
Rice Science ›› 2024, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (6): 673-687.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2024.07.001
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Fu Yiwei1,2, Wu Jiayelu1,2, Wu Mingming2, Ye Shenghai2, Zhai Rongrong2, Ye Jing2, Zhu Guofu2, Yu Faming2, Lu Yanting2, Zhang Xiaoming2( )
)
Received:2024-05-08
Accepted:2024-07-26
Online:2024-11-28
Published:2024-12-10
Contact:
Zhang Xiaoming (zhangxiaoming@zaas.ac.cn)
Fu Yiwei, Wu Jiayelu, Wu Mingming, Ye Shenghai, Zhai Rongrong, Ye Jing, Zhu Guofu, Yu Faming, Lu Yanting, Zhang Xiaoming. Progress on Molecular Mechanism of Heat Tolerance in Rice[J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(6): 673-687.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Gene | Gene characteristics | Regulation | Function period | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsGSK1 | Glycogen synthase kinase | + | Flowering | Koh et al, |
| OsMYB55 | MYB transcription factor | + | Seedling | El-Kereamy et al, |
| OsHSP1 | Heat-stimulated protein | + | Seedling | Moon et al, |
| SNAC3 | NAC transcription factor | + | Seedling | Fang et al, |
| TT1 | α2 subunit of the 26s proteasome | + | Seedling, flowering, filling | Li et al, |
| OsANN1 | Rice membrane-binding protein | + | Seedling | Qiao et al, |
| ER/ERECTA | Receptor kinase | + | Seedling, flowering | Shen et al, |
| OsHTAS | Ubiquitin ligase | + | Seedling | Liu et al, |
| OsTOGR1 | DEAD-box RNA helicase | + | Seedling | Wang et al, |
| OsMDHAR4 | Monodehydroascorbate reductase | − | Seedling | Liu et al, |
| OsRGB1 | Heterotrimeric G protein β subunit | + | Germination, seedling | Biswas et al, |
| OsRab7 | Small G protein | + | Seedling | El-Esawi and Alayafi, |
| OsHIRP1 | E3 ligase | + | Seedling | Kim et al, |
| OsFBN1 | Ciliary protein | + | Seedling, flowering, fertilization | Li et al, |
| OsUBP21 | Ubiquitin-specific protease | − | Seedling | Zhou et al, |
| OsCNGC14 | Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel protein | + | Seedling | Cui et al, |
| OsNSUN2 | m5C methyltransferase | + | Seedling | Tang et al, |
| SLG1 | Cytosolic tRNA 2-thiolated protein 2 | + | Seedling, flowering | Xu Y F et al, |
| HTS1 | β-Ketoacyl carrier protein reductase | + | Seedling | Chen F et al, |
| HTH5 | Pyridoxal phosphate-binding protein | + | Seedling | Cao et al, |
| TT2 | Heterotrimeric G protein γ subunit | − | Seedling, flowering | Kan et al, |
| TT3.1 | E3 ubiquitin ligase protein | + | Seedling | Zhang et al, |
| TT3.2 | Chloroplast precursor protein | − | Seedling | Zhang et al, |
| OsNCED1 | 9-cis-Epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase | + | Flowering | Zhou et al, |
| OsSGS3 | Gene silencing repressor | + | Seedling | Gu et al, |
| OsGRP3/OsGRP162 | RNA-binding protein | + | Seedling, booting, fertilization | Yang et al, |
Table 1. Functional genes related to heat tolerance in rice.
| Gene | Gene characteristics | Regulation | Function period | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsGSK1 | Glycogen synthase kinase | + | Flowering | Koh et al, |
| OsMYB55 | MYB transcription factor | + | Seedling | El-Kereamy et al, |
