
Rice Science ›› 2025, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (5): 727-746.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2025.05.005
• Experimental Technique • Previous Articles
Pan Pan1,2,3,#, Guo Wenlong4,5,#, Li Hengbo1,2,3, Shao Yifan1,2,3, Guo Zhihao1,2,3, Jin Ye4,5, Cheng Yanrong6,7, Yu Guoping3,8, Fu Zhenshi9, Hu Lin1,2,3( ), Zheng Xiaoming3,5,10(
), Zheng Xiaoming3,5,10( ), Zhou Guomin1,2,3,11, Zhang Jianhua1,2,3(
), Zhou Guomin1,2,3,11, Zhang Jianhua1,2,3( )
)
Received:2025-03-19
Accepted:2025-05-26
Online:2025-09-28
Published:2025-10-11
Contact:
Zhang Jianhua (About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work
Pan Pan, Guo Wenlong, Li Hengbo, Shao Yifan, Guo Zhihao, Jin Ye, Cheng Yanrong, Yu Guoping, Fu Zhenshi, Hu Lin, Zheng Xiaoming, Zhou Guomin, Zhang Jianhua. Accelerating Wild Rice Disease-Resistant Germplasm Exploration: Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Powered Wild Rice Blast Disease Level Evaluation and Disease-Resistance Identification[J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(5): 727-746.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
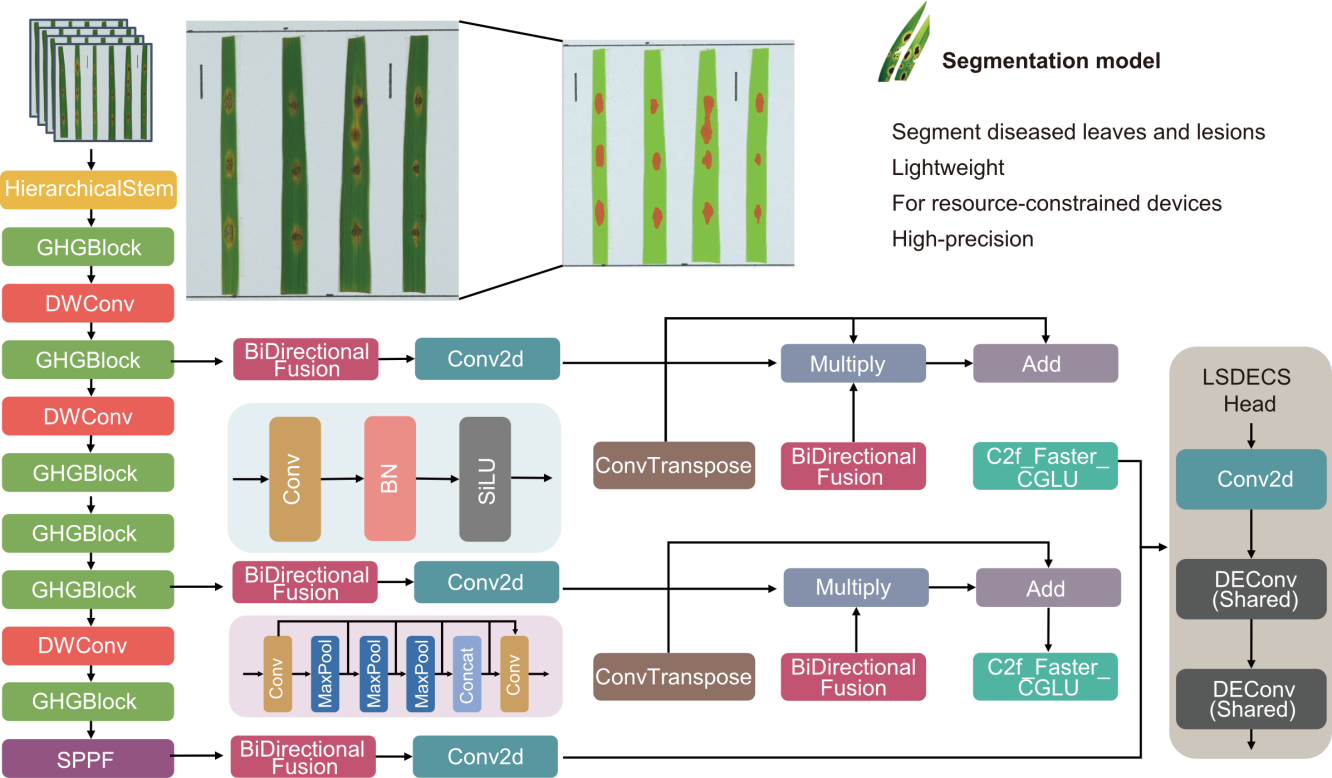
Fig. 2. Structural diagram of diseased leaf and lesion segmentation model. BN, Batch normalization; Deconv, Detail enhancement convolution; SPPF, Spatial pyramid pooling fast; Conv, Convolution; Concat, Concatenation; SiLU, Sigmoid linear unit; DWConv, Depth-wise convolution.
