
Rice Science ›› 2025, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 367-379.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2024.12.014
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xie Yuhao1,2,#, Xie Wenya1,2,#, Zhao Jianhua1,#, Xue Xiang3, Cao Wenlei1, Shi Xiaopin1, Wang Zhou1, Wang Yiwen1, Wang Guangda1, Feng Zhiming1,2, Hu Keming1,2, Chen Xijun1,2, Chen Zongxiang1,2, Zuo Shimin1,2,4( )
)
Received:2024-10-02
Accepted:2024-12-30
Online:2025-05-28
Published:2025-06-16
Contact:
Zuo Shimin (About author:First author contact:These authors contributed equally to this work
Xie Yuhao, Xie Wenya, Zhao Jianhua, Xue Xiang, Cao Wenlei, Shi Xiaopin, Wang Zhou, Wang Yiwen, Wang Guangda, Feng Zhiming, Hu Keming, Chen Xijun, Chen Zongxiang, Zuo Shimin. OsERF7 Negatively Regulates Resistance to Sheath Blight Disease by Inhibiting Phytoalexin Biosynthesis[J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(3): 367-379.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
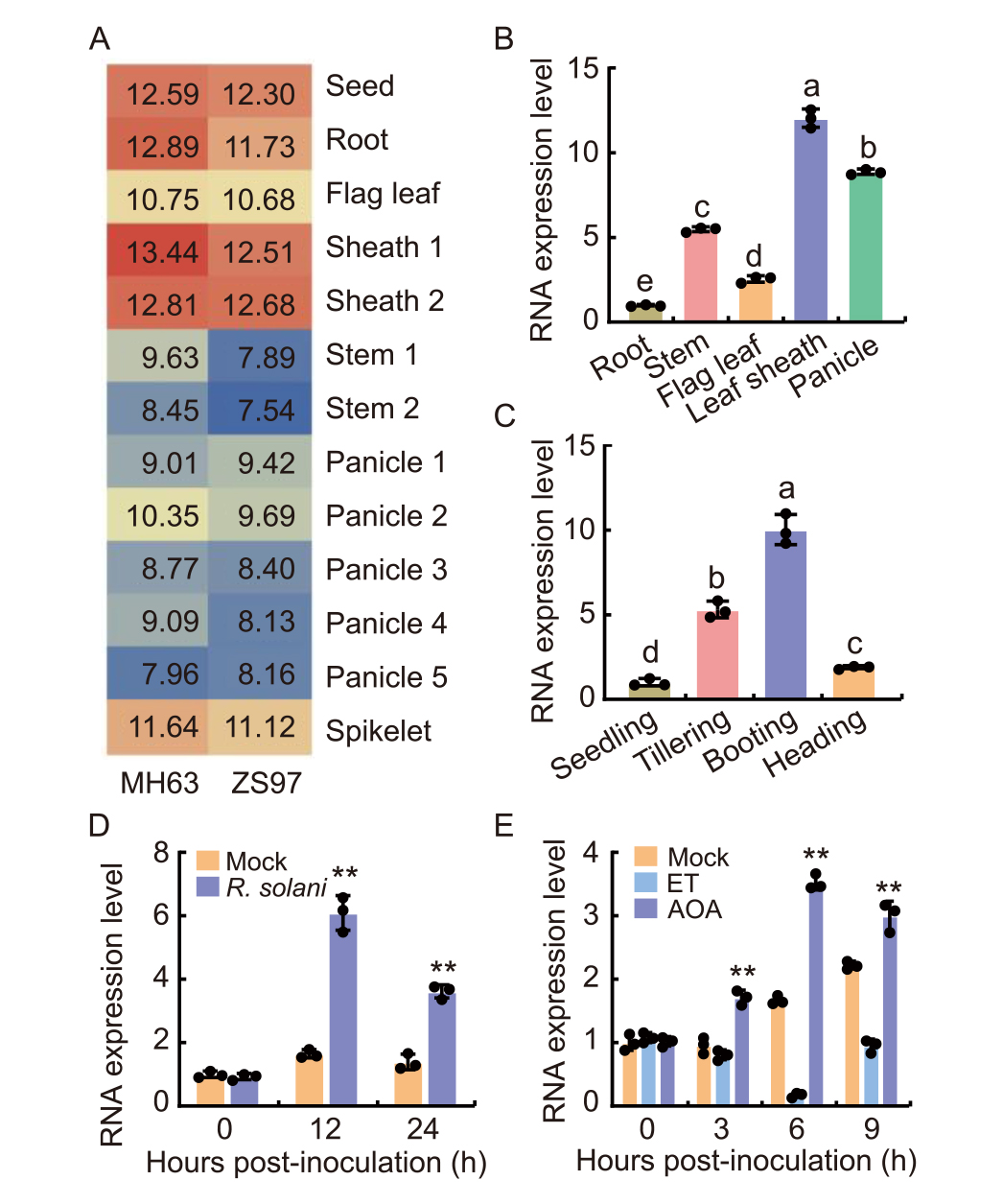
Fig. 1. Tissue-specificity and inducible expression of OsERF7. A, Gene expression atlas of OsERF7 in two representative indica varieties (Minghui 63, MH63, and Zhenshan 97, ZS97), retrieved from the CREP database (http://crep.ncpgr.cn/crep-cgi/home.pl). Expression values are all log2-transformed using the original signal values from the CREP database. Sheaths 1 and 2 indicate the sheath tissues collected from secondary-branch primordium differentiation at development stages and 4-5 cm young panicle development stage, respectively; Stems 1 and 2 indicate 5 d before the heading stage and at the heading stage, respectively; Panicles 1-5 represent panicles at the secondary-branch primordium differentiation stage, pistil and stamen primordium differentiation stage, pollen-mother cell formation stage, 4-5 cm young panicle, and the heading stage, respectively.B and C, RNA expression levels of OsERF7 in different tissues (B) at the maturity stage and in leaf sheath at different development stages (C) of Xudao 3. The OsActin gene was used as the internal control.D and E, RNA expression levels of OsERF7 in Xudao 3 in response to Rhizoctonia solani inoculation at the booting stage (D) and treatment with ethylene (ET) or aminooxyacetic acid (AOA) at the seedling stage (E). The OsActin gene was used as the internal control.In B to E, data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). Different lowercase letters above bars indicate statistically significant differences determined by one-way analysis followed by Tukey’s multiple test (P < 0.05). ** indicates significant differences at P < 0.01 determined by one-tailed Student’s t-test.
