
Rice Science ›› 2025, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 94-106.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2024.08.008
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jeberlin Prabina Bright1( ), Hemant S. Maheshwari2, Sugitha Thangappan3, Kahkashan Perveen4, Najat A. Bukhari4, Debasis Mitra5, Riyaz Sayyed6, Andrea Mastinu7(
), Hemant S. Maheshwari2, Sugitha Thangappan3, Kahkashan Perveen4, Najat A. Bukhari4, Debasis Mitra5, Riyaz Sayyed6, Andrea Mastinu7( )
)
Received:2024-03-06
Accepted:2024-08-23
Online:2025-01-28
Published:2025-03-25
Contact:
Jeberlin Prabina Bright, Andrea Mastinu
Jeberlin Prabina Bright, Hemant S. Maheshwari, Sugitha Thangappan, Kahkashan Perveen, Najat A. Bukhari, Debasis Mitra, Riyaz Sayyed, Andrea Mastinu. Biofilmed-PGPR: Next-Generation Bioinoculant for Plant Growth Promotion in Rice under Changing Climate[J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(1): 94-106.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Cyanobacterial isolate | Exopolysaccharide production (mg/mL) | Chlorophyll content (mg/g) | Nitrogenase activity (nmol/mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMP1 | 84.46 ± 0.57 b | 10.34 ± 0.13 de | 4.24 ± 0.03 b |
| AMP2 | 92.67 ± 0.04 a | 14.68 ± 0.02 a | 5.49 ± 0.03 a |
| ARP3 | 64.41 ± 1.04 g | 11.06 ± 0.06 c | 3.38 ± 0.28 c |
| ATP4 | 75.52 ± 0.44 d | 10.07 ± 0.04 e | 4.06 ± 0.03 b |
| NMP1 | 70.59 ± 1.14 ef | 9.34 ± 0.10 f | 3.50 ± 0.13 c |
| NRP2 | 80.36 ± 0.17 c | 10.71 ± 0.31 cd | 4.02 ± 0.01 b |
| NTP1 | 71.72 ± 0.74 e | 12.07 ± 0.04 b | 4.12 ± 0.02 b |
| NTP2 | 81.22 ± 0.89 c | 11.81 ± 0.16 b | 3.21 ± 0.12 cd |
| SMP1 | 69.78 ± 1.25 f | 9.52 ± 0.34 f | 2.87 ± 0.19 e |
| SMP2 | 65.88 ± 0.63 g | 10.34 ± 0.26 de | 3.02 ± 0.11 de |
| F value | 383.85 | 219.61 | 108.86 |
| P value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
Table 1. Exopolysaccharide production, chlorophyll content, and nitrogenase activity of selected cyanobacterial isolates.
| Cyanobacterial isolate | Exopolysaccharide production (mg/mL) | Chlorophyll content (mg/g) | Nitrogenase activity (nmol/mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMP1 | 84.46 ± 0.57 b | 10.34 ± 0.13 de | 4.24 ± 0.03 b |
| AMP2 | 92.67 ± 0.04 a | 14.68 ± 0.02 a | 5.49 ± 0.03 a |
| ARP3 | 64.41 ± 1.04 g | 11.06 ± 0.06 c | 3.38 ± 0.28 c |
| ATP4 | 75.52 ± 0.44 d | 10.07 ± 0.04 e | 4.06 ± 0.03 b |
| NMP1 | 70.59 ± 1.14 ef | 9.34 ± 0.10 f | 3.50 ± 0.13 c |
| NRP2 | 80.36 ± 0.17 c | 10.71 ± 0.31 cd | 4.02 ± 0.01 b |
| NTP1 | 71.72 ± 0.74 e | 12.07 ± 0.04 b | 4.12 ± 0.02 b |
| NTP2 | 81.22 ± 0.89 c | 11.81 ± 0.16 b | 3.21 ± 0.12 cd |
| SMP1 | 69.78 ± 1.25 f | 9.52 ± 0.34 f | 2.87 ± 0.19 e |
| SMP2 | 65.88 ± 0.63 g | 10.34 ± 0.26 de | 3.02 ± 0.11 de |
| F value | 383.85 | 219.61 | 108.86 |
| P value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
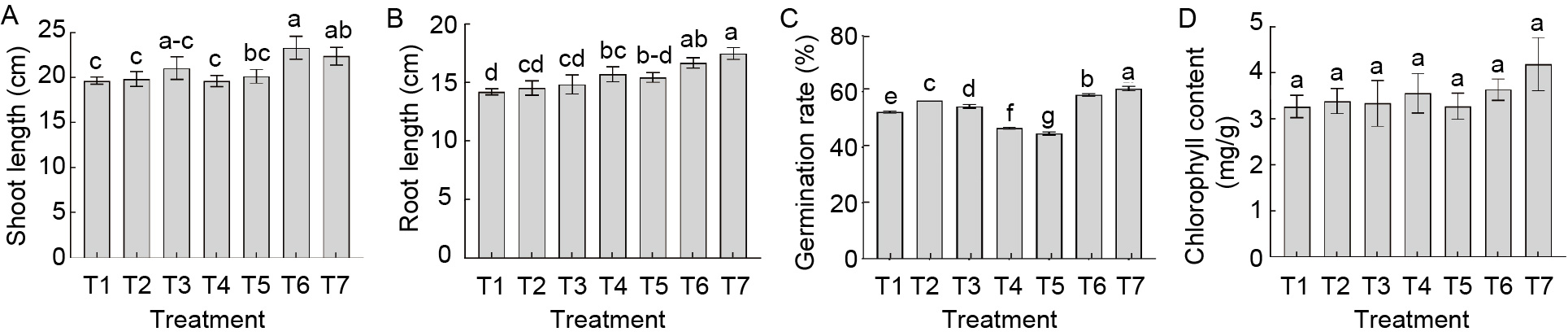