| OsHSP1 | Heat-stimulated protein | + | Seedling | Moon et al, |
| SNAC3 | NAC transcription factor | + | Seedling | Fang et al, |
| TT1 | α2 subunit of the 26s proteasome | + | Seedling, flowering, filling | Li et al, |
| OsANN1 | Rice membrane-binding protein | + | Seedling | Qiao et al, |
| ER/ERECTA | Receptor kinase | + | Seedling, flowering | Shen et al, |
| OsHTAS | Ubiquitin ligase | + | Seedling | Liu et al, |
| OsTOGR1 | DEAD-box RNA helicase | + | Seedling | Wang et al, |
| OsMDHAR4 | Monodehydroascorbate reductase | − | Seedling | Liu et al, |
| OsRGB1 | Heterotrimeric G protein β subunit | + | Germination, seedling | Biswas et al, |
| OsRab7 | Small G protein | + | Seedling | El-Esawi and Alayafi, |
| OsHIRP1 | E3 ligase | + | Seedling | Kim et al, |
| OsFBN1 | Ciliary protein | + | Seedling, flowering, fertilization | Li et al, |
| OsUBP21 | Ubiquitin-specific protease | − | Seedling | Zhou et al, |
| OsCNGC14 | Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel protein | + | Seedling | Cui et al, |
| OsNSUN2 | m5C methyltransferase | + | Seedling | Tang et al, |
| SLG1 | Cytosolic tRNA 2-thiolated protein 2 | + | Seedling, flowering | Xu Y F et al, |
| HTS1 | β-Ketoacyl carrier protein reductase | + | Seedling | Chen F et al, |
| HTH5 | Pyridoxal phosphate-binding protein | + | Seedling | Cao et al, |
| TT2 | Heterotrimeric G protein γ subunit | − | Seedling, flowering | Kan et al, |
| TT3.1 | E3 ubiquitin ligase protein | + | Seedling | Zhang et al, |
| TT3.2 | Chloroplast precursor protein | − | Seedling | Zhang et al, |
| OsNCED1 | 9-cis-Epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase | + | Flowering | Zhou et al, |
| OsSGS3 | Gene silencing repressor | + | Seedling | Gu et al, |
| OsGRP3/OsGRP162 | RNA-binding protein | + | Seedling, booting, fertilization | Yang et al, |
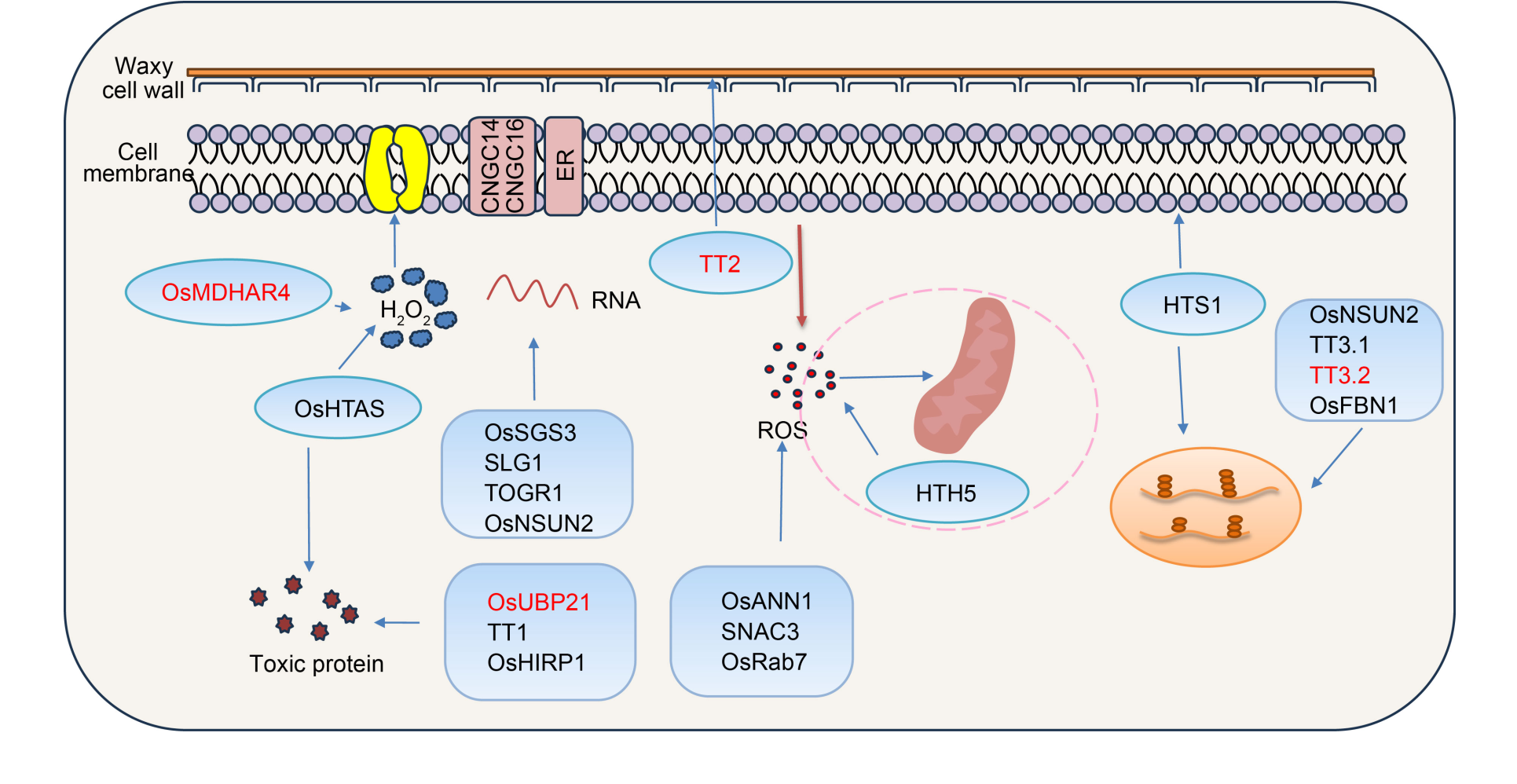
Fig. 2. Mechanism of action of relevant rice heat tolerance genes. Genes in red font negatively regulate heat tolerance in rice. ER, OsCNGC14, and OsCNGC16 enhance heat tolerance through signal-transduction pathways. TT2 enhances heat tolerance through wax synthesis. HTS1 enhances heat tolerance by regulating fatty acid biosynthesis and stress signal transduction. HTS1, TT3.1, TT3.2, OsFBN1, and OsNSUN2 contribute to heat tolerance by maintaining chloroplast stability. OsANN1, SNAC3, and OsRab7 maintain reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis by promoting the expression of ROS scavengers. HTH5 attenuates the impairment of mitochondrial metabolism caused by heat stress through regulating ROS homeostasis. TT1 and OsHIRP1 enhance heat tolerance by regulating protein form. OsUBP21 negatively regulates heat tolerance in rice by mediating protein deubiquitination. OsHTAS and OsMDHAR4 regulate heat tolerance by modulating H2O2-induced stomatal state. OsNSUN2, OsSGS3a, TOGR1, and SLG1 promote heat tolerance by enhancing the modification of the mRNAs of the detoxification system, modulating trans-acting small interfering RNAs targeting auxin response factors, promoting RNA deconjugating enzyme activity, and maintaining normal sulphated tRNA levels, respectively.
