
Rice Science ›› 2026, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 129-140.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2025.08.006
• Research Papers • Previous Articles
Zhu Junlin, Zheng Guangjie, Tao Yi, Liao Wenli, Ye Chang, Xu Ya’nan, Xiao Deshun, Chu Guang, Xu Chunmei, Wang Danying( )
)
Received:2025-04-17
Accepted:2025-08-09
Online:2026-01-28
Published:2026-02-03
Contact:
Wang Danying (About author:First author contact:# These authors contributed equally to this work
Zhu Junlin, Zheng Guangjie, Tao Yi, Liao Wenli, Ye Chang, Xu Ya’nan, Xiao Deshun, Chu Guang, Xu Chunmei, Wang Danying. Wood Vinegar Enhances Seedling Rate of Rice Seeds under Flooding Stress by Mitigating Oxidative Damage and Maintaining Energy Homeostasis[J]. Rice Science, 2026, 33(1): 129-140.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
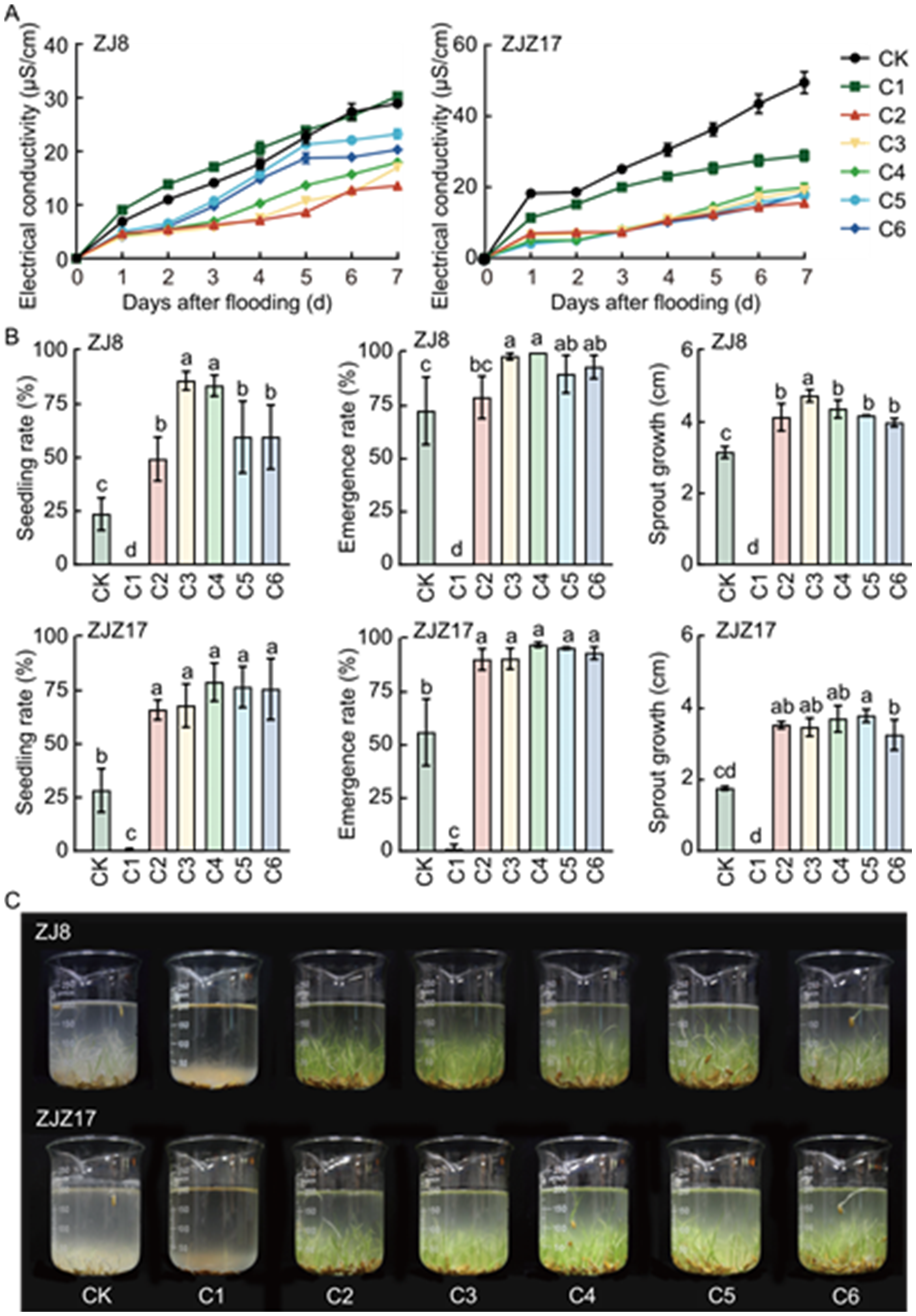
Fig. 1. Changes of water electrical conductivity (A), agronomic traits (B), and plant phenotype (C) under different wood vinegar soaking treatments. ZJ8, Zhongjia 8; ZJZ17, Zhongjiazao 17; CK, Control group (pure water); C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, and C6 were seeds soaked with wood vinegar dilutions of 25-, 50-, 75-, 100-, 125-, and 150-fold, respectively. In B, data are mean ± SD (n = 3). Different lowercase letters above bars indicate significant differences at P < 0.05 by the Duncan’s test.
