
Rice Science ›› 2017, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (5): 241-252.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2017.05.002
• Orginal Article • Next Articles
Koteswara Reddy Chagam1,2, Kimi Lalmuan1, Haripriya Sundaramoorthy1( ), Kang Nayoung2
), Kang Nayoung2
Received:2017-03-21
Accepted:2017-05-31
Online:2017-09-15
Published:2017-08-31
Koteswara Reddy Chagam, Kimi Lalmuan, Haripriya Sundaramoorthy, Kang Nayoung. Effects of Polishing on Proximate Composition, Physico- Chemical Characteristics, Mineral Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Pigmented Rice[J]. Rice Science, 2017, 24(5): 241-252.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Parameter | Chak-hao Amubi | Chak-hao Poireiton | Chak-hao Angangba | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | Polished | Raw | Polished | Raw | Polished | |||||
| Moisture content (%) | 11.40 ± 0.30 b | 8.72 ± 0.60 c | 12.05 ± 0.20 a | 8.54 ± 0.22 cd | 11.12 ± 0.70 b | 8.17 ± 0.10 d | ||||
| Ash content (%) | 0.83 ± 0.10 c | 0.33 ± 0.03 e | 1.79 ± 0.20 a | 0.57 ± 0.09 d | 1.38 ± 0.20 b | 0.31 ± 0.03 e | ||||
| Protein content (%) | 8.75 ± 1.20 a | 8.48 ± 0.17 a | 7.77 ± 0.05 b | 7.45 ± 0.04 c | 5.57 ± 0.10 d | 5.29 ± 0.07 e | ||||
| Fat content (%) | 3.33 ± 0.20 b | 0.41 ± 0.07 d | 3.73 ± 0.20 a | 0.34 ± 0.05 d | 3.05 ± 0.10 c | 0.21 ± 0.03 e | ||||
| Carbohydrate content (%) | 74.67 ± 1.40 d | 82.13 ± 0.61 b | 74.38 ± 1.50 d | 83.27 ± 0.30 b | 78.24 ± 2.60 c | 85.57 ± 0.47 a | ||||
| Amylose content (%) | 3.16 ± 0.30 c | 6.11 ± 0.39 a | 1.98 ± 0.10 d | 4.08 ± 0.09 b | 1.93 ± 0.10 d | 3.98 ± 0.15 b | ||||
| L* | 61.53 ± 1.10 e | 84.34 ± 0.72 b | 64.52 ± 0.90 d | 75.36 ± 0.58 c | 74.41 ± 1.20 c | 88.64 ± 0.43 a | ||||
| a* | 2.21 ± 0.19 d | 1.58 ± 0.07 e | 3.45 ± 0.09 b | 2.68 ± 0.18 c | 7.68 ± 0.07 a | 1.46 ± 0.26 e | ||||
| b* | 2.86 ± 0.12 c | 1.72 ± 0.07 d | 3.49 ± 0.16 b | 0.24 ± 0.06 e | 11.29 ± 0.11 a | 3.25 ± 0.15 bc | ||||
| Crystallinity (%) | 9.56 ± 0.12 c | 9.18 ± 0.15 d | 10.32 ± 0.22 b | 10.08 ± 0.15 b | 10.75 ± 0.21 a | 10.34 ± 0.18 b | ||||
| L*, Lightness to darkness; a*, Redness to greenness; b*, Blueness to yellowness. Values (Mean ± SD, n = 3) with the same lowercase letters in a row did not differ significantly (P < 0.05) by the Duncan’s multiple range method. | ||||||||||
Table 1 Proximate compositions, amylose content, colour parameters, and crystallinity of raw and polished pigmented rice.
