
Rice Science ›› 2026, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 30-38.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2025.08.008
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
An Shuaizu1, Lü Jun2, Ma Zemin1, Gao Xuanlin1, Zhang Biaoming1, Yang Pingfang1( ), Ke Yinggen1(
), Ke Yinggen1( )
)
Received:2025-05-24
Accepted:2025-08-28
Online:2026-01-28
Published:2026-02-03
Contact:
Ke Yinggen (An Shuaizu, Lü Jun, Ma Zemin, Gao Xuanlin, Zhang Biaoming, Yang Pingfang, Ke Yinggen. WRKY53: A Key Player in Stress Responses and Growth Regulation in Rice[J]. Rice Science, 2026, 33(1): 30-38.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
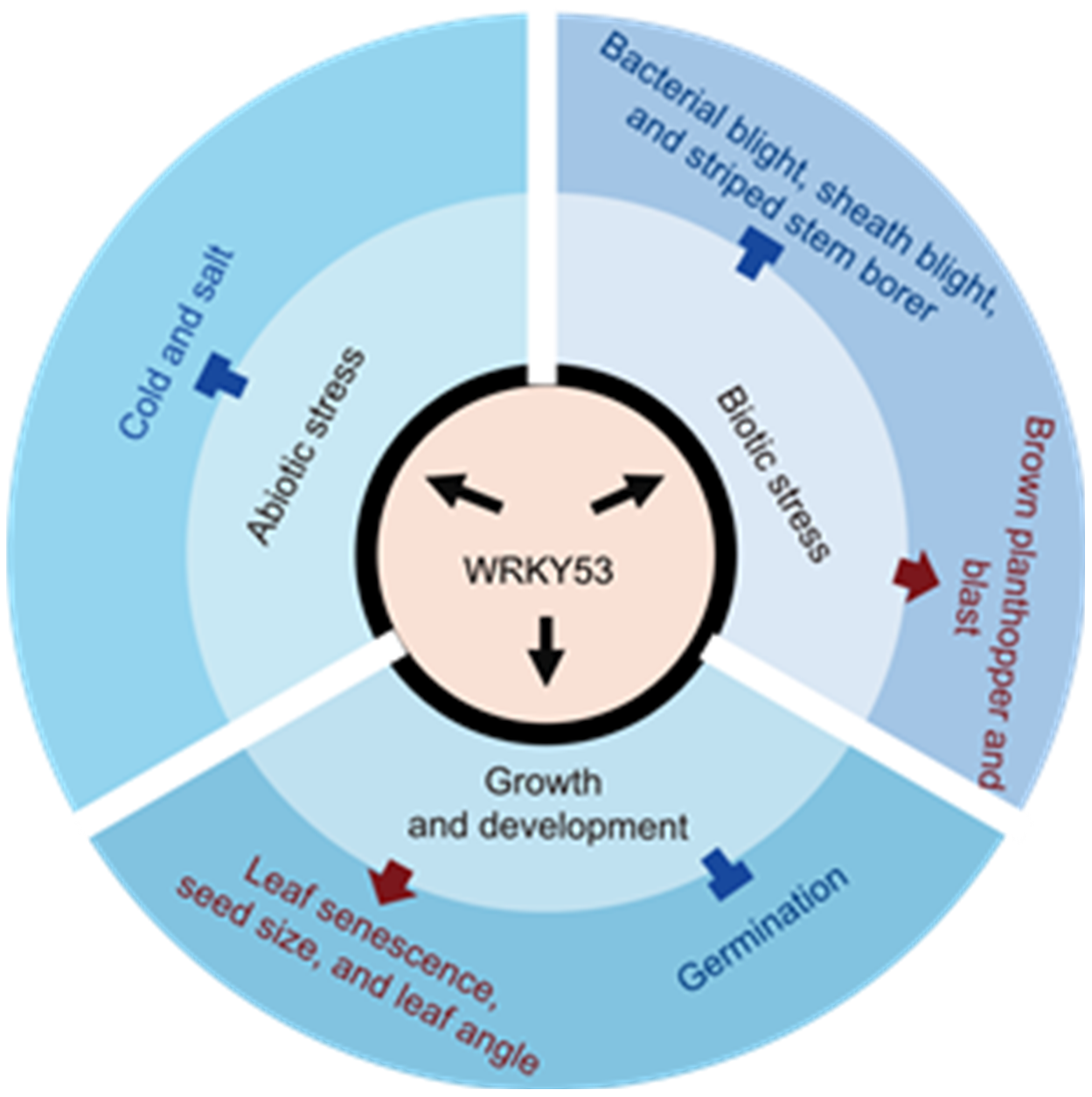
Fig. 1. Functions of WRKY53 in rice. The red ‘↑’ represent positive regulation, and the blue ‘┬’ represent negative regulation. In this network diagram, WRKY53 is at the center and connected to three major categories of biological processes: abiotic stress, biotic stress, and growth and development. These broad categories are further divided into specific physiological and developmental processes, such as cold tolerance, salt tolerance, and bacterial blight. Each process is linked to specific molecular mechanisms or signaling pathways, demonstrating the role of WRKY53 in regulating the response of rice to various stresses and developmental processes.