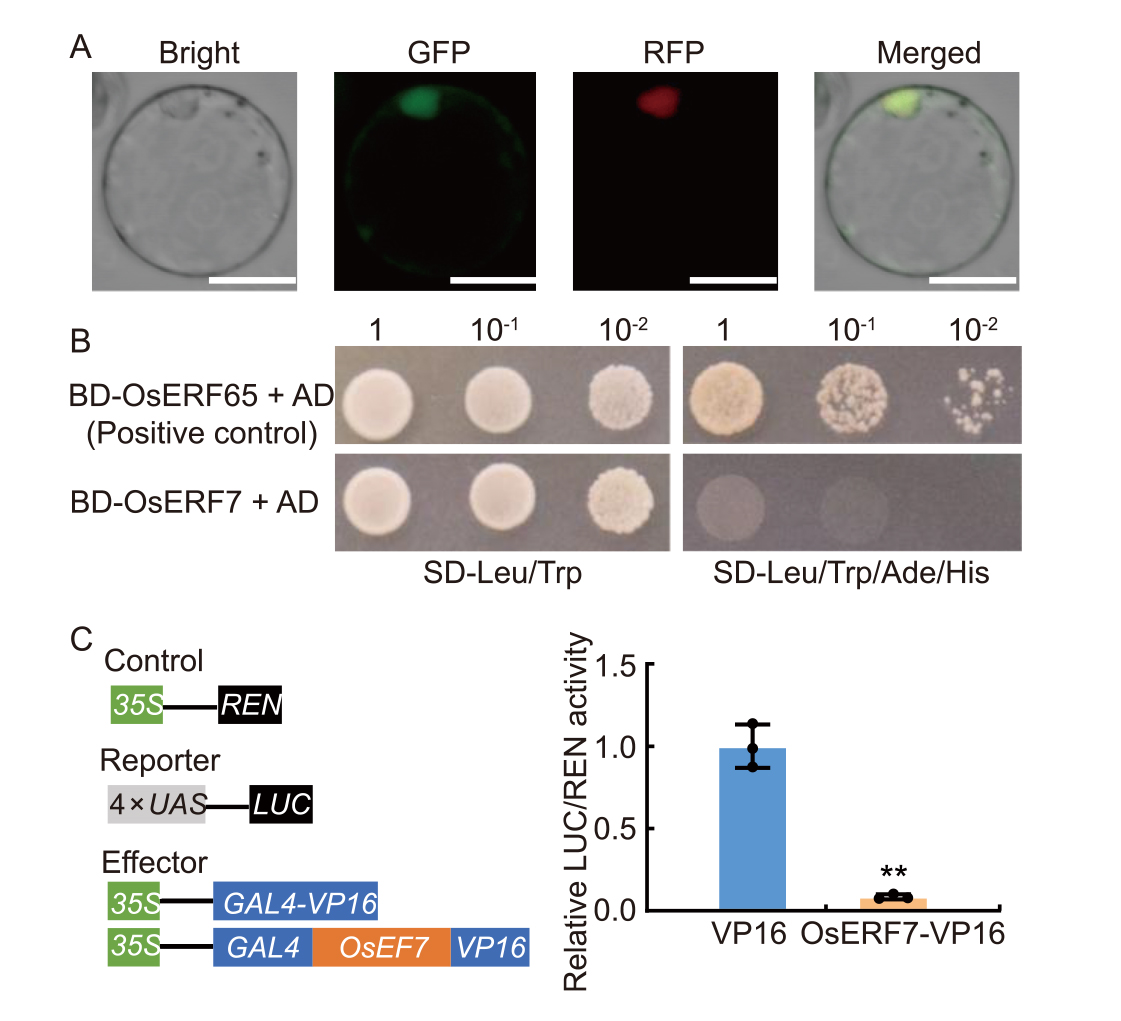
Fig. 2. Nuclear localization and transcriptional repression activity of OsERF7. A, Subcellular localization of OsERF7 in rice protoplasts. The NLS-RFP protein was used as a nuclear marker to localize the OsERF7-GFP fusion protein. GFP, Green fluorescent protein; RFP, Red fluorescent protein. Scale bars, 10 µm. B, Yeast one-hybrid assay for OsERF7. OsERF65, a transcriptional activator, was used as a positive control. BD, DNA-binding domain; AD, Activation domain; SD, Synthetic defined medium.C, Repression effects of OsERF7 on VP16-mediated transcriptional activation of 4× UAS-LUC in rice protoplasts. UAS, Upstream activating sequence; LUC, Firefly luciferase; REN, Renilla luciferase; 35S, CaMV35S promoter; GAL4, Yeast transcriptional activator. VP16 was used as a transcriptional activator. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). ** indicates significant differences at P < 0.01 determined by one-tailed Student’s t-test.
