
Rice Science ›› 2026, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 81-98.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2025.10.008
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jia Huichao1, Chun Yan1,2, Ashmit Kumar1,3, Mo Tianyu4, Wang Haifeng4, Guo Shengyuan1, Fang Jingjing1, Zhao Jinfeng1, Sun Wei4, Zhang Shiyong4, Yuan Shoujiang4, Li Xueyong1( )
)
Received:2025-07-24
Accepted:2025-10-21
Online:2026-01-28
Published:2026-02-03
Contact:
Li Xueyong (About author:First author contact:# These authors contributed equally to this work
Jia Huichao, Chun Yan, Ashmit Kumar, Mo Tianyu, Wang Haifeng, Guo Shengyuan, Fang Jingjing, Zhao Jinfeng, Sun Wei, Zhang Shiyong, Yuan Shoujiang, Li Xueyong. Suppressors of Cytokinin Receptor Mutant pal1/ohk4 Confer Favorable Alleles of Grain Number 1a (Gn1a) for Improving Grain Yield in japonica Rice[J]. Rice Science, 2026, 33(1): 81-98.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX

Fig. 1. Phenotypic analysis of wild type (WT, Huaidao 5), pal1, and suppressor mutants pal1s35, pal1s205, and pal1s242. A, Morphology of mature plants of WT, pal1, and suppressor mutants. Scale bar, 15 cm. B and C, Morphology of closed (B) and spread (C) panicles generated on the primary tillers of WT, pal1, and suppressor mutants. Scale bars, 3 cm. D-I, Comparison of plant height (D), primary tiller number (E), panicle length (F), primary branch number (G), secondary branch number (H), and grain number per panicle (I) among WT, pal1, and suppressor mutants. Panicles in (F) to (I) include only those generated on primary tillers. J and K, Cross‐sections (J) and front views (K) of the first (I), second (II), and third (III) internodes of WT, pal1, and suppressor mutants. Scale bars, 1 mm in (J) and 1 cm in (K), respectively. L-N, Comparison of the diameters of the first (internode I, L), second (internode II, M), and third (internode III, N) internodes among WT, pal1, and suppressor mutants. In D-I and L-N, data are mean ± SD (n = 10). Different lowercase letters above bars indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.

Fig. 2. Cloning of causal genes of three pal1 suppressor mutants through MutMap. A, Identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and candidate genes tightly linked with three pal1 suppressor mutants pal1s35, pal1s205, and pal1s242 through MutMap. The most likely candidate gene LOC_Os01g10110 (OsCKX2) is highlighted in red. Mut, Mutation; Chr, Chromosome; WT, Wild type; AA, Amino acid. B, Schematic representation of Gn1a/OsCKX2 gene structure and base and amino acid variations at the three sites in the suppressor mutants. The boxes and lines represent exons and introns, respectively. The start codon (ATG) and stop codon (TGA) are indicated. C, Alignment of partial sequences surrounding the mutation site indicated by a triangle in cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (CKX) homologs from different plant species, including Oryza sativa OsCKX2 (NP_001393243), OsCKX1 (NP_001388401), OsCKX5 (NP_001388663), OsCKX6 (XP_015624918), OsCKX7 (XP_015624361), and OsCKX10 (XP_025881924); Zea mays ZmCKX1 (NP_001105591), ZmCKX8 (AQK59741), and ZmCKX10 (XP_008660924); Arabidopsis thaliana AtCKX1 (NP_181682) and AtCKX6 (NP_191903); Hordeum vulgare HvCKX1 (KAE8806376) and HvCKX7 (XP_044954246); and Triticum aestivum TaCKX1 (AEK84310), TaCKX2 (AEV76971), and TaCKX7 (XP_044409379).
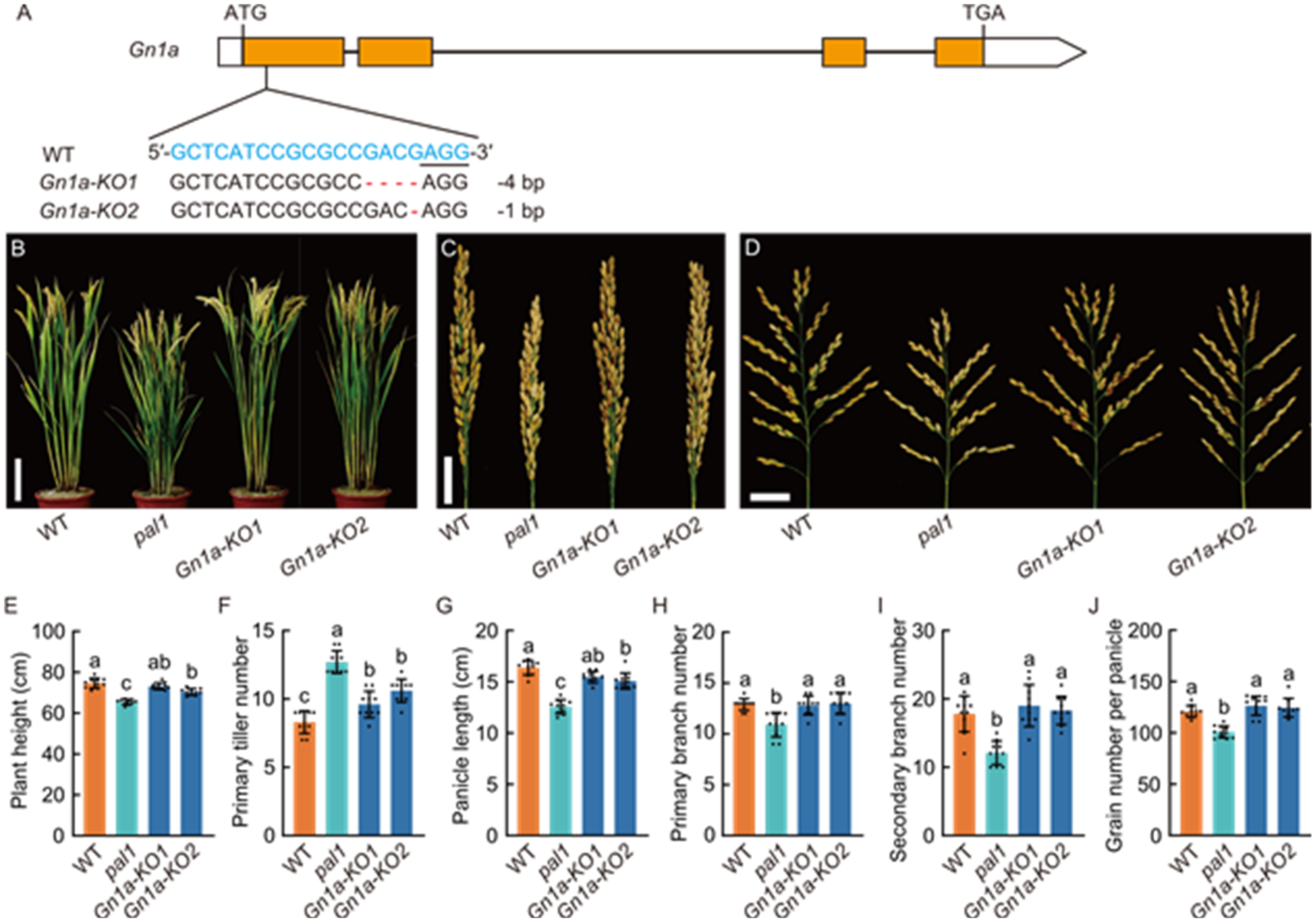