| Parameter | Chak-hao Amubi | Chak-hao Poireiton | Chak-hao Angangba | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | Polished | Raw | Polished | Raw | Polished | |||||
| Moisture content (%) | 11.40 ± 0.30 b | 8.72 ± 0.60 c | 12.05 ± 0.20 a | 8.54 ± 0.22 cd | 11.12 ± 0.70 b | 8.17 ± 0.10 d | ||||
| Ash content (%) | 0.83 ± 0.10 c | 0.33 ± 0.03 e | 1.79 ± 0.20 a | 0.57 ± 0.09 d | 1.38 ± 0.20 b | 0.31 ± 0.03 e | ||||
| Protein content (%) | 8.75 ± 1.20 a | 8.48 ± 0.17 a | 7.77 ± 0.05 b | 7.45 ± 0.04 c | 5.57 ± 0.10 d | 5.29 ± 0.07 e | ||||
| Fat content (%) | 3.33 ± 0.20 b | 0.41 ± 0.07 d | 3.73 ± 0.20 a | 0.34 ± 0.05 d | 3.05 ± 0.10 c | 0.21 ± 0.03 e | ||||
| Carbohydrate content (%) | 74.67 ± 1.40 d | 82.13 ± 0.61 b | 74.38 ± 1.50 d | 83.27 ± 0.30 b | 78.24 ± 2.60 c | 85.57 ± 0.47 a | ||||
| Amylose content (%) | 3.16 ± 0.30 c | 6.11 ± 0.39 a | 1.98 ± 0.10 d | 4.08 ± 0.09 b | 1.93 ± 0.10 d | 3.98 ± 0.15 b | ||||
| L* | 61.53 ± 1.10 e | 84.34 ± 0.72 b | 64.52 ± 0.90 d | 75.36 ± 0.58 c | 74.41 ± 1.20 c | 88.64 ± 0.43 a | ||||
| a* | 2.21 ± 0.19 d | 1.58 ± 0.07 e | 3.45 ± 0.09 b | 2.68 ± 0.18 c | 7.68 ± 0.07 a | 1.46 ± 0.26 e | ||||
| b* | 2.86 ± 0.12 c | 1.72 ± 0.07 d | 3.49 ± 0.16 b | 0.24 ± 0.06 e | 11.29 ± 0.11 a | 3.25 ± 0.15 bc | ||||
| Crystallinity (%) | 9.56 ± 0.12 c | 9.18 ± 0.15 d | 10.32 ± 0.22 b | 10.08 ± 0.15 b | 10.75 ± 0.21 a | 10.34 ± 0.18 b | ||||
| L*, Lightness to darkness; a*, Redness to greenness; b*, Blueness to yellowness. Values (Mean ± SD, n = 3) with the same lowercase letters in a row did not differ significantly (P < 0.05) by the Duncan’s multiple range method. | ||||||||||
| Parameter | Chak-hao Amubi | Chak-hao Poireiton | Chak-hao Angangba | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | Polished | Raw | Polished | Raw | Polished | |||
| Pasting temperature (ºC) | 69.61 ± 0.37 d | 76.40 ± 0.52 a | 69.10 ± 0.25 d | 73.27 ± 0.25 b | 69.24 ± 0.50 d | 70.13 ± 0.06 c | ||
| Peak viscosity (cP) | 3 171 ± 47 a | 813 ± 15 d | 1 536 ± 33 b | 679 ± 10 e | 1 114 ± 12 c | 697 ± 15 e | ||
| Hold viscosity (cP) | 1 410 ± 28 a | 658 ± 18 d | 991 ± 22 b | 810 ± 13 c | 386 ± 11 f | 572 ± 19 e | ||
| Final viscosity (cP) | 1 903 ± 26 a | 839 ± 16 d | 1 662 ± 10 b | 891 ± 15 c | 571 ± 11 f | 765 ± 21 e | ||
| Break down viscosity (cP) | 1 699 ± 17 a | 153 ± 8 d | 562 ± 11 c | 43 ± 4 f | 738 ± 19 b | 129 ± 7 e | ||
| Setback viscosity (cP) | 492 ± 7 b | 188 ± 5 d | 683 ± 18 a | 251 ± 6 c | 175 ± 11 d | 191 ± 6 d | ||
| T0 (ºC) | 70.79 ± 0.23 b | 56.30 ± 1.03 c | 75.26 ± 0.25 a | 56.50 ± 1.00 c | 74.94 ± 0.32 a | 53.80 ± 0.64 d | ||
| TP (ºC) | 81.70 ± 0.69 a | 77.13 ± 1.10 b | 82.10 ± 0.62 a | 73.56 ± 2.10 c | 81.80 ± 0.45 a | 74.07 ± 1.50 c | ||
| TC (ºC) | 93.11 ± 2.31 a | 89.02 ± 1.52 b | 91.98 ± 2.12 ab | 85.98 ± 1.20 c | 92.94 ± 2.32 a | 85.57 ± 0.60 c | ||
| ∆H (J/g) | 12.19 ± 0.34 a | 10.05 ± 0.33 c | 9.73 ± 0.15 c | 9.84 ± 0.17 c | 11.09 ± 0.75 b | 10.17 ± 0.11 c | ||
| T0, Onset temperature; TP, Peak temperature; TC, Conclusion temperature; ∆H, Gelatinization enthalpy. Values (Mean ± SD, n = 3) with the same lowercase letters in a row did not differ significantly (P < 0.05) by the Duncan’s multiple range method. | ||||||||
Table 2 Pasting and thermal properties of raw and polished pigmented rice.