| Cultivar type | Cultivar | Seedling rate (%) | Sprout growth (cm) | Dry matter accumulation (mg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | C4 treatment | Control | C4 treatment | Control | C4 treatment | |||||
| Inbred indica rice | Zhongzao 48 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 75.67 ± 4.16** | - | 3.04 ± 0.07 | - | 5.38 ± 0.41 | |||
| Zhongzao 39 | 1.33 ± 1.54 | 81.67 ± 9.50** | 1.23 ± 0.06 | 3.53 ± 0.07** | - | 8.91 ± 0.34 | ||||
| Yangdao 6 | 3.00 ± 2.65 | 88.67 ± 4.16** | 2.62 ± 0.08 | 3.93 ± 0.02** | - | 12.20 ± 0.53 | ||||
| Zhe 1708 | 31.67 ± 7.09 | 95.66 ± 2.52** | 2.41 ± 0.10 | 3.74 ± 0.21** | 6.53 ± 0.57 | 10.76 ± 0.76** | ||||
| Inbred japonica rice | Jia 58 | 98.67 ± 1.53 | 99.67 ± 0.58 | 4.73 ± 0.02 | 4.97 ± 0.06** | 13.80 ± 0.20 | 15.67 ± 0.15** | |||
| Zhejing 96 | 88.33 ± 2.31 | 92.00 ± 2.65 | 3.64 ± 0.15 | 4.64 ± 0.30** | 10.41 ± 0.44 | 12.13 ± 0.84* | ||||
| Zhejing 99 | 35.67 ± 7.50 | 100.00 ± 0.00** | 1.54 ± 0.03 | 4.27 ± 0.18** | 5.60 ± 0.44 | 11.00 ± 0.79** | ||||
| Jia 67 | 95.33 ± 2.89 | 97.33 ± 1.53 | 3.94 ± 0.27 | 5.40 ± 0.44** | 11.17 ± 0.47 | 12.30 ± 0.17* | ||||
| Indica-japonica hybrid rice | Yongyou 1540 | 25.00 ± 16.46 | 99.67 ± 0.58** | 2.68 ± 0.05 | 2.81 ± 0.07** | 7.07 ± 0.15 | 7.67 ± 0.21* | |||
| Yongyou 15 | 3.00 ± 1.73 | 90.67 ± 10.21** | 1.78 ± 0.08 | 3.72 ± 0.48** | - | 8.86 ± 0.57 | ||||
| Zhehangyou 220 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 70.67 ± 2.08** | - | 3.54 ± 0.12 | - | 5.83 ± 0.32 | ||||
| Chunyou 83 | 59.33 ± 8.08 | 90.67 ± 6.51** | 3.01 ± 0.19 | 4.30 ± 0.13** | 9.96 ± 0.60 | 12.03 ± 0.64* | ||||
Table 1. Effect of 100-fold diluted wood vinegar on agronomic characters of rice.
| Cultivar type | Cultivar | Seedling rate (%) | Sprout growth (cm) | Dry matter accumulation (mg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | C4 treatment | Control | C4 treatment | Control | C4 treatment | |||||
| Inbred indica rice | Zhongzao 48 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 75.67 ± 4.16** | - | 3.04 ± 0.07 | - | 5.38 ± 0.41 | |||
| Zhongzao 39 | 1.33 ± 1.54 | 81.67 ± 9.50** | 1.23 ± 0.06 | 3.53 ± 0.07** | - | 8.91 ± 0.34 | ||||