Fig. 1. Influence of cyanobacterial-bacterial biofilm (CBB) on rice seedlings. T1, Control Jensen’s plant nutrient solution (JPNS); T2, JPNS + seed treatment with CBB at 600 g/hm2; T3, JPNS + seed treatment with CBB at 800 g/hm2; T4, Seed treatment with CBB at 600 g/hm2; T5, Seed treatment with CBB at 800 g/hm2; T6, JPNS + CBB extract at 100 mL/kg; T7, JPNS + CBB extract at 200 mL/kg. Data are Mean ± SE (n = 3). Different letters on the bars represent significant differences at the level of 1% by the Duncan Multiple Range test.
| Treatment | Plant height (cm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tillering stage | Panicle initiation | Flowering stage | Heading stage | |
| T1 | 42.47 ± 1.66 a | 70.87 ± 5.27 a | 77.00 ± 3.45 b | 90.27 ± 0.59 b |
| T2 | 43.97 ± 1.63 a | 69.97 ± 2.86 a | 92.73 ± 2.44 a | 96.60 ± 1.24 b |
| T3 | 37.00 ± 1.82 a | 74.70 ± 3.91 a | 81.70 ± 0.92 ab | 96.87 ± 1.27 b |
| T4 | 44.80 ± 2.04 a | 77.73 ± 1.30 a | 79.41 ± 0.09 ab | 95.97 ± 1.52 b |
| T5 | 40.87 ± 1.86 a | 70.30 ± 1.62 a | 82.73 ± 2.19 ab | 93.03 ± 2.89 b |
| T6 | 41.40 ± 3.91 a | 73.10 ± 2.51 a | 84.60 ± 2.93 ab | 104.73 ± 1.12 a |
| Average | 41.75 ± 1.0 | 72.78 ± 1.29 | 83.03 ± 1.44 | 96.24 ± 1.21 |
| F value (df = 5, 12) | 1.448 | 0.894 | 5.535 | 9.224 |
| P value (< 0.01) | 0.277 | 0.515 | 0.007 | < 0.001 |
Table 2. Influence of cyanobacterial-bacterial biofilm (CBB) on rice plant height at different growth stages.
| Treatment | Plant height (cm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tillering stage | Panicle initiation | Flowering stage | Heading stage | |
| T1 | 42.47 ± 1.66 a | 70.87 ± 5.27 a | 77.00 ± 3.45 b | 90.27 ± 0.59 b |
| T2 | 43.97 ± 1.63 a | 69.97 ± 2.86 a | 92.73 ± 2.44 a | 96.60 ± 1.24 b |
| T3 | 37.00 ± 1.82 a | 74.70 ± 3.91 a | 81.70 ± 0.92 ab | 96.87 ± 1.27 b |
| T4 | 44.80 ± 2.04 a | 77.73 ± 1.30 a | 79.41 ± 0.09 ab | 95.97 ± 1.52 b |
| T5 | 40.87 ± 1.86 a | 70.30 ± 1.62 a | 82.73 ± 2.19 ab | 93.03 ± 2.89 b |
| T6 | 41.40 ± 3.91 a | 73.10 ± 2.51 a | 84.60 ± 2.93 ab | 104.73 ± 1.12 a |
| Average | 41.75 ± 1.0 | 72.78 ± 1.29 | 83.03 ± 1.44 | 96.24 ± 1.21 |
| F value (df = 5, 12) | 1.448 | 0.894 | 5.535 | 9.224 |
| P value (< 0.01) | 0.277 | 0.515 | 0.007 | < 0.001 |
| Treatment | Panicle length (cm) | 1000-grain weight (g) | No. of grains per panicle | Grain yield (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 22.97 ± 0.86 b | 23.97 ± 0.98 a | 154.33 ± 6.06 b | 6133.33 ± 60.09 c (122.67) |
| T2 | 27.03 ± 0.32 a | 24.10 ± 1.16 a | 175.67 ± 4.91 a | 6216.67 ± 33.33 bc (124.00) |
| T3 | 25.33 ± 0.84 ab | 21.43 ± 0.30 a | 165.33 ± 3.67 ab | 6383.33 ± 44.10 bc (127.67) |
| T4 | 27.10 ± 0.31 a | 25.10 ± 1.10 a | 177.00 ± 5.13 a | 6516.67 ± 109.29 ab (130.00) |
| T5 | 24.17 ± 0.92 ab | 24.20 ± 1.27 a | 168.67 ± 3.28 ab | 6250.00 ± 76.38 bc (125.00) |
| T6 | 23.77 ± 0.58 b | 25.30 ± 0.57 a | 182.67 ± 2.03 a | 6770.00 ± 90.74 a (135.40) |
| Average | 25.06 ± 0.45 | 24.02 ± 0.45 | 170.61 ± 2.69 | 6378.33 ± 57.78 (127.57) |
| F value (df = 5, 12) | 6.348 | 2.063 | 5.279 | 10.106 |
| P value (< 0.01) | 0.004 | 0.141 | 0.009 | < 0.001 |
Table 3. Influence of cyanobacterial-bacterial biofilm (CBB) on rice yield attributes and yield.