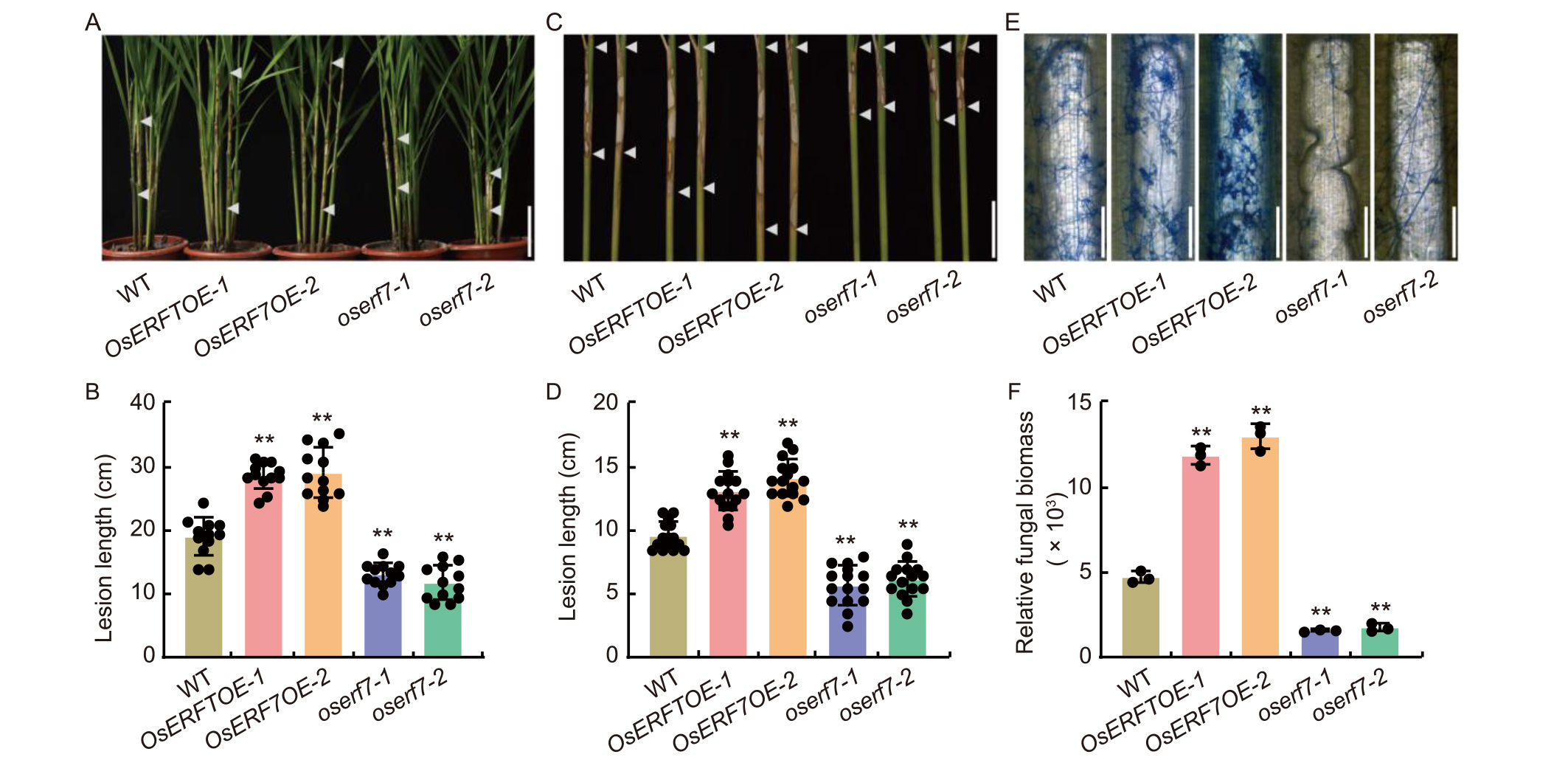
Fig. 3. OsERF7 negatively regulates rice resistance to Rhizoctonia solani. A and C, Disease levels of wild type (WT), OsERF7 overexpression lines (OsERF7OE-1 and OsERF7OE-2), and knockout (oserf7-1 and oserf7-2) mutants caused by R. solani in whole-plant (A) and detached leaf sheath (C). Pictures were taken and data were collected at 12 d post-inoculation (dpi) in A and 5 dpi in C. Scale bars, 10 cm in A and 5 cm in C, respectively. The arrowhead indicates the upper and lower boundaries of lesions.B and D, Quantitative lesion lengths of WT, OsERF7OE (OsERF7OE-1 and OsERF7OE-2), and oserf7 (oserf7-1 and oserf7-2) plants in whole plants (B) and detached leaf sheaths (D) after R. solani inoculation. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 12 in B; n = 15 in D). E, Lactophenol cotton blue staining for hyphae of R. solani in leaf sheaths of WT, OsERF7OE (OsERF7OE-1 and OsERF7OE-2), and oserf7 (oserf7-1 and oserf7-2) plants at 48 h post-inoculation. Scale bars, 300 µm. F, Relative abundance of R. solani biomass in infected leaf sheaths of WT, OsERF7OE (OsERF7OE-1 and OsERF7OE-2), and oserf7 (oserf7-1 and oserf7-2) plants at 48 h post inoculation, measured by qRT-PCR using specific primers for fungal 18S rRNA gene. The OsActin gene was used as the internal control. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). In B, D, and F, ** indicates significant differences at P < 0.01 determined by one-tailed Student’s t-test.