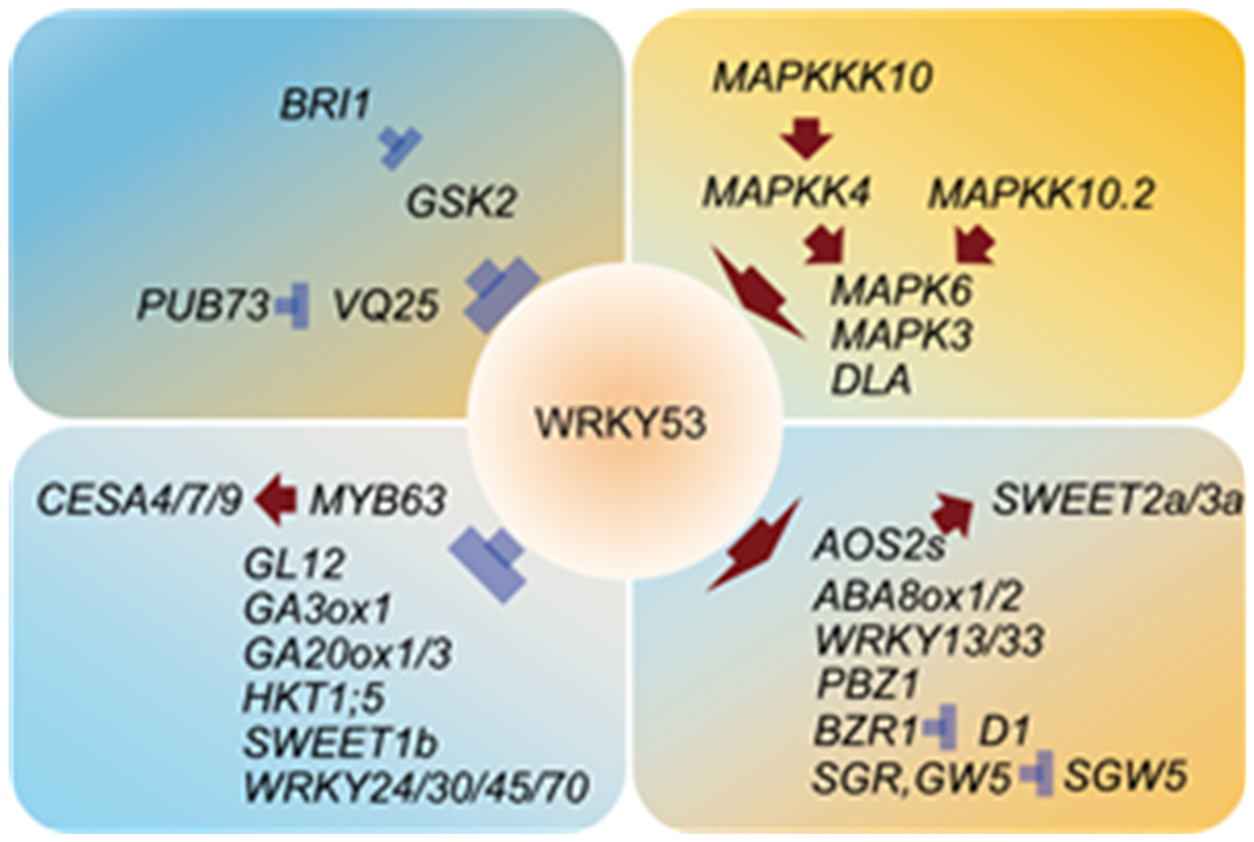
Fig. 2. WRKY53-centered gene network. The red ‘↑’ represent positive regulation, and the blue ‘┬’ represent negative regulation. In this network diagram, WRKY53 is at the center and is connected to multiple signaling pathways.
