
Rice Science ›› 2025, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 339-352.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2025.04.003
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lakshmi V. G. Ishwarya1, S. Vanisri2( ), P. S. Basavaraj3, M. Sreedhar4, Lakshmi V. Jhansi5, M. Muntazir6, C. Gireesh5, S. N. C. V. L. Pushpavalli2
), P. S. Basavaraj3, M. Sreedhar4, Lakshmi V. Jhansi5, M. Muntazir6, C. Gireesh5, S. N. C. V. L. Pushpavalli2
Received:2024-09-10
Accepted:2024-12-27
Online:2025-05-28
Published:2025-06-16
Contact:
S. Vanisri (Lakshmi V. G. Ishwarya, S. Vanisri, P. S. Basavaraj, M. Sreedhar, Lakshmi V. Jhansi, M. Muntazir, C. Gireesh, S. N. C. V. L. Pushpavalli. Harnessing Advanced Genomic Approaches to Unveil and Enhance Brown Planthopper Resistance in Rice[J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(3): 339-352.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Gene/QTL | Chr. | Position | Inheritance | Donor | Molecular marker | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bph1 | 12 | 21.20-22.10 Mb | Dominant | IR64 | RM28366-RM463 | Yang et al, | |
| 12L | - | Dominant | IR28 (from TKM6) | XNpb248-XNpb336 | Hirabayashi and Ogawa, | ||
| 12L | 2.9 cM | Dominant | Gayabyeo | RG634, RG457, RM247 | Jeon et al, | ||
| 12L | 22.81-22.93 Mb | Dominant | Cheongcheongbyeo | STS-pBPH4, STS-pBPH14 | Cha et al, | ||
| 12L | 22.13-23.18 Mb | Recessive | Norin-PL4 (IR1154-243) | G2140-C449 | Murata et al, | ||
| Recessive | Norin-PL4 (IR1154-243) | KAM3-KAM5 | Murai et al, | ||||
| 12L | 13.21-22.13 Mb | Recessive | ASD7 | RM1246-RM463 | Sun et al, | ||
| Qbph2 | 2 | 22.5-24.0 Mb | - | Col.5 Thailand | RM6843-RM3355 | Sun et al, | |
| qBph2 | 2 | 68.9 cM | - | Oryza rufipogon | RM29-RG157 | Huang et al, | |
| Bph3 | 4S | 6.2-7.00 Mb | Dominant | Rathu Heenati | RZ69 | Min et al, | |
| Dominant | Rathu Heenati | RHD9-RHC10 | Liu et al, | ||||
| Dominant | Rathu Heenati | 4M03980, 4M04041, MM28T | Qing et al, | ||||
| 6 | 1.21-1.40 Mb | Dominant | Rathu Heenati | RM589, RM588, RM19291-RM8072 | Jairin et al, | ||
| 6 | 0.44 Mb | Dominant | Rathu Heenati | RM508 | Temnykh et al, | ||
| Qbph3 | 3 | 48.6 cM | - | Rathu Heenati | RM313-RM7 | Sun et al, | |
| QBph3 | 3L | 35.63-35.67 Mb | - | Oryza officinalis | C3-14 | Hu et al, | |
| qBph-3-1 | 3 | 15.7-33.5 Mb | - | Rathu Heenati | RM231-RM3872 | Shabanimofrad et al, | |
| bph4 | 6S | 1.20-1.76 Mb | Recessive | Babawee | C76A, RM589-RM586 | Kawaguchi et al, | |
| QBph4 | 4 | 4.41-9.37 Mb | - | Rathu Heenati | RM8213-RM5953 | Sun et al, | |
| QBph4.1 | 4S | 6.70-6.90 Mb | - | O. officinalis | P17-xc-427 | Hu et al, | |
| QBph4.2 | 4 | 6.58-6.89 Mb | - | Oryza australiensis | RM261-S1, XC4-27 | Hu et al, | |
| qBph4.3 | 4S | 0.50-0.70 Mb | - | Salkathi | RM551-RM335 | Mohanty et al, | |
| qBph4.4 | 4S | 0.70-13.10 Mb | - | Salkathi | RM335-RM5633 | Mohanty et al, | |
| bph5 | - | - | Recessive | ARC10550 | - | Khush et al, | |
| Bph6 | 4L | 21.24-21.33 Mb | Dominant | Swarnalata | RM16994-RM119 | Kabis and Khush, | |
| 4L | 21.36-21.39 Mb | Dominant | Swarnalata | STSY9-STSY19 | Qiu et al, | ||
| 11 | 17.23-18.27 Mb | Dominant | O. officinalis | OPA16938a | Jena et al, | ||
| Qbph6 | 6 | 2.20-2.80 Mb | - | Col.5 Thailand | RM510-RM587 | Sun et al, | |
| qBPH6 | 6 | 23.00-23.50 Mb | - | ASD7 | RM28466-RM7376 | Mai et al, | |
| bph7 | 12L | 19.95-20.87 Mb | Recessive | T12 | RM3448-RM313 | Kabis and Khush, | |
| qBph7 | 7 | 19.2-25.4 Mb | - | O. rufipogon | RM11-RM234 | Huang et al, | |
| Qbph8 | 8 | 20.27 Mb | - | Swarnalatha | RM339-RM515 | Cheng et al, | |
| Bph9 | 12L | 19.11-22.13 Mb | Dominant | Kaharamana | RM5341-RM463 | Su et al, | |
| 12L | 19.00-22.50 Mb | Dominant | Pokkali | G2140, OPR04, S2545 | Murata et al, | ||
| 12L | 22.62-23.20 Mb | Dominant | Pokkali | RM28486-RM28438 | Zhao et al, | ||
| Bph10 | 12L | 9.00-23.00 Mb | Dominant | O. australiensis | RG457-CDO459, RM260-RM313 | Ishii et al, | |
| QBph10 | 10 | 21.06-22.43 Mb | - | Rathu Heenati | RM484-RM496 | Sun et al, | |
| bph11 | 3L | 35.60-35.80 Mb | Recessive | O. officinalis | G1318 | Hirabayashi et al, | |
| Qbph11 | 11 | - | - | DV85 | X202-C1172 | Su et al, | |
| bph12(t) | 4L | 20.20-21.20 Mb | Recessive | O. officinalis | G271-R93 | Hirabayashi et al, | |
| Bph12 | 4S | 5.21-5.66 Mb | Dominant | B14, Oryza latifolia | RM16459-RM1305 | Qiu et al, | |
| Bph12(t) | 4S | 6.57 Mb | Dominant | B14, O. latifolia | C946-RM261 | Yang et al, | |
| qBPH12 | 12 | 21.8-24.7 Mb | - | ASD7 | RM3326-RM28597 | Mai et al, | |
| Bph13(t) | 2L | 31.40-32.00 Mb | Dominant | Oryza eichingeri | RM240-RM250 | Liu et al, | |
| 3S | 5.18-5.70 Mb | Dominant | O. officinalis | RG100, RG191, AJ09b, AJ09c | Renganayaki et al, | ||
| Bph14 | 3L | 35.70-35.72 Mb | Dominant | B5, O. officinalis | R1925-R2443, R1925-G1318, SM1-G1318, Bph14 P/N | Huang et al, | |
| Bph15 | 4S | 6.68-6.90 Mb | Dominant | B5, O. officinalis | C820, S11182, RG1, RG2, RM261-S16 | Huang et al, | |
| Bph17(t) | 4S | 6.93-6.97 Mb | Dominant | Rathu Heenati | RM8213-RM5953 | Sun et al, | |
| Dominant | Rathu Heenati | RHD9-RHC10 | Liu et al, | ||||
| Dominant | Rathu Heenati | LecRK2-SNP, LecRK3-SNP | Kusumawati et al, | ||||
| Bph18(t) | 12L | 22.25-23.48 Mb | Dominant | O. australiensis | R10289S-RM6869, S15552-7312.T4A, BIM3-BN162 | Jena et al, | |
| Dominant | O. australiensis | KC1 | Liang et al, | ||||
| Dominant | O. australiensis | SNP23-SNP24 | Song et al, | ||||
| Dominant | O. australiensis | SNP Bph18 marker | Ramkumar et al, | ||||
| bph18(t) | 4L | 116.80 cM | Recessive | O. rufipogon | RZ565-RM273 | Li et al, | |
| bph19(t) | 3S | 7.18-7.24 Mb | Recessive | AS20-1 | RM6308-RM3134 | Chen et al, | |
| Bph20(t) | 4S | 8.20-9.60 Mb | Dominant | Oryza minuta | B42-B44, MS10-RM5953 | Rahman et al, | |
| Bph21(t) | 12L | 23.28-24.41 Mb | Dominant | O. minuta | B120, B122, RM3726, M5479 | Rahman et al, | |
| Bph22(t) | 6S | 3.40-3.41 Mb | Dominant | O. minuta | RM19429-RM584 | Harini et al, | |
| Bph25 | 6S | 0.20-1.71 Mb | Dominant | ADR52 | S00310-RM8101 | Myint et al, | |
| Bph26 | 12L | 22.13-23.18 Mb | Dominant | IR1154-243 | KAM4 | Murai et al, | |