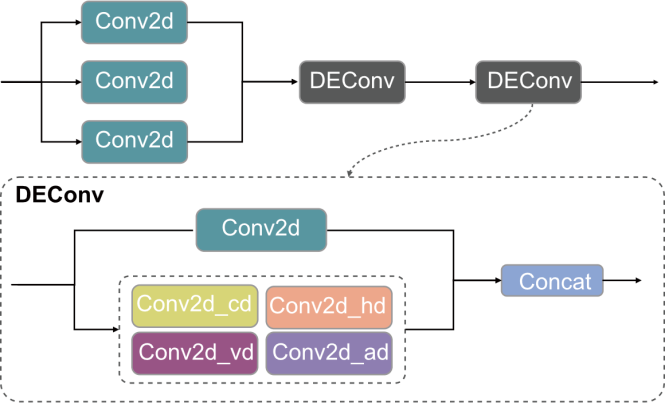
Fig. 5. Structural diagram of LSDECS Head. DEConv, Detail enhancement convolution; Conv2d_cd, Center difference convolution; Conv2d_hd, Horizontal difference convolution; Conv2d_vd, Vertical difference convolution; Conv2d_ad, Angle difference convolution.
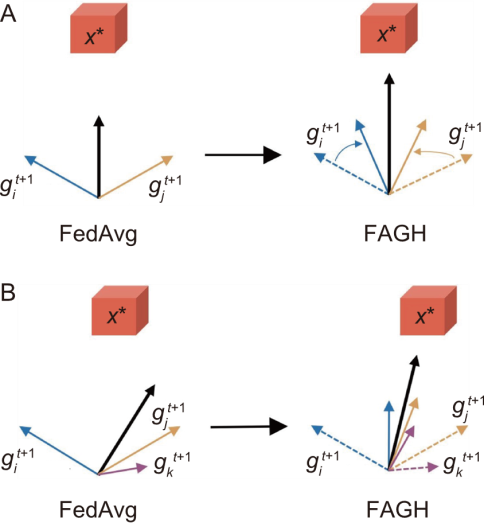
Fig. 6. Comparison of federated learning. A, Two gradients. B, Three gradients. FedAvg, Federated averaging; FAGH, Federated averaging with gradient harmonization.
| Disease level | Lesion coverage ratio (LCR) |
|---|---|
| L0 | 0 |
| L1 | 0 < LCR ≤ 0.010 |
| L2 | 0.010 < LCR ≤ 0.020 |
| L3 | 0.020 < LCR ≤ 0.035 |
| L4 | 0.035 < LCR ≤ 0.060 |
| L5 | 0.060 < LCR ≤ 0.100 |
| L6 | 0.100 < LCR ≤ 0.250 |
| L7 | 0.250 < LCR ≤ 0.500 |
| L8 | 0.500 < LCR ≤ 0.750 |
| L9 | 0.750 < LCR ≤ 1.000 |
Table 1. Criteria for evaluation blast disease and disease-resistance in identification.