| Yangdao 6 | 3.00 ± 2.65 | 88.67 ± 4.16** | 2.62 ± 0.08 | 3.93 ± 0.02** | - | 12.20 ± 0.53 | ||||
| Zhe 1708 | 31.67 ± 7.09 | 95.66 ± 2.52** | 2.41 ± 0.10 | 3.74 ± 0.21** | 6.53 ± 0.57 | 10.76 ± 0.76** | ||||
| Inbred japonica rice | Jia 58 | 98.67 ± 1.53 | 99.67 ± 0.58 | 4.73 ± 0.02 | 4.97 ± 0.06** | 13.80 ± 0.20 | 15.67 ± 0.15** | |||
| Zhejing 96 | 88.33 ± 2.31 | 92.00 ± 2.65 | 3.64 ± 0.15 | 4.64 ± 0.30** | 10.41 ± 0.44 | 12.13 ± 0.84* | ||||
| Zhejing 99 | 35.67 ± 7.50 | 100.00 ± 0.00** | 1.54 ± 0.03 | 4.27 ± 0.18** | 5.60 ± 0.44 | 11.00 ± 0.79** | ||||
| Jia 67 | 95.33 ± 2.89 | 97.33 ± 1.53 | 3.94 ± 0.27 | 5.40 ± 0.44** | 11.17 ± 0.47 | 12.30 ± 0.17* | ||||
| Indica-japonica hybrid rice | Yongyou 1540 | 25.00 ± 16.46 | 99.67 ± 0.58** | 2.68 ± 0.05 | 2.81 ± 0.07** | 7.07 ± 0.15 | 7.67 ± 0.21* | |||
| Yongyou 15 | 3.00 ± 1.73 | 90.67 ± 10.21** | 1.78 ± 0.08 | 3.72 ± 0.48** | - | 8.86 ± 0.57 | ||||
| Zhehangyou 220 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 70.67 ± 2.08** | - | 3.54 ± 0.12 | - | 5.83 ± 0.32 | ||||
| Chunyou 83 | 59.33 ± 8.08 | 90.67 ± 6.51** | 3.01 ± 0.19 | 4.30 ± 0.13** | 9.96 ± 0.60 | 12.03 ± 0.64* | ||||
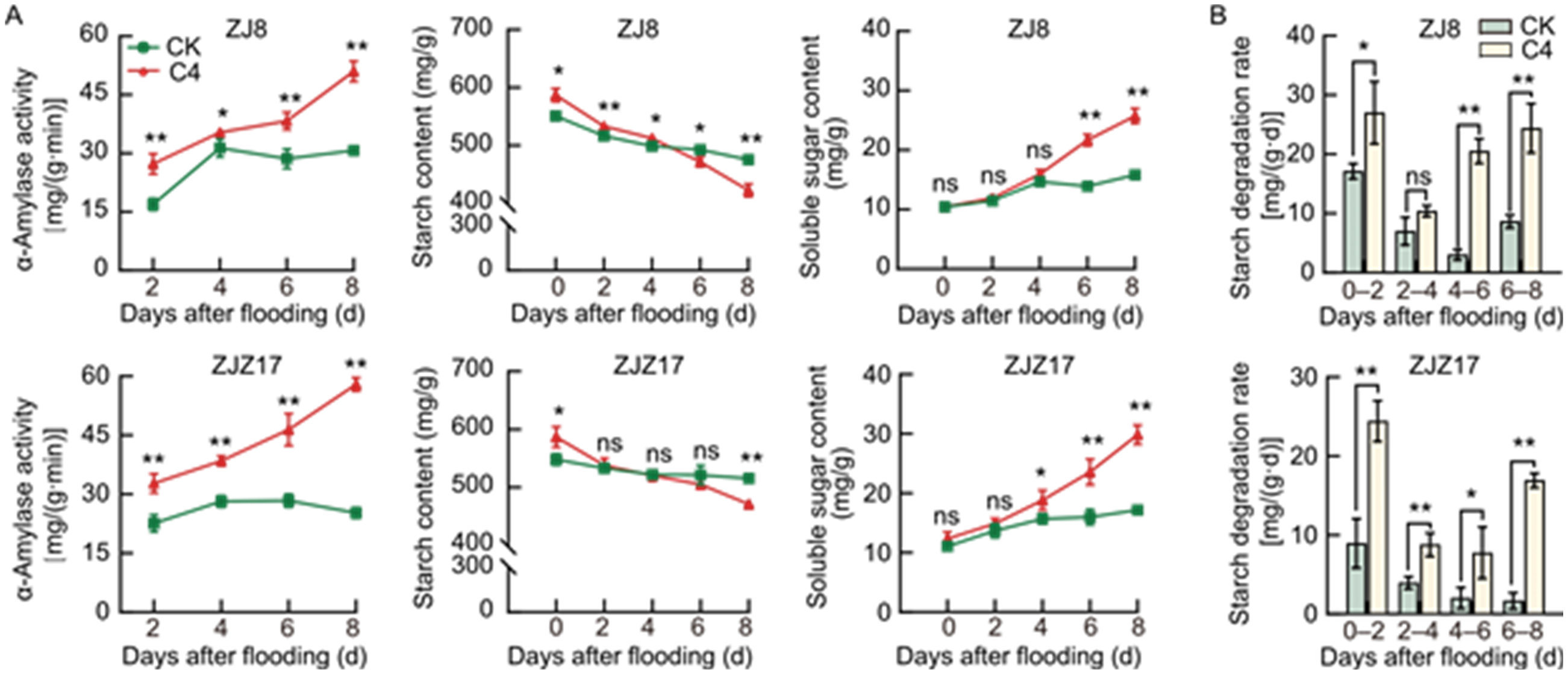
Fig. 2. Effects of wood vinegar soaking on α-amylase activity, starch and soluble sugar contents in seeds (A) and seed starch degradation rate (B) under flooding stress. ZJ8, Zhongjia 8; ZJZ17, Zhongjiazao 17. CK, Control group (pure water); C4, 100-fold diluted wood vinegar solution. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). * and ** represent significant differences at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels by the Duncan’s test. ns, No significance.
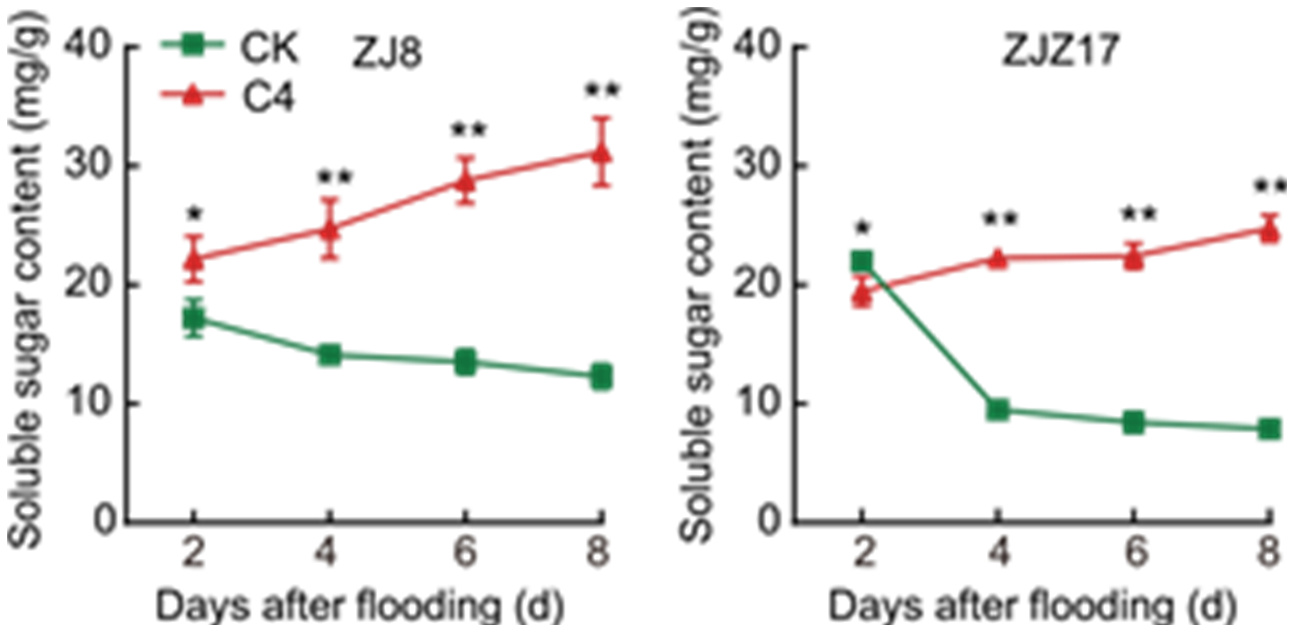
Fig. 3. Effects of wood vinegar soaking on soluble sugar content in sprouts under flooding stress. ZJ8, Zhongjia 8; ZJZ17, Zhongjiazao 17; CK, Control group (pure water); C4, 100-fold diluted wood vinegar solution. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). * and ** represent significant differences at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels by the Duncan’s test.