| 12L | 21.52-24.46 Mb | Dominant | ADR52 | RM5479, RM309, MSSR2, DS-72B4 | Myint et al, | ||
| Bph27 | 4L | 19.12-19.20 Mb | Dominant | O. rufipogon | RM16846-RM16853 | Huang et al, | |
| Bph27(t) | 4L | 20.79-21.33 Mb | Dominant | Balamawee | Q52-Q20 | He et al, | |
| Bph28(t) | 11L | 16.92-16.99 Mb | Dominant | DV85 | Indel55-Indel66 | Wu et al, | |
| bph20(t)/29 | 6S | 0.48-0.49 Mb | - | O. rufipogon | RM435-RM540, BYL8-BID2 | Yang et al, | |
| bph21(t)/30 | 10S | 12.90-15.00 cM | Recessive | O. rufipogon | RM222-RM244 | Yang et al, | |
| Bph30/40 | 4S | 0.90-0.94 Mb | Dominant | AC-1613 | RM16294, RM16299 | Wang et al, | |
| Bph31 | 3L | 26.26-26.74 Mb | Dominant | CR2711-76 | PA26, RM2334 | Prahalada et al, | |
| Bph32 | 6S | 1.21-1.40 Mb | Dominant | PTB33 | RM19291, RM8072, PASH6 | Ren et al, | |
| Dominant | Rathu Heenati | Bph32-SNP, SSR23 | Kusumawati et al, | ||||
| Bph33 | 4S | 0.91-0.97 Mb | Dominant | Kolayal/Poliyal | H99, H101 | Hu et al, | |
| Bph33(t) | 1 | 24.80-28.00 Mb | Dominant | RP2068-18-3-5 | RM488-RM11522 | Naik et al, | |
| Bph34 | 4L | 21.15-21.30 Mb | Dominant | Oryza nivara | RM16994-RM17007 | Kumar et al, | |
| Bph35 | 4 | 6.28-6.93 Mb | Dominant | O. rufipogon | PSM16, RM413 | Zhang et al, | |
| Bph36 | 4S | 5.57-6.66 Mb | Dominant | O. rufipogon | S13, X48, RM16465-RM16502 | Li et al, | |
| Bph37 | 1 | 33.00 Mb | Dominant | IR64 | RM302, Indel YM35 | Yang et al, | |
| Bph38 | 4 | 3.72-15.83 Mb | Dominant | O. rufipogon | RM16563-RM16763 | Yang et al, | |
| Bph38(t) | 1L | 20.71-21.23 Mb | Dominant | Khazar | SNP-693369-SNP-id10112165 | Balachiranjeevi et al, | |
| BPH41 | 4S | 0.40-1.50 Mb | - | SWD10 | SWRm_01617, SWRm_01522 | Tan et al, | |
| BPH42 | 4L | 12.5-14.8 Mb | - | SWD10 | SWRm_01695, SWRm_00328 | Tan et al, | |
| bph42 | 4S | 0.4-16.9 Mb | Recessive | CR100441, O. rufipogon | RM16282-RM16335 | Kaur et al, | |
| Bph43 | 11 | 16.2-17.6 Mb | Dominant | IRGC 8678 | 6-22-16-3 | Kim et al, | |
| Bph44 | 4L | 4.76-5.42 cM | Dominant | Balamwee | Q31, RM17007 | Kiswanto et al, | |
| Bph45 | 4 | 13.67-13.70 Mb | Dominant | IRGC102165, O. nivara | RM3317-RM16655 | Li et al, | |
| bph46 | 4S | 6.54-18.60 Mb | Recessive | IRGC93198, O. nivara | RM16285, M6314, RM6659 | Kaur et al, | |
Table 1. List of successfully mapped resistance genes/QTLs for brown planthopper (BPH) on different rice chromosomes.
| Gene/QTL | Chr. | Position | Inheritance | Donor | Molecular marker | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bph1 | 12 | 21.20-22.10 Mb | Dominant | IR64 | RM28366-RM463 | Yang et al, | |
| 12L | - | Dominant | IR28 (from TKM6) | XNpb248-XNpb336 | Hirabayashi and Ogawa, | ||
| 12L | 2.9 cM | Dominant | Gayabyeo | RG634, RG457, RM247 | Jeon et al, | ||
| 12L | 22.81-22.93 Mb | Dominant | Cheongcheongbyeo | STS-pBPH4, STS-pBPH14 | Cha et al, | ||
| 12L | 22.13-23.18 Mb | Recessive | Norin-PL4 (IR1154-243) | G2140-C449 | Murata et al, | ||
| Recessive | Norin-PL4 (IR1154-243) | KAM3-KAM5 | Murai et al, | ||||
| 12L | 13.21-22.13 Mb | Recessive | ASD7 | RM1246-RM463 | Sun et al, | ||
| Qbph2 | 2 | 22.5-24.0 Mb | - | Col.5 Thailand | RM6843-RM3355 | Sun et al, | |
| qBph2 | 2 | 68.9 cM | - | Oryza rufipogon | RM29-RG157 | Huang et al, | |
| Bph3 | 4S | 6.2-7.00 Mb | Dominant | Rathu Heenati | RZ69 | Min et al, | |
| Dominant | Rathu Heenati | RHD9-RHC10 | Liu et al, | ||||
| Dominant | Rathu Heenati | 4M03980, 4M04041, MM28T | Qing et al, | ||||
| 6 | 1.21-1.40 Mb | Dominant | Rathu Heenati | RM589, RM588, RM19291-RM8072 | Jairin et al, | ||
| 6 | 0.44 Mb | Dominant | Rathu Heenati | RM508 | Temnykh et al, | ||
| Qbph3 | 3 | 48.6 cM | - | Rathu Heenati | RM313-RM7 | Sun et al, | |
| QBph3 | 3L | 35.63-35.67 Mb | - | Oryza officinalis | C3-14 | Hu et al, | |
| qBph-3-1 | 3 | 15.7-33.5 Mb | - | Rathu Heenati | RM231-RM3872 | Shabanimofrad et al, | |
| bph4 | 6S | 1.20-1.76 Mb | Recessive | Babawee | C76A, RM589-RM586 | Kawaguchi et al, | |
| QBph4 | 4 | 4.41-9.37 Mb | - | Rathu Heenati | RM8213-RM5953 | Sun et al, | |
| QBph4.1 | 4S | 6.70-6.90 Mb | - | O. officinalis | P17-xc-427 | Hu et al, | |
| QBph4.2 | 4 | 6.58-6.89 Mb | - | Oryza australiensis | RM261-S1, XC4-27 | Hu et al, | |
| qBph4.3 | 4S | 0.50-0.70 Mb | - | Salkathi | RM551-RM335 | Mohanty et al, | |
| qBph4.4 | 4S | 0.70-13.10 Mb | - | Salkathi | RM335-RM5633 | Mohanty et al, | |
| bph5 | - | - | Recessive | ARC10550 | - | Khush et al, | |
| Bph6 | 4L | 21.24-21.33 Mb | Dominant | Swarnalata | RM16994-RM119 | Kabis and Khush, | |
| 4L | 21.36-21.39 Mb | Dominant | Swarnalata | STSY9-STSY19 | Qiu et al, | ||
| 11 | 17.23-18.27 Mb | Dominant | O. officinalis | OPA16938a | Jena et al, | ||
| Qbph6 | 6 | 2.20-2.80 Mb | - | Col.5 Thailand | RM510-RM587 | Sun et al, | |
| qBPH6 | 6 | 23.00-23.50 Mb | - | ASD7 | RM28466-RM7376 | Mai et al, | |
| bph7 | 12L | 19.95-20.87 Mb | Recessive | T12 | RM3448-RM313 | Kabis and Khush, | |
| qBph7 | 7 | 19.2-25.4 Mb | - | O. rufipogon | RM11-RM234 | Huang et al, | |
| Qbph8 | 8 | 20.27 Mb | - | Swarnalatha | RM339-RM515 | Cheng et al, | |
| Bph9 | 12L | 19.11-22.13 Mb | Dominant | Kaharamana | RM5341-RM463 | Su et al, | |
| 12L | 19.00-22.50 Mb | Dominant | Pokkali | G2140, OPR04, S2545 | Murata et al, | ||
| 12L | 22.62-23.20 Mb | Dominant | Pokkali | RM28486-RM28438 | Zhao et al, | ||
| Bph10 | 12L | 9.00-23.00 Mb | Dominant | O. australiensis | RG457-CDO459, RM260-RM313 | Ishii et al, | |
| QBph10 | 10 | 21.06-22.43 Mb | - | Rathu Heenati | RM484-RM496 | Sun et al, | |
| bph11 | 3L | 35.60-35.80 Mb | Recessive | O. officinalis | G1318 | Hirabayashi et al, | |
| Qbph11 | 11 | - | - | DV85 | X202-C1172 | Su et al, | |
| bph12(t) | 4L | 20.20-21.20 Mb | Recessive | O. officinalis | G271-R93 | Hirabayashi et al, | |
| Bph12 | 4S | 5.21-5.66 Mb | Dominant | B14, Oryza latifolia | RM16459-RM1305 | Qiu et al, | |
| Bph12(t) | 4S | 6.57 Mb | Dominant | B14, O. latifolia | C946-RM261 | Yang et al, | |
| qBPH12 | 12 | 21.8-24.7 Mb | - | ASD7 | RM3326-RM28597 | Mai et al, | |
| Bph13(t) | 2L | 31.40-32.00 Mb | Dominant | Oryza eichingeri | RM240-RM250 | Liu et al, | |