| Treatment | Panicle length (cm) | 1000-grain weight (g) | No. of grains per panicle | Grain yield (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 22.97 ± 0.86 b | 23.97 ± 0.98 a | 154.33 ± 6.06 b | 6133.33 ± 60.09 c (122.67) |
| T2 | 27.03 ± 0.32 a | 24.10 ± 1.16 a | 175.67 ± 4.91 a | 6216.67 ± 33.33 bc (124.00) |
| T3 | 25.33 ± 0.84 ab | 21.43 ± 0.30 a | 165.33 ± 3.67 ab | 6383.33 ± 44.10 bc (127.67) |
| T4 | 27.10 ± 0.31 a | 25.10 ± 1.10 a | 177.00 ± 5.13 a | 6516.67 ± 109.29 ab (130.00) |
| T5 | 24.17 ± 0.92 ab | 24.20 ± 1.27 a | 168.67 ± 3.28 ab | 6250.00 ± 76.38 bc (125.00) |
| T6 | 23.77 ± 0.58 b | 25.30 ± 0.57 a | 182.67 ± 2.03 a | 6770.00 ± 90.74 a (135.40) |
| Average | 25.06 ± 0.45 | 24.02 ± 0.45 | 170.61 ± 2.69 | 6378.33 ± 57.78 (127.57) |
| F value (df = 5, 12) | 6.348 | 2.063 | 5.279 | 10.106 |
| P value (< 0.01) | 0.004 | 0.141 | 0.009 | < 0.001 |
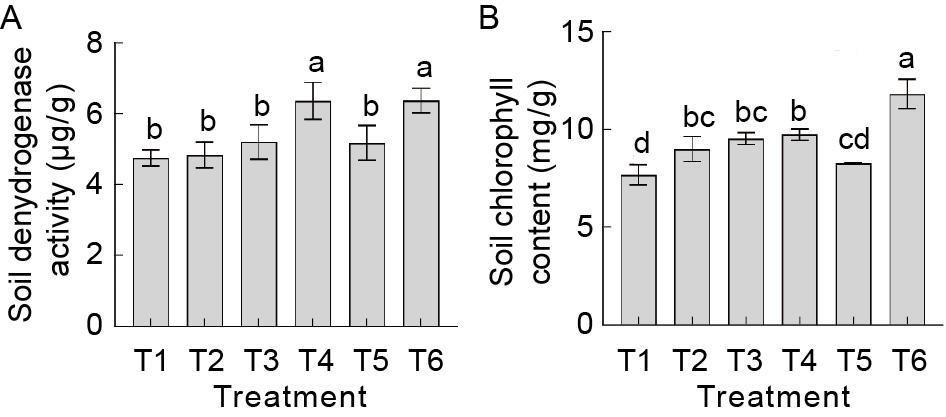
Fig. 3. Influence of cyanobacterial-bacterial biofilm (CBB) on soil dehydrogenase and chlorophyll contents. T1, 100% recommended dose of fertilizer (RDF); T2, 100% RDF + vermiculite conventional Anabaena sp. + phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) bacteria; T3, 75% RDF + vermiculite conventional Anabaena sp. + P and K bacteria; T4, 75% RDF + vermiculite CBB at 2 kg/hm2; T5, 100% RDF + vermiculite CBB at 2 kg/hm2; T6, 75% RDF + vermiculite CBB at 2 kg/hm2 + aqueous CBB at 5 mL/L at 15 and 30 d after transplanting. Data are Mean ± SE (n = 3). Different letters on bars represent significant differences at the level of 1% by the Duncan Multiple Range test.