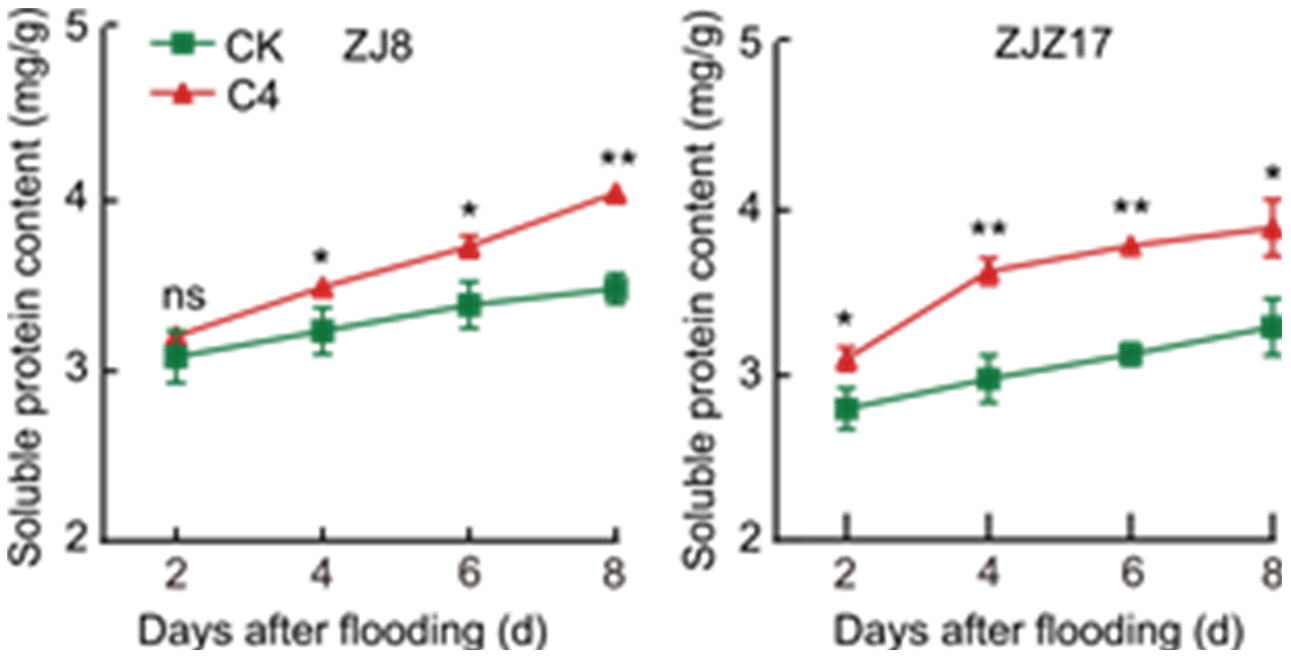
Fig. 4. Effects of wood vinegar soaking on soluble protein content in sprouts under flooding stress. ZJ8, Zhongjia 8; ZJZ17, Zhongjiazao 17; CK, Control group (pure water); C4, 100-fold diluted wood vinegar solution. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). * and ** represent significant differences at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels by the Duncan’s test. ns, No significance.
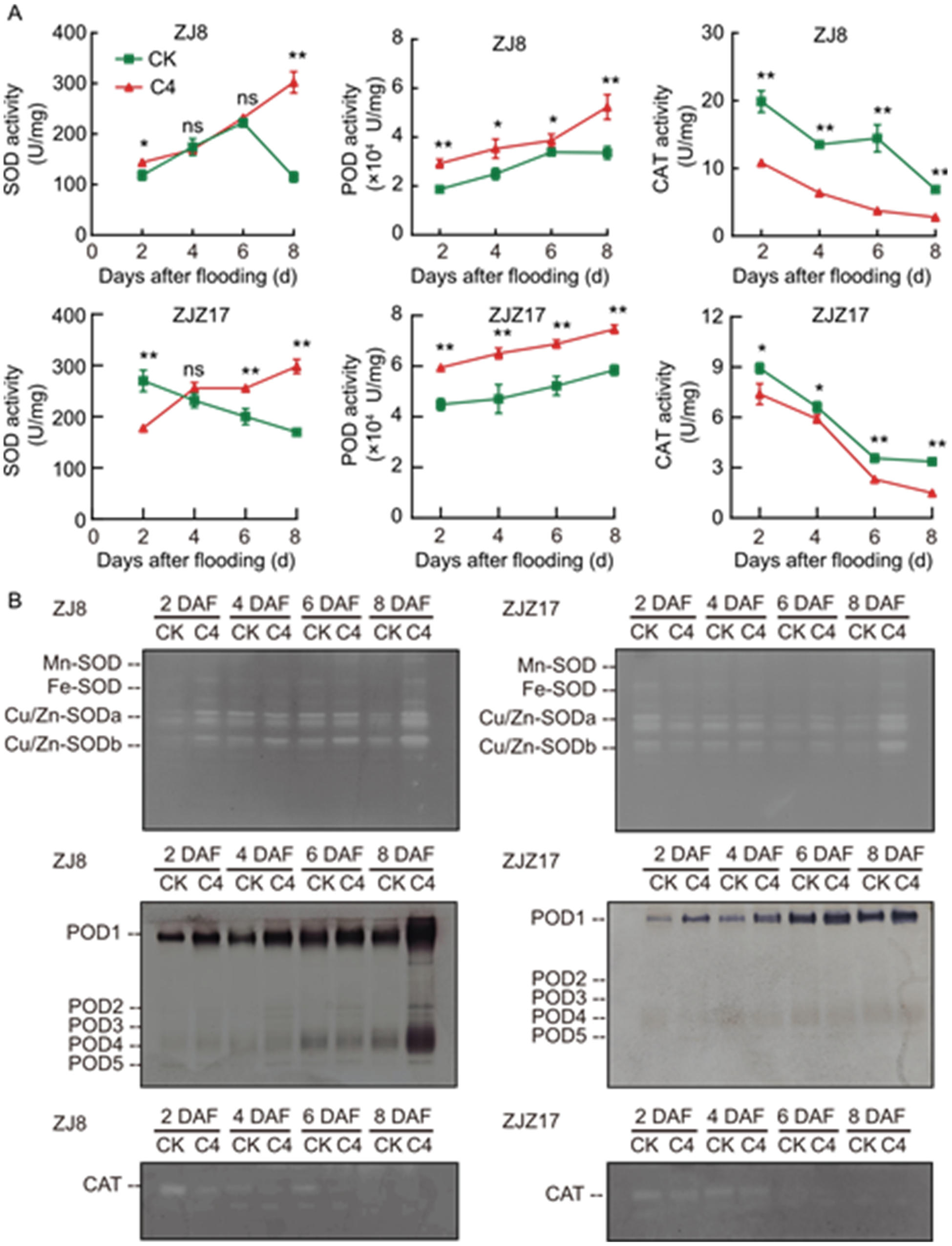
Fig. 5. Effects of seed soaking with wood vinegar on antioxidant enzyme activity (A) and isoenzyme of antioxidant enzyme (B) in sprouts under flooding stress. DAF, Days after flooding. ZJ8, Zhongjia 8; ZJZ17, Zhongjiazao 17; SOD, Superoxide dismutase; POD, Peroxidase; CAT, Catalase. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). * and ** represent significant differences at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels by the Duncan’s test. ns, No significance.