| 3S | 5.18-5.70 Mb | Dominant | O. officinalis | RG100, RG191, AJ09b, AJ09c | Renganayaki et al, | ||
| Bph14 | 3L | 35.70-35.72 Mb | Dominant | B5, O. officinalis | R1925-R2443, R1925-G1318, SM1-G1318, Bph14 P/N | Huang et al, | |
| Bph15 | 4S | 6.68-6.90 Mb | Dominant | B5, O. officinalis | C820, S11182, RG1, RG2, RM261-S16 | Huang et al, | |
| Bph17(t) | 4S | 6.93-6.97 Mb | Dominant | Rathu Heenati | RM8213-RM5953 | Sun et al, | |
| Dominant | Rathu Heenati | RHD9-RHC10 | Liu et al, | ||||
| Dominant | Rathu Heenati | LecRK2-SNP, LecRK3-SNP | Kusumawati et al, | ||||
| Bph18(t) | 12L | 22.25-23.48 Mb | Dominant | O. australiensis | R10289S-RM6869, S15552-7312.T4A, BIM3-BN162 | Jena et al, | |
| Dominant | O. australiensis | KC1 | Liang et al, | ||||
| Dominant | O. australiensis | SNP23-SNP24 | Song et al, | ||||
| Dominant | O. australiensis | SNP Bph18 marker | Ramkumar et al, | ||||
| bph18(t) | 4L | 116.80 cM | Recessive | O. rufipogon | RZ565-RM273 | Li et al, | |
| bph19(t) | 3S | 7.18-7.24 Mb | Recessive | AS20-1 | RM6308-RM3134 | Chen et al, | |
| Bph20(t) | 4S | 8.20-9.60 Mb | Dominant | Oryza minuta | B42-B44, MS10-RM5953 | Rahman et al, | |
| Bph21(t) | 12L | 23.28-24.41 Mb | Dominant | O. minuta | B120, B122, RM3726, M5479 | Rahman et al, | |
| Bph22(t) | 6S | 3.40-3.41 Mb | Dominant | O. minuta | RM19429-RM584 | Harini et al, | |
| Bph25 | 6S | 0.20-1.71 Mb | Dominant | ADR52 | S00310-RM8101 | Myint et al, | |
| Bph26 | 12L | 22.13-23.18 Mb | Dominant | IR1154-243 | KAM4 | Murai et al, | |
| 12L | 21.52-24.46 Mb | Dominant | ADR52 | RM5479, RM309, MSSR2, DS-72B4 | Myint et al, | ||
| Bph27 | 4L | 19.12-19.20 Mb | Dominant | O. rufipogon | RM16846-RM16853 | Huang et al, | |
| Bph27(t) | 4L | 20.79-21.33 Mb | Dominant | Balamawee | Q52-Q20 | He et al, | |
| Bph28(t) | 11L | 16.92-16.99 Mb | Dominant | DV85 | Indel55-Indel66 | Wu et al, | |
| bph20(t)/29 | 6S | 0.48-0.49 Mb | - | O. rufipogon | RM435-RM540, BYL8-BID2 | Yang et al, | |
| bph21(t)/30 | 10S | 12.90-15.00 cM | Recessive | O. rufipogon | RM222-RM244 | Yang et al, | |
| Bph30/40 | 4S | 0.90-0.94 Mb | Dominant | AC-1613 | RM16294, RM16299 | Wang et al, | |
| Bph31 | 3L | 26.26-26.74 Mb | Dominant | CR2711-76 | PA26, RM2334 | Prahalada et al, | |
| Bph32 | 6S | 1.21-1.40 Mb | Dominant | PTB33 | RM19291, RM8072, PASH6 | Ren et al, | |
| Dominant | Rathu Heenati | Bph32-SNP, SSR23 | Kusumawati et al, | ||||
| Bph33 | 4S | 0.91-0.97 Mb | Dominant | Kolayal/Poliyal | H99, H101 | Hu et al, | |
| Bph33(t) | 1 | 24.80-28.00 Mb | Dominant | RP2068-18-3-5 | RM488-RM11522 | Naik et al, | |
| Bph34 | 4L | 21.15-21.30 Mb | Dominant | Oryza nivara | RM16994-RM17007 | Kumar et al, | |
| Bph35 | 4 | 6.28-6.93 Mb | Dominant | O. rufipogon | PSM16, RM413 | Zhang et al, | |
| Bph36 | 4S | 5.57-6.66 Mb | Dominant | O. rufipogon | S13, X48, RM16465-RM16502 | Li et al, | |
| Bph37 | 1 | 33.00 Mb | Dominant | IR64 | RM302, Indel YM35 | Yang et al, | |
| Bph38 | 4 | 3.72-15.83 Mb | Dominant | O. rufipogon | RM16563-RM16763 | Yang et al, | |
| Bph38(t) | 1L | 20.71-21.23 Mb | Dominant | Khazar | SNP-693369-SNP-id10112165 | Balachiranjeevi et al, | |
| BPH41 | 4S | 0.40-1.50 Mb | - | SWD10 | SWRm_01617, SWRm_01522 | Tan et al, | |
| BPH42 | 4L | 12.5-14.8 Mb | - | SWD10 | SWRm_01695, SWRm_00328 | Tan et al, | |
| bph42 | 4S | 0.4-16.9 Mb | Recessive | CR100441, O. rufipogon | RM16282-RM16335 | Kaur et al, | |
| Bph43 | 11 | 16.2-17.6 Mb | Dominant | IRGC 8678 | 6-22-16-3 | Kim et al, | |
| Bph44 | 4L | 4.76-5.42 cM | Dominant | Balamwee | Q31, RM17007 | Kiswanto et al, | |
| Bph45 | 4 | 13.67-13.70 Mb | Dominant | IRGC102165, O. nivara | RM3317-RM16655 | Li et al, | |
| bph46 | 4S | 6.54-18.60 Mb | Recessive | IRGC93198, O. nivara | RM16285, M6314, RM6659 | Kaur et al, | |
| Gene | Locus name | Gene ID | Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bph3 | LOC_Os04g12540 | Os04g0201900 | Plasma membrane-localized lectin receptor kinases |
| LOC_Os04g12580 | Os04g0202500 | ||
| Bph15 | LOC_Os04g12390 | Os04g0200400 | Lectin receptor kinases |
| LOC_Os04g12460 | Os04g0201000 | ||
| Bph18 | LOC_Os12g37290 | Os12g0559400 | Resistance protein T10rga2-1A, putative, expressed |
| LOC_Os12g37280 | Os12g0559400 | ||
| Bph27 | LOC_Os04g31924 | Os04g0388700 | Putative nodulin protein |
| LOC_Os04g32000 | Os04g0389600 | Putative MYB transcription factor | |
| LOC_Os04g53190.2 | Os04g0623300 | TGF beta receptor associated protein | |
| bph29 | LOC_Os06g01850 | Os06g0107700 | Ferredoxin NADP reductase, chloroplast precursor |
| LOC_Os06g01860 | Os06g0107800 | Expressed protein | |
| Bph30 | LOC_Os04g08390 | Os04g0166000 | LRR family protein, expressed |
| Bph31 | LOC_Os03g46550 | Os03g0668300 | LRR domain protein |
| LOC_Os03g46454 | Os03g0667300 | Metal cation transporter, putative, expressed | |
| LOC_Os03g46440 | Os03g0667100 | BTB domain with Ankyrin repeat region, expressed | |
| Bph32 | LOC_Os06g03660 | Os06g0127000 | Peroxisomal biogenesis factor 11, putative |
| LOC_Os06g03890 | Os06g0129600 | Plasma membrane receptor proteins | |
| Bph33 | LOC_Os04g02520 | Os04g0115650 | LRR family protein |
| Bph33(t) | LOC_Os01g42190.1 | Os01g0606900 | Heat shock protein DnaJ, putative, expressed |
| Bph34 | LOC_Os04g35210 | Os04g0431700 | LRR family protein |
| Bph36 | LOC_Os04g11800 | Os04g0194400 | Hypothetical protein |
| LOC_Os04g11810 | Os04g0194466 | Acyltransferase family protein | |
| LOC_Os04g11820 | Os04g0194500 | White-brown complex homolog protein | |
| LOC_Os04g11830 | Os04g0194600 | TCP family transcription factor | |
| Bph37 | LOC_Os06g03500 | Os06g0125000 | NBS-LRR disease resistance protein, putative |
| Bph38(t) | LOC_Os01g37260 | Os01g0553400 | FBXL class of F-box protein possessing LRR |
| Bph43 | LOC_Os11g29000 | Os11g0479400 | Pollen signaling protein with adenylyl cyclase activity |
| LOC_Os11g29050 | Os11g0480000 | NBS-LRR type disease resistance protein | |
| LOC_Os11g29090 | Os11g0481000 | NB-ARC/LRR disease resistance protein | |
| LOC_Os11g29110 | Os11g0481150 | LRR family protein, expressed |
Table 2. List of rice genes resistant to brown planthopper (BPH) with their candidate genes and annotations.
