
Rice Science ›› 2015, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (4): 189-196.DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6308(14)60297-3
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ur Rehman Hafeez1( ), Kamran Muhammad1, Maqsood Ahmed Basra Shahzad1, Afzal Irfan1, Farooq Muhammad1,2,3
), Kamran Muhammad1, Maqsood Ahmed Basra Shahzad1, Afzal Irfan1, Farooq Muhammad1,2,3
Received:2014-09-29
Accepted:2015-03-23
Online:2015-07-28
Published:2015-05-27
About author:Corresponding author:Hafeez Ur REHMAN (hafeezcp@gmail.com)
Ur Rehman Hafeez, Kamran Muhammad, Maqsood Ahmed Basra Shahzad, Afzal Irfan, Farooq Muhammad. Influence of Seed Priming on Performance and Water Productivity of Direct Seeded Rice in Alternating Wetting and Drying[J]. Rice Science, 2015, 22(4): 189-196.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.org/EN/10.1016/S1672-6308(14)60297-3
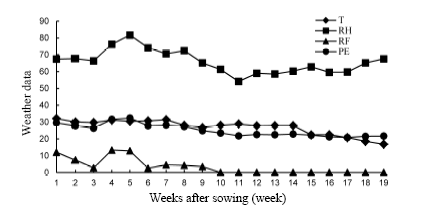
Fig. 1. Weather data at the experimental station during the crop growing period. T, Temperature (°C); RH, Relative humidity (%); RF, Rainfall (mm); PE, Pan evaporation (mm).
| Seed priming treatment | E0 (d) | E50 (d) | EI | FE | MET (d) |
| Hydro-priming | 4.67 ab | 4.30 b | 161.46 b | 205.00 d | 10.84 a |
| Osmo-priming (KCl) | 4.50 b | 4.11 b | 155.47 c | 216.83 c | 11.09 a |
| Osmo-priming (CaCl2) | 5.00 a | 5.55 a | 156.04 c | 228.33 b | 11.44 a |
| Osmo-priming (MLE) | 4.33 b | 2.86 c | 215.47 a | 314.00 a | 9.42 b |
| LSD | 0.47 | 0.45 | 2.75 | 2.83 | 0.70 |
| Values followed by different letters in a column are significantly different at the 0.05 level. E0, Time to start emergence; E50, Time to 50% emergence; EI, Emergence index; FE, Final emergence, and FE is presented by number of seedlings per unit area; MET, Mean emergence time; LSD, Least significant difference. | |||||
Table 1 Crop stand of direct seeded rice affected by seed priming.
| Seed priming treatment | E0 (d) | E50 (d) | EI | FE | MET (d) |
| Hydro-priming | 4.67 ab | 4.30 b | 161.46 b | 205.00 d | 10.84 a |
| Osmo-priming (KCl) | 4.50 b | 4.11 b | 155.47 c | 216.83 c | 11.09 a |
| Osmo-priming (CaCl2) | 5.00 a | 5.55 a | 156.04 c | 228.33 b | 11.44 a |
| Osmo-priming (MLE) | 4.33 b | 2.86 c | 215.47 a | 314.00 a | 9.42 b |
| LSD | 0.47 | 0.45 | 2.75 | 2.83 | 0.70 |
| Values followed by different letters in a column are significantly different at the 0.05 level. E0, Time to start emergence; E50, Time to 50% emergence; EI, Emergence index; FE, Final emergence, and FE is presented by number of seedlings per unit area; MET, Mean emergence time; LSD, Least significant difference. | |||||
| Seed priming treatment | Plant height (cm) | No. of productive tillers per m2 | No. of grains per panicle | Panicle length (cm) | Grain yield (t/hm2) | Biological yield (t/hm2) | Harvest index | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | |||||||||||||||||
| Hydro-priming | 75.0 b | 71.0 d | 337.0 d | 335.0 d | 62.0 d | 74.0 ab | 21.0 c | 22.0 ab | 2.08 d | 2.15 cd | 11.95 c | 10.84 d | 0.17 c | 0.19 a | ||||||||||||||||
| Osmo-priming (KCl) | 79.0 a | 70.0 d | 343.0 c | 336.0 d | 75.0 a | 74.0 ab | 23.0 a | 22.0 ab | 2.45 b | 2.18 cd | 12.20 c | 10.43 d | 0.20 a | 0.21 a | ||||||||||||||||
| Osmo-priming (CaCl2) | 61.0 e | 70.0 d | 301.0 f | 358.0 b | 66.0 c | 74.0 ab | 21.0 b | 22.0 ab | 2.24 c | 2.59 a | 13.28 b | 12.88 b | 0.17 c | 0.20 a | ||||||||||||||||