| Parameter | Chak-hao Amubi | Chak-hao Poireiton | Chak-hao Angangba | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | Polished | Raw | Polished | Raw | Polished | |||
| Pasting temperature (ºC) | 69.61 ± 0.37 d | 76.40 ± 0.52 a | 69.10 ± 0.25 d | 73.27 ± 0.25 b | 69.24 ± 0.50 d | 70.13 ± 0.06 c | ||
| Peak viscosity (cP) | 3 171 ± 47 a | 813 ± 15 d | 1 536 ± 33 b | 679 ± 10 e | 1 114 ± 12 c | 697 ± 15 e | ||
| Hold viscosity (cP) | 1 410 ± 28 a | 658 ± 18 d | 991 ± 22 b | 810 ± 13 c | 386 ± 11 f | 572 ± 19 e | ||
| Final viscosity (cP) | 1 903 ± 26 a | 839 ± 16 d | 1 662 ± 10 b | 891 ± 15 c | 571 ± 11 f | 765 ± 21 e | ||
| Break down viscosity (cP) | 1 699 ± 17 a | 153 ± 8 d | 562 ± 11 c | 43 ± 4 f | 738 ± 19 b | 129 ± 7 e | ||
| Setback viscosity (cP) | 492 ± 7 b | 188 ± 5 d | 683 ± 18 a | 251 ± 6 c | 175 ± 11 d | 191 ± 6 d | ||
| T0 (ºC) | 70.79 ± 0.23 b | 56.30 ± 1.03 c | 75.26 ± 0.25 a | 56.50 ± 1.00 c | 74.94 ± 0.32 a | 53.80 ± 0.64 d | ||
| TP (ºC) | 81.70 ± 0.69 a | 77.13 ± 1.10 b | 82.10 ± 0.62 a | 73.56 ± 2.10 c | 81.80 ± 0.45 a | 74.07 ± 1.50 c | ||
| TC (ºC) | 93.11 ± 2.31 a | 89.02 ± 1.52 b | 91.98 ± 2.12 ab | 85.98 ± 1.20 c | 92.94 ± 2.32 a | 85.57 ± 0.60 c | ||
| ∆H (J/g) | 12.19 ± 0.34 a | 10.05 ± 0.33 c | 9.73 ± 0.15 c | 9.84 ± 0.17 c | 11.09 ± 0.75 b | 10.17 ± 0.11 c | ||
| T0, Onset temperature; TP, Peak temperature; TC, Conclusion temperature; ∆H, Gelatinization enthalpy. Values (Mean ± SD, n = 3) with the same lowercase letters in a row did not differ significantly (P < 0.05) by the Duncan’s multiple range method. | ||||||||