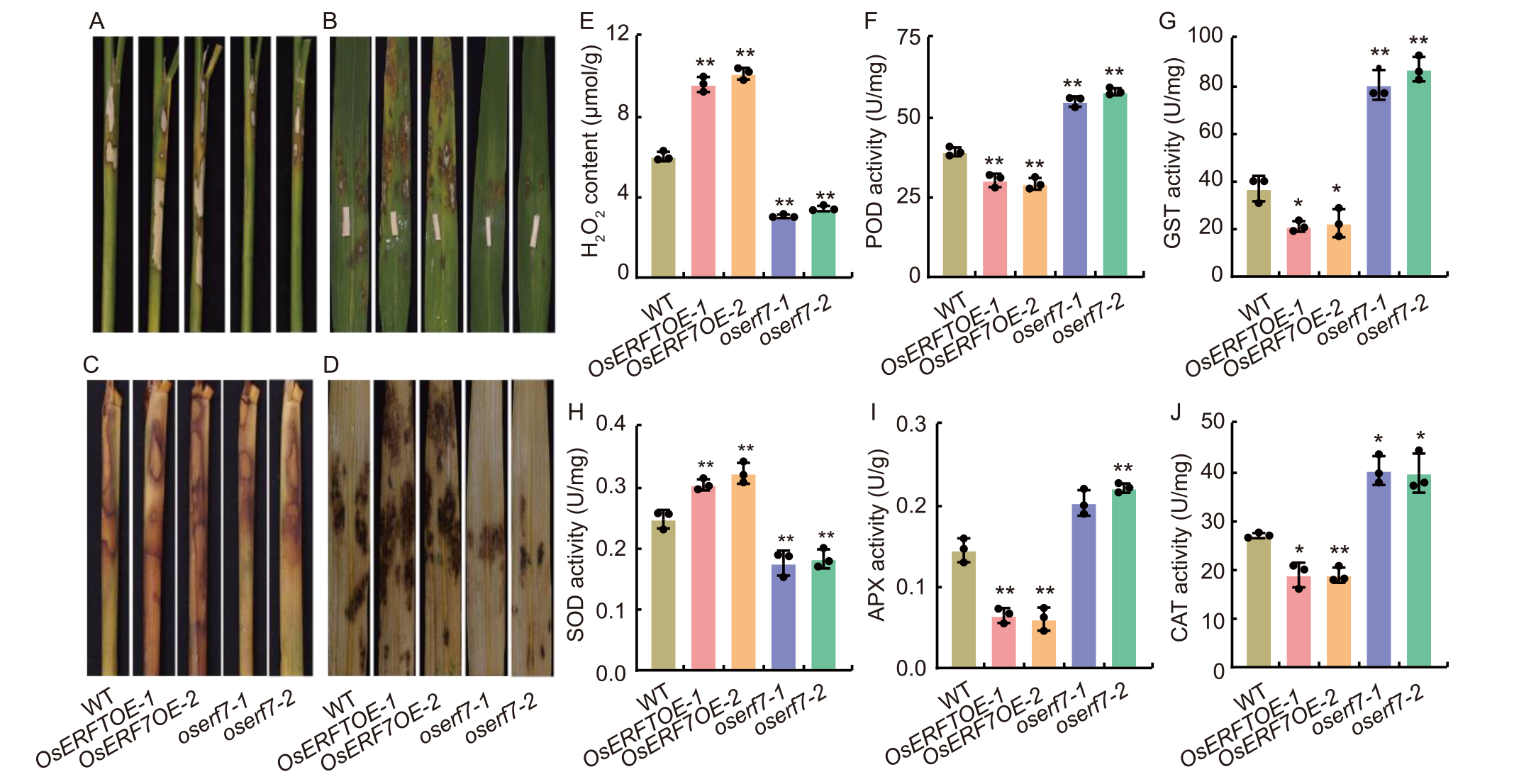
Fig. 4. Disease lesion length and activity of oxidoreductase enzymes after inoculation with Rhizoctonia solani. A and B, Disease lesions on detached leaf sheaths (A) and flag leaves (B) of wild type (WT), OsERF7 overexpression lines (OsERF7OE-1 and OsERF7OE-2), and knockout (oserf7-1 and oserf7-2) mutants at 72 h post-inoculation (hpi) with R. solani. C and D, Detached leaf sheaths (C) and flag leaves (D) from A and B were stained with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine to visualize H2O2 accumulation at the inoculation site. E-J, H2O2 content (E), peroxidase (POD) activity (F), glutathione-S-transferase (GST) activity (G), superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity (H), ascorbate peroxidase (APX) (I), and catalase (CAT) activity (J) in leaves of WT, OsERF7OE, and oserf7 lines at 72 hpi. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). * and ** indicate significant differences at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 determined by one-tailed Student’s t-test.
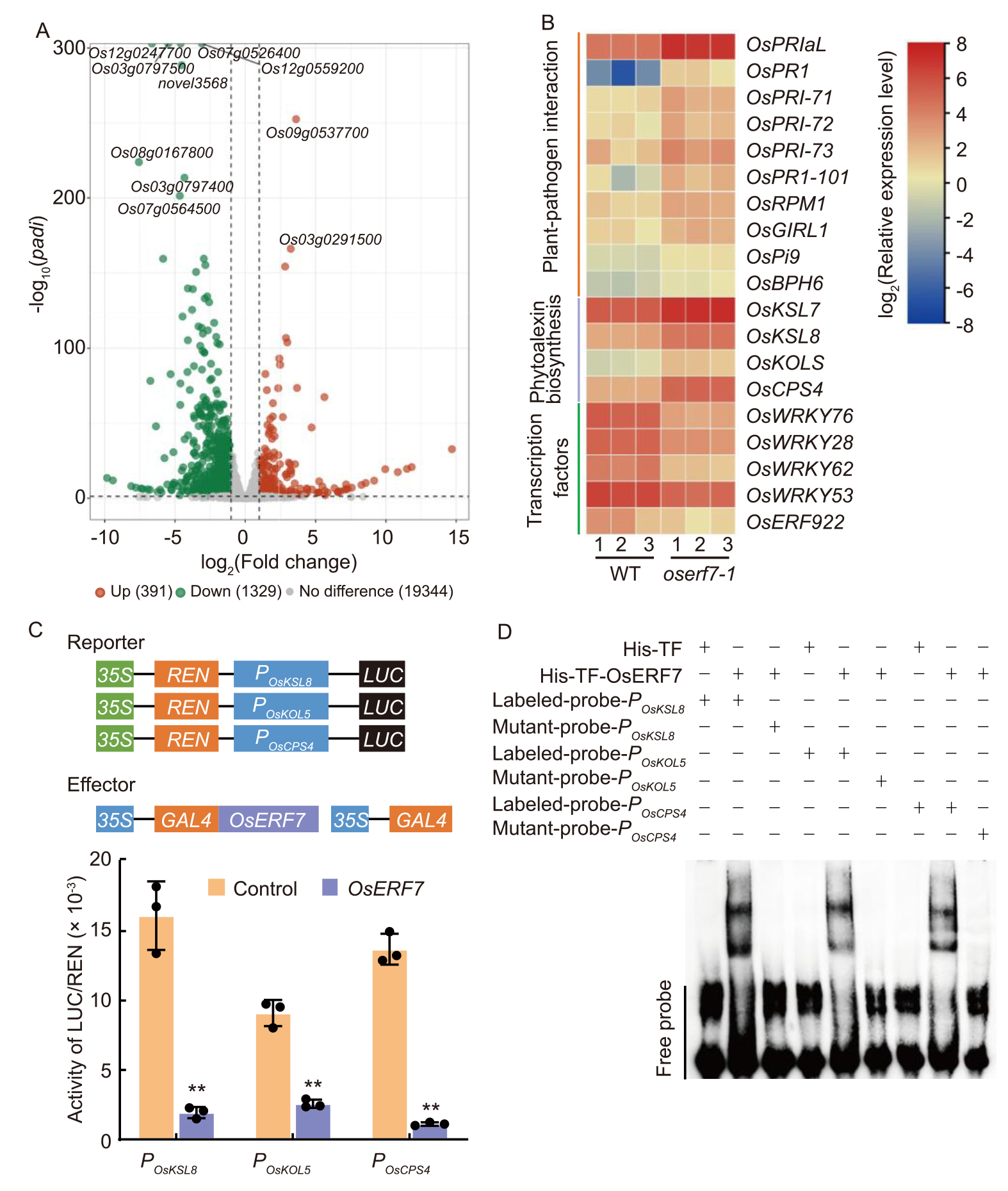
Fig. 5. Transcriptome analysis for changes in oserf7 plants in response to Rhizoctonia solani. A, Volcano plot for differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in oserf7 mutant relative to wild type (WT) plants at 12 h post-inoculation (hpi). Genes that are significantly upregulated and downregulated are depicted in red and green, respectively [Cut-off values: Padj < 0.05 and |log2(Fold change)| > 1]. B, Heatmap for the expression levels of DEGs involved in plant-pathogen interaction, diterpenoid biosynthesis pathway, or characterized as transcription factors in oserf7 and WT plants at 12 hpi with R. solani.C, Dual-luciferase reporter assay showed that OsERF7 suppresses the expression of three phytoalexin biosynthesis genes expression in rice protoplast. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). ** indicates significant differences at P < 0.01 determined by one-tailed Student’s t-test. REN, Renilla luciferase; LUC, Firefly luciferase; 35S, CaMV35S promoter; TF, Trigger factor; POsKSL8, OsKSL8 promoter; POsKOL5, OsKOL5 promoter; POsCPS4, OsCPS4 promoter. D, Electrophoretic mobility shift assay identified the binding ability of OsERF7 to the GCC-box on the promoters of OsKSL8, OsKOL5, and OsCPS4 genes, respectively. The probes are derived from a 30-bp sequence of their promoters that contains the GCC-box element, and the mutated probe has the GCC sequence mutated to GTT.
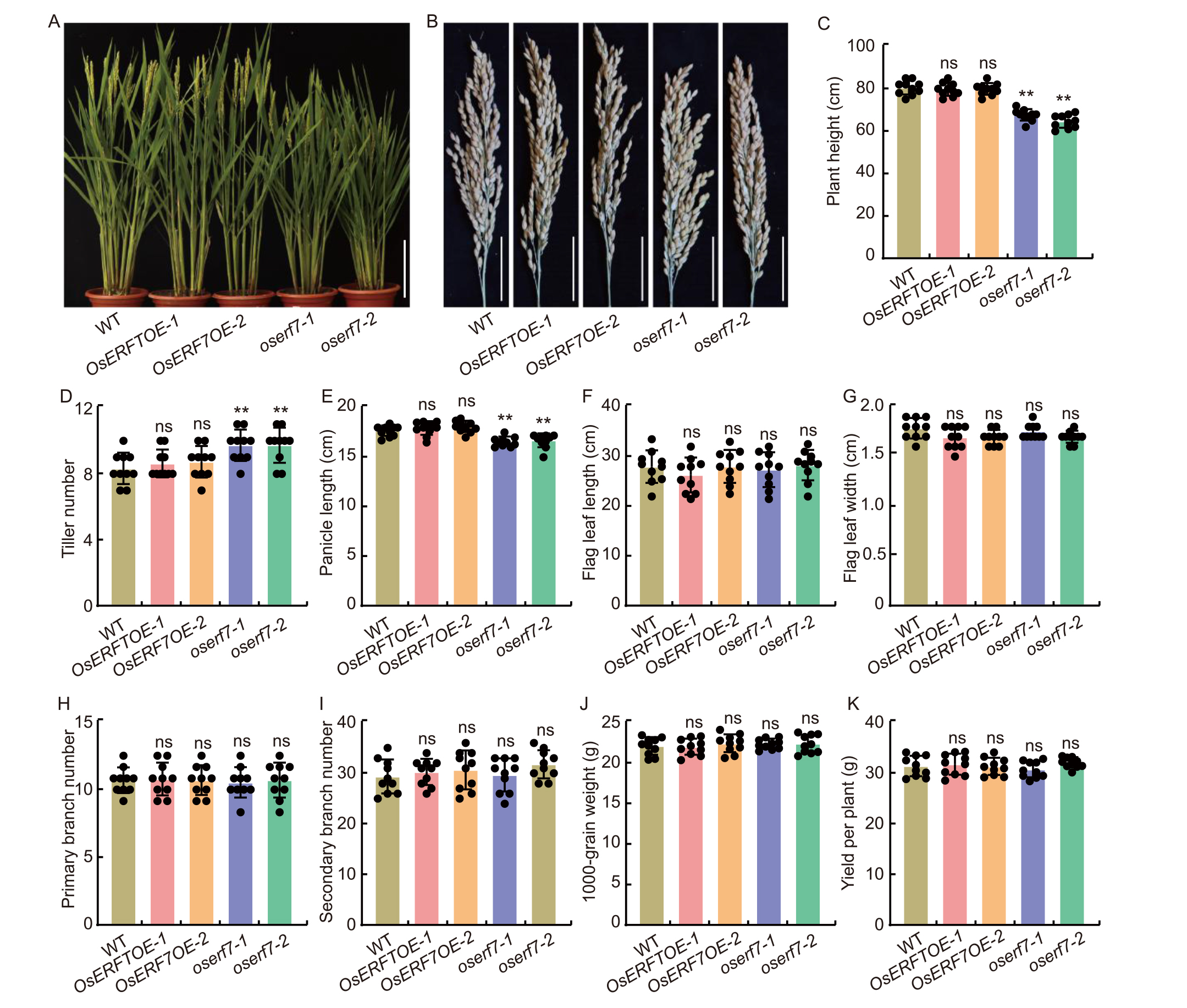
Fig. 6. Agronomic traits of wild type (WT), OsERF7 overexpression lines (OsERF7OE-1 and OsERF7OE-2), and knock out (oserf7-1 and oserf7-2) mutants. A and B, Whole plant morphology (A) and panicle morphology (B). Scale bar, 20 cm in A and 5 cm in B. C-K, Statistical analysis of plant height (C), tiller number (D), panicle length (E), flag leaf length (F), flag leaf width (G), primary branch number (H), secondary branch number (I), 1000-grain weight (J), and yield per plant (K) in WT, OsERF7OE (OsERF7OE-1 and OsERF7OE-2), and oserf7 (oserf7-1 and oserf7-2) plants. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 10). ** indicates significant difference at P < 0.01 determined by one-tailed Student’s t-test. ns, Not significant.
| [1] | Ahuja I, Kissen R, Bones A M. 2012. Phytoalexins in defense against pathogens. Trends Plant Sci, 17(2): 73-90. |