| Osmo-priming (MLE) | 72.0 c | 70.0 d | 311.0 e | 369.0 a | 74.0 ab | 74.0 ab | 23.0 a | 22.0 ab | 2.47 b | 2.61 a | 12.30 c | 14.07 a | 0.20 a | 0.18 b | ||||||||||||||||
| LSD interaction | 1.37 | 3.18 | 0.92 | 0.75 | 0.10 | 0.45 | 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Values followed by different letters in a column are significantly different at the 0.05 level. FC, Field capacity of direct seeded rice; AWD, Alternate wetting and drying of direct seeded rice; MLE, Moringa leaf extract; LSD, Least significant difference. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 2 Yield components and grain yield of direct seeded rice affected by irrigation regime and seed priming.
| Seed priming treatment | Plant height (cm) | No. of productive tillers per m2 | No. of grains per panicle | Panicle length (cm) | Grain yield (t/hm2) | Biological yield (t/hm2) | Harvest index | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | |||||||||||||||||
| Hydro-priming | 75.0 b | 71.0 d | 337.0 d | 335.0 d | 62.0 d | 74.0 ab | 21.0 c | 22.0 ab | 2.08 d | 2.15 cd | 11.95 c | 10.84 d | 0.17 c | 0.19 a | ||||||||||||||||
| Osmo-priming (KCl) | 79.0 a | 70.0 d | 343.0 c | 336.0 d | 75.0 a | 74.0 ab | 23.0 a | 22.0 ab | 2.45 b | 2.18 cd | 12.20 c | 10.43 d | 0.20 a | 0.21 a | ||||||||||||||||
| Osmo-priming (CaCl2) | 61.0 e | 70.0 d | 301.0 f | 358.0 b | 66.0 c | 74.0 ab | 21.0 b | 22.0 ab | 2.24 c | 2.59 a | 13.28 b | 12.88 b | 0.17 c | 0.20 a | ||||||||||||||||
| Osmo-priming (MLE) | 72.0 c | 70.0 d | 311.0 e | 369.0 a | 74.0 ab | 74.0 ab | 23.0 a | 22.0 ab | 2.47 b | 2.61 a | 12.30 c | 14.07 a | 0.20 a | 0.18 b | ||||||||||||||||
| LSD interaction | 1.37 | 3.18 | 0.92 | 0.75 | 0.10 | 0.45 | 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Values followed by different letters in a column are significantly different at the 0.05 level. FC, Field capacity of direct seeded rice; AWD, Alternate wetting and drying of direct seeded rice; MLE, Moringa leaf extract; LSD, Least significant difference. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Seed priming treatment | Normal grain (%) | Abortive grain (%) | Opaque grain (%) | Chalky grain (%) | Grain length (cm) | Grain width (cm) | Water productivity (kg/m3) | |||||||||||||
| FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | |||||||
| Hydro-priming | 49.00 bcd | 39.00 e | 12.00 ab | 14.00 ab | 7.00 | 9.00 | 32.00 ab | 38.00 a | 11.43 ab | 11.54 ab | 2.12 abc | 2.24 a | 0.14 c | 0.15 c | ||||||
| Osmo-priming (KCl) | 47.00 cd | 49.00 bcd | 16.00 a | 15.00 a | 7.00 | 9.00 | 30.00 ab | 27.00 b | 10.46 b | 11.67 a | 2.19 ab | 1.92 c | 0.16 ab | 0.14 c | ||||||
| Osmo-priming (CaCl2) | 57.00 a | 53.00 ab | 6.00 b | 11.00 ab | 8.00 | 9.00 | 29.00 ab | 27.00 b | 11.05 ab | 10.94 ab | 2.20 ab | 2.22 ab | 0.15 bc | 0.17 a | ||||||
| Osmo-priming (MLE) | 45.00 d | 51.00 bc | 17.00 a | 12.00 ab | 10.00 | 9.00 | 28.00 ab | 28.00 b | 11.02 ab | 11.09 ab | 1.97 bc | 1.89 c | 0.17 a | 0.17 a | ||||||
| LSD interaction | 5.83 | 6.41 | ns | 9.01 | 1.28 | 0.24 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||
| Values followed by different letters in a column are significantly different at the 0.05 level. FC, Field capacity of direct seeded rice; AWD, Alternate wetting and drying of direct seeded rice; MLE, Moringa leaf extract; LSD, Least significant difference; ns, Not significant. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Table 3 Grain quality and water productivity of direct seeded rice affected by irrigation regime and seed priming.