| Parameter | Chak-hao Amubi | Chak-hao Poireiton | Chak-hao Angangba | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | Polished | Raw | Polished | Raw | Polished | |||
| Calcium | 136.2 ± 1.2 a | 53.6 ± 1.5 e | 114.6 ± 3.1 b | 63.2 ± 1.1 d | 77.6 ± 1.5 c | 42.5 ± 1.1 f | ||
| Chlorine | 63.4 ± 2.1 a | 39.6 ± 1.2 d | 60.6 ± 0.7 b | 44.3 ± 0.9 c | 35.7 ± 0.9 e | 28.6 ± 1.9 e | ||
| Copper | 33.4 ± 0.5 a | 26.2 ± 1.1 c | 27.5 ± 1.7 c | 20.1 ± 0.7 e | 30.6 ± 0.6 b | 24.1 ± 1.8 d | ||
| Iron | 88.8 ± 0.9 a | 26.2 ± 0.7 e | 47.2 ± 0.6 c | 30.6 ± 0.4 d | 57.1 ± 0.7 b | 24.5 ± 0.5 f | ||
| Potassium | 1 606.6 ± 43.7 b | 566.1 ± 13.7 e | 1 843.6 ± 51.8 a | 966.4 ± 26.2 d | 1 546.8 ± 21.7 c | 449.2 ± 7.3 f | ||
| Magnesium | 377.2 ± 14.6 a | 106.6 ± 6.1 c | 387.6 ± 8.6 a | 215.8 ± 8.9 b | 379.1 ± 6.8 a | 56.8 ± 2.1 d | ||
| Manganese | 38.8 ± 1.2 b | 20.1 ± 1.2 d | 42.7 ± 1.9 a | 21.8 ± 1.5 d | 23.6 ± 2.5 c | 14.5 ± 1.1 e | ||
| Phosphorus | 2 062.1 ± 106.2 c | 718.5 ± 15.7 e | 2 529.7 ± 41.7 a | 1 401.6 ± 21.9 d | 2 248.1 ± 40.4 b | 456.7 ± 32.1 f | ||
| Sulphur | 976.1 ± 62.4 a | 847.4 ± 39.1 c | 916.5 ± 10.9 b | 795.8 ± 12.5 cd | 743.5 ± 7.6 d | 657.7 ± 27.8 e | ||
| Zinc | 53.9 ± 1.1 a | 24.6 ± 2.3 d | 42.4 ± 0.6 b | 24.7 ± 1.2 d | 34.9 ± 3.3 c | 20.2 ± 0.5 e | ||
| Values (Mean ± SD, n = 3) with the same lowercase letters in a row did not differ significantly (P < 0.05) by the Duncan’s multiple range method. | ||||||||
Table 3 Mineral compositions of raw and polished pigmented rice. mg/kg
| Parameter | Chak-hao Amubi | Chak-hao Poireiton | Chak-hao Angangba | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | Polished | Raw | Polished | Raw | Polished | |||