| Variety | Parameter | SR | EC | SG | SOD | POD | CAT | SP | α-Amy | Sta | SS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZJ8 | EC | -0.970** | |||||||||
| SG | 0.969** | -0.968** | |||||||||
| SOD | 0.962** | -0.996** | 0.953** | ||||||||
| POD | 0.929** | -0.927** | 0.907* | 0.893* | |||||||
| CAT | -0.986** | 0.983** | -0.972** | -0.968** | -0.958** | ||||||
| SP | 0.947** | -0.970** | 0.903* | 0.965** | 0.938** | -0.949** | |||||
| α-Amy | 0.953** | -0.993** | 0.942** | 0.995** | 0.902* | -0.973** | 0.958** | ||||
| Sta | -0.918** | 0.982** | -0.940** | -0.987** | -0.851* | 0.941** | -0.924** | -0.987** | |||
| SS | 0.991** | -0.980** | 0.974** | 0.968** | 0.950** | -0.984** | 0.968** | 0.955** | -0.928** | ||
| DS | 0.985** | -0.995** | 0.961** | 0.991** | 0.939** | -0.990** | 0.978** | 0.988** | -0.962** | 0.988** | |
| ZJZ17 | EC | -0.964** | |||||||||
| SG | 0.934** | -0.962** | |||||||||
| SOD | 0.948** | -0.980** | 0.983** | ||||||||
| POD | 0.932** | -0.967** | 0.954** | 0.992** | |||||||
| CAT | -0.943** | 0.993** | -0.979** | -0.989** | -0.972** | ||||||
| SP | 0.833* | -0.910* | 0.934** | 0.945** | 0.924** | -0.950** | |||||
| α-Amy | 0.960** | -0.991** | 0.987** | 0.989** | 0.971** | -0.992** | 0.914* | ||||
| Sta | -0.939** | 0.983** | -0.944** | -0.960** | -0.958** | 0.968** | -0.850* | -0.982** | |||
| SS | 0.933** | -0.969** | 0.993** | 0.979** | 0.958** | -0.977** | 0.905* | 0.993** | -0.970** | ||
| DS | 0.933** | -0.952** | 0.995** | 0.978** | 0.954** | -0.964** | 0.902* | 0.984** | -0.949** | 0.995** |
Table 2. Correlation between seedling rate and physiological and biochemical indexes of seed soaked with wood vinegar under flooding stress.
| Variety | Parameter | SR | EC | SG | SOD | POD | CAT | SP | α-Amy | Sta | SS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZJ8 | EC | -0.970** | |||||||||
| SG | 0.969** | -0.968** | |||||||||
| SOD | 0.962** | -0.996** | 0.953** | ||||||||
| POD | 0.929** | -0.927** | 0.907* | 0.893* | |||||||
| CAT | -0.986** | 0.983** | -0.972** | -0.968** | -0.958** | ||||||
| SP | 0.947** | -0.970** | 0.903* | 0.965** | 0.938** | -0.949** | |||||
| α-Amy | 0.953** | -0.993** | 0.942** | 0.995** | 0.902* | -0.973** | 0.958** | ||||
| Sta | -0.918** | 0.982** | -0.940** | -0.987** | -0.851* | 0.941** | -0.924** | -0.987** | |||
| SS | 0.991** | -0.980** | 0.974** | 0.968** | 0.950** | -0.984** | 0.968** | 0.955** | -0.928** | ||
| DS | 0.985** | -0.995** | 0.961** | 0.991** | 0.939** | -0.990** | 0.978** | 0.988** | -0.962** | 0.988** | |
| ZJZ17 | EC | -0.964** | |||||||||
| SG | 0.934** | -0.962** | |||||||||
| SOD | 0.948** | -0.980** | 0.983** | ||||||||
| POD | 0.932** | -0.967** | 0.954** | 0.992** | |||||||
| CAT | -0.943** | 0.993** | -0.979** | -0.989** | -0.972** | ||||||
| SP | 0.833* | -0.910* | 0.934** | 0.945** | 0.924** | -0.950** | |||||
| α-Amy | 0.960** | -0.991** | 0.987** | 0.989** | 0.971** | -0.992** | 0.914* | ||||
| Sta | -0.939** | 0.983** | -0.944** | -0.960** | -0.958** | 0.968** | -0.850* | -0.982** | |||
| SS | 0.933** | -0.969** | 0.993** | 0.979** | 0.958** | -0.977** | 0.905* | 0.993** | -0.970** | ||
| DS | 0.933** | -0.952** | 0.995** | 0.978** | 0.954** | -0.964** | 0.902* | 0.984** | -0.949** | 0.995** |
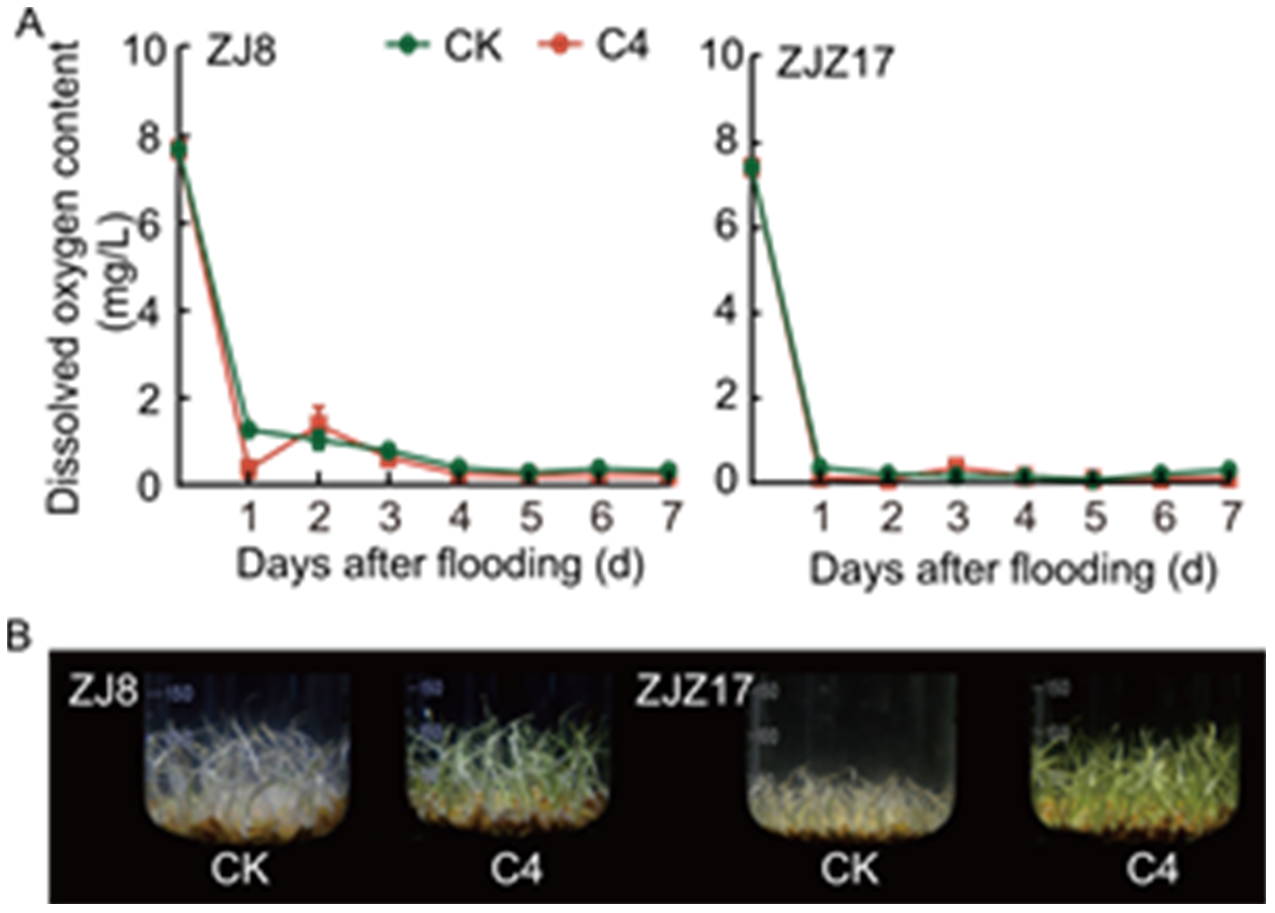
Fig. 6. Changes of dissolved oxygen content (A) and morphological difference after 3 d of flooding (B) under flooding stress. ZJ8, Zhongjia 8; ZJZ17, Zhongjiazao 17; CK, Control group (pure water); C4, 100-fold diluted wood vinegar solution. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3).