| [1] | Ashraf H, Ghouri F, Baloch F S, Nadeem M A, Fu X, Shahid M Q. 2024. Hybrid rice production: A worldwide review of floral traits and breeding technology, with special emphasis on China. Plants, 13(5): 578. |
| [2] | Bahuguna R N, Jha J, Pal M, Shah D, Lawas L M F, Khetarpal S, Jagadish K S V. 2015. Physiological and biochemical characterization of NERICA-L-44: A novel source of heat tolerance at the vegetative and reproductive stages in rice. Physiol Plant, 154(4): 543-559. |
| [3] | Battisti D S, Naylor R L. 2009. Historical warnings of future food insecurity with unprecedented seasonal heat. Science, 323: 240-244. |
| [4] | Bheemanahalli R, Sathishraj R, Manoharan M, Sumanth H N, Muthurajan R, Ishimaru T, Krishna J S V. 2017. Is early morning flowering an effective trait to minimize heat stress damage during flowering in rice? Field Crops Res, 203: 238-242. |
| [5] | Biswas S, Islam M N, Sarker S, Tuteja N, Seraj Z I. 2019. Overexpression of heterotrimeric G protein beta subunit gene (OsRGB1) confers both heat and salinity stress tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol Biochem, 144: 334-344. |
| [6] | Cai Y X, Liu C X, Wang W, Zhang H X, Zhang Z J, Yang J, Tang H Z. 2011. Dynamic differences of the RVA profile and gel consistency in two rice varieties with similar apparent amylose content during grain filling. Sci Agric Sin, 44(12): 2439-2445. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Cao Z B, Xie H W, Nie Y Y, Mao L H, Li Y H, Cai Y H. 2015. Mapping a QTL (qHTH5) for heat tolerance at the heading stage on rice chromosome 5 and its genetic effect analysis. Chin J Rice Sci, 29: 119-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Cao Z B, Tang X Y, Xiao W J, Mao L H, Nie Y Y, Li Y H, Xie H W, Cai Y H, Yuan L F. 2019. Identification and genetic effect analysis of QTL (qHTH10) for heat tolerance at heading and flowering stage of rice. Mol Plant Breed, 17(7): 2223-2230. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Cao Z B, Li Y, Tang H W, Zeng B H, Tang X Y, Long Q Z, Wu X F, Cai Y H, Yuan L F, Wan J L. 2020. Fine mapping of the qHTB1-1 QTL, which confers heat tolerance at the booting stage, using an Oryza rufipogon Griff. introgression line. Theor Appl Genet, 133(4): 1161-1175. |
| [10] | Cao Z B, Tang H W, Cai Y H, Zeng B H, Zhao J L, Tang X Y, Lu M, Wang H M, Zhu X J, Wu X F, Yuan L F, Wan J L. 2022. Natural variation of HTH5 from wild rice, Oryza rufipogon Griff., is involved in conferring high-temperature tolerance at the heading stage. Plant Biotechnol J, 20(8): 1591-1605. |
| [11] | Chandrakala J U, Chaturvedi A K, Ramesh K V, Rai P, Khetarpal S, Pal M. 2013. Acclimation response of signalling molecules for high temperature stress on photosynthetic characteristics in rice genotypes. Indian J Plant Physiol, 18(2): 142-150. |
| [12] | Chen F, Dong G J, Wang F, Shi Y Q, Zhu J Y, Zhang Y L, Ruan B P, Wu Y P, Feng X, Zhao C C, Yong M T, Holford P, Zeng D L, Qian Q, Wu L M, Chen Z H, Yu Y C. 2021. A β-ketoacyl carrier protein reductase confers heat tolerance via the regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis and stress signaling in rice. New Phytol, 232(2): 655-672. |
| [13] | Chen J, Xu Y D, Fei K Q, Wang R, He J, Fu L D, Shao S M, Li K, Zhu K Y, Zhang W Y, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. 2020. Physiological mechanism underlying the effect of high temperature during anthesis on spikelet-opening of photo-thermo-sensitive genic male sterile rice lines. Sci Rep, 10(1): 2210. |
| [14] | Chen J H, Chen S T, He N Y, Wang Q L, Zhao Y, Gao W, Guo F Q. 2020. Nuclear-encoded synthesis of the D1 subunit of photosystem II increases photosynthetic efficiency and crop yield. Nat Plants, 6(5): 570-580. |
| [15] | Chen L, Wang Q, Tang M Y, Zhang X L, Pan Y H, Yang X H, Gao G Q, Lv R H, Tao W, Jiang L G, Liang T F. 2021. QTL mapping and identification of candidate genes for heat tolerance at the flowering stage in rice. Front Genet, 11: 621871. |
| [16] | Cong S M, Yu E W, Cai Q, Xu Y, Zhou Y P, Xing Z P, Guo B W, Hu Y J, Zhang H C. 2023. Research progress on effects of temperature and light stress on yield and quality and starch physicochemical properties of rice at fruiting stage. Jiangsu Agric Sci, 51(10): 20-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Crossa J, Pérez P, Hickey J, Burgueño J, Ornella L, Cerón-Rojas J, Zhang X, Dreisigacker S, Babu R, Li Y, Bonnett D, Mathews K. 2014. Genomic prediction in CIMMYT maize and wheat breeding programs. Heredity, 112(1): 48-60. |
| [18] | Crossa J, Pérez-Rodríguez P, Cuevas J, Montesinos-López O, Jarquín D, de Los Campos G, Burgueño J, González-Camacho J M, Pérez-Elizalde S, Beyene Y, Dreisigacker S, Singh R, Zhang X C, Gowda M, Roorkiwal M, Rutkoski J, Varshney R K. 2017. Genomic selection in plant breeding: Methods, models, and perspectives. Trends Plant Sci, 22(11): 961-975. |
| [19] | Cui Y M, Lu S, Li Z, Cheng J W, Hu P, Zhu T Q, Wang X, Jin M, Wang X X, Li L Q, Huang S Y, Zou B H, Hua J. 2020. CYCLIC NUCLEOTIDE-GATED ION CHANNELs 14 and 16 promote tolerance to heat and chilling in rice. Plant Physiol, 183(4): 1794-1808. |
| [20] | Ding S B, Zhu B Y, Wu D Y, Zhang L. 2004. Effect of temperature and light on senescence of flag leaf and grain-filling after rice heading. J South China Normal Univ: Nat Sci, 1: 117-121. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Ding Y L, Shi Y T, Yang S H. 2020. Molecular regulation of plant responses to environmental temperatures. Mol Plant, 13(4): 544-564. |