| [2] | Bera S, Purkayastha R P. 1999. Multicomponent coordinated defence response of rice to Rhizoctonia solani causing sheath blight. Curr Sci, 76(10): 1376-1384. |
| [3] | Bian S Q, Li Z, Song S J, et al. 2024. Enhancing crop resilience: Insights from labdane-related diterpenoid phytoalexin research in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Curr Issues Mol Biol, 46(9): 10677-10695. |
| [4] | Cao W L, Zhang H M, Zhou Y, et al. 2022. Suppressing chlorophyll degradation by silencing OsNYC3 improves rice resistance to Rhizoctonia solani, the causal agent of sheath blight. Plant Biotechnol J, 20(2): 335-349. |
| [5] | Chen X J, Chen Y, Zhang L N, et al. 2016. Overexpression of OsPGIP1 enhances rice resistance to sheath blight. Plant Dis, 100(2): 388-395. |
| [6] | Cheng H T, Liu H B, Deng Y, et al. 2015. The WRKY45-2 WRKY13 WRKY42 transcriptional regulatory cascade is required for rice resistance to fungal pathogen. Plant Physiol, 167(3): 1087-1099. |
| [7] | Gao Y, Xue C Y, Liu J M, et al. 2021. Sheath blight resistance in rice is negatively regulated by WRKY53 via SWEET2a activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 585: 117-123. |
| [8] | Guo J P, Xu C X, Wu D, et al. 2018. Bph6 encodes an exocyst-localized protein and confers broad resistance to planthoppers in rice. Nat Genet, 50(2): 297-306. |
| [9] | Hasegawa M, Mitsuhara I, Seo S, et al. 2010. Phytoalexin accumulation in the interaction between rice and the blast fungus. Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 23(8): 1000-1011. |
| [10] | Hong Y B, Wang H, Gao Y Z, et al. 2022. ERF transcription factor OsBIERF3 positively contributes to immunity against fungal and bacterial diseases but negatively regulates cold tolerance in rice. Int J Mol Sci, 23(2): 606. |
| [11] | Karmakar S, Molla K A, Chanda P K, et al. 2016. Green tissue-specific co-expression of chitinase and oxalate oxidase 4 genes in rice for enhanced resistance against sheath blight. Planta, 243(1): 115-130. |
| [12] | Karmakar S, Molla K A, Das K, et al. 2017. Dual gene expression cassette is superior than single gene cassette for enhancing sheath blight tolerance in transgenic rice. Sci Rep, 7(1): 7900. |
| [13] | Karmakar S, Datta K, Molla K A, et al. 2019. Proteo-metabolomic investigation of transgenic rice unravels metabolic alterations and accumulation of novel proteins potentially involved in defence against Rhizoctonia solani. Sci Rep, 9(1): 10461. |
| [14] | Koga J, Shimura M, Oshima K, et al. 1995. Phytocassanes A, B, C and D, novel diterpene phytoalexins from rice, Oryza sativa L. Tetrahedron, 51: 7907-7918. |
| [15] | Kumar V, Chaudhary P, Prasad A, et al. 2023. Jasmonic acid limits Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA infection in rice by modulating reactive oxygen species homeostasis. Plant Physiol Biochem, 196: 520-530. |
| [16] | Li D Y, Li S, Wei S H, et al. 2021.Strategies to manage rice sheath blight: Lessons from interactions between rice and Rhizoctonia solani. Rice, 14(1): 21. |
| [17] | Li N, Wei S T, Chen J, et al. 2018. OsASR2 regulates the expression of a defence-related gene, Os2H16, by targeting the GT-1 cis-element. Plant Biotechnol J, 16(3): 771-783. |
| [18] | Liang X F, Moomaw E W, Rollins J A. 2015. Fungal oxalate decarboxylase activity contributes to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum early infection by affecting both compound appressoria development and function. Mol Plant Pathol, 16(8): 825-836. |