Fig. 3. Knocking out Gn1a in pal1 mutant (pal1 gn1a-ko1 and pal1 gn1a-ko2) using CRISPR/Cas9 system. A, Schematic representation of Gn1a target site and target sequence alignment of wild type (WT, Huaidao 5) and knockout (KO) lines (Gnla-KO1 and Gnla-KO2). The guide RNA target sequence is shown in blue, and the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence is underlined. Two mutations generated by CRISPR/Cas9 are shown in the lower panel. The start codon (ATG) and stop codon (TGA) are indicated. B, Morphology of mature plants of WT, pal1, and two homozygous KO lines. Scale bar, 15 cm. C and D, Morphology of closed (C) and spread (D) panicles generated on the primary tillers of WT, pal1, and two homozygous KO lines. Scale bars, 3 cm. E-J, Comparison of plant height (E), primary tiller number (F), panicle length (G), primary branch number (H), secondary branch number (I), and grain number per panicle (J) among WT, pal1, and two homozygous KO lines. Panicles in (G) to (J) only include those generated on primary tillers. Data are mean ± SD (n = 10). Different lowercase letters above histograms indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
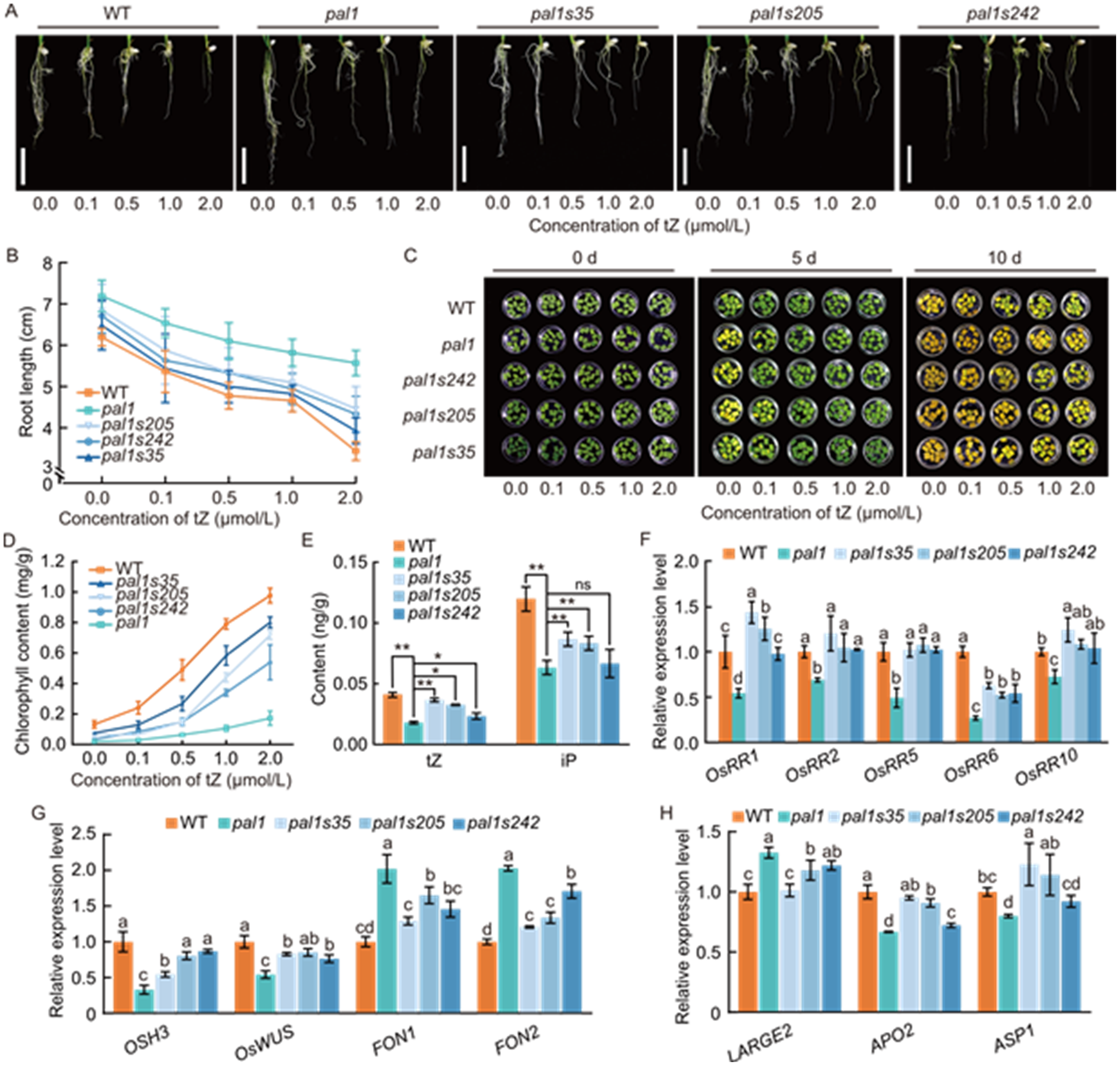
Fig. 4. Increased endogenous cytokinin levels and responsiveness in pal1 suppressor mutants pal1s35, pal1s205, and pal1s242. A, Seedling roots of wild type (WT), pal1, and pal1 suppressor mutants treated with various concentrations of trans-zeatin (tZ). Scale bars, 2 cm. B, Comparison of root length in WT, pal1, and pal1 suppressor mutants after 10 d of treatment with various concentrations of tZ. C, Effect of different concentrations of tZ on dark-induced leaf senescence in WT, pal1, and pal1 suppressor mutants. D, Quantification of chlorophyll content in leaves of WT, pal1, and pal1 suppressor mutants on 10 d of dark treatment. E, Comparison of cytokinin (tZ and isopentenyladenine) contents in young panicles (~0.5 cm) of WT, pal1, and pal1 suppressor mutants. F, Relative expression levels of type-A OsRRs genes in young panicles (~0.5 cm) of WT, pal1, and pal1 suppressor mutants. The rice Ubiquitin gene (LOC_Os03g13170) served as an internal control. G and H, Relative expression levels of genes related to meristem maintenance (G) and panicle development (H) in young panicles (~0.5 cm) of WT, pal1, and pal1 suppressor mutants. The rice Ubiquitin gene (LOC_Os03g13170) served as an internal control. In E-H, data are mean ± SD (n = 3). In E, ns, *, and ** indicate P > 0.05, P < 0.05, and P < 0.01, respectively, by Student’s t-test. In F-H, different lowercase letters above the bars indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.

Fig. 5. Effects of three variants G556D, G156D, and Y357C on OsCKX2 protein structure and enzymatic activity. A, Ribbon diagram of the three-dimensional structure of OsCKX2 predicted by AlphaFold3. The Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)-binding domain and substrate-binding domain are shown in blue and yellow, respectively. The FAD molecule is represented as a stick model in green. B-G, Diagrams showing mutation sites and their surrounding structure: G556 (B), G556D (C), G156 (D), G156D (E), Y357 (F), and Y357C (G). Mutation sites are shown in red. The FAD molecule is represented as a stick model in green and broken lines indicate potential H-bonds with FAD. H, In vitro OsCKX2 activity assay of recombinant maltose-binding protein (MBP)-OsCKX2 (WT) and three variants containing G556D, G156D, and Y357C. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). **, P < 0.01 by Student’s t-test.