| [22] | El-Esawi M A, Alayafi A A. 2019. Overexpression of rice Rab7 gene improves drought and heat tolerance and increases grain yield in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genes, 10(1): 56. |
| [23] | El-Kereamy A, Bi Y M, Ranathunge K, Beatty P H, Good A G, Rothstein S J. 2012. The rice R2R3-MYB transcription factor OsMYB55 is involved in the tolerance to high temperature and modulates amino acid metabolism. PLoS One, 7(12): e52030. |
| [24] | Fahad S, Hussain S, Saud S, Hassan S, Ihsan Z, Shah A N, Wu C, Yousaf M, Nasim W, Alharby H, Alghabari F, Huang J L. 2016a. Exogenously applied plant growth regulators enhance the morpho- physiological growth and yield of rice under high temperature. Front Plant Sci, 7: 1250. |
| [25] | Fahad S, Hussain S, Saud S, Hassan S, Tanveer M, Ihsan M Z, Shah A N, Ullah A, Nasrullah, Khan F, Ullah S, Alharby H, Nasim W, Wu C, Huang J L. 2016b. A combined application of biochar and phosphorus alleviates heat-induced adversities on physiological, agronomical and quality attributes of rice. Plant Physiol Biochem, 103: 191-198. |
| [26] | Fan F F, Cai M, Luo X, Liu M M, Yuan H R, Cheng M X, Ahmad A, Li N W, Li S Q. 2023. Novel QTLs from wild rice Oryza longistaminata confer strong tolerance to high temperature at seedling stage. Rice Sci, 30(6): 577-586. |
| [27] | Fang Y J, Liao K F, Du H, Xu Y, Song H Z, Li X H, Xiong L Z. 2015. A stress-responsive NAC transcription factor SNAC3 confers heat and drought tolerance through modulation of reactive oxygen species in rice. J Exp Bot, 66(21): 6803-6817. |
| [28] | Feng B H, Zhang C X, Chen T T, Zhang X F, Tao L X, Fu G F. 2018. Salicylic acid reverses pollen abortion of rice caused by heat stress. BMC Plant Biol, 18(1): 245. |
| [29] | Gong J L, Zhang H C, Hu Y J, Long H Y, Chang Y, Wang Y, Xing Z P, Huo Z Y. 2013. Effects of air temperature during rice grain-filing period on the formation of rice grain yield and its quality. Chin J Ecol, 32(2): 482-491. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Gou Y J, Zhu X Y, Wang H Y, Shen R X. 2022. Regulation mechanism and breeding application of rice floret-opening-time. J South China Agric Univ, 43(6): 48-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Gu X T, Si F Y, Feng Z X, Li S J, Liang D, Yang P, Yang C, Yan B, Tang J, Yang Y, Li T, Li L, Zhou J L, Li J, Feng L L, Liu J Y, Yang Y Z, Deng Y W, Wu X N, Zhao Z G, Wan J M, Cao X F, Song X W, He Z H, Liu J Z. 2023. The OsSGS3-tasiRNA- OsARF3 module orchestrates abiotic-biotic stress response trade-off in rice. Nat Commun, 14(1): 4441. |
| [32] | Hirabayashi H, Sasaki K, Kambe T, Gannaban R B, Miras M A, Mendioro M S, Simon E V, Lumanglas P D, Fujita D, Takemoto-Kuno Y, Takeuchi Y, Kaji R, Kondo M, Kobayashi N, Ogawa T, Ando I, Jagadish K S V, Ishimaru T. 2015. qEMF3, a novel QTL for the early-morning flowering trait from wild rice, Oryza officinalis, to mitigate heat stress damage at flowering in rice, Oryza officinalis, to mitigate heat stress damage at flowering in rice, O. sativa. J Exp Bot, 66(5): 1227-1236. |
| [33] | IPCC. 2014. Climate Change 2014:Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC, Geneva, Switzerland: 151. |
| [34] | IPCC. 2018. Summary for policymakers. In: Roberts D, Skea J, Shukla P R, Zhai P, Connors S. Global Warming of 1.5 ºC. Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA: Cambridge University Press. |
| [35] | Ishimaru T, Hirabayashi H, Ida M, Takai T, San-Oh Y A, Yoshinaga S, Ando I, Ogawa T, Kondo M. 2010. A genetic resource for early-morning flowering trait of wild rice Oryza officinalis to mitigate high temperature-induced spikelet sterility at anthesis. Ann Bot, 106(3): 515-520. |
| [36] | Jagadish S V K, Craufurd P Q, Wheeler T R. 2007. High temperature stress and spikelet fertility in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Exp Bot, 58(7): 1627-1635. |
| [37] | Jagadish S V K, Muthurajan R, Oane R, Wheeler T R, Heuer S, Bennett J, Craufurd P Q. 2010. Physiological and proteomic approaches to address heat tolerance during anthesis in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Exp Bot, 61(1): 143-156. |
| [38] | Jagadish S V K, Bahuguna R N, Djanaguiraman M, Gamuyao R, Prasad P V V, Craufurd P Q. 2016. Implications of high temperature and elevated CO2 on flowering time in plants. Front Plant Sci, 7: 913. |
| [39] | Ji D L, Xiao W H, Sun Z W, Liu L J, Gu J F, Zhang H, Harrison M T, Liu K, Wang Z Q, Wang W L. 2023. Translocation and distribution of carbon-nitrogen in relation to rice yield and grain quality as affected by high temperature at early panicle initiation stage. Rice Sci, 30(6): 598-612. |
| [40] | Ji P, Liu H, Ye S H, Liu J L, Kuang J L, Long S, Yang H T, Liu X L. 2023. Effect of heat stress at different reproductive growth stages on yield and grain quality in rice. J Nuclear Agric Sci, 37(9): 1872-1883. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [41] | Jia Z K, Zhu B Y. 1991. Preliminary study on the accumulation effect of amylose affected by the air temperature at the filling stage of rice. J Yunnan Agric Univ, 6(2): 65-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [42] | Kan Y, Mu X R, Zhang H, Gao J, Shan J X, Ye W W, Lin H X. 2022. TT2 controls rice thermotolerance through SCT1-dependent alteration of wax biosynthesis. Nat Plants, 8(1): 53-67. |
| [43] | Kan Y, Mu X R, Gao J, Lin H X, Lin Y S. 2023. The molecular basis of heat stress responses in plants. Mol Plant, 16(10): 1612-1634. |
