
Rice Science ›› 2021, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (6): 532-546.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2021.05.013
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Muduli Lakesh1, Kumar Pradhan Sukanta2, Mishra Abinash1, Nath Bastia Debendra1, Chandra Samal Kailash3, Kumar Agrawal Pawan1, Dash Manasi1( )
)
Received:2020-12-23
Accepted:2021-05-16
Online:2021-11-28
Published:2021-11-28
Muduli Lakesh, Kumar Pradhan Sukanta, Mishra Abinash, Nath Bastia Debendra, Chandra Samal Kailash, Kumar Agrawal Pawan, Dash Manasi. Understanding Brown Planthopper Resistance in Rice: Genetics, Biochemical and Molecular Breeding Approaches[J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(6): 532-546.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Chr | Gene | Flanking marker | Location (Mb) | Germplasm source | Resistant to biotype | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bph33(t) | RM488, RM11522 | 24.80-28.00 | RP2068 | ND | |
| 1L | BPH38(t) | SNPs 693, 369, 10, 112, 165 | 20.71-21.23 | Khazar | Biotype 3 | |
| 1 | BPH37 | RM302, YM35 | ND | IR64 | ND | |
| 3 | bph11 | ND | 35.60-35.80 | O. officinalis | ND | |
| 3S | Bph13(t) | AJ09b230, AJ09c | 5.18-5.70 | IR54745-2-21 (O. officinalis) | Biotypes 1, 2, 3 and 4 | |
| 3S | bph19 | RM6308, RM3134 | 7.18-7.24 | AS20-1 | Biotype 2 | |
| 3 | qBph3 | RM3180, RM2453 | 18.27-20.25 | Rathu Heenati | ND | |
| 3L | BPH31 | PA26, RM2334 | 26.26-26.74 | CR2711-76 (indica) | Biotype 4 | |
| 4S | Bph12 | RM16459, RM1305 | 5.21-5.66 | B14 (O. latifolia) | ND | |
| 4S | Bph15 | RM261, S16 | 6.68-6.90 | B5 (O. officinalis) | ND | |
| 4S | QBph4.1 | P17, xc4-27 | 6.70-6.90 | IR02W101 (O. officinalis) | ND | |
| 4S | QBph4.2 | RM261, S1 | 6.58-6.89 | IR65482-17-511 (O. australiensis) | ND | |
| 4S | Bph17 | RM8213, RM5953 | 6.93-6.97 | Rathu Heenati | ND | |
| 4S | Bph20(t) | MS10, RM5953 | 8.20-9.60 | IR71033-121-15 (O. minuta) | ND | |
| 4S | Bph30 | RM16294, RM16299 | 0.90-0.94 | AC-1613 (O. indica) | Biotypes 1, 2 and 3 | |
| 4S | Bph33 | H99, H101 | 0.91-0.97 | Kolayal and Poliyal | ND | |
| 4S | Bph36 | S13, X48 | ND | O. rufipogon Griff | Biotypes 1 and 2 | |
| 4S | Bph12 | RM16459, RM1305 | 5.21-5.66 | B14 (O. latifolia) | Biotype 2 | |
| 4L | Bph6 | Y19, RM119 | 21.36-21.39 | Swarnalata | Biotype 4 | |
| 4L | Bph34 | RM16994, RM17007 | 21.15-21.30 | IRGC104646 (O. nivara) | Biotype 4 | |
| 4L | Bph27 | RM273, RM471 | 19.12-19.20 | GX2183 (O. rufipogon) | Biotype 2 | |
| 4L | Bph27(t) | RM471, RM5742 | 20.79-21.33 | Balamawee | ND | |
| 4L | Bph35 | PSM16, RM413 | 6.28-6.93 | RBPH660 | ND | |
| 6S | Bph3 | RM469, RM588 | 1.21-1.40 | Rathu Heenati | Biotypes 1, 2, 3 and 4 | |
| 6S | bph4 | RM190, C76A | 1.20-1.76 | Babawee | Biotypes 1, 2, 3 and 4 | |
| 6S | BPH25 | S00310 | 0.20-1.71 | ADR52 | ND | |
| 6S | BPH29 | BYL7, BID2 | 0.48-0.49 | RBPH54 (O. rufipogon) | Biotypes 1 and 2 | |
| 6S | Bph32 | RM19291, RM8072 | 1.21-1.40 | Ptb33 | ND | |
| 11L | Bph28(t) | Indel55, Indel66 | ND | DV85 | ND | |
| 12 | BPH10 | RM260, RM313 | 19.00-23.00 | O. australiensis | ND | |
| 12 | Bph1 | BpE18-3 | 13.10-13.28 | Mudgo, TKM6 | Biotypes 1 and 3 | |
| 12L | bph2/Bph26 | KAM4 | 22.13-23.18 | IR1154-243 | Biotypes 1 and 2 | |
| 12L | bph2 | RM463, RM7102 | 13.21-22.13 | ASD7 | ND | |
| 12L | bph7 | RM3448, RM313 | 19.95-20.87 | T12 | Biotype 4 | |
| 12L | BPH9 | RM463, RM5341 | 19.11-22.13 | Kaharamana | Biotypes 1, 2 and 3 | |
| 12L | BPH9 | OPR04, S2545 | 19.00-22.50 | Pokkali | ND | |
| 12L | BPH18(t) | RM463, S15552, 7312.T4A | 22.25-23.48 | IR65482-7-216 (O. australiensis) | Biotypes 1, 2, 3 and 4 | |
| 12L | Bph21(t) | RM3726, RM5479 | 23.28-24.41 | IR71033-121-15 (O. minuta) | Biotype 1 |
Table 1 List of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance genes in rice.