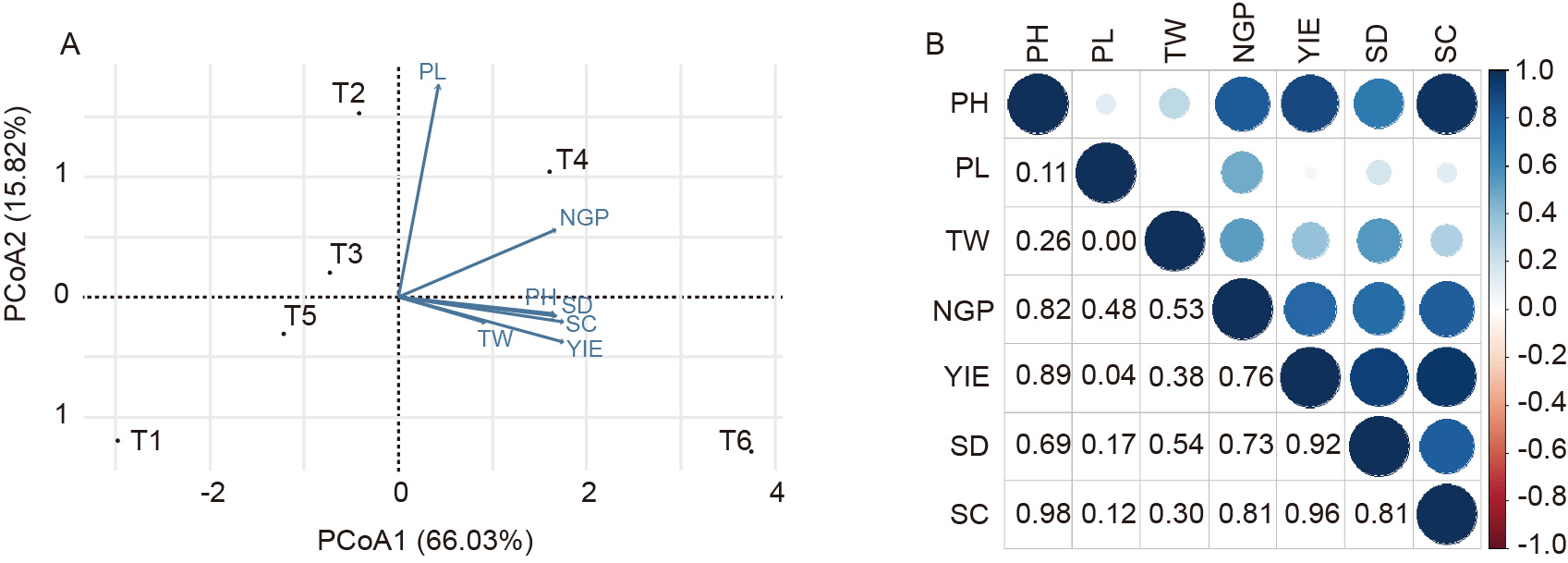
Fig. 4. Principal component analysis (A) and Pearson correlation analysis (B) of cyanobacterial-bacterial biofilm (CBB) formulations influence on rice.
| [1] | Abinandan S, Subashchandrabose S R, Venkateswarlu K, et al. 2019. Soil microalgae and cyanobacteria: The biotechnological potential in the maintenance of soil fertility and health. Crit Rev Biotechnol, 39(8): 981-998. |
| [2] | Adessi A, de Carvalho R C, de Philippis R, et al. 2018. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances improve water retention in dryland biological soil crusts. Soil Biol Biochem, 116: 67-69. |
| [3] | Ajijah N, Fiodor A, Pandey A K, et al. 2023. Plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) with biofilm-forming ability: A multifaceted agent for sustainable agriculture. Diversity, 15(1): 112. |
| [4] | Allen M M, Stanier R Y. 1968. Selective isolation of blue-green algae from water and soil. J Gen Microbiol, 51(2): 203-209. |
| [5] | Al-Manhel A J, Niamah A K. 2015. Effect of aqueous and alcoholic plant extracts on inhibition of some types of microbes and causing spoilage of food. J Nutr Food Sci, S5: 006. |
| [6] | Amaya-Gómez C V, Porcel M, Mesa-Garriga L, et al. 2020. A framework for the selection of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria based on bacterial competence mechanisms. Appl Environ Microbiol, 86(14): e00760-e00720. |
| [7] | Anand N. 1990. Handbook of blue-green algae of rice fields of South India. Dehradun, India: Bishen Singh Mahendra Pal Singh. |
| [8] | Anjana K, Kiran B, Mona S, et al. 2012. Biological photohydrogen production by cyanobacteria: Future prospects as a fuel. J Environ Res Devel, 6: 779-783. |
| [9] | Armstrong L, Vaz M G M V, Genuário D B, et al. 2019. Volatile compounds produced by cyanobacteria isolated from mangrove environment. Curr Microbiol, 76(5): 575-582. |
| [10] | Arora N K, Fatima T, Mishra I, et al. 2020. Microbe-based inoculants: Role in next green revolution. In: Shukla V, Kumar N. Environmental Concerns and Sustainable Development. Singapore: Springer: 191-246. |
| [11] | Bakhshandeh E, Pirdashti H, Shahsavarpour Lendeh K, et al. 2020. Effects of plant growth promoting microorganisms inoculums on mineral nutrition, growth and productivity of rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Plant Nutr, 43(11): 1643-1660. |
| [12] | Bidyarani N, Prasanna R, Babu S, et al. 2016. Enhancement of plant growth and yields in Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) through novel cyanobacterial and biofilmed inoculants. Microbiol Res, 188/189: 97-105. |
| [13] | Bolton J R. 1996. Solar photoproduction of hydrogen: A review. Sol Energy, 57(1): 37-50. |
| [14] | Budamagunta V, Shameem N, Irusappan S, et al. 2023. Nanovesicle and extracellular polymeric substance synthesis from the remediation of heavy metal ions from soil. Environ Res, 219: 114997. |
| [15] | Bystrianský L, Hujslová M, Hršelová H, et al. 2019. Observations on two microbial life strategies in soil: Planktonic and biofilm- forming microorganisms are separable. Soil Biol Biochem, 136: 107535. |
| [16] | Carezzano M E, Alvarez Strazzi F B, Pérez V, et al. 2023. Exopolysaccharides synthesized by rhizospheric bacteria: A review focused on their roles in protecting plants against stress. Appl Microbiol, 3(4): 1249-1261. |
| [17] | Casida L E J R, Klein D A, Santoro T. 1964. Soil dehydrogenase activity. Soil Sci, 98(6): 371-376. |
| [18] | Chaudhary T, Dixit M, Gera R, et al. 2020. Techniques for improving formulations of bioinoculants. 3 Biotech, 10(5): 199. |
| [19] | das Astapati A, Nath S. 2023. The complex interplay between plant-microbe and virus interactions in sustainable agriculture: Harnessing phytomicrobiomes for enhanced soil health, designer plants, resource use efficiency, and food security. Crop Des, 2(1): 100028. |