| [19] | Lin Y J, Zhang Q F. 2005. Optimising the tissue culture conditions for high efficiency transformation of indica rice. Plant Cell Rep, 23(8): 540-547. |
| [20] | Liu D F, Chen X J, Liu J Q, et al. 2012. The rice ERF transcription factor OsERF922 negatively regulates resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae and salt tolerance. J Exp Bot, 63(10): 3899-3911. |
| [21] | Liu J, Tang D Z. 2023. Plant immunity research in China. Phytopathol Res, 5(1): 37. |
| [22] | Liu J Z, Shen Y T, Cao H X, et al. 2022. OsbHLH057 targets the AATCA cis-element to regulate disease resistance and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Cell Rep, 41(5): 1285-1299. |
| [23] | Lu X, Zhang J, Brown B, et al. 2018. Inferring roles in defense from metabolic allocation of rice diterpenoids. Plant Cell, 30(5): 1119-1131. |
| [24] | Ma Z M, Hu L J, Jiang W Z. 2024. Understanding AP2/ERF transcription factor responses and tolerance to various abiotic stresses in plants: A comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci, 25(2): 893. |
| [25] | Molla K A, Karmakar S, Chanda P K, et al. 2013. Rice oxalate oxidase gene driven by green tissue-specific promoter increases tolerance to sheath blight pathogen (Rhizoctonia solani) in transgenic rice. Mol Plant Pathol, 14(9): 910-922. |
| [26] | Molla K A, Karmakar S, Chanda P K, et al. 2016. Tissue-specific expression of Arabidopsis NPR1 gene in rice for sheath blight resistance without compromising phenotypic cost. Plant Sci, 250: 105-114. |
| [27] | Molla K A, Karmakar S, Molla J, et al. 2020. Understanding sheath blight resistance in rice: The road behind and the road ahead. Plant Biotechnol J, 18(4): 895-915. |
| [28] | Park H L, Yoo Y, Hahn T R, et al. 2014. Antimicrobial activity of UV-induced phenylamides from rice leaves. Molecules, 19(11): 18139-18151. |
| [29] | Park S, Moon J C, Park Y C, et al. 2014. Molecular dissection of the response of a rice leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase (LRR-RLK) gene to abiotic stresses. J Plant Physiol, 171(17): 1645-1653. |
| [30] | Peng X X, Hu Y J, Tang X K, et al. 2012. Constitutive expression of rice WRKY30 gene increases the endogenous jasmonic acid accumulation, PR gene expression and resistance to fungal pathogens in rice. Planta, 236(5): 1485-1498. |
| [31] | Peng X X, Wang H H, Jang J C, et al. 2016. OsWRKY80-OsWRKY 4 module as a positive regulatory circuit in rice resistance against Rhizoctonia solani. Rice, 9(1): 63. |
| [32] | Qu S H, Liu G F, Zhou B, et al. 2006. The broad-spectrum blast resistance gene Pi9 encodes a nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of a multigene family in rice. Genetics, 172(3): 1901-1914. |
| [33] | Sayari M, Babaeizad V, Ghanbari M, et al. 2014. Expression of the pathogenesis related proteins, NH-1, PAL, and lipoxygenase in the Iranian Tarom and Khazar rice cultivars, in reaction to Rhizoctonia solani: The causal agent of rice sheath blight. J Plant Prot Res, 54(1): 36-43. |
| [34] | Tan J Y, Zhang X B, Shang H H, et al. 2023. ORYZA SATIVA SPOTTED-LEAF 41 (OsSPL41) negatively regulates plant immunity in rice. Rice Sci, 30(5): 426-436. |
| [35] | Tezuka D, Kawamata A, Kato H, et al. 2019. The rice ethylene response factor OsERF 83 positively regulates disease resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant Physiol Biochem, 135: 263-271. |
| [36] | Wang A J, Shu X Y, Jing X, et al. 2021. Identification of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genes involved in sheath blight resistance via a genome-wide association study. Plant Biotechnol J, 19(8): 1553-1566. |