| Gene | Locus name | Gene ID | Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bph3 | LOC_Os04g12540 | Os04g0201900 | Plasma membrane-localized lectin receptor kinases |
| LOC_Os04g12580 | Os04g0202500 | ||
| Bph15 | LOC_Os04g12390 | Os04g0200400 | Lectin receptor kinases |
| LOC_Os04g12460 | Os04g0201000 | ||
| Bph18 | LOC_Os12g37290 | Os12g0559400 | Resistance protein T10rga2-1A, putative, expressed |
| LOC_Os12g37280 | Os12g0559400 | ||
| Bph27 | LOC_Os04g31924 | Os04g0388700 | Putative nodulin protein |
| LOC_Os04g32000 | Os04g0389600 | Putative MYB transcription factor | |
| LOC_Os04g53190.2 | Os04g0623300 | TGF beta receptor associated protein | |
| bph29 | LOC_Os06g01850 | Os06g0107700 | Ferredoxin NADP reductase, chloroplast precursor |
| LOC_Os06g01860 | Os06g0107800 | Expressed protein | |
| Bph30 | LOC_Os04g08390 | Os04g0166000 | LRR family protein, expressed |
| Bph31 | LOC_Os03g46550 | Os03g0668300 | LRR domain protein |
| LOC_Os03g46454 | Os03g0667300 | Metal cation transporter, putative, expressed | |
| LOC_Os03g46440 | Os03g0667100 | BTB domain with Ankyrin repeat region, expressed | |
| Bph32 | LOC_Os06g03660 | Os06g0127000 | Peroxisomal biogenesis factor 11, putative |
| LOC_Os06g03890 | Os06g0129600 | Plasma membrane receptor proteins | |
| Bph33 | LOC_Os04g02520 | Os04g0115650 | LRR family protein |
| Bph33(t) | LOC_Os01g42190.1 | Os01g0606900 | Heat shock protein DnaJ, putative, expressed |
| Bph34 | LOC_Os04g35210 | Os04g0431700 | LRR family protein |
| Bph36 | LOC_Os04g11800 | Os04g0194400 | Hypothetical protein |
| LOC_Os04g11810 | Os04g0194466 | Acyltransferase family protein | |
| LOC_Os04g11820 | Os04g0194500 | White-brown complex homolog protein | |
| LOC_Os04g11830 | Os04g0194600 | TCP family transcription factor | |
| Bph37 | LOC_Os06g03500 | Os06g0125000 | NBS-LRR disease resistance protein, putative |
| Bph38(t) | LOC_Os01g37260 | Os01g0553400 | FBXL class of F-box protein possessing LRR |
| Bph43 | LOC_Os11g29000 | Os11g0479400 | Pollen signaling protein with adenylyl cyclase activity |
| LOC_Os11g29050 | Os11g0480000 | NBS-LRR type disease resistance protein | |
| LOC_Os11g29090 | Os11g0481000 | NB-ARC/LRR disease resistance protein | |
| LOC_Os11g29110 | Os11g0481150 | LRR family protein, expressed |
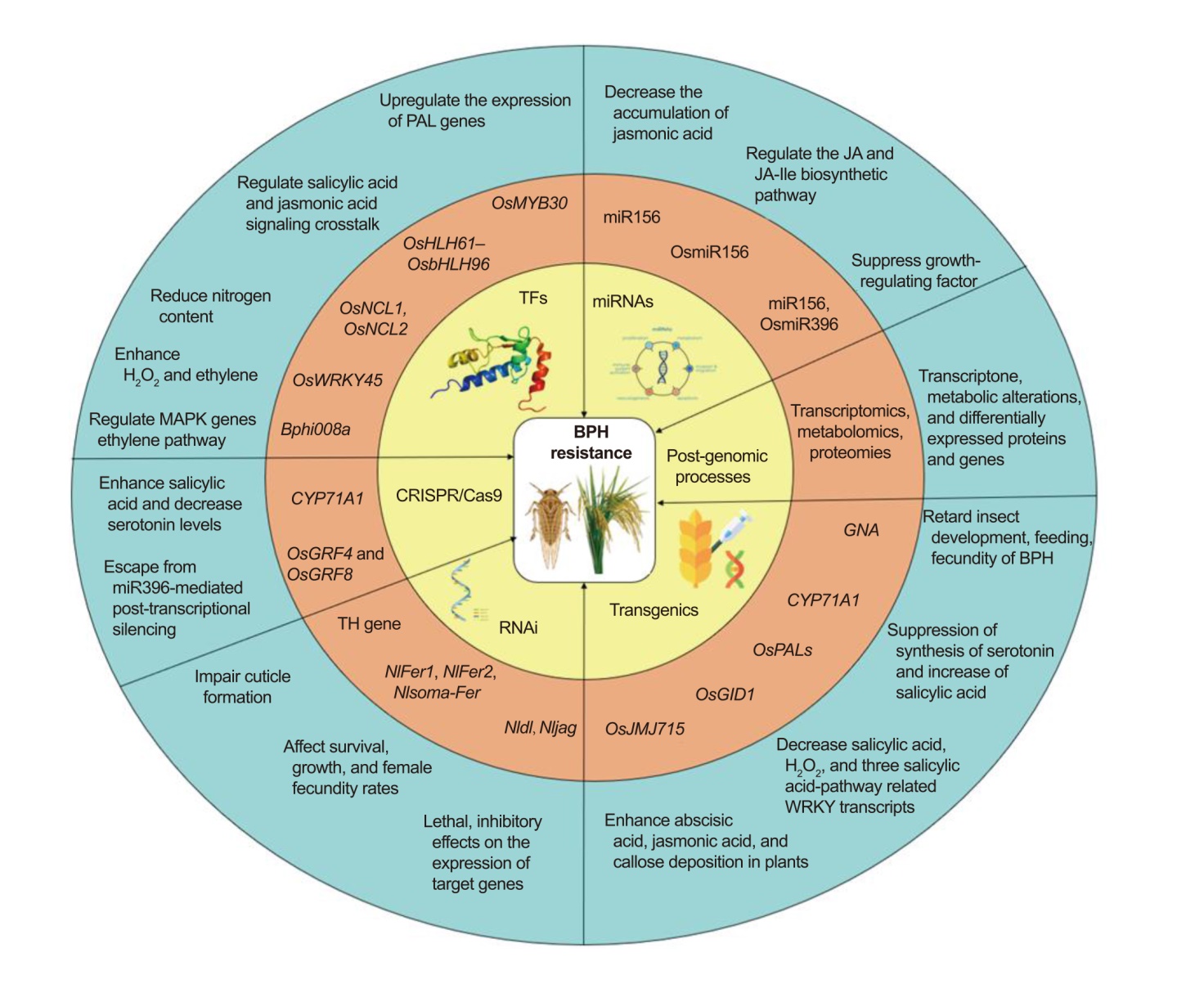
Fig. 1. Schematic model representing different approaches with genes and their mode of action conferring brown planthopper (BPH) resistance. BPH, Brown planthopper; RNAi, RNA interference; TF, Transcription factor; JA, Jasmonic acid; JA-Ile, Jasmonoyl-isoleucine; PAL, Phenylalanine ammonia- lyase; H2O2, Hydrogen peroxide; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; TH, Tryptamine 5-hydroxylase; GNA, Galanthus nivalis agglutinin.