| Chr | Gene | Flanking marker | Location (Mb) | Germplasm source | Resistant to biotype | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bph33(t) | RM488, RM11522 | 24.80-28.00 | RP2068 | ND | |
| 1L | BPH38(t) | SNPs 693, 369, 10, 112, 165 | 20.71-21.23 | Khazar | Biotype 3 | |
| 1 | BPH37 | RM302, YM35 | ND | IR64 | ND | |
| 3 | bph11 | ND | 35.60-35.80 | O. officinalis | ND | |
| 3S | Bph13(t) | AJ09b230, AJ09c | 5.18-5.70 | IR54745-2-21 (O. officinalis) | Biotypes 1, 2, 3 and 4 | |
| 3S | bph19 | RM6308, RM3134 | 7.18-7.24 | AS20-1 | Biotype 2 | |
| 3 | qBph3 | RM3180, RM2453 | 18.27-20.25 | Rathu Heenati | ND | |
| 3L | BPH31 | PA26, RM2334 | 26.26-26.74 | CR2711-76 (indica) | Biotype 4 | |
| 4S | Bph12 | RM16459, RM1305 | 5.21-5.66 | B14 (O. latifolia) | ND | |
| 4S | Bph15 | RM261, S16 | 6.68-6.90 | B5 (O. officinalis) | ND | |
| 4S | QBph4.1 | P17, xc4-27 | 6.70-6.90 | IR02W101 (O. officinalis) | ND | |
| 4S | QBph4.2 | RM261, S1 | 6.58-6.89 | IR65482-17-511 (O. australiensis) | ND | |
| 4S | Bph17 | RM8213, RM5953 | 6.93-6.97 | Rathu Heenati | ND | |
| 4S | Bph20(t) | MS10, RM5953 | 8.20-9.60 | IR71033-121-15 (O. minuta) | ND | |
| 4S | Bph30 | RM16294, RM16299 | 0.90-0.94 | AC-1613 (O. indica) | Biotypes 1, 2 and 3 | |
| 4S | Bph33 | H99, H101 | 0.91-0.97 | Kolayal and Poliyal | ND | |
| 4S | Bph36 | S13, X48 | ND | O. rufipogon Griff | Biotypes 1 and 2 | |
| 4S | Bph12 | RM16459, RM1305 | 5.21-5.66 | B14 (O. latifolia) | Biotype 2 | |
| 4L | Bph6 | Y19, RM119 | 21.36-21.39 | Swarnalata | Biotype 4 | |
| 4L | Bph34 | RM16994, RM17007 | 21.15-21.30 | IRGC104646 (O. nivara) | Biotype 4 | |
| 4L | Bph27 | RM273, RM471 | 19.12-19.20 | GX2183 (O. rufipogon) | Biotype 2 | |
| 4L | Bph27(t) | RM471, RM5742 | 20.79-21.33 | Balamawee | ND | |
| 4L | Bph35 | PSM16, RM413 | 6.28-6.93 | RBPH660 | ND | |
| 6S | Bph3 | RM469, RM588 | 1.21-1.40 | Rathu Heenati | Biotypes 1, 2, 3 and 4 | |
| 6S | bph4 | RM190, C76A | 1.20-1.76 | Babawee | Biotypes 1, 2, 3 and 4 | |
| 6S | BPH25 | S00310 | 0.20-1.71 | ADR52 | ND | |
| 6S | BPH29 | BYL7, BID2 | 0.48-0.49 | RBPH54 (O. rufipogon) | Biotypes 1 and 2 | |
| 6S | Bph32 | RM19291, RM8072 | 1.21-1.40 | Ptb33 | ND | |
| 11L | Bph28(t) | Indel55, Indel66 | ND | DV85 | ND | |
| 12 | BPH10 | RM260, RM313 | 19.00-23.00 | O. australiensis | ND | |
| 12 | Bph1 | BpE18-3 | 13.10-13.28 | Mudgo, TKM6 | Biotypes 1 and 3 | |
| 12L | bph2/Bph26 | KAM4 | 22.13-23.18 | IR1154-243 | Biotypes 1 and 2 | |
| 12L | bph2 | RM463, RM7102 | 13.21-22.13 | ASD7 | ND | |
| 12L | bph7 | RM3448, RM313 | 19.95-20.87 | T12 | Biotype 4 | |
| 12L | BPH9 | RM463, RM5341 | 19.11-22.13 | Kaharamana | Biotypes 1, 2 and 3 | |
| 12L | BPH9 | OPR04, S2545 | 19.00-22.50 | Pokkali | ND | |
| 12L | BPH18(t) | RM463, S15552, 7312.T4A | 22.25-23.48 | IR65482-7-216 (O. australiensis) | Biotypes 1, 2, 3 and 4 | |
| 12L | Bph21(t) | RM3726, RM5479 | 23.28-24.41 | IR71033-121-15 (O. minuta) | Biotype 1 |
| Gene | Chr | Candidate locus | Encoded protein | Germplasm source | Defense signalling pathway | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bph3 | 4 | OsLecRK1-OsLecRK3 | Lectin receptor kinases | Rathu Heenati | - | |
| Bph6 | 4 | Gene1 (NCBI accession KX818197) | Atypical LRR | Swarnalata | JA↑, SA↑, CK↑ (Synergistic) | |
| BPH9 | 12 | R2 | CC-NBS-NBS-LRR | Pokkali | JA↑, SA↓ (Antagonistic) | |
| Bph14 | 3 | Ra (Os03g0848700) | CC-NB-LRR | B5 | SA↑ | |
| Bph15 | 4 | LOC_Os04g12390, LOC_Os04g12460 | LRR and JRL | B5 | DEGs↑ | |
| BPH18 | 12 | LOC_Os12g37280, LOC_Os12g37290 | CC-NBS-NBS-LRR | IR65482-7-216-1-2 | - | |
| BPH26 | 12 | Os12g0559300, Os12g0559400, Os12g0559600 | CC-NB-LRR | ADR52 | JA↑, SA↑, ET↑, PR1b↑ | |
| BPH29 | 6 | G5 (Os06g0107800) | B3 DNA-binding domain | RBPH54 | JA↓, SA↑ (Antagonistic) | |
| Bph32 | 6 | Os06g123200 | Unknown SCR domain | PTB33 | - |
Table 2 Characterization of brown planthopper (BPH) resistant genes in rice.