| [37] | Wang F J, Wang C L, Liu P Q, et al. 2016. Enhanced rice blast resistance by CRISPR/Cas9-targeted mutagenesis of the ERF transcription factor gene OsERF922. PLoS One, 11(4): e0154027. |
| [38] | Wang L P, Fu J Y, Shen Q Q, et al. 2023. OsWRKY10 extensively activates multiple rice diterpenoid phytoalexin biosynthesis genes to enhance rice blast resistance. Plant J, 115(3): 758-771. |
| [39] | Wang Q, Hillwig M L, Wu Y S, et al. 2012. CYP701A8: A rice ent-kaurene oxidase paralog diverted to more specialized diterpenoid metabolism. Plant Physiol, 158(3): 1418-1425. |
| [40] | Wu L J, Han C, Wang H M, et al. 2024. OsbZIP53 negatively regulates immunity response by involving in reactive oxygen species and salicylic acid metabolism in rice. Rice Sci, 31(2): 190-202. |
| [41] | Xie W, Ding C Q, Hu H T, et al. 2022. Molecular events of rice AP2/ERF transcription factors. Int J Mol Sci, 23(19): 12013. |
| [42] | Xie W Y, Ke Y G, Cao J B, et al. 2021. Knock out of transcription factor WRKY53 thickens sclerenchyma cell walls, confers bacterial blight resistance. Plant Physiol, 187(3): 1746-1761. |
| [43] | Xie W Y, Cao W L, Lu S B, et al. 2023. Knockout of transcription factor OsERF65 enhances ROS scavenging ability and confers resistance to rice sheath blight. Mol Plant Pathol, 24(12): 1535-1551. |
| [44] | Xue X, Cao Z X, Zhang X T, et al. 2016. Overexpression of OsOSM1 enhances resistance to rice sheath blight. Plant Dis, 100(8): 1634-1642. |
| [45] | Yamamura C, Mizutani E, Okada K, et al. 2015. Diterpenoid phytoalexin factor, a bHLH transcription factor, plays a central role in the biosynthesis of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice. Plant J, 84(6): 1100-1113. |
| [46] | Yang C, Li W, Cao J D, et al. 2017. Activation of ethylene signaling pathways enhances disease resistance by regulating ROS and phytoalexin production in rice. Plant J, 89(2): 338-353. |
| [47] | Yu J, Chai C Y, Ai G, et al. 2020. A Nicotiana benthamiana AP2/ERF transcription factor confers resistance to Phytophthora parasitica. Phytopathol Res, 2: 4. |
| [48] | Yuan D P, Xu X F, Hong W J, et al. 2020. Transcriptome analysis of rice leaves in response to Rhizoctonia solani infection and reveals a novel regulatory mechanism. Plant Biotechnol Rep, 14(5): 559-573. |
| [49] | Zhao X S, Zhang T B, Feng H J, et al. 2021. OsNBL1, a multi- organelle localized protein, plays essential roles in rice senescence, disease resistance, and salt tolerance. Rice, 14(1): 10. |
| [50] | Zuo S M, Yin Y J, Pan C H, et al. 2013. Fine mapping of qSB-11LE, the QTL that confers partial resistance to rice sheath blight. Theor Appl Genet, 126(5): 1257-1272. |
| [1] | Chen Su, Ma Feilong, Chen Jiaoyang, Qi Man, Wei Qianshu, Tao Zhihuan, Sun Bo. Function of R2R3-Type Myeloblastosis Transcription Factors in Plants [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(3): 307-321. |
| [2] | Yang Yajun, Lu Yanhui, Tian Junce, Zheng Xusong, Guo Jiawen, Liu Xiaowei, Lü Zhongxian, Xu Hongxing. Sustainable Management Strategies for Rice Leaffolder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Guenée): Progress and Prospects [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(3): 322-338. |
| [3] | Chaemyeong Lim, Sae Hyun Lee, Haeun Lee, So-Yon Park, Kiyoon Kang, Hyeryung Yoon, Tae-Jin Yang, Gary Stacey, Nam-Chon Paek, Sung-Hwan Cho. Global Transcriptome Analysis of Rice Seedlings in Response to Extracellular ATP [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(3): 380-399. |