| [1] | Abbas W, Shalmani A, Zhang J, et al. 2024. The GW5-WRKY53-SGW5 module regulates grain size variation in rice. New Phytol, 242(5): 2011-2025. |
| [2] | Bai M Y, Zhang L Y, Gampala S S, et al. 2007. Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104: 13839-13844. |
| [3] | Bonaventure G. 2012. Perception of insect feeding by plants. Plant Biol, 14(6): 872-880. |
| [4] | Chen D, Shi Y R, Zhang P, et al. 2024. Deletion of the sugar importer gene OsSWEET1b accelerates sugar starvation-promoted leaf senescence in rice. Plant Physiol, 195(3): 2176-2194. |
| [5] | Chen J, Wang L H, Yuan M. 2021. Update on the roles of rice MAPK cascades. Int J Mol Sci, 22(4): 1679. |
| [6] | Chen M, Shelton A, Ye G Y. 2011. Insect-resistant genetically modified rice in China: From research to commercialization. Annu Rev Entomol, 56: 81-101. |
| [7] | Chujo T, Takai R, Akimoto-Tomiyama C, et al. 2007. Involvement of the elicitor-induced gene OsWRKY53 in the expression of defense-related genes in rice. Biochim Biophys Acta-Gene Struct Expression, 1769(7/8): 497-505. |
| [8] | Chujo T, Sugioka N, Masuda Y, et al. 2009. Promoter analysis of the elicitor-induced WRKY gene OsWRKY53, which is involved in defense responses in rice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 73(8): 1901-1904. |
| [9] | Chujo T, Miyamoto K, Ogawa S, et al. 2014. Overexpression of phosphomimic mutated OsWRKY53 leads to enhanced blast resistance in rice. PLoS One, 9(6): e98737. |
| [10] | Duan P G, Rao Y C, Zeng D L, et al. 2014. SMALL GRAIN 1, which encodes a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4, influences grain size in rice. Plant J, 77(4): 547-557. |
| [11] | Erb M, Meldau S, Howe G A. 2012. Role of phytohormones in insect-specific plant reactions. Trends Plant Sci, 17(5): 250-259. |
| [12] | Gao Y, Xue C Y, Liu J M, et al. 2021. Sheath blight resistance in rice is negatively regulated by WRKY53 via SWEET2a activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 585: 117-123. |
| [13] | Guo T, Chen K, Dong N Q, et al. 2018. GRAIN SIZE AND NUMBER1 negatively regulates the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMPK6 cascade to coordinate the trade-off between grain number per panicle and grain size in rice. Plant Cell, 30(4): 871-888. |
| [14] | Hao Z Y, Tian J F, Fang H, et al. 2022. A VQ-motif-containing protein fine-tunes rice immunity and growth by a hierarchical regulatory mechanism. Cell Rep, 40(7): 111235. |
| [15] | Hu L F, Ye M, Li R, et al. 2016. OsWRKY53, a versatile switch in regulating herbivore-induced defense responses in rice. Plant Signal Behav, 11: e1169357. |
| [16] | Hu L Y, Ye M, Li R, et al. 2015. The rice transcription factor WRKY53 suppresses herbivore-induced defenses by acting as a negative feedback modulator of mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. Plant Physiol, 169(4): 2907-2921. |
| [17] | Huang Y, Guo Y M, Liu Y T, et al. 2018. 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase 3 regulates plant growth and enhances multi-abiotic stress tolerance in rice. Front Plant Sci, 9: 162. |
| [18] | Huang Y S, Dong H, Mou C L, et al. 2022. Ribonuclease H-like gene SMALL GRAIN2 regulates grain size in rice through brassinosteroid signaling pathway. J Integr Plant Biol, 64(10): 1883-1900. |
| [19] | Jung K H, Han M J, Lee Y S, et al. 2005. Rice Undeveloped Tapetum1 is a major regulator of early tapetum development. Plant Cell, 17(10): 2705-2722. |
| [20] | Ke Y G, Deng H Q, Wang S P. 2017. Advances in understanding broad-spectrum resistance to pathogens in rice. Plant J, 90(4): 738-748. |
| [21] | Kim J. 2019. Sugar metabolism as input signals and fuel for leaf senescence. Genes Genomics, 41(7): 737-746. |
| [22] | Li N, Xu R, Li Y H. 2019. Molecular networks of seed size control in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 70: 435-463. |