| [20] | Das D, Ullah H, Tisarum R, et al. 2023. Morpho-physiological responses of tropical rice to potassium and silicon fertilization under water-deficit stress. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr, 23(1): 220-237. |
| [21] | Gayathri M, Shunmugam S, Thajuddin N, et al. 2017. Phyto- hormones and free volatile fatty acids from cyanobacterial biomass wet extract (BWE) elicit plant growth promotion. Algal Res, 26: 56-64. |
| [22] | Gosselin K M, Nelson R K, Spivak A C, et al. 2021. Production of two highly abundant 2-methyl-branched fatty acids by blooms of the globally significant marine cyanobacteria Trichodesmium erythraeum. ACS Omega, 6(35): 22803-22810. |
| [23] | Gulia U, Shukla J, Nishanth S, et al. 2022. Fortifying nursery soil-less media with cyanobacteria for enhancing the growth of tomato. S Afr J Bot, 146: 564-572. |
| [24] | Hashtroudi M S, Ghassempour A, Riahi H, et al. 2013. Endogenous auxins in plant growth-promoting Cyanobacteria: Anabaena vaginicola and Nostoc calcicola. J Appl Phycol, 25(2): 379-386. |
| [25] | Ilyas N, Mumtaz K, Akhtar N, et al. 2020. Exo-polysaccharides producing bacteria for the amelioration of drought stress in wheat. Sustainability, 12(21): 8876. |
| [26] | Kitwetch B, Rangseekaew P, Chromkaew Y, et al. 2023. Employing a plant probiotic actinomycete for growth promotion of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. var. longifolia) cultivated in a hydroponic system under nutrient limitation. Plants, 12(22): 3793. |
| [27] | Kokila V, Prasanna R, Kumar A, et al. 2022. Cyanobacterial inoculation in elevated CO2 environment stimulates soil C enrichment and plant growth of tomato. Environ Technol Innov, 26: 102234. |
| [28] | Kour D, Rana K L, Kaur T, et al. 2020. Microbial biofilms: Functional annotation and potential applications in agriculture and allied sectors. In: Yadav M K, Singh B P. New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering: Microbial Biofilms. Amsterdam: Elsevier: 283-301. |
| [29] | Limoli D H, Jones C J, Wozniak D J. 2015. Bacterial extracellular polysaccharides in biofilm formation and function. Microbiol Spectr, 3(3): 10.1128/microbiolspec.MB-0011-2014. |
| [30] | MacKinney G. 1941. Absorption of light by chlorophyll solutions. J Biol Chem, 140(2): 315-322. |
| [31] | Mahmud K, Missaoui A, Lee K, et al. 2021. Rhizosphere microbiome manipulation for sustainable crop production. Curr Plant Biol, 27: 100210. |
| [32] | Manjunath M, Kanchan A, Ranjan K, et al. 2016. Beneficial cyanobacteria and eubacteria synergistically enhance bioavailability of soil nutrients and yield of okra. Heliyon, 2(2): e00066. |
| [33] | Meena A, Rao K S. 2021. Assessment of soil microbial and enzyme activity in the rhizosphere zone under different land use/cover of a semiarid region, India. Ecol Process, 10(1): 16. |
| [34] | Meena S K, Rakshit A, Meena V S. 2016. Effect of seed bio-priming and N doses under varied soil type on nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under greenhouse conditions. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol, 6: 68-75. |
| [35] | Montoya J P, Voss M, Kahler P, et al. 1996. A simple, high- precision, high-sensitivity tracer assay for N(inf2) fixation. Appl Environ Microbiol, 62(3): 986-993. |
| [36] | Morcillo R J L, Manzanera M. 2021. The effects of plant-associated bacterial exopolysaccharides on plant abiotic stress tolerance. Metabolites, 11(6): 337. |
| [37] | Múnera-Porras L M, García-Londoño S, Ríos-Osorio L A. 2020. Action mechanisms of plant growth promoting cyanobacteria in crops in situ: A systematic review of literature. Int J Agron, 2020: 2690410. |
| [38] | Nayak S, Prasanna R, Pabby A, et al. 2004. Effect of urea, blue green algae and Azolla on nitrogen fixation and chlorophyll accumulation in soil under rice. Biol Fertil Soils, 40(1): 67-72. |