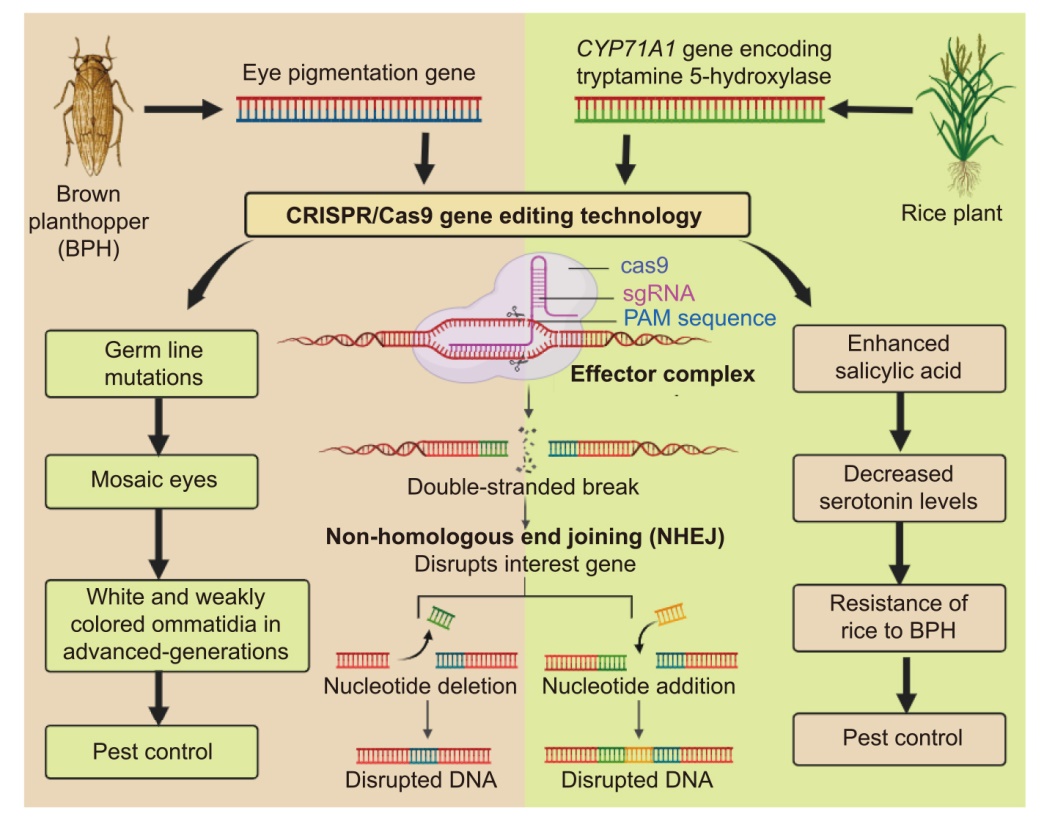
Fig. 2. Development of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance through genome editing in the pest and crop. sgRNA, Single-guide RNA; PAM, Protospacer adjacent motif; NHEJ, Non-homologous end joining.
| [1] | Angeles E R, Khush G S, Heinrichs E A. 1986. Inheritance of resistance to planthoppers and leafhoppers in rice. Rice Genetics, 537-549. |
| [2] | Athwal D S, Pathak M D, Bacalangco E H, et al. 1971. Genetics of resistance to brown planthoppers and green leafhoppers in Oryza sativa L. Crop Sci, 11(5): 747-750. |
| [3] | Balachiranjeevi C H, Prahalada G D, Mahender A, et al. 2019. Identification of a novel locus, BPH38(t), conferring resistance to brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal.) using early backcross population in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica, 215(11): 185. |
| [4] | Boddupally D, Tamirisa S, Gundra S R, et al. 2018. Expression of hybrid fusion protein (Cry1Ac:: ASAL) in transgenic rice plants imparts resistance against multiple insect pests. Sci Rep, 8(1): 8458. |
| [5] | Cha Y S, Ji H, Yun D W, et al. 2008. Fine mapping of the rice Bph1 gene, which confers resistance to the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål.), and development of STS markers for marker-assisted selection. Mol Cells, 26(2): 146-151. |
| [6] | Chen C L, Rodiger J, Chung V, et al. 2020. SNP-CRISPR: A web tool for SNP-specific genome editing. G3, 10(2): 489-494. |
| [7] | Chen J, Liu Q, Yuan L Y, et al. 2023. Osa-miR162a enhances the resistance to the brown planthopper via α-linolenic acid metabolism in rice (Oryza sativa). J Agric Food Chem, 71(31): 11847-11859. |
| [8] | Chen J W, Wang L, Pang X F, et al. 2006. Genetic analysis and fine mapping of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene bph19(t). Mol Genet Genomics, 275(4): 321-329. |
| [9] | Cheng X Y, Zhu L L, He G C. 2013. Towards understanding of molecular interactions between rice and the brown planthopper. Mol Plant, 6(3): 621-634. |
| [10] | Du B, Zhang W L, Liu B F, et al. 2009. Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106: 22163-22168. |
| [11] | España U M, López-Moya J J. 2014. Interference with insect transmission to control plant-pathogenic viruses. In: Gaur R K, Hohn T, Sharma P. Plant Virus-Host Interaction. Molecular Approaches and Viral Evolution. Oxford, UK: Academic Press: 79-103. |
| [12] | Ge Y F, Han J Y, Zhou G X, et al. 2018. Silencing of miR156 confers enhanced resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Planta, 248(4): 813-826. |
| [13] | Guo J P, Xu C X, Wu D, et al. 2018. Bph6 encodes an exocyst-localized protein and confers broad resistance to planthoppers in rice. Nat Genet, 50(2): 297-306. |
| [14] | Harini A, Lakshmi S, Kumar S S, et al. 2010. Validation and fine-mapping of genetic locus associated with resistance to brown plant hopper [Nilaparvata lugens (Stål.)] in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Asian J Biol Sci, 5: 32-37. |
| [15] | He J, Liu Y Q, Liu Y L, et al. 2013. High-resolution mapping of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance gene Bph27(t) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed, 31(3): 549-557. |
| [16] | Hirabayashi H, Ogawa T. 1995. RFLP mapping of bph-1 (brown planthopper resistance gene) in rice. Jpn J Breed, 45: 369-371. |
| [17] | Hirabayashi H, Angeles E R, Kaji R, et al. 1998. Identification of brown planthopper resistance gene derived from O. officinalis using molecular markers in rice. Breed Sci, 48: 82. |
| [18] | Hirabayashi H, Kaji R, Angeles E R, et al. 1999. RFLP analysis of a new gene for resistance to brown planthopper derived from O. officinalis on rice chromosome 4 Breed Res, 1: 48. |
| [19] | Hsu P D, Lander E S, Zhang F. 2014. Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering. Cell, 157(6): 1262-1278. |
| [20] | Hu J, Xiao C, Cheng M X, et al. 2015a. Fine mapping and pyramiding of brown planthopper resistance genes QBph3 and QBph4 in an introgression line from wild rice O. officinalis. Mol Breed, 35(1): 3. |
| [21] | Hu J, Xiao C, Cheng M X, et al. 2015b. A new finely mapped Oryza australiensis-derived QTL in rice confers resistance to brown planthopper. Gene, 561(1): 132-137. |
| [22] | Hu J, Chang X Y, Zou L, et al. 2018. Identification and fine mapping of Bph33, a new brown planthopper resistance gene in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice, 11(1): 55. |
| [23] | Hu L, Wu Y, Wu D, et al. 2017. The coiled-coil and nucleotide binding domains of BROWN PLANTHOPPER RESISTANCE14 function in signaling and resistance against planthopper in rice. Plant Cell, 29(12): 3157-3185. |
| [24] | Hu L, Wu Y, Wu D, et al. 2018. The coiled-coil and nucleotide binding domains of brown planthopper resistance14 function in signaling and resistance against planthopper in rice. Plant Cell, 29: 3157-3185. |
| [25] | Huang D, Qiu Y, Zhang Y, et al. 2013. Fine mapping and characterization of BPH27 a brown planthopper resistance gene from wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Theor Appl Genet, 126(1): 219-229. |
| [26] | Huang D R, Chen J, Lai F X, et al. 2012. Analysis of quantitative trait loci for resistance to brown planthopper in Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Acta Agron Sin, 38(2): 210-214. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Huang F J, Jiancai L, Ran L, et al. 2016. The transcription factor OsWRKY45 negatively modulates the resistance of rice to the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Int J Mol Sci, 17(6): 697. |
| [28] | Huang H J, Liu C W, Cai Y F, et al. 2015. A salivary sheath protein essential for the interaction of the brown planthopper with rice plants. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 66: 77-87. |
| [29] | Huang J, Zhang N, Shan J H, et al. 2020. Salivary protein 1 of brown planthopper is required for survival and induces immunity response in plants. Front Plant Sci, 11: 571280. |
| [30] | Huang Z, He G, Shu L, et al. 2001. Identification and mapping of two brown planthopper resistance genes in rice. Theor Appl Genet, 102: 929-934. |
| [31] | Ikeda R, Kaneda C. 1981. Genic analysis for resistance to brown planthoppers in rice. Jpn J Breed, 31(3): 279-285. |
| [32] | Ishii T, Brar D S, Multani D S, et al. 1994. Molecular tagging of genes for brown planthopper resistance and earliness introgressed from Oryza australiensis into cultivated rice, O. sativa. Genome, 37(2): 217-221. |
| [33] | Ishwarya L V G, Sreedhar M, Lakshmi V J, et al. 2021a. Molecular diversity assessment of rice genotypes for brown planthopper resistance using microsatellite markers. Electron J Plant Breed, 12(2): 499-506. |
| [34] | Ishwarya L V G, Sreedhar M, Lakshmi V J, et al. 2021b. Phenotypic screening and single marker analysis for Brown planthopper resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Res Pjtsau, 49(1/2): 1-9. |
| [35] | Ishwarya L V G, Sreedhar M, JhansiLakshmi V, et al. 2022. Development and validation of diagnostic KASP markers for brown planthopper resistance in rice. Front Genet, 13: 914131. |