| Seed priming treatment | Normal grain (%) | Abortive grain (%) | Opaque grain (%) | Chalky grain (%) | Grain length (cm) | Grain width (cm) | Water productivity (kg/m3) | |||||||||||||
| FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | |||||||
| Hydro-priming | 49.00 bcd | 39.00 e | 12.00 ab | 14.00 ab | 7.00 | 9.00 | 32.00 ab | 38.00 a | 11.43 ab | 11.54 ab | 2.12 abc | 2.24 a | 0.14 c | 0.15 c | ||||||
| Osmo-priming (KCl) | 47.00 cd | 49.00 bcd | 16.00 a | 15.00 a | 7.00 | 9.00 | 30.00 ab | 27.00 b | 10.46 b | 11.67 a | 2.19 ab | 1.92 c | 0.16 ab | 0.14 c | ||||||
| Osmo-priming (CaCl2) | 57.00 a | 53.00 ab | 6.00 b | 11.00 ab | 8.00 | 9.00 | 29.00 ab | 27.00 b | 11.05 ab | 10.94 ab | 2.20 ab | 2.22 ab | 0.15 bc | 0.17 a | ||||||
| Osmo-priming (MLE) | 45.00 d | 51.00 bc | 17.00 a | 12.00 ab | 10.00 | 9.00 | 28.00 ab | 28.00 b | 11.02 ab | 11.09 ab | 1.97 bc | 1.89 c | 0.17 a | 0.17 a | ||||||
| LSD interaction | 5.83 | 6.41 | ns | 9.01 | 1.28 | 0.24 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||
| Values followed by different letters in a column are significantly different at the 0.05 level. FC, Field capacity of direct seeded rice; AWD, Alternate wetting and drying of direct seeded rice; MLE, Moringa leaf extract; LSD, Least significant difference; ns, Not significant. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Seed priming treatment | Total expenditure (PKR/hm2) | Gross income (PKR/hm2) | Net income (PKR/hm2) | Benefit cost ratio | |||||||
| FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | ||||
| Hydro-priming | 83 555 | 80 955 | 71 275 | 73 538 | -12 279 | -7 417 | 0.85 | 0.91 | |||
| Osmo-priming (KCl) | 89 742 | 87 142 | 83 785 | 74 513 | -5 957 | -12 629 | 0.93 | 0.86 | |||
| Osmo-priming (CaCl2) | 89 742 | 87 142 | 76 795 | 88 571 | -12 947 | 1 429 | 0.86 | 1.02 | |||
| Osmo-priming (MLE) | 83 743 | 81 143 | 84 469 | 89 353 | 726 | 8 210 | 1.01 | 1.10 | |||
| FC, Field capacity of direct seeded rice; AWD, Alternate wetting and drying of direct seeded rice; MLE, Moringa leaf extract; PKR, Pakistani rupee. | |||||||||||
Table 4 Benefit cost ratio of direct seeded rice affected by irrigation regime and seed priming.