| Gene | Chr | Candidate locus | Encoded protein | Germplasm source | Defense signalling pathway | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bph3 | 4 | OsLecRK1-OsLecRK3 | Lectin receptor kinases | Rathu Heenati | - | |
| Bph6 | 4 | Gene1 (NCBI accession KX818197) | Atypical LRR | Swarnalata | JA↑, SA↑, CK↑ (Synergistic) | |
| BPH9 | 12 | R2 | CC-NBS-NBS-LRR | Pokkali | JA↑, SA↓ (Antagonistic) | |
| Bph14 | 3 | Ra (Os03g0848700) | CC-NB-LRR | B5 | SA↑ | |
| Bph15 | 4 | LOC_Os04g12390, LOC_Os04g12460 | LRR and JRL | B5 | DEGs↑ | |
| BPH18 | 12 | LOC_Os12g37280, LOC_Os12g37290 | CC-NBS-NBS-LRR | IR65482-7-216-1-2 | - | |
| BPH26 | 12 | Os12g0559300, Os12g0559400, Os12g0559600 | CC-NB-LRR | ADR52 | JA↑, SA↑, ET↑, PR1b↑ | |
| BPH29 | 6 | G5 (Os06g0107800) | B3 DNA-binding domain | RBPH54 | JA↓, SA↑ (Antagonistic) | |
| Bph32 | 6 | Os06g123200 | Unknown SCR domain | PTB33 | - |
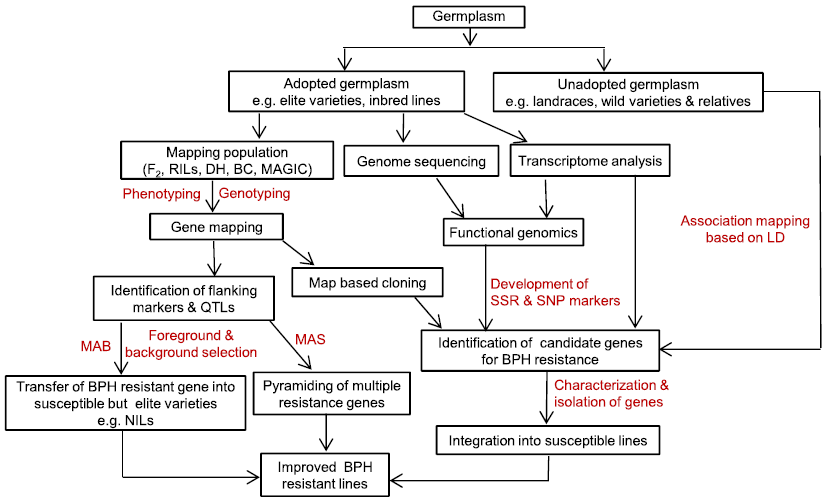
Fig. 1. Flowchart indicating use of molecular breeding and genomics method for developing brown planthopper (BPH) resistant rice lines.BC, Backcross; DH, Double haploid; LD, Linkage disequilibrium; MAB, Marker-assisted breeding; MAS, Marker-assisted selection; MAGIC, Multi-parental advanced generation intercross; NILs, Near isogenic lines; QTLs, Quantitative trait loci; RILs, Recombinant inbred lines; SNP, Single nucleotide polymorphism; SSR, Simple sequence repeat.