| Disease level | Lesion coverage ratio (LCR) |
|---|---|
| L0 | 0 |
| L1 | 0 < LCR ≤ 0.010 |
| L2 | 0.010 < LCR ≤ 0.020 |
| L3 | 0.020 < LCR ≤ 0.035 |
| L4 | 0.035 < LCR ≤ 0.060 |
| L5 | 0.060 < LCR ≤ 0.100 |
| L6 | 0.100 < LCR ≤ 0.250 |
| L7 | 0.250 < LCR ≤ 0.500 |
| L8 | 0.500 < LCR ≤ 0.750 |
| L9 | 0.750 < LCR ≤ 1.000 |
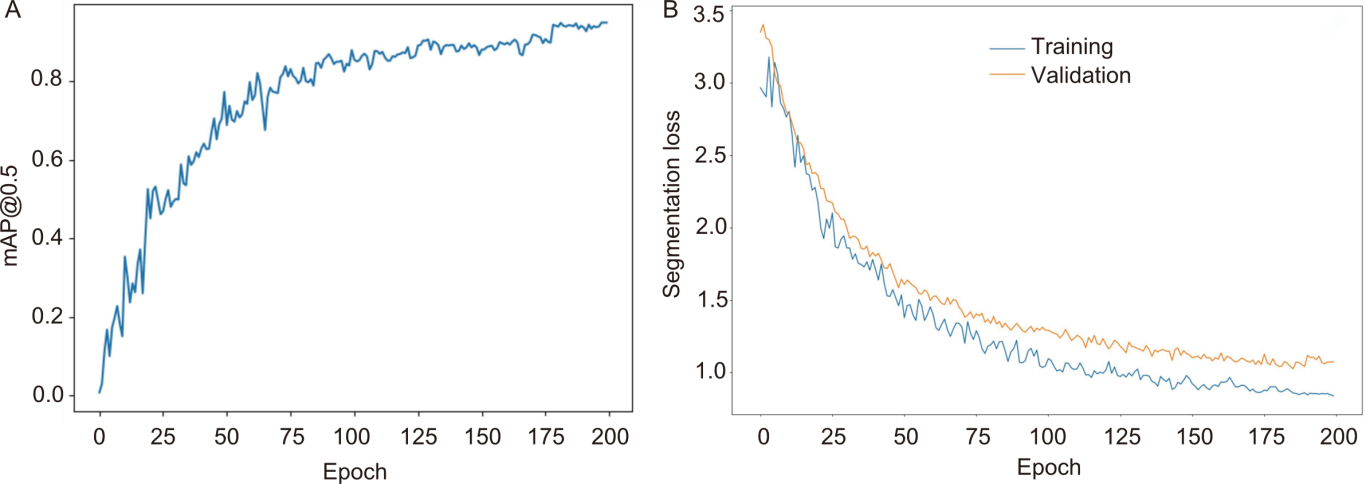
Fig. 8. Metrics variation during model training. A, Variation of mean average precision (mAP@0.5) across training epochs. B, Variation of segmentation loss across training epochs.
| Baseline | GhostHierarchicalNet | CAHSFPN | LSDECS Head | mAP@0.5 (%) | Parameter (M) | FLOPs (G) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | 94.4 | 3.2 | 12.0 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | 95.4 | 2.5 | 10.7 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 95.0 | 1.4 | 9.4 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 95.7 | 2.2 | 11.3 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 94.5 | 1.8 | 9.8 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 94.7 | 2.4 | 10.0 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 93.4 | 1.7 | 8.7 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 95.0 | 1.2 | 9.0 |
Table 2. Comparative results of ablation experiments.
| Baseline | GhostHierarchicalNet | CAHSFPN | LSDECS Head | mAP@0.5 (%) | Parameter (M) | FLOPs (G) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | 94.4 | 3.2 | 12.0 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | 95.4 | 2.5 | 10.7 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 95.0 | 1.4 | 9.4 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 95.7 | 2.2 | 11.3 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 94.5 | 1.8 | 9.8 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 94.7 | 2.4 | 10.0 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 93.4 | 1.7 | 8.7 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 95.0 | 1.2 | 9.0 |
| Treatment | mAP@0.5 (%) | FLOPs (G) | Parameter (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before pruning | 95.0 | 9.0 | 1.20 |
| After pruning | 96.3 | 5.3 | 0.22 |
Table 3. Model performance before and after pruning.
