain yield and the contents of protein and fat in a recombinant inbred population of rice. J Cereal Sci, 50(1): 121-125. |
| [113] | Zhang W W, Bi J C, Chen L M, Zheng L N, Ji S L, Xia Y M, Xie K, Zhao Z G, Wang Y H, Liu L L, Jiang L, Wan J M. 2008. QTL mapping for crude protein and protein fraction contents in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Cereal Sci, 48(2): 539-547. |
| [114] | Zhang X, Shi L L, Ding D L, Wang S W, Cui J. 2014. The relationship between rice protein related character and the RVA characteristic profile and palatability character. Food Sci Technol, 39(10): 188-191. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [115] | Zhao L X, Pan T, Cai C H, Wang J, Wei C X. 2016. Application of whole sections of mature cereal seeds to visualize the morphology of endosperm cell and starch and the distribution of storage protein. J Cereal Sci, 71: 19-27. |
| [116] | Zheng L N, Zhang W W, Chen X G, Ma J, Chen W W, Zhao Z G, Zhai H Q, Wan J M. 2011. Dynamic QTL analysis of rice protein content and protein index using recombinant inbred lines. J Plant Biol, 54(5): 321-328. |
| [117] | Zhong Y G. 2019. Electronic Nose for Food Sensory Evaluation:Evaluation Technologies for Food Quality. Amsterdam, the Netherland: Elsevier: 7-22. |
| [118] | Zhou H, Xia D, He Y Q. 2020. Rice grain quality: Traditional traits for high quality rice and health-plus substances. Mol Breed, 40(1): 1-17. |
| [119] |
Zhu J P, Ren Y L, Wang Y L, Liu F, Teng X, Zhang Y Y, Duan E C, Wu M M, Zhong M S, Hao Y Y, Zhu X P, Lei J, Wang Y F, Yu Y F, Pan T, Bao Y Q, Wang Y H, Wan J M. 2019. OsNHX5-mediated pH homeostasis is required for post-Golgi trafficking of seed storage proteins in rice endosperm cells. BMC Plant Biol, 19(1): 295.
PMID |
| [120] |
Zhu J P, Ren Y L, Zhang Y Y, Yang J, Duan E C, Wang Y L, Liu F, Wu M M, Pan T, Wang Y F, Hu T T, Hao Y Y, Teng X, Zhu X P, Lei J, Jing R N, Yu Y F, Sun Y L, Bao X H, Bao Y Q, Wang Y H, Wan J M. 2021. Subunit E isoform 1 of vacuolar H+-ATPase OsVHA enables post-Golgi trafficking of rice seed storage proteins. Plant Physiol, 187(4): 2192-2208.
PMID |
| [121] | Zhu L, Sun J, Wu G C, Wang Y N, Zhang H, Wang L, Qian H F, Qi X G. 2018. Identification of rice varieties and determination of their geographical origin in China using Raman spectroscopy. J Cereal Sci, 82: 175-182. |
| [1] | Sibo Chen, Liang Tang, Jian Sun, Quan Xu, Zhengjin Xu, Wenfu Chen. Contribution and Prospect of Erect Panicle Type to japonica Super Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(5): 431-441. |
| [2] | Danying Wang, Chang Ye, Chunmei Xu, Zaiman Wang, Song Chen, Guang Chu, Xiufu Zhang. Soil Nitrogen Distribution and Plant Nitrogen Utilization in Direct-Seeded Rice in Response to Deep Placement of Basal Fertilizer-Nitrogen [J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(6): 404-415. |
| [3] | Sung Jwakyung, Lee Suyeon, Chung Jong-Wook, Edwards Gerald, Ryu Hojin, Kim Taewan. Photosynthesis, Metabolite Composition and Anatomical Structure of Oryza sativa and Two Wild Relatives, O. grandiglumis and O. alta [J]. Rice Science, 2017, 24(4): 218-227. |
| [4] | Kumar Verma Deepak, Prakash Srivastav Prem. Proximate Composition, Mineral Content and Fatty Acids Analyses of Aromatic and Non-Aromatic Indian Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2017, 24(1): 21-31. |
| [5] | Tao Chen, Hao Wu, Ya-dong Zhang, Zhen Zhu, Qi-yong Zhao, Li-hui Zhou, Shu Yao, Ling Zhao, Xin Yu, Chun-fang Zhao, Cai-lin Wang. Genetic Improvement of Japonica Rice Variety Wuyujing 3 for Stripe Disease Resistance and Eating Quality by Pyramiding Stv-bi and Wx-mq [J]. Rice Science, 2016, 23(2): 69-77. |
| [6] | J. Kale S., K. Jha S., K. Jha G., P. Sinha J., B. Lal S.. Soaking Induced Changes in Chemical Composition, Glycemic Index and Starch Characteristics of Basmati Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2015, 22(5): 227-236. |
| [7] | ZHANG Ya-jie, HUA Jing-jing, LI Ya-chao, CHEN Ying-ying, YANG Jian-chang. Effects of Phosphorus on Grain Quality of Upland and Paddy Rice under Different Cultivation [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2012, 19(2): 135-142. |
| [8] | CHENG Zai-quan1, YING Fu-you1, LI Ding-qing1, YU Teng-qiong1, FU Jian1, YAN Hui-jun2, ZHONG Qiao-fang1, ZHANG Dun-yu1, LI Wei-jiao1, HUANG Xing-qi1, 2 . Genetic Diversity of Wild Rice Species in Yunnan Province of China [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2012, 19(1): 21-28. |
| [9] | WANG Yan-rong, QIU Fu-lin, HUA Ze-tian, DAI Gui-jin . Relationship of Parental Indica-Japonica Indexes with Yield and Grain Quality Traits of Japonica Hybrid Rice in Northern China [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2010, 17(3): 199-205 . |
| [10] | JIANG Nan, DI Yu-ting, ZHAO Guo-chen, XU Ke-zhang, WU Zhi-hai, ZHANG Zhi-an, LING Feng-lou. Biomasses in Different Organs of Rice Cultivars Developed During Recent Forty-Seven Years in Jilin Province, China [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2010, 17(3): 206-212 . |
| [11] | SUN Min-jie, LIU Wei-hong, LIN Mao-song. Effects of Temperature, Humidity and Different Rice Growth Stages on Vertical Migration of Aphelenchoides besseyi [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2009, 16(4): 301-306 . |
| [12] | WEI Ke-su, CHENG Fang-min, ZHANG Qi-fang, LIU Kui-gang. Temperature Stress at Grain Filling Stage Mediates Expression of Three Isoform Genes Encoding Starch Branching Enzymes in Rice Endosperm [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2009, 16(3): 187-193 . |
| [13] | Gerson Luis FACCIN, Leila do Nascimento VIEIRA, Letícia Adélia MIOTTo, Pedro Luiz Manique BARRETO, Edna Regina AMANTE . Chemical, Sensorial and Rheological Properties of a New Organic Rice Bran Beverage [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2009, 16(3): 226-234 . |
| [14] | Hiroshi Ikehashi. Why are There Indica Type and Japonica Type in Rice?--History of the Studies and a View for Origin of Two Types [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2009, 16(1): 1-13 . |
| [15] | ZHU Xiao-biao, SUN Da-yun, CHENG Bao-shan, HONG De-lin. Distribution Characterization of Leaf and Hull Pubescences and Genetic Analysis of Their Numbers in japonica Rice (Oryza sativa) [J]. RICE SCIENCE, 2008, 15(4): 267-275 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||