| [1] | Alam S N, Cohen M B. 1998. Detection and analysis of QTLs for resistance to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, in a doubled-haploid rice population. Theor Appl Genet, 97: 1370-1379. |
| [2] | Athwal D S, Pathak M D, Bacalangco E H, Pura C D. 1971. Genetics of resistance to brown planthoppers and green leafhoppers in Oryza sativa L. Crop Sci, 11(5): 747-750. |
| [3] | Balachiranjeevi C H, Prahalada G D, Mahender A, Jamaloddin M, Sevilla M A L, Marfori-Nazarea C M, Vinarao R, Sushanto U, Baehaki S E, Li Z K, Ali J. 2019. Identification of a novel locus, BPH38(t), conferring resistance to brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål.) using early backcross population in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica, 215(11): 185. |
| [4] | Brar D S, Virk P S, Jena K K, Khush G S. 2009. Breeding for resistance to planthoppers in rice. In: Planthoppers: New Threats to the Sustainability of Intensive Rice Production Systems in Asia. Los Banos, the Philippine: International Rice Research Institute: 401-427. |
| [5] | Cabauatan P Q, Cabunagan R C, Choi I R. 2009. Rice viruses transmitted by the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Stål. In: Heong K L, Hardy B. Planthoppers: New threats to the sustainability of intensive rice production systems in Asia. Los Banos, the Philippine: International Rice Research Institute: 357-368. |
| [6] | Chen J W, Wang L, Pang X F, Pan Q H. 2006. Genetic analysis and fine mapping of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene bph19(t). Mol Genet Genomics, 275(4): 321-329. |
| [7] | Cheng A X, Xiang C Y, Li J X, Yang C Q, Hu W L, Wang L J, Lou Y G, Chen X Y. 2007. The rice (E)-beta-caryophyllene synthase (OsTPS3) accounts for the major inducible volatile sesquiterpenes. Phytochemistry, 68(12): 1632-1641. |
| [8] | Cheng X Y, Wu Y, Guo J P, Du B, Chen R Z, Zhu L L, He G C. 2013. A rice lectin receptor-like that is involved in innate immune responses also contributes to seed germination. Plant J, 76(4): 687-698. |
| [9] | Deen R, Ramesh K, Padmavathi G, Viraktamath B C, Ram T. 2017. Mapping of brown planthopper [Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)] resistance gene (bph5) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica, 213(2): 35. |
| [10] | Dodds P N, Rathjen J P. 2010. Plant immunity: Towards an integrated view of plant-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Genet, 11: 539-548. |
| [11] | Du B, Zhang W L, Liu B F, Hu J, Wei Z, Shi Z Y, He R F, Zhu L L, Chen R Z, Han B, He G C. 2009. Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106(52): 22163-22168. |
| [12] | Du B, Chen R Z, Guo J P, He G C. 2020. Current understanding of the genomic, genetic, and molecular control of insect resistance in rice. Mol Breeding, 40(2): 24. |
| [13] | Fujita D, Kohli A, Horgan F G. 2013. Rice resistance to planthoppers and leafhoppers. Crit Rev Plant Sci, 32(3): 162-191. |
| [14] | Guo J P, Xu C X, Wu D, Zhao Y, Qiu Y F, Wang X X, Ouyang Y D, Cai B D, Liu X, Jing S L, Shangguan X X, Wang H Y, Ma Y H, Hu L, Wu Y, Shi S J, Wang W L, Zhu L L, Xu X, Chen R Z, Feng Y Q, Du B, He G C. 2018. Bph6 encodes an exocyst- localized protein and confers broad resistance to planthoppers in rice. Nat Genet, 50(2): 297-306. |
| [15] | Haliru B S, Rafii M Y, Mazlan N, Ramlee S I, Muhammad I I, Silas Akos I, Halidu J, Swaray S, Rini Bashir Y. 2020. Recent strategies for detection and improvement of brown planthopper resistance genes in rice: A review. Plants, 9(9): 1202. |
| [16] | Hao P Y, Lu C F, Ma Y, Xu L B, Zhu J J, Yu X P. 2015. Roles of NlAKTIP in the growth and eclosion of the rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stål, as revealed by RNA interference. Int J Mol Sci, 16(9): 22888-22903. |
| [17] | Hirabayashi H, Angeles E R, Kaji R, Ogawa T, Brar D S, Khush G S. 1998. Identification of a brown planthopper resistance gene derived fromO. officinalis using molecular markers in rice. Breeding Sci, 48: 82. (in Japanese) |
| [18] | He J, Liu Y Q, Liu Y L, Jiang L, Wu H, Kang H Y, Liu S J, Chen L M, Liu X, Cheng X N, Wan J M. 2013. High-resolution mapping of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance gene Bph27(t) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breeding, 31(3): 549-557. |
| [19] | Hu J, Li X, Wu C J, Yang C J, Hua H X, Gao G J, Xiao J H, He Y Q. 2012. Pyramiding and evaluation of the brown planthopper resistance genes Bph14 and Bph15 in hybrid rice. Mol Breeding, 29: 61-69. |
| [20] | Hu J, Cheng M X, Gao G J, Zhang Q L, Xiao J H, He Y Q. 2013. Pyramiding and evaluation of three dominant brown planthopper resistance genes in the elite indica rice 9311 and its hybrids. Pest Manag Sci, 69(7): 802-808. |
| [21] | Hu J, Xiao C, Cheng M X, Gao G J, Zhang Q L, He Y Q. 2015a. Fine mapping and pyramiding of brown planthopper resistance genes QBph3 and QBph4 in an introgression line from wild rice O. officinalis. Mol Breeding, 35(1): 3. |
| [22] | Hu J, Xiao C, Cheng M X, Gao G J, Zhang Q L, He Y Q. 2015b. A new finely mapped Oryza australiensis-derived QTL in rice confers resistance to brown planthopper. Gene, 561(1): 132-137. |
| [23] | Hu J, Xiao C, He Y Q. 2016. Recent progress on the genetics and molecular breeding of brown planthopper resistance in rice. Rice, 9(1): 30. |