| [44] | Kilasi N L, Singh J, Vallejos C E, Ye C R, Jagadish S V K, Kusolwa P, Rathinasabapathi B. 2018. Heat stress tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Identification of quantitative trait loci and candidate genes for seedling growth under heat stress. Front Plant Sci, 9: 1578. |
| [45] | Kim J H, Lim S D, Jang C S. 2019. Oryza sativa heat-induced RING finger protein 1 (OsHIRP1) positively regulates plant response to heat stress. Plant Mol Biol, 99(6): 545-559. |
| [46] | Koh S, Lee S C, Kim M K, Koh J H, Lee S, An G, Choe S, Kim S R. 2007. T-DNA tagged knockout mutation of rice OsGSK1, an orthologue of Arabidopsis BIN2, with enhanced tolerance to various abiotic stresses. Plant Mol Biol, 65(4): 453-466. |
| [47] | Kumar S, Tripathi S, Singh S P, Prasad A, Akter F, Abu Syed M, Badri J, Das S P, Bhattarai R, Natividad M A, Quintana M, Venkateshwarlu C, Raman A, Yadav S, Singh S K, Swain P, Anandan A, Yadaw R B, Mandal N P, Verulkar S B, Kumar A, Henry A. 2021. Rice breeding for yield under drought has selected for longer flag leaves and lower stomatal density. J Exp Bot, 72(13): 4981-4992. |
| [48] | Lafarge T, Bueno C, Frouin J, Jacquin L, Courtois B, Ahmadi N. 2017. Genome-wide association analysis for heat tolerance at flowering detected a large set of genes involved in adaptation to thermal and other stresses. PLoS One, 12(2): e0171254. |
| [49] | Latif A, Sun Y, Pu C X, Ali N. 2023. Rice curled its leaves either adaxially or abaxially to combat drought stress. Rice Sci, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [50] | Latif S, Wang L P, Khan J, Ali Z, Sehgal S K, Babar M A, Wang J P, Quraishi U M. 2020. Deciphering the role of stay-green trait to mitigate terminal heat stress in bread wheat. Agronomy, 10(7): 1001. |
| [51] | Li J J, Yang J, Zhu B H, Xie G S. 2019. Overexpressing OsFBN1 enhances plastoglobule formation, reduces grain-filling percent and jasmonate levels under heat stress in rice. Plant Sci, 285: 230-238. |
| [52] | Li J Y, Yang C, Xu J M, Lu H P, Liu J X. 2023. The hot science in rice research: How rice plants cope with heat stress. Plant Cell Environ, 46(4): 1087-1103. |
| [53] | Li W C, Zhu Q S, Wang Y S, Wang S M, Chen X C, Zhang D W, Wang W L. 2013. The relationships between physiological and biochemical indexes and the yield characteristics of rice under high temperature stress. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 29(9): 5-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [54] | Li X M, Chao D Y, Wu Y, Huang X H, Chen K, Cui L G, Su L, Ye W W, Chen H, Chen H C, Dong N Q, Guo T, Shi M, Feng Q, Zhang P, Han B, Shan J X, Gao J P, Lin H X. 2015. Natural alleles of a proteasome α2 subunit gene contribute to thermo- tolerance and adaptation of African rice. Nat Genet, 47(7): 827-833. |
| [55] | Liang C Y, Wu M M, Huang F M, Zhai R R, Ye J, Zhu G F, Yu F M, Zhang X M, Ye S H. 2024. Prospects for the application of gene editing and genomic selection in rice breeding. Chin J Rice Sci, 38(1): 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [56] | Liu J, Hasanuzzaman M, Wen H L, Zhang J, Peng T, Sun H W, Zhao Q Z. 2019. High temperature and drought stress cause abscisic acid and reactive oxygen species accumulation and suppress seed germination growth in rice. Protoplasma, 256(5): 1217-1227. |
| [57] | Liu J P, Zhang C C, Wei C C, Liu X, Wang M G, Yu F F, Xie Q, Tu J M. 2016. The RING finger ubiquitin E3 ligase OsHTAS enhances heat tolerance by promoting H2O2-induced stomatal closure in rice. Plant Physiol, 170(1): 429-443. |
| [58] | Liu J P, Sun X J, Xu F Y, Zhang Y J, Zhang Q, Miao R, Zhang J H, Liang J S, Xu W F. 2018. Suppression of OsMDHAR4 enhances heat tolerance by mediating H2O2-induced stomatal closure in rice plants. Rice, 11(1): 38. |
| [59] | Liu K, Deng J, Lu J, Wang X Y, Lu B L, Tian X H, Zhang Y B. 2019. High nitrogen levels alleviate yield loss of super hybrid rice caused by high temperatures during the flowering stage. Front Plant Sci, 10: 357. |
| [60] | Liu Q, Yang T F, Yu T, Zhang S H, Mao X X, Zhao J L, Wang X F, Dong J F, Liu B. 2017. Integrating small RNA sequencing with QTL mapping for identification of miRNAs and their target genes associated with heat tolerance at the flowering stage in rice. Front Plant Sci, 8: 43. |
| [61] | Liu T T, Zou J P, Yang X, Wang K J, Rao Y C, Wang C. 2023. Development and application of prime editing in plants. Rice Sci, 30(6): 509-522. |
| [62] | Lobell D B, Schlenker W, Costa-Roberts J. 2011. Climate trends and global crop production since 1980. Science, 333: 616-620. |
| [63] | Lyman N B, Jagadish K S V, Nalley L L, Dixon B L, Siebenmorgen T. 2013. Neglecting rice milling yield and quality underestimates economic losses from high-temperature stress. PLoS One, 8(8): e72157. |
| [64] | Matsui T, Omasa K. 2002. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars tolerant to high temperature at flowering: Anther characteristics. Ann Bot, 89(6): 683-687. |
| [65] | Matsui T, Hasegawa T. 2019. Effect of long anther dehiscence on seed set at high temperatures during flowering in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci Rep, 9(1): 20363. |
| [66] | Mishra A, Singh B B, Shakil N A, Shamim M D, Homa F, Chaudhary R, Yadav P, Srivastava D, Fatima P, Sharma V, Yadav M K, Kumar P. 2024. Effect of high temperature stress on metabolome and aroma in rice grains. Plant Gene, 38: 100450. |
| [67] | Moon J C, Ham D J, Hwang S G, Park Y C, Lee C H, Jang C S. 2014. Molecular characterization of a heat inducible rice gene, OsHSP1, and implications for rice thermotolerance. Genes Genom, 36(2): 151-161. |