| Treatment | mAP@0.5 (%) | FLOPs (G) | Parameter (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before pruning | 95.0 | 9.0 | 1.20 |
| After pruning | 96.3 | 5.3 | 0.22 |
| Class | Precision | Recall | mAP@0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diseased leaf | 99.5 | 100.0 | 99.5 |
| Lesion | 94.0 | 90.6 | 93.1 |
| All | 96.7 | 95.3 | 96.3 |
Table 4. Performance evaluation on diseased leaf and lesion segmentation. %
| Class | Precision | Recall | mAP@0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diseased leaf | 99.5 | 100.0 | 99.5 |
| Lesion | 94.0 | 90.6 | 93.1 |
| All | 96.7 | 95.3 | 96.3 |
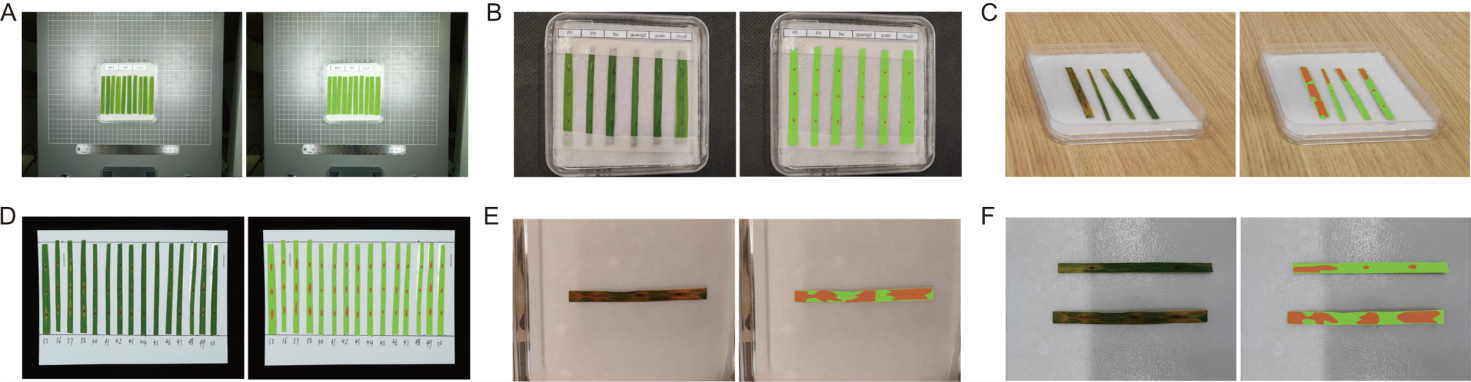
Fig. 9. Segmentation results under various conditions. A, Small diseased leaves and lesions in the image. B, Diseased leaves partially obstructed by wet filter paper, with water droplets obscuring the lesions. C, Misalignment of augmented reality (AR) glasses relative to diseased leaf during image capture. D, Re-evaluating historical experiment data in archive room. E, Warm color tone due to laboratory lighting conditions. F, Shadows affecting segmentation under high-speed scanner’s view. The left image shows original image, while the right image presents segmentation results. Green indicates diseased leaves, and orange represents lesions.
| Model | mAP@0.5 (%) | FLOPs (G) | Parameter (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FastInst | 83.1 | 112.9 | 53.0 |
| SparseInst | 88.5 | 86.0 | 51.2 |
| CondInst | 79.7 | 102.3 | 38.0 |
| BlendMask | 50.4 | 85.2 | 49.3 |
| Mask R-CNN | 58.8 | 149.0 | 44.7 |
| YOLOv8-Seg | 94.4 | 12.0 | 3.2 |
| YOLOv11-Seg | 91.2 | 10.4 | 2.8 |
| YOLOv12-Seg | 92.0 | 9.9 | 2.7 |
| Ours | 96.3 | 5.3 | 0.2 |
Table 5. Performance comparison of different segmentation models.
| Model | mAP@0.5 (%) | FLOPs (G) | Parameter (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FastInst | 83.1 | 112.9 | 53.0 |
| SparseInst | 88.5 | 86.0 | 51.2 |
| CondInst | 79.7 | 102.3 | 38.0 |
| BlendMask | 50.4 | 85.2 | 49.3 |
| Mask R-CNN | 58.8 | 149.0 | 44.7 |
| YOLOv8-Seg | 94.4 | 12.0 | 3.2 |
| YOLOv11-Seg | 91.2 | 10.4 | 2.8 |
| YOLOv12-Seg | 92.0 | 9.9 | 2.7 |
| Ours | 96.3 | 5.3 | 0.2 |
| Disease level | Number | Correct evaluation | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| L0 | 0 | 0 | ‒ |
| L1 | 4 | 4 | 100.0 |
| L2 | 68 | 67 | 98.5 |
| L3 | 55 | 53 | 96.4 |
| L4 | 202 | 202 | 100.0 |
| L5 | 225 | 225 | 100.0 |
| L6 | 272 | 272 | 100.0 |
| L7 | 203 | 203 | 100.0 |
| L8 | 65 | 65 | 100.0 |
| L9 | 42 | 42 | 100.0 |
| Overall | 1 136 | 1 133 | 99.7 |
Table 6. Evaluation accuracy for different disease levels in test set.