| [4] | Zeng Deyong, Cui Jie, Yin Yishu, Dai Cuihong, Yu Wencheng, Zhao Haitian, Guan Shuanghong, Cheng Dayou, Sun Yeqing, Lu Weihong. Generational Genetic Mechanism of Space Mutagenesis in Rice Based on Multi-Omics [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(3): 400-425. |
| [5] | Sanchika Snehi, Ravi Kiran Kt, Sanket Rathi, Sameer Upadhyay, Suneetha Kota, Satish Kumar Sanwal, Lokeshkumar Bm, Arun Balasubramaniam, Nitish Ranjan Prakash, Pawan Kumar Singh. Discerning Genes to Deliver Varieties: Enhancing Vegetative- and Reproductive-Stage Flooding Tolerance in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(2): 160-176. |
| [6] | Nie Lixiao, Guo Xiayu, Wang Weiqin, Qi Yucheng, Ai Zhiyong, He Aibin. Regulation of Regeneration Rate to Enhance Ratoon Rice Production [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(2): 177-192. |
| [7] | Wang Shuman, Zhang Linqi, Gao Ruiren, Wei Guangbo, Dong Weiguo, Xu Jiming, Wang Zhiye. Establishing Programmable CRISPR/Cas13b-Mediated Knockdown System in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(2): 217-227. |
| [8] | Uthpal Krishna Roy, Babita Pal, Soumen Bhattacharjee. A Novel Approach for Screening Salinity-Tolerant Rice Germplasm by Exploring Redox-Regulated Cytological Fingerprint [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(2): 228-242. |
| [9] | He Zhenrui, Zhao Wenhua, Cheng Baoping, Yang Mei, Yang Yingqing, Zhu Yiming, Zhou Erxun. Molecular and Biological Characterization of Novel Mitovirus Infecting Phytopathogenic Fungus Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(2): 243-258. |
| [10] | He Chen, Ruan Yunze, Jia Zhongjun. A Meta-Analysis of 30 Years in China and Micro-District Experiments Shows Organic Fertilizer Quantification Combined with Chemical Fertilizer Reduction Enhances Rice Yield on Saline-Alkali Land [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(2): 259-272. |
| [11] | Xu Liting, He Kaiwei, Guo Chunyu, Quan Cantao, Ma Yahuan, Zhang Wei, Ren Lifen, Wang Long, Song Li, Ouyang Qing, Yin Junjie, Zhu Xiaobo, Tang Yongyan, He Min, Chen Xuewei, Li Weitao. Spireoside Controls Blast Disease by Disrupting Membrane Integrity of Magnaporthe oryzae [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(1): 107-117. |
| [12] | Wang Mingyue, Zhao Weibo, Feng Xiaoya, Chen Yi, Li Junhao, Fu Jinmei, Yan Yingchun, Chu Zhaohui, Huang Wenchao. Disruption of Energy Metabolism and Reactive Oxygen Species Homeostasis in Honglian Type-Cytoplasmic Male Sterility (HL-CMS) Rice Pollen [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(1): 81-93. |
| [13] | Intan Farahanah, Shariza Sahudin, Hannis Fadzillah Mohsin, Siti Alwani Ariffin, Liyana Dhamirah Aminuddin. Understanding Investigational Perspective of Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(1): 15-31. |
| [14] | Jeberlin Prabina Bright, Hemant S. Maheshwari, Sugitha Thangappan, Kahkashan Perveen, Najat A. Bukhari, Debasis Mitra, Riyaz Sayyed, Andrea Mastinu. Biofilmed-PGPR: Next-Generation Bioinoculant for Plant Growth Promotion in Rice under Changing Climate [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(1): 94-106. |
| [15] | Wang Haoran, Chen Guoqing, Feng Guozhong. Expanding Viral Diversity in Rice Fields by Next-Generation Sequencing [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(1): 44-51. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||