| [68] | Nevame A Y M, Emon R M, Malek M A, Hasan M M, Alam M A, Muharam F M, Aslani F, Rafii M Y, Ismail M R. 2018. Relationship between high temperature and formation of chalkiness and their effects on quality of rice. Biomed Res Int, 2018: 1653721. |
| [69] | Nosaka Y, Nosaka A Y. 2017. Generation and detection of reactive oxygen species in photocatalysis. Chem Rev, 117(17): 11302-11336. |
| [70] | Oh-e I, Saitoh K, Kuroda T. 2007. Effects of high temperature on growth, yield and dry-matter production of rice grown in the paddy field. Plant Prod Sci, 10(4): 412-422. |
| [71] | Prasad P V V, Boote K J, Allen Jr L H, Sheehy J E, Thomas J M G. 2006. Species, ecotype and cultivar differences in spikelet fertility and harvest index of rice in response to high temperature stress. Field Crops Res, 95(2/3): 398-411. |
| [72] | Qiao B, Zhang Q, Liu D L, Wang H Q, Yin J Y, Wang R, He M L, Cui M, Shang Z L, Wang D K, Zhu Z G. 2015. A calcium-binding protein, rice annexin OsANN1, enhances heat stress tolerance by modulating the production of H2O2. J Exp Bot, 66(19): 5853-5866. |
| [73] | Ren H M, Bao J P, Gao Z X, Sun D Y, Zheng S Z, Bai J T. 2023. How rice adapts to high temperatures. Front Plant Sci, 14: 1137923. |
| [74] | Rieu I, Twell D, Firon N. 2017. Pollen development at high temperature: From acclimation to collapse. Plant Physiol, 173(4): 1967-1976. |
| [75] | Sakai H, Cheng W G, Chen C P, Hasegawa T. 2022. Short-term high nighttime temperatures pose an emerging risk to rice grain failure. Agric For Meteorol, 314: 108779. |
| [76] | Satake T, Yoshida S. 1978. High temperature-induced sterility in indica rices at flowering. Jpn J Crop Sci, 47(1): 6-17. |
| [77] | Shen H, Zhong X B, Zhao F F, Wang Y M, Yan B X, Li Q, Chen G Y, Mao B Z, Wang J J, Li Y S, Xiao G Y, He Y K, Xiao H, Li J M, He Z H. 2015. Overexpression of receptor-like kinase ERECTA improves thermotolerance in rice and tomato. Nat Biotechnol, 33(9): 996-1003. |
| [78] | Takehara K, Murata K, Yamaguchi T, Yamaguchi K, Chaya G, Kido S, Iwasaki Y, Ogiwara H, Ebitani T, Miura K. 2018. Thermo- responsive allele of Sucrose synthase 3 (Sus3) provides high- temperature tolerance during the ripening stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed Sci, 68(3): 336-342. |
| [79] | Tang S, Zhang H X, Li L, Liu X, Chen L, Chen W Z, Ding Y F. 2018. Exogenous spermidine enhances the photosynthetic and antioxidant capacity of rice under heat stress during early grain- filling period. Funct Plant Biol, 45(9): 911-921. |
| [80] | Tang Y Y, Gao C C, Gao Y, Yang Y, Shi B Y, Yu J L, Lyu C, Sun B F, Wang H L, Xu Y Y, Yang Y G, Chong K. 2020. OsNSUN2- mediated 5-methylcytosine mRNA modification enhances rice adaptation to high temperature. Dev Cell, 53(3): 272-286.e7. |
| [81] | Tiwari M, Kumar R, Min D, Jagadish S V K. 2022. Genetic and molecular mechanisms underlying root architecture and function under heat stress: A hidden story. Plant Cell Environ, 45(3): 771-788. |
| [82] | Wang D, Qin B X, Li X, Tang D, Zhang Y E, Cheng Z K, Xue Y B. 2016. Nucleolar DEAD-box RNA helicase TOGR1 regulates thermotolerant growth as a pre-rRNA chaperone in rice. PLoS Genet, 12(2): e1005844. |
| [83] | Wang M, Liu Y, Zhang H Q, Liu A M, Xiao C L, Tang R, Yang Y B, Jiang L Y, Li X X. 2017. Effect of high temperature on outcrossing characteristics at the fertile sensitive stage of photo thermosensitive genic male sterile (PTGMS) rice lines. J Hunan Agric Univ: Nat Sci, 43(4): 347-352. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [84] | Wang M M, Zhu X P, Peng G Q, Liu M L, Zhang S Q, Chen M H, Liao S T, Wei X Y, Xu P, Tan X Y, Li F P, Li Z C, Deng L, Luo Z L, Zhu L Y, Zhao S, Jiang D G, Li J, Liu Z L, Xie X R, Wang S K, Wu A M, Zhuang C X, Zhou H. 2022. Methylesterification of cell-wall pectin controls the diurnal flower-opening times in rice. Mol Plant, 15(6): 956-972. |
| [85] | Wang X, Li L, Yang Z, Zheng X, Yu S, Xu C, Hu Z. 2022. Predicting rice hybrid performance using univariate and multivariate GBLUP models based on North Carolina mating design II. Heredity, 118(3): 302-310. |
| [86] | Wei Z R, Yuan Q L, Lin H, Li X X, Zhang C, Gao H S, Zhang B, He H Y, Liu T J, Jie Z, Gao X, Shi S D, Wang B, Gao Z Y, Kong L R, Qian Q, Shang L G. 2021. Linkage analysis, GWAS, transcriptome analysis to identify candidate genes for rice seedlings in response to high temperature stress. BMC Plant Biol, 21(1): 85. |
| [87] | Wu C, Cui K H, Wang W C, Li Q, Fahad S, Hu Q Q, Huang J L, Nie L X, Peng S B. 2016. Heat-induced phytohormone changes are associated with disrupted early reproductive development and reduced yield in rice. Sci Rep, 6: 34978. |
| [88] | Wu C, Cui K H, Wang W C, Li Q, Fahad S, Hu Q Q, Huang J L, Nie L X, Mohapatra P K, Peng S B. 2017. Heat-induced cytokinin transportation and degradation are associated with reduced panicle cytokinin expression and fewer spikelets per panicle in rice. Front Plant Sci, 8: 371. |
| [89] | Wu X L, Shiroto Y, Kishitani S, Ito Y, Toriyama K. 2009. Enhanced heat and drought tolerance in transgenic rice seedlings over- expressing OsWRKY11 under the control of HSP101 promoter. Plant Cell Rep, 28(1): 21-30. |
| [90] | Wu Y S, Yang C Y. 2019. Ethylene-mediated signaling confers thermotolerance and regulates transcript levels of heat shock factors in rice seedlings under heat stress. Bot Stud, 60(1): 23. |