| Seed priming treatment | Total expenditure (PKR/hm2) | Gross income (PKR/hm2) | Net income (PKR/hm2) | Benefit cost ratio | |||||||
| FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | FC | AWD | ||||
| Hydro-priming | 83 555 | 80 955 | 71 275 | 73 538 | -12 279 | -7 417 | 0.85 | 0.91 | |||
| Osmo-priming (KCl) | 89 742 | 87 142 | 83 785 | 74 513 | -5 957 | -12 629 | 0.93 | 0.86 | |||
| Osmo-priming (CaCl2) | 89 742 | 87 142 | 76 795 | 88 571 | -12 947 | 1 429 | 0.86 | 1.02 | |||
| Osmo-priming (MLE) | 83 743 | 81 143 | 84 469 | 89 353 | 726 | 8 210 | 1.01 | 1.10 | |||
| FC, Field capacity of direct seeded rice; AWD, Alternate wetting and drying of direct seeded rice; MLE, Moringa leaf extract; PKR, Pakistani rupee. | |||||||||||
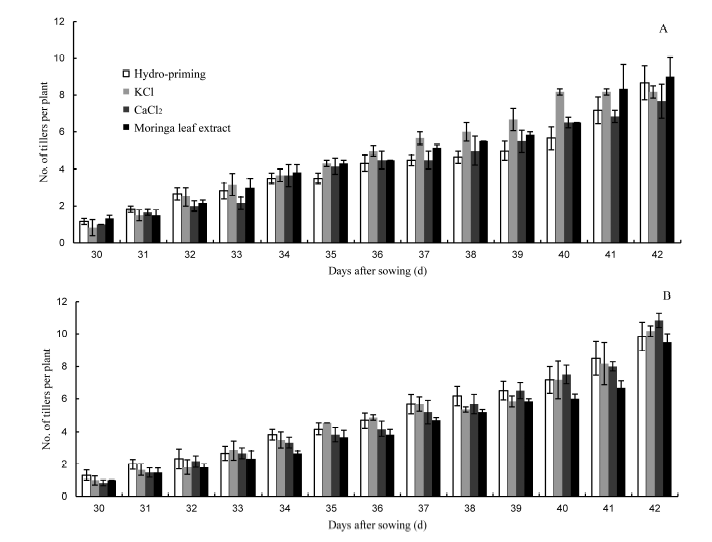
Fig. 2. Tillering emergence rate in direct seeded rice (DSR) affected by seed priming when irrigated at field capacity (A) and alternate wetting and drying (B).
| 1 | Afzal I, Hussain B, Basra S M A, Rehman H U.2012. Priming with moringa leaf extract reduces imbibitional chilling injury in spring maize.Seed Sci Technol, 40: 271-276. |
| 2 | Ahmad R, Hussain S, Farooq M, Rehman A U, Jabbar A.2013. Improving the performance of direct seeded system of rice intensification by seed priming.Int J Agric Biol, 15(4): 791-794. |
| 3 | Anwar M P, Juraimi A S, Mohamed M T M, Uddin M K, Samedani B, Puteh A, Man A. 2013. Integration of agronomic practices with herbicides for sustainable weed management in aerobic rice.Sci World J, 2013: 1-12. |
| 4 | Association of Official Seed Analysis (AOSA). 1983. Seed vigor hand testing book, Contribution No. 32 to the handbook on seed testing. Association of Official Seed Analysis. Springerfield, IL. |
| 5 | Beldar P, Bouman B A M, Spiertz J H J, Cabangon R J, Guoan L, Quilang E J P, Yuanhua L, Tuong T P.2004. Effect of water and nitrogen management on water use and yield of irrigated rice.Agric Water Manag, 65: 193-210. |
| 6 | Belder P, Spiertz H J, Boumanb B A M, Lu G, Tuong T P.2005. Nitrogen economy and water productivity of lowland rice under water-saving irrigation.Field Crops Res, 93(2/3): 169-185. |
| 7 | Bouman B A M, Tuong T P.2001. Field water management to save water and increase its productivity in irrigated lowland rice.Agric Water Manag, 49(1): 11-30. |
| 8 | Bouman B A M, Yang X G, Wang H Q, Wang Z M, Zhao J F, Chen B.2006. Performance of aerobic rice varieties under irrigated conditions in North China.Field Crops Res, 97(1): 53-56. |
| 9 | Cabangon R J, Tuong T P, Castillo E G, Bao L X, Lu G A, Wang G H, Cui Y L, Bouman B A M, Li Y H, Chen C D, Wang J Z.2004. Effect of irrigation method and N-fertilizer management on rice yield, water productivity and nutrient-use efficiencies in typical lowland rice conditions in China.Paddy Water Environ, 2(4): 195-206. |
| 10 | Du L V, Tuong T P.2002. Enhancing the performance of dry-seeded rice: Effects of seed priming, seedling rate, and time of seedling. In: Pandey S, Mortimer M, Wade L, Tuong T P, Lopez K, Hardy B. Direct Seeding: Research Strategies and Opportunities. Manila, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute: 241-256. |
| 11 | Ella E S, Dionisio-Sese M L, Ismail A M.2011. Seed pre-treatment in rice reduces damage, enhances carbohydrate mobilization and improves emergence and seedling establishment under flooded conditions. AoB Plants: plr007. |