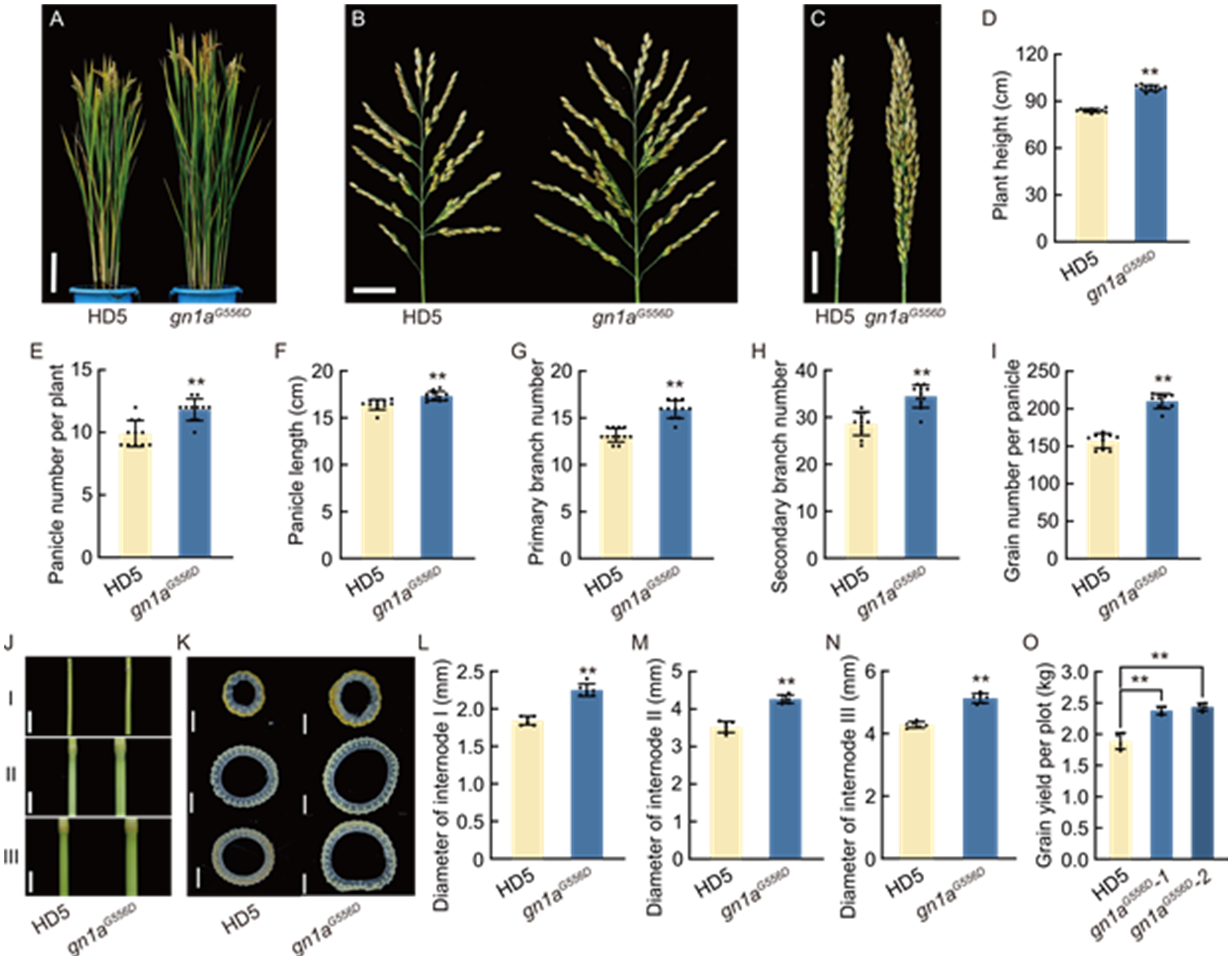
Fig. 6. Improvement of agronomic traits of Huaidao 5 by pal1 suppressor mutation. A, Morphology of mature plants of Huaidao 5 (HD5) and gn1aG556D. Scale bar, 15 cm. B and C, Morphologies of spread (B) and closed (C) panicles from the primary tillers of HD5 and gn1aG556D lines. Scale bars, 3 cm. D-I, Comparison of plant height (D), panicle number per plant (E), panicle length (F), primary branch number (G), secondary branch number (H), and grain number per panicle (I) between WT and gn1aG556D lines. Panicles in (D) to (I) include only those from primary tillers. J and K, Front views (J) and cross-sections (K) of the first (I), second (II), and third (III) internodes of HD5 and gn1aG556D. Scale bars, 1 cm in (J) and 1 mm in (K). L-N, Comparison of the diameters of first (internode I, L), second (internode II, M), and third (internode III, N) internodes between HD5 and gn1aG556D. O, Grain yield per plot (1.5 m2) of HD5 and gn1aG556D lines in the field. In D-I and L-O, data are mean ± SD (n = 10). **, P < 0.01 by Student’s t-test.
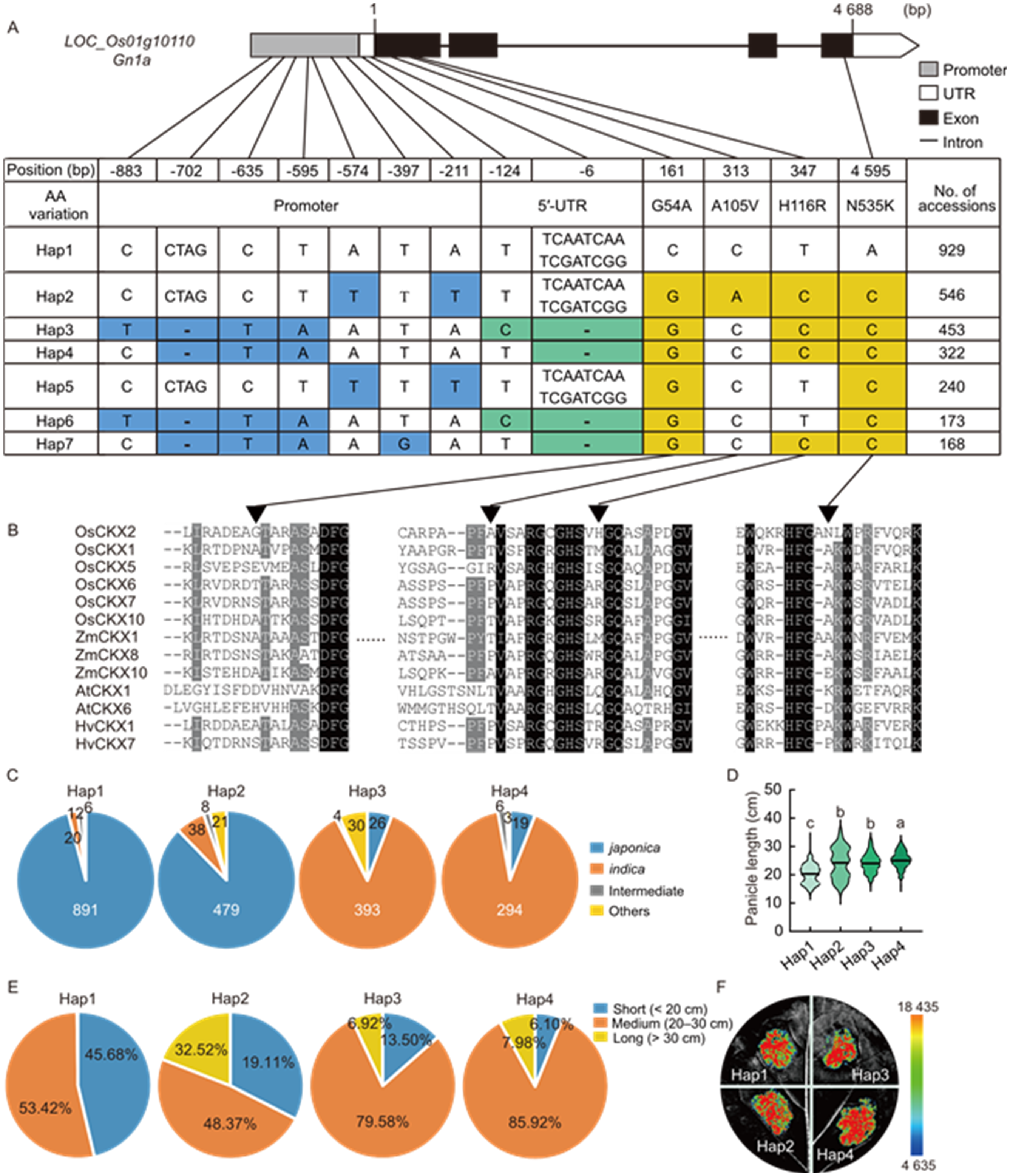
Fig. 7. Haplotype analysis of Gn1a. A, Structure and natural variations of Gn1a gene in the 3K Rice Genomes dataset. AA, Amino acid; UTR, Untranslated region. Blue, green, and yellow represent single nucleotide polymorphisms or insert/deletions in the promoter region, 5′-UTR, and coding region, respectively. B, Sequence alignment around the variation sites among each haplotype in the coding region (▼, Difference variation sites). Os, Oryza sativa; Zm, Zea mays; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Hv, Hordeum vulgare. C, Composition of Hap1, Hap2, Hap3, and Hap4 in rice subspecies. D, Comparison of panicle length among Hap1, Hap2, Hap3, and Hap4. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. E, Statistical analysis of panicle length for Hap1, Hap2, Hap3, and Hap4. F, Comparison of transcriptional activity of promoters from different Gnla haplotypes. The luciferase gene driven by the Gn1a promoter was transiently expressed in Nicotoana benthamiana leaves.
| [1] | Abe A, Kosugi S, Yoshida K, et al. 2012. Genome sequencing reveals agronomically important loci in rice using MutMap. Nat Biotechnol, 30(2): 174-178. |
| [2] | Abramson J, Adler J, Dunger J, et al. 2024. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature, 630: 493-500. |
| [3] | Ashikari M, Sakakibara H, Lin S Y, et al. 2005. Cytokinin oxidase regulates rice grain production. Science, 309: 741-745. |
| [4] | Bae E, Bingman C A, Bitto E, et al. 2008. Crystal structure of Arabidopsis thaliana cytokinin dehydrogenase. Proteins, 70(1): 303-306. |
| [5] | Brownlee B G, Hall R H, Whitty C D. 1975. 3-Methyl-2-butenal: An enzymatic degradation product of the cytokinin, N6-(∆2-isopentenyl) adenine. Can J Biochem, 53(1): 37-41. |
| [6] | Burr C A, Sun J J, Yamburenko M V, et al. 2020. The HK5 and HK6 cytokinin receptors mediate diverse developmental pathways in rice. Development, 147(20): dev191734. |
| [7] | Chun Y, Kumar A, Li X Y. 2022. Genetic and molecular pathways controlling rice inflorescence architecture. Front Plant Sci, 13: 1010138. |