| [39] | Nowruzi B, Bouaïcha N, Metcalf J S, et al. 2021. Plant- cyanobacteria interactions: Beneficial and harmful effects of cyanobacterial bioactive compounds on soil-plant systems and subsequent risk to animal and human health. Phytochemistry, 192: 112959. |
| [40] | Nozari R M, Ortolan F, Astarita L V, et al. 2021. Streptomyces spp. enhance vegetative growth of maize plants under saline stress. Braz J Microbiol, 52(3): 1371-1383. |
| [41] | Olanrewaju O S, Babalola O O. 2022. The rhizosphere microbial complex in plant health: A review of interaction dynamics. J Integr Agric, 21(8): 2168-2182. |
| [42] | Osman M E H, El-Sheekh M M, El-Naggar A H, et al. 2010. Effect of two species of cyanobacteria as biofertilizers on some metabolic activities, growth, and yield of pea plant. Biol Fertil Soils, 46(8): 861-875. |
| [43] | Park Y S, Dutta S, Ann M, et al. 2015. Promotion of plant growth by Pseudomonas fluorescens strain SS101 via novel volatile organic compounds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 461(2): 361-365. |
| [44] | Patel A, Mishra S, Pawar R, et al. 2005. Purification and characterization of C-Phycocyanin from cyanobacterial species of marine and freshwater habitat. Protein Expr Purif, 40(2): 248-255. |
| [45] | Pathan S I, Ceccherini M T, Sunseri F, et al. 2020. Rhizosphere as hotspot for plant-soil-microbe interaction. In: Datta R, Meena R, Pathan S, Ceccherini M. Carbon and Nitrogen Cycling in Soil. Singapore: Springer: 17-43. |
| [46] | Poveda J. 2021. Cyanobacteria in plant health: Biological strategy against abiotic and biotic stresses. Crop Prot, 141: 105450. |
| [47] | Prasanna R, Jaiswal P, Nayak S, et al. 2009. Cyanobacterial diversity in the rhizosphere of rice and its ecological significance. Indian J Microbiol, 49(1): 89-97. |
| [48] | Prasanna R, Joshi M, Rana A, et al. 2012. Influence of co- inoculation of bacteria-cyanobacteria on crop yield and C-N sequestration in soil under rice crop. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 28(3): 1223-1235. |
| [49] | Prasanna R, Triveni S, Bidyarani N, et al. 2014. Evaluating the efficacy of cyanobacterial formulations and biofilmed inoculants for leguminous crops. Arch Agron Soil Sci, 60(3): 349-366. |
| [50] | Prasanna R, Renuka N, Nain L, et al. 2021. Natural and constructed cyanobacteria-based consortia for enhancing crop growth and soil fertility. In: Seneviratne G, Zavahir J S. Role of Microbial Communities for Sustainability. Singapore: Springer: 333-362. |
| [51] | Rai A N, Singh A K, Syiem M B. 2019. Plant growth-promoting abilities in cyanobacteria. In: Mishra A K, Tiwari D N, Rai A N. Cyanobacteria. Amsterdam: Elsevier: 459-476. |
| [52] | Raja D, Sivakumar R. 2010. Studies on the growth of Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina) as influenced by inorganic (Zarrouk’s) and organic medium. J Pure Appl Microbiol, 4(2): 907-910. |
| [53] | Rana K L, Kour D, Yadav A N, et al. 2020. Agriculturally important microbial biofilms:Biodiversity, ecological significances, and biotechnological applications. In: Singh H B, Vaishnav A. New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering: Microbial Biofilms. Amsterdam: Elsevier: 221-265. |
| [54] | Rather M A, Gupta K, Mandal M. 2021. Microbial biofilm: Formation, architecture, antibiotic resistance, and control strategies. Braz J Microbiol, 52(4): 1701-1718. |
| [55] | Rathnathilaka T, Premarathna M, Madawala S, et al. 2023. Biofilm biofertilizer application rapidly increases soil quality and grain yield in large scale conventional rice cultivation: A case study. J Plant Nutr, 46(7): 1220-1230. |
| [56] | Salama A. 2015. Response of rice plants to inoculation with indigenous strains of cyanobacterial along with different levels of inorganic N-fertilizers. Adv Biochem Biotechnol, 1(1): 1-14. |