| [36] | Jairin J, Phengrat K, Teangdeerith S, et al. 2007a. Mapping of a broad-spectrum brown planthopper resistance gene, Bph3, on rice chromosome 6 Mol Breed, 19(1): 35-44. |
| [37] | Jairin J, Teangdeerith S N, Leelagud P, et al. 2007b. Physical mapping of Bph3, a brown planthopper resistance locus in rice. Maejo Int J Sci Technol, 1(2): 166-177. |
| [38] | Jairin J, Sansen K, Wongboon W, et al. 2010. Detection of a brown planthopper resistance gene bph4 at the same chromosomal position of Bph3 using two different genetic backgrounds of rice. Breed Sci, 60(1): 71-75. |
| [39] | Jena K K, Pasalu I C, Rao Y K, et al. 2003. Molecular tagging of a gene for resistance to brown planthopper in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica, 129(1): 81-88. |
| [40] | Jena K K, Jeung J U, Lee J H, et al. 2006. High-resolution mapping of a new brown planthopper (BPH) resistance gene, Bph18(t), and marker-assisted selection for BPH resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet, 112(2): 288-297. |
| [41] | Jeon Y H, Ahn S N, Choi H C, et al. 1999. Identification of a RAPD marker linked to a brown planthopper resistance gene in rice. Euphytica, 107(1): 23-28. |
| [42] | Ji H, Kim S R, Kim Y H, et al. 2016. Map-based cloning and characterization of the BPH18 gene from wild rice conferring resistance to brown planthopper (BPH) insect pest. Sci Rep, 6: 34376. |
| [43] | Lü J, Liu J H, Chen L, et al. 2022. Screening of brown planthopper resistant miRNAs in rice and their roles in regulation of brown planthopper fecundity. Rice Sci, 29(6): 559-568. |
| [44] | Kabis A, Khush G S. 1988. Genetic analysis of resistance to brown planthopper in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Breed, 100(1): 54-58. |
| [45] | Kaur P, Neelam K, Sarao P S, et al. 2022. Molecular mapping and transfer of a novel brown planthopper resistance gene bph42 from Oryza rufipogon (Griff.) To cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Biol Rep, 49(9): 8597-8606. |
| [46] | Kaur P, Neelam K, Sarao P S, et al. 2023. Mapping of a novel recessive brown planthopper resistance gene bph46 from wild rice (Oryza nivara). Euphytica, 220(4): 61. |
| [47] | Kawaguchi M, Murata K, Ishii T, et al. 2001. Assignment of a brown planthopper ( Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene bph4 to the rice chromosome 6. Breed Sci, 51(1): 13-18. |
| [48] | Khush G S. 1992. Selecting rice for simply inherited resistances. In: Stalker H T, Murphy J P. Plant Breeding in the 1990s. Wallingford, UK: CAB International: 303-322. |
| [49] | Khush G S. 2013. Strategies for increasing the yield potential of cereals: Case of rice as an example. Plant Breed, 132(5): 433-436. |
| [50] | Khush G S, Karim A N M R, Angeles E R. 1985. Genetics of resistance of rice cultivar ARC10550 to Bangladesh brown pianthopper teletype. J Genet, 64(2): 121-125. |
| [51] | Kim J, An X, Yang K, et al. 2022. Molecular mapping of a new brown planthopper resistance gene Bph43 in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Agronomy, 12(4): 808. |
| [52] | Kiswanto I, Soetopo L, Adiredjo A L. 2022. Identification of novel candidate of brown planthopper resistance gene Bph44 in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genome, 65(10): 505-511. |
| [53] | Kumar K, Sarao P S, Bhatia D, et al. 2018. High-resolution genetic mapping of a novel brown planthopper resistance locus, Bph34 in Oryza sativa L. × Oryza nivara (Sharma & Shastry) derived interspecific F2 population. Theor Appl Genet, 131(5): 1163-1171. |
| [54] | Kumar K, Kaur P, Kishore A, et al. 2020. Recent advances in genomics-assisted breeding of brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) resistance in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Breed, 139(6): 1052-1066. |
| [55] | Kusumawati L, Chumwong P, Jamboonsri W, et al. 2018. Candidate genes and molecular markers associated with brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance in rice cultivar Rathu Heenati. Mol Breed, 38: 88. |
| [56] | Lakshminarayana A, Khush G S. 1977. New genes for resistance to the brown planthopper in rice. Crop Sci, 17(1): 96-100. |
| [57] | Li C P, Wu D H, Huang S H, et al. 2023. The Bph45 gene confers resistance against brown planthopper in rice by reducing the production of limonene. Int J Mol Sci, 24(2): 1798. |
| [58] | Li F H, Yan L H, Shen J, et al. 2024. Fine mapping and breeding application of two brown planthopper resistance genes derived from landrace rice. PLoS One, 19(4): e0297945. |
| [59] | Li R, Li S, Wei Y, et al. 2010. The evaluation and utilization of new genes for brown planthopper resistance in common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Mol Entomol, 4: 365-371. |
| [60] | Li Z H, Xue Y X, Zhou H L, et al. 2019. High-resolution mapping and breeding application of a novel brown planthopper resistance gene derived from wild rice (Oryza. rufipogon Griff). Rice, 12(1): 41. |
| [61] | Liang Y T, Wang C L, Lai F X, et al. 2010. Development of STS marker KC1 for brown planthopper resistance gene Bph18(t) and marker assisted selection efficiency. Chin J Rice Sci, 24(3): 244-250. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [62] | Liu G Q, Yan H H, Fu Q, et al. 2001. Mapping of a new gene for brown planthopper resistance in cultivated rice introgressed from Oryza eichingeri. Chin Sci Bull, 46(17): 1459-1462. |
| [63] | Liu S H, Yang B J, Wang A Y, et al. 2020. RNA interference of tyrosine hydroxylase caused rapid mortality by impairing cuticle formation in Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Pest Manag Sci, 76(6): 2225-2232. |
| [64] | Liu Y Q, Wu H, Chen H, et al. 2015. A gene cluster encoding lectin receptor kinases confers broad-spectrum and durable insect resistance in rice. Nat Biotechnol, 33(3): 301-305. |
| [65] | Lu H P, Luo T, Fu H W, et al. 2018. Resistance of rice to insect pests mediated by suppression of serotonin biosynthesis. Nat Plants, 4(6): 338-344. |
| [66] | Lv W T, Du B, Shangguan X X, et al. 2014. BAC and RNA sequencing reveal the brown planthopper resistance gene BPH15 in a recombination cold spot that mediates a unique defense mechanism. BMC Genomics, 15(1): 674. |
| [67] | Mai T V, Fujita D, Matsumura M, et al. 2015. Genetic basis of multiple resistance to the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) and the green rice leafhopper (Nephotettix cincticeps Uhler) in the rice cultivar ‘ASD7’ (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). Breed Sci, 65(5): 420-429. |
| [68] | Min Y H, Rui Q I N, Wei J W, et al. 2002. Comparative physical mapping of Bph3 with BAC-FISH in Oryza officinalis and O. sativa. J Integr Plant Biol, 44(5): 583. |
| [69] | Mohanty S K, Panda R S, Mohapatra S L, et al. 2017. Identification of novel quantitative trait loci associated with brown planthopper resistance in the rice landrace Salkathi. Euphytica, 213(2): 38. |
| [70] | Murai H, Hashimoto Z, Sharma P N, et al. 2001. Construction of a high-resolution linkage map of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)) resistance gene bph2. Theor Appl Genet, 103(4): 526-532. |
| [71] | Murata K, Fujiwara M, Kaneda C, et al. 1998. RFLP mapping of a brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)) resistance gene bph2 of indica rice introgressed into a japonica breeding line ‘Norin-PL4’. Genes Genet Syst, 73(6): 359-364. |