| Calcium | 136.2 ± 1.2 a | 53.6 ± 1.5 e | 114.6 ± 3.1 b | 63.2 ± 1.1 d | 77.6 ± 1.5 c | 42.5 ± 1.1 f | ||
| Chlorine | 63.4 ± 2.1 a | 39.6 ± 1.2 d | 60.6 ± 0.7 b | 44.3 ± 0.9 c | 35.7 ± 0.9 e | 28.6 ± 1.9 e | ||
| Copper | 33.4 ± 0.5 a | 26.2 ± 1.1 c | 27.5 ± 1.7 c | 20.1 ± 0.7 e | 30.6 ± 0.6 b | 24.1 ± 1.8 d | ||
| Iron | 88.8 ± 0.9 a | 26.2 ± 0.7 e | 47.2 ± 0.6 c | 30.6 ± 0.4 d | 57.1 ± 0.7 b | 24.5 ± 0.5 f | ||
| Potassium | 1 606.6 ± 43.7 b | 566.1 ± 13.7 e | 1 843.6 ± 51.8 a | 966.4 ± 26.2 d | 1 546.8 ± 21.7 c | 449.2 ± 7.3 f | ||
| Magnesium | 377.2 ± 14.6 a | 106.6 ± 6.1 c | 387.6 ± 8.6 a | 215.8 ± 8.9 b | 379.1 ± 6.8 a | 56.8 ± 2.1 d | ||
| Manganese | 38.8 ± 1.2 b | 20.1 ± 1.2 d | 42.7 ± 1.9 a | 21.8 ± 1.5 d | 23.6 ± 2.5 c | 14.5 ± 1.1 e | ||
| Phosphorus | 2 062.1 ± 106.2 c | 718.5 ± 15.7 e | 2 529.7 ± 41.7 a | 1 401.6 ± 21.9 d | 2 248.1 ± 40.4 b | 456.7 ± 32.1 f | ||
| Sulphur | 976.1 ± 62.4 a | 847.4 ± 39.1 c | 916.5 ± 10.9 b | 795.8 ± 12.5 cd | 743.5 ± 7.6 d | 657.7 ± 27.8 e | ||
| Zinc | 53.9 ± 1.1 a | 24.6 ± 2.3 d | 42.4 ± 0.6 b | 24.7 ± 1.2 d | 34.9 ± 3.3 c | 20.2 ± 0.5 e | ||
| Values (Mean ± SD, n = 3) with the same lowercase letters in a row did not differ significantly (P < 0.05) by the Duncan’s multiple range method. | ||||||||
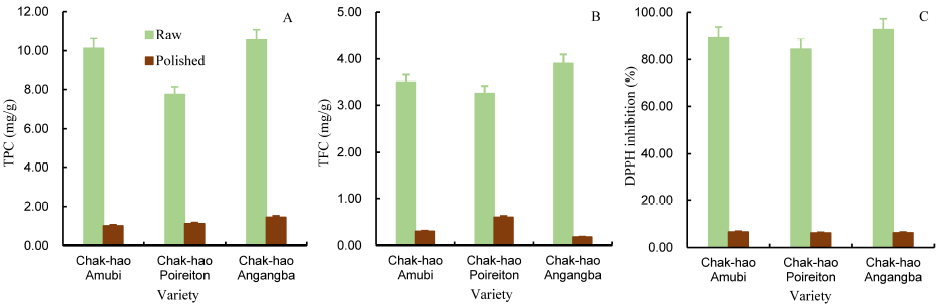
Fig. 3. Total phenolic content (TPC, A), total flavonoid content (TFC, B) and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) inhibition (C) of raw and polished pigmented rice varieties.
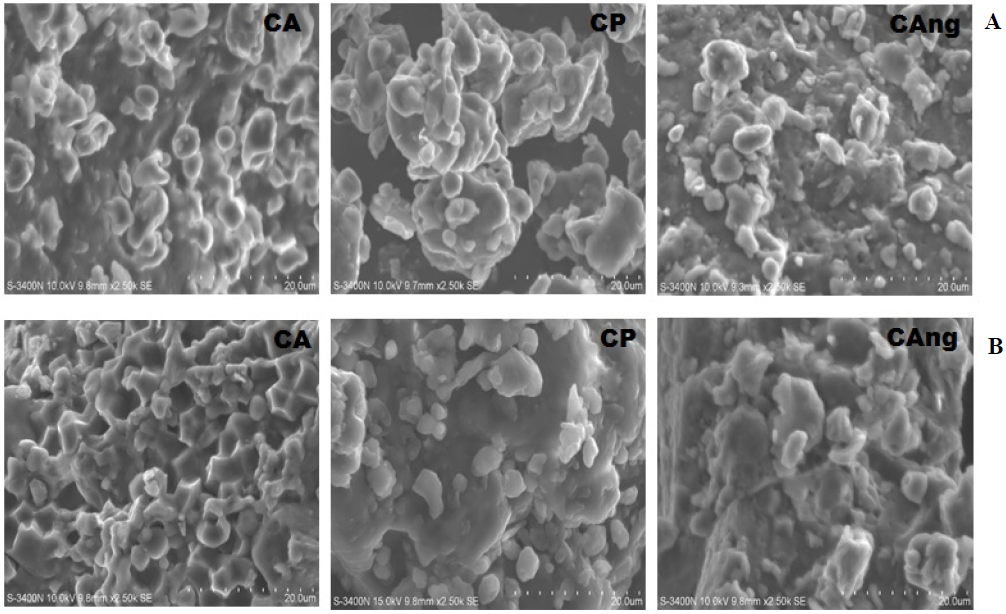
Fig. 4. Scanning electron micrographs (SEM) of raw (A) and polished (B) pigmented rice varieties. ^CA, Chak-hao Amubi; CP, Chak-hao Poireiton; CAng, Chak-hao Angangba.