| [57] | Sammauria R, Kumawat S, Kumawat P, et al. 2020. Microbial inoculants: Potential tool for sustainability of agricultural production systems. Arch Microbiol, 202(4): 677-693. |
| [58] | Seneviratne G, Jayasinghearachchi H S. 2005. A rhizobial biofilm with nitrogenase activity alters nutrient availability in a soil. Soil Biol Biochem, 37(10): 1975-1978. |
| [59] | Shahane A A, Shivay Y S, Prasanna R, et al. 2019. Nitrogen nutrition and use efficiency in rice as influenced by crop establishment methods, cyanobacterial and phosphate solubilizing bacterial consortia and zinc fertilization. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal, 50(12): 1487-1499. |
| [60] | Sheikh T, Hamid B, Baba Z, et al. 2022. Extracellular polymeric substances in psychrophilic cyanobacteria: A potential bioflocculant and carbon sink to mitigate cold stress. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol, 42: 102375. |
| [61] | Shivay Y S, Prasanna R, Mandi S, et al. 2022. Cyanobacterial inoculation enhances nutrient use efficiency and grain quality of basmati rice in the system of rice intensification. ACS Agric Sci Technol, 2(4): 742-753. |
| [62] | Supraja K V, Behera B, Balasubramanian P. 2020. Efficacy of microalgal extracts as biostimulants through seed treatment and foliar spray for tomato cultivation. Ind Crops Prod, 151: 112453. |
| [63] | Sutherland I W, Wilkinson J F. 1971. Chapter IV chemical extraction methods of microbial cells. In: Norris J R, Ribbons D W. Methods in Microbiology. State of Utah, USA: Academic Press: 345-383. |
| [64] | Swarnalakshmi K, Prasanna R, Kumar A, et al. 2013. Evaluating the influence of novel cyanobacterial biofilmed biofertilizers on soil fertility and plant nutrition in wheat. Eur J Soil Biol, 55: 107-116. |
| [65] | Terekhova E A, Stepicheva N A, Pshenichnikova A B, et al. 2010. Stearic acid methyl ester: A new extracellular metabolite of the obligate methylotrophic bacterium Methylophilus quaylei. Appl Biochem Microbiol, 46(2): 166-172. |
| [66] | Toribio A J, Suárez-Estrella F, Jurado M M, et al. 2022. Design and validation of cyanobacteria-rhizobacteria consortia for tomato seedlings growth promotion. Sci Rep, 12(1): 13150. |
| [67] | Triveni S, Prasanna R, Saxena A K. 2012. Optimization of conditions for in vitro development of Trichoderma viride-based biofilms as potential inoculants. Folia Microbiol, 57(5): 431-437. |
| [68] | Vonshak A, Richmond A. 1988. Mass production of the blue-green alga Spirulina: An overview. Biomass, 15(4): 233-247. |
| [69] | Vu B, Chen M, Crawford R J, et al. 2009. Bacterial extracellular polysaccharides involved in biofilm formation. Molecules, 14(7): 2535-2554. |
| [70] | Wang S C, Zhao Y T, Breslawec A P, et al. 2023. Strategy to combat biofilms: A focus on biofilm dispersal enzymes. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes, 9(1): 63. |
| [71] | Wang T T, Xu J X, Chen J, et al. 2024. Progress in microbial fertilizer regulation of crop growth and soil remediation research. Plants, 13(3): 346. |
| [72] | Zahra Z, Choo D H, Lee H, et al. 2020. Cyanobacteria: Review of current potentials and applications. Environments, 7(2): 13. |
| [73] | Zakeel M C M, Safeena M I S. 2019. Biofilmed biofertilizer for sustainable agriculture. In: Ansari R, Mahmood I. Plant Health under Biotic Stress. Springer, Singapore: 65-82. |
| [1] | Wang Mingyue, Zhao Weibo, Feng Xiaoya, Chen Yi, Li Junhao, Fu Jinmei, Yan Yingchun, Chu Zhaohui, Huang Wenchao. Disruption of Energy Metabolism and Reactive Oxygen Species Homeostasis in Honglian Type-Cytoplasmic Male Sterility (HL-CMS) Rice Pollen [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(1): 81-93. |
| [2] | Intan Farahanah, Shariza Sahudin, Hannis Fadzillah Mohsin, Siti Alwani Ariffin, Liyana Dhamirah Aminuddin. Understanding Investigational Perspective of Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(1): 15-31. |