| [23] | Li R, Afsheen S, Xin Z J, et al. 2013. OsNPR1 negatively regulates herbivore-induced JA and ethylene signaling and plant resistance to a chewing herbivore in rice. Physiol Plant, 147(3): 340-351. |
| [24] | Lim P O, Kim H J, Gil Nam H. 2007. Leaf senescence. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 58: 115-136. |
| [25] | Liu S Y, Hua L, Dong S J, et al. 2015. OsMAPK6, a mitogen-activated protein kinase, influences rice grain size and biomass production. Plant J, 84(4): 672-681. |
| [26] | Lou Y G, Du M H, Turlings T C J, et al. 2005. Exogenous application of jasmonic acid induces volatile emissions in rice and enhances parasitism of Nilaparvata lugens eggs by the parasitoid Anagrus nilaparvatae. J Chem Ecol, 31(9): 1985-2002. |
| [27] | Lu J, Ju H P, Zhou G X, et al. 2011. An EAR-motif-containing ERF transcription factor affects herbivore-induced signaling, defense and resistance in rice. Plant J, 68(4): 583-596. |
| [28] | Lu J, Li J C, Ju H P, et al. 2014. Contrasting effects of ethylene biosynthesis on induced plant resistance against a chewing and a piercing-sucking herbivore in rice. Mol Plant, 7(11): 1670-1682. |
| [29] | Mao C J, Lu S C, Lv B, et al. 2017. A rice NAC transcription factor promotes leaf senescence via ABA biosynthesis. Plant Physiol, 174(3): 1747-1763. |
| [30] | Meng F W, Zheng X M, Wang J, et al. 2024. The GRAS protein OsDLA involves in brassinosteroid signalling and positively regulates blast resistance by forming a module with GSK2 and OsWRKY53 in rice. Plant Biotechnol J, 22(2): 363-378. |
| [31] | Qi J F, Zhou G X, Yang L J, et al. 2011. The chloroplast-localized phospholipases D α4 and α5 regulate herbivore-induced direct and indirect defenses in rice. Plant Physiol, 157(4): 1987-1999. |
| [32] | Qiao S L, Sun S Y, Wang L L, et al. 2017. The RLA1/SMOS1 transcription factor functions with OsBZR1 to regulate brassinosteroid signaling and rice architecture. Plant Cell, 29(2): 292-309. |
| [33] | Ren Z H, Gao J P, Li L G, et al. 2005. A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat Genet, 37(10): 1141-1146. |
| [34] | Rubia-Sanchez E, Suzuki Y, Miyamoto K, et al. 1999. The potential for compensation of the effects of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Stal (Homoptera: Delphacidae) feeding on rice. Crop Prot, 18(1): 39-45. |
| [35] | Rushton P J, Somssich I E, Ringler P, et al. 2010. WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci, 15(5): 247-258. |
| [36] | Song S, Wang G F, Wu H, et al. 2020. OsMFT2 is involved in the regulation of ABA signaling-mediated seed germination through interacting with OsbZIP23/66/72 in rice. Plant J, 103(2): 532-546. |
| [37] | Tang J Q, Tian X J, Mei E Y, et al. 2022. WRKY53 negatively regulates rice cold tolerance at the booting stage by fine-tuning anther gibberellin levels. Plant Cell, 34(11): 4495-4515. |
| [38] | Tian X J, Li X F, Zhou W J, et al. 2017. Transcription factor OsWRKY53 positively regulates brassinosteroid signaling and plant architecture. Plant Physiol, 175(3): 1337-1349. |
| [39] | Tian X J, He M L, Mei E Y, et al. 2021. WRKY53 integrates classic brassinosteroid signaling and the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway to regulate rice architecture and seed size. Plant Cell, 33(8): 2753-2775. |
| [40] | Tong H N, Liu L C, Jin Y, et al. 2012. DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase to mediate brassinosteroid responses in rice. Plant Cell, 24(6): 2562-2577. |
| [41] | van Loon L C, Rep M, Pieterse C M J. 2006. Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol, 44: 135-162. |
| [42] | Wang H P, Chen W Q, Xu Z Y, et al. 2023. Functions of WRKYs in plant growth and development. Trends Plant Sci, 28(6): 630-645. |
| [43] | Wang Q, Li J C, Hu L F, et al. 2013. OsMPK3 positively regulates the JA signaling pathway and plant resistance to a chewing herbivore in rice. Plant Cell Rep, 32(7): 1075-1084. |