| [91] | Xu J M, Henry A, Sreenivasulu N. 2020. Rice yield formation under high day and night temperatures: A prerequisite to ensure future food security. Plant Cell Environ, 43(7): 1595-1608. |
| [92] | Xu P Z, Wu T K, Ali A, Zhang H Y, Liao Y X, Chen X Q, Tian Y H, Wang W M, Fu X D, Li Y, Fan J, Wang H, Tian Y F, Liu Y T, Jiang Q S, Sun C H, Zhou H, Wu X J. 2022. EARLY MORNING FLOWERING1 (EMF1) regulates the floret opening time by mediating lodicule cell wall formation in rice. Plant Biotechnol J, 20(8): 1441-1443. |
| [93] | Xu Y, Ma K X, Zhao Y, Wang X, Zhou K, Yu G N, Li C, Li P C, Yang Z F, Xu C W, Xu S Z. 2021. Genomic selection: A break- through technology in rice breeding. Crop J, 9(3): 669-677. |
| [94] | Xu Y F, Zhang L, Ou S J, Wang R C, Wang Y M, Chu C C, Yao S G. 2020. Natural variations of SLG1 confer high-temperature tolerance in indica rice. Nat Commun, 11(1): 5441. |
| [95] | Xu Y F, Chu C C, Yao S G. 2021. The impact of high-temperature stress on rice: Challenges and solutions. Crop J, 9(5): 963-976. |
| [96] | Xu Y J, Ying Y N, Ouyang S H, Duan X L, Sun H, Jiang S K, Sun S C, Bao J S. 2018. Factors affecting sensory quality of cooked japonica rice. Rice Sci, 25(6): 330-339. |
| [97] | Yamakawa H, Hakata M. 2010. Atlas of rice grain filling-related metabolism under high temperature: Joint analysis of metabolome and transcriptome demonstrated inhibition of starch accumulation and induction of amino acid accumulation. Plant Cell Physiol, 51(5): 795-809. |
| [98] | Yang C, Luo A N, Lu H P, Davis S J, Liu J X. 2024. Diurnal regulation of alternative splicing associated with thermotolerance in rice by two glycine-rich RNA-binding proteins. Sci Bull, 69(1): 59-71. |
| [99] | Yang J, Chen X R, Zhu C L, Peng X S, He X P, Fu J R, Ouyang L J, Bian J M, Hu L F, Sun X T, Xu J, He H H. 2015. Using RNA-seq to profile gene expression of spikelet development in response to temperature and nitrogen during meiosis in rice (Oryza sativa L.). PLoS One, 10(12): e0145532. |
| [100] | Yang Y X, Zhang C, Zhu D, He H Y, Wei Z R, Yuan Q L, Li X X, Gao X, Zhang B, Gao H S, Wang B, Cao S M, Wang T Y, Li Y H, Yu X M, Guo L B, Hu G J, Qian Q, Shang L G. 2022. Identifying candidate genes and patterns of heat-stress response in rice using a genome-wide association study and transcriptome analyses. Crop J, 10(6): 1633-1643. |
| [101] | Yao D P, Wu J, Luo Q H, Li J W, Zhuang W, Xiao G, Deng Q Y, Lei D Y, Bai B. 2020. Influence of high natural field temperature during grain filling stage on the morphological structure and physicochemical properties of rice (Oryza sativa L.) starch. Food Chem, 310: 125817. |
| [102] | Ye C R, Argayoso M A, Redoña E D, Sierra S N, Laza M A, Dilla C J, Mo Y, Thomson M J, Chin J, Delaviña C B, Diaz G Q, Hernandez J E. 2012. Mapping QTL for heat tolerance at flowering stage in rice using SNP markers. Plant Breed, 131(1): 33-41. |
| [103] | Yu G H, Xie Z N, Chen W, Xu B, Huang B R. 2022. Knock down of NON-YELLOW COLOURING 1-like gene or chlorophyllin application enhanced chlorophyll accumulation with antioxidant roles in suppressing heat-induced leaf senescence in perennial ryegrass. J Exp Bot, 73(1): 429-444. |
| [104] | Zang Q, Han X, Zhang M J, Huang X M, Jiang M, Huang L F. 2022. Effects of high temperature on quality of japonica rice at early and middle heading stage under different planting modes. Agronomy, 12(8): 1833. |
| [105] | Zhang C X, Li G Y, Chen T T, Feng B H, Fu W M, Yan J X, Islam M R, Jin Q Y, Tao L X, Fu G F. 2018. Heat stress induces spikelet sterility in rice at anthesis through inhibition of pollen tube elongation interfering with auxin homeostasis in pollinated pistils. Rice, 11(1): 14. |
| [106] | Zhang G L, Zhang S T, Xiao L T, Tang W B, Xiao Y H, Chen L Y. 2014. Effect of high temperature stress on physiological characteristics of anther, pollen, and stigma of rice during heading-flowering stage. Chin J Rice Sci, 28(2): 155-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [107] | Zhang H, Xu H, Jiang Y Y, Zhang H, Wang S Y, Wang F L, Zhu Y. 2021. Genetic control and high temperature effects on starch biosynthesis and grain quality in rice. Front Plant Sci, 12: 757997. |
| [108] | Zhang H, Zhou J F, Kan Y, Shan J X, Ye W W, Dong N Q, Guo T, Xiang Y H, Yang Y B, Li Y C, Zhao H Y, Yu H X, Lu Z Q, Guo S Q, Lei J J, Liao B, Mu X R, Cao Y J, Yu J J, Lin Y S, Lin H X. 2022. A genetic module at one locus in rice protects chloroplasts to enhance thermotolerance. Science, 376: 1293-1300. |
| [109] | Zhang N, Wang Y H, Wang Z M, Yue Z Y, Niu Y. 2021. Heat shock transcription factor family in plants: A review. Chin J Biotechnol, 37(4): 1155-1167. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [110] | Zhang Q L, Wei Y X, Peng C L. 2018. Effects of endogenous ascorbic acid on resistance to high-temperature stress in excised rice leaves. Photosynthetica, 56(4): 1453-1458. |
| [111] | Zhao C, Liu B, Piao S L, Wang X H, Lobell D B, Huang Y, Huang M T, Yao Y T, Bassu S, Ciais P, Durand J L, Elliott J, Ewert F, Janssens I A, Li T, Lin E D, Liu Q, Martre P, Müller C, Peng S S, Peñuelas J, Ruane A C, Wallach D, Wang T, Wu D H, Liu Z, Zhu Y, Zhu Z C, Asseng S. 2017. Temperature increase reduces global yields of major crops in four independent estimates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 114(35): 9326-9331. |
| [112] | Zhao C J, Xie J Q, Li L, Cao C J. 2017. Comparative transcriptomic analysis in paddy rice under storage and identification of differentially regulated genes in response to high temperature and humidity. J Agric Food Chem, 65(37): 8145-8153. |