| [24] | Hu J, Chang X Y, Zou L, Tang W Q, Wu W R. 2018. Identification and fine mapping of Bph33, a new brown planthopper resistance gene in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice, 11(1): 55. |
| [25] | Huang D, Qiu Y F, Zhang Y, Huang F, Meng J, Wei S, Li R, Chen B S. 2013. Fine mapping and characterization of BPH27, a brown planthopper resistance gene from wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Theor Appl Genet, 126(1): 219-229. |
| [26] | Ikeda R, Kaneda C. 1981. Genetic analysis of resistance to BPH Nilaparvata lugens Stål in rice. Jpn J Breeding, 31: 279-285. |
| [27] | Ishii T, Brar D S, Multani D S, Khush G S. 1994. Molecular tagging of genes for brown planthopper resistance and earliness introgressed from Oryza australiensis into cultivated rice O. sativa. Genome, 37(2): 217-221. |
| [28] | Jairin J, Teangdeerith S N, Leelagud P, Phengrat K, Vanavichit A, Toojinda T. 2007. Physical mapping of Bph3, a brown planthopper resistance locus in rice. Maejo Int J Sci Technol, 1(2): 166-177. |
| [29] | Jairin J, Teangdeerith S, Leelagud P, Kothcharerk J, Sansen K, Yi M, Vanavichit A, Toojinda T. 2009. Development of rice introgression lines with brown planthopper resistance and KDML105 grain quality characteristics through marker-assisted selection. Field Crops Res, 110(3): 263-271. |
| [30] | Jena K K, Jeung J U, Lee J H, Choi H C, Brar D S. 2006. High-resolution mapping of a new brown planthopper (BPH) resistance gene, Bph18(t), and marker-assisted selection for BPH resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet, 112: 288-297. |
| [31] | Jena K K, Kim S M. 2010. Current status of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance and genetics. Rice, 3: 161-171. |
| [32] | Jena K K, Hechanova S L, Verdeprado H, Prahalada G D, Kim S R. 2017. Development of 25 near-isogenic lines (NILs) with ten BPH resistance genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Production, resistance spectrum, and molecular analysis. Theor Appl Genet, 130(11): 2345-2360. |
| [33] | Ji H, Kim S R, Kim Y H, Suh J P, Park H M, Sreenivasulu N, Misra G, Kim S M, Hechanova S L, Kim H, Lee G S, Yoon U H, Kim T H, Lim H, Suh S C, Yang J, An G, Jena K K. 2016. Map-based cloning and characterization of the BPH18 gene from wild rice conferring resistance to brown planthopper (BPH) insect pest. Sci Rep, 6(1): 34376. |
| [34] | Ji R, Ye W F, Chen H D, Zeng J M, Li H, Yu H X, Li J C, Lou Y G. 2017. A salivary endo-β-1,4-glucanase acts as an effector that enables the brown planthopper to feed on rice. Plant Physiol, 173: 1920-1932. |
| [35] | Jing S L, Zhang L, Ma Y H, Liu B F, Zhao Y, Yu H J, Zhou X, Qin R, Zhu L L, He G C. 2014. Genome-wide mapping of virulence in brown planthopper identifies loci that break down host plant resistance. PLoS One, 9(6): e98911. |
| [36] | Jones J D G, Dangl J L. 2006. The plant immune system. Nature, 444: 323-329. |
| [37] | Kabis A, Khush G S. 1988. Genetic analysis of resistance to brown planthopper in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Breeding, 100(1): 54-58. |
| [38] | Kawaguchi M, Murata K, Ishii T, Takumi S, Mori N, Nakamura C. 2001. Assignment of a brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene bph4 to the rice chromosome 6. Breeding Sci, 51(1): 13-18. |
| [39] | Khush G S. 1971. Rice breeding for disease and insect resistance at IRRI. Oryza, 8: 111-119. |
| [40] | Khush G S, Karim A N M R, Angeles E R. 1985. Genetics of resistance of rice cultivar ARC10550 to Bangladesh brown planthopper teletype. J Genet, 64: 121-125. |
| [41] | Khush G S. 1992. Selecting rice for simply inherited resistance. In: Stalker H T, Murphy J P. Plant Breeding in the 1990s. Wallingford, UK: CAB International: 303-322. |
| [42] | Kim S M, Sohn J K. 2005. Identification of a rice gene (Bph1) conferring resistance to brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) using STS markers. Mol Cells, 20(1): 30-34. |
| [43] | Klingler J, Creasy R, Gao L L, Nair R M, Calix A S, Jacob H S, Edwards O R, Singh K B. 2005. Aphid resistance in Medicago truncatula involves antixenosis and phloem-specific, inducible antibiosis, and maps to a single locus flanked by NBS-LRR resistance gene analogs. Plant Physiol, 137(4): 1445-1455. |
| [44] | Kumar K, Sarao P S, Bhatia D, Neelam K, Kaur A, Mangat G S, Brar D S, Singh K. 2018. High-resolution genetic mapping of a novel brown planthopper resistance locus, Bph34 in Oryza sativa L. × Oryza nivara (Sharma & Shastry) derived interspecific F2 population. Theor Appl Genet, 131: 1163-1171. |
| [45] | Kumari S, Sheba J M, Marappan M, Ponnuswamy S, Seetharaman S, Pothi N, Subbarayalu M, Muthurajan R, Natesan S. 2010. Screening of IR50 × Rathu Heenati F7 RILs and identification of SSR markers linked to brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Biotechnol, 46(1): 63-71. |
| [46] | Lakashminarayana A, Khush G S. 1977. New genes for resistance to the brown planthopper in rice. Crop Sci, 17: 96-100. |
| [47] | Li J B, Xia M Y, Qi H X, He G C, Wan B L, Zha Z P. 2006. Marker-assisted selection for brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance genes Bph14 and Bph15 in rice. Sci Agric Sin, 39(10): 2132-2137. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [48] | Li Z H, Xue Y X, Zhou H L, Li Y, Usman B, Jiao X Z, Wang X Y, Liu F, Qin B X, Li R B, Qiu Y F. 2019. High-resolution mapping and breeding application of a novel brown planthopper resistance gene derived from wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff). Rice, 12(1): 41. |