| [72] | Murata K, Fujiwara M, Murai H, et al. 2001. Mapping of a brown planthopper ( Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene Bph9 on the long arm of rice chromosome 12. Cereal Res Commun, 29(3): 245-250. |
| [73] | Myint K K M, Fujita D, Matsumura M, et al. 2012. Mapping and pyramiding of two major genes for resistance to the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens [Stål]) in the rice cultivar ADR52 Theor Appl Genet, 124(3): 495-504. |
| [74] | Nagadhara D, Ramesh S, Pasalu I C, et al. 2003. Transgenic indica rice resistant to sap-sucking insects. Plant Biotechnol J, 1(3): 231-240. |
| [75] | Naik S B, Divya D, Sahu N, et al. 2018. A new gene Bph33(t) conferring resistance to brown planthopper (BPH), Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) in rice line RP2068-18-3-5. Euphytica, 214(3): 53. |
| [76] | Nanda S, Yuan S Y, Lai F X, et al. 2020. Identification and analysis of miRNAs in IR56 rice in response to BPH infestations of different virulence levels. Sci Rep, 10(1): 19093. |
| [77] | NRRI. National Institute of Rice Research, Cuttack, India. 2021. https://icar-nrri.in/released-varieties/. |
| [78] | Panda N, Heinrichs E A. 1983. Levels of tolerance and antibiosis in rice varieties having moderate resistance to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Environ Entomol, 12(4): 1204-1214. |
| [79] | Pathak M D, Cheng C H, Fortuno M E. 1969. Resistance to Nephotettix impicticeps and Nilaparvata lugens in varieties of rice. Nature, 223: 502-504. |
| [80] | Pathichindachote W, Panyawut N, Sikaewtung K, et al. 2021. Proteomic analysis of isogenic rice lines under brown planthopper infestation. Khon Kaen Agric J, 49(5): 1324-1336. |
| [81] | Prahalada G D, Shivakumar N, Lohithaswa H C, et al. 2017. Identification and fine mapping of a new gene, BPH31 conferring resistance to brown planthopper biotype 4 of India to improve rice, Oryza sativa L. Rice, 10(1): 41. |
| [82] | Qing D J, Dai G X, Zhou W Y, et al. 2019. Development of molecular marker and introgression of Bph3 into elite rice cultivars by marker-assisted selection. Breed Sci, 69(1): 40-46. |
| [83] | Qiu Y F, Guo J P, Jing S L, et al. 2010. High-resolution mapping of the brown planthopper resistance gene Bph6 in rice and characterizing its resistance in the 9311 and Nipponbare near isogenic backgrounds. Theor Appl Genet, 121(8): 1601-1611. |
| [84] | Qiu Y F, Guo J P, Jing S L, et al. 2012. Development and characterization of japonica rice lines carrying the brown planthopper-resistance genes BPH12 and BPH6. Theor Appl Genet, 124(3): 485-494. |
| [85] | Qiu Y F, Guo J P, Jing S L, et al. 2014. 93-11 background. Euphytica, 198(3): 369-379. |
| [86] | Rahman M L, Jiang W Z, Chu S H, et al. 2009. High-resolution mapping of two rice brown planthopper resistance genes, Bph20(t) and Bph21(t), originating from Oryza minuta. Theor Appl Genet, 119(7): 1237-1246. |
| [87] | Ramkumar G, Prahalada G D, Hechanova S L, et al. 2016. Exploring genetic diversity of rice cultivars for the presence of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance genes and development of SNP marker for Bph18. Plant Breed, 135(3): 301-308. |
| [88] | Rao K V, Rathore K S, Hodges T K, et al. 1998. Expression of snowdrop lectin (GNA) in transgenic rice plants confers resistance to rice brown planthopper. Plant J, 15(4): 469-477. |
| [89] | Ren J S, Gao F Y, Wu X T, et al. 2016. Bph32, a novel gene encoding an unknown SCR domain-containing protein, confers resistance against the brown planthopper in rice. Sci Rep, 6: 37645. |
| [90] | Ren X, Wang X, Yuan H, et al. 2004. Mapping quantitative trait loci and expressed sequence tags related to brown planthopper resistance in rice. Plant Breed, 123(4): 342-348. |
| [91] | Renganayaki K, Fritz A K, Sadasivam S, et al. 2002. Mapping and progress toward map-based cloning of brown planthopper biotype-4 resistance gene introgressed from Oryza officinalis into cultivated rice, O. sativa. Crop Sci, 42(6): 2112-2117. |
| [92] | Satturu V, Vattikuti J L, J D S, et al. 2020. Multiple genome wide association mapping models identify quantitative trait nucleotides for brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) resistance in MAGIC Indica population of rice. Vaccines, 8(4): 608. |
| [93] | Shabanimofrad M, Rafii M Y, Ashkani S, et al. 2017. Mapping of QTLs conferring resistance in rice to brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Entomol Exp Appl, 162(1): 60-68. |
| [94] | Shi S J, Wang H Y, Nie L Y, et al. 2021. Bph30confers resistance to brown planthopper by fortifying sclerenchyma in rice leaf sheaths. Mol Plant, 14(10): 1714-1732. |
| [95] | Shi S J, Zha W J, Yu X Y, et al. 2023. Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis provide insight into the resistance response of rice against brown planthopper. Front Plant Sci, 14: 1213257. |
| [96] | Sidhu G S, Khush G S. 1979. Linkage relationships of some genes for disease and insect resistance and semidwarf stature in rice. Euphytica, 28(2): 233-237. |
| [97] | Song J Y, Ouk S, Nogoy F M, et al. 2016. Application and utilization of marker assisted selection for biotic stress resistance in hybrid rice (Oryza sativaL.). J Plant Biotechnol, 43(3): 317-331. |
| [98] | Su C C, Wan J, Zhai H Q, et al. 2005. A new locus for resistance to brown planthopper identified in the indica rice variety DV85. Plant Breed, 124(1): 93-95. |
| [99] | Su C C, Zhai H Q, Wang C M, et al. 2006. SSR mapping of brown planthopper resistance gene Bph9 in Kaharamana, an indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Genet Sin, 33(3): 262-268. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [100] | Sun B, Shen Y J, Chen S, et al. 2023. A novel transcriptional repressor complex MYB22-TOPLESS-HDAC1 promotes rice resistance to brown planthopper by repressing F3′H expression. New Phytol, 239(2): 720-738. |
| [101] | Sun L H, Su C C, Wang C M, et al. 2005. Mapping of a major resistance gene to the brown planthopper in the rice cultivar rathu heenati. Breed Sci, 55(4): 391-396. |
| [102] | Sun L H, Wang C M, Su C C, et al. 2006. Mapping and marker-assisted selection of a brown planthopper resistance gene bph2in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Genet Sin, 33(8): 717-723. |
| [103] | Sun L H, Liu Y Q, Jiang L, et al. 2007. Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to brown planthopper in the indica rice cultivar Col.5 Thailand. Hereditas, 144(2): 48-52. |
| [104] | Tamura Y, Hattori M, Yoshioka H, et al. 2014. Map-based cloning and characterization of a brown planthopper resistance gene BPH26 from Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica cultivar ADR52. Sci Rep, 4: 5872. |
| [105] | Tan H Q, Palyam S, Gouda J, et al. 2022. Identification of two QTLs, BPH41 and BPH42and their respective gene candidates for brown planthopper resistance in rice. Sci Rep, 12(1): 18538. |
| [106] | Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, et al. 2001. Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res, 11(8): 1441-1452. |