| [8] | Chun Y, Fang J J, Savelieva E M, et al. 2023. The cytokinin receptor OHK4/OsHK4 regulates inflorescence architecture in rice via an IDEAL PLANT ARCHITECTURE1/WEALTHY FARMER’S PANICLE-mediated positive feedback circuit. Plant Cell, 36(1): 40-64. |
| [9] | D’Agostino I B, Deruère J, Kieber J J. 2000. Characterization of the response of the Arabidopsis response regulator gene family to cytokinin. Plant Physiol, 124(4): 1706-1717. |
| [10] | Dabravolski S A, Isayenkov S V. 2021. Evolution of the cytokinin dehydrogenase (CKX) domain. J Mol Evol, 89(9/10): 665-677. |
| [11] | Deveshwar P, Prusty A, Sharma S, et al. 2020. Phytohormone-mediated molecular mechanisms involving multiple genes and QTL govern grain number in rice. Front Genet, 11: 586462. |
| [12] | Duan J B, Yu H, Yuan K, et al. 2019. Strigolactone promotes cytokinin degradation through transcriptional activation of CYTOKININ OXIDASE/DEHYDROGENASE 9 in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 116(28): 14319-14324. |
| [13] | Fekih R, Takagi H, Tamiru M, et al. 2013. MutMap+: Genetic mapping and mutant identification without crossing in rice. PLoS One, 8(7): e68529. |
| [14] | Feng X M, Wang C, Nan J Z, et al. 2017. Updating the elite rice variety Kongyu 131 by improving the Gn1a locus. Rice, 10(1): 35. |
| [15] | Fraaije M W, van Berkel W J, Benen J A, et al. 1998. A novel oxidoreductase family sharing a conserved FAD-binding domain. Trends Biochem Sci, 23(6): 206-207. |
| [16] | Frébort I, Šebela M, Galuszka P, et al. 2002. Cytokinin oxidase/ cytokinin dehydrogenase assay: Optimized procedures and applications. Anal Biochem, 306(1): 1-7. |
| [17] | Frébort I, Kowalska M, Hluska T, et al. 2011. Evolution of cytokinin biosynthesis and degradation. J Exp Bot, 62(8): 2431-2452. |
| [18] | Frébortová J, Fraaije M W, Galuszka P, et al. 2004. Catalytic reaction of cytokinin dehydrogenase: Preference for quinones as electron acceptors. Biochem J, 380(Pt 1): 121-130. |
| [19] | Guo T, Chen K, Dong N Q, et al. 2018. GRAIN SIZE AND NUMBER1 negatively regulates the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMPK6 cascade to coordinate the trade-off between grain number per panicle and grain size in rice. Plant Cell, 30(4): 871-888. |
| [20] | Guo T, Lu Z Q, Shan J X, et al. 2020. ERECTA1 acts upstream of the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMPK6 cascade to control spikelet number by regulating cytokinin metabolism in rice. Plant Cell, 32(9): 2763-2779. |
| [21] | Han Y C, Hu Q F, Gong N, et al. 2024. Natural variation in MORE GRAINS 1 regulates grain number and grain weight in rice. J Integr Plant Biol, 66(7): 1440-1458. |
| [22] | Heyl A, Schmülling T. 2003. Cytokinin signal perception and transduction. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 6(5): 480-488. |
| [23] | Hiei Y, Komari T. 2008. Agrobacterium -mediated transformation of rice using immature embryos or calli induced from mature seed. Nat Protoc, 3(5): 824-834. |
| [24] | Hirose N, Makita N, Kojima M, et al. 2007. Overexpression of a type-A response regulator alters rice morphology and cytokinin metabolism. Plant Cell Physiol, 48(3): 523-539. |
| [25] | Howell S H, Lall S, Che P. 2003. Cytokinins and shoot development. Trends Plant Sci, 8(9): 453-459. |
| [26] | Huang X Z, Qian Q, Liu Z B, et al. 2009. Natural variation at the DEP1 locus enhances grain yield in rice. Nat Genet, 41(4): 494-497. |
| [27] | Hwang I, Sheen J. 2001. Two-component circuitry in Arabidopsis cytokinin signal transduction. Nature, 413(6854): 383-389. |