| [49] | Lison P, Rodrigo I, Conejero V. 2006. A novel function for the cathepsin D inhibitor in tomato. Plant Physiol, 142: 1329-1339. |
| [50] | Liu C X, Hao F H, Hu J, Zhang W L, Wan L L, Zhu L L, Tang H R, He G C. 2010. Revealing different systems responses to brown planthopper infestation for pest susceptible and resistant rice plants with the combined metabonomic and gene-expression analysis. J Proteome Res, 9: 6774-6785. |
| [51] | Liu J L, Du H T, Ding X, Zhou Y D, Xie P F, Wu J C. 2017. Mechanisms of callose deposition in rice regulated by exogenous abscisic acid and its involvement in rice resistance to Nilaparvata lugens Stål (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Pest Manag Sci, 73: 2559-2568. |
| [52] | Liu S H, Yang B J, Wang A Y, Luo J, Tang J. 2020. RNA interference of tyrosine hydroxylase caused rapid mortality by impairing cuticle formation in Nilaparvata lugens (Hemitera: Delphacidae). Pest Manag Sci, 76(6): 2225-2232. |
| [53] | Liu Y Q, Wu H, Chen H, Liu Y L, He J, Kang H Y, Sun Z G, Pan G, Wang Q, Hu J L, Zhou F, Zhou K N, Zheng X M, Ren Y L, Chen L M, Wang Y H, Zhao Z G, Lin Q B, Wu F Q, Zhang X, Guo X P, Cheng X N, Jiang L, Wu C Y, Wang H Y, Wan J M. 2015. A gene cluster encoding lectin receptor kinases confers broad-spectrum and durable insect resistance in rice. Nat Biotechnol, 33(3): 301-305. |
| [54] | Lu H P, Luo T, Fu H W, Wang L, Tan Y Y, Huang J Z, Wang Q, Ye G Y, Gatehouse A M R, Lou Y G, Shu Q Y. 2018. Resistance of rice to insect pests mediated by suppression of serotonin biosynthesis. Nat Plants, 4: 338-344. |
| [55] | Lü W T, Du B, Shangguan X X, Zhao Y, Pan Y F, Zhu L L, He Y Q, He G C. 2014. BAC and RNA sequencing reveal the brown planthopper resistance gene Bph15 in a recombination cold spot that mediates a unique defense mechanism. BMC Genom, 15(1): 674. |
| [56] | McCouch S R. 2008. Gene nomenclature system for rice. Rice, 1: 72-84. |
| [57] | Min S, Lee S W, Choi B R, Lee S H, Kwon D H. 2014. Insecticide resistance monitoring and correlation analysis to select appropriate insecticides against Nilaparvata lugens (Stål), a migratory pest in Korea. J Asia-Pac Entomol, 17(4): 711-716. |
| [58] | Murai H, Hashimoto Z, Sharma P N, Shimizu T, Murata K, Takumi S, Mori N, Kawasaki S, Nakamura C. 2001. Construction of a high-resolution linkage map of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene bph2. Theor Appl Genet, 103(4): 526-532. |
| [59] | Murata K, Fujiwara M, Murai H, Takumi S, Mori N, Nakamura C. 2001. Mapping of a brown planthopper (Nilaparvat lugens Stål) resistance gene BPH9 on the long arm of rice chromosome 12. Cereal Res Commun, 29: 245-250. |
| [60] | Myint K K M, Yasui H, Takagi M, Matsumura M. 2009. Virulence of long-term laboratory populations of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål), and white backed planthopper, Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) (Homoptera: Delphacidae), on rice differential varieties. Appl Entomol Zool, 44(1): 149-153. |
| [61] | Myint K K M, Fujita D, Matsumura M, Sonoda T, Yoshimura A, Yasui H. 2012. Mapping and pyramiding of two major genes for resistance to the brown planthopper (Nilaparva talugens [Stål]) in the rice cultivar ADR52. Theor Appl Genet, 124(3): 495-504. |
| [62] | Naik S B, Divya D, Sahu N, Sundaram R M, Sarao P S, Singh K, Lakshmi V J, Bentur J S. 2018. A new gene Bph33(t) conferring resistance to brown planthopper (BPH), Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) in rice line RP2068-18-3-5. Euphytica, 214(3): 53. |
| [63] | Nemoto H, Ikeda R, Kaneda C. 1989. New genes for resistance to brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stål, in rice. Jpn J Breeding, 39(1): 23-28. |
| [64] | Pan G, Liu Y Q, Ji L S, Zhang X, He J, Huang J, Qiu Z Y, Liu D M, Sun Z G, Xu T T, Liu L L, Wang C M, Jiang L, Cheng X N, Wan J M. 2018. Brassino steroids mediate susceptibility to brown planthopper by integrating with the salicylic acid and jasmonic acid pathways in rice. J Exp Bot, 69: 4433-4442. |
| [65] | Panda N, Heinrichs E A. 1983. Levels of tolerance and antibiosis in rice varieties having moderate resistance to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Environ Entomol, 12(4): 1204-1214. |
| [66] | Panda N, Khush G A. 1995. Host plant resistance to insects. In: Host Plant Resistance to Insects. Wallingford: CAB International: 431. |
| [67] | Pathak M D, Cheng C H, Furtuno M E. 1969. Resistance to Nephotettix cincticeps and Nilaparvata lugens in varieties of rice. Nature, 223: 502-504. |
| [68] | Pathak P K, Saxena R C, Heinrichs E A. 1982. Parafilm sachet for measuring honeydew excretion by Nilaparvata lugens on rice. J Econ Entomol, 75(2): 194-195. |
| [69] | Pieterse C M J, van der Does D, Zamioudis C, Leon-Reyes A, van Wees S C M. 2012. Hormonal modulation of plant immunity. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol, 28: 489-521. |
| [70] | Prahalada G D, Shivakumar N, Lohithaswa H C, Gowda D K S, Ramkumar G, Kim S R, Ramachandra C, Hittalmani S, Mohapatra T, Jena K K. 2017. Identification and fine mapping of a new gene, BPH31 conferring resistance to brown planthopper biotype 4 of India to improve rice, Oryza sativa L. Rice, 10(1): 41. |