| [3] | Wang Haoran, Chen Guoqing, Feng Guozhong. Expanding Viral Diversity in Rice Fields by Next-Generation Sequencing [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(1): 44-51. |
| [4] | Surangkana Chimthai, Sulaiman Cheabu, Wanchana Aesomnuk, Siriphat Ruengphayak, Siwaret Arikit, Apichart Vanavichit, Chanate Malumpong. Breeding for Heat Tolerant Aromatic Rice Varieties and Identification of Novel QTL Regions Associated with Heat Tolerance During Reproductive Phase by QTL-Seq [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(1): 67-80. |
| [5] | Durga Prasad Mullangie, Kalaimagal Thiyagarajan, Manonmani Swaminathan, Jagadeesan Ramalingam, Sritharan Natarajan, Senthilkumar Govindan. Breeding Resilience: Exploring Lodging Resistance Mechanisms in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(6): 659-672. |
| [6] | Fu Yiwei, Wu Jiayelu, Wu Mingming, Ye Shenghai, Zhai Rongrong, Ye Jing, Zhu Guofu, Yu Faming, Lu Yanting, Zhang Xiaoming. Progress on Molecular Mechanism of Heat Tolerance in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(6): 673-687. |
| [7] | Yang Yigang, Xu Ya’nan, Bai Yeran, Zhang Yuanpei, Han Wei, Makoto Saito, Lü Guohua, Song Jiqing, Bai Wenbo. Mixed-Oligosaccharides Promote Seedling Growth of Direct-Seeded Rice under Salt and Alkaline Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(6): 712-724. |
| [8] | Ren Jian, Hu Kelin, Feng Puyu, William D. Batchelor, Liu Haitao, Lü Shihua. Simulating Responses of Rice Yield and Nitrogen Fates to Ground Cover Rice Production System under Different Types of Precipitation Years [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(6): 725-739. |
| [9] | Tao Yi, Xiao Deshun, Ye Chang, Liu Kancheng, Tang Xinxin, Ma Hengyu, Chu Guang, Yu Kai, Xu Chunmei, Wang Danying. Compound Microbial Agent Improves Soil Redox Status to Reduce Methane Emissions from Paddy Fields [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(6): 740-750. |
| [10] | Sitthikorn Bodeerath, Jeeraporn Veeradittakit, Sansanee Jamjod, Chanakan Prom-U-Thai. Applying Boron Fertilizer at Different Growth Stages Promotes Boron Uptake and Productivity in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(6): 751-760. |
| [11] | Kunhikrishnan Hemalatha Dhanyalakshmi, Reshma Mohan, Sasmita Behera, Uday Chand Jha, Debashis Moharana, Ahalya Behera, Sini Thomas, Preman Rejitha Soumya, Rameswar Prasad Sah, Radha Beena. Next Generation Nutrition: Genomic and Molecular Breeding Innovations for Iron and Zinc Biofortification in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(5): 526-544. |
| [12] | Zhang Youliang, Zhu Kaican, Tang Yongqi, Feng Shaoyuan. Rice Cultivation under Film Mulching Can Improve Soil Environment and Be Beneficial for Rice Production in China [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(5): 545-555. |
| [13] | Chirag Maheshwari, Nitin Kumar Garg, Archana Singh, Aruna Tyagi. Ameliorative Effects of Paclobutrazol via Physio-Biochemical and Molecular Manifestation in Rice under Water Deficit Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(5): 603-616. |
| [14] | Hong Weiyuan, Li Ziqiu, Feng Xiangqian, Qin Jinhua, Wang Aidong, Jin Shichao, Wang Danying, Chen Song. Estimating Key Phenological Dates of Multiple Rice Accessions Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-Based Plant Height Dynamics for Breeding [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(5): 617-628. |
| [15] | Liyana Sara, Sompop Saeheng, Panupong Puttarak, Lompong Klinnawee. Changes in Metabolites and Allelopathic Effects of Non-Pigmented and Black-Pigmented Lowland Indica Rice Varieties in Phosphorus Deficiency [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(4): 434-448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||