| [28] | Joerger A C, Fersht A R. 2007. Structure-function-rescue: The diverse nature of common p 53 cancer mutants. Oncogene, 26(15): 2226-2242. |
| [29] | Joerger A C, Ang H C, Veprintsev D B, et al. 2005. Structures of p53 cancer mutants and mechanism of rescue by second-site suppressor mutations. J Biol Chem, 280(16): 16030-16037. |
| [30] | Joerger A C, Ang H C, Fersht A R. 2006. Structural basis for understanding oncogenic p53 mutations and designing rescue drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103(41): 15056-15061. |
| [31] | Kellogg E A. 2022. Genetic control of branching patterns in grass inflorescences. Plant Cell, 34(7): 2518-2533. |
| [32] | Kopecný D, Sebela M, et al.2005. High-level expression and characterization of Zea mays cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase in Yarrowia lipolytica. Biochimie, 87(11): 1011-1022. |
| [33] | Kopečný D, Šebela M, Briozzo P, et al. 2008. Mechanism-based inhibitors of cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase attack FAD cofactor. J Mol Biol, 380(5): 886-899. |
| [34] | Kopečný D, Briozzo P, Popelková H, et al. 2010. Phenyl- and benzylurea cytokinins as competitive inhibitors of cytokinin oxidase/ dehydrogenase: A structural study. Biochimie, 92(8): 1052-1062. |
| [35] | Kopečný D, Končitíková R, Popelka H, et al. 2016. Kinetic and structural investigation of the cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase active site. FEBS J, 283(2): 361-377. |
| [36] | Kurakawa T, Ueda N, Maekawa M, et al. 2007. Direct control of shoot meristem activity by a cytokinin-activating enzyme. Nature, 445(7128): 652-655. |
| [37] | Liu D P, Zhao H, Xiao Y H, et al. 2022. A cryptic inhibitor of cytokinin phosphorelay controls rice grain size. Mol Plant, 15(2): 293-307. |
| [38] | Liu Z, Wei F, Feng Y Q. 2010. Determination of cytokinins in plant samples by polymer monolith microextraction coupled with hydrophilic interaction chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Methods, 2(11): 1676-1685. |
| [39] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 25(4): 402-408. |
| [40] | Ma X L, Liu Y G. 2016. CRISPR/Cas9-based multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants. Curr Protoc Mol Biol, 115(1): 31.6.1-31.6.21. |
| [41] | Malito E, Coda A, Bilyeu K D, et al. 2004. Structures of Michaelis and product complexes of plant cytokinin dehydrogenase: Implications for flavoenzyme catalysis. J Mol Biol, 341(5): 1237-1249. |
| [42] | Mok D W, Mok M C. 2001. Cytokinin metabolism and action. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 52: 89-118. |
| [43] | Morris R O, Bilyeu K D, Laskey J G, et al. 1999. Isolation of a gene encoding a glycosylated cytokinin oxidase from maize. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 255(2): 328-333. |
| [44] | Naeem M, Ali Z, Khan A, et al. 2022. Omics: A tool for resilient rice genetic improvement strategies. Mol Biol Rep, 49(6): 5075-5088. |
| [45] | Peng H, Wang K, Chen Z, et al. 2020. MBKbase for rice: An integrated omics knowledgebase for molecular breeding in rice. Nucleic Acids Res, 48(D1): D1085-D1092. |
| [46] | Rashid A, Achary V M M, Abdin M Z, et al. 2024. Cytokinin oxidase2-deficient mutants improve panicle and grain architecture through cytokinin accumulation and enhance drought tolerance in indica rice. Plant Cell Rep, 43(8): 207. |