| [71] | Qiu Y F, Guo J P, Jing S L, Zhu L L, He G C. 2010. High- resolution mapping of the brown planthopper resistance gene Bph6 in rice and characterizing its resistance in the 9311 and Nipponbare near isogenic backgrounds. Theor Appl Genet, 121(8): 1601-1611. |
| [72] | Qiu Y F, Guo J P, Jing S L, Zhu L L, He G C. 2012. Development and characterization of japonica rice lines carrying the brown planthopper-resistance genes BPH12 and Bph6. Theor Appl Genet, 124(3): 485-494. |
| [73] | Qiu Y F, Guo J P, Jing S L, Zhu L L, He G C. 2014. Fine mapping of the rice brown planthopper resistance gene bph7 and characterization of its resistance in the 93-11 background. Euphytica, 198(3): 369-379. |
| [74] | Rahman M L, Jiang W Z, Chu S H, Qiao Y L, Ham T H, Woo M O, Lee J, Khanam M S, Chin J H, Jeung J U, Brar D S, Jena K K, Koh H J. 2009. High-resolution mapping of two rice brown planthopper resistance genes, Bph20(t) and Bph21(t), originating from Oryza minuta. Theor Appl Genet, 119(7): 1237-1246. |
| [75] | Ren J S, Gao F Y, Wu X T, Lu X J, Zeng L H, Lv J Q, Su X W, Luo H, Ren G J. 2016. Bph32, a novel gene encoding an unknown SCR domain-containing protein, confers resistance against the brown planthopper in rice. Sci Rep, 6: 37645. |
| [76] | Renganayaki K, Fritz A K, Sadasivam S, Pammi S, Harrington S E, McCouch S R, Kumar S M, Reddy A S. 2002. Mapping and progress toward map-based cloning of brown planthopper biotype-4 resistance gene introgressed from Oryza officinalis into cultivated rice, O. sativa. Crop Sci, 42(6): 2112-2117. |
| [77] | Samuels L, Kunst L, Jetter R. 2008. Sealing plant surfaces: Cuticular wax formation by epidermal cells. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 59: 683-707. |
| [78] | Sangha J S, Chen Y H, Palchamy K, Jahn G C, Maheswaran M, Adalla C B, Leung H. 2008. Categories and inheritance of resistance to Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) in mutants of indica rice ‘IR64’. J Econ Entomol, 101(2): 575-583. |
| [79] | Santamaria M E, Martinez M, Cambra I, Grbic V, Diaz I. 2013. Understanding plant defence responses against herbivore attacks: An essential first step towards the development of sustainable resistance against pests. Transg Res, 22(4): 697-708. |
| [80] | Satturu V, Vattikuti J L, Sai J D, Kumar A, Singh R K, Prasad M S, Zaw H, Jubay M L, Satish L, Rathore A, Mulinti S, Vg I L, Chakraborty A, Thirunavukkarasu N. 2020. Multiple genome wide association mapping models identify quantitative trait nucleotides for brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) resistance in MAGIC indica population of rice. Vaccines, 8(4): 608. |
| [81] | Shangguan X X, Zhang J, Liu B F, Zhao Y, Wang H Y, Wang Z Z, Guo J P, Rao W W, Jing S L, Guan W, Ma Y H, Wu Y, Hu L, Chen R Z, Du B, Zhu L L, Yu D Z, He G C. 2018. A mucin-like protein of planthopper is required for feeding and induces immunity response in plants. Plant Physiol, 176(1): 552-565. |
| [82] | Sharma P N, Torii A, Takumi S, Mori N, Nakamura C. 2004. Marker-assisted pyramiding of brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance genes Bph1 and bph2 on rice chromosome 12. Hereditas, 140(1): 61-69. |
| [83] | Shepherd T, Wynne G D. 2006. The effects of stress on plant cuticular waxes. New Phytol, 171(3): 469-499. |
| [84] | Sogawa K. 1978. Quantitative morphological variations among biotypes of the brown planthopper. Rice Res Newsl, 3: 9-10. |
| [85] | Soundararajan R P, Kadirvel P, Gunathilagaraj K, Maheswaran M. 2004. Mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to brown planthopper in rice by means of a doubled haploid population. Crop Sci, 44(6): 2214-2220. |
| [86] | Stadlmeier M, Hartl L, Mohler V. 2018. Usefulness of a multiparent advanced generation intercross population with a greatly reduced mating design for genetic studies in winter wheat. Front Plant Sci, 9: 1825. |
| [87] | Strauss S Y, Agrawal A A. 1999. The ecology and evolution of plant tolerance to herbivory. Trends Ecol Evol, 14(5): 179-185. |
| [88] | Su C C, Zhai H Q, Wang C M, Sun L H, Wan J M. 2006. SSR mapping of brown planthopper resistance gene Bph9 in Kaharamana, an indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Genet Sin, 33(3): 262-268. |
| [89] | Suh J P, Yang X G, Jeung J U, Pamplona A, Kim J J, Lee J H, Hong H C, Yang C I, Kim Y G, Jena K K. 2011. Development of elite breeding lines conferring BPH18 gene-derived resistance to brown planthopper (BPH) by marker-assisted selection and genome-wide background analysis in japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Field Crops Res, 120(2): 215-222. |
| [90] | Sun L H, Su C C, Wang C M, Zhai H Q, Wan J M. 2005. Mapping of a major resistance gene to the brown planthopper in the rice cultivar Rathu Heenati. Breeding Sci, 55(4): 391-396. |
| [91] | Sun L H, Liu Y, Jiang L, Su C C, Wang C M, Zhai H R, Wan J M. 2007. Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to brown planthopper in the indica rice cultivar Col. 5 Thailand. Hereditas, 144(2): 48-52. |
| [92] | Tamura Y, Hattori M, Yoshioka H, Yoshioka M, Takahashi A, Wu J Z, Sentoku N, Yasui H. 2014. Map-based cloning and characterization of a brown planthopper resistance gene BPH26 from Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica cultivar ADR52. Sci Rep, 4(1): 5872. |