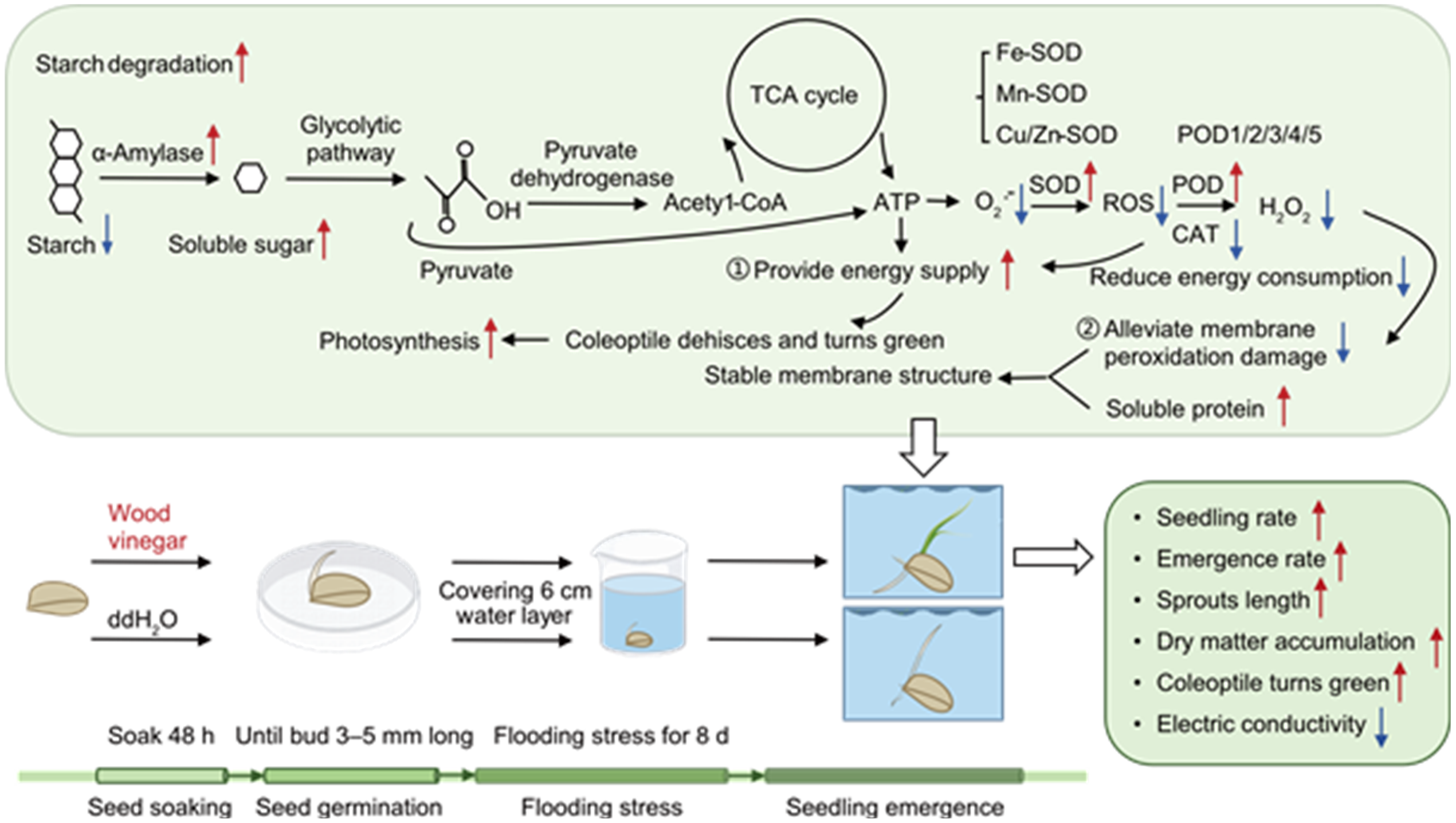
Fig. 7. Schematic diagram of wood vinegar soaking rice seeds to alleviate flooding stress and promote seedling emergence. ATP, Adenosine triphosphate; O2·̄, Superoxide anion; SOD, Superoxide dismutase; POD, Peroxidase; CAT, Catalase; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; TCA, Trichloroacetic acid.