| [1] | AOAC.1990. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Analytical Chemists. 15th edn. Washington, USA: Association of Official Agricultural Chemists. |
| [2] | Chávez-Murillo C E, Wang Y J, Quintero-Gutierrez A G, Bello-Pérez L A.2011. Physicochemical, textural, and nutritional characterization of mexican rice cultivars.Cereal Chem, 88(3): 245-252. |
| [3] | Chen J J, Lu S, Lii C Y.1999. Effects of milling on the physicochemical characteristics of waxy rice in Taiwan.Cereal Chem, 76(5): 796-799. |
| [4] | Cheng Z H, Moore J, Yu L L.2006. High-throughput relative DPPH radical scavenging capacity assay.J Agric Food Chem, 54(20): 7429-7436. |
| [5] | Choi Y, Jeong H S, Lee J.2007. Antioxidant activity of methanolic extracts from some grains consumed in Korea.Food Chem, 103(1): 130-138. |
| [6] | Dewanto V, Wu X Z, Adom K K, Liu R H.2002. Thermal processing enhances the nutritional value of tomatoes by increasing total antioxidant activity.J Agric Food Chem, 50(10): 3010-3014. |
| [7] | Falade K O, Christopher A S.2015. Physical, functional, pasting and thermal properties of flours and starches of six Nigerian rice cultivars.Food Hydroc, 44: 478-490. |
| [8] | Friedman M.2013. Rice brans, rice bran oils, and rice hulls: Composition, food and industrial uses, and bioactivities in humans, animals, and cells.J Agric Food Chem, 61(45): 10626-10641. |
| [9] | Gujral H S, Rosell C M.2004. Improvement of the breadmaking quality of rice flour by glucose oxidase.Food Res Int, 37(1): 75-81. |
| [10] | Heinemann R J B, Fagundes P L, Pinto E A, Penteado M V C, Lanfer-Marquez U M.2005. Comparative study of nutrient composition of commercial brown, parboiled and milled rice from Brazil.J Food Comp Anal, 18(4): 287-296. |
| [11] | Itani T, Tamaki M, Arai E, Horino T.2002. Distribution of amylose, nitrogen, and minerals in rice kernels with various characters.J Agric Food Chem, 50(19): 5326-5332. |
| [12] | Kong S, Lee J.2010. Antioxidants in milling fractions of black rice cultivars.Food Chem, 120(1): 278-281. |
| [13] | Lamberts L, de Bie E, Vandeputte G E, Veraverbeke W S, Derycke V, de Man W, Delcour J A.2007. Effect of milling on colour and nutritional properties of rice.Food Chem, 100(4): 1496-1503. |
| [14] | Min B, McClung A, Chen M H.2014. Effects of hydrothermal processes on antioxidants in brown, purple and red bran whole grain rice (Oryza sativa L.).Food Chem, 159: 106-115. |
| [15] | Monks J L F, Vanier N L, Casaril J, Berto R M, de Oliveira M, Gomes C B, de Carvalho M P, Dias A R G, Elias M C.2013. Effects of milling on proximate composition, folic acid, fatty acids and technological properties of rice.J Food Comp Anal, 30(2): 73-79. |
| [16] | Nile S H, Keum Y S, Saini R K, Patel R V.2016. Characterization of total phenolics, antioxidant and antiplatelet activity of unpolished and polished rice varieties.J Food Meas Character, 11(1): 236-244. |
| [17] | Okarter N, Liu C S, Sorrells M E, Liu R H.2010. Phytochemical content and antioxidant activity of six diverse varieties of whole wheat.Food Chem, 119(1): 249-257. |
| [18] | Paiva F F, Vanier N L, Berrios J D J, Pan J, de Almeida Villanova F, Takeoka G, Elias M C.2014. Physicochemical and nutritional properties of pigmented rice subjected to different degrees of milling.J Food Comp Anal, 35(1): 10-17. |
| [19] | Paiva F F, Vanier N L, Berrios J D J, Pinto V Z, Wood D, Williams T, Pan J, Elias M C.2016. Polishing and parboiling effect on the nutritional and technological properties of pigmented rice.Food Chem, 191: 105-112. |
| [20] | Patil S B, Khan M K.2011. Germinated brown rice as a value added rice product: A review.J Food Sci Technol, 48(6): 661-667. |
| [21] | Reddy C K, Vidya P V, Haripriya S.2015. Effect of chemical modification on molecular structure and functional properties of Musa AAB starch.Int J Biol Macromol, 81: 1039-1045. |