| [47] | Rezaei E E, Webber H, Asseng S, et al. 2023. Climate change impacts on crop yields. Nat Rev Earth Environ, 4(12): 831-846. |
| [48] | Riou-Khamlichi C, Huntley R, Jacqmard A, et al. 1999. Cytokinin activation of Arabidopsis cell division through a D-type cyclin. Science, 283(5407): 1541-1544. |
| [49] | Rong C Y, Liu Y X, Chang Z Y, et al. 2022. Cytokinin oxidase/ dehydrogenase family genes exhibit functional divergence and overlap in rice growth and development, especially in control of tillering. J Exp Bot, 73(11): 3552-3568. |
| [50] | Růžička K, Šimášková M, Duclercq J, et al. 2009. Cytokinin regulates root meristem activity via modulation of the polar auxin transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106(11): 4284-4289. |
| [51] | Schmülling T, Werner T, Riefler M, et al. 2003. Structure and function of cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase genes of maize, rice, Arabidopsis and other species. J Plant Res, 116(3): 241-252. |
| [52] | Su W, Howell S H. 1992. A single genetic locus, Ckr1, defines Arabidopsis mutants in which root growth is resistant to low concentrations of cytokinin. Plant Physiol, 99(4): 1569-1574. |
| [53] | Sun L J, Zhang Q, Wu J X, et al. 2014. Two rice authentic histidine phosphotransfer proteins, OsAHP1 and OsAHP2, mediate cytokinin signaling and stress responses in rice. Plant Physiol, 165(1): 335-345. |
| [54] | Takeda S, Matsuoka M. 2008. Genetic approaches to crop improvement: Responding to environmental and population changes. Nat Rev Genet, 9(6): 444-457. |
| [55] | Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S. 2021. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol, 38(7): 3022-3027. |
| [56] | Taniguchi M, Kiba T, Sakakibara H, et al. 1998. Expression of Arabidopsis response regulator homologs is induced by cytokinins and nitrate. FEBS Lett, 429(3): 259-262. |
| [57] | To J P C, Deruère J, Maxwell B B, et al. 2007. Cytokinin regulates type-A Arabidopsis response regulator activity and protein stability via two-component phosphorelay. Plant Cell, 19(12): 3901-3914. |
| [58] | Tu B, Tao Z, Wang S G, et al. 2022. Loss of Gn1a/OsCKX2 confers heavy-panicle rice with excellent lodging resistance. J Integr Plant Biol, 64(1): 23-38. |
| [59] | Ueda Y, Siddique S, Frei M. 2015. A novel gene, OZONE-RESPONSIVE APOPLASTIC PROTEIN1, enhances cell death in ozone stress in rice. Plant Physiol, 169(1): 873-889. |
| [60] | Ueguchi C, Sato S, Kato T, et al. 2001. The AHK4 gene involved in the cytokinin-signaling pathway as a direct receptor molecule in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol, 42(7): 751-755. |
| [61] | Wang H M, Tong X H, Tang L Q, et al. 2022. RLB (RICE LATERAL BRANCH) recruits PRC2-mediated H3K27 tri-methylation on OsCKX4 to regulate lateral branching. Plant Physiol, 188(1): 460-476. |
| [62] | Wang J, Xu H X, Li N W, et al. 2015. Artificial selection of Gn1a plays an important role in improving rice yields across different ecological regions. Rice, 8(1): 37. |
| [63] | Wang S G, Ma B T, Gao Q, et al. 2018. Dissecting the genetic basis of heavy panicle hybrid rice uncovered Gn1a and GS3 as key genes. Theor Appl Genet, 131(6): 1391-1403. |
| [64] | Wang T, Zou T, He Z Y, et al. 2019. GRAIN LENGTH AND AWN 1 negatively regulates grain size in rice. J Integr Plant Biol, 61(10): 1036-1042. |
| [65] | Wang W S, Mauleon R, Hu Z Q, et al. 2018. Genomic variation in 3, 010 diverse accessions of Asian cultivated rice. Nature, 557(7703): 43-49. |