| [44] | Wang S K, Li S, Liu Q, et al. 2015. The OsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rice yield and grain quality. Nat Genet, 47(8): 949-954. |
| [45] | Wang Y Y, Chen W X, Xing M, et al. 2024. Wild rice GL12 synergistically improves grain length and salt tolerance in cultivated rice. Nat Commun, 15(1): 9453. |
| [46] | Watanabe T, Kitagawa H. 2000. Photosynthesis and translocation of assimilates in rice plants following phloem feeding by the planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Homoptera: Delphacidae). J Econ Entomol, 93(4): 1192-1198. |
| [47] | Woo H R, Kim H J, Lim P O, et al. 2019. Leaf senescence: Systems and dynamics aspects. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 70: 347-376. |
| [48] | Xie W Y, Ke Y G, Cao J B, et al. 2021. Knock out of transcription factor WRKY53 thickens sclerenchyma cell walls, confers bacterial blight resistance. Plant Physiol, 187(3): 1746-1761. |
| [49] | Xie W Y, Li X R, Wang S P, et al. 2022. OsWRKY53 promotes abscisic acid accumulation to accelerate leaf senescence and inhibit seed germination by downregulating abscisic acid catabolic genes in rice. Front Plant Sci, 12: 816156. |
| [50] | Xu R, Duan P G, Yu H Y, et al. 2018. Control of grain size and weight by the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMAPK 6 signaling pathway in rice. Mol Plant, 11(6): 860-873. |
| [51] | Yan A, Chen Z. 2017. The pivotal role of abscisic acid signaling during transition from seed maturation to germination. Plant Cell Rep, 36(5): 689-703. |
| [52] | Yang S, Fu Y W, Zhang Y, et al. 2023. Rhizoctonia solani transcriptional activator interacts with rice WRKY53 and grassy tiller 1 to activate SWEET transporters for nutrition. J Adv Res, 50: 1-12. |
| [53] | Yoo S J, Kim S H, Kim M J, et al. 2014. Involvement of the OsMKK4-OsMPK1 cascade and its downstream transcription factor OsWRKY53 in the wounding response in rice. Plant Pathol J, 30(2): 168-177. |
| [54] | Yu J, Zhu C S, Xuan W, et al. 2023. Genome-wide association studies identify OsWRKY53 as a key regulator of salt tolerance in rice. Nat Commun, 14(1): 3550. |
| [55] | Yu J T, Mao C J, Zhong Q, et al. 2021. OsNAC2 is involved in multiple hormonal pathways to mediate germination of rice seeds and establishment of seedling. Front Plant Sci, 12: 699303. |
| [56] | Zebosi B, Vollbrecht E, Best N B. 2024. Brassinosteroid biosynthesis and signaling: Conserved and diversified functions of core genes across multiple plant species. Plant Commun, 5(9): 100982. |
| [57] | Zhang D S, Liang W Q, Yuan Z, et al. 2008. Tapetum degeneration retardation is critical for aliphatic metabolism and gene regulation during rice pollen development. Mol Plant, 1(4): 599-610. |
| [58] | Zhang M M, Su J B, Zhang Y, et al. 2018. Conveying endogenous and exogenous signals: MAPK cascades in plant growth and defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 45: 1-10. |
| [59] | Zhao D S, Li Q F, Zhang C Q, et al. 2018. GS9 acts as a transcriptional activator to regulate rice grain shape and appearance quality. Nat Commun, 9(1): 1240. |
| [60] | Zhou G X, Qi J F, Ren N, et al. 2009. Silencing OsHI-LOX makes rice more susceptible to chewing herbivores, but enhances resistance to a phloem feeder. Plant J, 60(4): 638-648. |
| [1] | Zhu Junlin, Zheng Guangjie, Tao Yi, Liao Wenli, Ye Chang, Xu Ya’nan, Xiao Deshun, Chu Guang, Xu Chunmei, Wang Danying. Wood Vinegar Enhances Seedling Rate of Rice Seeds under Flooding Stress by Mitigating Oxidative Damage and Maintaining Energy Homeostasis [J]. Rice Science, 2026, 33(1): 129-140. |
| [2] | Huang Qina, Wu Lijuan, Jiang Hongrui, He Yan, Liu Song, Yang Changdeng, Liang Yan. NRAMPs: Versatile Transporters Involved in Metal Ion Homeostasis and Their Applications in Rice Breeding [J]. Rice Science, 2026, 33(1): 39-58. |