| [113] | Zhao L, Lei J G, Huang Y J, Zhu S, Chen H P, Huang R L, Peng Z Q, Tu Q H, Shen X H, Yan S. 2016. Mapping quantitative trait loci for heat tolerance at anthesis in rice using chromosomal segment substitution lines. Breed Sci, 66(3): 358-366. |
| [114] | Zhao L, Zhou S C, Wang C R, Li H, Huang D Q, Wang Z D, Zhou D G, Chen Y B, Gong R, Pan Y Y. 2022. Breeding effects and genetic compositions of a backbone parent (Fengbazhan) of modern indica rice in China. Rice Sci, 29(5): 397-401. |
| [115] | Zheng S Z, Liu Y L, Li B, Shang Z L, Zhou R G, Sun D Y. 2012. Phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C9 is involved in the thermotolerance of Arabidopsis. Plant J, 69(4): 689-700. |
| [116] | Zhou H, Wang Y F, Zhang Y J, Xiao Y H, Liu X, Deng H B, Lu X D, Tang W B, Zhang G L. 2022. Comparative analysis of heat- tolerant and heat-susceptible rice highlights the role of OsNCED1 gene in heat stress tolerance. Plants, 11(8): 1062. |
| [117] | Zhou H F, Wang X L, Huo C M, Wang H, An Z C, Sun D Y, Liu J Z, Tang W Q, Zhang B W. 2019. A quantitative proteomics study of early heat-regulated proteins by two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis identified OsUBP21 as a negative regulator of heat stress responses in rice. Proteomics, 19(20): e1900153. |
| [118] | Zhu S, Huang R L, Wai H P, Xiong H L, Shen X H, He H H, Yan S. 2017. Mapping quantitative trait loci for heat tolerance at the booting stage using chromosomal segment substitution lines in rice. Physiol Mol Biol Plants, 23(4): 817-825. |
| [1] | Pei Mengtian, Cao Yingying, Xie Xuze, Cao Ying, Chen Jia, Zhang Xi, Wang Zonghua, Lu Guodong, Zhang Shenghang. Synergy in Rice Immunity: Exploring Strategies of Coordinated Disease Defense Through Receptor-Like Kinases and Receptor- Like Cytoplasmic Kinases [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(6): 643-658. |
| [2] | Durga Prasad Mullangie, Kalaimagal Thiyagarajan, Manonmani Swaminathan, Jagadeesan Ramalingam, Sritharan Natarajan, Senthilkumar Govindan. Breeding Resilience: Exploring Lodging Resistance Mechanisms in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(6): 659-672. |
| [3] | Li Wei, Zhang Mengchen, Yang Yaolong, Weng Lin, Hu Peisong, Wei Xinghua. Molecular Evolution of Rice Blast Resistance Gene bsr-d1 [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(6): 700-711. |
| [4] | Ren Jian, Hu Kelin, Feng Puyu, William D. Batchelor, Liu Haitao, Lü Shihua. Simulating Responses of Rice Yield and Nitrogen Fates to Ground Cover Rice Production System under Different Types of Precipitation Years [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(6): 725-739. |
| [5] | Ravindran Lalithambika Visakh, Sreekumar Anand, Sukumaran Nair Arya, Behera Sasmita, Uday Chand Jha, Rameswar Prasad Sah, Radha Beena. Rice Heat Tolerance Breeding: A Comprehensive Review and Forward Gaze [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(4): 375-400. |
| [6] | Zhao Mei, Liu Xiaoxue, Wan Jun, Zhou Erxun, Shu Canwei. Host-Induced Gene Silencing of Effector AGLIP1 Enhanced Resistance of Rice to Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(4): 463-474. |
| [7] | Deng Bowen, Zhang Yanni, Zhang Fan, Wang Wensheng, Xu Jianlong, Zhang Yu, Bao Jinsong. Genome-Wide Association Study of Cooked Rice Textural Attributes and Starch Physicochemical Properties in indica Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(3): 300-316. |
| [8] | Zhu Chengqi, Ye Yuxuan, Qiu Tian, Huang Yafan, Ying Jifeng, Shen Zhicheng. Drought-Tolerant Rice at Molecular Breeding Eras: An Emerging Reality [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(2): 179-189. |
| [9] | Ji Dongling, Xiao Wenhui, Sun Zhiwei, Liu Lijun, Gu Junfei, Zhang Hao, Matthew Tom Harrison, Liu Ke, Wang Zhiqin, Wang Weilu. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 598-612. |
| [10] | Sundus Zafar, Xu Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 523-536. |
| [11] | Xia Xiaodong, Zhang Xiaobo, Wang Zhonghao, Cheng Benyi, Sun Huifeng, Xu Xia, Gong Junyi, Yang Shihua, Wu Jianli, Shi Yongfeng, Xu Rugen. Mapping and Functional Analysis of LE Gene in a Lethal Etiolated Rice Mutant at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 567-576. |
| [12] | B. M. Lokeshkumar, S. L. Krishnamurthy, Suman Rathor, Arvinder Singh Warriach, N. M. Vinaykumar, B. M. Dushyanthakumar, Parbodh Chander Sharma. Morphophysiological Diversity and Haplotype Analysis of Saltol QTL Region in Diverse Rice Landraces for Salinity Tolerance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(4): 306-320. |
| [13] | Zhu Jinling, Wei Ruping, Wang Xin, Zheng Chaoqun, Wang Mengmeng, Yang Yicheng, Yang Liuyan. Polyphosphate Accelerates Transformation of Nonstructural Carbohydrates to Improve Growth of ppk-Expressing Transgenic Rice in Phosphorus Deficiency Culture [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(3): 235-246. |
| [14] | Long Xinkang, Guan Chunmin, Wang Lin, Jia Liting, Fu Xiangjin, Lin Qinlu, Huang Zhengyu, Liu Chun. Rice Storage Proteins: Focus on Composition, Distribution, Genetic Improvement and Effects on Rice Quality [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(3): 207-221. |
| [15] | Li Shuyan, Yan Qiling, Wang Jieyu, Jiang Huidan, Li Zuren, Peng Qiong. Root Endophyte Shift and Key Genera Discovery in Rice under Barnyardgrass Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(2): 160-170. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||