| [93] | Tanaka K, Endo S, Kazano H. 2000. Toxicity of insecticides to predators of rice planthoppers: Spiders, the mirid bug and the dryinid wasp. Appl Entomol Zool, 35(1): 177-187. |
| [94] | Tong X H, Qi J F, Zhu X D, Mao B Z, Zeng L J, Wang B H, Li Q, Zhou G X, Xu X J, Lou Y G, He Z H. 2012. The rice hydroperoxide lyase OsHPL3 functions in defense responses by modulating the oxylipin pathway. Plant J, 71(5): 763-775. |
| [95] | Varshney R K, Graner A, Sorrells M E. 2005. Genomics-assisted breeding for crop improvement. Trends Plant Sci, 10(12): 621-630. |
| [96] | Wang H Y, Shi S J, Guo Q, Nie L Y, Du B, Chen R Z, Zhu L L, He G C. 2018. High-resolution mapping of a gene conferring strong antibiosis to brown planthopper and developing resistant near-isogenic lines in 9311 background. Mol Breeding, 38(8): 107. |
| [97] | Wang Y, Cao L M, Zhang Y X, Cao C X, Liu F, Huang F K, Qiu Y F, Li R B, Luo X J. 2015. Map-based cloning and characterization of BPH29, a B3 domain-containing recessive gene conferring brown planthopper resistance in rice. J Exp Bot, 66(19): 6035-6045. |
| [98] | Woodhead S, Padgham D E. 1988. The effect of plant surface characteristics on resistance of rice to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Entomol Exp Appl, 47: 15-22. |
| [99] | Wu H, Liu Y Q, He J, Liu Y L, Jiang L, Liu L H, Wang C M, Cheng X N, Wan J M. 2014. Fine mapping of brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene Bph28(t) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breeding, 33: 909-918. |
| [100] | Xiao C, Hu J, Ao Y T, Cheng M X, Gao G J, Zhang Q L, He G C, He Y Q. 2016. Development and evaluation of near-isogenic lines for brown planthopper resistance in rice cv. 9311. Sci Rep, 6: 38159. |
| [101] | Xu Y D. 2013. Pyramiding of two BPH resistance genes and Stv-bi gene using marker-assisted selection in japonica rice. Crop Breeding Appl Biotechnol, 13(2): 99-106. |
| [102] | Yang H Y, You A Q, Yang Z F, Zhang F T, He R F, Zhu L L, He G C. 2004. High-resolution genetic mapping at the Bph15 locus for brown planthopper resistance in rice Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet, 110(1): 182-191. |
| [103] | Yang L, Zhang W L. 2016. Genetic and biochemical mechanisms of rice resistance to planthopper. Plant Cell Rep, 35(8): 1559-1572. |
| [104] | Yang M, Cheng L, Yan L H, Shu W, Wang X Y, Qiu Y F. 2019. Mapping and characterization of a quantitative trait locus resistance to the brown planthopper in the rice variety IR64. Hereditas, 156(1): 22. |
| [105] | Zhang J, Luo T, Wang W W, Cao T T, Li R, Lou Y G. 2017. Silencing OsSLR1 enhances the resistance of rice to the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Plant Cell Environ, 40(10): 2147-2159. |
| [106] | Zhang J J, Li Y, Guo J P, Du B, He G C, Zhang J J, Chen R Z, Li J R. 2018. Lipid profiles reveal different responses to brown planthopper infestation for pest susceptible and resistant rice plants. Metabolomics, 14(9): 120. |
| [107] | Zhang W L, Yang L, Li M, Ma B J, Yan C Q, Chen J P. 2015. Omics-based comparative transcriptional profiling of two contrasting rice genotypes during early infestation by small brown planthopper. Int J Mol Sci, 16(12): 28746-28764. |
| [108] | Zhang Y X, Qin G, Ma Q Q, Wei M Y, Yang X H, Ma Z F, Liang H F, Liu C, Li Z J, Liu F, Huang D H, Li R B. 2020. Identification of a major resistance locus Bph35 to brown planthopper in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice Sci, 27(3): 237-245. |
| [109] | Zhao Y, Huang J, Wang Z Z, Jing S L, Wang Y, Ouyang Y D, Cai B D, Xin X F, Liu X, Zhang C X, Pan Y F, Ma R, Li Q F, Jiang W H, Shangguan X X, Wang H Y, Du B, Zhu L L, Xu X, Feng Y Q, He S Y, Chen R Z, Zhang Q F, He G C. 2016. Allelic diversity in an NLR gene BPH9 enables rice to combat planthopper variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 113(45): 12850-12855. |
| [1] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [2] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [3] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [4] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [5] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [6] | LIU Tingting, ZOU Jinpeng, YANG Xi, WANG Kejian, RAO Yuchun, WANG Chun. Development and Application of Prime Editing in Plants [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 3-. |
| [7] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [8] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [9] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [10] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [11] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [12] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [13] | Tan Jingyi, Zhang Xiaobo, Shang Huihui, Li Panpan, Wang Zhonghao, Liao Xinwei, Xu Xia, Yang Shihua, Gong Junyi, Wu Jianli. ORYZA SATIVA SPOTTED-LEAF 41 (OsSPL41) Negatively Regulates Plant Immunity in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 426-436. |
| [14] | Monica Ruffini Castiglione, Stefania Bottega, Carlo Sorce, Carmelina SpanÒ. Effects of Zinc Oxide Particles with Different Sizes on Root Development in Oryza sativa [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 449-458. |
| [15] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||