| [1] | Asada K. 2006. Production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in chloroplasts and their functions. Plant Physiol, 141(2): 391-396. |
| [2] | Chang Q, Wang Y L, Zhang Q, et al. 2018. Promoting effect of wood vinegar on germination of eggplant seed. J Shanxi Agric Sci, 46(8): 1269-1273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Chang R, Jang C J H, Branco-Price C, et al. 2012. Transient MPK6 activation in response to oxygen deprivation and reoxygenation is mediated by mitochondria and aids seedling survival in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol, 78(1/2): 109-122. |
| [4] | Chapman J M, Muhlemann J K, Gayomba S R, et al. 2019. RBOH-dependent ROS synthesis and ROS scavenging by plant specialized metabolites to modulate plant development and stress responses. Chem Res Toxicol, 32(3): 370-396. |
| [5] | Chen D, Li Q, Peng Y, et al. 2019. Effect of melatonin on rice seedling growth under submergence stress. Acta Agricul Bor-Sin, 34(3): 129-136. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Das A, Uchimiya H. 2002. Oxygen stress and adaptation of a semi-aquatic plant: Rice (Oryza sativa). J Plant Res, 115(5): 315-320. |
| [7] | Edwards J M, Roberts T H, Atwell B J. 2012. Quantifying ATP turnover in anoxic coleoptiles of rice (Oryza sativa) demonstrates preferential allocation of energy to protein synthesis. J Exp Bot, 63(12): 4389-4402. |
| [8] | Gao J S, Zhuang S Y, Zhang Y H, et al. 2022. Exogenously applied spermidine alleviates hypoxia stress in Phyllostachys praecox seedlings via changes in endogenous hormones and gene expression. BMC Plant Biol, 22(1): 200. |
| [9] | Giannopolitis C N, Ries S K. 1977. Superoxide dismutases: I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol. 59(2): 309-314. |
| [10] | Grainge G, Nakabayashi K, Iza F, et al. 2022. Gas-plasma-activated water impact on photo-dependent dormancy mechanisms in Nicotiana tabacum seeds. Int J Mol Sci, 23(12): 6709. |
| [11] | Huang S B, Greenway H, Colmer T D. 2003. Anoxia tolerance in rice seedlings: Exogenous glucose improves growth of an anoxia-‘intolerant’, but not of a ‘tolerant’ genotype. J Exp Bot, 54: 2363-2373. |
| [12] | Huang Y B, Han J, Xia Y, et al. 2024. Effects of spraying wood vinegar on growth and physiology of Isatis indigotica at seedling stage. North Hortic, 15: 96-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Li J X, Zhao T T, Chen L, et al. 2022. Artemisia argyi allelopathy: A generalist compromises hormone balance, element absorption, and photosynthesis of receptor plants. BMC Plant Biol, 22(1): 368. |
| [14] | Li Y Y, Tian B, Wang Y, et al. 2022. The transcription factor MYB37 positively regulates photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative damage in Arabidopsis leaves under salt stress. Front Plant Sci, 13: 943153. |
| [15] | Liu L C, Min J, Liu S X, et al. 2022. Production situation and varieties breeding strategies of direct seeding rice. China Rice, 28(5): 44-48/56. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Liu Z G, Ma C Y, Hou L, et al. 2022. Exogenous SA affects rice seed germination under salt stress by regulating Na+/K+ balance and endogenous GAs and ABA homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci, 23(6): 3293. |
| [17] | Ma J Y, Islam F, Ayyaz A, et al. 2022. Wood vinegar induces salinity tolerance by alleviating oxidative damages and protecting photosystem II in rapeseed cultivars. Ind Crops Prod, 189: 115763. |
| [18] | Ma M Y, Ma H Y, Li S Y, et al. 2022. Effects of wood vinegar priming on seed germination and seedling growth of Leymus chinensis under salt stress. Chin J Ecol, 41(8): 1588-1593. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Maehly A C, Chance B. 1954. The assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods Biochem Anal, 1: 357-424. |
| [20] | Magneschi L, Perata P. 2009. Rice germination and seedling growth in the absence of oxygen. Ann Bot, 103(2): 181-196. |
| [21] | Miro B, Ismail A M. 2013. Tolerance of anaerobic conditions caused by flooding during germination and early growth in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front Plant Sci, 4: 269. |
| [22] | Panda D, Barik J. 2021. Flooding tolerance in rice: Focus on mechanisms and approaches. Rice Sci, 28(1): 43-57. |
| [23] | Pedrini S, Merritt D J, Stevens J, et al. 2017. Seed coating: Science or marketing spin? Trends Plant Sci, 22(2): 106-116. |
| [24] | Shao X W, Song F B, Wang F R, et al. 1994. The effect of different acidic water soaking seeds on seedhng quality and yield of rice. Jilin Agric Sci, 19(1): 18-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Smethurst C F, Shabala S. 2003. Screening methods for waterlogging tolerance in lucerne: Comparative analysis of waterlogging effects on chlorophyll fluorescence, photosynthesis, biomass and chlorophyll content. Funct Plant Biol, 30(3): 335-343. |
| [26] | Steffens B, Steffen-Heins A, Sauter M. 2013. Reactive oxygen species mediate growth and death in submerged plants. Front Plant Sci, 4: 179. |
| [27] | Tang X D, An B Y, Cao D M, et al. 2020. Improving photosynthetic capacity, alleviating photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress under low temperature stress with exogenous hydrogen sulfide in blueberry seedlings. Front Plant Sci, 11: 108. |
| [28] | Tang Z Q, Zhang L Y, He N, et al. 2022. Influence of planting methods and organic amendments on rice yield and bacterial communities in the rhizosphere soil. Front Microbiol, 13: 918986. |
| [29] | Wang H Y, Chen L, Ma X W, et al. 2019. Effect of wood vinegar on cold resistance of rice seedlings under low temperature stress. J Northeast Agric Univ, 50(2): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Wang S. 2023. Regulation effects of H2O2 priming on yield formation of waterlogged summer maize during the seedling stage. Tai’an, China: Shandong Agricultural University. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Wu Q M, Zhang S Y, Hou B X, et al. 2015. Study on the preparation of wood vinegar from biomass residues by carbonization process. Bioresour Technol, 179: 98-103. |