| Disease level | Number | Correct evaluation | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| L0 | 0 | 0 | ‒ |
| L1 | 4 | 4 | 100.0 |
| L2 | 68 | 67 | 98.5 |
| L3 | 55 | 53 | 96.4 |
| L4 | 202 | 202 | 100.0 |
| L5 | 225 | 225 | 100.0 |
| L6 | 272 | 272 | 100.0 |
| L7 | 203 | 203 | 100.0 |
| L8 | 65 | 65 | 100.0 |
| L9 | 42 | 42 | 100.0 |
| Overall | 1 136 | 1 133 | 99.7 |
| Disease-resistance level | Number | Correct evaluation | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| R0 | 0 | 0 | ‒ |
| R1 | 3 | 3 | 100.0 |
| R2 | 2 | 2 | 100.0 |
| R3 | 12 | 11 | 91.7 |
| R4 | 11 | 11 | 100.0 |
| R5 | 10 | 10 | 100.0 |
| R6 | 26 | 26 | 100.0 |
| R7 | 23 | 23 | 100.0 |
| R8 | 8 | 8 | 100.0 |
| R9 | 5 | 5 | 100.0 |
| Overall | 100 | 99 | 99.0 |
Table 7. Disease-resistance identification accuracy for different disease resistance in practical testing.
| Disease-resistance level | Number | Correct evaluation | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| R0 | 0 | 0 | ‒ |
| R1 | 3 | 3 | 100.0 |
| R2 | 2 | 2 | 100.0 |
| R3 | 12 | 11 | 91.7 |
| R4 | 11 | 11 | 100.0 |
| R5 | 10 | 10 | 100.0 |
| R6 | 26 | 26 | 100.0 |
| R7 | 23 | 23 | 100.0 |
| R8 | 8 | 8 | 100.0 |
| R9 | 5 | 5 | 100.0 |
| Overall | 100 | 99 | 99.0 |
| Disease level | Number | Correct evaluating | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| L0 | 1 | 1 | 100.0 |
| L1 | 8 | 7 | 87.5 |
| L2 | 11 | 11 | 100.0 |
| L3 | 14 | 14 | 100.0 |
| L4 | 10 | 10 | 100.0 |
| L5 | 11 | 11 | 100.0 |
| L6 | 13 | 13 | 100.0 |
| L7 | 14 | 13 | 92.9 |
| L8 | 15 | 13 | 86.7 |
| L9 | 3 | 3 | 100.0 |
| Total | 100 | 96 | 96.0 |
Table 9. Identification accuracy for different disease levels in generalization testing.
| Disease level | Number | Correct evaluating | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| L0 | 1 | 1 | 100.0 |
| L1 | 8 | 7 | 87.5 |
| L2 | 11 | 11 | 100.0 |
| L3 | 14 | 14 | 100.0 |
| L4 | 10 | 10 | 100.0 |
| L5 | 11 | 11 | 100.0 |
| L6 | 13 | 13 | 100.0 |
| L7 | 14 | 13 | 92.9 |
| L8 | 15 | 13 | 86.7 |
| L9 | 3 | 3 | 100.0 |
| Total | 100 | 96 | 96.0 |
| [1] | Abràmoff M D, Magalhães P J, Ram S J. 2004. Image processing with ImageJ. In: Biophotonics International. Pittsfield, Massachusetts, USA: Laurin Publishing Co. Inc.: 36-42. |
| [2] | Cai X H, Lai Q X, Wang Y W, et al. 2024. Poly kernel inception network for remote sensing detection. arXiv e-prints: 2403.06258. https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.06258v2. |
| [3] | Campo S, Martín-Cardoso H, Olivé M, et al. 2020. Effect of root colonization by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth, productivity and blast resistance in rice. Rice, 13(1): 42. |
| [4] | Chen H, Sun K Y, Tian Z, et al. 2020. BlendMask: Top-down meets bottom-up for instance segmentation. arXiv e-prints: 2001.00309. https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.00309v3. |
| [5] | Chen J R, Kao S H, He H, et al. 2023. Run, don’t walk: Chasing higher FLOPS for faster neural networks. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). June 17-24, 2023, Vancouver, BC, Canada: IEEE: 12021-12031. |
| [6] | Chen Y, Liu Z Q, Meng S, et al. 2023. OsCERK1 contributes to cupric oxide nanoparticles induced phytotoxicity and basal resistance against blast by regulating the anti-oxidant system in rice. J Fungi, 9(1): 36. |
| [7] | Chen Y F, Zhang C Y, Chen B, et al. 2024. Accurate leukocyte detection based on deformable-DETR and multi-level feature fusion for aiding diagnosis of blood diseases. Comput Biol Med, 170: 107917. |
| [8] | Chen Z X, He Z W, Lu Z M. 2024. DEA-net: Single image dehazing based on detail-enhanced convolution and content-guided attention. IEEE Trans Image Process, 33: 1002-1015. |
| [9] | Cheng T H, Wang X G, Chen S Y, et al. 2022. Sparse instance activation for real-time instance segmentation. arXiv e-prints: 2203.12827. https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.12827v1. |