| [66] | Wang Y H, Li J Y. 2008. Molecular basis of plant architecture. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 59: 253-279. |
| [67] | Worthen J M, Yamburenko M V, Lim J, et al. 2019. Type-B response regulators of rice play key roles in growth, development and cytokinin signaling. Development, 146(13): dev174870. |
| [68] | Wu B, Meng J H, Liu H B, et al. 2023. Suppressing a phosphohydrolase of cytokinin nucleotide enhances grain yield in rice. Nat Genet, 55(8): 1381-1389. |
| [69] | Xing Y Z, Zhang Q F. 2010. Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 61: 421-442. |
| [70] | Xu R, Duan P G, Yu H Y, et al. 2018. Control of grain size and weight by the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMAPK 6 signaling pathway in rice. Mol Plant, 11(6): 860-873. |
| [71] | Yamburenko M V, Kieber J J, Schaller G E. 2017. Dynamic patterns of expression for genes regulating cytokinin metabolism and signaling during rice inflorescence development. PLoS One, 12(4): e0176060. |
| [72] | Yeh S Y, Chen H W, Ng C Y, et al. 2015. Down-regulation of cytokinin oxidase 2 expression increases tiller number and improves rice yield. Rice, 8(1): 36. |
| [73] | Yoon J, Jeong H J, Baek G, et al. 2021. A VIN3-like protein OsVIL1 is involved in grain yield and biomass in rice. Plants, 11(1): 83. |
| [74] | Zhang J H, Lin Q B, Wang X, et al. 2024. The DENSE AND ERECT PANICLE1-GRAIN NUMBER ASSOCIATED module enhances rice yield by repressing CYTOKININ OXIDASE 2 expression. Plant Cell, 37(1): koae309. |
| [75] | Zheng X L, Zhang S T, Liang Y L, et al. 2023. Loss-function mutants of OsCKX gene family based on CRISPR-Cas systems revealed their diversified roles in rice. Plant Genome, 16(2): e20283. |
| [76] | Zürcher E, Liu J C, di Donato M, et al. 2016. Plant development regulated by cytokinin sinks. Science, 353(6303): 1027-1030. |
| [1] | Nairiane dos Santos Bilhalva, Paulo Carteri Coradi, Rosana Santos de Moraes, Dthenifer Cordeiro Santana, Larissa Ribeiro Teodoro, Paulo Eduardo Teodoro, Marisa Menezes Leal. Physical and Physicochemical Classification of Parboiled Rice Using VNIR-SWIR Spectroscopy and Machine Learning [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(6): 857-867. |
| [2] | Zhou Lin, Jiang Hong, Huang Long, Li Ziang, Yao Zhonghao, Li Linhan, Ji Kangwei, Li Yijie, Tang Haijuan, Cheng Jinping, Bao Yongmei, Huang Ji, Zhang Hongsheng, Chen Sunlu. Genome-Wide Association Study of Brown Rice Weight Identifies an RNA-Binding Protein Antagonistically Regulating Grain Weight and Panicle Number [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(4): 525-536. |
| [3] | Lai Changkai, Hu Shikai, Jiao Guiai, Wang Ling, Shao Gaoneng, Zhao Fengli, Xie Lihong, Wei Xiangjin, Lü Yusong, Sheng Zhonghua, Tang Shaoqing, Hu Peisong. Enhancing Folate Content in Japonica Rice Through Co-expression of OsADCS and OsGTPCHI Indica Alleles [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(3): 353-366. |
| [4] | Sara Cannavò, Chiara Paleni, Alma Costarelli, Maria Cristina Valeri, Martina Cerri, Antonietta Saccomanno, Veronica Gregis, Graziella Chini Zittelli, Petre I. Dobrev, Lara Reale, Martin M. Kater, Francesco Paolocci. Assessing Changes in Root Architecture, Developmental Timing, Transcriptional and Hormonal Profiles in Rice Co-Cultivated with Azolla filiculoides [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(3): 426-444. |