| [107] | Wang H Y, Shi S J, Guo Q, et al. 2018. High resolution mapping of a gene conferring strong antibiosis to BPH and developing resistant near-isogenic lines in 9311 background. Mol Breed, 38(8): 1-10. |
| [108] | Wang Y, Cao L M, Zhang Y X, et al. 2015. Map-based cloning and characterization of BPH29 a B3 domain-containing recessive gene conferring brown planthopper resistance in rice. J Exp Bot, 66(19): 6035-6045. |
| [109] | Wu H, Liu Y Q, He J, et al. 2014. Fine mapping of brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene Bph28(t) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed, 33(4): 909-918. |
| [110] | Xue W H, Xu N, Yuan X B, et al. 2018. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of two eye pigmentation genes in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 93: 19-26. |
| [111] | Yan L H, Luo T P, Huang D H, et al. 2023. Recent advances in molecular mechanism and breeding utilization of brown planthopper resistance genes in rice: An integrated review. Int J Mol Sci, 24(15): 12061. |
| [112] | Yang H Y, Ren X, Weng Q M, et al. 2002. Molecular mapping and genetic analysis of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene. Hereditas, 136(1): 39-43. |
| [113] | Yang L, Li R B, Li Y R, et al. 2012. Genetic mapping of bph20(t) and bph21(t) loci conferring brown planthopper resistance to Nilaparvata lugens Stål in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica, 183(2): 161-171. |
| [114] | Yang M, Cheng L, Yan L H, et al. 2019. Mapping and characterization of a quantitative trait locus resistance to the brown planthopper in the rice variety IR64 Hereditas, 156: 22. |
| [115] | Yang M, Lin J B, Cheng L, et al. 2020. Identification of a novel planthopper resistance gene from wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Crop J, 8(6): 1057-1070. |
| [116] | Yang X F, Liu S K, Lu W H, et al. 2022. Delta and jagged are candidate target genes of RNAi biopesticides for the control of Nilaparvata lugens. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 10: 1023729. |
| [117] | Zhang Y B, Chen M T, Zhou S X, et al. 2021. Silencing an E3 ubiquitin ligase gene OsJMJ715 enhances the resistance of rice to a piercing-sucking herbivore by activating ABA and JA signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci, 22(23): 13020. |
| [118] | Zhang Y X, Qin G, Ma Q Q, et al. 2020. Identification of major locus Bph35 resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Rice Sci, 27(3): 237-245. |
| [119] | Zhao Y, Huang J, Wang Z Z, et al. 2016. Allelic diversity in an NLR gene BPH9 enables rice to combat planthopper variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 113: 12850-12855. |
| [120] | Zhou C, Zhang Q, Chen Y, Huang J, Guo Q, Li Y. 2021. Balancing selection and wild gene pool contribute to resistance in global rice germplasm against planthopper. J Integr Plant Biol, 63(10): 1695-1711. |
| [121] | Zhou L, Chen Z J, Lang X Y, et al. 2013. Development and validation of a PCR-based functional marker system for the brown planthopper resistance gene Bph14 in rice. Breed Sci, 63(3): 347-352. |
| [1] | Wang Shuman, Zhang Linqi, Gao Ruiren, Wei Guangbo, Dong Weiguo, Xu Jiming, Wang Zhiye. Establishing Programmable CRISPR/Cas13b-Mediated Knockdown System in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(2): 217-227. |
| [2] | Ravindran Lalithambika Visakh, Sreekumar Anand, Sukumaran Nair Arya, Behera Sasmita, Uday Chand Jha, Rameswar Prasad Sah, Radha Beena. Rice Heat Tolerance Breeding: A Comprehensive Review and Forward Gaze [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(4): 375-400. |
| [3] | Li Dian, Duan Wenjing, Liu Qun’en, Wu Weixun, Zhan Xiaodeng, Sun Lianping, Zhang Yingxin, Cheng Shihua. Gapless Genome Assembly of ZH8015 and Preliminary Multi-Omics Analysis to Investigate ZH8015’s Responses Against Brown Planthopper Infestation [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(3): 317-327. |
| [4] | Xia Xiaodong, Zhang Xiaobo, Wang Zhonghao, Cheng Benyi, Sun Huifeng, Xu Xia, Gong Junyi, Yang Shihua, Wu Jianli, Shi Yongfeng, Xu Rugen. Mapping and Functional Analysis of LE Gene in a Lethal Etiolated Rice Mutant at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 567-576. |
| [5] | Liu Tingting, Zou Jinpeng, Yang Xi, Wang Kejian, Rao Yuchun, Wang Chun. Development and Application of Prime Editing in Plants [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 509-522. |
| [6] | Tan Quanya, Zhu Haitao, Liu Hui, Ni Yuerong, Wu Shengze, Luan Xin, Liu Junwei, Yang Weifeng, Yang Zifeng, Zeng Ruizhen, Liu Guifu, Wang Shaokui, Zhang Guiquan. Fine Mapping of QTLs for Stigma Exsertion Rate from Oryza glaberrima by Chromosome Segment Substitution [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(1): 55-66. |
| [7] | Muduli Lakesh, Kumar Pradhan Sukanta, Mishra Abinash, Nath Bastia Debendra, Chandra Samal Kailash, Kumar Agrawal Pawan, Dash Manasi. Understanding Brown Planthopper Resistance in Rice: Genetics, Biochemical and Molecular Breeding Approaches [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(6): 532-546. |
| [8] | Mishra Rukmini, Zheng Wei, Kumar Joshi Raj, Kaijun Zhao. Genome Editing Strategies Towards Enhancement of Rice Disease Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(2): 133-145. |
| [9] | Fei Shang, Wenbin Mou, Hao Wu, Furong Xu, Chunyan Xiang, Jianfei Wang. New Allele of HL6 Regulates Trichome Elongation in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(6): 480-492. |
| [10] | Yuyu Chen, Aike Zhu, Pao Xue, Xiaoxia Wen, Yongrun Cao, Beifang Wang, Yue Zhang, Liaqat Shah, Shihua Cheng, Liyong Cao, Yingxin Zhang. Effects of GS3 and GL3.1 for Grain Size Editing by CRISPR/Cas9 in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(5): 405-413. |
| [11] | Yuexiong Zhang, Gang Qin, Qianqian Ma, Minyi Wei, Xinghai Yang, Zengfeng Ma, Haifu Liang, Chi Liu, Zhenjing Li, Fang Liu, Dahui Huang, Rongbai Li. Identification of Major Locus Bph35 Resistance to Brown Planthopper in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(3): 237-245. |
| [12] | Hussain Kashif, Yingxing Zhang, Anley Workie, Riaz Aamir, Abbas Adil, Hasanuzzaman Rani Md., Hong Wang, Xihong Shen, Liyong Cao, Shihua Cheng. Association Mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci for Grain Size in Introgression Line Derived from Oryza rufipogon [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(3): 246-254. |
| [13] | Wenhui Wang, Linlin Wang, Yujun Zhu, Yeyang Fan, Jieyun Zhuang. Fine-Mapping of qTGW1.2a, a Quantitative Trait Locus for 1000-Grain Weight in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(4): 220-228. |
| [14] | Ran Qin, Akhter Delara, Chengcong Yang, Kumar Nath Ujjal, Eshag Jamal, Xiaoli Jin, Chunhai Shi. SRG1, Encoding a Kinesin-4 Protein, Is an Important Factor for Determining Grain Shape in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2018, 25(6): 297-307. |
| [15] | Hua Zhang, Xu Liu, Yongyi Yang, Ning Xuan, Fangyin Yao. Mapping of Hd-6-2 for Heading Date Using Two Secondary Segregation Populations in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2018, 25(3): 161-168. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||