| [3] | Pratap Kalita, Bedanta Bhattacharjee, Bhrigu Kumar Das, Saikat Sen, Raja Chakraborty, Abdul Baquee Ahmed. Rice Bran as Nutrient-Dense Food in Gut Health and Beyond [J]. Rice Science, 2026, 33(1): 59-80. |
| [4] | Zhou Jiaren, Song Qingfeng, Li Wanwan, Zhang Mengqi, Zhang Man, Zhu Xinguang, Wang Minjuan. High Throughput 3D Phenotyping of Canopy Occupation Volume as Major Predictor of Rice Canopy Photosynthesis [J]. Rice Science, 2026, 33(1): 99-112. |
| [5] | D. Priyanga, K. Amudha, N. Sakthivel, P. Sivasakthivelan, S. Utharasu, D. Uma, M. Sudha. Functional and Nutraceutical Potential of Indian Rice Landraces: A Comprehensive Scientific Review [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(6): 777-796. |
| [6] | Fazli Hameed, Shah Fahad Rahim, Anis Ur Rehman Khalil, Ram L. Ray, Xu Junzeng, Alhaj Yousef Hamoud, Akhtar Ali, Ning Tangyuan. Comparing Genotype and Climate Change Effects on Simulated Historical Rice Yields Using AquaCrop [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(6): 845-856. |
| [7] | Hong Chen, Luo Ju, Feng Zelin, Ling Heping, Li Lingyi, Wu Jian, Yao Qing, Liu Shuhua. Intelligent Survey Method for Tiny Rice Pests and Their Natural Predators in Paddy Fields Using Augmented Reality (AR) Glasses [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(6): 868-884. |
| [8] | Daisy Wilson, Valeria Gonzalez, Hamidreza Sharifan. Evaluating Efficacy of ZnO and MgO Nanoparticles on Post-Harvested Rice to Enhance Food Security Against Agroterrorism [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(5): 717-726. |
| [9] | Mareyam Mukhtar, Amresh Kumar, Ashfak S. Mujawar, Bhuvnesh Sareen, Suhas G. Karkute, Rohini Sreevathsa, Amitha Mithra Sevanthi, Amolkumar U. Solanke. Genome-Wide Identification of Dopamine β-Monooxygenase N-Terminal Gene Family in Rice and Its Role in Response to Blast Disease and Abiotic Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(5): 685-703. |
| [10] | Li Haifeng, Fan Jiayi. Functions of Rice E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Response to Environmental Stress and in Regulating Grain Size [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(5): 649-657. |
| [11] | Wu Zhaozhong, Zhong Zhengzheng, Xu Peng, Liu Ling, Wang Beifang, Yang Qinqin, Wen Xiaoxia, Ma Guifang, Luo Mili, Zhang Yingxin, Liu Qun’en, Peng Zequn, Zhan Xiaodeng, Cao Liyong, Cheng Shihua, Wu Weixun. OsELF3.1-OsCATA-Ghd7 Pathway Regulates Rice Heading [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(5): 658-672. |
| [12] | Pan Pan, Guo Wenlong, Li Hengbo, Shao Yifan, Guo Zhihao, Jin Ye, Cheng Yanrong, Yu Guoping, Fu Zhenshi, Hu Lin, Zheng Xiaoming, Zhou Guomin, Zhang Jianhua. Accelerating Wild Rice Disease-Resistant Germplasm Exploration: Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Powered Wild Rice Blast Disease Level Evaluation and Disease-Resistance Identification [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(5): 727-746. |
| [13] | Sabarinathan Selvaraj, Parameswaran Chidambaranathan, Goutam Kumar Dash, Priyadarsini Sanghamitra, Kishor Pundlik Jeughale, Cayalvizhi Balasubramaniasai, Devraj Lenka, Basavantraya Navadagi Devanna, Seenichamy Rathinam Prabhukarthikeyan, Sanghamitra Samantaray, Amaresh Kumar Nayak. Long-Range Admixture Linkage Disequilibrium and Allelic Responses of Sub1 and TPP7 under Consecutive Stress in Rice Validated Through Mendelian Randomization [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(5): 704-716. |
| [14] | Yong Jin Choi, Sun-Hwa Ha. Metabolic Engineering in Rice for Functional Metabolite Production [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(4): 475-498. |
| [15] | Dinuka Nuwan Tharaka, Nadeeka D. Tissera, Gayan Priyadarshana, Damayanthi Dahanayake. A Comprehensive Review of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Synthesis from Rice Husk [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(4): 499-511. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||