| [32] | Xu J L. 1981. Soaking rice seeds with acid solution and raising seedlings have many benefits. Jiangxi Agric Sci Technol, 6: 10-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [33] | Yu B, Yang Q W, Zhang Y H, et al. 2023. Effects of gibberellin and weak acid on seed germination and physiological characteristics of the eelgrass Zostera marina. Prog Fish Sci, 44(4): 26-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] | Zeng H L, Liu M H, Wang X, et al. 2022. Seed-soaking with melatonin for the improvement of seed germination, seedling growth, and the antioxidant defense system under flooding stress. Agronomy, 12(8): 1918. |
| [35] | Zhang C X, Fu G F, Yang X Q, et al. 2016. Heat stress effects are stronger on spikelets than on flag leaves in rice due to differences in dissipation capacity. J Agron Crop Sci, 202(5): 394-408. |
| [36] | Zhang E R, Ren Y Y, Li X H. 2012. Effect of Ca2+ on growth and carbohydrate contents of pepper seedlings under root-zone flood stress. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 28(22): 151-157. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [37] | Zhang K. 2024. Mechanism of wood vinegar and biochar to promote seed germination and plant growth of water-saving and drought-resistance rice under drought stress. Wuhan, China: Huazhong Agricultural University. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [38] | Zhang K K, Khan Z, Liu J H, et al. 2022. Germination and growth performance of water-saving and drought-resistant rice enhanced by seed treatment with wood vinegar and biochar under dry direct-seeded system. Agronomy, 12(5): 1223. |
| [39] | Zhao Q, Guan X Y, Zhou L J, et al. 2023. ABA-triggered ROS burst in rice developing anthers is critical for tapetal programmed cell death induction and heat stress-induced pollen abortion. Plant Cell Environ, 46(5): 1453-1471. |
| [40] | Zhou H Y, Shen Y, Zhang N M, et al. 2024. Wood fiber biomass pyrolysis solution as a potential tool for plant disease management: A review. Heliyon, 10(3): e25509. |
| [1] | An Shuaizu, Lü Jun, Ma Zemin, Gao Xuanlin, Zhang Biaoming, Yang Pingfang, Ke Yinggen. WRKY53: A Key Player in Stress Responses and Growth Regulation in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2026, 33(1): 30-38. |
| [2] | Huang Qina, Wu Lijuan, Jiang Hongrui, He Yan, Liu Song, Yang Changdeng, Liang Yan. NRAMPs: Versatile Transporters Involved in Metal Ion Homeostasis and Their Applications in Rice Breeding [J]. Rice Science, 2026, 33(1): 39-58. |
| [3] | Pratap Kalita, Bedanta Bhattacharjee, Bhrigu Kumar Das, Saikat Sen, Raja Chakraborty, Abdul Baquee Ahmed. Rice Bran as Nutrient-Dense Food in Gut Health and Beyond [J]. Rice Science, 2026, 33(1): 59-80. |
| [4] | Zhou Jiaren, Song Qingfeng, Li Wanwan, Zhang Mengqi, Zhang Man, Zhu Xinguang, Wang Minjuan. High Throughput 3D Phenotyping of Canopy Occupation Volume as Major Predictor of Rice Canopy Photosynthesis [J]. Rice Science, 2026, 33(1): 99-112. |
| [5] | D. Priyanga, K. Amudha, N. Sakthivel, P. Sivasakthivelan, S. Utharasu, D. Uma, M. Sudha. Functional and Nutraceutical Potential of Indian Rice Landraces: A Comprehensive Scientific Review [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(6): 777-796. |
| [6] | Fazli Hameed, Shah Fahad Rahim, Anis Ur Rehman Khalil, Ram L. Ray, Xu Junzeng, Alhaj Yousef Hamoud, Akhtar Ali, Ning Tangyuan. Comparing Genotype and Climate Change Effects on Simulated Historical Rice Yields Using AquaCrop [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(6): 845-856. |
| [7] | Hong Chen, Luo Ju, Feng Zelin, Ling Heping, Li Lingyi, Wu Jian, Yao Qing, Liu Shuhua. Intelligent Survey Method for Tiny Rice Pests and Their Natural Predators in Paddy Fields Using Augmented Reality (AR) Glasses [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(6): 868-884. |
| [8] | Daisy Wilson, Valeria Gonzalez, Hamidreza Sharifan. Evaluating Efficacy of ZnO and MgO Nanoparticles on Post-Harvested Rice to Enhance Food Security Against Agroterrorism [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(5): 717-726. |
| [9] | Mareyam Mukhtar, Amresh Kumar, Ashfak S. Mujawar, Bhuvnesh Sareen, Suhas G. Karkute, Rohini Sreevathsa, Amitha Mithra Sevanthi, Amolkumar U. Solanke. Genome-Wide Identification of Dopamine β-Monooxygenase N-Terminal Gene Family in Rice and Its Role in Response to Blast Disease and Abiotic Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(5): 685-703. |
| [10] | Li Haifeng, Fan Jiayi. Functions of Rice E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Response to Environmental Stress and in Regulating Grain Size [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(5): 649-657. |
| [11] | Wu Zhaozhong, Zhong Zhengzheng, Xu Peng, Liu Ling, Wang Beifang, Yang Qinqin, Wen Xiaoxia, Ma Guifang, Luo Mili, Zhang Yingxin, Liu Qun’en, Peng Zequn, Zhan Xiaodeng, Cao Liyong, Cheng Shihua, Wu Weixun. OsELF3.1-OsCATA-Ghd7 Pathway Regulates Rice Heading [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(5): 658-672. |
| [12] | Pan Pan, Guo Wenlong, Li Hengbo, Shao Yifan, Guo Zhihao, Jin Ye, Cheng Yanrong, Yu Guoping, Fu Zhenshi, Hu Lin, Zheng Xiaoming, Zhou Guomin, Zhang Jianhua. Accelerating Wild Rice Disease-Resistant Germplasm Exploration: Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Powered Wild Rice Blast Disease Level Evaluation and Disease-Resistance Identification [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(5): 727-746. |
| [13] | Sabarinathan Selvaraj, Parameswaran Chidambaranathan, Goutam Kumar Dash, Priyadarsini Sanghamitra, Kishor Pundlik Jeughale, Cayalvizhi Balasubramaniasai, Devraj Lenka, Basavantraya Navadagi Devanna, Seenichamy Rathinam Prabhukarthikeyan, Sanghamitra Samantaray, Amaresh Kumar Nayak. Long-Range Admixture Linkage Disequilibrium and Allelic Responses of Sub1 and TPP7 under Consecutive Stress in Rice Validated Through Mendelian Randomization [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(5): 704-716. |
| [14] | Yong Jin Choi, Sun-Hwa Ha. Metabolic Engineering in Rice for Functional Metabolite Production [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(4): 475-498. |
| [15] | Dinuka Nuwan Tharaka, Nadeeka D. Tissera, Gayan Priyadarshana, Damayanthi Dahanayake. A Comprehensive Review of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Synthesis from Rice Husk [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(4): 499-511. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||