| [22] | Reddy C K, Kimi L, Haripriya S.2016. Variety difference in molecular structure, functional properties, phytochemical content and antioxidant capacity of pigmented rice.J Food Meas Character, 10(3): 605-613. |
| [23] | Roy P, Ijiri T, Okadome H, Nei D, Orikasa T, Nakamura N, Shiina T.2008. Effect of processing conditions on overall energy consumption and quality of rice (Oryza sativa L.).J Food Engin, 89(3): 343-348. |
| [24] | Saikia S, Dutta H, Saikia D, Mahanta C L.2012. Quality characterisation and estimation of phytochemicals content and antioxidant capacity of aromatic pigmented and non-pigmented rice varieties.Food Res Int, 46(1): 334-340. |
| [25] | Savitha Y S, Singh V.2011. Status of dietary fiber contents in pigmented and non-pigmented rice varieties before and after parboiling.LWT Food Sci Technol, 44(10): 2180-2184. |
| [26] | Setyawati Y D, Ahsan S F, Ong L K, Soetaredjo F E, Ismadji S, Ju Y H.2016. Production of glutinous rice flour from broken rice via ultrasonic assisted extraction of amylose.Food Chem, 203: 158-164. |
| [27] | Shin S I, Choi H J, Chung K M, Hamaker B R, Park K H, Moon T W.2004. Slowly digestible starch from debranched waxy sorghum starch: Preparation and properties.Cereal Chem, 81(3): 404-408. |
| [28] | Singh N, Singh H, Kaur K, Bakshi M S.2000. Relationship between the degree of milling, ash distribution pattern and conductivity in brown rice.Food Chem, 69(2): 147-151. |
| [29] | Singh N, Kaur L, Sodhi N S, Sekhon K S.2005. Physicochemical, cooking and textural properties of milled rice from different Indian rice cultivars.Food Chem, 89(2): 253-259. |
| [30] | Singh N, Kaur L, Sandhu K S, Kaur J, Nishinari K.2006. Relationships between physicochemical, morphological, thermal, rheological properties of rice starches.Food Hydroc, 20(4): 532-542. |
| [31] | Sompong R, Siebenhandl-Ehn S, Linsberger-Martin G, Berghofer E.2011. Physicochemical and antioxidative properties of red and black rice varieties from Thailand, China and Sri Lanka.Food Chem, 124(1): 132-140. |
| [32] | Sowbhagya C M, Bhattacharya K R.1979. Simplified determination of amylose in milled rice.Starch Stärke, 31(5): 159-163. |
| [33] | Ti H H, Li Q, Zhang R F, Zhang M W, Deng Y Y, Wei Z C, Chi J W, Zhang Y.2014. Free and bound phenolic profiles and antioxidant activity of milled fractions of different indica rice varieties cultivated in southern China.Food Chem, 159: 166-174. |
| [34] | Tian S, Nakamura K, Kayahara H.2004. Analysis of phenolic compounds in white rice, brown rice, and germinated brown rice.J Agric Food Chem, 52(15): 4808-4813. |
| [35] | Tsukada H, Hasegawa H, Takeda A, Hisamatsu S.2007. Concentrations of major and trace elements in polished rice and paddy soils collected in Aomori, Japan.J Radioanal Nucl Chem, 273(1): 199-203. |
| [36] | Tuncel N B, Yılmaz N.2011. Gamma-oryzanol content, phenolic acid profiles and antioxidant activity of rice milling fractions.Eur Food Res Technol, 233(4): 577-585. |
| [37] | Wang K M, Wu J G, Li G, Zhang D P, Yang Z W, Shi C H.2011. Distribution of phytic acid and mineral elements in three indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars.J Cereal Sci, 54(1): 116-121. |
| [38] | Yu S F, Ma Y, Menager L, Sun D W.2012. Physicochemical properties of starch and flour from different rice cultivars.Food Bioproc Technol, 5(2): 626-637. |
| [39] | Zhang C Q, Zhou L H, Zhu Z B, Lu H W, Zhou X Z, Qian Y T, Li Q F, Lu Y, Gu M H, Liu Q Q.2016. Characterization of grain quality and starch fine structure of two japonica rice (Oryza sativa) cultivars with good sensory properties at different temperatures during the filling stage.J Agric Food Chem, 64(20): 4048-4057. |
| [40] | Zhang H C, Shao Y F, Bao J S, Beta T.2015. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant properties of breeding lines between the white and black rice.Food Chem, 172: 630-639. |