| [10] | Culjak I, Abram D, Pribanic T, et al. 2012. A brief introduction to OpenCV. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Convention MIPRO. 21-25 May 2012, Opatija, Croatia: IEEE: 1725-1730. |
| [11] | Das A, Soubam D, Singh P K, et al. 2012. A novel blast resistance gene, Pi54rh cloned from wild species of rice, Oryza rhizomatis confers broad spectrum resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae. Funct Integr Genomics, 12(2): 215-228. |
| [12] | Devi S J S R, Singh K, Umakanth B, et al. 2015. Development and identification of novel rice blast resistant sources and their characterization using molecular markers. Rice Sci, 22(6): 300-308. |
| [13] | Fahad S, Adnan M, Noor M, et al. 2019. Major constraints for global rice production. In: Hasanuzzaman M, Fujita M, Nahar K, et al. Advances in Rice Research for Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier: 1-22. |
| [14] | Fernandez J, Lopez V, Kinch L, et al. 2021. Role of two metacaspases in development and pathogenicity of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. mBio, 12(1): e03471-20. |
| [15] | Han Q, Fan Z J, Dai Q, et al. 2021. On the connection between local attention and dynamic depth-wise convolution. arXiv e-prints: 2106.04263. https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.04263v5. |
| [16] | He J J, Li P Y, Geng Y F, et al. 2023. FastInst: A simple query-based model for real-time instance segmentation. arXiv e-prints: 2303. 08594. https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.08594v2. |
| [17] | He K M, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, et al. 2018. Mask R-CNN. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 42(2): 386-397. |
| [18] | Huang C L, Hwang S Y, Chiang Y C, et al. 2008. Molecular evolution of the Pi-ta gene resistant to rice blast in wild rice (Oryza rufipogon). Genetics, 179(3): 1527-1538. |
| [19] | Laha G S, Singh R, Ladhalakshmi D, et al. 2017. Importance and management of rice diseases: A global perspective. In: Chauhan B S, Jabran K, Mahajan Gulshan. Rice Production Worldwide. Cham: Springer International Publishing: 303-360. |
| [20] | Lamba S, Kukreja V, Baliyan A, et al. 2023. A novel hybrid severity prediction model for blast paddy disease using machine learning. Sustainability, 15(2): 1502. |
| [21] | Lee J, Park S, Mo S, et al. 2020. Layer-adaptive sparsity for the magnitude-based pruning. arXiv e-prints: 2010.07611. https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.07611v2. |
| [22] | Li W, Zhang M C, Yang Y L, et al. 2024. Molecular evolution of rice blast resistance gene bsr-d1. Rice Sci, 31(6): 700-711. |
| [23] | Li W T, Chern M, Yin J J, et al. 2019. Recent advances in broad-spectrum resistance to the rice blast disease. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 50: 114-120. |
| [24] | Liang Y, Yi Z F, Zhuang W, et al. 2025. Optimizing hybrid with improved resistance to rice blast and superior ratooning ability. Rice Sci, 32(3): 292-297. |
| [25] | Lin S D, Yao Y, Li J Y, et al. 2023. Application of UAV-based imaging and deep learning in assessment of rice blast resistance. Rice Sci, 30(6): 652-660. |
| [26] | Liu W D, Wang G L. 2016. Plant innate immunity in rice: A defense against pathogen infection. Natl Sci Rev, 3(3): 295-308. |
| [27] | Liu Y B, Lei B, Hu L, et al. 2020. The grading determination of rice blast: HSV color space method based on machine vision. J Agric, 10(10): 83-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Liu Y L, Feng N J, Zhong F T. 2022. First report of Pyricularia oryzae causing blast in wild rice (Oryza rufipogon) in China. Plant Dis, 106(11): 2997. |
| [29] | Meng F, He Y G, Chen J, et al. 2021. Analysis of natural variation of the rice blast resistance gene Pike and identification of a novel allele Pikg. Mol Genet Genomics, 296(4): 939-952. |