| [5] | Wang Jingqing, Wang Yaliang, Chen Yulin, Chen Huizhe, Xiang Jing, Zhang Yikai, Wang Zhigang, Zhang Yuping. Progress on Physiological Mechanisms of Rice Spikelet Degeneration at Different Panicle Positions Caused by Abiotic Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(2): 193-202. |
| [6] | Chen Ya, Liu Zhiquan, Yang Linyin, Wu Fujie, Cao Zijian, Shi Huanbin, Qiu Jiehua, Kou Yanjun. OsCERK1 Interacts with OsHPP08 to Regulate Copper Uptake and Blast Resistance in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(2): 203-216. |
| [7] | Jiang Nan, Qiu Jiehua, Tian Dagang, Shi Huanbin, Liu Zhiquan, Wen Hui, Xie Shuwei, Chen Huizhe, Wu Meng, Kou Yanjun. Mixture of Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens and Bacillus Pumilus Modulates Community Structures of Rice Rhizosphere Soil to Suppress Rice Seedling Blight [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(1): 118-130. |
| [8] | Yu Shicong, Luo Ruxian, Zheng Shuqin, Ning Jing, Shi Yuanzhu, Guo Daiming, Jia Liangmeng, Wang Sen, Xiao Guizong, Guo Pengwang, Li Yang, Ma Xiaoding. CHOLINE TRANSPORTER-RELATED 4 (CTR4) Is Involved in Drought and Saline Tolerance in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2025, 32(1): 52-66. |
| [9] | Xue Chao, Zhao Xinru, Chen Xu, Cai Xingjing, Hu Yingying, Li Xiya, Zhou Yong, Gong Zhiyun. Histone Acetyltransferase GCN5 Regulates Rice Growth and Development and Enhances Salt Tolerance [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(6): 688-699. |
| [10] | Hu Yunchao, Yan Tiancai, Gao Zhenyu, Wang Tiankang, Lu Xueli, Yang Long, Shen Lan, Zhang Qiang, Hu Jiang, Ren Deyong, Zhang Guangheng, Zhu Li, Li Li, Zeng Dali, Qian Qian, Li Qing. Appropriate Supply of Ammonium Nitrogen and Ammonium Nitrate Reduces Cadmium Content in Rice Seedlings by Inhibiting Cadmium Uptake and Transport [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(5): 587-602. |
| [11] | Xie Shuwei, Shi Huanbin, Wen Hui, Liu Zhiquan, Qiu Jiehua, Jiang Nan, Kou Yanjun. Carbon Catabolite Repressor UvCreA is Required for Development and Pathogenicity in Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(2): 203-214. |
| [12] | Xia Xiaodong, Zhang Xiaobo, Wang Zhonghao, Cheng Benyi, Sun Huifeng, Xu Xia, Gong Junyi, Yang Shihua, Wu Jianli, Shi Yongfeng, Xu Rugen. Mapping and Functional Analysis of LE Gene in a Lethal Etiolated Rice Mutant at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 567-576. |
| [13] | Md. Dhin Islam, Adam H. Price, Paul D. Hallett. Effects of Root Growth of Deep and Shallow Rooting Rice Cultivars in Compacted Paddy Soils on Subsequent Rice Growth [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 459-472. |
| [14] | Sheikh Faruk Ahmed, Hayat Ullah, May Zun Aung, Rujira Tisarum, Suriyan Cha-Um, Avishek Datta. Iron Toxicity Tolerance of Rice Genotypes in Relation to Growth, Yield and Physiochemical Characters [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(4): 321-334. |
| [15] | Yousef Alhaj Hamoud, Hiba Shaghaleh, Wang Ruke, Willy Franz Gouertoumbo, Amar Ali Adam hamad, Mohamed Salah Sheteiwy, Wang Zhenchang, Guo Xiangping. Wheat Straw Burial Improves Physiological Traits, Yield and Grain Quality of Rice by Regulating Antioxidant System and Nitrogen Assimilation Enzymes under Alternate Wetting and Drying Irrigation [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(5): 473-488. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||