| 12 | Ellis R H, Roberts E H.1981. The quantification of ageing and survival in orthodox seeds.Seed Sci Technol, 9(2): 373-409. |
| 13 | Farooq M, Basra S M A, Tabassum R, Afzal I.2006. Enhancing the performance of direct seeded fine rice by seed priming.Plant Prod Sci, 9(4): 446-456. |
| 14 | Farooq M, Siddique K H M, Rehman H U, Aziz T, Lee D J, Wahid A.2011. Rice direct seeding: Experiences, challenges and opportunities.Soil Till Res, 111: 87-98. |
| 15 | Foidl N, Makkar H P S, Becker K.2001. The potential of Moringa oleifera for agricultural and industrial uses. In: What development potential for Moringa products? Dar-es-Salaam, Tanzania: 47-67. |
| 16 | Fuglie L J.1999. The miracle tree: Moringa oleifera: Natural Nutrition for the Tropics. Dakar, Senegal: Church World Service: 68. |
| 17 | Guerra L C, Bhuiyan S I, Tuong T P, Barker R.1998. Producing more rice with less water from irrigated systems. SWIM paper. Colombia, Sri Lanka: International Irrigation Management Institute (IIMI): 24. |
| 18 | Haloi B, Saud R K, Dey P C.2006. Seed priming and potassium nutrition as the management tools for drought mitigation in upland summer rice. In: Trivedi P C. Advances in Plant Physiology. I.K. International: 250-257. |
| 19 | Li Y H, Barker R.2004. Increasing water productivity for paddy irrigation in China.Paddy Water Environ, 2(4): 187-193. |
| 20 | Malik R K, Yadav A.2008. Direct-seeded rice in the Indo-Gangetic Plain: Progress, problems and opportunities. In: Humphreys E, Roth C H. Permanent Beds and Rice Residue Management for Rice-Wheat Systems in the Indo-Gangetic Plains. Proceedings of a Workshop Held in Ludhiana, India. 7-9 September, 2006. Canberra, Australia: Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR): 133-143. |
| 21 | Nagato K, Chaudhry F M.1969. A comparative study of ripening process and kernel development in japonica and indica rice.Jpn J Crop Sci, 38(3): 425-433. |
| 22 | Rehman H U, Basra S M A, Basra A, Farooq M.2011a. Field appraisal of seed priming to improve the growth, yield and quality of direct seeded rice.Turk J Agric Forest, 35: 357-365. |
| 23 | Rehman H U, Basra S M A, Farooq M, Ahmed N, Afzal I.2011b. Seed priming with CaCl2 improves the stand establishment, yield and quality attributes in direct seeded rice (Oryza sativa).Inter J Agric Biol, 13(5): 786-790. |
| 24 | Rehman H U, Basra S M A, Wahid A.2013. Optimizing nitrogen-split application time to improve dry matter accumulation and yield in dry direct seeded rice.Int J Agric Biol, 15(1): 41-47. |
| 25 | Rehman H U, Nawaz M Q, Basra S M A, Afzal I, Yasmeen A, ul-Hassan F.2014. Seed priming influence on early crop growth, phenological development and yield performance of linola (Linum usitatissimum L.).J Integ Agric, 13(5): 990-996. |
| 26 | Ruan S, Xue Q, Tylkowska K.2002. The influence of priming on germination of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seeds and seedling emergence and performance in flooded soil.Seed Sci Technol, 30(1): 61-67. |
| 27 | Sarkar R K.2012. Seed priming improves agronomic trait performance under flooding and non-flooding conditions in rice with QTL SUB1.Rice Sci, 19(4): 286-294. |
| 28 | Sudhir-Yadav, Gill G, Humphreys E, Kukal S S, Walia U S.2011a. Effect of water management on dry seeded and puddled transplanted rice. Part 1: Crop performance.Field Crops Res, 120(1): 112-122. |