| [1] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [2] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [3] | Wang Cuili, Guo Wen, Hu Peisong, Wei Xiangjin, Tang Shaoqing, Jiao Guiai. Differences of Physicochemical Properties Between Chalky and Translucent Parts of Rice Grains [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(6): 577-588. |
| [4] | Suhas Gorakh Karkute, Vishesh Kumar, Mohd Tasleem, Dwijesh Chandra Mishra, Krishna Kumar Chaturvedi, Anil Rai, Amitha Mithra Sevanthi, Kishor Gaikwad, Tilak Raj Sharma, Amolkumar U. Solanke. Genome-Wide Analysis of von Willebrand Factor A Gene Family in Rice for Its Role in Imparting Biotic Stress Resistance with Emphasis on Rice Blast Disease [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(4): 375-384. |
| [5] | Punia Sneh, Kumar Manoj, Kumar Siroha Anil, Singh Purewal Sukhvinder. Rice Bran Oil: Emerging Trends in Extraction, Health Benefit, and Its Industrial Application [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(3): 217-232. |
| [6] | Xiaoqin Zeng, Hui Zhuang, Qinglan Cheng, Jun Tang, Fayu Yang, Mingjiang Huang, Ziyi Wang, Zhongcheng Li, Honghui Zhu, Rui Chen, Guanghua He, Yunfeng Li. SB1 Encoding RING-Like Zinc-Finger Protein Regulates Branch Development as a Transcription Repressor [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(3): 243-256. |
| [7] | Karmakar Aritra, Bhattacharya Sananda, Sengupta Shinjini, Ali Nusrat, Nath Sarkar Sailendra, Datta Karabi, K. Datta Swapan. RNAi-Mediated Silencing of ITPK Gene Reduces Phytic Acid Content, Alters Transcripts of Phytic Acid Biosynthetic Genes, and Modulates Mineral Distribution in Rice Seeds [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(4): 315-328. |
| [8] | Yaling Chen, Yuehan Pang, Jinsong Bao. Expression Profiles and Protein Complexes of Starch Biosynthetic Enzymes from White-Core and Waxy Mutants Induced from High Amylose Indica Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(2): 152-161. |
| [9] | Moe Kyi, Moh Moh Seinn, Zaw Htwe Aung, Kajihara Yoshinori, Yamakawa Takeo. Effects of Integrated Organic and Inorganic Fertilizers on Yield and Growth Parameters of Rice Varieties [J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(5): 309-318. |
| [10] | Xiujie Zhang, Wujun Jin, Wentao Xu, Xiaying Li, Ying Shang, Sha Li, Hongsheng Ouyang. Comparison of Five Endogenous Reference Genes for Specific PCR Detection and Quantification of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(4): 248-256. |
| [11] | Yunyan Fei, Jie Yang, Fangquan Wang, Fangjun Fan, Wenqi Li, Jun Wang, Yang Xu, Jinyan Zhu, Weigong Zhong. Production of Two Elite Glutinous Rice Varieties by Editing Wx Gene [J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(2): 118-124. |
| [12] | Fernando Polesi Luís, Bruder Silveira Sarmento Silene, Guidolin Canniatti-Brazaca Solange. Starch Digestibility and Functional Properties of Rice Starch Subjected to Gamma Radiation [J]. Rice Science, 2018, 25(1): 42-51. |
| [13] | Mohibul Alam Khan Md, Haque Effi, Chandra Paul Narayan, Abdul Khaleque Md, M. S. Al-Garni Saleh, Rahman Mahfuzur, Tofazzal Islam Md. Enhancement of Growth and Grain Yield of Rice in Nutrient Deficient Soils by Rice Probiotic Bacteria [J]. Rice Science, 2017, 24(5): 264-273. |
| [14] | Vivitha P., Raveendran M., Vijayalakshmi D.. Introgression of QTLs Controlling Spikelet Fertility Maintains Membrane Integrity and Grain Yield in Improved White Ponni Derived Progenies Exposed to Heat Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2017, 24(1): 32-40. |
| [15] | Fernando Polesi Luís, Divino da Matta Junior Manoel, Bruder Silveira Sarmento Silene, Guidolin Canniatti-Brazaca Solange. Starch Digestibility and Physicochemical and Cooking Properties of Irradiated Rice Grains [J]. Rice Science, 2017, 24(1): 48-55. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||