| [30] | Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. 2014. Technical specification for identification and evaluation of blast resistance in rice variety regional test: NY-T 2646-2014. Beijing, China: China Standards Press. [2025-02-25]. (in Chinese) |
| [31] | Pan P, Zhang J H, Zheng X M, et al. 2023a. Research progress of deep learning in intelligent identification of disease resistance of crops and their related species. Acta Agric Zhejiang, 35(8): 1993-2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Pan P, Guo W, Zheng X, et al. 2023b. Xoo-YOLO: A detection method for wild rice bacterial blight in the field from the perspective of unmanned aerial vehicles. Front Plant Sci, 14: 1256545. |
| [33] | Pan P, Yao Q, Shen J, et al. 2024a. CVW-etr: A high-precision method for estimating the severity level of cotton verticillium wilt disease. Plants-Basel, 13(21): 2960. |
| [34] | Pan P, Shao M, He P, et al. 2024b. Lightweight cotton diseases real-time detection model for resource-constrained devices in natural environments. Front Plant Sci, 15: 1383863. |
| [35] | Patil R R, Kumar S, Chiwhane S, et al. 2023. An artificial-intelligence-based novel rice grade model for severity estimation of rice diseases. Agriculture, 13(1): 47. |
| [36] | Qu S H, Liu G F, Zhou B, et al. 2006. The broad-spectrum blast resistance gene Pi9 encodes a nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of a multigene family in rice. Genetics, 172(3): 1901-1914. |
| [37] | Ritharson P I, Raimond K, Mary X A, et al. 2024. DeepRice: A deep learning and deep feature based classification of rice leaf disease subtypes. Artif Intell Agric, 11: 34-49. |
| [38] | Russell B C, Torralba A, Murphy K P, et al. 2008. LabelMe: A database and web-based tool for image annotation. Int J Comput Vis, 77(1): 157-173. |
| [39] | Shen Q, Li Y, Zhang Y X, et al. 2025. CSW-YOLO: A traffic sign small target detection algorithm based on YOLOv8. PLoS One, 20(3): e0315334. |
| [40] | Sheng C, Yu D, Li X, et al. 2022. OsAPX1 positively contributes to rice blast resistance. Front Plant Sci, 13: 843271. |
| [41] | Shi D. 2023. TransNeXt: Robust foveal visual perception for vision transformers. arXiv e-prints: 2311.17132. https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.17132v3. |
| [42] | Tang Y H, Han K, Guo J Y, et al. 2022. GhostNetV2: Enhance cheap operation with long-range attention. arXiv e-prints: 2211.12905. https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.12905v1. |
| [43] | Terensan S, Salgadoe A S A, Kottearachchi N S, et al. 2024. Proximally sensed RGB images and colour indices for distinguishing rice blast and brown spot diseases by k-means clustering: Towards a mobile application solution. Smart Agric Technol, 9: 100532. |
| [44] | Tian Z, Shen C H, Chen H, et al. 2020. Conditional convolutions for instance segmentation. arXiv e-prints: 2003.05664. https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.05664v4. |
| [45] | Wing R A, Purugganan M D, Zhang Q F. 2018. The rice genome revolution: From an ancient grain to Green Super Rice. Nat Rev Genet, 19(8): 505-517. |
| [46] | Yang Z Y, Xu Z J, Yang Q W, et al. 2022. Conservation and utilization of genetic resources of wild rice in China. Rice Sci, 29(3): 216-224. |
| [47] | Zheng X M, Peng Y L, Qiao J Y, et al. 2024. Wild rice: Unlocking the future of rice breeding. Plant Biotechnol J, 22(11): 3218-3226. |
| [48] | Zhu X M, Li L, Wang J Y, et al. 2021. Vacuolar protein-sorting receptor MoVps13 regulates conidiation and pathogenicity in rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. J Fungi, 7(12): 1084. |
| [1] | Li Haifeng, Fan Jiayi. Functions of Rice E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Response to Environmental Stress and in Regulating Grain Size [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(5): 649-657. |