| 29 | Sudhir-Yadav, Humphreys E, Kukal S S, Gill G, Rangarajan R.2011b. Effect of water management on dry seeded and puddled transplanted rice: Part 2: Water balance and water productivity.Field Crops Res, 120(1): 123-132. |
| 30 | Thakur A K, Rath S, Patil D U, Kumar A.2011. Effects on rice plant morphology and physiology of water and associated management practices of the system of rice intensification and their implications for crop performance.Paddy Water Environ, 9(1): 13-24. |
| 31 | Tuong T P, Singh A K, Siopongco J D L C, Wade L J.2000. Constraints to high yield of dry seeded rice in the rainy season of a humid tropic environment.Plant Prod Sci, 3(2): 164-172. |
| 32 | Yang J C, Zhang J H.2010. Crop management techniques to enhance harvest index in rice.J Exp Bot, 61(12): 3177-3189. |
| 33 | Yasmeen A, Basra S M A, Wahid A, Nouman W, Rehman H U.2013. Exploring the potential of Moringa oleifera leaf extract (MLE) as a seed priming agent in improving wheat performance.Turk J Bot, 37: 512-520. |
| 34 | Yasmeen A, Nouman W, Basra S M A, Wahid A, Rehman H U, Hussain N, Afzal I.2014. Morphological and physiological response of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) to natural and synthetic cytokinin sources: A comparative study.Acta Physiol Plant, 36(12): 3147-3155. |
| 35 | Zhang H, Zhang S F, Yang J C, Zhang J H, Wang Z Q.2008. Postanthesis moderate wetting drying improves both quality and quantity of rice yield.Agron J, 100(3): 726-734. |
| 36 | Zhang H, Tan G L, Yang L N, Yang J C, Zhang J H, Zhao B H.2009. Hormones in the grains and roots in relation to post-anthesis development of inferior and superior spikelets in japonica/indica hybrid rice.Plant Physiol Biochem, 47(3): 195-204. |
| 37 | Zhang H, Chen T T, Wang Z Q, Yang J C, Zhang J H.2010. Involvement of cytokinins in the grain filling of rice under alternate wetting and drying irrigation.J Exp Bot, 61(13): 3719-3733. |
| 38 | Zhang L M, Lin S, Bouman B A M, Xue C Y, Wei F T, Tao H B, Yang X G, Wang H Q, Zhao D L, Dittert K.2009. Response of aerobic rice growth and grain yield to N fertilizer at two contrasting sites near Beijing, China.Field Crops Res, 114(1): 45-53. |
| 39 | (Managing Editor: Fang Hongmin) |
| [1] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [2] | Lu Xuedan, Li Fan, Xiao Yunhua, Wang Feng, Zhang Guilian, Deng Huabing, Tang Wenbang. Grain Shape Genes: Shaping the Future of Rice Breeding [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 379-404. |
| [3] | Salar Monajjem, Elias Soltani, Ebrahim Zainali, Masoud Esfahani, Farshid Ghaderi-Far, Maryam Hosseini Chaleshtori, Atefeh Rezaei. Seed Priming Improves Enzymatic and Biochemical Performances of Rice During Seed Germination under Low and High Temperatures [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(4): 335-347. |
| [4] | Jiang Hongzhen, Wang Yamei, Lai Liuru, Liu Xintong, Miao Changjian, Liu Ruifang, Li Xiaoyun, Tan Jinfang, Gao Zhenyu, Chen Jingguang. OsAMT1.1 Expression by Nitrate-Inducible Promoter of OsNAR2.1 Increases Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Rice Yield [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(3): 222-234. |
| [5] | Zhou Longfei, Meng Ran, Yu Xing, Liao Yigui, Huang Zehua, Lü Zhengang, Xu Binyuan, Yang Guodong, Peng Shaobing, Xu Le. Improved Yield Prediction of Ratoon Rice Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-Based Multi-Temporal Feature Method [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(3): 247-256. |
| [6] | Ernieca Lyngdoh Nongbri, Sudip Das, Karma Landup Bhutia, Aleimo G. Momin, Mayank Rai, Wricha Tyagi. Differential Expression of Iron Deficiency Responsive Rice Genes under Low Phosphorus and Iron Toxicity Conditions and Association of OsIRO3 with Yield in Acidic Soils [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(1): 58-69. |
| [7] | Liu Yantong, Li Ting, Jiang Zhishu, Zeng Chuihai, He Rong, Qiu Jiao, Lin Xiaoli, Peng Limei, Song Yongping, Zhou Dahu, Cai Yicong, Zhu Changlan, Fu Junru, He Haohua, Xu Jie. Characterization of a Novel Weak Allele of RGA1/D1 and Its Potential Application in Rice Breeding [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(6): 522-534. |
| [8] | Yousef Alhaj Hamoud, Hiba Shaghaleh, Wang Ruke, Willy Franz Gouertoumbo, Amar Ali Adam hamad, Mohamed Salah Sheteiwy, Wang Zhenchang, Guo Xiangping. Wheat Straw Burial Improves Physiological Traits, Yield and Grain Quality of Rice by Regulating Antioxidant System and Nitrogen Assimilation Enzymes under Alternate Wetting and Drying Irrigation [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(5): 473-488. |
| [9] | Md Rokonuzzaman, Li Wai Chin, Man Yu Bon, Tsang Yiu Fai, Ye Zhihong. Arsenic Accumulation in Rice: Sources, Human Health Impact and Probable Mitigation Approaches [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(4): 309-327. |
| [10] | Luo Haowen, He Longxin, Du Bin, Pan Shenggang, Mo Zhaowen, Yang Shuying, Zou Yingbin, Tang Xiangru. Epoxiconazole Improved Photosynthesis, Yield Formation, Grain Quality and 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline Biosynthesis of Fragrant Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(2): 189-196. |
| [11] | Saichompoo Uthomphon, Narumol Possawat, Nakwilai Pawat, Thongyos Peeranut, Nanta Aekchupong, Tippunya Patompong, Ruengphayak Siriphat, Itthisoponkul Teerarat, Bueraheng Niranee, Cheabu Sulaiman, Malumpong Chanate. Breeding Novel Short Grain Rice for Tropical Region to Combine Important Agronomical Traits, Biotic Stress Resistance and Cooking Quality in Koshihikari Background [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(5): 479-792. |
| [12] | Matsue Yuji, Takasaki Katsuya, Abe Jun. Water Management for Improvement of Rice Yield, Appearance Quality and Palatability with High Temperature During Ripening Period [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(4): 409-416. |
| [13] | Panigrahy Madhusmita, Das Subhashree, Poli Yugandhar, Kumar Sahoo Pratap, Kumari Khushbu, C. S. Panigrahi Kishore. Carbon Nanoparticle Exerts Positive Growth Effects with Increase in Productivity by Down-Regulating Phytochrome B and Enhancing Internal Temperature in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(3): 289-300. |
| [14] | Minghua Zhang, Zhaowen Mo, Juan Liao, Shenggang Pan, Xiongfei Chen, Le Zheng, Xiwen Luo, Zaiman Wang. Lodging Resistance Related to Root Traits for Mechanized Wet-Seeding of Two Super Rice Cultivars [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(2): 200-208. |
| [15] | Jan Mehmood, Shah Gulmeena, Yuqing Huang, Xuejiao Liu, Peng Zheng, Hao Du, Hao Chen, Jumin Tu. Development of Heat Tolerant Two-Line Hybrid Rice Restorer Line Carrying Dominant Locus of OsHTAS [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(1): 99-108. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||