| [2] | Li Xinyan, Weng Lüshui, Xiao Youlun, Li Jinjiang, Deng Lihua, Liu Qing, Kang Weiwei, Duan Yaping, Yang Daji, Xiao Guoying. Characteristic Analysis of Penta-Resistance Restorer Line for Hybrid Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(4): 512-524. |
| [3] | Fan Fengfeng, Cai Meng, Luo Xiong, Liu Manman, Yuan Huanran, Cheng Mingxing, Ayaz Ahmad, Li Nengwu, Li Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 577-586. |
| [4] | Lin Shaodan, Yao Yue, Li Jiayi, Li Xiaobin, Ma Jie, Weng Haiyong, Cheng Zuxin, Ye Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 652-660. |
| [5] | Si Fengfeng, Fan Fengfeng, Wei Xiao, He Shihao, Li Xianlong, Peng Xiaojue, Li Shaoqing. Quantitative Trait Locus Mapping of High Photosynthetic Efficiency and Biomass in Oryza longistaminata [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(6): 569-576. |
| [6] | Liu Yantong, Li Ting, Jiang Zhishu, Zeng Chuihai, He Rong, Qiu Jiao, Lin Xiaoli, Peng Limei, Song Yongping, Zhou Dahu, Cai Yicong, Zhu Changlan, Fu Junru, He Haohua, Xu Jie. Characterization of a Novel Weak Allele of RGA1/D1 and Its Potential Application in Rice Breeding [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(6): 522-534. |
| [7] | Wu Zhongling, Qiu Jiehua, Shi Huanbin, Lin Chuyu, Yue Jiangnan, Liu Zhiquan, Xie Wei, Naweed I. Naqvi, Kou Yanjun, Tao Zeng. Polycomb Repressive Complex 2-Mediated H3K27 Trimethylation Is Required for Pathogenicity in Magnaporthe oryzae [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(4): 363-374. |
| [8] | Suhas Gorakh Karkute, Vishesh Kumar, Mohd Tasleem, Dwijesh Chandra Mishra, Krishna Kumar Chaturvedi, Anil Rai, Amitha Mithra Sevanthi, Kishor Gaikwad, Tilak Raj Sharma, Amolkumar U. Solanke. Genome-Wide Analysis of von Willebrand Factor A Gene Family in Rice for Its Role in Imparting Biotic Stress Resistance with Emphasis on Rice Blast Disease [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(4): 375-384. |
| [9] | Yang Ziyi, Xu Zhijian, Yang Qingwen, Qiao Weihua. Conservation and Utilization of Genetic Resources of Wild Rice in China [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(3): 216-224. |
| [10] | Nie Yuanyuan, Xia Hui, Ma Xiaosong, Lou Qiaojun, Liu Yi, Zhang Anling, Cheng Liang, Yan Longan, Luo Lijun. Dissecting Genetic Basis of Deep Rooting in Dongxiang Wild Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(3): 277-287. |
| [11] | Zhou Ying, Wan Tao, Yuan Bin, Lei Fang, Chen Meijuan, Wang Qiong, Huang Ping, Kou Shuyan, Qiu Wenxiu, Liu Li. Improving Rice Blast Resistance by Mining Broad-Spectrum Resistance Genes at Pik Locus [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(2): 133-142. |
| [12] | Junhua Lu, Xuemei Yang, Jinfeng Chen, Tingting Li, Zijin Hu, Ying Xie, Jinlu Li, Jiqun Zhao, Mei Pu, Hui Feng, Jing Fan, Yanyan Huang, Jiwei Zhang, Wenming Wang, Yan Li. Osa-miR439 Negatively Regulates Rice Immunity Against Magnaporthe oryzae [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(2): 156-165. |
| [13] | Yanchang Luo, Tingchen Ma, Teo Joanne, Zhixiang Luo, Zefu Li, Jianbo Yang, Zhongchao Yin. Marker-Assisted Breeding of Thermo-Sensitive Genic Male Sterile Line 1892S for Disease Resistance and Submergence Tolerance [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(1): 89-98. |
| [14] | Ning Xiao, Yunyu Wu, Aihong Li. Strategy for Use of Rice Blast Resistance Genes in Rice Molecular Breeding [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(4): 263-277. |
| [15] | B. ANGELES-SHIM Rosalyn, P. REYES Vincent, M. del VALLE Marilyn, S. LAPIS Ruby, SHIM Junghyun, SUNOHARA Hidehiko, K. JENA Kshirod, ASHIKARI Motoyuki, DOI Kazuyuki. Marker-Assisted Introgression of Quantitative Resistance Gene pi21 Confers Broad Spectrum Resistance to Rice Blast [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(2): 113-123. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||